Submitted:
06 November 2023
Posted:
06 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
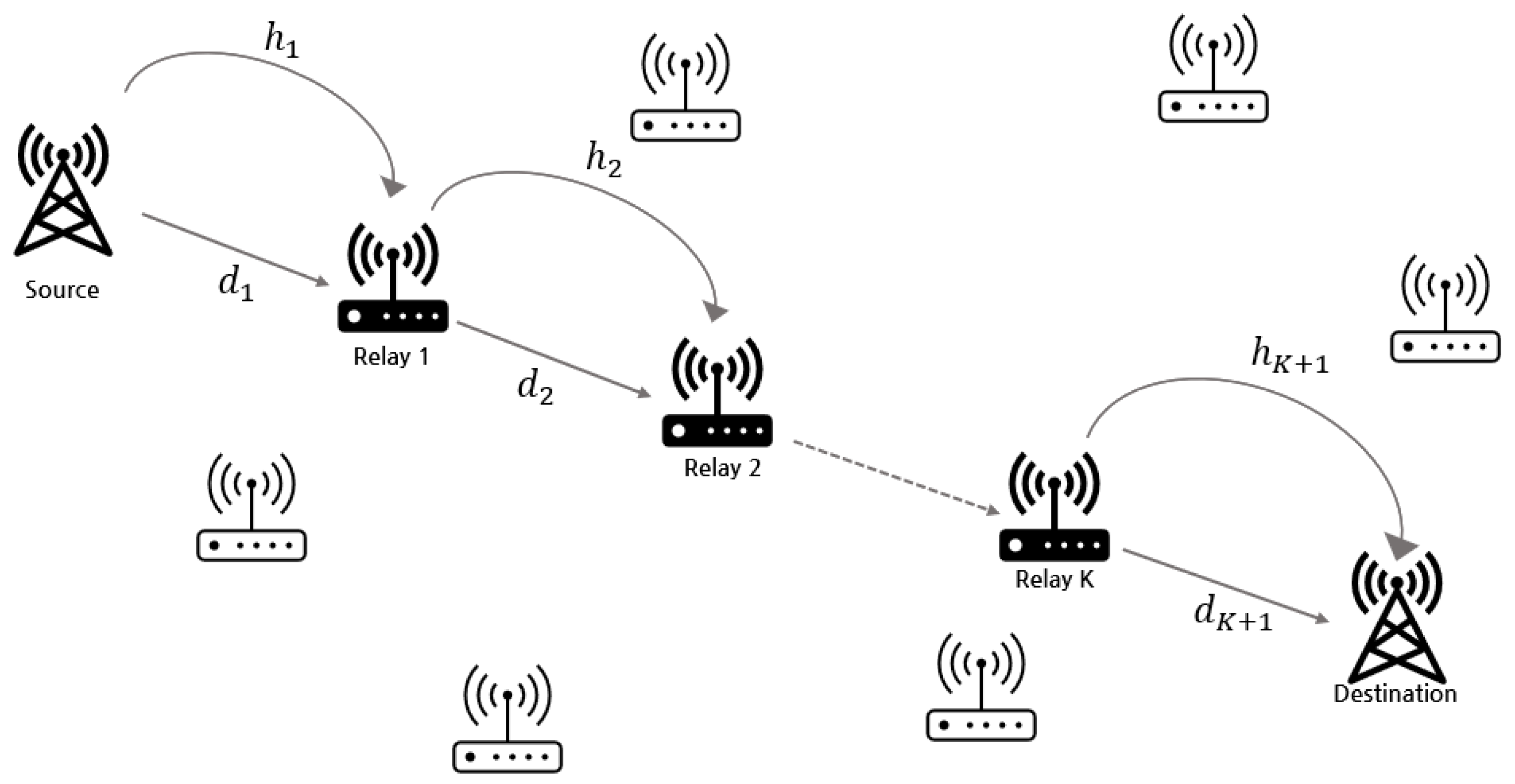
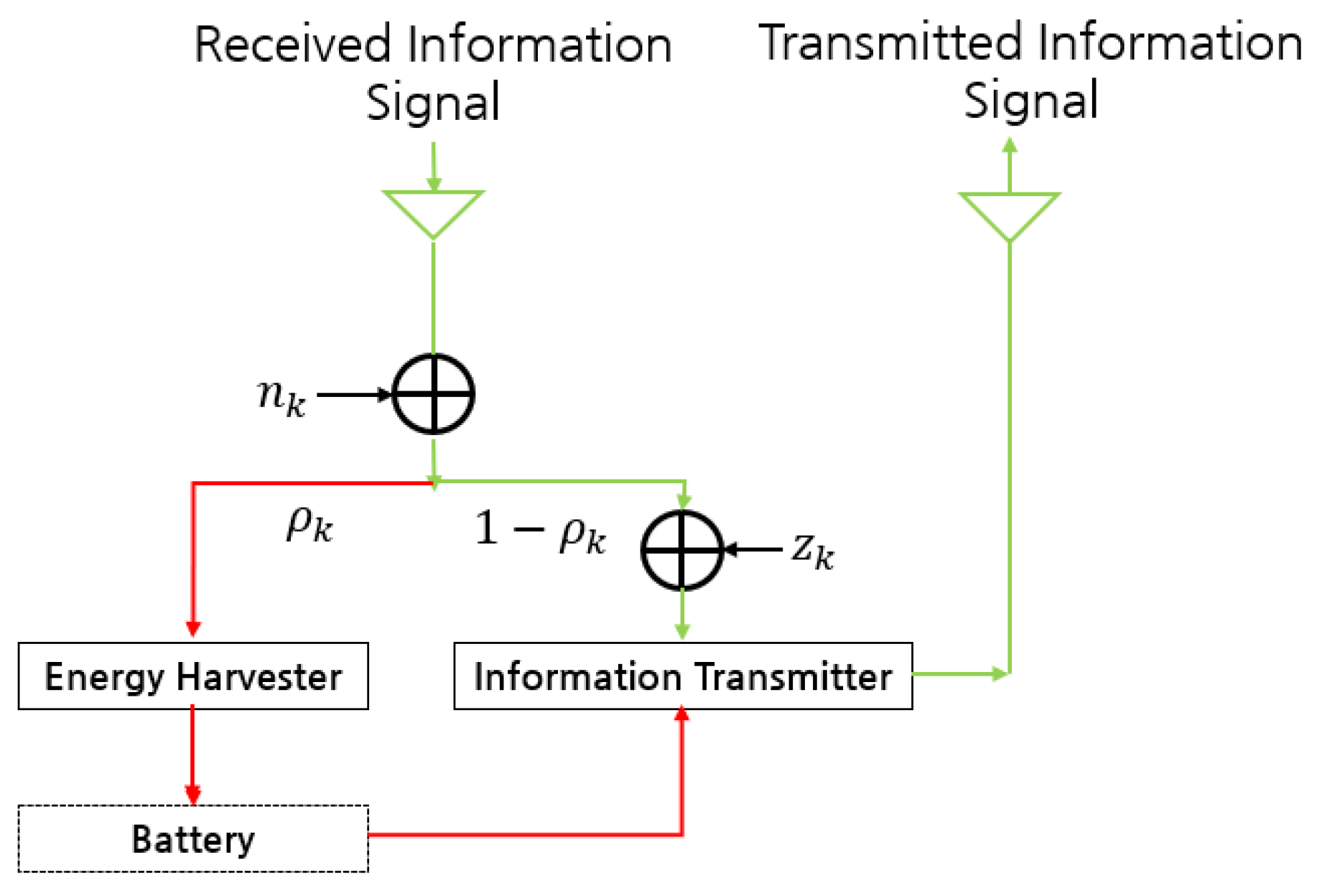
2. System Model and Problem Formulation
3. Problem Solution
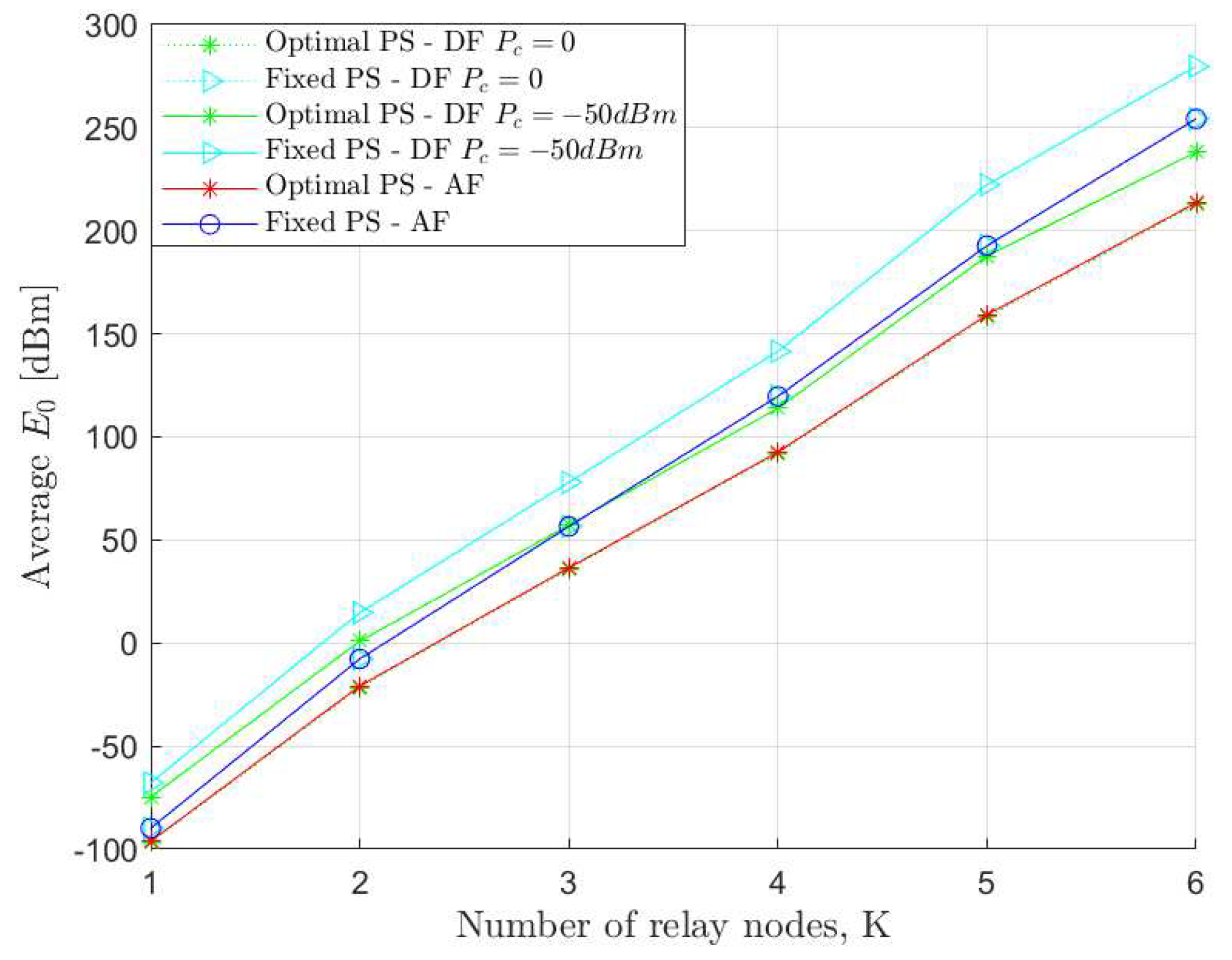
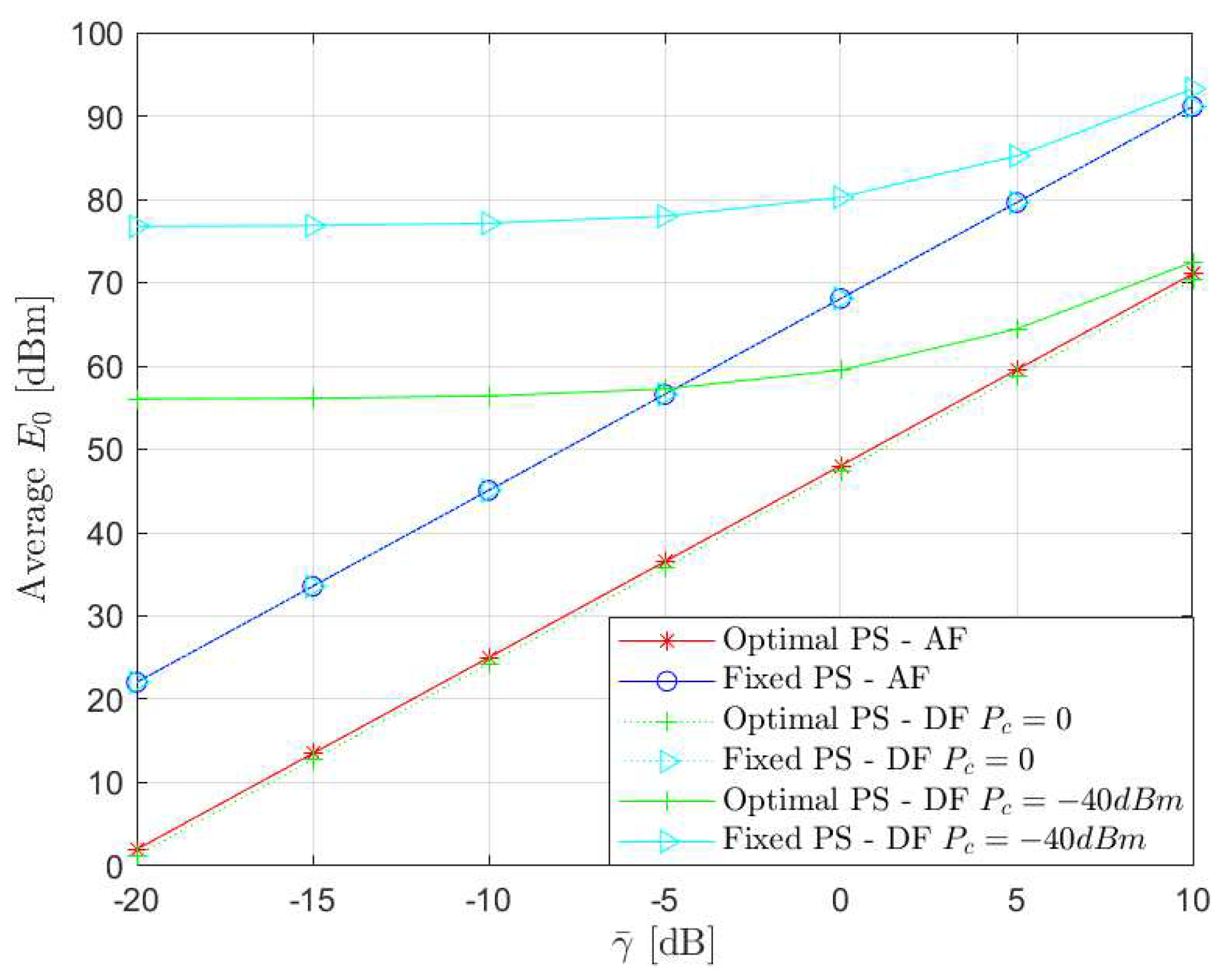
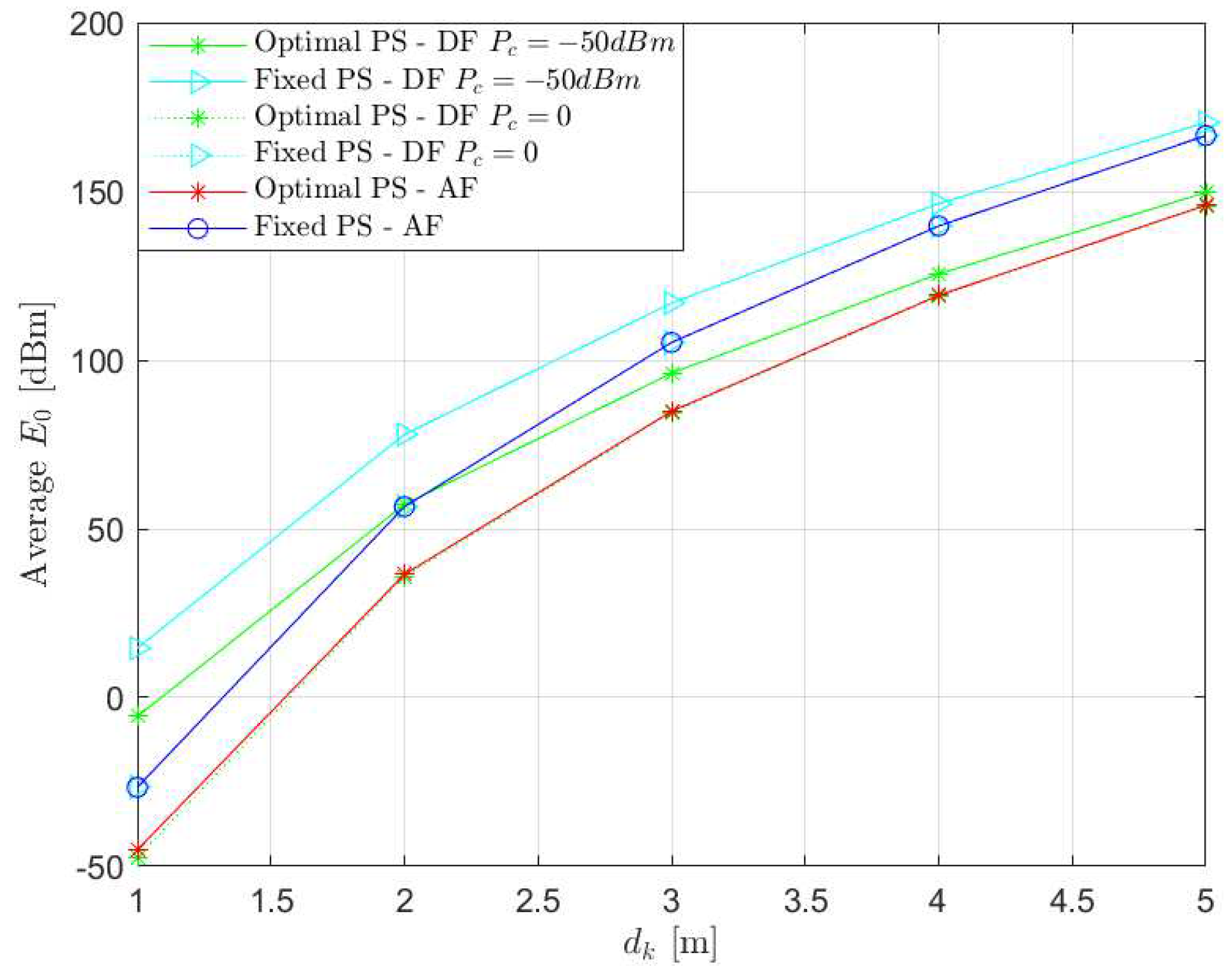
4. Simulation Results
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Appendix A
References
- Asiedu, D. K. P.; Lee, H.; Lee, K.-J. Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer for decode-and-forward Multihop Relay systems in energy-constrained IoT networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 9413–9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahama, S.; Asiedu, D. K. P.; Lee, K.-J. Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer for cooperative relay networks with battery. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 13171–13178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiedu, D. K. P.; Mahama, S.; Jeon, S.-W.; Lee, K.-J. Optimal power splitting for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer in amplify-and-forward multiple-relay systems. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3459–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, K.-J.; Kim, H.; Lee, I. Joint transceiver optimization for MISO SWIPT systems with time switching. IEEE Trans. on Wireless Commun. 2018, 17, 3298–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, K.-J.; Kim, H.; Lee, I. Wireless information and power exchange for energy-constrained device-to-device communications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 3175–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerckx, B.; Zhang, R.; Schober, R.; Ng, D. W. K.; Kim, D. I.; Poor, H. V. Fundamentals of wireless information and power transfer: From RF energy harvester models to signal and system designs. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2018, 37, 4–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Xie, K.; Chen, W.; Zhang, D.; Wen, J. Energy-aware routing for SWIPT in multi-hop energy-constrained wireless network. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 17996–18008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wen, Z.; Liu, D.; Zou, J.; Li, S. Joint source and relay beamforming design in wireless multi-hop sensor networks with SWIPT. Sensors 2019, 19, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djiroun, F. Z.; Djenouri, D. Mac protocols with wake-up radio for wireless sensor networks: A review. IEEE Commun. Surveys & Tutorials 2017, 19, 587–618. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Pang, H.; Georgiadis, A.; Cecati, C. ; Wireless power transfer - an overview. IEEE Trans. Indust. Elect. 2018, 66, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuonzo, D.; Rossi, P. S.; Dey, S. Massive MIMO channelaware decision fusion. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 604–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, P. S.; Ciuonzo, D.; Kansanen, K.; Ekman, T. Performance analysis of energy detection for MIMO decision fusion in wireless sensor networks over arbitrary fading channels. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 2016, 15, 7794–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, C. S.; Sivalingam, K. M.; Znati, T. Wireless Sensor Networks.; Publisher: Springer USA, New York, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, M.; Cao, N.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y. Multi-hop relaying using energy harvasting. IEEE Wirless Commun. Letters 2015, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Sabor, N.; Sasaki, S.; Abo-Zahhad, M.; Ahmed, S. M. A comprehensive survey on hierarchical-based routing protocols for mobile wireless sensor networks: Review, taxonomy, and future directions. Wireless Commun. Mobile Comput. 2017, 2017, Art. no. 2818542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djiroun, F. Z.; Djenouri, D. MAC protocols with wake-up radio for wireless sensor networks: A review. IEEE Commun. Surveys Tuts. 2017, 19, 587–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, D. N.; Kumar, V. Review on clustering, coverage and connectivity in underwater wireless sensor networks: A communication techniques perspective. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 11176–11199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



