Submitted:
18 July 2024
Posted:
18 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
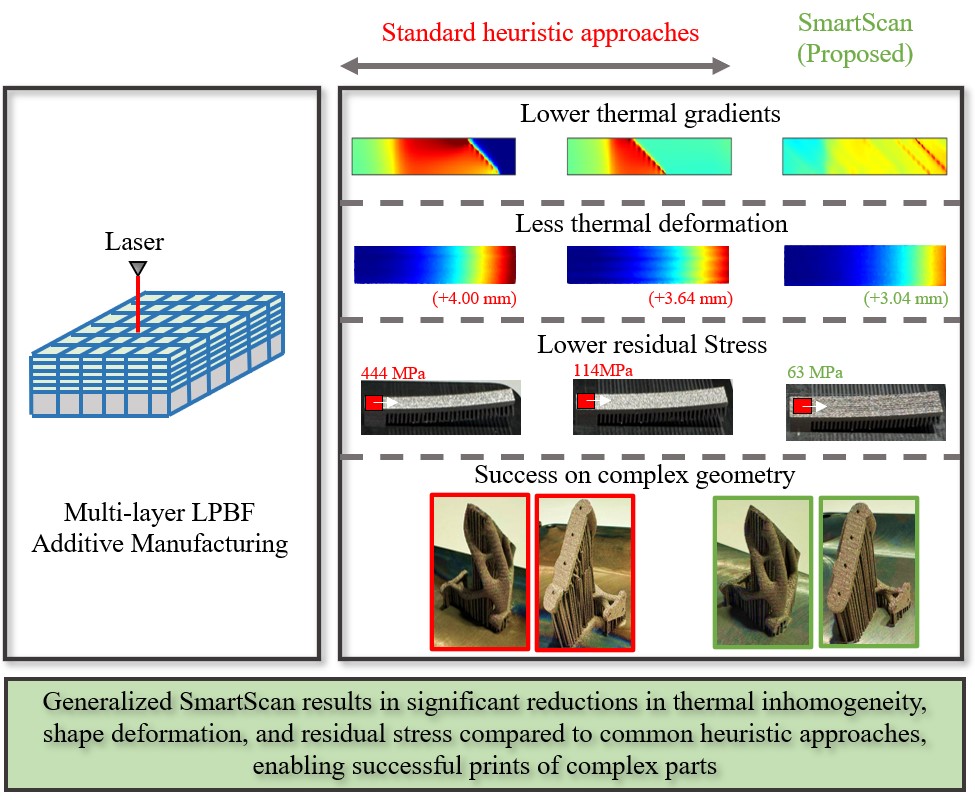
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- It extends the 2D thermal model and objective function of the original SmartScan [31] to incorporate 3D thermal effects, while introducing simplifying assumptions to reduce computational complexity due to larger model sizes.
- It generalizes the modeling and optimization methods of the original SmartScan to enable them to handle arbitrary scan patterns with scan vectors of varying lengths and inclination angles within each layer.
- It improves the original SmartScan’s greedy optimization strategy, which was prone to getting stuck in local optima, by balancing exploration and exploitation. This enables more efficient optimization of temperature distribution for part geometries with overhangs or other heat traps.
- It further reduces the dimension of the model significantly, thereby enhancing computational efficiency by using singular value decomposition (SVD).
2. Methodology
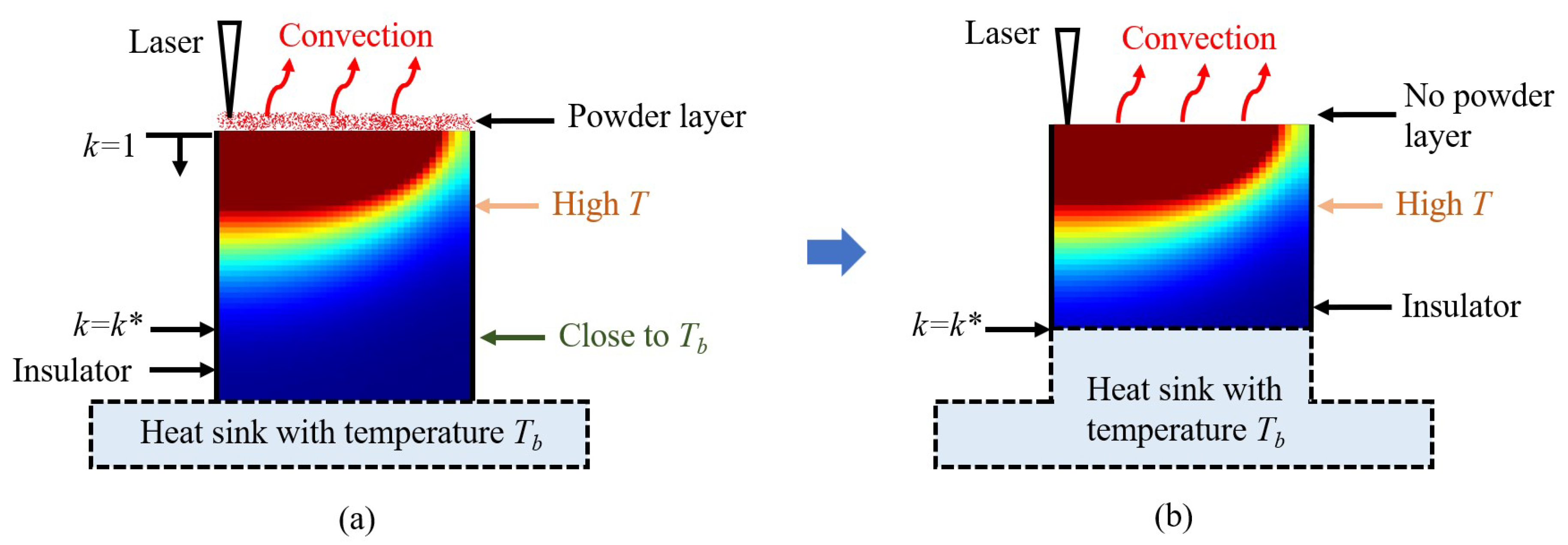
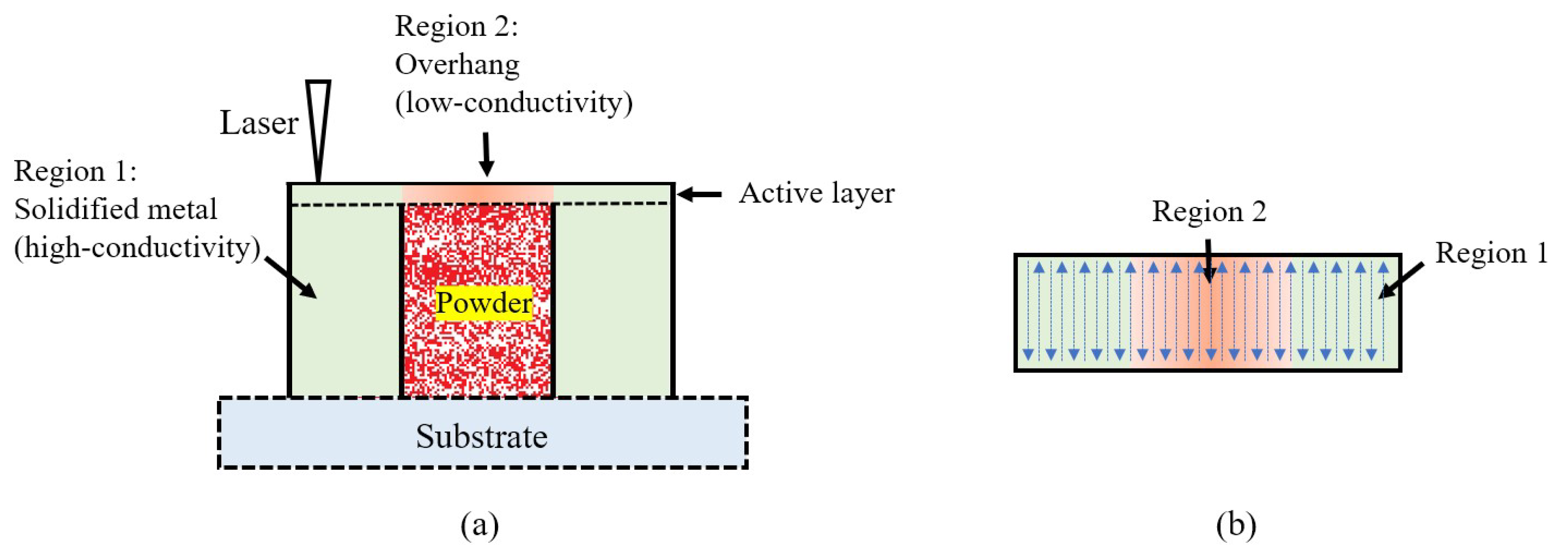
2.1. Extension of FDM Modeling to Arbitrary 3D Geometries and Scan Patterns
2.2. Objective Function and Optimization
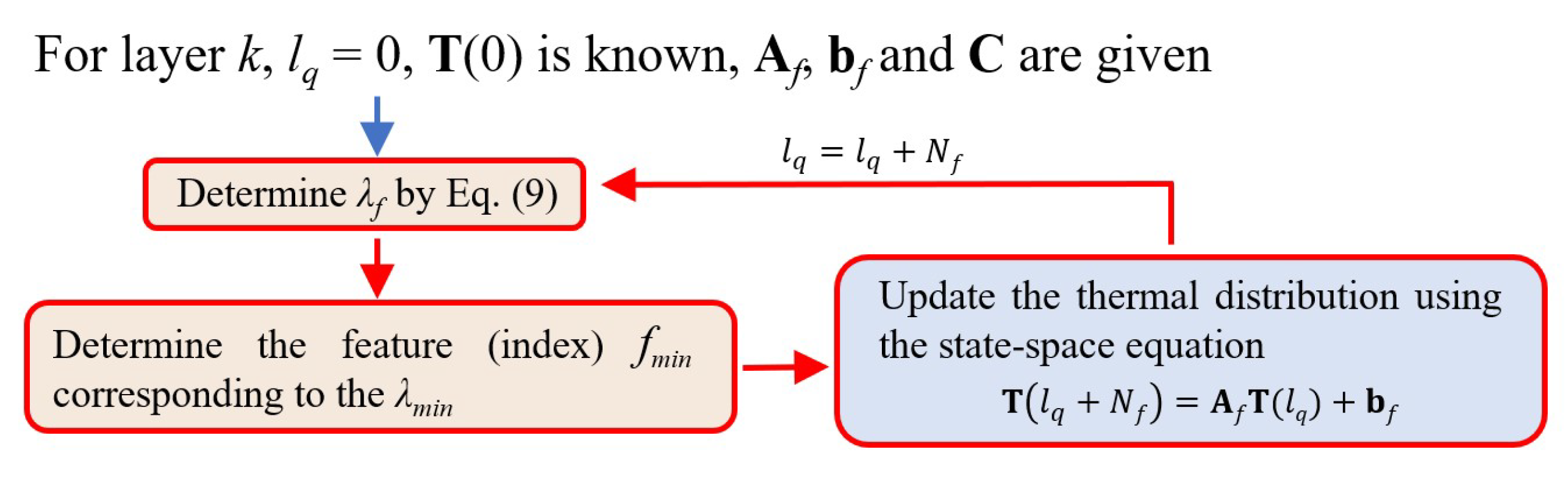
2.3. Relaxation of the Greediness of the Optimization Algorithm
2.4. SVD-based Model Order Reduction
3. Simulation and Experimental Case Studies
3.1. Simulation and Experimental Setup
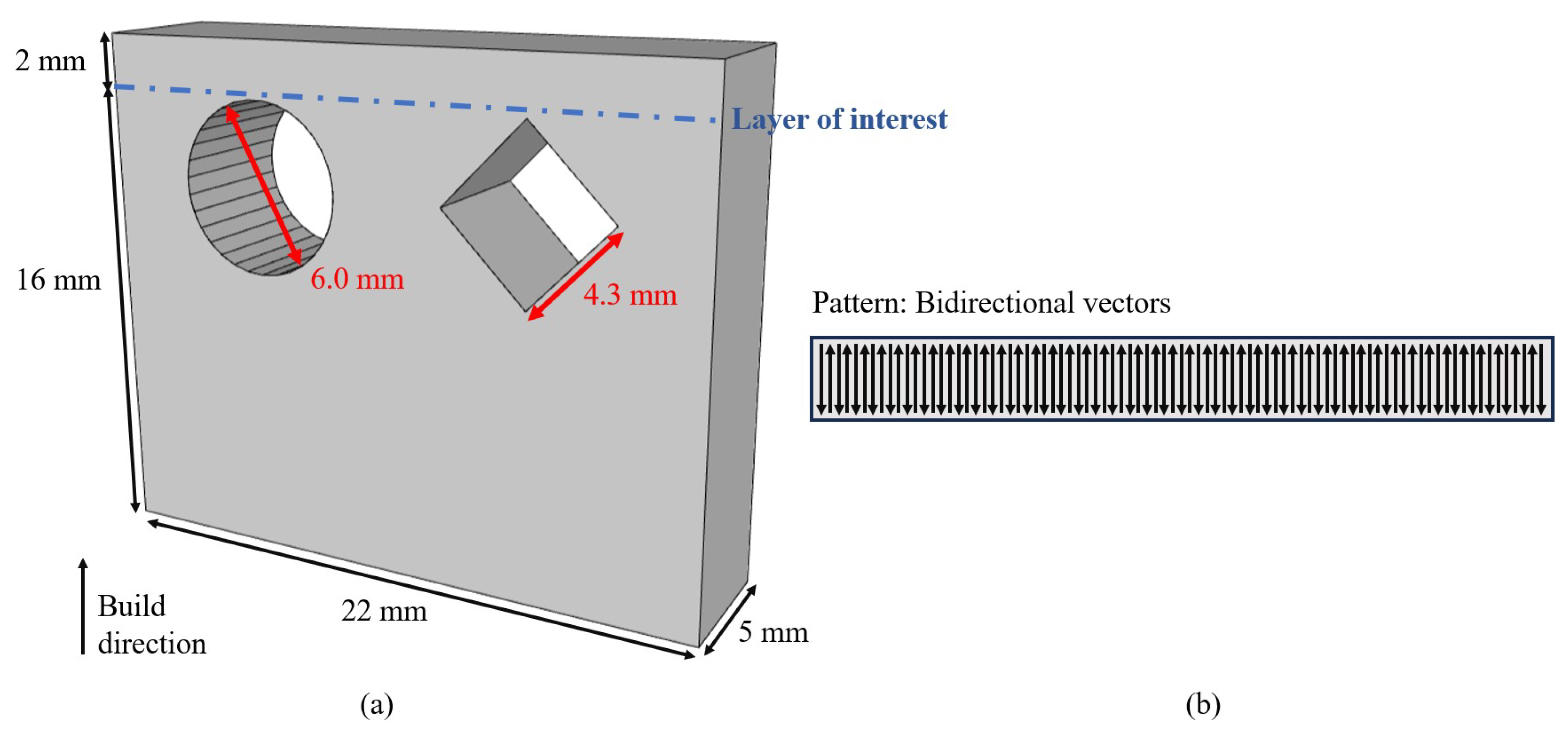
3.2. Case Study 1: Block with Circular and Diamond-shaped Channels
3.3. Case Study 2: Cantilever Beam
3.4. Case Study 3: Complex 3D Part
4. Conclusions and Future Work
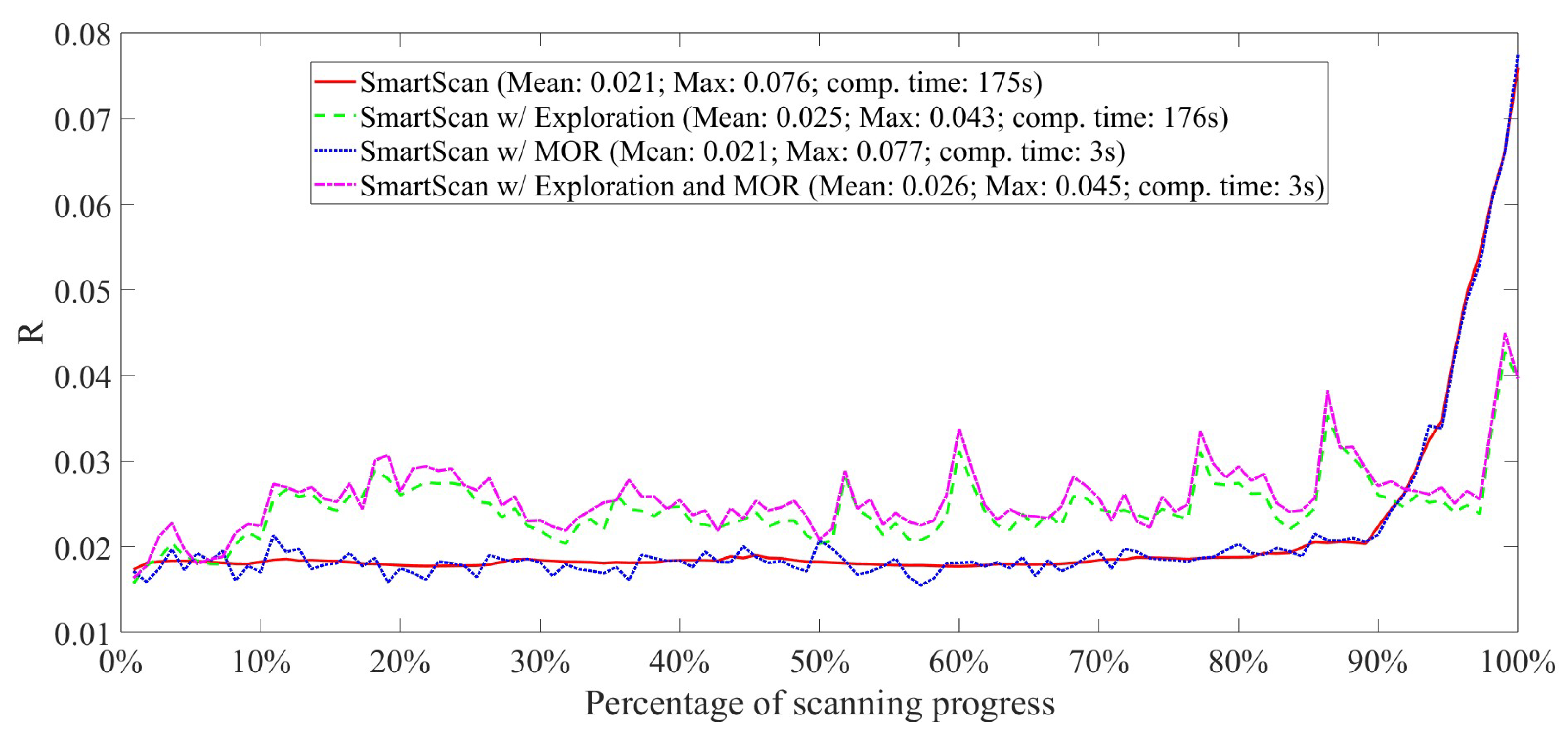
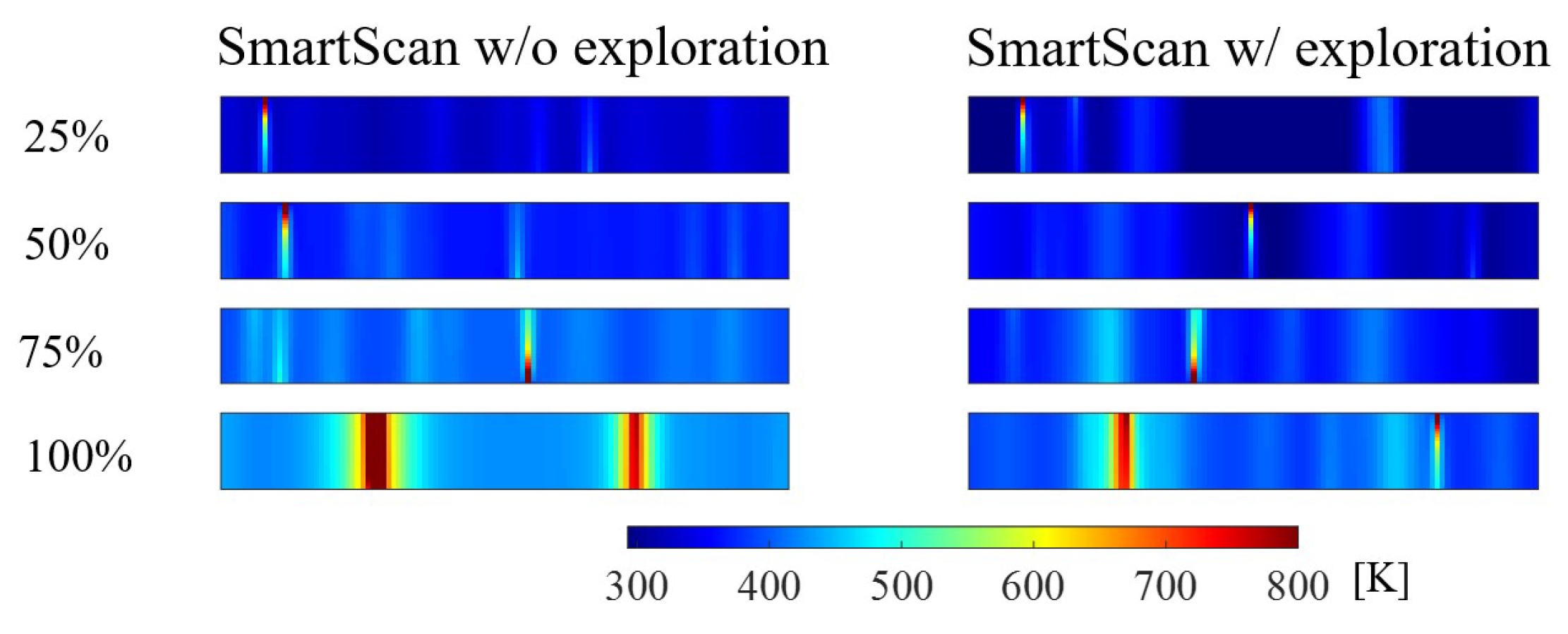
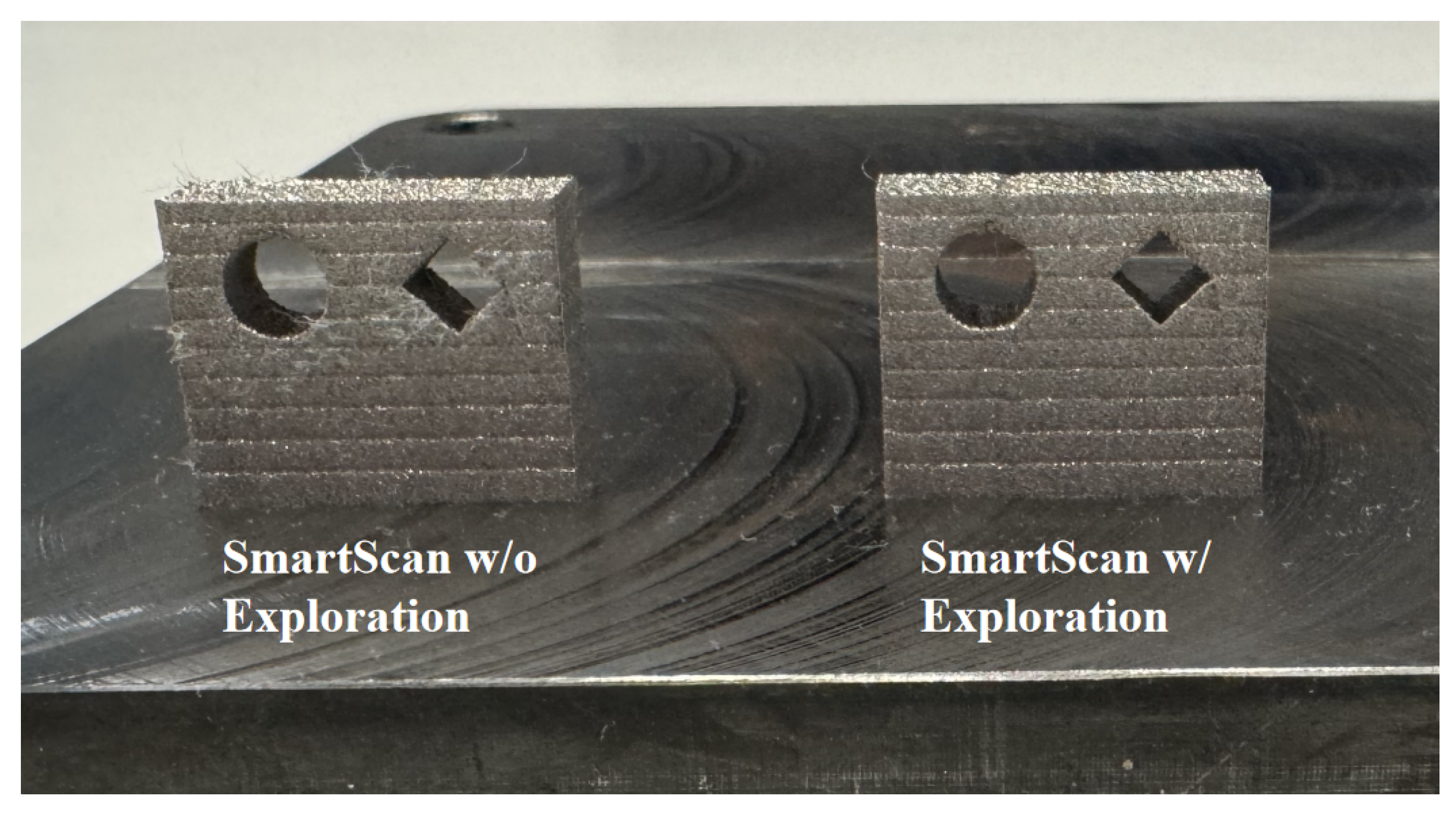
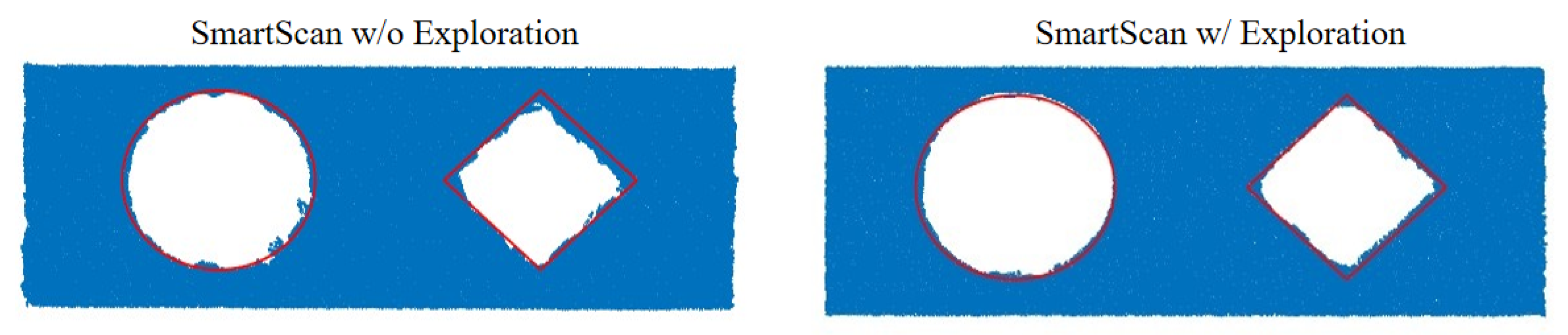
- The incorporation of probabilistic exploration enables SmartScan to be less greedy, allowing it to process 3D geometries with overhangs and heat traps without excessive local overheating. This capability was shown to yield up to 50% improvement in geometric accuracy of a test artifact compared to a version of SmartScan without probabilistic exploration.
- The addition of SVD-based MOR to SmartScan improved its computational efficiency significantly with little or no losses its accuracy. In a case study, this contribution resulted in up to 58 times reduction in computation time compared to a version of SmartScan without MOR.
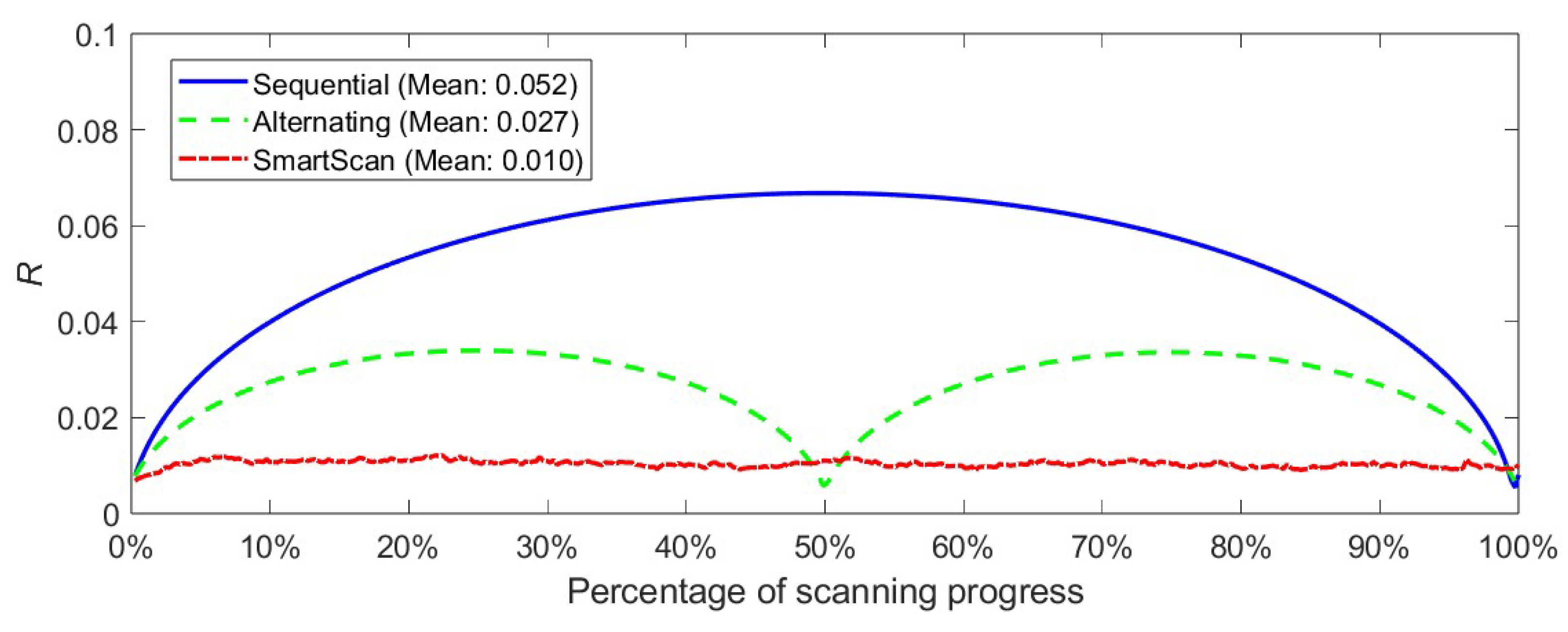
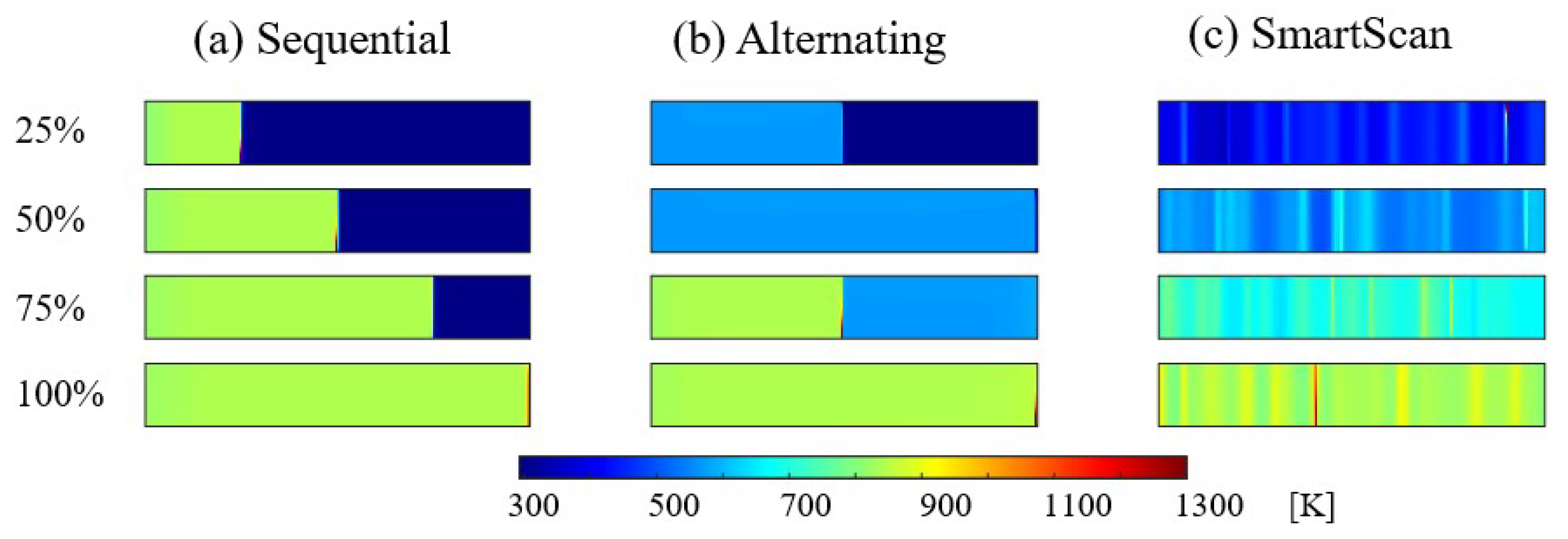
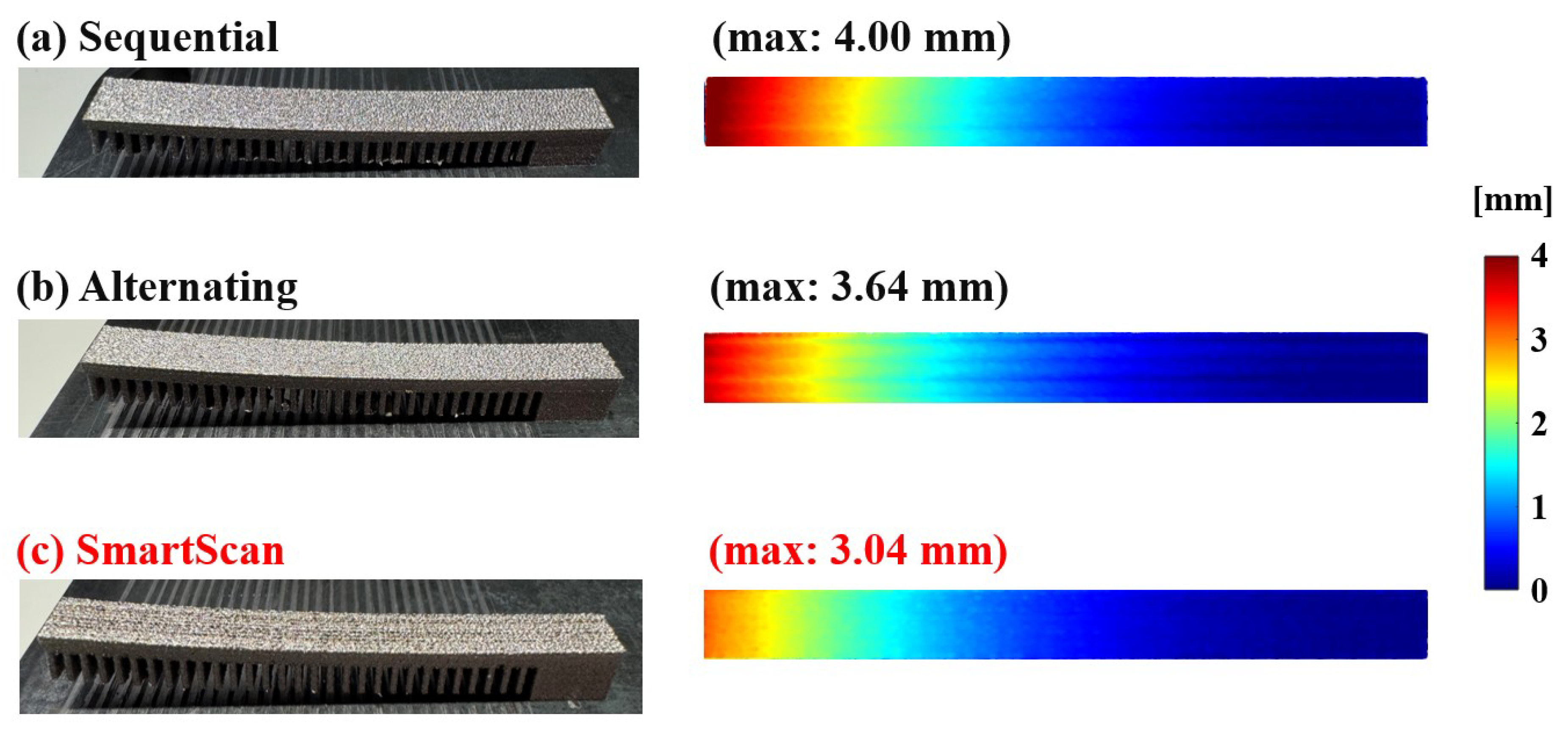
- Similar to the results seen in 2D case studies in our prior work [31,34], SmartScan demonstrated significant reductions in thermal inhomogeneity, residual stress and deformation compared to commonly-used heuristic scan sequences, with minimal increases in printing time. These were demonstrated on a cantilever beam case study where reductions of up to 92% in temperature inhomogeneity, 86% in residual stress, and 24% in maximum deflection were achieved, with only 5% increase in printing time.
- The computational cost of SmartScan is very reasonable for practical applications. It generally optimizes each layer in less than the typical interlayer powder recoating time of LPBF, which makes it practical for offline or online implementation.
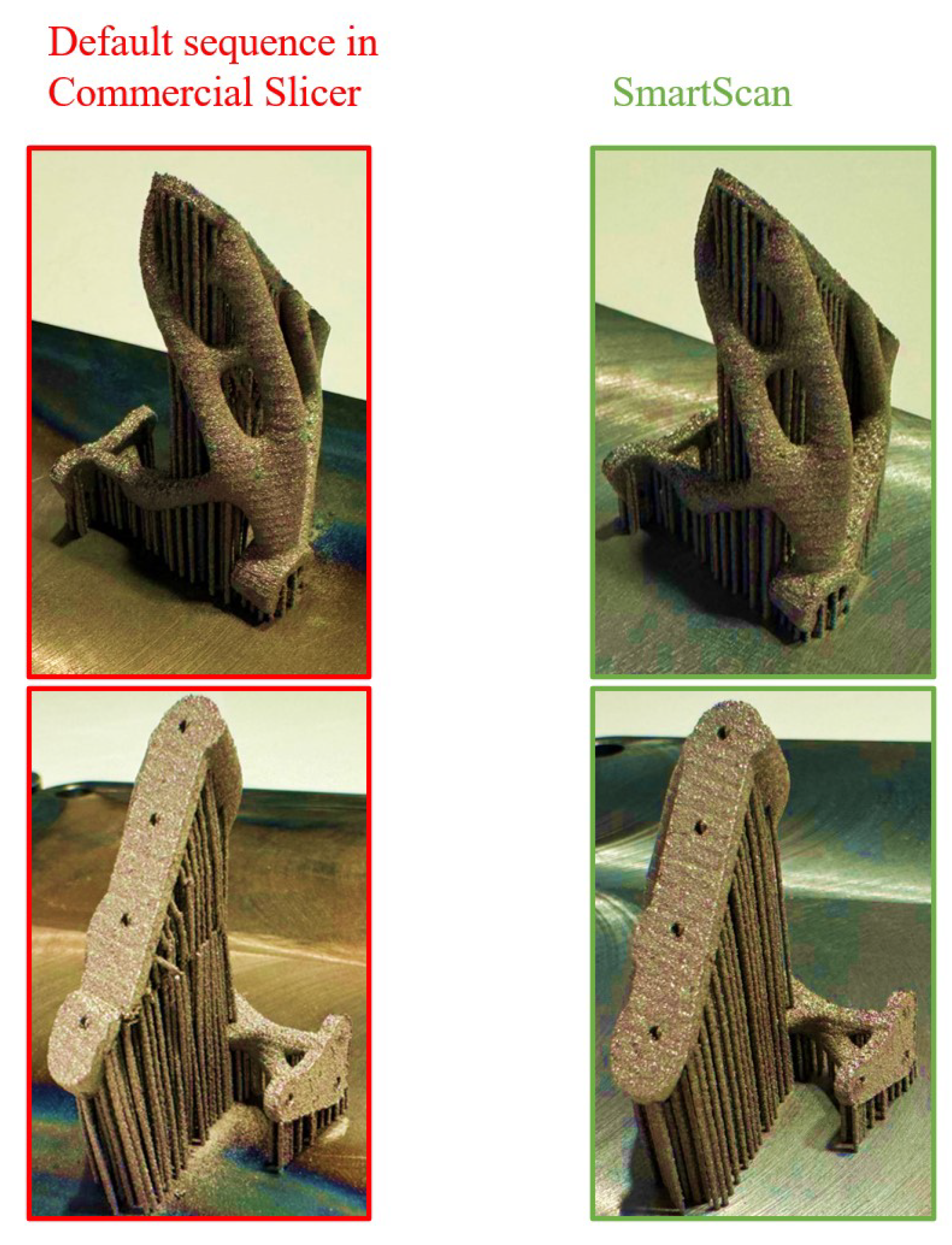
- SmartScan can readily be deployed in practice for processing complex 3D parts by, for example, integrating it as a plug-in to commercial slicing software. This capability was demonstrated using a case study of a complex 3D bracket where the SmartScan plug-in to a commercial slicer was used to produce a successful print while the default scanning sequence of the commercial slicer resulted in a failed print.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Notation | Definition | Unit |
| AM | Additive manufacturing | |
| CLI | Common layer interface | |
| LHI | Least heat influence | |
| LPBF | Laser powder bed fusion | |
| MOR | Model order reduction | |
| SVD | Singular value decomposition | |
| TH | Time-homogenization | |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction | |
| State matrix | ||
| Feature-level state matrix of fth feature | ||
| Reduced state matrix | ||
| Input matrix | ||
| Reduced input matrix | ||
| Output matrix | ||
| Reduced output matrix | ||
| Specific heat capacity | ||
| Identity matrix | ||
| The number of time steps to trace feature f | ||
| R | Temperature uniformity metric | |
| The internal dynamics for all candidates | ||
| T | Temperature | K |
| Temperature state vector | ||
| Reduced state | ||
| Ambient temperature | K | |
| Mean temperature | K | |
| Temperature of the substrate (base plate) | K | |
| Melting point of the material | K | |
| Feature-level input vector of fth feature | ||
| Feature index | ||
| The set of all time steps associated with feature f | ||
| h | Convection coefficient | |
| i | Spatial index of the element in the x-axis | |
| j | Spatial index of the element in the y-axis | |
| k | Spatial index of each layer | |
| Conductivity | ||
| Spatial index of the FDM bottom layer | ||
| l | Temporal index | |
| Notation | Definition | Unit |
| The number of features in a layer | ||
| Number of elements in layer k | ||
| Number of elements in full-scale model | ||
| Number of elements in reduced model | ||
| Probability | ||
| t | Time | s |
| Time step | s | |
| Power per unit volume | ||
| x | Spatial coordinate in the x-axis | |
| Dimensions of each element in the x-axis | m | |
| y | Spatial coordinate in the y-axis | |
| Dimensions of each element in the y-axis | m | |
| z | Spatial coordinate in the z-axis | |
| Dimensions of each element in the z-axis | m | |
| All-ones column vector | ||
| Null matrix | ||
| Projection matrix | ||
| Diffusivity | ||
| Pre-computed scalar | ||
| Pre-computed vector | ||
| Pre-computed matrix | ||
| Absorptance | ||
| Selection metric | ||
| Mean of Gaussian distribution | ||
| Standard deviation of Gaussian distribution | ||
| Density |
Appendix A
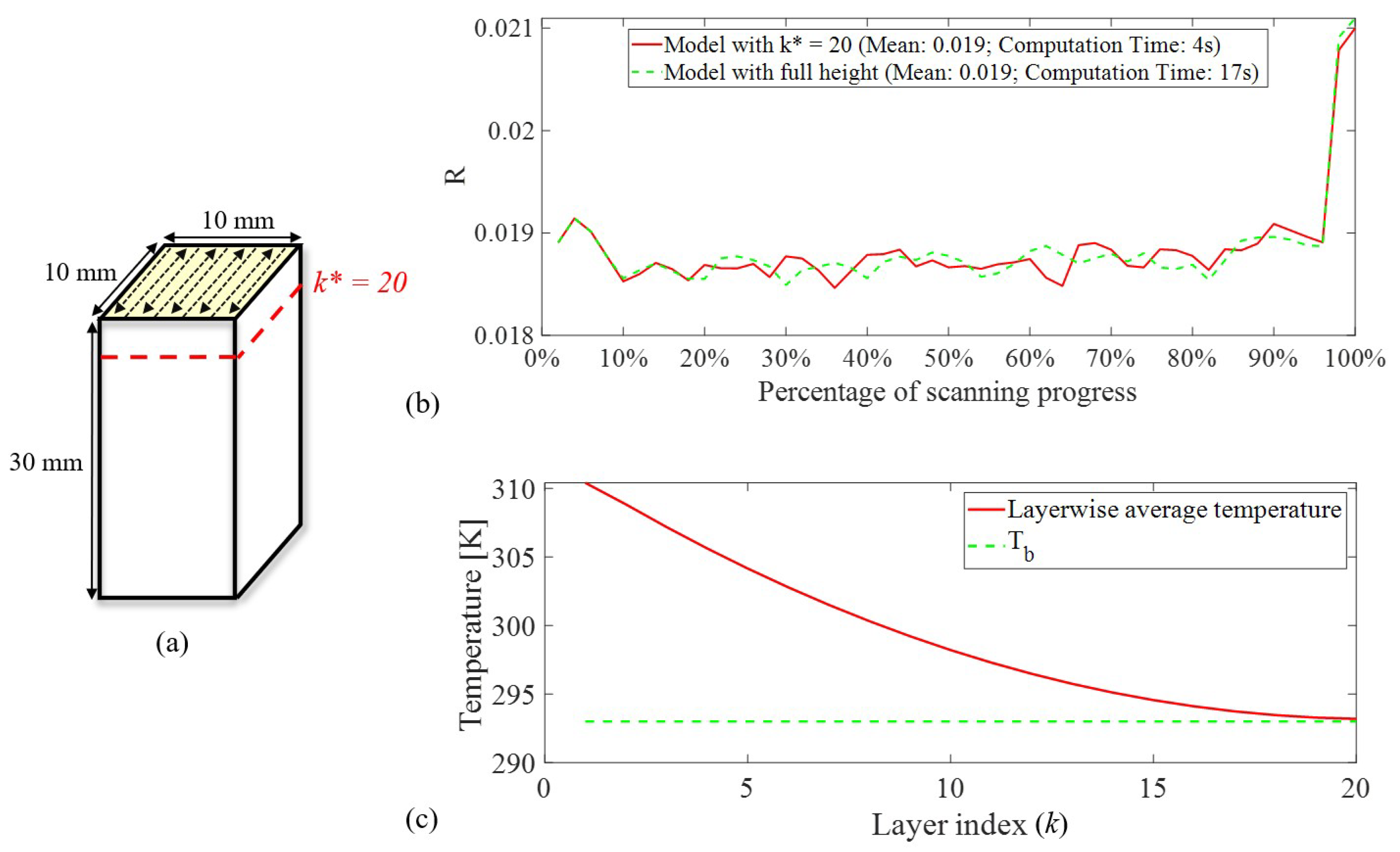
Appendix A.1. Validation of the Effectiveness of the Chosen Values for k *
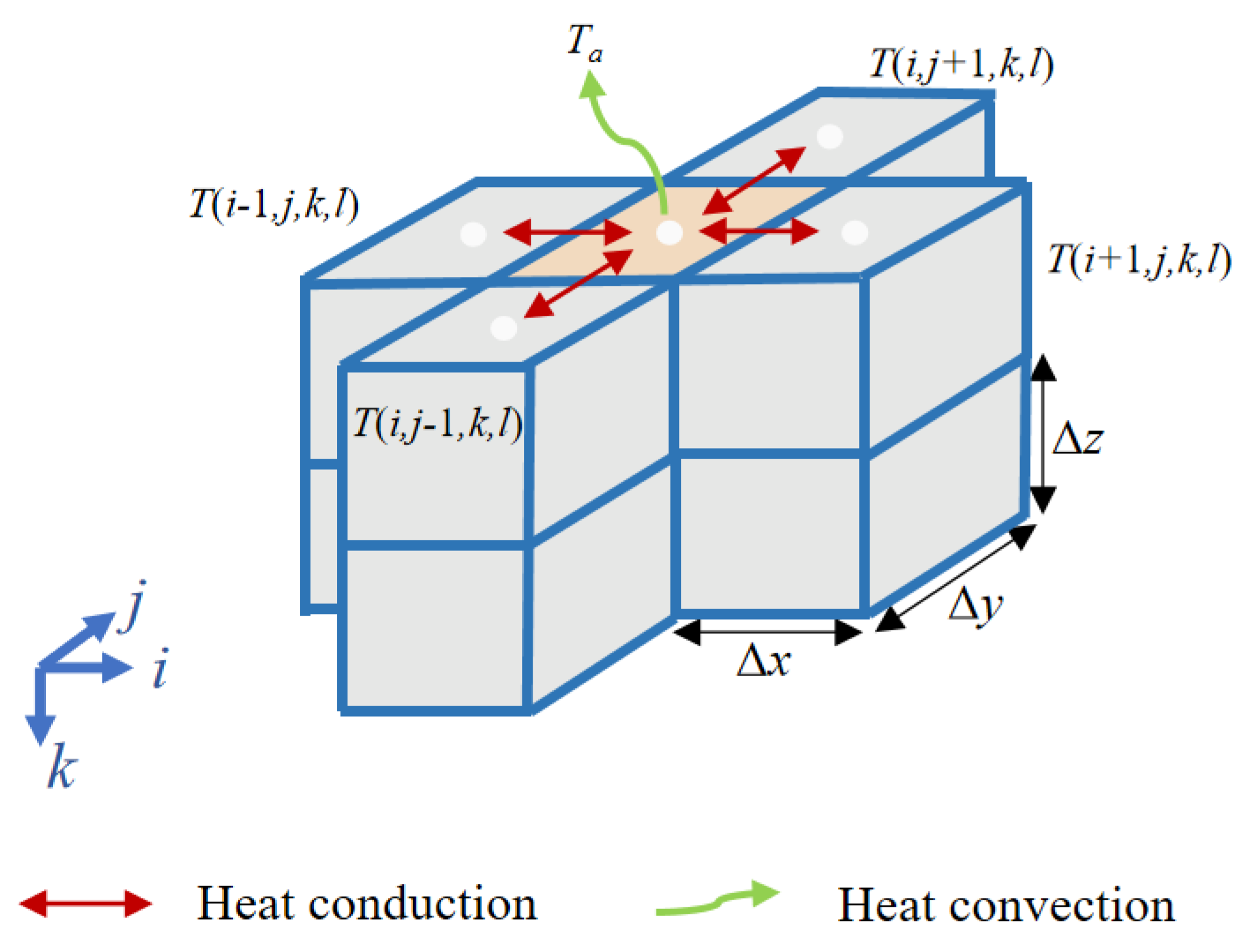
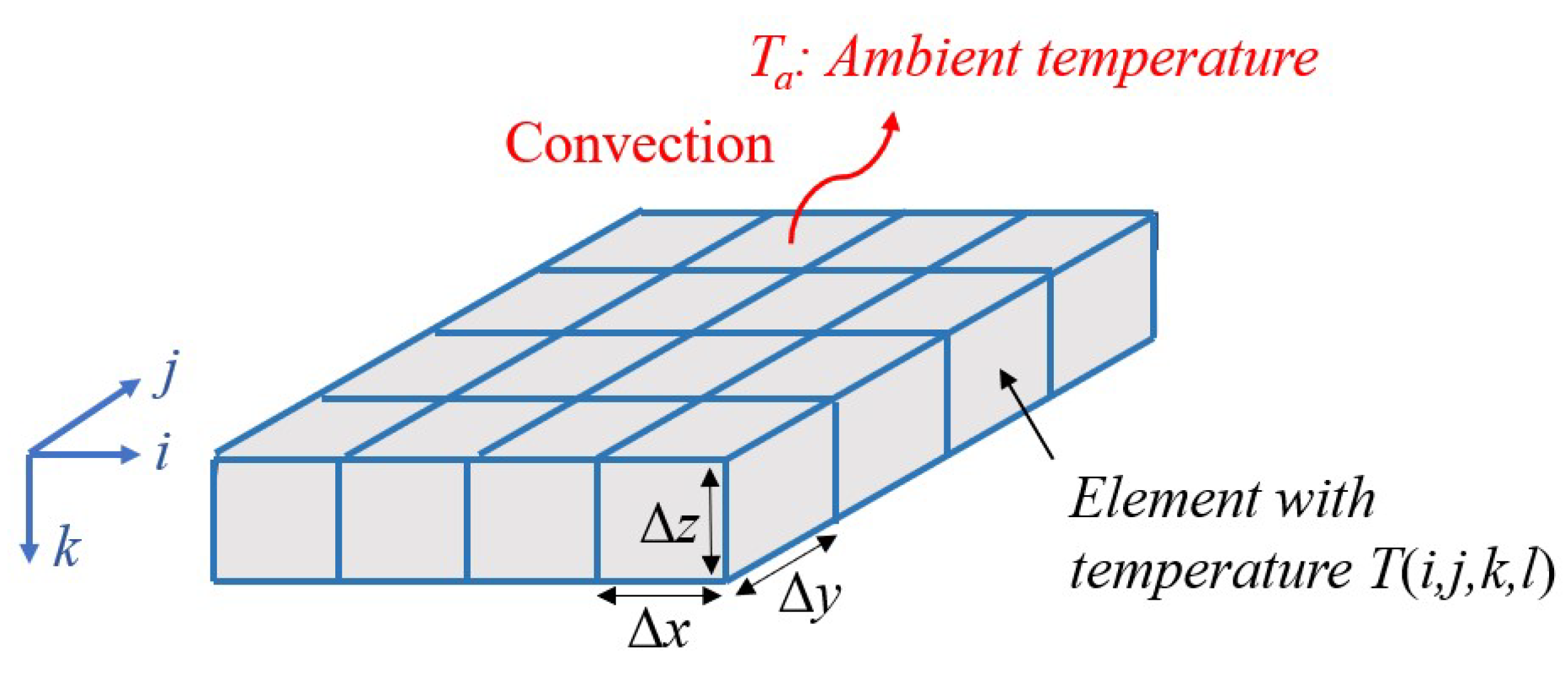
Appendix A.2. Construction of the System Matrix Included in Equation (uid11)
| Left boundary | Interior | Right boundary | |
|---|---|---|---|
References
- Chowdhury, S.; Yadaiah, N.; Prakash, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Dixit, S.; Gupta, L.R.; Buddhi, D. Laser powder bed fusion: a state-of-the-art review of the technology, materials, properties & defects, and numerical modelling. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2022, 20, 2109–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Kotadia, H.; Gibbons, G.; Das, A.; Howes, P. A review of Laser Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing of aluminium alloys: Microstructure and properties. Additive Manufacturing 2021, 46, 102155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, L.; Ashcroft, I.; Wildman, R. Understanding the effect of laser scan strategy on residual stress in selective laser melting through thermo-mechanical simulation. Additive Manufacturing 2016, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Wong, J.C.; Lestandi, L.; Mikula, J.; Vastola, G.; Jhon, M.H.; Dao, M.H.; Kizhakkinan, U.; Ford, C.S.; Rosen, D.W. A part-scale, feature-based surrogate model for residual stresses in the laser powder bed fusion process. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2022, 304, 117541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Taylor, H.; Takezawa, A.; Liang, X.; Jimenez, X.; Wicker, R.; To, A.C. Island scanning pattern optimization for residual deformation mitigation in laser powder bed fusion via sequential inherent strain method and sensitivity analysis. Additive Manufacturing 2021, 46, 102116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zou, Y.; Lim, C.V.S.; Wu, X. Review of laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) fabricated Ti-6Al-4V: process, post-process treatment, microstructure, and property. Light: Advanced Manufacturing 2021, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Li, S.; Shi, S.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Ward, R.M. Effect of processing parameters on surface roughness, porosity and cracking of as-built IN738LC parts fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2020, 285, 116788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.M.; Karabulut, Y.; Kitay, O.; Kaynak, Y.; Jawahir, I.S. Influence of the post-processing operations on surface integrity of metal components produced by laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing: a review. Machining Science and Technology 2021, 25, 118–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.P.; Jebaraj, A.V. Comprehensive review on residual stress control strategies in laser-based powder bed fusion process– Challenges and opportunities. Lasers in Manufacturing and Materials Processing 2023, 10, 400–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiff, C.; Bubeck, W.; Krawczyk, D.; Steeb, M.; Lechler, A.; Verl, A. Learning Feedforward Control for Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Procedia CIRP 2021, 96, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Moumni, Z.; Zhu, J.; Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, W. Effect of scanning speed on fatigue behavior of 316L stainless steel fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2023, 319, 118043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riensche, A.; Bevans, B.D.; Smoqi, Z.; Yavari, R.; Krishnan, A.; Gilligan, J.; Piercy, N.; Cole, K.; Rao, P. Feedforward control of thermal history in laser powder bed fusion: Toward physics-based optimization of processing parameters. Materials & Design 2022, 224, 111351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Standfield, B.; Dou, C.; Law, A.C.; Kong, Z.J. Real-time process monitoring and closed-loop control on laser power via a customized laser powder bed fusion platform. Additive Manufacturing 2023, 66, 103449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Patel, S.; Liu, Z.; Lyu, T.; Wang, Y.; Hua, Y.; Wang, W.; Hattrick-Simpers, J.; Vlasea, M.; Zou, Y. A data-driven framework to improve the wear resistance of a low-alloy steel fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Journal of Manufacturing Processes 2024, 115, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Gao, S.; Tai, J.; Qu, S.; Ding, J.; Song, X.; Fan, Z. Columnar grain width control for SS316L via hatch spacing manipulation in laser powder bed fusion. Materials Research Letters 2023, 11, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Xiao, X. Effects of hatch distance on the microstructure and mechanical anisotropy of 316 L stainless steel fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance 2023, 32, 4757–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissier, M.; Allaire, G.; Tournier, C. Time Dependent Scanning Path Optimization for the Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing Process. Computer-Aided Design 2022, 142, 103122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Hart, A.J. A spiral laser scanning routine for powder bed fusion inspired by natural predator-prey behaviour. Virtual and Physical Prototyping 2022, 17, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, K.; Cheng, T.; Zhao, D.; Li, W.; Teng, Q.; Wei, Q. An optimized scanning strategy to mitigate excessive heat accumulation caused by short scanning lines in laser powder bed fusion process. Additive Manufacturing 2022, 60, 103256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Qu, S.; Ding, J.; Song, X.; Gao, S.; Wang, C.C.; Liao, W.H. Adaptive toolpath generation for distortion reduction in laser powder bed fusion process. Additive Manufacturing 2023, 64, 103432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potočnik, P.; Jeromen, A.; Govekar, E. Genetic Algorithm-Based Framework for Optimization of Laser Beam Path in Additive Manufacturing. Metals 2024, 14, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wu, Y.; Huang, l.; Pan, C.; Sun, Y.; Tian, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y. Scanning strategies for the 316L part with lattice structures fabricated by selective laser melting. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2024, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Ding, J.; Qu, S.; Song, X.; Wang, C.C.; Liao, W.H. Deep reinforcement learning based toolpath generation for thermal uniformity in laser powder bed fusion process. Additive Manufacturing 2024, 79, 103937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Billingham, J.; Axinte, D.; Liao, Z. A rational approach to beam path planning in additive manufacturing: the inverse heat placement problem. Proceedings of the Royal Society A 2023, 479, 20220386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugwagwa, L.; Dimitrov, D.; Matope, S.; Yadroitsev, I. Evaluation of the impact of scanning strategies on residual stresses in selective laser melting. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2019, 102, 2441–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fu, C.; Guo, Y.; Fang, F. A multiscale modeling approach for fast prediction of part distortion in selective laser melting. Journal of materials processing technology 2016, 229, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, D.; Belblidia, F.; Sienz, J. New scanning strategy to reduce warpage in additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing 2019, 28, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruth, J.; Froyen, L.; Vaerenbergh, J.V.; Mercelis, P.; Rombouts, M.; Lauwers, B. Selective laser melting of iron-based powder. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2004, 149, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, P.; Salvemini, F.; Proper, S.; Luzin, V.; Simonsson, K.; Sjöström, S.; Hosseini, S.; Peng, R.L.; Moverare, J. A study of the influence of novel scan strategies on residual stress and microstructure of L-shaped LPBF IN718 samples. Materials & Design 2022, 214, 110386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kang, D.; Yeon, S.M.; Son, Y.; Park, S.H. Interval Island Laser-Scanning Strategy of Ti–6Al–4V Part Additively Manufactured for Anisotropic Stress Reduction. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, K.S.; He, C.; Tsai, Y.L.; Okwudire, C.E. SmartScan: An Intelligent Scanning Approach for Uniform Thermal Distribution, Reduced Residual Stresses and Deformations in PBF Additive Manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing 2022, 102643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Ramani, K.S.; Tsai, Y.L.; Okwudire, C.E. A Simplified Scan Sequence Optimization Approach for PBF Additive Manufacturing of Complex Geometries. Proc. IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), 2022, pp. 1004–1009. [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Tsai, Y.L.; Okwudire, C.E. A Comparative Study on the Effects of an Advanced Scan Pattern and Intelligent Scan Sequence on Thermal Distribution, Part Deformation, and Printing Time in PBF Additive Manufacturing. Proc. International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, 2022. [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Ramani, K.S.; Okwudire, C.E. An intelligent scanning strategy (SmartScan) for improved part quality in multi-laser PBF additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing 2023, 64, 103427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Okwudire, C. Scan Sequence Optimization for Reduced Residual Stress and Distortion in PBF Additive Manufacturing – An AISI 316L Case Study. Proc. Ground Vehicle Systems Engineering and Technology Symposium (GVSETS), 2023.
- Scheel, P.; Markovic, P.; Van Petegem, S.; Makowska, M.G.; Wrobel, R.; Mayer, T.; Leinenbach, C.; Mazza, E.; Hosseini, E. A close look at temperature profiles during laser powder bed fusion using operando X-ray diffraction and finite element simulations. Additive Manufacturing Letters 2023, 6, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, R.; Williams, R.; Riensche, A.; Hooper, P.A.; Cole, K.D.; Jacquemetton, L.; Halliday, H.S.; Rao, P.K. Thermal modeling in metal additive manufacturing using graph theory – Application to laser powder bed fusion of a large volume impeller. Additive Manufacturing 2021, 41, 101956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.C.; Ehrlich, L.E.; Powell-Palm, M.J.; Montgomery, C.; Beuth, J.; Malen, J.A. Thermal conductivity of metal powders for powder bed additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing 2018, 21, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodkhani, Y.; Ali, U.; Shahabad, S.I.; Kasinathan, A.R.; Esmaeilizadeh, R.; Keshavarzkermani, A.; Marzbanrad, E.; Toyserkani, E. On the measurement of effective powder layer thickness in laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing of metals. Progress in Additive Manufacturing 2019, 4, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Sievers, D.E.; Garmestani, H.; Liang, S.Y. Analytical Thermal Modeling of Metal Additive Manufacturing by Heat Sink Solution. Materials 2019, 12, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zariphopoulou, T.; Zhou, X. Exploration versus exploitation in reinforcement learning: A stochastic control approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.01552, arXiv:1812.01552 2018.
- Chung, J.J.; Lawrance, N.R.; Sukkarieh, S. Gaussian processes for informative exploration in reinforcement learning. Proc. IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, 2013, pp. 2633–2639.
- Lipowski, A.; Lipowska, D. Roulette-wheel selection via stochastic acceptance. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2012, 391, 2193–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhang, W. Influence of the scanning angle on the grain growth and mechanical properties of Ni10Cr6W1Fe9Ti1 HEA fabricated using the LPBF–AM method. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2023, 864, 144596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afazov, S.; Denmark, W.A.; Toralles, B.L.; Holloway, A.; Yaghi, A. Distortion prediction and compensation in selective laser melting. Additive Manufacturing 2017, 17, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.J.; Vecchiato, F.; Kelleher, J.; Wenman, M.R.; Hooper, P.A.; Davies, C.M. Effects of heat treatment on residual stresses in the laser powder bed fusion of 316L stainless steel: Finite element predictions and neutron diffraction measurements. Journal of Manufacturing Processes 2020, 57, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, N.; Pitts, Z.; Thompson, S.; Saharan, A. Benchmarking build simulation software for laser powder bed fusion of metals. Additive Manufacturing 2020, 36, 101531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Clare, A.T.; Bennett, C.; Jin, X. Informing directed energy deposition strategies through understanding the evolution of residual stress. Additive Manufacturing 2024, 79, 103907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, S. Chapter 2 - The Finite Difference Method. In Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations; Mazumder, S., Ed.; Academic Press, 2016; pp. 51–101. [CrossRef]







| Parameter (Units) | Value |
|---|---|
| Laser power, P (W) | 290 |
| Laser spot diameter () | 77 |
| Absorptance, | 0.37 |
| Mark/scan speed (mm/s) | 1200 |
| Jump speed (mm/s) | 6000 |
| Hatch spacing () | 100 |
| Layer thickness () | 50 |
| Conductivity, () | 22.5 |
| Diffusivity, () | |
| Melting temperature, (K) | 1658 |
| Convection coefficient, h () | 25 |
| Ambient temperature, (K) | 293 |
| Vector Pattern | Print Time [min] |
|---|---|
| Sequential | 37 |
| Alternating | 37 |
| SmartScan | 39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





