Submitted:
13 November 2023
Posted:
13 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
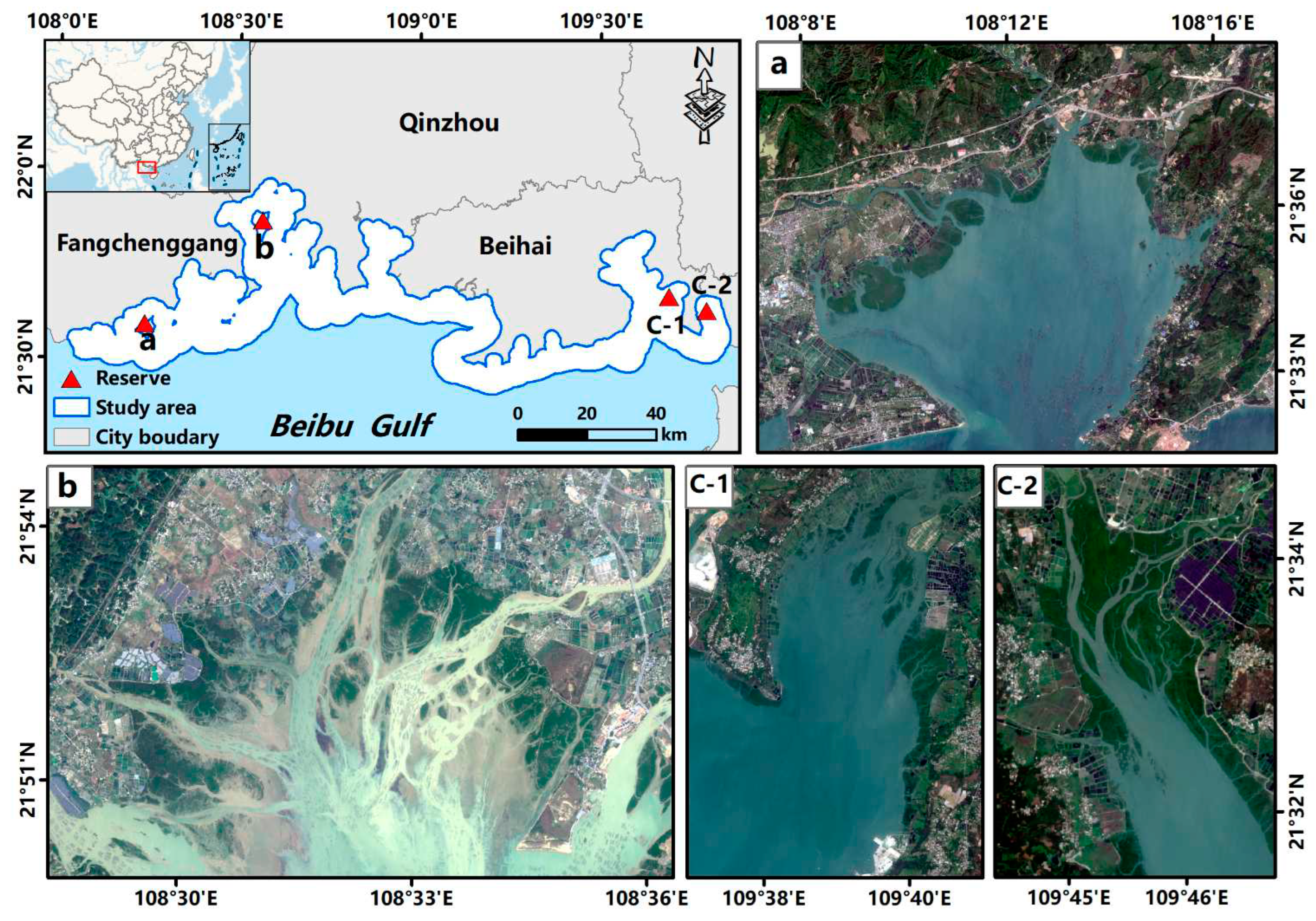
2.Study area
2.Sentinel-2 data acquisition and pre-processing
2.Field Investigation and other data
2.Object-based image analysis and Random Forest classification
2.Spatial structure of mangroves
2.Assessment of ESV
- (1)
- Material production value
- (2)
- Soil conservation value
- (3)
- Wave absorbing revetment
- (4)
- Climate regulation
- (5)
- Pollution purification
- (6)
- Water conservation
- (7)
- Habitat
- (8)
- Nutrient accumulation
- (9)
- Scientific research and education
- (10)
- Recreation
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy assessment
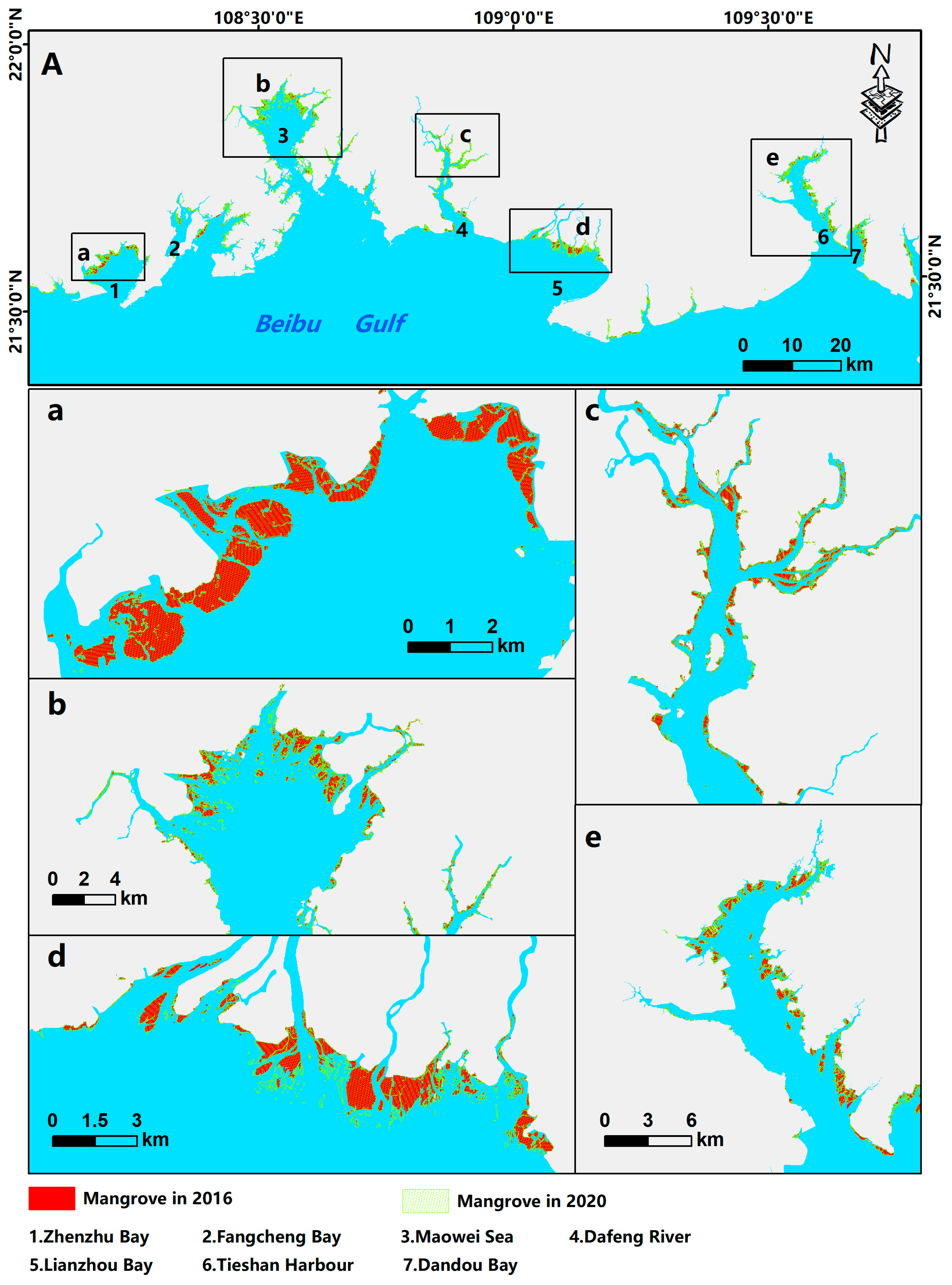
3.Spatial distribution and structure of Guangxi’s mangroves
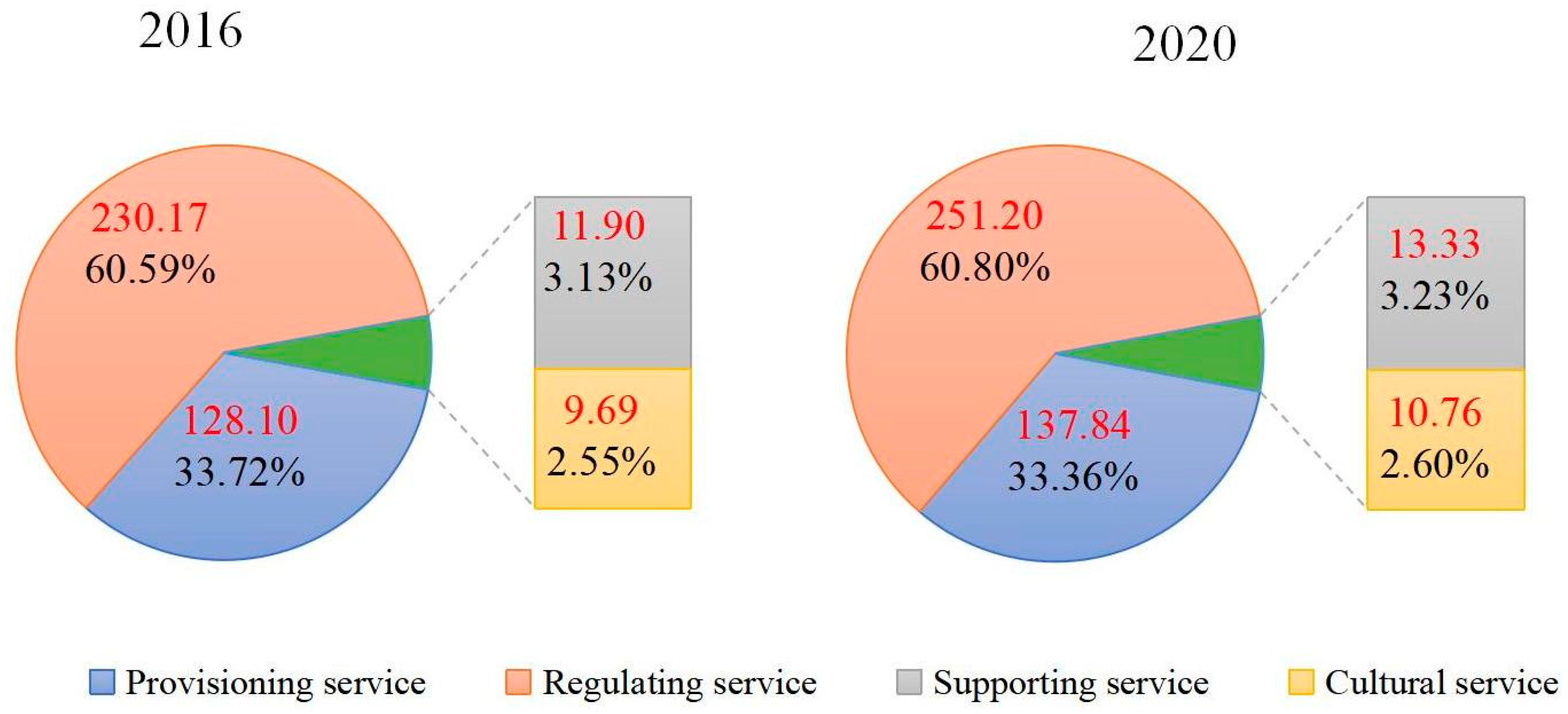
3.Variations of ESV
4. Discussion
4.Factors driving changes in spatial characteristics
4.The rationality and existing problems of selecting evaluation index
4.Threatened situations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Myint, S.W.; Giri, C.P.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Gillette, S.C. Identifying Mangrove Species and Their Surrounding Land Use and Land Cover Classes Using an Object-Oriented Approach with a Lacunarity Spatial Measure. GIScience & Remote Sensing 2008, 45, 188–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, N.; Sutherland, W.J.; Dicks, L.; Hugé, J.; Koedam, N.; Dahdouh-Guebas, F. Ecosystem Service Valuations of Mangrove Ecosystems to Inform Decision Making and Future Valuation Exercises. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Jia, M.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Ren, C.; Zhao, C. Monitoring the Light Pollution Changes of China’s Mangrove Forests from 1992-2020 Using Nighttime Light Data. Frontiers in Marine Science 2023. [CrossRef]
- Cherrington, E.A.; Griffin, R.E.; Anderson, E.R.; Hernandez Sandoval, B.E.; Flores-Anderson, A.I.; Muench, R.E.; Markert, K.N.; Adams, E.C.; Limaye, A.S.; Irwin, D.E. Use of Public Earth Observation Data for Tracking Progress in Sustainable Management of Coastal Forest Ecosystems in Belize, Central America. Remote Sensing of Environment 2020, 245, 111798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovelock, C.E.; Barbier, E.; Duarte, C.M. Tackling the Mangrove Restoration Challenge. PLoS Biol 2022, 20, e3001836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendleton, L.; Mongruel, R.; Beaumont, N.; Hooper, T.; Charles, M. A Triage Approach to Improve the Relevance of Marine Ecosystem Services Assessments. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 530, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, S.; Chakraborti, S.; Joshi, P.K.; Keesstra, S.; Sen, S.; Paul, S.K.; Kreuter, U.; Sutton, P.C.; Jha, S.; Dang, K.B. Ecosystem Service Value Assessment of a Natural Reserve Region for Strengthening Protection and Conservation. Journal of Environmental Management 2019, 244, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himes-Cornell, A.; Grose, S.O.; Pendleton, L. Mangrove Ecosystem Service Values and Methodological Approaches to Valuation: Where Do We Stand? Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Li, J.; Ye, M.; Pu, R.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Feng, B.; Song, X. Changes of Ecosystem Service Value in a Coastal Zone of Zhejiang Province, China, during Rapid Urbanization. IJERPH 2018, 15, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligate, E.J.; Chen, C.; Wu, C. Evaluation of Tropical Coastal Land Cover and Land Use Changes and Their Impacts on Ecosystem Service Values. Ecosyst Health Sustain 2018, 4, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, G.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Giannetti, B.F.; Wang, J.; Casazza, M. Donor-Side Evaluation of Coastal and Marine Ecosystem Services. Water Research 2019, 166, 115028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, R.; Brander, L.; Van Der Ploeg, S.; Costanza, R.; Bernard, F.; Braat, L.; Christie, M.; Crossman, N.; Ghermandi, A.; Hein, L.; et al. Global Estimates of the Value of Ecosystems and Their Services in Monetary Units. Ecosystem Services 2012, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Brander, L.; J. Wagtendonk, A.; S. Hussain, S.; McVittie, A.; Verburg, P.H.; De Groot, R.S.; Van Der Ploeg, S. Ecosystem Service Values for Mangroves in Southeast Asia: A Meta-Analysis and Value Transfer Application. Ecosystem Services 2012, 1, 62–69. [CrossRef]
- Gaodi, X.; Lin, Z.; Chunxia, L.; Yu, X.; Wenhua, L. Applying Value Transfer Method for Eco-Service Valuation in China. Journal of Resources and Ecology 2010, 1, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Valdez, V.; Ruiz-Luna, A.; Ghermandi, A.; Berlanga-Robles, C.A.; Nunes, P.A.L.D. Effects of Land Use Changes on the Ecosystem Service Values of Coastal Wetlands. Environmental Management 2014, 54, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harborne, A.R.; Mumby, P.J.; Micheli, F.; Perry, C.T.; Dahlgren, C.P.; Holmes, K.E.; Brumbaugh, D.R. The Functional Value of Caribbean Coral Reef, Seagrass and Mangrove Habitats to Ecosystem Processes. In Advances in Marine Biology; Elsevier, 2006; Vol. 50, pp. 57–189 ISBN 978-0-12-026151-2.
- Li, Y.; Wen, H.; Wang, F. Analysis of the Evolution of Mangrove Landscape Patterns and Their Drivers in Hainan Island from 2000 to 2020. Sustainability 2022, 15, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Gong, H.; Shi, C.; Zhong, R.; Liu, X. Comparison of UAV and WorldView-2 Imagery for Mapping Leaf Area Index of Mangrove Forest. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2017, 61, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Ni, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Shen, M.; Cao, Z.; Qi, T.; Xiao, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Cai, Y.; et al. A New Technique for Quantifying Algal Bloom, Floating/Emergent and Submerged Vegetation in Eutrophic Shallow Lakes Using Landsat Imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment 2023, 287, 113480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejicek, L.; Kopackova, V. Changes in Croplands as a Result of Large Scale Mining and the Associated Impact on Food Security Studied Using Time-Series Landsat Images. Remote Sensing 2010, 2, 1463–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jia, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, X.; Tan, Y.; Cheng, L. A Comparison of Gaofen-2 and Sentinel-2 Imagery for Mapping Mangrove Forests Using Object-Oriented Analysis and Random Forest. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sensing 2021, 14, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jia, M.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Wang, Y. Toward a Better Understanding of Coastal Salt Marsh Mapping: A Case from China Using Dual-Temporal Images. Remote Sensing of Environment 2023, 295, 113664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanian, A.; Zaghian, S.; Asiyabi, R.M.; Amani, M.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Jamali, S. Mangrove Ecosystem Mapping Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Satellite Images and Random Forest Algorithm in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, S. Discussion about the Eco-function of Mangrove Wetlands of Beibu gulf of Guangxi Zhuang Nationality Autonomous Region. Anhui Agri. Sci. Bull. 2010, 16, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Quantitative distribution of mangroves in Guangxi Zhuang Autonmous Region. Journal of Beijing Forestry University 2004, 26, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Ren, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Rapid, Robust, and Automated Mapping of Tidal Flats in China Using Time Series Sentinel-2 Images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing of Environment 2021, 255, 112285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Ren, C.; Song, K.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Xiao, X.; Wang, Y. Mapping Global Distribution of Mangrove Forests at 10-m Resolution. Science Bulletin 2023, 68, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, R.P.; Hay, G.J.; Chen, G. How Wetland Type and Area Differ through Scale: A GEOBIA Case Study in Alberta’s Boreal Plains. Remote Sensing of Environment 2012, 117, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, C.; Luo, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, M. Urban Impervious Surface Extraction Based on Multi-Features and Random Forest. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 226609–226623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuolo, F.; Neuwirth, M.; Immitzer, M.; Atzberger, C.; Ng, W.-T. How Much Does Multi-Temporal Sentinel-2 Data Improve Crop Type Classification? International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2018, 72, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xia, Y. ; Dai, huabing Temporal Analysis on Spatial Structure of Mangrove Distribution in Guangxi, China from 1960 to 2010. Wetland Science 2015, 13, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Hou, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, H. Ecosystem Services Valuation in China: A Meta-Analysis. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 809, 151122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Forestry and Grassland Statistical Yearbook; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, 2020.
- Han, W.; Gao, X.; Lu, C.; Lin, P. The Ecological Values of Mangrove Ecosystems in China. Ecologic Science 2000, 19, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, L.; Pan, L. A study on the baseline value of the Chinese mangrove services and allocation of the value to individual tree. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2022, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, B.; Cui, H. Relationship Between Land Use and Soil Erosion in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation 2018, 38, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Guangxi Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, 2020.
- Zhang, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Jia, G. Evaluation of Value of Wetland Ecosystem Services of Zhangjiang Estuary Mangrove National Nature Reserve. Wetland Science 2013, 11, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X. Wetland protection and management; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Lei, M. ; Chen, wenhui; Li, S. Improvement of the Evaluation Method for Ecosystem Service Value Based on Per Unit Area. Journal of Natural Resources 2015, 30, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, X. Value of Ecosystem Services in China. Chin.Sci.Bull. 2000, 45, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; Groot, R. de; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; Robert, V. O’Neill; Jose Paruelo; et al. The Value of the World‘s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Agricultural Products Cost Return Assembly The Price Department of the State Development and Reform Commission of China; China Statistics Press: Beijing, 2020.
- Chen, S.; Wen, Z. Estimating Forest Ecosystem Service Function of Carbon Sequestration and Oxygen Release in Guangxi Province. Journal of Agro-Forestry Economics and Management 2016, 15, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, A.M.; Felson, A.J.; Friess, D.A. Mangrove Rehabilitation and Restoration as Experimental Adaptive Management. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenbach, S.; Kugel, C.; Lausch, A.; Seppelt, R. Analysis of Historic Changes in Regional Ecosystem Service Provisioning Using Land Use Data. Ecological Indicators 2011, 11, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anneboina, L.R.; Kavi Kumar, K.S. Economic Analysis of Mangrove and Marine Fishery Linkages in India. Ecosystem Services 2017, 24, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, C.; Song, K. Landsat-Based Estimation of Mangrove Forest Loss and Restoration in Guangxi Province, China, Influenced by Human and Natural Factors. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sensing 2015, 8, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; Xu, X.; Zou, Z.; Chen, B.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, J.; Liu, D.; Pan, L.; et al. Rebound in China’s Coastal Wetlands Following Conservation and Restoration. Nat Sustain 2021, 4, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Structure | Description |
|---|---|
| Abundance of mangrove | The area of mangroves per unit length of coastline (ha/km). |
| Number of patches | The number of mangrove patches. |
| Average patch area | The average area of all mangrove patches (ha). |
| Mangrove shoreline | Shoreline with mangroves (km) |
| Shoreline mangrove | Mangroves with a minimum distance between the landward boundary and the coastline less than 30 m. |
| Ideally distributed mangrove | Shoreline mangrove with a patch width ≥100 m and coverage ≥0.4 |
| Category | Type | Evaluation index | Data source and reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provisioning service |
Material production value | Wood production | [34] [35] |
| Fishery | [36] | ||
| Regulating service | Soil conservation value | Soil conservation | [37] [38] |
| Fertilizer conservation | [36] | ||
| wave absorbing revetment | Mangrove shoreline | [39] | |
| Climate regulation | CO2 |
[36] |
|
| O2 | |||
| CH4 | |||
| Pollution purification | Degrade pollutants | ||
| Water conservation | Water | [40] [38] |
|
| Supporting service |
Biodiversity Conservation | Habitat | [41] |
| Nutrient accumulation | Nutrient | [35] | |
| Culturalservice | Cultural | Scientific research and education | [42] [43] |
| Recreation | Recreation | [41] [44] |
| Year | Type | mangrove | non- mangrove |
Total | User's accuracy |
Producer's accuracy |
Overall accuracy |
Kappa coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | mangrove | 210 | 14 | 224 | 93.75% | 89.36% | 93.05% | 0.86 |
| non- mangrove |
25 | 312 | 337 | 92.58% | 95.71% | |||
| 2020 | mangrove | 215 | 9 | 224 | 95.98% | 92.67% | 95.37% | 0.90 |
| non- mangrove |
17 | 320 | 337 | 94.96% | 97.26% |
| Spatial structures | Year of 2016 | Year of 2020 | Proportion of Changes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abundance of mangrove (ha/km) | 3.70 | 3.91 | 5.71% |
| Number of patches (pcs) | 1018 | 1060 | 4.13% |
| Average patch area (ha) | 6.14 | 6.37 | 3.80% |
| Mangrove shoreline (km) | 578.90 | 597.37 | 3.19% |
| Shoreline mangrove (ha) | 5436.97 | 5692.19 | 4.69% |
| Ideally distributed mangrove (ha) | 5114.972 | 5201.398 | 4.20% |
| Service | 2016 | 2020 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Proportion | Value | Proportion | |
| Wood | 3.44 | 0.90% | 3.10 | 0.75% |
| Fishery | 124.66 | 32.82% | 134.74 | 32.61% |
| Soil consolidation | 0.12 | 0.03% | 0.13 | 0.03% |
| Fertilizer conservation |
81.11 | 21.35% | 87.66 | 21.22% |
| Wave absorbing revement | 54.20 | 14.27% | 55.60 | 13.46% |
| Carbon fixation | 25.85 | 6.81% | 27.65 | 6.69% |
| Oxygen release | 11.98 | 3.15% | 18.66 | 4.52% |
| Methane release | -1.31 | -0.35% | -1.42 | -0.34% |
| Pollution purification | 38.42 | 10.11% | 41.52 | 10.05% |
| Water conservation | 19.80 | 5.21% | 21.40 | 5.18% |
| Habitat | 11.19 | 2.95% | 12.56 | 3.04% |
| Nutrient accumulation | 0.71 | 0.19% | 0.77 | 0.19% |
| Scientific research | 2.97 | 0.78% | 3.21 | 0.78% |
| Recreation | 6.72 | 1.77% | 7.55 | 1.83% |
| Total | 379.85 | 413.13 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





