Submitted:
13 November 2023
Posted:
14 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
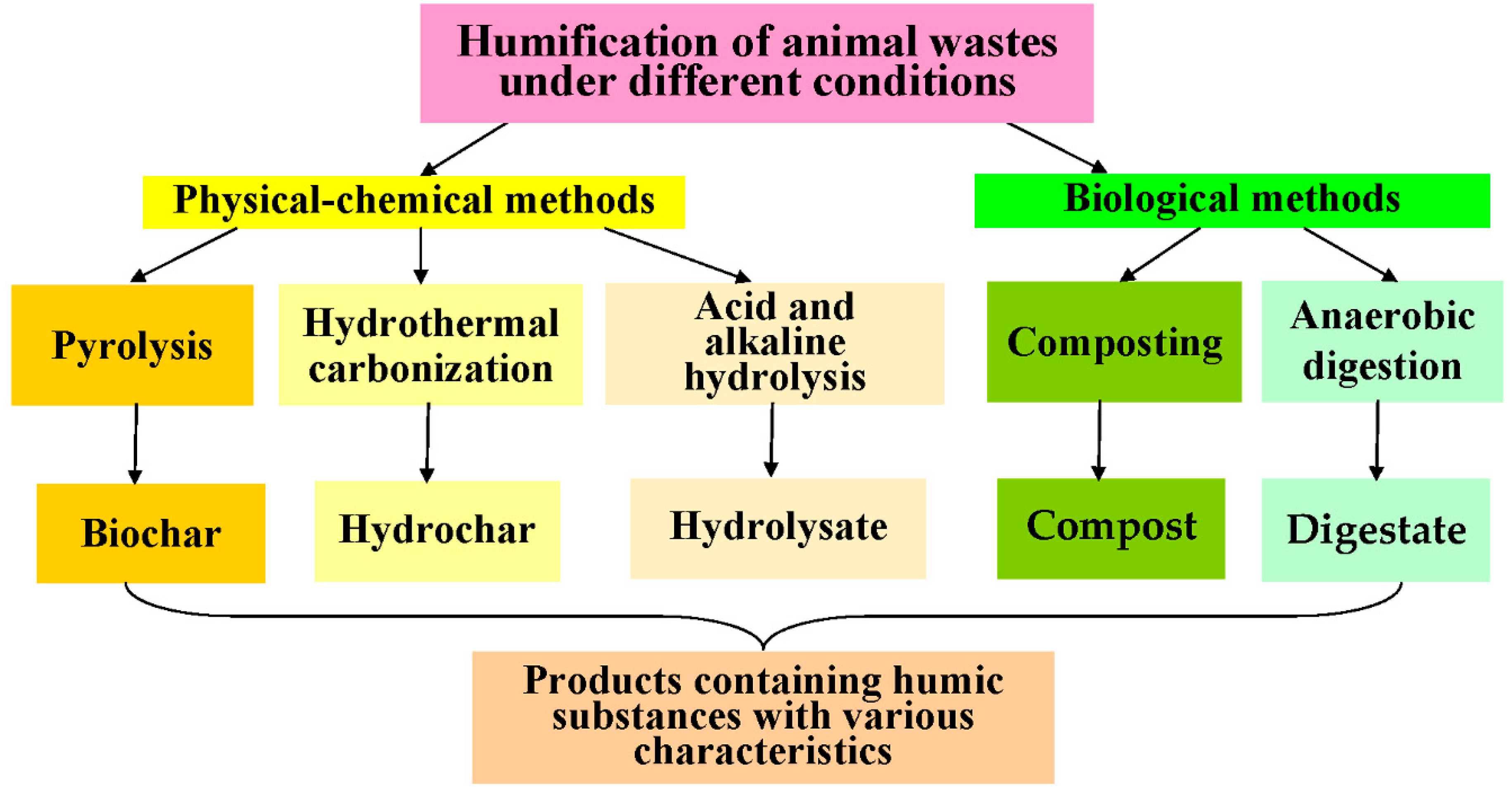
2. Different methods used for artificial HF of animal wastes (AW)
2.1. HF by composting of AW
2.2. HF by anaerobic digestion of AW
2.3. Hydrothermal carbonation and wet torrefaction of AW
2.4. HF of AW by pyrolysis
2.5. Acid and alkaline hydrolysis as HF method of AW
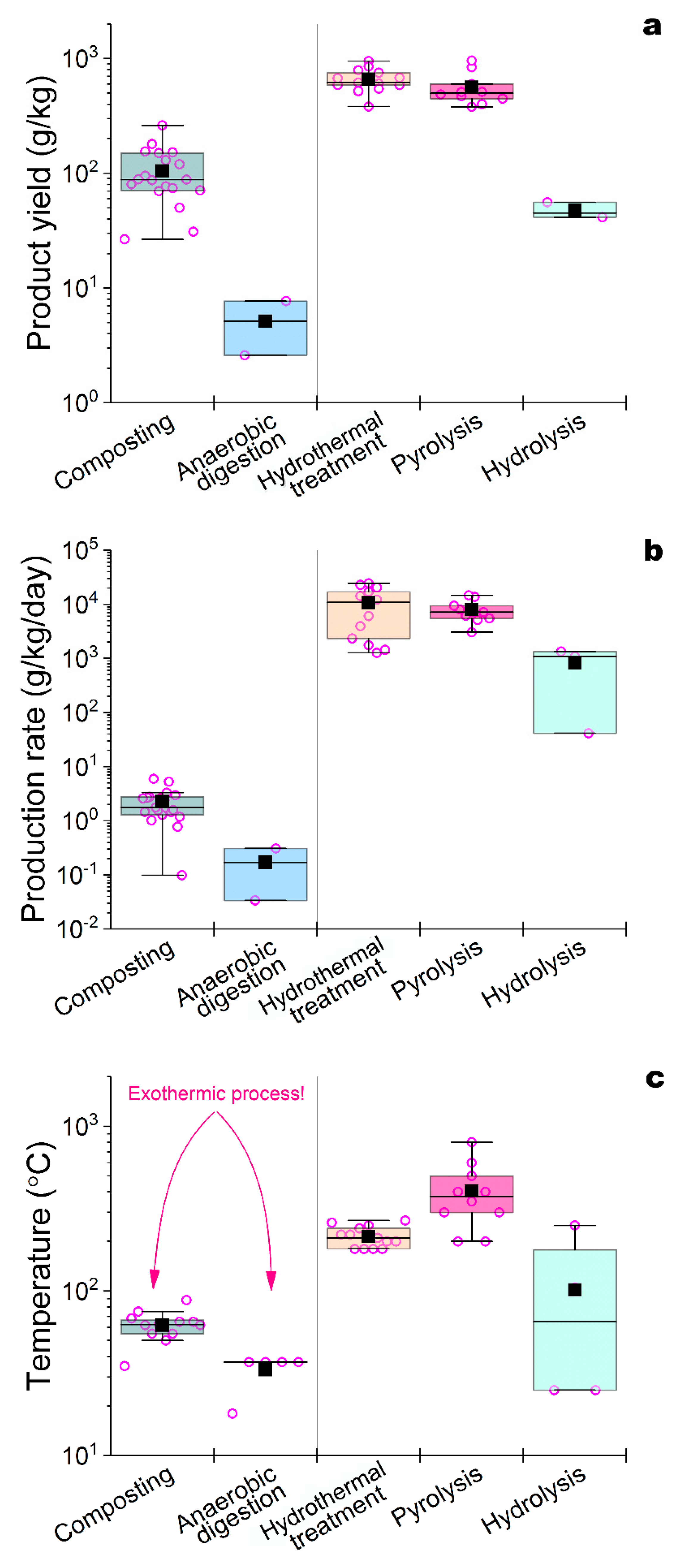
3. Approaches to intensification of artificial HF of AW
3.1. Composting
3.2. Anaerobic digestion
3.3. Hydrothermal carbonation and pyrolysis
4. Comparison of characteristics of natural and artificial HS obtained in various processes of HF of AW
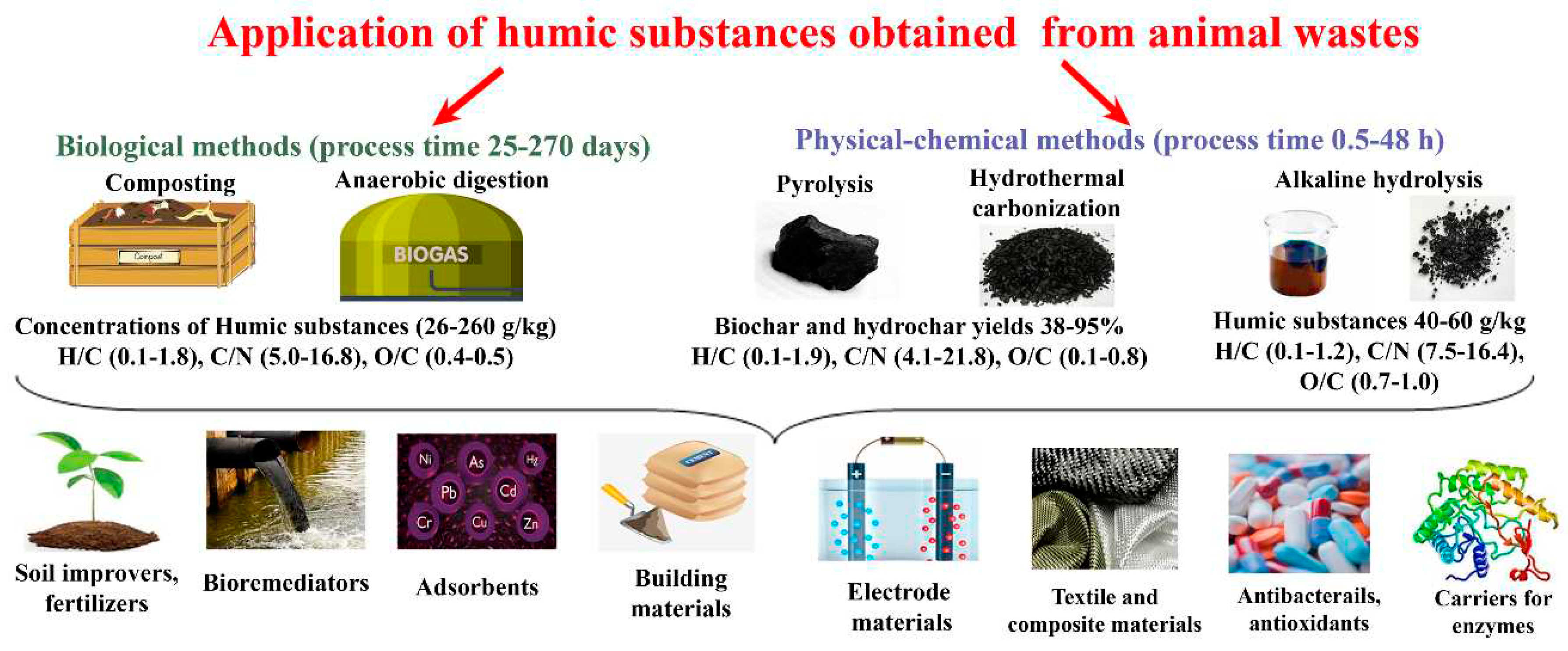
5. Prospects and preferences for the use of HS-containing products, obtained by HF of AW
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filho, J.F.D.C.L.; Thomason, W.E.; Evanylo, G.K.; Zhang, X.; Strickland, M.S.; Chim, B.K.; Diatta, A.A. The synergistic effects of humic substances and biofertilizers on plant development and microbial activity: a review. Int. J. Plant. Soil Sci. 2020, 32, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, N.A.; Perminova, I.V. Interactions between humic substances and microorganisms and their implications for nature-like bioremediation technologies. Molecules 2021, 26, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Tang, C.; Antonietti, M. Natural and artificial humic substances to manage minerals, ions, water, and soil microorganisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 6221–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huezo, L.; Shah, A. Effect of hydrochar from anaerobically digested sewage sludge and manure as a soil amendment on soil properties and plant responses. Bioenerg. Res. 2023, 16, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinčák, S.; Semjon, B.; Marcinčáková, D.; Reitznerová, A.; Mudroňová, D.; Vašková, J.; Nagy, J. Humic substances as a feed supplement and the benefits of produced chicken meat. Life 2023, 13, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vašková, J.; Stupák, M.; Vidová Ugurbaş, M.; Žatko, D.; Vaško, L. Therapeutic efficiency of humic acids in intoxications. Life 2023, 13, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font-Palma, C. Methods for the treatment of cattle manure - A review. C 2019, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Deng, Y.; Li, J.; Ji, M.; Ruan, W. Role of the proportion of cattle manure and biogas residue on the degradation of lignocellulose and humification during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 122941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgutis, L.J.; Slepetiene, A.; Volungevicius, J.; Amaleviciute-Volunge, K. Biogas production from chicken manure at different organic loading rates in a mesophilic full scale anaerobic digestion plant. Biomass Bioenerg. 2020, 141, 105693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, K.V.; Apolônio, F.C.; Wisniewski, A. Valorization of cattle manure by thermoconversion process in a rotary kiln reactor to produce environmentally friendly products. Bioenergy Res. 2020, 13, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achinas, S.; Euverink, G.J.W. Rambling facets of manure-based biogas production in Europe: A briefing. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2020, 119, 109566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlat, N.; Fahl, F.; Dallemand, J.F.; Monforti, F.; Motola, V. A spatial analysis of biogas potential from manure in Europe. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2018, 94, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.Y.; Hassan, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Kafy, A.A.; Ara, I.; Javed, A.; Rahman, M.R. Life cycle energy and cost analysis of small scale biogas plant and solar PV system in rural areas of Bangladesh. Energy Procedia 2019, 160, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, R.; Valavan, S.E. Wealth from poultry waste: an overview. Worlds Poult. Sci J. 2021, 77, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manogaran, M.D.; Shamsuddin, R.; Yusoff, M.H.M.; Lay, M.; Siyal, A.A. A review on treatment processes of chicken manure. Cleaner Circ. Bioecon. 2022, 2, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, I.; Lomazov, V.; Petrosov, D.; Oskina, A. Bioenergetics’ potential of the poultry and swine wastes in Belgorod region of Russia. IOP Conf. Se.r Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 845, 012147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakdar, A.; Sürmeli, R.Ö.; Çalli, B. Anaerobic digestion of chicken manure by a leach-bed process coupled with side-stream membrane ammonia separation. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Suárez, J.L.; Ritter, A.; González, J.M.; Pérez, A.C. Biogas from animal manure: A sustainable energy opportunity in the Canary Islands. Renew Sust. Energ. Rev. 2019, 104, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyerr, N.; Trois, C.; Workneh, T. Identification and characterization of potential feedstock for biogas production in South Africa. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenko, E.; Senko, O.; Stepanov, N.; Aslanli, A.; Maslova, O.; Lyagin, I. Quorum sensing as a trigger that improves characteristics of microbial biocatalysts. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslova, O.; Senko, O.; Stepanov, N.; Gladchenko, M.; Gaydamaka, S.; Akopyan, A.; Eseva, E.; Anisimov, A.; Efremenko, E. Sulfur containing mixed wastes in anaerobic processing by new immobilized synthetic consortia. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, I.; Yusoff, M.S.; Abd Manan, T.S.B.; Koroma, M. Microplastics in manure: sources, analytical methods, toxicodynamic, and toxicokinetic endpoints in livestock and poultry. Environ. Adv. 2023, 12, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfk, A.; Eraky, M.; Osman, A.; Ai, P.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, F.; Rooney, D. Bioenergy production from chicken manure: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 2707–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Gao, J.; Liang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Jin, H. Thermal pretreatment enhances the degradation and humification of lignocellulose by stimulating thermophilic bacteria during dairy manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Ji, K.; Su, L.; Wu, M.; Zhou, X.; Duan, E. Effects of FeSO4 dosage on nitrogen loss and humification during the composting of cow dung and corn straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, R.; Lu, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, D.; Nie, Z.; Wei, Z. Effect of the addition of exogenous precursors on humic substance formation during composting. Waste Manage. 2018, 79, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, Q. A compost-derived thermophilic microbial consortium enhances the humification process and alters the microbial diversity during composting. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 243, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Meng, Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Li, Q. Humification process and mechanisms investigated by Fenton-like reaction and laccase functional expression during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Awasthi, M.K.; He, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Improvement of humification and mechanism of nitrogen transformation during pig manure composting with Black Tourmaline. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Yan, H.; Meng, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Li, Q. Hydrogen peroxide plus ascorbic acid enhanced organic matter deconstructions and composting performances via changing microbial communities. J. Environ. Manage 2021, 295, 113126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Liao, H.; Bai, Y.; Li, X. , Zhao, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Yi, Z.; Zhou, S. Hyperthermophilic composting reduces nitrogen loss via inhibiting ammonifiers and enhancing nitrogenous humic substance formation. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 692, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Sun, E.; Butterly, C.; Xu, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, J.; Chang, Z. Spectroscopic evidence for hyperthermophilic pretreatment intensifying humification during pig manure and rice straw composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 22131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, M.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Kang, K.; Wu, Y. Influence of malonic acid and manganese dioxide on humic substance formation and inhibition of CO2 release during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, J.; Zhu, L.; Wei, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, C. Effect of tricarboxylic acid cycle regulators on the formation of humic substance during composting: The performance in labile and refractory materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 121949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Wei, D.; Yang, T.; Wei, Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, X. Effects of aeration rates on the structural changes in humic substance during co-composting of digestates and chicken manure. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 658, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Yao, T.; Su, M.; Ran, F.; Li, J.; He, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, H. Effects of swine manure composting by microbial inoculation: heavy metal fractions, humic substances, and bacterial community metabolism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Zhu, Q.; Li, G.; Ma, C.; Li, Q.; Meng, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q. Impacts of red mud on lignin depolymerization and humic substance formation mediated by laccase-producing bacterial community during composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Niu, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, S.; Meng, Q.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Ma, C.; Li, Q. Biochar reinforced the populations of cbbL-containing autotrophic microbes and humic substance formation via sequestrating CO2 in composting process. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 333, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Li, J.; Song, C.; Chen, X.; Zhao, M. Lignite drove phenol precursors to participate in the formation of humic acid during chicken manure composting. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 874, 162609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X.; Kang, K.; Jia, L. Modified montmorillonite and illite adjusted the preference of biotic and abiotic pathways of humus formation during chicken manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Huang, Y.; Chen, M.; Qi, X.; Hou, H. Comprehensive evaluation of spent mushroom substrate-chicken manure co-composting by garden waste improvement: physicochemical properties, humification process, and the spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 8987–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanc, A.; Enev, V.; Hrebeckova, T.; Klucakova, M.; Pekar, M. Characterization of humic acids in a continuous-feeding vermicomposting system with horse manure. Waste Manage. 2019, 99, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lyu, T.; Dong, R.; Liu, H.; Wu, S. Dynamic evolution of humic acids during anaerobic digestion: Exploring an effective auxiliary agent for heavy metal remediation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Muhmood, A.; Lyu, T.; Dong, R.; Liu, H.; Wu, S. Mechanisms of genuine humic acid evolution and its dynamic interaction with methane production in anaerobic digestion processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolando, C.; Elba, V.; Carlos, R. Anaerobic mono-digestion of Turkey manure: Efficient revaluation to obtain methane and soil conditioner. J. Water. Resource Prot. 2011, 3, 6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestonaro, T.; de Mendonça Costa, M.S.S.; de Mendonça Costa, L.A.; Rozatti, M.A.T.; Pereira, D.C.; Lorin, H.E.F.; Carneiro, L.J. The anaerobic co-digestion of sheep bedding and 50% cattle manure increases biogas production and improves biofertilizer quality. Waste Manage. 2015, 46, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renjiie, D.; Zijia, Z.; Sheng, L.; Yanfang, M.; Shan, L. Effects of hydrothermal pretreatments on the anaerobic digestion of pig manure and ecological safety of biogas slurry. TCSAE 2022, 38, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.; Jiao, W.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, D.; Ma, J.; Gai, C. Properties of hydrochars derived from swine manure by CaO assisted hydrothermal carbonization. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 233, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, V.; Arye, G.; Gross, A. Poultry litter hydrochar as an amendment for sandy soils. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 271, 110959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, B.M.; Kwapinski, W.; Leahy, J.J. Hydrothermal carbonisation of poultry litter: Effects of initial pH on yields and chemical properties of hydrochars. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Gholizadeh, M.; Hu, X.; Yuan, X.; Sarkar, B.; Ok, Y.S. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of swine and chicken manure: Influence of cross-interaction on hydrochar and liquid characteristics. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 786, 147381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lin, H.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, X.; Gholizadeh, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Hu, S.; Hu, X. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of swine manure and cellulose: Influence of mutual interaction of intermediates on properties of the products. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 791, 148134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Gai, C. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of lignocellulosic biomass and swine manure: Hydrochar properties and heavy metal transformation behavior. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Shan, S.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Q.; Yrjälä, K.; Zheng, H.; Cao, Y. The comparison of dissolved organic matter in hydrochars and biochars from pig manure. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 720, 137423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.B.; Pan, Z.Q.; Xiao, X.F.; Huang, H.J.; Lai, F.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Chen, S.W. Study on the hydrothermal carbonization of swine manure: The effect of process parameters on the yield/properties of hydrochar and process water. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 144, 104692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, E.M.P.; Domínguez, R.E.; López, D.A.; Téllez, J.F.; Marino, M.D.; Almada, N. .; Gange, J.M.; Moyano, E.L. Chicken litter: A waste or a source of chemicals? Fast pyrolysis and hydrothermal conversion as alternatives in the valorisation of poultry waste. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 169, 105796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascó, G.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Álvarez, M.L.; Saa, A.; Méndez, A. Biochars and hydrochars prepared by pyrolysis and hydrothermal carbonisation of pig manure. Waste Manage. 2018, 79, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liang, H.; Han, L.; Huang, G.; Yang, Z. The influence of manure feedstock, slow pyrolysis, and hydrothermal temperature on manure thermochemical and combustion properties. Waste Manage. 2019, 88, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isemin, R.; Mikhalev, A.; Milovanov, O.; Nebyvaev, A. Some results of poultry litter processing into a fertilizer by the wet torrefaction method in a fluidized bed. Energies 2022, 5, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diker, İ.; Ozkan, G.M. An investigation on implementing wet torrefaction to dewatered poultry sludge. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2022, 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arauzo, P.J.; Maziarka, P.A.; Olszewski, M.P.; Isemin, R.L.; Muratova, N.S.; Ronsse, F.; Kruse, A. Valorization of the poultry litter through wet torrefaction and different activation treatments. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 732, 139288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskinen, R.; Hyväluoma, J.; Sohlo, L.; Help, H.; Rasa, K. Fertilizer and soil conditioner value of broiler manure biochars. Biochar 2019, 1, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.S.D.S.; Lustosa Filho, J.F.; Nardis, B.O.; Ribeiro-Soares, J.; Zinn, Y.L.; Melo, L.C.A. Carbon stability of engineered biochar-based phosphate fertilizers. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14203–14212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atienza-Martínez, M.; Ábrego, J.; Gea, G.; Marías, F. Pyrolysis of dairy cattle manure: evolution of char characteristics. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 145, 104724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogdu, A.E.; Polat, R.; Ozbay, G. Pyrolysis of goat manure to produce bio-oil. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfi Bavariani, M.; Ronaghi, A.; Ghasemi, R. Influence of pyrolysis temperatures on FTIR analysis, nutrient bioavailability, and agricultural use of poultry manure biochars. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 50, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellera, C.; Abaalkheel, I.; Rovira, P.; Alrefai, A. Obtaining commercial humic products from uncomposted manures: previous acid hydrolysis to enhance yields. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agricult. 2015, 4, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, B.; Srinivasamurthy, C.; Vasanthi, B.; Naveen, D.; Prakash, N.; Bhaskar, S. Extraction and charactrisation of humic acid from different organic wastes and its physico-chemical properties. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2020, 8, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosa, A.; Taha, A.A.; Elsaeid, M. In-situ and ex-situ remediation of potentially toxic elements by humic acid extracted from different feedstocks: Experimental observations on a contaminated soil subjected to long-term irrigation with sewage effluents. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushkova, S.; Minkina, T.; Chaplygin, V.; Nevidomskaya, D.; Rajput, V.; Bauer, T.; Mazarji, M.; Bren, A.B.; Popov, I.; Mazanko, M. Subcritical water extraction of organic acids from chicken manure. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.P.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Moral, R. Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5444–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelico, R.; Colombo, C.; Di Iorio, E.; Brtnický, M.; Fojt, J.; Conte, P. Humic substances: from supramolecular aggregation to fractal conformation—Is there time for a new paradigm? Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenko, E.; Stepanov, N.; Senko, O.; Maslova, O.; Volikov, A.; Zhirkova, A.; Perminova, I. ; Strategies for variable regulation of methanogenesis efficiency and velocity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6833–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, M.Q.; Borja, V.M. Pretreatment of animal manure biomass to improve biogas production: A Review. Energies 2020, 13, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Liu, H.; Zhou, T.; Zheng, L.; Huang, S.; Gao, L.; Lin, C.S.K.; Wang, Q. Effect of humic substances on the anaerobic digestion of secondary sludge in wastewater treatment plants: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023; 21, 3023–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wei, D.; Wu, J.; Zhao, X.; Hao, J.; Wei, Z. Driving effects of minerals on humic acid formation during chicken manure composting: Emphasis on the carrier role of bacterial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zou, B. Improving the humification by additives during composting: A review. Waste Manage. 2023, 158, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Deng, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, H.; Xie, X.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H. Identifying the role of exogenous amino acids in catalyzing lignocellulosic biomass into humus during straw composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.R.; Karthikeyan, K.G. Effects of severe pretreatment conditions and lignocellulose-derived furan byproducts on anaerobic digestion of dairy manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Sun, C.; Liu, R.; Yellezuome, D.; Zhu, X.; Bai, R.; Liu, M.; Sun, M. Anaerobic co-digestion of corn stover and chicken manure using continuous stirred tank reactor: The effect of biochar addition and urea pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Gnanasekar, P.; Tratnik, N.; Tanguy, N.R.; Guo, X.; Zhu, M.; Qui, L.; Yan, N.; Chen, H. Low-temperature torrefaction assisted with solid-state KOH/urea pretreatment for accelerated methane production in wheat straw anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 377, 128940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Güiza, M.S.; Vila, J.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Chimenos, J.M.; Astals, S. The role of additives on anaerobic digestion: a review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2016, 58, 1486–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senko, O.; Gladchenko, M.; Maslova, O.; Efremenko, E. Long-term storage and use of artificially immobilized anaerobic sludge as a powerful biocatalyst for conversion of various wastes including those containing xenobiotics to biogas. Catalysts 2019, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenko, E.; Senko, O.; Maslova, O.; Lyagin, I.; Aslanli, A.; Stepanov, N. Destruction of mycotoxins in poultry waste under anaerobic conditions within methanogenesis catalyzed by artificial microbial consortia. Toxins, 3390. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuravleva, E.A.; Shekhurdina, S.V.; Kotova, I.B.; Loiko, N.G.; Popova, N.M.; Kryukov, E.; Kovalev, A.A.; Kovalev, D.A.; Litti, Y.V. Effects of various materials used to promote the direct interspecies electron transfer on anaerobic digestion of low-concentration swine manure. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 839, 156073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, J.J.; Gaston, L.A.; Zhou, B.; Park, J.H.; Li, R.; Dodla, S.K.; Zhang, Z. Biochar produced from mineral salt-impregnated chicken manure: fertility properties and potential for carbon sequestration. Waste Manage. 2018, 78, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieweś, D.; Biegun, M.; Huculak-Mączka, M.; Marecka, K.; Kaniewski, M.; Zieliński, J.; Hoffmann, J. Extraction of humic acid from peat and lignite and the thermal behavior of their mixtures with ammonium nitrate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavins, M.; Purmalis, O. Characterization of humic acids from raised bog peat. Latv. J. Chem. 2014, 52, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, N.; Jamal, A.; Huang, Z.; Liaquat, R.; Ahmad, B.; Haider, R.; Ali, M.I.; Shoukat, T.; Alothman, Z.A.; Ouladsmane, M.; Ali, T. Extraction and chemical characterization of humic acid from nitric acid treated lignite and bituminous coal samples. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, V.; Zazovskaya, E.; Abakumov, E. Molecular composition of humic substances isolated from selected soils and cryconite of the Grønfjorden area, Spitsbergen. Pol. Polar. Res. 2019, 40, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudzari, J.M.; Tartakovsky, B.; Raghavan, G.V. Effect of C/N ratio and salinity on power generation in compost microbial fuel cells. Waste Manage. 2016, 48, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, E.; Somerville, C.J.; Luster, J. The C:N:P:S stoichiometry of soil organic matter. Biogeochemistry 2016, 130, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thang, P.Q.; Jitae, K.; Giang, B.L.; Viet, N.M.; Huong, P.T. Potential application of chicken manure biochar towards toxic phenol and 2, 4-dinitrophenol in wastewaters. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 251, 109556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Feng, C.; Qin, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, N.; Li, Y.; Ni, Z.; Xu, Z.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Qiu, R. Mechanisms of Pb and/or Zn adsorption by different biochars: Biochar characteristics, stability, and binding energies. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 136894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Zhang, E.; Yang, Y.; Sun, K.; Fang, L. Highly efficient U (VI) removal by chemically modified hydrochar and pyrochar derived from animal manure. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minale, M.; Guadie, A.; Liu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J. Insight into adsorption behavior of chlortetracycline and cadmium in aqueous solution using a novel manganese ferrite loaded swine manure hydrochar. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Wang, B.; Feng, Y.; Fu, H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, H.; Xue, L. Livestock manure-derived hydrochar improved rice paddy soil nutrients as a cleaner soil conditioner in contrast to raw material. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Sun, H.; Ro, K.S.; Sun, K.; Libra, J.A.; Xing, B. Removal of antimony (III) and cadmium (II) from aqueous solution using animal manure-derived hydrochars and pyrochars. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huezo, L.; Shah, A. Effect of hydrochar from anaerobically digested sewage sludge and manure as a soil amendment on soil properties and plant responses. Bioenerg. Res. 2023, 16, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Rizwan, M.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Zubair, M.; Riaz, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Alharby, H.S.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Ali, S. Application of co-composted farm manure and biochar increased the wheat growth and decreased cadmium accumulation in plants under different water regimes. Chemosphere 2020, 2020 246, 125809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A.; Spaccini, R.; De Martino, A.; Scognamiglio, F.; di Meo, V. Soil washing with solutions of humic substances from manure compost removes heavy metal contaminants as a function of humic molecular composition. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, M.; Yan, S.; Yong, X.; Zhang, X.; Awasthi, M.K.; Xi, Y.; Zhou, J. Effects of hydrochar and biogas slurry reflux on methane production by mixed anaerobic digestion of cow manure and corn straw. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Awasthi, S.K.; Liu, T.; Duan, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Z.; Pandey, A.; Awasthi, M.K. Effects of microbial culture and chicken manure biochar on compost maturity and greenhouse gas emissions during chicken manure composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingaretti, D.; Lominchar, M.A.; Verginelli, I.; Santos, A.; Baciocchi, R. Humic acids extracted from compost as amendments for Fenton treatment of diesel-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22225–22234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguey-González, J.A.; Nava-Ramírez, M.dJ.; Gómez-Rosales, S.; Ángeles, M.d.L.; Solís-Cruz, B.; Hernández-Patlán, D.; Merino-Guzmán, R.; Hernández-Velasco, X.; Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.dD.; Vázquez-Durán, A.; Hargis, B.M.; Tellez-Isaisas, J.d.D. Humic acids preparation, characterization, and their potential adsorption capacity for aflatoxin B1 in an in vitro poultry digestive model. Toxins 2023, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, F.; Wang, Q.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, W. The effect of different remediation treatments on soil fungal communities in rare earth tailings soil. Forests 2022, 13, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Zou, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Awasthi, M.K.; Xi, Y.; Jiang, J. Biochar improves compost humification, maturity and mitigates nitrogen loss during the vermicomposting of cattle manure-maize straw. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 325, 116432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Duan, Y.; Awasthi, S.K.; Liu, T.; Chen, H.; Pandey, A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Emerging applications of biochar: Improving pig manure composting and attenuation of heavy metal mobility in mature compost. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primozic, M.; Podrepsek, G.H.; Pavlovic, I.; Skerget, M.; Knez, Z.; Leitgeb, M. Enzyme immobilization onto biochar produced by the hydrothermal carbonization of biomass. Acta Chim. Slov. 2019, 66, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Jia, B.; Wei, J.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Tang, S.; Wu, Z.; Chen, G. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal preparation of corn straw hydrochar as supercapacitor electrode materials. ACS omega 2020, 5, 26084–26093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrillo, M.; Salzano, M.; Savy, D.; Di Meo, V.; Valentini, M.; Cozzolino, V.; Piccolo, A. Antibacterial and antioxidant properties of humic substances from composted agricultural biomasses. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, N.A.; Filippova, O.I.; Volikov, A.B.; Perminova, I.V. Slow nitrogen release from humic substances modified with aminoorganosilanes. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wystalska, K.; Malińska, K.; Barczak, M. Poultry manure derived biochars – the impact of pyrolysis temperature on selected properties and potentials for further modifications. J. Sustainable Dev. Energy Water Environ. Syst. 2021, 9, 246295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkevich, E.V.; Yudina, N.V.; Savel’eva, A.V. Role of humic acids in the detoxification of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil. Solid Fuel Chem. 2021, 55, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Gong, P.; Li, P.; Tian, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xue, B. Preliminary studies on how to reduce the effects of salinity. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wang, L.; Nan, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Kumar, T.V.; Wang, C. Phosphorus adsorption by functionalized biochar: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 497–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Fawzy, S.; Farghali, M.; El-Azazy, M.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Fahim, R.A.; Maksoud, M.A.; Ajlan, A.A.; Yousry, M.; Saleem, Y.; Rooney, D.W. Biochar for agronomy, animal farming, anaerobic digestion, composting, water treatment, soil remediation, construction, energy storage, and carbon sequestration: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2385–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoumi, S.; Borugadda, V.B.; Nanda, S.; Dalai, A.K. Hydrochar: a review on its production technologies and applications. Catalysts 2021, 11, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, M.; Popov, A.I.; Zelenkov, V.N.; Teplyakova, T.V.; Rashad, M. Humic substances as an environmental-friendly organic wastes potentially help as natural anti-virus to inhibit COVID-19. Sci. Arch. 2020, 1, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinčák, S.; Semjon, B.; Marcinčáková, D.; Reitznerová, A.; Mudroňová, D.; Vašková, J.; Nagy, J. Humic substances as a feed supplement and the benefits of produced chicken meat. Life 2023, 13, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legan, M.; Gotvajn, A.Ž.; Zupan, K. Potential of biochar use in building materials. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 309, 114704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Pan, D.; Zhang, X. Construction and application of biochar-based composite phase change materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çay, A.; Yanık, J.; Akduman, Ç.; Duman, G.; Ertaş, H. Application of textile waste derived biochars onto cotton fabric for improved performance and functional properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Country / Reference | Animal wastes [Refference] | AP* |
|---|---|---|
| USA | Dairy manure [7] | 24 000 |
| China | Livestock manure [8] | 3 800 |
| Chicken manure [9] | 155.0 | |
| Brazil | Cattle manure [10] | 1 900 |
| EU] | Farm manure [11] | 1 200 |
| France | Farm manure [12] | 214.3 |
| Germany | Farm manure [12] | 175.7 |
| United Kingdom | Farm manure [12] | 112.0 |
| Spain | Farm manure [12] | 108.3 |
| Bangladesh | Cow manure [13] | 102.6 |
| Poland | Farm manure [12] | 91.3 |
| Italy | Farm manure [12] | 89.4 |
| India | Poultry manure [14] | 38.0 |
| Malaysia | Chicken manure [15] | 23.1 |
| Serbia | Farm manure [12] | 18.6 |
| Greece | Farm manure [12] | 16.9 |
| Belgorod Region, Russia | Total manure [16] | 14.2 |
| Turkey | Chicken manure [17] | 11.0 |
| Canary Islands | Livestock manure [18] | 0.5 |
| Malta | Farm manure [12] | 0.3 |
| South Africa | Cattle manure [19] | 0.1 |
| Substrate (Reference) | Conditions/Additives | Products |
|---|---|---|
| Composting | ||
| Dairy manure [24] | Thermal pretreatment (90oC, 4 h), 60 days | Compost with 75.0-77.0 g HS/kg |
| Cow dung and corn straw (ratio 1:2) [25] | Addition of 2.5-5% (d.w.) FeSO4,50 days | Compost with 109.8-129.9 g HS/kg |
| Maize straw and chicken manure (ratio 6:1) [26] | Addition of benzoic acid (5% d.w.) and soybean residue after oil extraction (15% d.w.), 62 days | Compost with 150.0 g HS/kg |
| Dairy manure and sugarcane leaves and (ratio 4:1) [27] | Two-step inoculation (0 and 9 days) by Bacillus licheniformis, Aspergillus nidulans and A. oryzae cells (ratio 1:1:1 w/w/w) - 2% d.w., 45 days | Compost with 70.0 g HS/kg |
| Fresh dairy manure and sawdust (ratio 3.5:1) [28] | Treatment by 0.2 M H2O2 (0.5 L) and CuCl2 (0.5 g/kg of compost), 46 days | Compost with 151.9 g HS/kg |
| Pig manure and sawdust (ratio 2:1) [29] | Addition of Black Tourmaline - 10% d.w., 42 days | Compost with 50.2 g HA/kg and 24.0 g FA/kg |
| The dairy manure and bagasse pith (ratio 3:1) [30] | Addition of H2O2 (2.14 mmol/kg) and ascorbic acid (3.57 mmol/kg of the d.w.), 34 days | Compost with 180.0 g HS/kg |
| Chicken manure and rice husk (ratio 6.7:1) [31] | Hyper thermophilic pretreatment (≥80°C) for 1-9 days and total process for 44 days | Compost with 65% HS of TS (according to calculations ~260 g HS/kg) |
| Pig manure and rice straw (C/N = 25) [32] | Hyper thermophilic pretreatment (90°C, 4 h), 60 days | Compost with 87.8 g HS/kg |
| Chicken manure and corn straw (C/N = 20) [33] | Addition of malonic acid (0.5%), MnO2 (0.5% d.w.) or their combination, 60 days | Compost with 75.0-87.0 g HS/kg |
| Chicken manure, sawdust and urea (C/N = 30) [34] | Addition of 0.1% adenosine triphosphate or 0.5% malonic acid (d.w.), 49 days | Compost with 40.0-50.0 g HS/kg |
| Digestates and chicken manure [35] | Without additives, 60 days | Compost with 90.0-95.0 g HS/kg |
| Swine manure and corn stalk (ratio 6:1) [36] | Addition of 1.0% (v/w) Acinetobacter pittii, Bacillus subtilis, B. altitudinis (ratio 1:2:1 v/v), 32 days | Compost with 88.1 g HS/kg |
| Cattle manure (6.7-30% dry basis), rice straw (21.7-31.7%), biogas residue (30-70%), food waste (8.3%) [8] | Without additives, 30 days | Compost with 75.0-88.5 g HS/kg |
| Dairy manure and bagasse [37] | Addition of 10% Red mud (d.w.), pH 8.7, 45 days | Compost with 115.0-120.0 g HS/kg |
| Cow manure and sugar cane straw (ratio 5:1) [38] | Addition of 5% biochar from wood obtained via high temperature gasification (400−550oC), 40 days | Compost with 29.0-31.0 g HS/kg |
| Chicken manure and rice hulls (C/N = 25) [39] | Addition of lignite (15 % w/w), 55 days | Compost with 80.2 g HS/kg |
| Chicken manure and rice straw (C/N =25-30) [40] | Addition of 7.5% montmorillonite (w/w) and pretreatment at 550oC, 60 days | Compost with 67.0-71 g HS/kg |
| Chicken manure and spent mushroom substrate (ratio 1:1.2) [41] | Addition of Garden waste (15% fresh weight), 60 days | Compost with 145.0-155.0 g HS/kg |
| Horse manure (C/N = 33) [42] | Vermicomposting (10 g earthworms Eisenia Andrei/kg), 35oC, 6-9 months | Compost with 26.0-26.6 g HA/kg |
| Anaerobic digestion | ||
| Chicken manure [43] | 37oC, 10.0% of TS, 7.9% of VS, 40 days | Digestate – relative content of HLC (34%) and FLC (6%). HS yield was not controlled |
| Chicken manure [44] | 37oC, 10.0% TS and 7.9%VS, 25 days | Digestate – 7.7 g HA/L |
| Turkey manure [45] | 37oC, 51.2% (w/w wet basis) TS and 71.5% (w/w dry basis) VS, OLR – 0.5 2.5 kg VS/m3 per day, 77 days | Content HS in liquid fraction of the effluent and entire effluent (with digestate) – 2.36 (2.32 HA, 0.04 FA) and 2.6 (2.04 HA, 0.60 FA) g/L |
| Sheep bedding and cattle manure [46] | 18 ± 4oC, sheep bedding to cattle manure ratios: 0:100, 25:75, 50:50, 75:25, and 100:0, final content of TS –5%, 5 months | Digestate with HA/FA – 1.3-3.0. HS yield was not controlled |
| Pig manure [47] | Hydrotermal pretreatment (70 – 170 oC, 0.5 h), 37oC, 30 days | Digestate with HLC and FLC – 58.0-65.9 and 35.5-42.0%, respectively. HS yield was not controlled. |
| Hydrothermal carbonization | ||
| Dried swine manure [48] | 180°C, 1 MPa, 15wt.% CaO, 10 h | HCmy – 75.2% |
| Dried poultry litter [49] | 180°C, 1 MPa, 1 h | HCmy – 60.4% |
| Dried poultry litter [50] | 250°C, 4-5 MPa, H2SO4 (pH 2.0), 2 h | HCmy – 38.1% |
| Dry swine and chicken manure [51] | 240°C, 3-4MPa, 10 h | HCmy – 54.6% |
| Dried swine manure with cellulose [52] | 210°C, 2 MPa, 5 h | HCmy – 52.0% |
| Dried swine manure with sawdust [53] | 220°C, 2-3 MPa, 10 h | HCmy – 61.8% |
| Dried pig manure [54] | 180°C, 1 MPa, 1–1.5 g KOH per 100 g manure, 1 h | HCmy – 79.0% |
| Dried swine manure [55] | 200°C, 2 MPa, 30 min | HCmy – 58.7% |
| Chicken litter [56] | 220°C, 2-3 MPa, 20 min | HCmy – 68.0% |
| Air-dried pig manure [57] | 200oC, 2 MPa, 2 h | HCmy – 58.8% |
| Poultry and swine manure, dairy and beef cattle manure, broiler and layer chicken litter [58] | 180oC, 1 MPa, 1 h | HCmy – 67.3% |
| Mixture of chicken manure with sawdust [59] | 260°C, 40 min | Biochar yield – 95.1% |
| Dewatered poultry sludge [60] | 268°C, 47 min | Biochar yield – 85.0 % |
| Pyrolysis | ||
| Dried pig manure [54] | 200°C, 1 h | Biochar yield – 40.0% |
| Poultry litter [61] | Wet torrefaction pretreatment (300°C), 600 or 800°C, supercritical CO2, 1.5–2 h | Biochar yield – 51.2% |
| Chicken litter [56] | 400°C, 20 min | Biochar yield – 38.0% |
| Pre-dried broiler manure [62] | 350°C, 1 h | Biochar yield – 47% |
| Dried poultry litter [63] | 500°C, Mixed with H3PO4 and MgO (biomass:H3PO4 ratio = 1:0.5 (w/w), molar P:Mg ratio - 1:1), 2 h | Biochar yield – 60.0% |
| Air-dried pig manure [57] | 300oC, 1 h | Biochar yield – 84% |
| Dried digested cattle manure [64] | 600°C, 30 min | Biochar yield – 44.8% |
| Poultry and swine manure, dairy and beef cattle manure, broiler and layer chicken litter [58] | 400oC, 1 h | Biochar yield – 51.0% |
| Dried goat manure [65] | 300oC, 30 min | Biochar yield – 48.6% |
| Air-dried poultry manure [66] | 200oC, 4 h | Biochar yield – 95.8% |
| Hydrolysis | ||
| Air dried sheep or cow manures [67] | Acid hydrolysis (0.1-1.0 N HCl or H2SO4) at 105°C and extraction (1N KOH), 1 h | HS yield – 45 g/kg (sheep waste) and 56 g/kg (cow waste) |
| Air dried poultry manure [68] | 25°C, 0.1 N NaOH, 24 h | HA – 28.1 g/kg. FA – 13.3 g/kg |
| Farmyard manure [69] | 25oC, 0.1 M NaOH, 450 rpm, 48 h | HA yield – 10% |
| Fresh chicken manure [70] | Subcritical water extraction (230-250°C, 6 MPa) | Liquid phase with 31.0 g HA/kg and 20 g FA/kg |
| Sample of waste [Reference] | Chemical elements (%) | Ratios | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | O | S | H/C | C/N | O/C | |
| Composting | ||||||||
| Chicken manure and rice husk [31] | 41.10 | 3.40a | 5.70 a | n/d | n/d | 0.08 | 7.14 | n/d |
| Horse manure [42] | 38.42a | 42.36a | 2.29a | 17.19a | n/d | 1.10b | 16.76b | 0.47b |
| Anaerobic digestion | ||||||||
| Chiken manure [44] | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d | 1.78b | 5.01b | n/d |
| Hydrothermal carbonization | ||||||||
| Dried swine manure [48] | 35.09 | 4.64 | 1.97 | 26.65 | n/d | 0.13 | 17.8 | 0.76 |
| Dried poultry liter [49] | 33.61 | 3.91 | 1.95 | 20.84 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 17.2 | 0.62 |
| Dried poultry liter [50] | 56.40 | 4.99 | 5.13 | 7.78 | 1.22 | 0.09 | 11.0 | 0.14 |
| Dried swine manure [51] | 40.61 | 4.15 | 2.11 | 11.72 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 19.2 | 0.29 |
| Dried poultry manure [51] | 28.44 | 2.84 | 2.05 | 5.65 | 0.25 | 0.10 | 13.9 | 0.20 |
| Dried swine manure [52] | 40.42 | 3.71 | 1.94 | 18.10 | 0.18 | 1.10b | 20.8 | 0.33b |
| Dried swine manure with sawdust [48] | 40.85 | 6.30 | 3.73 | 31.30 | 0.42 | 1.55b | 11.0 | 0.57b |
| Poultry liter [56] | 37.5 | n/d | 8.01 | n/d | n/d | n/d | 4.7 | n/d |
| Dewatered poultry sludge [60] | 53.43 | 8.17 | 3.67 | 11.24 | 0.52 | 1.86b | 14.6 | 0.16b |
| Air-dried pig manure [57] | 33.77 | 4.22 | 2.49 | 14.96 | 0.55 | 1.50b | 13.6 | 0.33b |
| Swine manure Zhou [58] | 35.96 | 4.36 | 2.02 | 22.30 | 0.54 | 0.12 | 17.8 | 0.62 |
| Daily cattle manure [58] | 43.63 | 5.27 | 2.17 | 26.92 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 20.1 | 0.62 |
| Beef cattle manure [58] | 38.79 | 4.33 | 1.78 | 24.10 | 0.48 | 0.11 | 21.8 | 0.62 |
| Broiler liter [58] | 38.19 | 4.53 | 3.45 | 23.57 | 0.65 | 0.12 | 11.1 | 0.62 |
| Layer chicken liter [58] | 39.58 | 5.02 | 2.09 | 22.04 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 18.9 | 0.56 |
| Pyrolysis | ||||||||
| Dried poultry manure [63] | 43.30 | 2.15 | n/d | n/d | n/d | 0.05b | n/d | n/d |
| Air-dried pig manure [57] | 29.04 | 1.41 | 1.36 | 0.29 | 4.82 | 0.58b | 21.6 | 0.12b |
| Air-dried poultry manure [57] | 39.70 | 5.62 | 3.53 | 42.3 | n/d | 0.14 | 11.2 | 1.07 |
| Dried digested dairy cattle manure [64] | 39.60 | 0.85 | 1.84 | n/d | 0.94 | 0.02 | 21.5 | n/d |
| Swine manure [58] | 34.89 | 1.96 | 2.44 | 10.16 | 0.51 | 0.06 | 14.3 | 0.29 |
| Daily cattle manure [58] | 42.27 | 2.41 | 2.46 | 11.39 | 0.57 | 0.06 | 17.2 | 0.27 |
| Beef cattle manure [58] | 40.55 | 2.09 | 2.04 | 11.39 | 0.45 | 0.05 | 19.9 | 0.28 |
| Broiler liter [58] | 37.59 | 2.18 | 4.57 | 6.13 | 1.06 | 0.06 | 8.23 | 0.16 |
| Layer chicken liter [58] | 35.39 | 1.98 | 2.52 | 7.76 | 0.88 | 0.06 | 14.0 | 0.22 |
| Alkaline hydrolysis | ||||||||
| Air dried poultry manure [68] | 45.06 | 4.08 | 6.01 | 44.85 | n/d | 0.09b | 7.49 | 0.99b |
| Farmyard manure [69] | 53.10 | 5.45 | 3.24 | 37.63 | 0.58 | 0.10b | 16.39b | 0.71b |
| Natural HS extracted from different environmental sources (for comparison) | ||||||||
| HA from peat [87] | 40.1 | 4.2 | 2.5 | n/d | 2.2 | 0.10 | 16.0 | n/d |
| HA from peat [88] | 52.25 | 4.51 | 2.59 | n/d | 0.77 | 1.03b | 20.2 | 0.57b |
| HA from peat [88] | 56.34 | 5.71 | 2.34 | n/d | 0.88 | 1.20b | 24.1 | 0.45b |
| HA from raw lignite coal [89] | 72.20 | 4.44 | 1.97 | 18.07 | 3.31 | 0.06b | 36.6 | 0.25b |
| HA from native bituminous coal [89] | 56.20 | 10.99 | 3.07 | 18.59 | 11.15 | 0.19b | 18.3 | 0.18b |
| Product with HS | Application | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| HS from animal wastes | ||
| Chicken manure biochar [93] | Adsorbent for the removal of phenol and 2,4-dinitrophenol from wastewater | Maximum adsorption capacity: 106.2 mg/g phenol, 148.6 mg/g 2,4-dinitrophenol |
| Chicken manure biochar [94] | Remediation of metals from water and soil | Removal efficiency: 98% of Pb2+; 42% of Zn2+ |
| Swine manure biochar [95] | Adsorption of U(VI) | Maximum adsorption capacity: 221.4 mg/g |
| Swine manure hydrochar modified with manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) nanoparticles [96] | Removal of chlortetracycline and Cd (II) from water | Maximum adsorption capacity: 753.0 mg/g (chlortetracycline), 62.2 mg/g (Cd (II)), |
| Cattle manure hydrochar [97] | Soil conditioner | Hydrochar improves: total soil phosphorus (by 6.8–18.9%), soil organic carbon (by 8.2%), dissolved organic carbon (by 18.7%), rice yield (by 36.9%) |
| Swine manure hydrochar [98] | Removal of metal from aqueous solutions | Maximum adsorption capacity (mg/g): 81.1 (Cd II), 13.1 (Sb III) |
| Hydrochar made from digestate of manure [99] | Soil amendment | Increase of soil pH (from 7.0 to 7.4), cation exchange capacity (from 11.5 to 12.6 meq/100 g soil), soil organic matter (from 2.4 to 2.8%), P, K, Ca, Mg content. Twice increase in dry weights of roots, leaves, and plant Lactuca sativa |
| Compost made from farm yard manure with addition of biochar [100] | Soil amendment | Increase of growth, yield and chlorophyll content and decrease of Cd content in wheat tissues |
| HS extracted from compost containing cow manure [101] | Biosurfactant | Percent of metal removal: Cu - 17%, Pb - 35%, Zn 8%, Cd -38% and Cr - 0.6% |
| Hydrochar from digestate of cow manure and corn straw [102] | Additive to AD | Enhancing of CH4 yield - 34% |
| Chicken manure biochar [103] | Additive to composting mass | Decrease in emission of N2O, CH4 and NH3 on 27.4 %, 55.9 % and 56.9%, respectively |
| HS from other types of wastes | ||
| HA from compost [104] | Treatment of diesel-contaminated soil | Diesel removal - 89.4% |
| HA from vermicompost [105] | Adsorption of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) from maize-soybean meal for broiler chickens (100 µg AFB1/kg) | Improved adsorption - 99.7% |
| Mixture of bamboo biochar and pig manure [106] | Soil remediation | Soil treatment with biochar–pig manure increased concentration of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi |
| Biochar obtained in pyrolysis of bamboo and rice husk [107] | Additive to composting mass | Improving of organic matter decomposition, enhanced HA concentration (>80 g/kg), reduced volatilization of NH3 and N2O (40%) |
| Wheat straw biochar [108] | Additive to composting mass | Notable prolongation of thermophilic period of pig manure composting with stabilization of bacteria richness. |
| Hydrochar from olive mill waste and cellulose [109] | Enzyme immobilization | Absorption immobilization of enzyme - 20-30% |
| Corn straw hydrochar [110] | Electrode material | The mass-specific capacitance - 98 F/g. Power density - 9500 W/kg. Energy density - 77 W h/kg at 20 A/g |
| HS extracted from composted artichoke residues [111] | Antibacterial agent and antioxidant | Minimal inhibitory concentrations (mg/L) against bacterial cells in concentration of 5×105 CFU/mL: against Staphylococcus aureus - 1.2, Pseudomonas aeruginosa – 1.8, Enterococcus faecalis – 2.0, Escherichia coli – 1.7, Klebsiella pneumoniae – 2.3. Antioxidant activity (expressed as gallic acid equivalents) – 150 mol/g. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





