Submitted:
07 November 2023
Posted:
08 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CTHs
2.3. CIDF Characterization
2.4. CTH Characterization
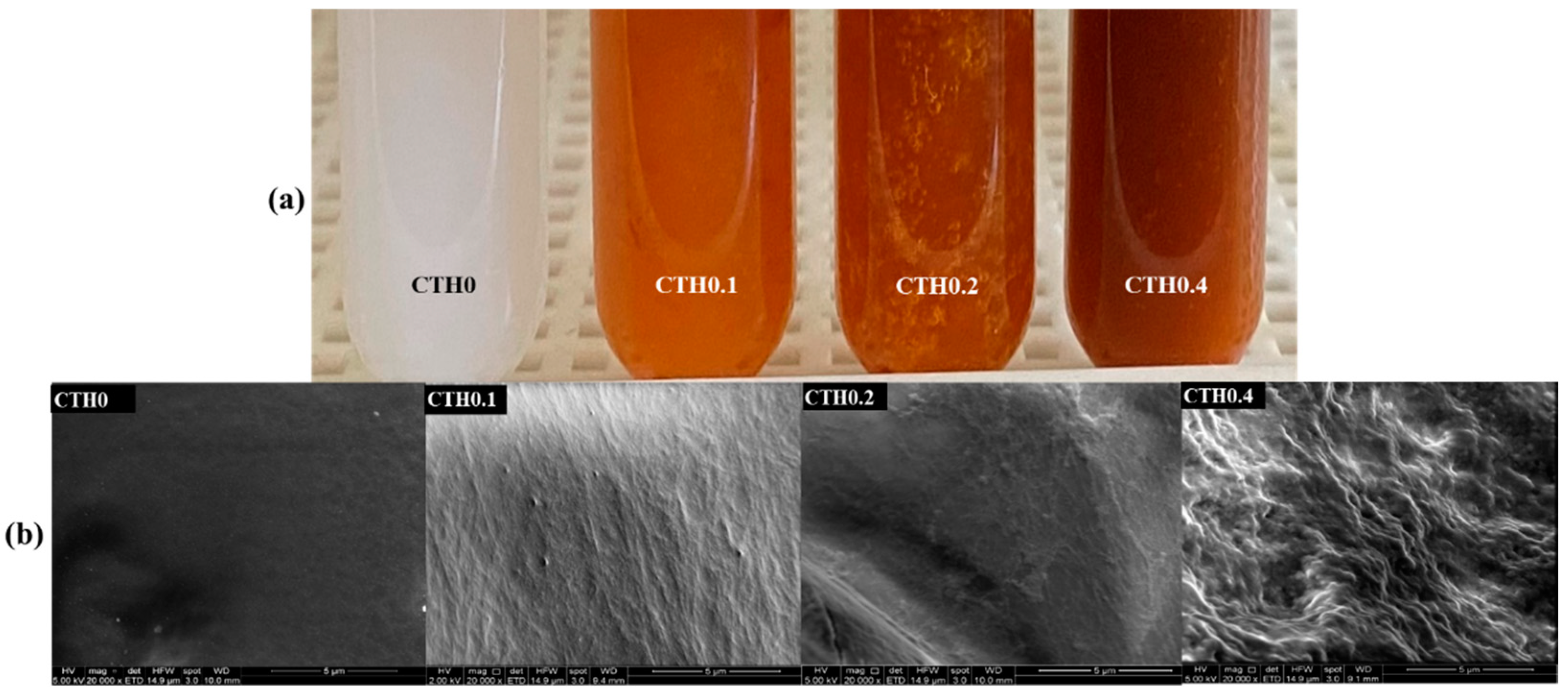
2.4.1. Macroscopic Appearance
2.4.2. Electron Microscopy
2.4.3. pH
2.4.4. IDP Content
2.4.5. Viscosity and Sol-Gel Transition Time
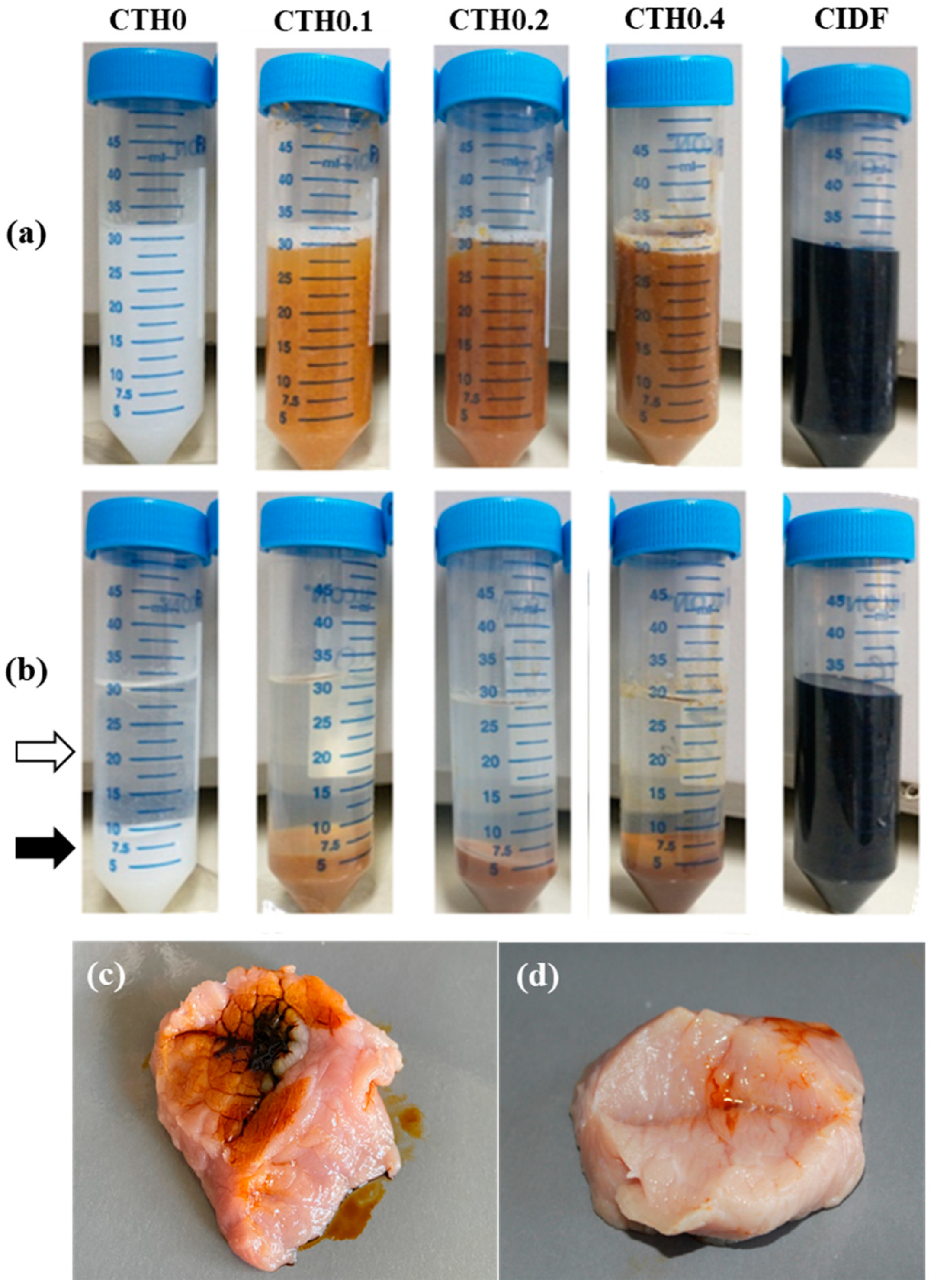
2.4.6. Water-Gel Phase Separation
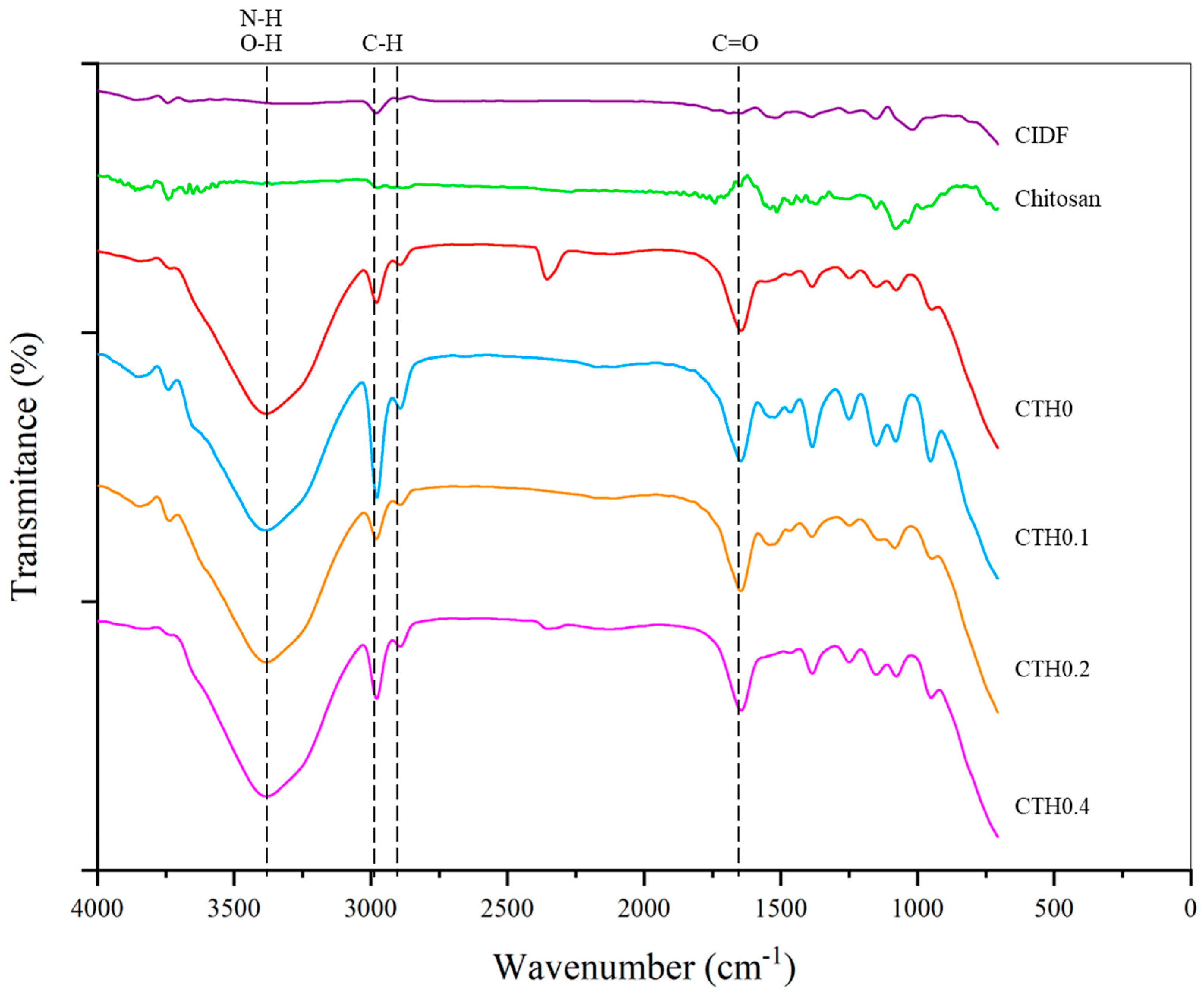
2.4.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
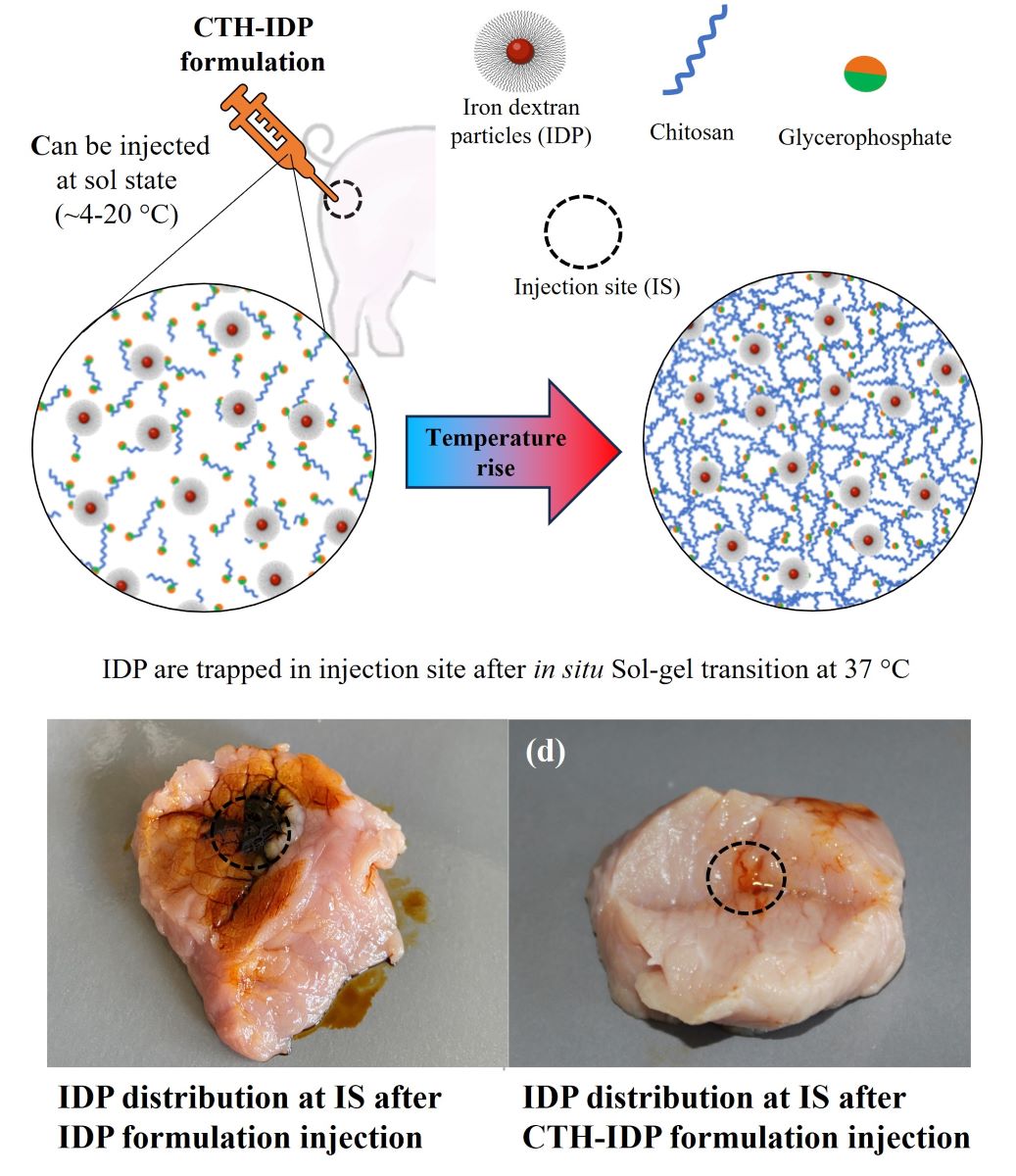
2.4.8. Injectability in Pork Meat
2.4.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. CIDF Characterization
3.2. CTH Characterization
3.2.1. Macroscopic Appearance
3.2.2. Electron Microscopy
3.2.3. pH
3.2.4. IDP Content
3.2.5. Viscosity and Sol-Gel Transition Time
3.2.6. Water-Gel Phase Separation
3.2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.2.8. Injectability in Pork Meat
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Camaschella, C. Iron-deficiency anemia. N. Eng. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, W.; Kassebaum, N. Global, regional, and national prevalence of anemia and its causes in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönfeldt, H.; Hall, N. Determining iron bio-availability with a constant heme iron value. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 738–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Hurrell, R. Nutritional iron deficiency. Lancet 2007, 370, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubham, K.; Anukiruthika, T.; Dutta, S.; Kashyap, A.; Moses, J.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Iron deficiency anemia: a comprehensive review on iron absorption, bioavailability and emerging food fortification approaches. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 99, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, C.; Allen, V. The use of parenteral iron therapy for the treatment of postpartum anemia. J. Obstet. Gyn. Can. 2015, 37, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avni, T.; Bieber, A.; Grossman, A.; Green, H.; Leibovici, L.; Gafter-Gvili, A. The safety of intravenous iron preparations: systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, M.; Drábek, J. Intramuscular versus subcutaneous administration of iron dextran in suckling piglets. Acta Vet. Brno. 2007, 76, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antileo, R.; Figueroa, J.; Valenzuela, C. Characterization of an encapsulated oral iron supplement to prevent iron–deficiency anemia in neonatal piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, A.; Friendship, R.; Harding, J.; O’sullivan, T. An investigation of iron deficiency and anemia in piglets and the effect of iron status at weaning on post-weaning performance. J. Swine Health Prod. 2016, 24, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg, P.; Chen, J. Aplastic anemia: what have we learned from animal models and from the clinic. Semin. Hematol. 2013, 50, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, Y.; Díaz-Castro, J. Advantages and disadvantages of the animal models v. In vitro studies in iron metabolism: a review. Animal 2013, 7, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, E. The molecular formula and proposed structure of the iron–dextran complex, imferon. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.; Manso, A.; Martín-Jiménez, T.; Karembe, H.; Sperling, D. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics and efficacy of two different iron supplementation products in suckling piglets. J. Swine Health Prod. 2018, 26, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starzyński, R.; Laarakkers, C.; Tjalsma, H.; Swinkels, D.; Pieszka, M.; Styś, A.; Mickiewicz, M.; Lipiński, P. Iron supplementation in suckling piglets: how to correct iron deficiency anemia without affecting plasma hepcidin levels. Plos ONE 2013, 8, e64022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toxqui, L.; Piero, A.; Courtois, V.; Bastida, S.; Sánchez-Muniz, F.; Vaquero, M. Iron deficiency and overload. Implications in oxidative stress and cardiovascular health. Nutr. Hosp. 2010, 25, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lipiński, P.; Starzyński, R.; Canonne-Hergaux, F.; Tudek, B.; Oliński, R.; Kowalczyk, P.; Dziaman, P.; Thibaudeau, O.; Gralak, M.; Smuda, E.; et al. Benefits and risks of iron supplementation in anemic neonatal pigs. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supper, S.; Anton, N.; Seidel, N.; Riemenschnitter, M.; Curdy, C.; Vandamme, T. Thermosensitive chitosan/glycerophosphate-based hydrogel and its derivatives in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Expert Opin. Drug Del. 2014, 11, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, L.; Cao, P.; Li, J.; Chen, X. Glycerophosphate-based chitosan thermosensitive hydrogels and their biomedical applications. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 117, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Biocompatibility and characteristics of injectable chitosan-based thermosensitive hydrogel for drug delivery. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 83, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, O.; Lau, W.; Khutoryanskiy, V. Chitosan/β-glycerophosphate in situ gelling mucoadhesive systems for intravesical delivery of mitomycin-c. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Ma, W.; Su, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, H. The osteogenic differentiation of dog bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a thermo-sensitive injectable chitosan/collagen/beta-glycerophosphate hydrogel: in vitro and in vivo. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. M 2011, 22, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wat, E.; Hui, P.; Chan, B.; Ng, F.; Kan, C. Wang, X.; Hu, H.; Wong, E.; Lau, C.; et al. Dual-functional transdermal drug delivery system with controllable drug loading based on thermosensitive poloxamer hydrogel for atopic dermatitis treatment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żelechowska, E.; Przybylski, W.; Jaworska, D.; Santé-Lhoutellier, V. Technological and sensory pork quality in relation to muscle and drip loss protein profiles. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 234, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, M. Parenteral products: the preparation and quality control of products for injection; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rychen, G.; Aquilina, G.; Azimonti, G.; Bampidis, V.; Bastos, M.; Mantovani, A. Safety and efficacy of iron dextran as a feed additive for piglets. Efsa J. 2017, 15, e04701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juluri, A.; Modepalli, N.; Jo, S.; Repka, M.; Shivakumar, H.; Murthy, S. Minimally invasive transdermal delivery of iron–dextran. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honary, S.; Zahir, F. Effect of zeta potential on the properties of nano-drug delivery systems-a review (part 1). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Shen, H.; Xu, J.; Xu, J.; Li, X.J.; Xiong, X. Core-shell structure and magnetic properties of magnetite magnetic fluids stabilized with dextran. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 252, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Cheng, X.; Ji, Q.; Kang, C.; Chen, X. Effect of organic and inorganic acids on chitosan/glycerophosphate thermosensitive hydrogel. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Techn. 2009, 50, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Samadikuchaksaraei, A.; Mozafari, M. Insight into the interactive effects of β-glycerophosphate molecules on thermosensitive chitosan-based hydrogels. Bioinspir. Biomim. Nan. 2016, 5, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lang, C.; Ding, Y.; Sun, S.; Sun, G. Chitosan with enhanced deprotonation for accelerated thermosensitive gelation with β-glycerophosphate. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 112229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filion, D.; Lavertu, M.; Buschmann, M. Ionization and solubility of chitosan solutions related to thermosensitive chitosan/glycerol-phosphate systems. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3224–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skwarczynska, A.; Kaminska, M.; Owczarz, P.; Bartoszek, N.; Walkowiak, B.; Modrzejewska, Z. The structural (FTIR, XRD, and XPS) and biological studies of thermosensitive chitosan chloride gels with β-glycerophosphate disodium. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, A.; Kang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S. Enhanced gelation of chitosan/β-sodium glycerophosphate thermosensitive hydrogel with sodium bicarbonate and biocompatibility evaluated. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 78, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, T.; Sarhan, A. Characterization and molecular dynamic studies of chitosan–iron complexes. B Mater. Sci. 2021, 44, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Formulation | pH | Sol-gel transition time (s) |
IDP content (mg/mL) |
Viscosity (MPa·s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 °C | 25 °C | 37 °C | ||||
| CTH0 | 6.88 ± 0.07 | 90 a | - | 45 ± 10 a | 65 ± 13 a | 2925 ± 108 b |
| CTH0.1 | 6.83 ± 0.07 | 120 b | 2.0 ± 0.3 a | 72 ± 15 a | 383 ± 33 a | 2807 ± 284 b |
| CTH0.2 | 6.62 ± 0.01 | 120 b | 4.0 ± 0.8 a | 74 ± 9 a | 269 ± 40 a | 3052 ± 421 b |
| CTH0.4 | 6.68 ± 0.07 | 300 c | 13 ± 2 a | 134 ± 14 a | 447 ± 13 a | 3060 ± 151 b |
| CIDF | 6.38 ± 0.03 | - | 186.7 ± 2.5 b | 23.8 ± 0.2 a | 12.9 ± 0.2 a | 10.2 ± 0.5 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





