Submitted:
06 November 2023
Posted:
07 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials used in nanoparticle preparation
2.1. Clay minerals
2.2. Minerals
2.3. Nano-biochar
2.4. Other nano-materials
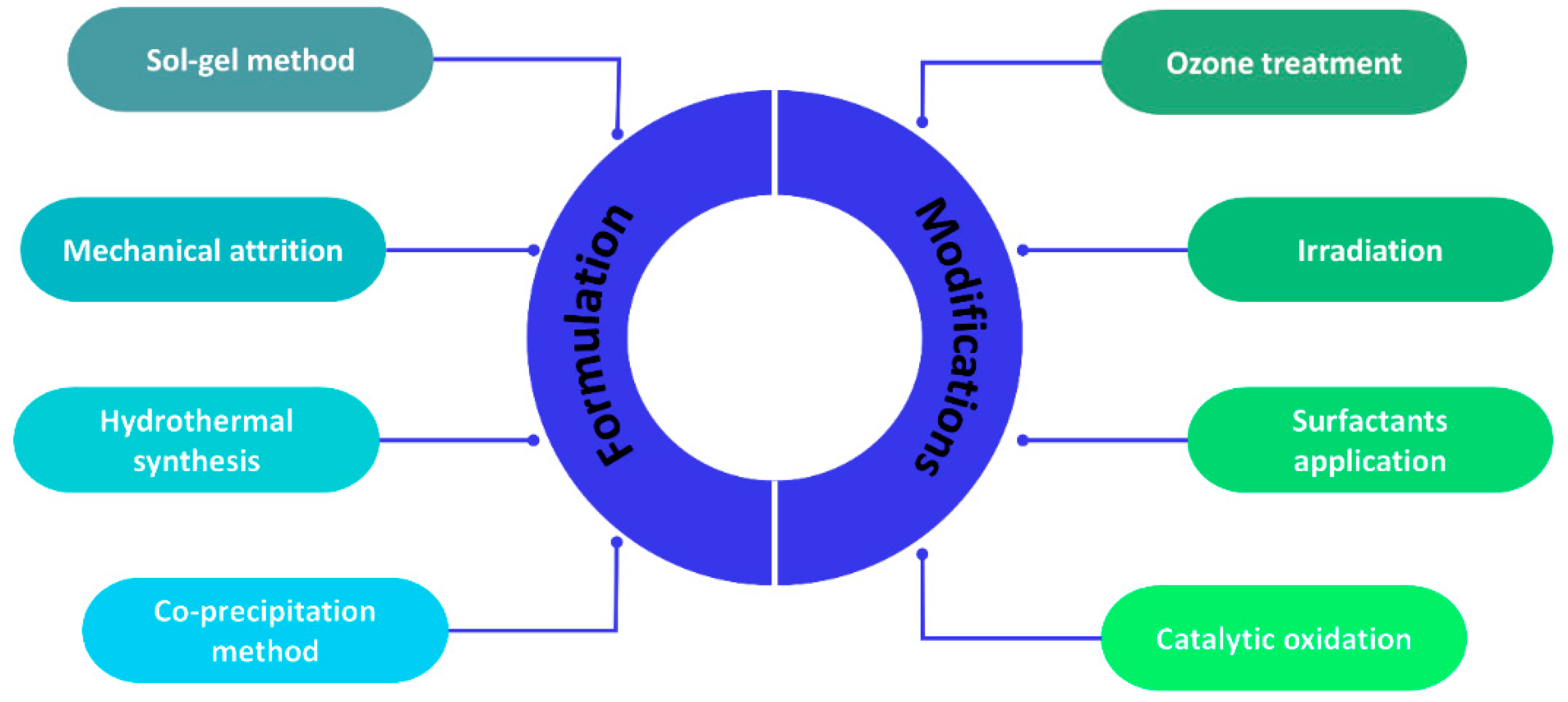
3. Methods of nanoparticle formulations and modifications for preparing NNFs
3.1. Nanoparticle Formulation Methods
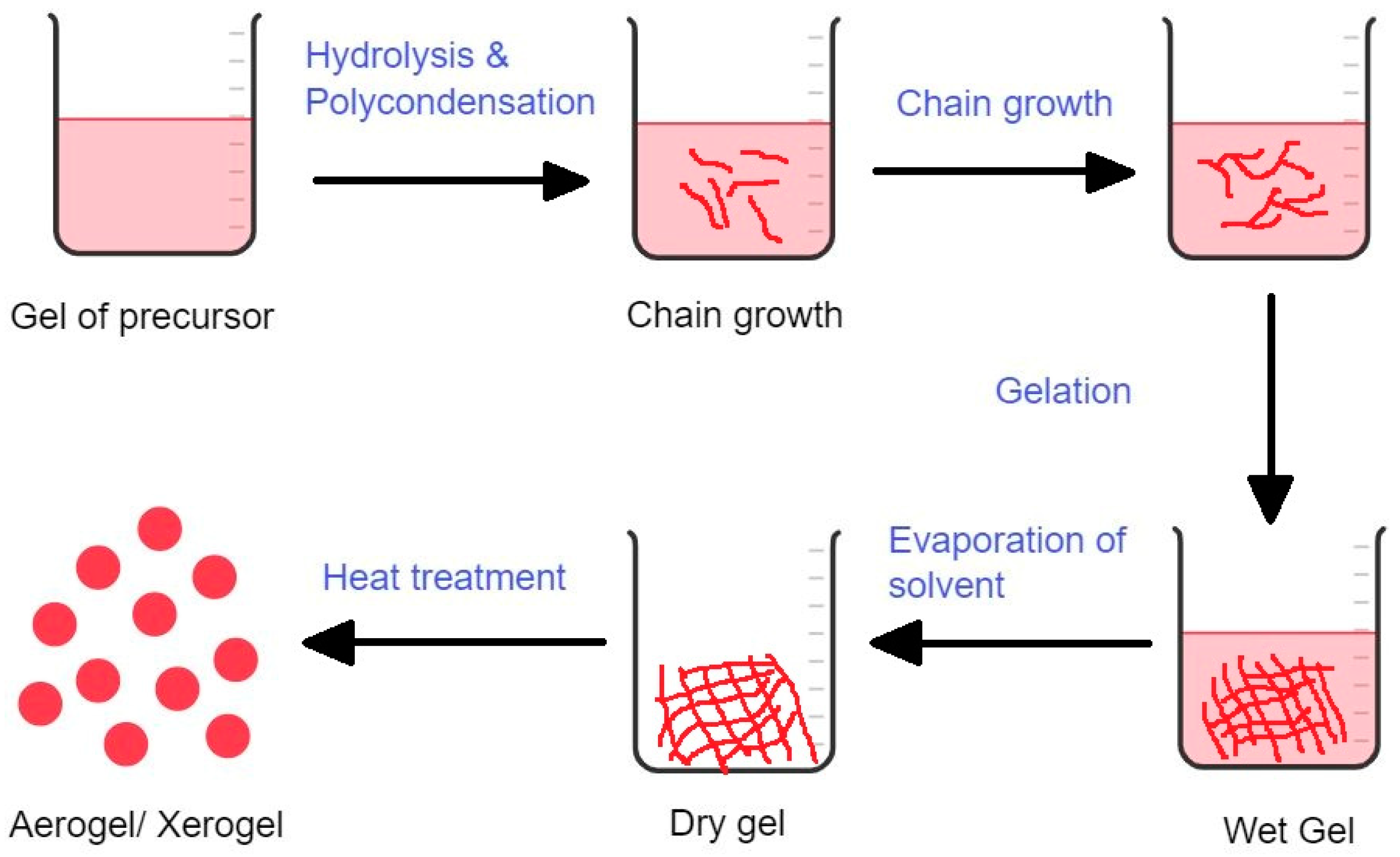
3.1.1. Sol-gel method
3.1.2. Mechanical attrition
3.1.3. Hydrothermal synthesis
3.1.4. Co-precipitation method
3.2. Nanoparticles modification methods
| Fertiliser | N source | Nutrients | NP used | NP preparation or modification method | Binder/ other components | Method of SRF preparation | N release | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnBenVegU | Urea | N & Zn | Zn fortified nano-bentonite | Soil-gel | Vegetable oil | Coating | 10 days | [15] |
| ZnBenParU | Urea | N & Zn | Zn fortified nano-bentonite | Soil-gel | stearic acid, paraffin oil, paraffin wax | Coating | 15 days | [15] |
| QAL-Ben-U | Urea | N | Bentonite | Soil-gel | Quaternary ammoniumlignin (QAL) | Matrix and coating | N/A | [22] |
| Nano-biochar SRF | Sodium Nitrate | N, P, K, Ca and micronutrients | Nano-biochar | Physical crushing | N/A | Impregnation | >10 days | [36] |
| U-CAM | Urea | N, Fe & Ca | Carboxylated nano-cellulose (CNF) | Catalytic oxidation | hydrogel | Matrix | >30 days | [38] |
| BNC fertiliser | sodium nitrate | N, Ca, P, K, Mg and micronutrients | Nano-biochar | Physical crushing | N/A | Impregnation | >14 days | [37] |
| WNLCU | Urea | N | Attapulgite (HA) | High-energy electron beam (HEEB) irradiation |
sodium polyacrylate (P) and polyacrylamide (M) | Matrix | 66% lower than control | [16] |
| WNLCN | Ammonium chloride | N | Attapulgite (HA) | High-energy electron beam (HEEB) irradiation |
sodium polyacrylate (P) and polyacrylamide (M) | Matrix | 90% lower than control | [16] |
| Loss control urea (LCU) | Urea | N | Attapulgite | Irradiated by high-energy electron beam and O3 treatment | Polyacrylamide (P) | Matrix | 50% lower than urea | [25] |
| Coated urea | Urea | N | Kaoline and Polystyrene-starch |
Ultrahigh speed cutting and semi-emulsification |
None | Coating | N/A | [17] |
| Kao-urea | Urea | N | Kaolin | None | Chitosan | Matrix | >30 days | [27] |
| Kao-urea | Urea | N | Kaolin | Milling | None | Matrix | >7 days | [28] |
| Gal-ADP | Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP) | N, K, P and other micronutrients | Glauconite | Chemical and mechanochemical method | Na2CO3 as extender | Matrix | > 56 days | [18] |
| HA-POL-Urea | Urea | N, K and P | Hydroxyapatite (HDA) | Sol-gel | Cellulose fibre, polyacrylamide | Matrix | 112 days | [39] |
| Zeo-AN | Ammonium nitrate (AN) | N | Zeolite (Surface modified) | Hydrothermally synthesized | None | Surface carrier | 35% lower than CF | [31] |
| Nano Zn-MAP and Nano Zn-Urea | Monoammonium phosphate (MAP) and Urea | N | ZnO | N/A | Water | Coating | N/A | [32] |
| Zeolite | Sodium nitrate | N and other macro and micronutrients | Zeolite | Co-precipitation method |
None | Surface carrier | >7 days- water & >16 days- soil | [30] |
| Zn-MAP & Zn-Urea | Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP) and Urea |
N and Zn | ZnO | None | Water | Coating | N/A | [34] |
4. Crop responses for nano-nitrogen fertilisers
4.1. Yield responses
4.2. Crop nitrogen uptake
4.3. Nitrogen utilisation efficiency (NUE)
4.4. Germination of seeds
4.5. Chlorophyll content
4.6. Gene expression
| Fertiliser & Nanoparticle | Application rate (kg/ha) |
Crop | Crop response | Study country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urea (U)+nano carbon (NC) synergist | N - 525 NC – 1.575 |
Wheat | Leaf N accumulation is significantly higher by 55-65% than the control. Glutamine synthetase activity and nitrate transporter gene were higher than the control |
China | [10] |
| Urea (U)+nano calcium Carbonate (NCa) synergist |
N - 525 NCa - 1.575 |
Wheat | Leaf N accumulation is significantly higher by 20-30% than control Glutamine synthetase activity and nitrate transporter gene were higher than the control |
China | [10] |
| Urea+ Carboxylated nano-cellulose | 16.45 | Wheat | Germination rate, tiller number, photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll Content were higher than urea treatment |
China | [38] |
| Urea/ NH4NO3 in attapulgite sodium polyacry- late polyacrylamide complex | 81 | Corn | Higher 15N abundance and TN in leaf Increased the height and stem diameter than the control |
China | [16] |
| Nano-nitrogen chelate (NNC) fertilizers | 80-161 | Sugarcane | The NUE of NNC was significantly higher than urea (control) treatment. | Iran | [61] |
| Nano ADP - Glauconite | 50 | Oat | The germination rate, plant height and yield were significantly (P<0.05) higher than non-NNF treated plot. | Russia | [18] |
| Nano-hydroxyapatite (nHA) with Cellulose fibre and polyacrylamide + urea | 45-223 | Maize | At a lower application rate, growth parameters were significantly (P<0.05) lower than conventional fertilisers (CF). However, at a high application rate, no significant difference was observed. | Kenya | [44] |
| nHA with Cellulose fibre and polyacrylamide + urea | 45-223 | Kale | At a high application level, NNF showed a significantly (P<0.05) higher yield than CF. At a low application rate herbage N was significantly lower by 33% than CF. |
Kenya | [44] |
| nHA with Cellulose fibre and polyacrylamide + urea | 45-223 | Capsicum | At a high application level, NNF showed a significantly (P<0.05) higher yield by 54% than conventional fertilisers. At a low application rate herbage N was significantly lower by 43% than CF. |
Kenya | [44] |
| Zno-np/vegetable oil (VO) coated urea (ZN-VO-Urea) | 100 mg-N kg-1 soil | Wheat | ZN-VO-Urea fertilisers showed significantly (P<0.05) higher yield than VO-coated urea. But plant N was not significantly different between them. However, there was no significant difference between nano- and bulk-ZN-VO coated urea. This suggests that Zno has a synergetic effect with fertiliser than the nano size of the particle in the coating. |
United States | [45] |
| Nano-urea | 0-150 | Maize and mustard | At 113 kg-N ha-1 application rate, nano fertiliser showed a significant (P<0.05) yield than CF. | India | [47] |
| Quaternary ammonium lignin (QAL) modified nano-bentonite coated urea | 75-300 | Tomato | Most of the NNF significantly increased yield and N uptake by tomato than urea. | Egypt | [22] |
| Urea–HA nanohybrid fertilizer | 240 | Tea | The tea yield increase was noticed in the low country and Uva region but not in mid country. | Sri Lanka | [48] |
| Urea-chitosan nanohybrid fertiliser (UCNH) | Urea (66-165 kg N ha-1) + Urea-chitosan (0-500 mg N L-1) | Rice | The best treatment was the application of 500 mg N L-1 compensatory level of UCNH with 60% of the recommended urea level (99 kg N ha-1). | Egypt | [49] |
| Urea surface-modified hydroxy appetite (HA) nanoparticles | 0-33 kg N ha-1 | Almond | Nano fertiliser at a higher application rate significantly increased the germination of almonds than urea and ammonium sulphate. | Egypt | [55] |
| NNF | Ammonium nitrate (AN) (0-100%) and/or NNF (0-75%) | Lettuce | In both study years, NUE was significantly increased for 100% NNF application than 100% AN application. | Egypt | [53] |
| Kao-urea NNF | 150 kg ha-1. | Rice | The best NNF significantly increased the yield but not the leaf N content compared to urea. | Malaysia | [46] |
5. Disadvantages of nanoparticles for crops and the environment
6. Limitations in the studies and future research directions
- It is worth noting that certain studies have compared nanofertilizers (NNFs) to untreated control groups, which inherently results in superior performance by the NNFs. However, to provide a more comprehensive evaluation, it is important for studies to include appropriate control groups for comparison. These control groups should consist of conventional fertilizers or other smart fertilisers or other commercially available nano-fertilisers commonly used in agricultural systems. Comparing NNFs against these control groups allows for a more accurate assessment of the effectiveness and added benefits of newly developed NNFs.
- Many studies on nanoparticles have been conducted in controlled laboratory settings, which may not fully represent real-world agricultural conditions. More field studies are required to validate the findings and assess the practical implications in agricultural settings.
- Nanoparticles have the potential to persist in the environment over the long term. It is important to understand the fate and behaviour of these particles to assess any potential risks. However, currently, there is a lack of publicly available studies specifically addressing long-term trials and their impact on the environment. Further research is needed to comprehensively evaluate the long-term effects of nanoparticles and ensure their safe and sustainable use in agricultural applications.
- Some nanocarriers have the potential to be phytotoxic which may have negative impacts namely stunted growth, reduced biomass accumulation, chlorosis, wilting, and even plant death. Therefore, studies focusing on the accumulation of nanoparticles by plants and their long-term effects need to be conducted.
- Further research is needed to investigate the transmission of nanoparticles (NPs) through the food chain. Understanding how NPs can potentially accumulate and transfer from one organism to another within the food web is crucial for assessing their overall impact on human health and the environment.
- The fate of NPs ingested by the crops and their negative impacts on the crop itself and the living beings consuming them needs to be analysed rigorously.
7. Conclusion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abhiram, G.; Grafton, M.; Jeyakumar, P.; Bishop, P.; Davies, C.E.; McCurdy, M. Iron-rich sand promoted nitrate reduction in a study for testing of lignite based new slow-release fertilisers. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 864, 160949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiertz, J. Nitrogen, sustainable agriculture and food security: a review. Sustainable agriculture 2009, 635–651. [Google Scholar]
- Gnaratnam, A.; McCurdy, M.; Grafton, M.; Jeyakumar, P.; Bishop, P.; Davies, C. Assessment of nitrogen fertilizers under controlled environment–a lysimeter design. 2019.
- Mahmud, K.; Panday, D.; Mergoum, A.; Missaoui, A. Nitrogen losses and potential mitigation strategies for a sustainable agroecosystem. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhiram, G.; Grafton, M.; Jeyakumar, P.; Bishop, P.; Davies, C.E.; McCurdy, M. The nitrogen dynamics of newly developed lignite-based controlled-release fertilisers in the soil-plant cycle. Plants 2022, 11, 3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaratnam, A. Design and fabrication of a climate-controlled lysimeter and testing of new controlled-release fertilisers: a thesis presented in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (PHD) in Agricultural Engineering and Environmental Sciences at Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand. Massey University, 2021.
- Abhiram, G.; McCurdy, M.; Davies, C.E.; Grafton, M.; Jeyakumar, P.; Bishop, P. An innovative lysimeter system for controlled climate studies. Biosystems Engineering 2023, 228, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhiram, G.; Bishop, P.; Jeyakumar, P.; Grafton, M.; Davies, C.E.; McCurdy, M. Formulation and characterization of polyester-lignite composite coated slow-release fertilizers. Journal of Coatings Technology and Research 2023, 20, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkel, M. Slow-and Controlled-Release and Stabilized Fertilizers: An Option for Enhancing Nutrient Use Effiiency in Agriculture, International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA), 2010.
- Yang, M.; Dong, C.; Shi, Y. Nano fertilizer synergist effects on nitrogen utilization and related gene expression in wheat. BMC Plant Biology 2023, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liao, J.; Song, H.; Yang, Y.; Guan, C.; Zhang, Z. A biochar-based route for environmentally friendly controlled release of nitrogen: urea-loaded biochar and bentonite composite. Scientific reports 2019, 9, 9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakor, A.S.; Gambhir, S.S. Nanooncology: the future of cancer diagnosis and therapy. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 2013, 63, 395–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shweta; Sood, S.; Sharma, A.; Chadha, S.; Guleria, V. Nanotechnology: A cutting-edge technology in vegetable production. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology 2021, 96, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiumei, L.; Fudao, Z.; Shuqing, Z.; Xusheng, H.; Rufang, W.; Zhaobin, F.; Yujun, W. Responses of peanut to nano-calcium carbonate. Plant Nutrition and Fertitizer Science 2005, 11, 385–389. [Google Scholar]
- Umar, W.; Czinkota, I.; Gulyás, M.; Aziz, T.; Hameed, M.K. Development and characterization of slow release N and Zn fertilizer by coating urea with Zn fortified nano-bentonite and ZnO NPs using various binders. Environmental Technology & Innovation 2022, 26, 102250. [Google Scholar]
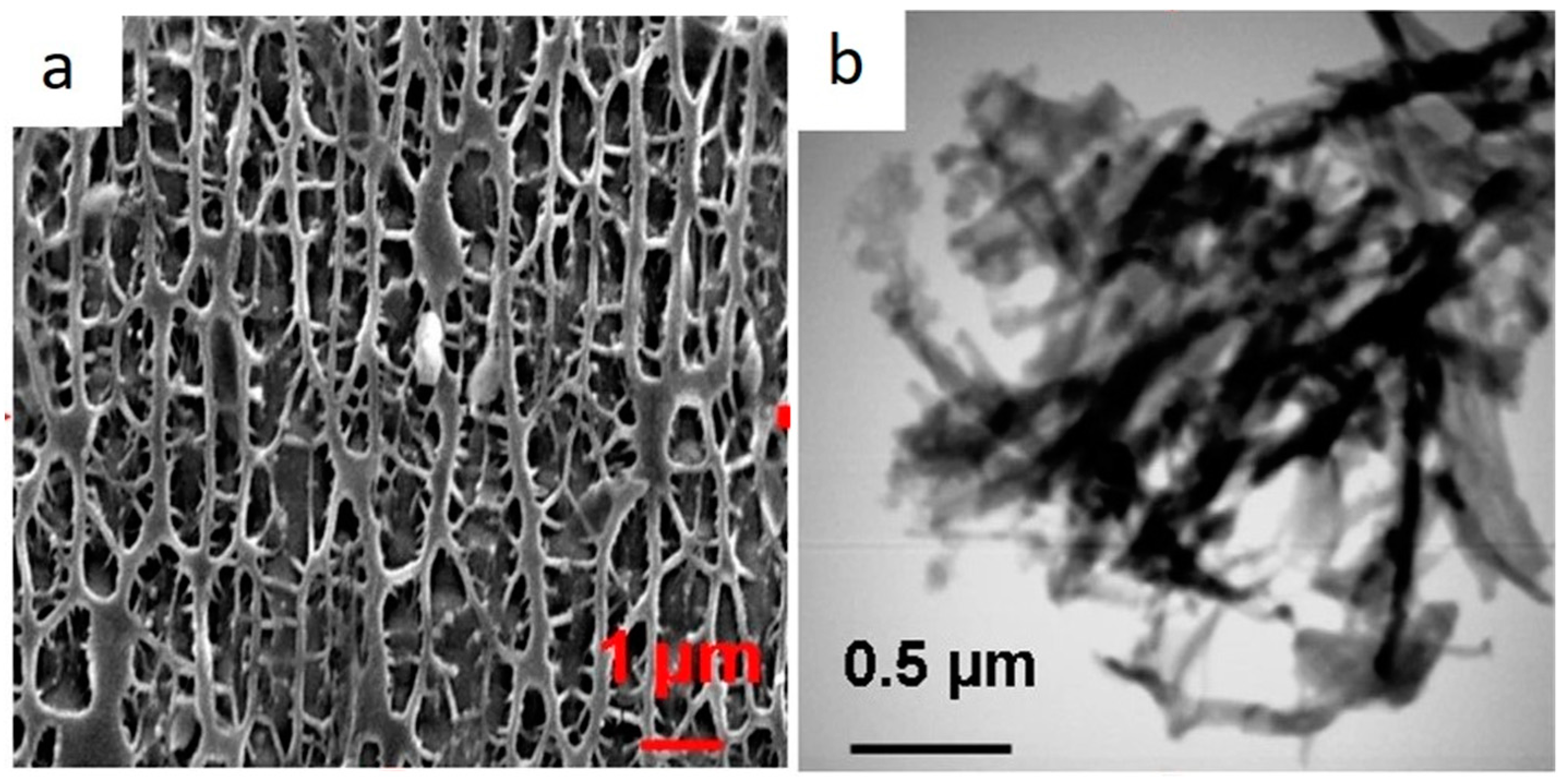
- Zhou, L.; Cai, D.; He, L.; Zhong, N.; Yu, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z. Fabrication of a high-performance fertilizer to control the loss of water and nutrient using micro/nano networks. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2015, 3, 645–653. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.-M.; Feng, Z.-B.; Zhang, F.-D.; Zhang, S.-Q.; He, X.-S. Preparation and testing of cementing and coating nano-subnanocomposites of slow/controlled-release fertilizer. Agricultural Sciences in China 2006, 5, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudmin, M.; Makarov, B.; López-Quirós, A.; Maximov, P.; Lokteva, V.; Ibraeva, K.; Kurovsky, A.; Gummer, Y.; Ruban, A. Preparation, Features, and Efficiency of Nanocomposite Fertilisers Based on Glauconite and Ammonium Dihydrogen Phosphate. Materials 2023, 16, 6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, M. Bentonite clay as a natural remedy: a brief review. Iranian journal of public health 2017, 46, 1176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, D.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Soni, B. Naturally occurring bentonite clay: Structural augmentation, characterization and application as catalyst. Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 57, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.A.; Abdelfattah, M.A.; Taha, F.K. Developments in soil salinity assessment and reclamation: innovative thinking and use of marginal soil and water resources in irrigated agriculture; Springer Science & Business Media, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Helal, M.I.; El-Mogy, M.M.; Khater, H.A.; Fathy, M.A.; Ibrahim, F.E.; Li, Y.C.; Tong, Z.; Abdelgawad, K.F. A Controlled-Release Nanofertilizer Improves Tomato Growth and Minimizes Nitrogen Consumption. Plants 2023, 12, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
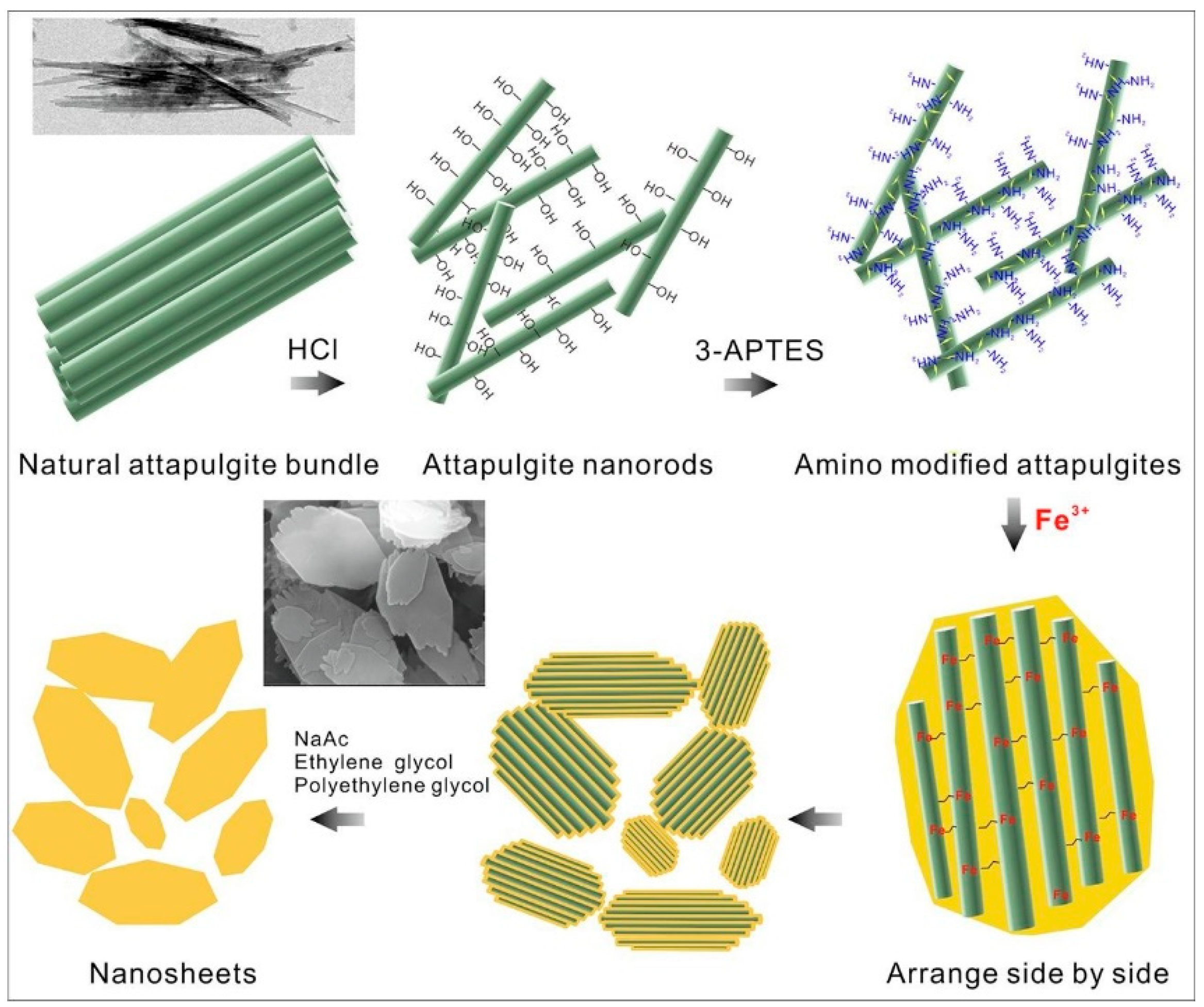
- Liu, J.; Zhong, J.; Chen, Z.; Mao, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Ren, S. Preparation, characterization, application and structure evolution of attapulgite: from nanorods to nanosheets. Applied Surface Science 2021, 565, 150398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpaletha, P.; Lalithambika, M. Modified attapulgite: an efficient solid acid catalyst for acetylation of alcohols using acetic acid. Applied Clay Science 2011, 51, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wu, Y.; Feng, H.; Brown, I.G.; Chu, P.K.; Yu, Z. Controlling nitrogen migration through micro-nano networks. Scientific reports 2014, 4, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, A.K.; Mishra, B.G.; Mishra, D.K.; Singh, R.K. Effect of sulphuric acid treatment on the physico-chemical characteristics of kaolin clay. Colloids and surfaces A: Physicochemical and engineering aspects 2010, 363, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanravan, B.; Soltani, S.M.; Rashid, S.A.; Mahdavi, F.; Yusop, M.K. Enhancement of nitrogen release properties of urea–kaolinite fertilizer with chitosan binder. Chemical Speciation & Bioavailability 2015, 27, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- AlShamaileh, E.M.; Al-Rawajfeh, A.E.; Alrbaihat, M.R. Solid-state mechanochemical synthesis of Kaolinite-Urea complexes for application as slow release fertilizer. Journal of Ecological Engineering 2019, 20, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.S.; Baioumy, H.M. Structural and chemical alteration of glauconite under progressive acid treatment. Clays and clay minerals 2006, 54, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateef, A.; Nazir, R.; Jamil, N.; Alam, S.; Shah, R.; Khan, M.N.; Saleem, M. Synthesis and characterization of zeolite based nano–composite: An environment friendly slow release fertilizer. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 2016, 232, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, D.; Tomar, R. Use of surface modified inorganic nano materials as slow release nitrogen fertilizer. Sustainable Agricultural Development: Recent Approaches in Resources Management and Environmentally-Balanced Production Enhancement 2011, 171-184.
- Milani, N.; Hettiarachchi, G.M.; Kirby, J.K.; Beak, D.G.; Stacey, S.P.; McLaughlin, M.J. Fate of zinc oxide nanoparticles coated onto macronutrient fertilizers in an alkaline calcareous soil. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0126275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, G.; Hund-Rinke, K.; Kuhlbusch, T.; Van den Brink, N.; Nickel, C. Fate and bioavailability of engineered nanoparticles in soils: a review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 2014, 44, 2720–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, N.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Stacey, S.P.; Kirby, J.K.; Hettiarachchi, G.M.; Beak, D.G.; Cornelis, G. Dissolution kinetics of macronutrient fertilizers coated with manufactured zinc oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2012, 60, 3991–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashidhar, P.; Kochar, M.; Singh, B.; Gupta, M.; Cahill, D.; Adholeya, A.; Dubey, M. Biochar for delivery of agri-inputs: Current status and future perspectives. Science of the Total Environment 2020, 703, 134892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.A.; Naqvi, S.R.; Mehran, M.T.; Khoja, A.H.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Juchelková, D.; Atabani, A. A performance evaluation study of nano-biochar as a potential slow-release nano-fertilizer from wheat straw residue for sustainable agriculture. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateef, A.; Nazir, R.; Jamil, N.; Alam, S.; Shah, R.; Khan, M.N.; Saleem, M. Synthesis and characterization of environmental friendly corncob biochar based nano-composite–A potential slow release nano-fertilizer for sustainable agriculture. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management 2019, 11, 100212. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Shaghaleh, H.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Xu, X.; Liu, H. Synthesis of a pH-responsive nano-cellulose/sodium alginate/MOFs hydrogel and its application in the regulation of water and N-fertilizer. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2021, 187, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rop, K.; Karuku, G.N.; Mbui, D.; Michira, I.; Njomo, N. Formulation of slow release NPK fertilizer (cellulose-graft-poly (acrylamide)/nano-hydroxyapatite/soluble fertilizer) composite and evaluating its N mineralization potential. Annals of Agricultural Sciences 2018, 63, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, S.; Peinado, S.; Morillas-Gutiérrez, F.; La Rubia, M.D.; Moya, A.J. Nanocellulose from agricultural wastes: Products and applications—A review. Processes 2021, 9, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratne, G.P.; Kottegoda, N.; Madusanka, N.; Munaweera, I.; Sandaruwan, C.; Priyadarshana, W.M.G.I.; Siriwardhana, A.; Madhushanka, B.A.D.; Rathnayake, U.A.; Karunaratne, V. Two New Plant Nutrient Nanocomposites Based on Urea Coated Hydroxyapatite: Efficacy and Plant Uptake. Indian J Agr Sci 2016, 86, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottegoda, N.; Sandaruwan, C.; Priyadarshana, G.; Siriwardhana, A.; Rathnayake, U.A.; Berugoda Arachchige, D.M.; Kumarasinghe, A.R.; Dahanayake, D.; Karunaratne, V.; Amaratunga, G.A. Urea-hydroxyapatite nanohybrids for slow release of nitrogen. ACS nano 2017, 11, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, N. Methods of preparation of nanoparticles-a review. International Journal of Advances in Engineering & Technology 2015, 7, 1806. [Google Scholar]
- Rop, K.; Karuku, G.N.; Mbui, D.; Njomo, N.; Michira, I. Evaluating the effects of formulated nano-NPK slow release fertilizer composite on the performance and yield of maize, kale and capsicum. Annals of Agricultural Sciences 2019, 64, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Andrews, J.; Fugice, J.; Singh, U.; Bindraban, P.S.; Elmer, W.H.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; White, J.C. Facile coating of urea with low-dose ZnO nanoparticles promotes wheat performance and enhances Zn uptake under drought stress. Frontiers in plant science 2020, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanravan, B.; Mahmoud Soltani, S.; Mahdavi, F.; Abdul Rashid, S.; Khanif Yusop, M. Preparation of encapsulated urea-kaolinite controlled release fertiliser and their effect on rice productivity. Chemical Speciation & Bioavailability 2014, 26, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, P.K.; Dey, A.; Singh, V.K.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Singh, T.; GA, R.; Babu, S.; Rathore, S.S.; Singh, R.K.; Shekhawat, K. Conjoint application of nano-urea with conventional fertilizers: An energy efficient and environmentally robust approach for sustainable crop production. Plos one 2023, 18, e0284009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raguraj, S.; Wijayathunga, W.M.S.; Gunaratne, G.P.; Amali, R.K.A.; Priyadarshana, G.; Sandaruwan, C.; Karunaratne, V.; Hettiarachchi, L.S.K.; Kottegoda, N. Urea–hydroxyapatite nanohybrid as an efficient nutrient source in Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze (tea). Journal of Plant Nutrition 2020, 43, 2383–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshayb, O.M.; Nada, A.M.; Farroh, K.Y.; AL-Huqail, A.A.; Aljabri, M.; Binothman, N.; Seleiman, M.F. Utilizing urea–chitosan nanohybrid for minimizing synthetic urea application and maximizing Oryza sativa l. productivity and n uptake. Agriculture 2022, 12, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, M.; Kaur, K.; Sahu, B.K.; Sharma, S.; Panneerselvam, R.; Shanmugam, V. Promise of nano-carbon to the next generation sustainable agriculture. Carbon 2022, 188, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; ALmoshadak, A.S.; Shafi, M.E.; Albaqami, N.M.; Saad, A.M.; El-Tahan, A.M.; Desoky, E.-S.M.; Elnahal, A.S.; Almakas, A.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A. Vital roles of sustainable nano-fertilizers in improving plant quality and quantity-an updated review. Saudi journal of biological sciences 2021, 28, 7349–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, D.; Gao, Z.; Du, C.; Guan, E.; Wang, G. Effects of Nano-carbon on nitrogen transformation and N2O emissions from tobacco planting soils. Soils 2021, 53, 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Sharaf-Eldin, M.A.; Elsawy, M.B.; Eisa, M.Y.; El-Ramady, H.; Usman, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M. Application of nano-nitrogen fertilizers to enhance nitrogen efficiency for lettuce growth under different irrigation regimes. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Sciences 2022, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Hao, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, S.; Sun, G. Transcriptome analysis reveals differentially expressed genes (DEGs) related to lettuce (Lactuca sativa) treated by TiO 2/ZnO nanoparticles. Plant Growth Regulation 2017, 83, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, A.; Savin, I. Effect of nano-fertilizer on seed germination and first stages of bitter almond seedlings’ growth under saline conditions. BioNanoScience 2018, 8, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakovskaya, M.; Dervishi, E.; Mahmood, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Watanabe, F.; Biris, A.S. Carbon nanotubes are able to penetrate plant seed coat and dramatically affect seed germination and plant growth. ACS nano 2009, 3, 3221–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, S.-C.; Chandrasekaran, M. Chitosan and chitosan nanoparticles induced expression of pathogenesis-related proteins genes enhances biotic stress tolerance in tomato. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2019, 125, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syu, Y.-y.; Hung, J.-H.; Chen, J.-C.; Chuang, H.-w. Impacts of size and shape of silver nanoparticles on Arabidopsis plant growth and gene expression. Plant physiology and biochemistry 2014, 83, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.; Saini, R.V.; Singh, P.; Raizada, P.; Thakur, V.K.; Saini, A.K. Nanoparticles as an emerging tool to alter the gene expression: Preparation and conjugation methods. Materials Today Chemistry 2020, 17, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, J.; Joseph, S.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, M.; Taherymoosavi, S.; Munroe, P.; Mitchell, D.R.; Pan, G. Biochar-based fertiliser enhances nutrient uptake and transport in rice seedlings. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 826, 154174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimohammadi, M.; Panahpour, E.; Naseri, A. Assessing the effects of urea and nano-nitrogen chelate fertilizers on sugarcane yield and dynamic of nitrate in soil. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 2020, 66, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doak, S.H.; Dusinska, M. NanoGenotoxicology: present and the future. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Riaz, M.; Adrees, M.; Hussain, A.; Zahir, Z.A.; Rinklebe, J. Effects of nanoparticles on trace element uptake and toxicity in plants: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2021, 221, 112437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.T.; Musarrat, J.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A. Countering drug resistance, infectious diseases, and sepsis using metal and metal oxides nanoparticles: current status. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Murmu, G.; Mukherjee, K.; Saha, S.; Maity, D. A comprehensive overview of nanotechnology in sustainable agriculture. Journal of Biotechnology 2022, 355, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




