Submitted:
14 November 2023
Posted:
16 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Discovery and Evolving Knowledge of Stem Cells in Adult AML
2.1. Functional Definitions and Immunophenotype
2.2. LSC Transcriptional Signatures
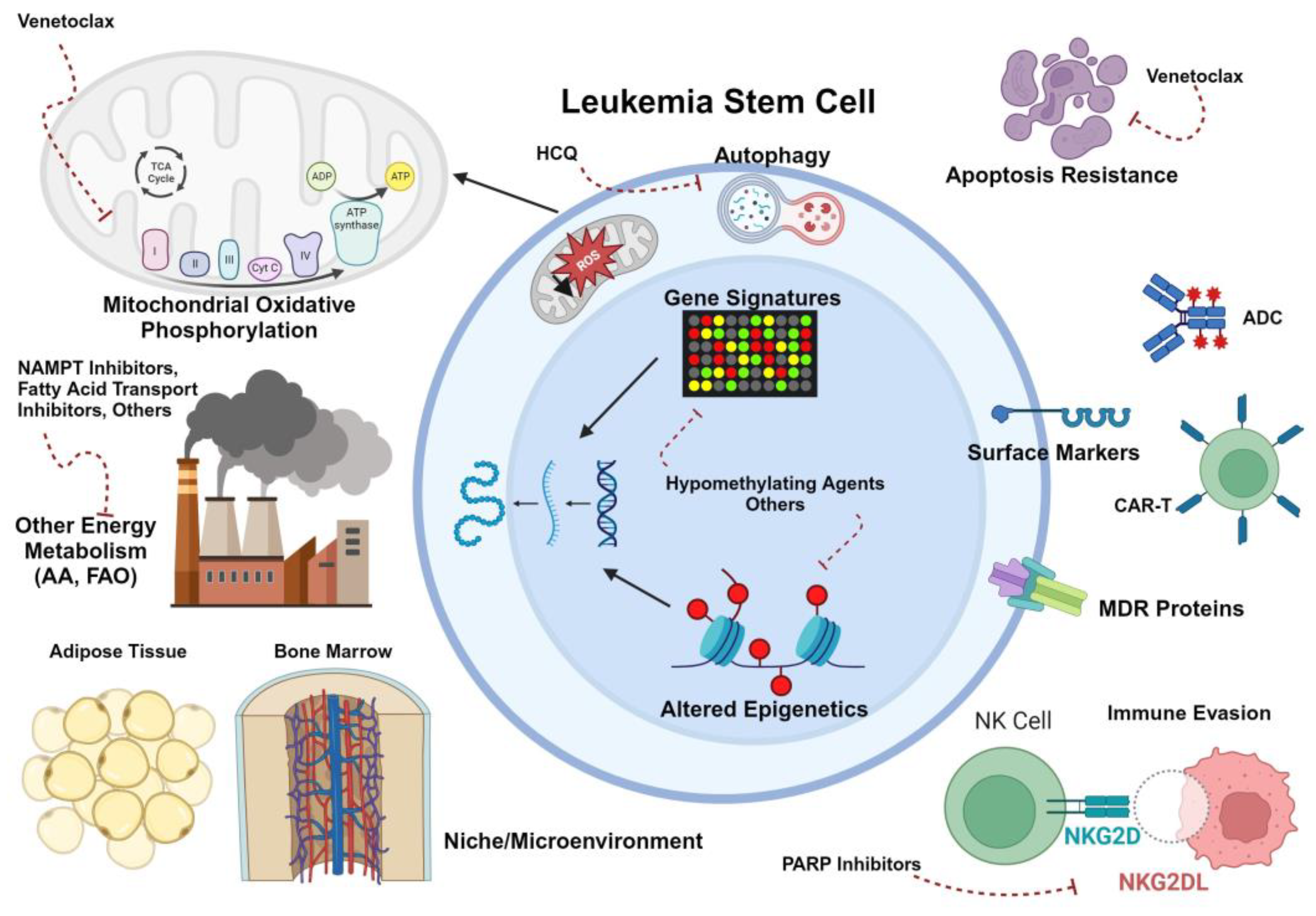
2.3. LSC metabolism, Microenvironment, and Drug Resistance
3. LSC Biology in Pediatric Myeloid Disease
3.1. Immunophenotype
3.2. LSC Transcriptional Signatures
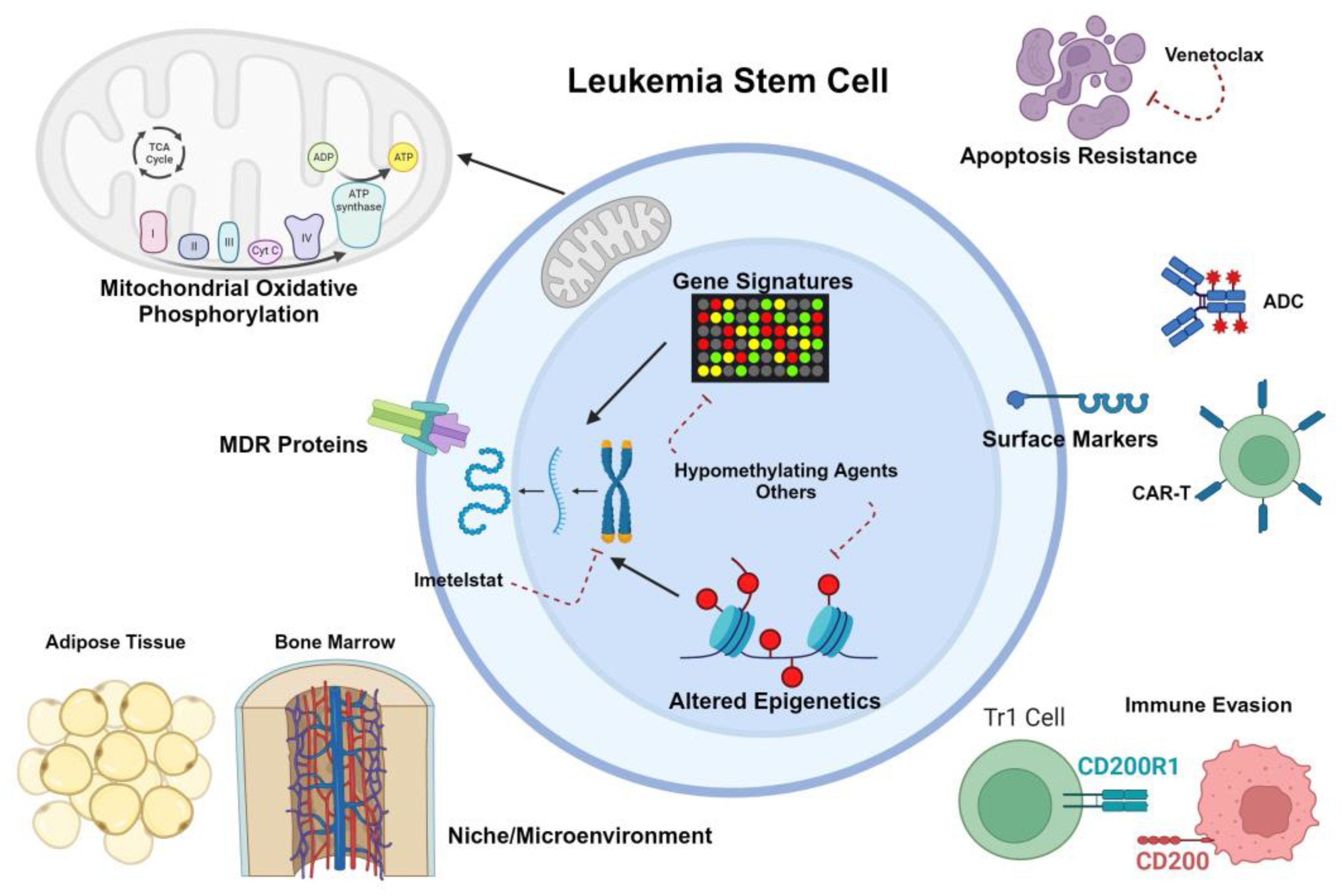
3.3. LSC Metabolism, Microenvironment, and Drug Resistance
4. Immunotherapies
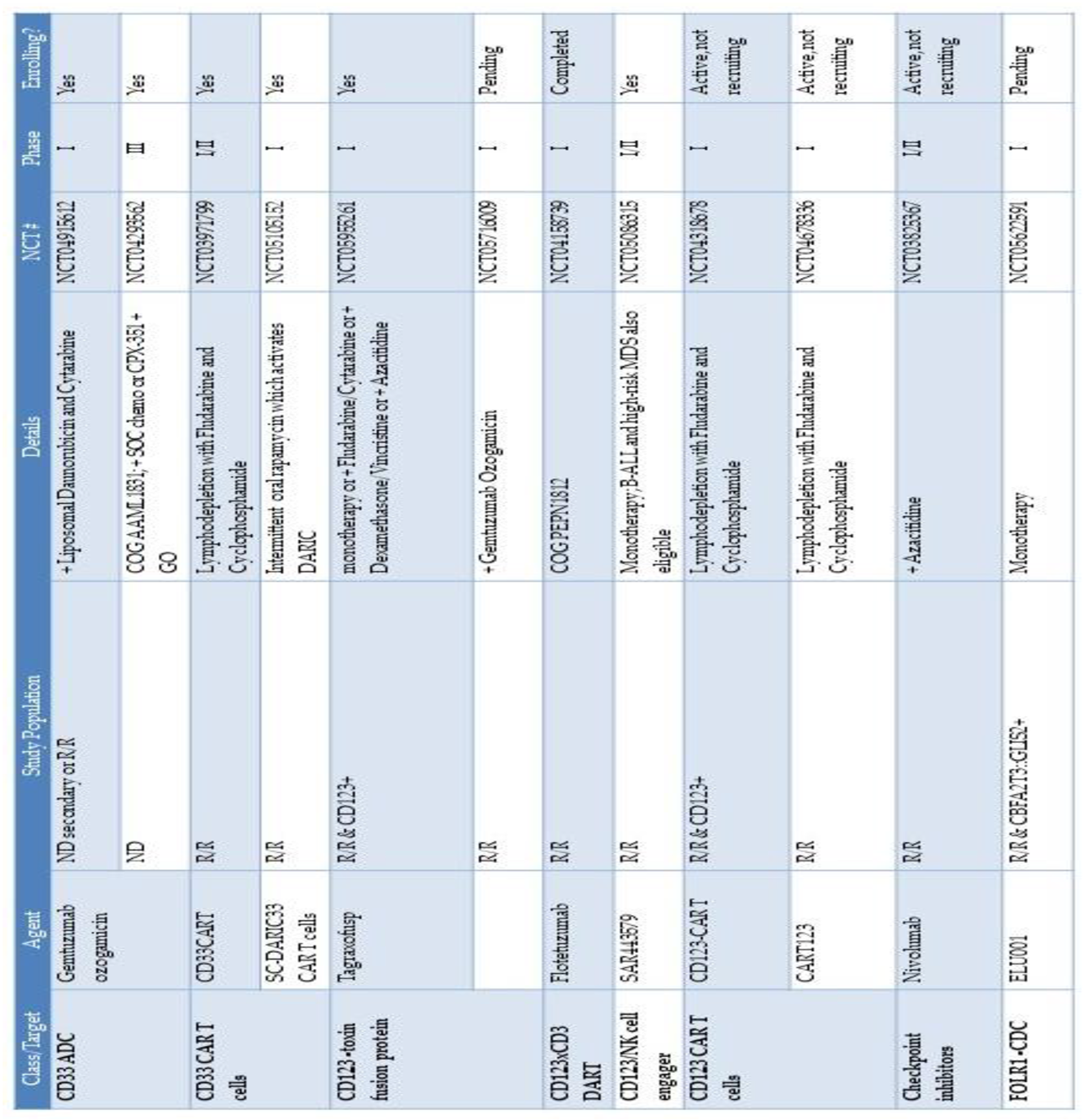
4.1. CD33
4.2. CD123
4.3. Checkpoint Inhibitors
4.4. CD47
4.5. Folate Receptor 1/Folate Receptor-Alpha
5. Other Novel Agents
5.1. FLT3 Inhibitors
5.2. Menin Inhibitors
5.3. Venetoclax
5.4. PARP Inhibitors
5.5. Epigenetic Modifiers
5.6. Selinexor
5.7. Niclosamide
5.8. Uproleselan
5.9. Enasidenib
5.10. Pevonedistat
6. Future Targets
6.1. Immunotherapies
- CD70 is a tumor necrosis factor receptor ligand that is not normally expressed in normal tissues or on HSCs during hematopoiesis. It is upregulated on immune cells upon activation but not on resting B or T lymphocytes[221]. It has been demonstrated that CD34+ AML cells and LSCs express CD70 and its receptor CD27, that CD70/CD27 signaling in AML cells activates stem cell expression programs, and that the promoter for CD70 is sensitive to methylation[222,223]. For these reasons, blocking CD70/CD27 signaling in conjunction with hypomethylating agents is being considered as a potential treatment concept for AML. Currently, a CD70-targeting antibody, cusatuzumab, in combination with azaciditine or venetoclax, remains under clinical investigation with promising initial responses but short follow-up of treated patients to date[224].
- Surface expression of CD69 was enriched on LSCs from patients whose disease proved chemoresistant in one study, and CD69 expression in transcriptional data from large retrospective cohorts of pediatric patients correlated with poor outcomes[66]. Therefore, CD69 could represent a future LSC targeting strategy for pediatric AML, although CD69 expression on regulatory T cells and other specialized T-cell subsets may indicate unwanted side effects of immune dysregulation with CD69 targeting[225].
6.2. Other Novel Agents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shallis, R.M.; Wang, R.; Davidoff, A.; Ma, X.; Zeidan, A.M. Epidemiology of acute myeloid leukemia: Recent progress and enduring challenges. Blood Rev 2019, 36, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, D.; Antoniou, E.; Waack, K. Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Past, Present, and Future. J Clin Med 2022, 11, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uy, G.L.; Duncavage, E.J.; Chang, G.S.; Jacoby, M.A.; Miller, C.A.; Shao, J.; Heath, S.; Elliott, K.; Reineck, T.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. Dynamic changes in the clonal structure of MDS and AML in response to epigenetic therapy. Leukemia 2017, 31, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolouri, H.; Farrar, J.E.; Triche, T., Jr.; Ries, R.E.; Lim, E.L.; Alonzo, T.A.; Ma, Y.; Moore, R.; Mungall, A.J.; Marra, M.A.; et al. The molecular landscape of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia reveals recurrent structural alterations and age-specific mutational interactions. Nat Med 2018, 24, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWolf, S.; Tallman, M.S. How I treat relapsed or refractory AML. Blood 2020, 136, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thol, F. What to use to treat AML: The role of emerging therapies. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2021, 2021, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fialkow, P.J.; Gartler, S.M.; Yoshida, A. Clonal origin of chronic myelocytic leukemia in man. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1967, 58, 1468–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, E. Stem cells in normal and leukemic hemopoiesis (Henry Stratton Lecture, 1982). 1983.
- Griffin, J.D.; Lowenberg, B. Clonogenic cells in acute myeloblastic leukemia. 1986.
- Bonnet, D.; Dick, J.E. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med 1997, 3, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rhenen, A.; Feller, N.; Kelder, A.; Westra, A.H.; Rombouts, E.; Zweegman, S.; van der Pol, M.A.; Waisfisz, Q.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Schuurhuis, G.J. High stem cell frequency in acute myeloid leukemia at diagnosis predicts high minimal residual disease and poor survival. Clin Cancer Res 2005, 11, 6520–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeijlemaker, W.; Grob, T.; Meijer, R.; Hanekamp, D.; Kelder, A.; Carbaat-Ham, J.C.; Oussoren-Brockhoff, Y.J.M.; Snel, A.N.; Veldhuizen, D.; Scholten, W.J.; et al. CD34(+)CD38(-) leukemic stem cell frequency to predict outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, C.T.; Upchurch, D.; Szilvassy, S.J.; Guzman, M.L.; Howard, D.S.; Pettigrew, A.L.; Meyerrose, T.; Rossi, R.; Grimes, B.; Rizzieri, D.A.; et al. The interleukin-3 receptor alpha chain is a unique marker for human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells. Leukemia 2000, 14, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, B.M.; Khan, N.; D'Alessandro, A.; Nemkov, T.; Winters, A.; Jones, C.L.; Zhang, W.; Pollyea, D.A.; Jordan, C.T. Characterization and targeting of malignant stem cells in patients with advanced myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarry, J.E.; Murphy, K.; Perry, R.; Sanchez, P.V.; Secreto, A.; Keefer, C.; Swider, C.R.; Strzelecki, A.C.; Cavelier, C.; Recher, C.; et al. Human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells are rare and heterogeneous when assayed in NOD/SCID/IL2Rgammac-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 2011, 121, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.C.; LaMere, M.; Stevens, B.M.; Ashton, J.M.; Myers, J.R.; O'Dwyer, K.M.; Liesveld, J.L.; Mendler, J.H.; Guzman, M.; Morrissette, J.D.; et al. Evolution of acute myelogenous leukemia stem cell properties after treatment and progression. Blood 2016, 128, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, K.; Sarver, A.L.; Noble-Orcutt, K.E.; LaRue, R.S.; Antony, M.L.; Chang, D.; Lee, Y.; Navis, C.M.; Hillesheim, A.L.; Nykaza, I.R.; et al. Single-Cell Gene Expression Analyses Reveal Distinct Self-Renewing and Proliferating Subsets in the Leukemia Stem Cell Compartment in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Res 2020, 80, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonen, M.; Sun, Z.; Figueroa, M.E.; Patel, J.P.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Racevskis, J.; Ketterling, R.P.; Fernandez, H.; Rowe, J.M.; Tallman, M.S.; et al. CD25 expression status improves prognostic risk classification in AML independent of established biomarkers: ECOG phase 3 trial, E1900. Blood 2012, 120, 2297–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.H.; Roy, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Desrichard, A.; Chung, S.S.; Woolthuis, C.M.; Hu, W.; Berezniuk, I.; Garrett-Bakelman, F.E.; Hamann, J.; et al. CD97 is a critical regulator of acute myeloid leukemia stem cell function. J Exp Med 2019, 216, 2362–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczulla, A.M.; Rothfelder, K.; Raffel, S.; Konantz, M.; Steinbacher, J.; Wang, H.; Tandler, C.; Mbarga, M.; Schaefer, T.; Falcone, M.; et al. Absence of NKG2D ligands defines leukaemia stem cells and mediates their immune evasion. Nature 2019, 572, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersten, B.; Valkering, M.; Wouters, R.; van Amerongen, R.; Hanekamp, D.; Kwidama, Z.; Valk, P.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Zeijlemaker, W.; Kaspers, G.; et al. CD45RA, a specific marker for leukaemia stem cell sub-populations in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2016, 173, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikushige, Y.; Miyamoto, T. TIM-3 as a novel therapeutic target for eradicating acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells. Int J Hematol 2013, 98, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askmyr, M.; Agerstam, H.; Hansen, N.; Gordon, S.; Arvanitakis, A.; Rissler, M.; Juliusson, G.; Richter, J.; Jaras, M.; Fioretos, T. Selective killing of candidate AML stem cells by antibody targeting of IL1RAP. Blood 2013, 121, 3709–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eppert, K.; Takenaka, K.; Lechman, E.R.; Waldron, L.; Nilsson, B.; van Galen, P.; Metzeler, K.H.; Poeppl, A.; Ling, V.; Beyene, J.; et al. Stem cell gene expression programs influence clinical outcome in human leukemia. Nat Med 2011, 17, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.W.; Mitchell, A.; Kennedy, J.A.; Chen, W.C.; McLeod, J.; Ibrahimova, N.; Arruda, A.; Popescu, A.; Gupta, V.; Schimmer, A.D.; et al. A 17-gene stemness score for rapid determination of risk in acute leukaemia. Nature 2016, 540, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, N.; Dai, B.; Gentles, A.J.; Majeti, R.; Feinberg, A.P. An LSC epigenetic signature is largely mutation independent and implicates the HOXA cluster in AML pathogenesis. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 8489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xue, M.; Deng, X.; Dong, L.; Nguyen, L.X.T.; Ren, L.; Han, L.; Li, C.; Xue, J.; Zhao, Z.; et al. TET2-mediated mRNA demethylation regulates leukemia stem cell homing and self-renewal. Cell Stem Cell 2023, 30, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Han, G.; Li, Y.; Yin, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; et al. Decoding m(6)A RNA methylome identifies PRMT6-regulated lipid transport promoting AML stem cell maintenance. Cell Stem Cell 2023, 30, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Han, G.; Zhang, T.; Chang, J.; Yin, R.; Shan, Y.; Wen, J.; Xie, X.; et al. Leukemogenic Chromatin Alterations Promote AML Leukemia Stem Cells via a KDM4C-ALKBH5-AXL Signaling Axis. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabal-Hierro, L.; van Galen, P.; Prado, M.A.; Higby, K.J.; Togami, K.; Mowery, C.T.; Paulo, J.A.; Xie, Y.; Cejas, P.; Furusawa, T.; et al. Chromatin accessibility promotes hematopoietic and leukemia stem cell activity. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paubelle, E.; Zylbersztejn, F.; Maciel, T.T.; Carvalho, C.; Mupo, A.; Cheok, M.; Lieben, L.; Sujobert, P.; Decroocq, J.; Yokoyama, A.; et al. Vitamin D Receptor Controls Cell Stemness in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and in Normal Bone Marrow. Cell Rep 2020, 30, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacPherson, L.; Anokye, J.; Yeung, M.M.; Lam, E.Y.N.; Chan, Y.C.; Weng, C.F.; Yeh, P.; Knezevic, K.; Butler, M.S.; Hoegl, A.; et al. HBO1 is required for the maintenance of leukaemia stem cells. Nature 2020, 577, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.; Morgan, M.; Campos, J.; Spencer, G.J.; Shmakova, A.; Ivanova, I.; Mapperley, C.; Lawson, H.; Wotherspoon, D.A.; Sepulveda, C.; et al. Targeting the RNA m(6)A Reader YTHDF2 Selectively Compromises Cancer Stem Cells in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 25, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagadinou, E.D.; Sach, A.; Callahan, K.; Rossi, R.M.; Neering, S.J.; Minhajuddin, M.; Ashton, J.M.; Pei, S.; Grose, V.; O'Dwyer, K.M.; et al. BCL-2 inhibition targets oxidative phosphorylation and selectively eradicates quiescent human leukemia stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, S.; Pollyea, D.A.; Gustafson, A.; Stevens, B.M.; Minhajuddin, M.; Fu, R.; Riemondy, K.A.; Gillen, A.E.; Sheridan, R.M.; Kim, J.; et al. Monocytic Subclones Confer Resistance to Venetoclax-Based Therapy in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Discov 2020, 10, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollyea, D.A.; Stevens, B.M.; Jones, C.L.; Winters, A.; Pei, S.; Minhajuddin, M.; D'Alessandro, A.; Culp-Hill, R.; Riemondy, K.A.; Gillen, A.E.; et al. Venetoclax with azacitidine disrupts energy metabolism and targets leukemia stem cells in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Med 2018, 24, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Velasco-Hernandez, T.; Mess, J.; Lalioti, M.E.; Romero-Mulero, M.C.; Obier, N.; Karantzelis, N.; Rettkowski, J.; Schonberger, K.; Karabacz, N.; et al. GPRC5C Drives Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Leukemogenesis. Blood Adv 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.L.; Stevens, B.M.; D'Alessandro, A.; Culp-Hill, R.; Reisz, J.A.; Pei, S.; Gustafson, A.; Khan, N.; DeGregori, J.; Pollyea, D.A.; et al. Cysteine depletion targets leukemia stem cells through inhibition of electron transport complex II. Blood 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.L.; Stevens, B.M.; D'Alessandro, A.; Reisz, J.A.; Culp-Hill, R.; Nemkov, T.; Pei, S.; Khan, N.; Adane, B.; Ye, H.; et al. Inhibition of Amino Acid Metabolism Selectively Targets Human Leukemia Stem Cells. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 724–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culp-Hill, R.; Stevens, B.M.; Jones, C.L.; Pei, S.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Minhajuddin, M.; Jordan, C.T.; D'Alessandro, A. Therapy-Resistant Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells Are Resensitized to Venetoclax + Azacitidine by Targeting Fatty Acid Desaturases 1 and 2. Metabolites 2023, 13, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subedi, A.; Liu, Q.; Ayyathan, D.M.; Sharon, D.; Cathelin, S.; Hosseini, M.; Xu, C.; Voisin, V.; Bader, G.D.; D'Alessandro, A.; et al. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase inhibitors selectively induce apoptosis of AML stem cells by disrupting lipid homeostasis. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 1851–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Adane, B.; Khan, N.; Sullivan, T.; Minhajuddin, M.; Gasparetto, M.; Stevens, B.; Pei, S.; Balys, M.; Ashton, J.M.; et al. Leukemic Stem Cells Evade Chemotherapy by Metabolic Adaptation to an Adipose Tissue Niche. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, B.M.; Jones, C.L.; Pollyea, D.A.; Culp-Hill, R.; D'Alessandro, A.; Winters, A.; Krug, A.; Abbott, D.; Goosman, M.; Pei, S.; et al. Fatty acid metabolism underlies venetoclax resistance in acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Nat Cancer 2020, 1, 1176–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.R.; Sheth, V.; Li, H.; Harris, M.W.; Qiu, S.; Crossman, D.K.; Kumar, H.; Agarwal, P.; Nagasawa, T.; Paterson, A.J.; et al. Microenvironmental CXCL12 deletion enhances Flt3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia stem cell response to therapy by reducing p38 MAPK signaling. Leukemia 2023, 37, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, R.; Ma, S.; Tian, L.; Lu, T.; Zhang, J.; Mundy-Bosse, B.L.; Zhang, B.; Marcucci, G.; Caligiuri, M.A.; et al. ILC1s control leukemia stem cell fate and limit development of AML. Nat Immunol 2022, 23, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Grouw, E.P.; Raaijmakers, M.H.; Boezeman, J.B.; van der Reijden, B.A.; van de Locht, L.T.; de Witte, T.J.; Jansen, J.H.; Raymakers, R.A. Preferential expression of a high number of ATP binding cassette transporters in both normal and leukemic CD34+CD38- cells. Leukemia 2006, 20, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.M.; Hogge, D.E.; Ling, V. MDR1 and BCRP1 expression in leukemic progenitors correlates with chemotherapy response in acute myeloid leukemia. Exp Hematol 2008, 36, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulf, G.G.; Wang, R.Y.; Kuehnle, I.; Weidner, D.; Marini, F.; Brenner, M.K.; Andreeff, M.; Goodell, M.A. A leukemic stem cell with intrinsic drug efflux capacity in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2001, 98, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.E.; Eom, J.I.; Jeung, H.K.; Cheong, J.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Min, Y.H. AMPK-ULK1-Mediated Autophagy Confers Resistance to BET Inhibitor JQ1 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. Clin Cancer Res 2017, 23, 2781–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.E.; Eom, J.I.; Jeung, H.K.; Chung, H.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, J.S.; Cheong, J.W.; Min, Y.H. PERK/NRF2 and autophagy form a resistance mechanism against G9a inhibition in leukemia stem cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2020, 39, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Kumar, H.; Yan, C.; Li, H.; Paterson, A.J.; Anderson, N.R.; He, J.; Yang, J.; Xie, M.; Crossman, D.K.; et al. Autophagy inhibition impairs leukemia stem cell function in FLT3-ITD AML but has antagonistic interactions with tyrosine kinase inhibition. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2621–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykstra, K.M.; Fay, H.R.S.; Massey, A.C.; Yang, N.; Johnson, M.; Portwood, S.; Guzman, M.L.; Wang, E.S. Inhibiting autophagy targets human leukemic stem cells and hypoxic AML blasts by disrupting mitochondrial homeostasis. Blood Adv 2021, 5, 2087–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollyea, D.A.; Jordan, C.T. Therapeutic targeting of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Blood 2017, 129, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabon, C.M.; Abbas, H.A.; Konopleva, M. Acute myeloid leukemia: Therapeutic targeting of stem cells. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2022, 26, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrie, D.; Helgason, G.V.; Copland, M. The leukaemia stem cell: Similarities, differences and clinical prospects in CML and AML. Nat Rev Cancer 2020, 20, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelmach, P.; Trumpp, A. Leukemic stem cells and therapy resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2023, 108, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez-Gonzalez, A.; Dorantes-Acosta, E.; Moreno-Lorenzana, D.; Alvarado-Moreno, A.; Arriaga-Pizano, L.; Mayani, H. Expression of CD90, CD96, CD117, and CD123 on different hematopoietic cell populations from pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Arch Med Res 2014, 45, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.A.; Rosenberg, C.A.; Brondum, R.F.; Aggerholm, A.; Kjeldsen, E.; Rahbek, O.; Ludvigsen, M.; Hasle, H.; Roug, A.S.; Bill, M. Immunophenotypically defined stem cell subsets in paediatric AML are highly heterogeneous and demonstrate differences in BCL-2 expression by cytogenetic subgroups. Br J Haematol 2022, 197, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Werf, I.; Mondala, P.K.; Steel, S.K.; Balaian, L.; Ladel, L.; Mason, C.N.; Diep, R.H.; Pham, J.; Cloos, J.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; et al. Detection and targeting of splicing deregulation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Cell Rep Med 2023, 4, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeel, E.Z.; Madney, Y.; Eldin, D.N.; Shafik, N.F. Overexpression of CD200 and CD123 is a major influential factor in the clinical course of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Exp Mol Pathol 2021, 118, 104597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakral, D.; Singh, V.K.; Gupta, R.; Jha, N.; Khan, A.; Kaur, G.; Rai, S.; Kumar, V.; Supriya, M.; Bakhshi, S.; et al. Integrated single-cell transcriptome analysis of CD34 + enriched leukemic stem cells revealed intra- and inter-patient transcriptional heterogeneity in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol 2023, 102, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depreter, B.; De Moerloose, B.; Vandepoele, K.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Van Damme, A.; Terras, E.; Denys, B.; Dedeken, L.; Dresse, M.F.; Van der Werff Ten Bosch, J.; et al. Deciphering molecular heterogeneity in pediatric AML using a cancer vs. normal transcriptomic approach. Pediatr Res 2021, 89, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamble, A.J.; Eidenschink Brodersen, L.; Alonzo, T.A.; Wang, J.; Pardo, L.; Sung, L.; Cooper, T.M.; Kolb, E.A.; Aplenc, R.; Tasian, S.K.; et al. CD123 Expression Is Associated With High-Risk Disease Characteristics in Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report From the Children's Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 2022, 40, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbrich, S.; Baran, N.; Cai, T.; Weng, C.; Aitken, M.J.L.; Post, S.M.; Henderson, J.; Shi, C.; Richard-Carpentier, G.; Sauvageau, G.; et al. Overexpression of CD200 is a Stem Cell-Specific Mechanism of Immune Evasion in AML. J Immunother Cancer 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieniewicz, B.; Uyeda, M.J.; Chen, P.P.; Sayitoglu, E.C.; Liu, J.M.; Andolfi, G.; Greenthal, K.; Bertaina, A.; Gregori, S.; Bacchetta, R.; et al. Engineered type 1 regulatory T cells designed for clinical use kill primary pediatric acute myeloid leukemia cells. Haematologica 2021, 106, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; He, F.; Tian, Y.; Hu, H.; Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, A.; Hu, Y.; Fan, L.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals multiple chemoresistant properties in leukemic stem and progenitor cells in pediatric AML. Genome Biol 2023, 24, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duployez, N.; Marceau-Renaut, A.; Villenet, C.; Petit, A.; Rousseau, A.; Ng, S.W.K.; Paquet, A.; Gonzales, F.; Barthelemy, A.; Lepretre, F.; et al. The stem cell-associated gene expression signature allows risk stratification in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2018. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, A.H.; Rafiee, R.; Cao, X.; Raimondi, S.; Downing, J.R.; Ribeiro, R.; Fan, Y.; Gruber, T.A.; Baker, S.; Klco, J.; et al. A six-gene leukemic stem cell score identifies high risk pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.J.; Smith, J.L.; Farrar, J.E.; Wang, Y.C.; Umeda, M.; Ries, R.E.; Leonti, A.R.; Crowgey, E.; Furlan, S.N.; Tarlock, K.; et al. Integrated stem cell signature and cytomolecular risk determination in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, L.A.; Ma, W.; Ladel, L.; Pham, J.; Balaian, L.; Steel, S.K.; Mondala, P.K.; Diep, R.H.; Wu, C.N.; Mason, C.N.; et al. Reversal of malignant ADAR1 splice isoform switching with Rebecsinib. Cell Stem Cell 2023, 30, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceraulo, A.; Lapillonne, H.; Cheok, M.H.; Preudhomme, C.; Dombret, H.; Terre, C.; Lambert, J.; Leverger, G.; Bertrand, Y.; Mortreux, F.; et al. Prognostic impact of ABCA3 expression in adult and pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: An ALFA-ELAM02 joint study. Blood Adv 2022, 6, 2773–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, H.R.; Oh, I.H. Age-related differences in the bone marrow stem cell niche generate specialized microenvironments for the distinct regulation of normal hematopoietic and leukemia stem cells. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgel, E.; Genkinger, J.M.; Aggarwal, D.; Sung, L.; Nieder, M.; Ladas, E.J. Association of body mass index and survival in pediatric leukemia: A meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr 2016, 103, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, D.J.A.; Asdahl, P.H.; Abrahamsson, J.; Ha, S.Y.; Jonsson, O.G.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; Koskenvuo, M.; Lausen, B.; De Moerloose, B.; Palle, J.; et al. Associations between pretherapeutic body mass index, outcome, and cytogenetic abnormalities in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Med 2019, 8, 6634–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, I.D. CD33 as a target for selective ablation of acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Lymphoma 2002, 2 Suppl 1, S9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauswirth, A.W.; Florian, S.; Printz, D.; Sotlar, K.; Krauth, M.T.; Fritsch, G.; Schernthaner, G.H.; Wacheck, V.; Selzer, E.; Sperr, W.R.; et al. Expression of the target receptor CD33 in CD34+/CD38-/CD123+ AML stem cells. Eur J Clin Invest 2007, 37, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, I.D. Monoclonal antibodies to the myeloid stem cells: Therapeutic implications of CMA-676, a humanized anti-CD33 antibody calicheamicin conjugate. Leukemia 2000, 14, 474–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeti, R. Monoclonal antibody therapy directed against human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bross, P.F.; Beitz, J.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.H.; Duffy, E.; Kieffer, L.; Roy, S.; Sridhara, R.; Rahman, A.; Williams, G.; et al. Approval summary: Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in relapsed acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2001, 7, 1490–1496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petersdorf, S.H.; Kopecky, K.J.; Slovak, M.; Willman, C.; Nevill, T.; Brandwein, J.; Larson, R.A.; Erba, H.P.; Stiff, P.J.; Stuart, R.K.; et al. A phase 3 study of gemtuzumab ozogamicin during induction and postconsolidation therapy in younger patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 4854–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamis, A.S.; Alonzo, T.A.; Meshinchi, S.; Sung, L.; Gerbing, R.B.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.A.; Kahwash, S.B.; Heerema-McKenney, A.; Winter, L.; et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in children and adolescents with de novo acute myeloid leukemia improves event-free survival by reducing relapse risk: Results from the randomized phase III Children's Oncology Group trial AAML0531. J Clin Oncol 2014, 32, 3021–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, J.A.; Loken, M.; Gerbing, R.B.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.A.; Aplenc, R.; Bernstein, I.D.; Gamis, A.S.; Alonzo, T.A.; Meshinchi, S. CD33 Expression and Its Association With Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin Response: Results From the Randomized Phase III Children's Oncology Group Trial AAML0531. J Clin Oncol 2016, 34, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, A.K.; Hills, R.K.; Milligan, D.; Kjeldsen, L.; Kell, J.; Russell, N.H.; Yin, J.A.; Hunter, A.; Goldstone, A.H.; Wheatley, K. Identification of patients with acute myeloblastic leukemia who benefit from the addition of gemtuzumab ozogamicin: Results of the MRC AML15 trial. J Clin Oncol 2011, 29, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hills, R.K.; Castaigne, S.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Delaunay, J.; Petersdorf, S.; Othus, M.; Estey, E.H.; Dombret, H.; Chevret, S.; Ifrah, N.; et al. Addition of gemtuzumab ozogamicin to induction chemotherapy in adult patients with acute myeloid leukaemia: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol 2014, 15, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaigne, S.; Pautas, C.; Terre, C.; Raffoux, E.; Bordessoule, D.; Bastie, J.N.; Legrand, O.; Thomas, X.; Turlure, P.; Reman, O.; et al. Effect of gemtuzumab ozogamicin on survival of adult patients with de-novo acute myeloid leukaemia (ALFA-0701): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2012, 379, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.; Pautas, C.; Terre, C.; Raffoux, E.; Turlure, P.; Caillot, D.; Legrand, O.; Thomas, X.; Gardin, C.; Gogat-Marchant, K.; et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin for de novo acute myeloid leukemia: Final efficacy and safety updates from the open-label, phase III ALFA-0701 trial. Haematologica 2019, 104, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarlock, K.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.A.; Sung, L.; Pollard, J.A.; Aplenc, R.; Loken, M.R.; Gamis, A.S.; et al. Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin Reduces Relapse Risk in FLT3/ITD Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report from the Children's Oncology Group. Clin Cancer Res 2016, 22, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jen, E.Y.; Ko, C.W.; Lee, J.E.; Del Valle, P.L.; Aydanian, A.; Jewell, C.; Norsworthy, K.J.; Przepiorka, D.; Nie, L.; Liu, J.; et al. FDA Approval: Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin for the Treatment of Adults with Newly Diagnosed CD33-Positive Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2018, 24, 3242–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, J.A.; Alonzo, T.A.; Loken, M.; Gerbing, R.B.; Ho, P.A.; Bernstein, I.D.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.; Franklin, J.; Walter, R.B.; et al. Correlation of CD33 expression level with disease characteristics and response to gemtuzumab ozogamicin containing chemotherapy in childhood AML. Blood 2012, 119, 3705–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung Sutherland, M.S.; Walter, R.B.; Jeffrey, S.C.; Burke, P.J.; Yu, C.; Kostner, H.; Stone, I.; Ryan, M.C.; Sussman, D.; Lyon, R.P.; et al. SGN-CD33A: A novel CD33-targeting antibody-drug conjugate using a pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer is active in models of drug-resistant AML. Blood 2013, 122, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, A.T.; Erba, H.P.; Lancet, J.E.; Stein, E.M.; Ravandi, F.; Faderl, S.; Walter, R.B.; Advani, A.S.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Kovacsovics, T.J.; et al. A phase 1 trial of vadastuximab talirine combined with hypomethylating agents in patients with CD33-positive AML. Blood 2018, 132, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, E.M.; Walter, R.B.; Erba, H.P.; Fathi, A.T.; Advani, A.S.; Lancet, J.E.; Ravandi, F.; Kovacsovics, T.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Bixby, D.; et al. A phase 1 trial of vadastuximab talirine as monotherapy in patients with CD33-positive acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2018, 131, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedin, S.; Guru Murthy, G.S.; Szabo, A.; Hamadani, M.; Michaelis, L.C.; Carlson, K.-S.; Runaas, L.; Gauger, K.; Desai, A.G.; Chen, M.M. Lintuzumab-Ac225 with combination with intensive chemotherapy yields high response rate and MRD negativity in R/R AML with adverse features. Blood 2022, 140, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.R.; Sukumaran, S.; Hristopoulos, M.; Totpal, K.; Stainton, S.; Lu, E.; Wong, A.; Tam, L.; Newman, R.; Vuillemenot, B.R. An anti-CD3/anti–CLL-1 bispecific antibody for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2017, 129, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseini, S.; Cheung, N. Acute myeloid leukemia targets for bispecific antibodies. Blood cancer journal 2017, 7, e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, M.; Henn, A.; Raum, T.; Bajtus, M.; Matthes, K.; Hendrich, L.; Wahl, J.; Hoffmann, P.; Kischel, R.; Kvesic, M. Preclinical characterization of AMG 330, a CD3/CD33-bispecific t-cell–engaging antibody with potential for treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia. Molecular cancer therapeutics 2014, 13, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, K.H.; Gudgeon, C.J.; Laszlo, G.S.; Newhall, K.J.; Sinclair, A.M.; Frankel, S.R.; Kischel, R.; Chen, G.; Walter, R.B. The broad anti-AML activity of the CD33/CD3 BiTE antibody construct, AMG 330, is impacted by disease stage and risk. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupka, C.; Kufer, P.; Kischel, R.; Zugmaier, G.; Bögeholz, J.; Köhnke, T.; Lichtenegger, F.S.; Schneider, S.; Metzeler, K.H.; Fiegl, M. CD33 target validation and sustained depletion of AML blasts in long-term cultures by the bispecific T-cell–engaging antibody AMG 330. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2014, 123, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hussaini, M.; Rettig, M.P.; Ritchey, J.K.; Karpova, D.; Uy, G.L.; Eissenberg, L.G.; Gao, F.; Eades, W.C.; Bonvini, E.; Chichili, G.R. Targeting CD123 in acute myeloid leukemia using a T-cell–directed dual-affinity retargeting platform. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2016, 127, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.-s.; Wang, Y.; Lv, H.-y.; Han, Q.-w.; Fan, H.; Guo, B.; Wang, L.-l.; Han, W.-d. Treatment of CD33-directed chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in one patient with relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Molecular therapy 2015, 23, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Yu, K.R.; Kenderian, S.S.; Ruella, M.; Chen, S.; Shin, T.H.; Aljanahi, A.A.; Schreeder, D.; Klichinsky, M.; Shestova, O.; et al. Genetic Inactivation of CD33 in Hematopoietic Stem Cells to Enable CAR T Cell Immunotherapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell 2018, 173, 1439–1453 e1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehninger, A.; Kramer, M.; Rollig, C.; Thiede, C.; Bornhauser, M.; von Bonin, M.; Wermke, M.; Feldmann, A.; Bachmann, M.; Ehninger, G.; et al. Distribution and levels of cell surface expression of CD33 and CD123 in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J 2014, 4, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.; Steidl, U. Targeting Immunophenotypic Markers on Leukemic Stem Cells: How Lessons from Current Approaches and Advances in the Leukemia Stem Cell (LSC) Model Can Inform Better Strategies for Treating Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pemmaraju, N.; Konopleva, M. Approval of tagraxofusp-erzs for blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Blood Adv 2020, 4, 4020–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, R.; Goswami, S.; Gopalakrishnan, B.; Ramaswamy, R.; Wasmuth, R.; Tran, M.; Mo, X.; Gordon, A.; Bucci, D.; Lucas, D.M.; et al. The interleukin-3 receptor CD123 targeted SL-401 mediates potent cytotoxic activity against CD34(+)CD123(+) cells from acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome patients and healthy donors. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkharabsheh, O.; Frankel, A.E. Clinical Activity and Tolerability of SL-401 (Tagraxofusp): Recombinant Diphtheria Toxin and Interleukin-3 in Hematologic Malignancies. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovtun, Y.; Jones, G.E.; Adams, S.; Harvey, L.; Audette, C.A.; Wilhelm, A.; Bai, C.; Rui, L.; Laleau, R.; Liu, F.; et al. A CD123-targeting antibody-drug conjugate, IMGN632, designed to eradicate AML while sparing normal bone marrow cells. Blood Adv 2018, 2, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daver, N.G.; Montesinos, P.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Wang, E.S.; Papadantonakis, N.; Deconinck, E.; Erba, H.P.; Pemmaraju, N.; Lane, A.A.; Rizzieri, D.A. Clinical profile of IMGN632, a novel CD123-targeting antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN). Blood 2019, 134, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daver, N.G.; Montesinos, P.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Wang, E.S.; Todisco, E.; Tarella, C.; Martinelli, G.; Erba, H.P.; Deconinck, E.; Sweet, K.L. A phase I/II study of IMGN632, a novel CD123-targeting antibody-drug conjugate, in patients with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm, and other CD123-positive hematologic malignancies. 2020.
- Uy, G.L.; Aldoss, I.; Foster, M.C.; Sayre, P.H.; Wieduwilt, M.J.; Advani, A.S.; Godwin, J.E.; Arellano, M.L.; Sweet, K.L.; Emadi, A.; et al. Flotetuzumab as salvage immunotherapy for refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2021, 137, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, G.L.; Godwin, J.; Rettig, M.P.; Vey, N.; Foster, M.; Arellano, M.L.; Rizzieri, D.A.; Topp, M.S.; Huls, G.; Lowenberg, B. Preliminary results of a phase 1 study of flotetuzumab, a CD123 x CD3 bispecific Dart® protein, in patients with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2017, 130, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, L.; Virone-Oddos, A.; Beninga, J.; Rossi, B.; Nicolazzi, C.; Amara, C.; Blanchard-Alvarez, A.; Gourdin, N.; Courta, J.; Basset, A. Control of acute myeloid leukemia by a trifunctional NKp46-CD16a-NK cell engager targeting CD123. Nature Biotechnology 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.S.; Jongen-Lavrencic, M.; Garciaz, S.; Huls, G.A.; Maiti, A.; Boissel, N.; De Botton, S.; Fleming, S.; Zwaan, C.M.; C. de Leeuw, D. A first-in-human study of CD123 NK cell engager SAR443579 in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia, B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, or high-risk myelodysplasia. 2023.
- Budde, L.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, Y.; Blanchard, S.; Wagner, J.; Stein, A.S.; Weng, L.; Del Real, M.; Hernandez, R.; Marcucci, E. Remissions of acute myeloid leukemia and blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm following treatment with CD123-specific CAR T cells: A first-in-human clinical trial. Blood 2017, 130, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masarova, L.; Kantarjian, H.; Ravandi, F.; Sharma, P.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Daver, N. Update on Immunotherapy in AML and MDS: Monoclonal Antibodies and Checkpoint Inhibitors Paving the Road for Clinical Practice. Adv Exp Med Biol 2018, 995, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masarova, L.; Kantarjian, H.; Garcia-Mannero, G.; Ravandi, F.; Sharma, P.; Daver, N. Harnessing the Immune System Against Leukemia: Monoclonal Antibodies and Checkpoint Strategies for AML. Adv Exp Med Biol 2017, 995, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestipino, A.; Emhardt, A.J.; Aumann, K.; O'Sullivan, D.; Gorantla, S.P.; Duquesne, S.; Melchinger, W.; Braun, L.; Vuckovic, S.; Boerries, M.; et al. Oncogenic JAK2(V617F) causes PD-L1 expression, mediating immune escape in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Sci Transl Med 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, S.J.; Vervoort, S.J.; Deswal, S.; Ott, C.J.; Li, J.; Cluse, L.A.; Beavis, P.A.; Darcy, P.K.; Martin, B.P.; Spencer, A.; et al. BET-Bromodomain Inhibitors Engage the Host Immune System and Regulate Expression of the Immune Checkpoint Ligand PD-L1. Cell Rep 2017, 18, 2162–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthon, C.; Driss, V.; Liu, J.; Kuranda, K.; Leleu, X.; Jouy, N.; Hetuin, D.; Quesnel, B. In acute myeloid leukemia, B7-H1 (PD-L1) protection of blasts from cytotoxic T cells is induced by TLR ligands and interferon-gamma and can be reversed using MEK inhibitors. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2010, 59, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronig, H.; Kremmler, L.; Haller, B.; Englert, C.; Peschel, C.; Andreesen, R.; Blank, C.U. Interferon-induced programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1/B7-H1) expression increases on human acute myeloid leukemia blast cells during treatment. Eur J Haematol 2014, 92, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daver, N.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Basu, S.; Boddu, P.C.; Alfayez, M.; Cortes, J.E.; Konopleva, M.; Ravandi-Kashani, F.; Jabbour, E.; Kadia, T. Efficacy, safety, and biomarkers of response to azacitidine and nivolumab in relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia: A nonrandomized, open-label, phase II study. Cancer discovery 2019, 9, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reville, P.K.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Ravandi, F.; Jabbour, E.; DiNardo, C.D.; Daver, N.; Pemmaraju, N.; Ohanian, M.; Alvarado, Y.; Xiao, L.; et al. Nivolumab maintenance in high-risk acute myeloid leukemia patients: A single-arm, open-label, phase II study. Blood Cancer J 2021, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.; Basu, S.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Hourigan, C.S.; Oetjen, K.A.; Cortes, J.E.; Ravandi, F.; Jabbour, E.J.; Al-Hamal, Z.; Konopleva, M.; et al. The distribution of T-cell subsets and the expression of immune checkpoint receptors and ligands in patients with newly diagnosed and relapsed acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2019, 125, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeti, R.; Chao, M.P.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Pang, W.W.; Jaiswal, S.; Gibbs, K.D., Jr.; van Rooijen, N.; Weissman, I.L. CD47 is an adverse prognostic factor and therapeutic antibody target on human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Cell 2009, 138, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, M.P.; Takimoto, C.H.; Feng, D.D.; McKenna, K.; Gip, P.; Liu, J.; Volkmer, J.P.; Weissman, I.L.; Majeti, R. Therapeutic Targeting of the Macrophage Immune Checkpoint CD47 in Myeloid Malignancies. Front Oncol 2019, 9, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.; Gip, P.; McKenna, K.M.; Zhao, F.; Mata, O.; Choi, T.S.; Duan, J.; Sompalli, K.; Majeti, R.; Weissman, I.L. Combination treatment with 5F9 and azacitidine enhances phagocytic elimination of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2018, 132, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallman, D.A.; Asch, A.S.; Al Malki, M.M.; Lee, D.J.; Donnellan, W.B.; Marcucci, G.; Kambhampati, S.; Daver, N.G.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Komrokji, R.S. The first-in-class anti-CD47 antibody magrolimab (5F9) in combination with azacitidine is effective in MDS and AML patients: Ongoing phase 1b results. Blood 2019, 134, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masetti, R.; Pigazzi, M.; Togni, M.; Astolfi, A.; Indio, V.; Manara, E.; Casadio, R.; Pession, A.; Basso, G.; Locatelli, F. CBFA2T3-GLIS2 fusion transcript is a novel common feature in pediatric, cytogenetically normal AML, not restricted to FAB M7 subtype. Blood 2013, 121, 3469–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Le, Q.; Castro, S.; Pardo, L.; McKay, C.N.; Perkins, L.; Smith, J.; Kirkey, D.; Abrahams, C.; Bedard, K.; et al. Targeting FOLR1 in high-risk CBF2AT3-GLIS2 pediatric AML with STRO-002 FOLR1-antibody-drug conjugate. Blood Adv 2022, 6, 5933–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.; Hadland, B.; Smith, J.L.; Leonti, A.; Huang, B.J.; Ries, R.; Hylkema, T.A.; Castro, S.; Tang, T.T.; McKay, C.N.; et al. CBFA2T3-GLIS2 model of pediatric acute megakaryoblastic leukemia identifies FOLR1 as a CAR T cell target. J Clin Invest 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshinchi, S.; Miller, L.; Massaro, S.; Williams, R.; Krieger, E.; Pauly, M.; Nelson, C.; Bhojwani, D.; Johnson, R.; Horton, T.M. Anti-Leukemic Activity of STRO-002 a Novel Folate Receptor-α (FR-α)-Targeting ADC in Relapsed/Refractory CBF2AT3-GLIS2 AML. Blood 2022, 140, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.; Chen, F.; Tang, T.; McKay, C.N.; Wu, F.; Turker, M.; Gardinier, T.; Patel, V.; Venkatesan, A.; Khor, T. Therapeutic targeting of CBFA2T3-GLIS2 infant AML with ELU001-folate receptor alpha-directed C’Dot-drug-conjugate. Cancer Research 2022, 82, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetani, H.; Garcia-Cadenas, I.; Nerreter, T.; Thomas, S.; Rydzek, J.; Meijide, J.B.; Bonig, H.; Herr, W.; Sierra, J.; Einsele, H.; et al. CAR T-cells targeting FLT3 have potent activity against FLT3(-)ITD(+) AML and act synergistically with the FLT3-inhibitor crenolanib. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, R.M.; Mandrekar, S.J.; Sanford, B.L.; Laumann, K.; Geyer, S.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Thiede, C.; Prior, T.W.; Dohner, K.; Marcucci, G.; et al. Midostaurin plus Chemotherapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia with a FLT3 Mutation. N Engl J Med 2017, 377, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlenk, R.F.; Weber, D.; Fiedler, W.; Salih, H.R.; Wulf, G.; Salwender, H.; Schroeder, T.; Kindler, T.; Lubbert, M.; Wolf, D.; et al. Midostaurin added to chemotherapy and continued single-agent maintenance therapy in acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3-ITD. Blood 2019, 133, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burchert, A.; Bug, G.; Fritz, L.V.; Finke, J.; Stelljes, M.; Rollig, C.; Wollmer, E.; Wasch, R.; Bornhauser, M.; Berg, T.; et al. Sorafenib Maintenance After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Acute Myeloid Leukemia With FLT3-Internal Tandem Duplication Mutation (SORMAIN). J Clin Oncol 2020, 38, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serve, H.; Krug, U.; Wagner, R.; Sauerland, M.C.; Heinecke, A.; Brunnberg, U.; Schaich, M.; Ottmann, O.; Duyster, J.; Wandt, H.; et al. Sorafenib in combination with intensive chemotherapy in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia: Results from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Oncol 2013, 31, 3110–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollig, C.; Serve, H.; Huttmann, A.; Noppeney, R.; Muller-Tidow, C.; Krug, U.; Baldus, C.D.; Brandts, C.H.; Kunzmann, V.; Einsele, H.; et al. Addition of sorafenib versus placebo to standard therapy in patients aged 60 years or younger with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukaemia (SORAML): A multicentre, phase 2, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2015, 16, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perl, A.E.; Martinelli, G.; Cortes, J.E.; Neubauer, A.; Berman, E.; Paolini, S.; Montesinos, P.; Baer, M.R.; Larson, R.A.; Ustun, C.; et al. Gilteritinib or Chemotherapy for Relapsed or Refractory FLT3-Mutated AML. N Engl J Med 2019, 381, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.; Perl, A.E.; Dohner, H.; Kantarjian, H.; Martinelli, G.; Kovacsovics, T.; Rousselot, P.; Steffen, B.; Dombret, H.; Estey, E.; et al. Quizartinib, an FLT3 inhibitor, as monotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia: An open-label, multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 2018, 19, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, T.M.; Cassar, J.; Eckroth, E.; Malvar, J.; Sposto, R.; Gaynon, P.; Chang, B.H.; Gore, L.; August, K.; Pollard, J.A.; et al. A Phase I Study of Quizartinib Combined with Chemotherapy in Relapsed Childhood Leukemia: A Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia & Lymphoma (TACL) Study. Clin Cancer Res 2016, 22, 4014–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarlock, K.; Chang, B.; Cooper, T.; Gross, T.; Gupta, S.; Neudorf, S.; Adlard, K.; Ho, P.A.; McGoldrick, S.; Watt, T.; et al. Sorafenib treatment following hematopoietic stem cell transplant in pediatric FLT3/ITD acute myeloid leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, J.A.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.; Brown, P.; Fox, E.; Choi, J.; Fisher, B.; Hirsch, B.; Kahwash, S.; Getz, K.; et al. Sorafenib in Combination With Standard Chemotherapy for Children With High Allelic Ratio FLT3/ITD+ Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report From the Children's Oncology Group Protocol AAML1031. J Clin Oncol 2022, 40, 2023–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levis, M.; Murphy, K.M.; Pham, R.; Kim, K.T.; Stine, A.; Li, L.; McNiece, I.; Smith, B.D.; Small, D. Internal tandem duplications of the FLT3 gene are present in leukemia stem cells. Blood 2005, 106, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, J.A.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Woods, W.G.; Lange, B.J.; Sweetser, D.A.; Radich, J.P.; Bernstein, I.D.; Meshinchi, S. FLT3 internal tandem duplication in CD34+/CD33- precursors predicts poor outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2006, 108, 2764–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mawali, A.; Gillis, D.; Lewis, I. Immunoprofiling of leukemic stem cells CD34+/CD38-/CD123+ delineate FLT3/ITD-positive clones. J Hematol Oncol 2016, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corces-Zimmerman, M.R.; Hong, W.J.; Weissman, I.L.; Medeiros, B.C.; Majeti, R. Preleukemic mutations in human acute myeloid leukemia affect epigenetic regulators and persist in remission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 2548–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmalbrock, L.K.; Dolnik, A.; Cocciardi, S.; Strang, E.; Theis, F.; Jahn, N.; Panina, E.; Blatte, T.J.; Herzig, J.; Skambraks, S.; et al. Clonal evolution of acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3-ITD mutation under treatment with midostaurin. Blood 2021, 137, 3093–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.S.; Greenblatt, S.M.; Shirley, C.M.; Duffield, A.S.; Bruner, J.K.; Li, L.; Nguyen, B.; Jung, E.; Aplan, P.D.; Ghiaur, G.; et al. All-trans retinoic acid synergizes with FLT3 inhibition to eliminate FLT3/ITD+ leukemia stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2016, 127, 2867–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.C.; Levis, M.J.; Frankfurt, O.; Pagel, J.M.; Roboz, G.J.; Stone, R.M.; Wang, E.S.; Severson, P.L.; West, B.L.; Le, M.H.; et al. A phase 1/2 study of the oral FLT3 inhibitor pexidartinib in relapsed/refractory FLT3-ITD-mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv 2020, 4, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minson, K.A.; Smith, C.C.; DeRyckere, D.; Libbrecht, C.; Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Huey, M.G.; Lasater, E.A.; Kirkpatrick, G.D.; Stashko, M.A.; Zhang, W.; et al. The MERTK/FLT3 inhibitor MRX-2843 overcomes resistance-conferring FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e85630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winters, A.C.; Bernt, K.M. MLL-Rearranged Leukemias-An Update on Science and Clinical Approaches. Front Pediatr 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivtsov, A.V.; Twomey, D.; Feng, Z.; Stubbs, M.C.; Wang, Y.; Faber, J.; Levine, J.E.; Wang, J.; Hahn, W.C.; Gilliland, D.G.; et al. Transformation from committed progenitor to leukaemia stem cell initiated by MLL-AF9. Nature 2006, 442, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, A.; Somervaille, T.C.; Smith, K.S.; Rozenblatt-Rosen, O.; Meyerson, M.; Cleary, M.L. The menin tumor suppressor protein is an essential oncogenic cofactor for MLL-associated leukemogenesis. Cell 2005, 123, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, A.; Cleary, M.L. Menin critically links MLL proteins with LEDGF on cancer-associated target genes. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivtsov, A.V.; Evans, K.; Gadrey, J.Y.; Eschle, B.K.; Hatton, C.; Uckelmann, H.J.; Ross, K.N.; Perner, F.; Olsen, S.N.; Pritchard, T.; et al. A Menin-MLL Inhibitor Induces Specific Chromatin Changes and Eradicates Disease in Models of MLL-Rearranged Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M.W.; Song, E.; Feng, Z.; Sinha, A.; Chen, C.W.; Deshpande, A.J.; Cusan, M.; Farnoud, N.; Mupo, A.; Grove, C.; et al. Targeting Chromatin Regulators Inhibits Leukemogenic Gene Expression in NPM1 Mutant Leukemia. Cancer Discov 2016, 6, 1166–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uckelmann, H.J.; Kim, S.M.; Wong, E.M.; Hatton, C.; Giovinazzo, H.; Gadrey, J.Y.; Krivtsov, A.V.; Rucker, F.G.; Dohner, K.; McGeehan, G.M.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of preleukemia cells in a mouse model of NPM1 mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Science 2020, 367, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasouli, M.; Blair, H.; Troester, S.; Szoltysek, K.; Cameron, R.; Ashtiani, M.; Krippner-Heidenreich, A.; Grebien, F.; McGeehan, G.; Zwaan, C.M.; et al. The MLL-Menin Interaction is a Therapeutic Vulnerability in NUP98-rearranged AML. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeda, M.; Ma, J.; Huang, B.J.; Hagiwara, K.; Westover, T.; Abdelhamed, S.; Barajas, J.M.; Thomas, M.E.; Walsh, M.P.; Song, G.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies UBTF Tandem Duplications as a Recurrent Lesion in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood Cancer Discov 2022, 3, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barajas, J.M.; Rasouli, M.; Umeda, M.; Hiltenbrand, R.L.; Abdelhamed, S.; Mohnani, R.; Arthur, B.; Westover, T.; Thomas, M.E., 3rd; Ashtiani, M.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemias with UBTF tandem duplications are sensitive to Menin inhibitors. Blood 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, G.C.; Aldoss, I.; DiPersio, J.; Cuglievan, B.; Stone, R.; Arellano, M.; Thirman, M.J.; Patel, M.R.; Dickens, D.S.; Shenoy, S.; et al. The menin inhibitor revumenib in KMT2A-rearranged or NPM1-mutant leukaemia. Nature 2023, 615, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiskus, W.; Daver, N.; Boettcher, S.; Mill, C.P.; Sasaki, K.; Birdwell, C.E.; Davis, J.A.; Das, K.; Takahashi, K.; Kadia, T.M.; et al. Activity of menin inhibitor ziftomenib (KO-539) as monotherapy or in combinations against AML cells with MLL1 rearrangement or mutant NPM1. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2729–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenstein, C.D.; Niswander, L.M.; Kessler, L.; Tomkinson, B.; Burrows, F.; Tasian, S.K. Preclinical In Vivo Activity of the Menin Inhibitor Ziftomenib (KO-539) in Pediatric KMT2A-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2022, 140, 3491–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erba, H.P.; Fathi, A.T.; Issa, G.C.; Altman, J.K.; Montesinos, P.; Patnaik, M.M.; Foran, J.M.; De Botton, S.; Baer, M.R.; Schiller, G.J. Update on a phase 1/2 first-in-human study of the menin-KMT2A (MLL) inhibitor ziftomenib (KO-539) in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2022, 140, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souers, A.J.; Leverson, J.D.; Boghaert, E.R.; Ackler, S.L.; Catron, N.D.; Chen, J.; Dayton, B.D.; Ding, H.; Enschede, S.H.; Fairbrother, W.J.; et al. ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat Med 2013, 19, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.W.; Davids, M.S.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Puvvada, S.D.; Gerecitano, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Brown, J.R.; Gressick, L.; et al. Targeting BCL2 with Venetoclax in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N Engl J Med 2016, 374, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, A.H.; Strickland, S.A., Jr.; Hou, J.Z.; Fiedler, W.; Lin, T.L.; Walter, R.B.; Enjeti, A.; Tiong, I.S.; Savona, M.; Lee, S.; et al. Venetoclax Combined With Low-Dose Cytarabine for Previously Untreated Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Results From a Phase Ib/II Study. J Clin Oncol 2019, 37, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Pratz, K.W.; Letai, A.; Jonas, B.A.; Wei, A.H.; Thirman, M.; Arellano, M.; Frattini, M.G.; Kantarjian, H.; Popovic, R.; et al. Safety and preliminary efficacy of venetoclax with decitabine or azacitidine in elderly patients with previously untreated acute myeloid leukaemia: A non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol 2018, 19, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Jonas, B.A.; Pullarkat, V.; Thirman, M.J.; Garcia, J.S.; Wei, A.H.; Konopleva, M.; Dohner, H.; Letai, A.; Fenaux, P.; et al. Azacitidine and Venetoclax in Previously Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Lachowiez, C.A.; Takahashi, K.; Loghavi, S.; Xiao, L.; Kadia, T.; Daver, N.; Adeoti, M.; Short, N.J.; Sasaki, K.; et al. Venetoclax Combined With FLAG-IDA Induction and Consolidation in Newly Diagnosed and Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2021, 39, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Hogdal, L.J.; Benito, J.M.; Bucci, D.; Han, L.; Borthakur, G.; Cortes, J.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Debose, L.; Mu, H.; et al. Selective BCL-2 inhibition by ABT-199 causes on-target cell death in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Discov 2014, 4, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, S.; Shelton, I.T.; Gillen, A.E.; Stevens, B.M.; Gasparetto, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Brunetti, T.M.; Engel, K.; et al. A Novel Type of Monocytic Leukemia Stem Cell Revealed by the Clinical Use of Venetoclax-Based Therapy. Cancer Discov 2023, 13, 2032–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winters, A.C.; Maloney, K.W.; Treece, A.L.; Gore, L.; Franklin, A.K. Single-center pediatric experience with venetoclax and azacitidine as treatment for myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, T.; Li, Y.; Ashcraft, E.; Karol, S.E.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Epperly, R.; Madden, R.; Mamcarz, E.; Obeng, E.; Qudeimat, A. Venetoclax-based therapy as a bridge to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in children with relapsed/refractory AML. Bone Marrow Transplantation 2023, 58, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinoff, A.E.; Aaronson, K.; Agrawal, A.K.; Braun, B.S.; Golden, C.; Huang, B.J.; Michlitsch, J.; Southworth, E.; Thrall, A.; Vo, K.T.; et al. Venetoclax in combination with chemotherapy as treatment for pediatric advanced hematologic malignancies. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabal, A.; Gibson, A.; He, J.; McCall, D.; Roth, M.; Nunez, C.; Garcia, M.; Buzbee, M.; Toepfer, L.; Bidikian, A.; et al. Venetoclax for Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Pediatric Patients: A Texas Medical Center Experience. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masetti, R.; Baccelli, F.; Leardini, D.; Gottardi, F.; Vendemini, F.; Di Gangi, A.; Becilli, M.; Lodi, M.; Tumino, M.; Vinci, L.; et al. Venetoclax-based therapies in pediatric advanced MDS and relapsed/refractory AML: A multicenter retrospective analysis. Blood Adv 2023, 7, 4366–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimentova, M.; Shelikhova, L.; Ilushina, M.; Kozlovskaya, S.; Blagov, S.; Popov, A.; Kashpor, S.; Fadeeva, M.; Olshanskaya, J.; Glushkova, S.; et al. Targeted Therapy With Venetoclax and Daratumumab as Part of HSCT Preparative Regimen in Children With Chemorefractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Transplant Cell Ther 2023, 29, 127 e121–127 e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karol, S.E.; Alexander, T.B.; Budhraja, A.; Pounds, S.B.; Canavera, K.; Wang, L.; Wolf, J.; Klco, J.M.; Mead, P.E.; Das Gupta, S.; et al. Venetoclax in combination with cytarabine with or without idarubicin in children with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia: A phase 1, dose-escalation study. Lancet Oncol 2020, 21, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuani, L.; Jager, A.; Sahal, A.; Koladiya, A.; Sarno, J.; Domizi, P.; Liu, Y.; De Mas, V.; Recher, C.; Vergez, F. Single-Cell Proteomic Analysis Defines Metabolic Heterogeneity in Response to Venetoclax in AML. Blood 2022, 140, 1028–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hege, K.; Kalpage, H.; Hüttemann, M.; Pitman, H.; Taub, J.W.; Polin, L.; Li, J.; Ge, Y. Enhancing the antileukemic activity of venetoclax against leukemia stem cells by targeting oxidative phosphorylation through dual inhibition of PI3K and HDAC. Cancer Research 2021, 81, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlen, M.; Klusmann, J.H.; Hoell, J.I. Molecular Approaches to Treating Pediatric Leukemias. Front Pediatr 2019, 7, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; So, C.W. PARP-inhibitor-induced synthetic lethality for acute myeloid leukemia treatment. Exp Hematol 2016, 44, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, L.; Triche, T.J., Jr.; Farrar, J.E.; Wai, D.; Legendre, C.; Gooden, G.C.; Liang, W.S.; Carpten, J.; Lee, D.; Alvaro, F.; et al. A multicenter, randomized study of decitabine as epigenetic priming with induction chemotherapy in children with AML. Clin Epigenetics 2017, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommert, L.; Schafer, E.S.; Malvar, J.; Gossai, N.; Florendo, E.; Pulakanti, K.; Heimbruch, K.; Stelloh, C.; Chi, Y.Y.; Sposto, R.; et al. Decitabine and vorinostat with FLAG chemotherapy in pediatric relapsed/refractory AML: Report from the therapeutic advances in childhood leukemia and lymphoma (TACL) consortium. Am J Hematol 2022, 97, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, E.S.; Chao, K.; Stevens, A.M.; Jo, E.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Gossai, N.P.; Doan, A.; Colace, S.I.; Guinipero, T.; Otterson, D.; et al. Real-world experience in treating pediatric relapsed/refractory or therapy-related myeloid malignancies with decitabine, vorinostat, and FLAG therapy based on a phase 1 study run by the TACL consortium. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, B.; Zhao, Q.; Mims, A.S.; Vasu, S.; Behbehani, G.K.; Larkin, K.; Blachly, J.S.; Badawi, M.A.; Hill, K.L.; Dzwigalski, K.R.; et al. Phase 1 study of selinexor in combination with salvage chemotherapy in Adults with relapsed or refractory Acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pianigiani, G.; Gagliardi, A.; Mezzasoma, F.; Rocchio, F.; Tini, V.; Bigerna, B.; Sportoletti, P.; Caruso, S.; Marra, A.; Peruzzi, S.; et al. Prolonged XPO1 inhibition is essential for optimal antileukemic activity in NPM1-mutated AML. Blood Adv 2022, 6, 5938–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, P.; Kashyap, T.; Yu, X.; Meng, X.; Lai, T.H.; McNeil, B.; Bhatnagar, B.; Shacham, S.; Kauffman, M.; Dorrance, A.M.; et al. XPO1 Inhibition using Selinexor Synergizes with Chemotherapy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Targeting DNA Repair and Restoring Topoisomerase IIalpha to the Nucleus. Clin Cancer Res 2016, 22, 6142–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Gai, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Edwards, H.; Ge, Y.; Wang, G. Venetoclax enhances DNA damage induced by XPO1 inhibitors: A novel mechanism underlying the synergistic antileukaemic effect in acute myeloid leukaemia. J Cell Mol Med 2022, 26, 2646–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.A.; Friedlander, S.Y.; Arrate, M.P.; Chang, H.; Gorska, A.E.; Fuller, L.D.; Ramsey, H.E.; Kashyap, T.; Argueta, C.; Debler, S.; et al. Venetoclax response is enhanced by selective inhibitor of nuclear export compounds in hematologic malignancies. Blood Adv 2020, 4, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etchin, J.; Montero, J.; Berezovskaya, A.; Le, B.T.; Kentsis, A.; Christie, A.L.; Conway, A.S.; Chen, W.C.; Reed, C.; Mansour, M.R.; et al. Activity of a selective inhibitor of nuclear export, selinexor (KPT-330), against AML-initiating cells engrafted into immunosuppressed NSG mice. Leukemia 2016, 30, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchin, J.; Berezovskaya, A.; Conway, A.S.; Galinsky, I.A.; Stone, R.M.; Baloglu, E.; Senapedis, W.; Landesman, Y.; Kauffman, M.; Shacham, S.; et al. KPT-8602, a second-generation inhibitor of XPO1-mediated nuclear export, is well tolerated and highly active against AML blasts and leukemia-initiating cells. Leukemia 2017, 31, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon, R.; Savona, M.; Baz, R.; Andreeff, M.; Gabrail, N.; Gutierrez, M.; Savoie, L.; Mau-Sorensen, P.M.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Yee, K.; et al. A phase 1 clinical trial of single-agent selinexor in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 3165–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klement, P.; Fiedler, W.; Gabdoulline, R.; Dallmann, L.K.; Wienecke, C.P.; Schiller, J.; Kandziora, C.; Teich, K.; Heida, B.; Buttner, K.; et al. Molecular response patterns in relapsed/refractory AML patients treated with selinexor and chemotherapy. Ann Hematol 2023, 102, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Sanchez, M.P.; Megias-Vericat, J.E.; Rodriguez-Veiga, R.; Vives, S.; Bergua, J.M.; Torrent, A.; Suarez-Varela, S.; Boluda, B.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; Cano-Ferri, I.; et al. A phase I trial of selinexor plus FLAG-Ida for the treatment of refractory/relapsed adult acute myeloid leukemia patients. Ann Hematol 2021, 100, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, J.; Lowenberg, B.; Manz, M.; Biemond, B.J.; Westerweel, P.E.; Klein, S.K.; Fehr, M.; Sinnige, H.A.M.; Efthymiou, A.; Legdeur, M.; et al. Addition of the nuclear export inhibitor selinexor to standard intensive treatment for elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia and high risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, T.B.; Lacayo, N.J.; Choi, J.K.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Pui, C.H.; Rubnitz, J.E. Phase I Study of Selinexor, a Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export, in Combination With Fludarabine and Cytarabine, in Pediatric Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2016, 34, 4094–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, Z.; Ding, K.; Li, J.; Du, X.; Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Pan, J. Antineoplastic mechanisms of niclosamide in acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells: Inactivation of the NF-kappaB pathway and generation of reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 2516–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, H.D.; Cox, N.; Dahl, G.V.; Lacayo, N.J.; Davis, K.L.; Capolicchio, S.; Smith, M.; Sakamoto, K.M. Niclosamide suppresses acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation through inhibition of CREB-dependent signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 4301–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcicki, A.; Chae, H.-D.; Han, K.; Youn, M.; Wilkes, M.C.; Lacayo, N.J.; Bassik, M.; Sakamoto, K.M. Genetic Modulators of Niclosamide Sensitivity and Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2020, 136, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, V.; Erbani, J.; Fiveash, C.; Davies, J.M.; Tay, J.; Tallack, M.R.; Lowe, J.; Magnani, J.L.; Pattabiraman, D.R.; Perkins, A.C.; et al. Endothelial E-selectin inhibition improves acute myeloid leukaemia therapy by disrupting vascular niche-mediated chemoresistance. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeAngelo, D.J.; Jonas, B.A.; Liesveld, J.L.; Bixby, D.L.; Advani, A.S.; Marlton, P.; Magnani, J.L.; Thackray, H.M.; Feldman, E.J.; O'Dwyer, M.E.; et al. Phase 1/2 study of uproleselan added to chemotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2022, 139, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amatangelo, M.D.; Quek, L.; Shih, A.; Stein, E.M.; Roshal, M.; David, M.D.; Marteyn, B.; Farnoud, N.R.; de Botton, S.; Bernard, O.A.; et al. Enasidenib induces acute myeloid leukemia cell differentiation to promote clinical response. Blood 2017, 130, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, A.K.; Miller, D.W.; Lynch, J.A.; Lemoff, A.S.; Cai, Z.; Pounds, S.B.; Radtke, I.; Yan, B.; Schuetz, J.D.; Rubnitz, J.E.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in pediatric acute leukemia. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, M.E.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Lu, C.; Ward, P.S.; Patel, J.; Shih, A.; Li, Y.; Bhagwat, N.; Vasanthakumar, A.; Fernandez, H.F.; et al. Leukemic IDH1 and IDH2 mutations result in a hypermethylation phenotype, disrupt TET2 function, and impair hematopoietic differentiation. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Botton, S.; Montesinos, P.; Schuh, A.C.; Papayannidis, C.; Vyas, P.; Wei, A.H.; Ommen, H.; Semochkin, S.; Kim, H.J.; Larson, R.A.; et al. Enasidenib vs conventional care in older patients with late-stage mutant-IDH2 relapsed/refractory AML: A randomized phase 3 trial. Blood 2023, 141, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, E.M.; DiNardo, C.D.; Pollyea, D.A.; Fathi, A.T.; Roboz, G.J.; Altman, J.K.; Stone, R.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Levine, R.L.; Flinn, I.W.; et al. Enasidenib in mutant IDH2 relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2017, 130, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Botton, S.; Brandwein, J.M.; Wei, A.H.; Pigneux, A.; Quesnel, B.; Thomas, X.; Legrand, O.; Recher, C.; Chantepie, S.; Hunault-Berger, M.; et al. Improved survival with enasidenib versus standard of care in relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia associated with IDH2 mutations using historical data and propensity score matching analysis. Cancer Med 2021, 10, 6336–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Schuh, A.C.; Stein, E.M.; Montesinos, P.; Wei, A.H.; de Botton, S.; Zeidan, A.M.; Fathi, A.T.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Bennett, J.M.; et al. Enasidenib plus azacitidine versus azacitidine alone in patients with newly diagnosed, mutant-IDH2 acute myeloid leukaemia (AG221-AML-005): A single-arm, phase 1b and randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 2021, 22, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.M.; DiNardo, C.D.; Fathi, A.T.; Mims, A.S.; Pratz, K.W.; Savona, M.R.; Stein, A.S.; Stone, R.M.; Winer, E.S.; Seet, C.S.; et al. Ivosidenib or enasidenib combined with intensive chemotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed AML: A phase 1 study. Blood 2021, 137, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swords, R.T.; Kelly, K.R.; Smith, P.G.; Garnsey, J.J.; Mahalingam, D.; Medina, E.; Oberheu, K.; Padmanabhan, S.; O'Dwyer, M.; Nawrocki, S.T.; et al. Inhibition of NEDD8-activating enzyme: A novel approach for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2010, 115, 3796–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrocki, S.T.; Kelly, K.R.; Smith, P.G.; Keaton, M.; Carraway, H.; Sekeres, M.A.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Carew, J.S. The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 disrupts nucleotide metabolism and augments the efficacy of cytarabine. Clinical cancer research 2015, 21, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swords, R.T.; Erba, H.P.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Bixby, D.L.; Altman, J.K.; Maris, M.; Hua, Z.; Blakemore, S.J.; Faessel, H.; Sedarati, F.; et al. Pevonedistat (MLN4924), a First-in-Class NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndromes: A phase 1 study. Br J Haematol 2015, 169, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekeres, M.A.; Watts, J.; Radinoff, A.; Sangerman, M.A.; Cerrano, M.; Lopez, P.F.; Zeidner, J.F.; Campelo, M.D.; Graux, C.; Liesveld, J.; et al. Randomized phase 2 trial of pevonedistat plus azacitidine versus azacitidine for higher-risk MDS/CMML or low-blast AML. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ades, L.; Girshova, L.; Doronin, V.A.; Diez-Campelo, M.; Valcarcel, D.; Kambhampati, S.; Viniou, N.A.; Woszczyk, D.; De Paz Arias, R.; Symeonidis, A.; et al. Pevonedistat plus azacitidine vs azacitidine alone in higher-risk MDS/chronic myelomonocytic leukemia or low-blast-percentage AML. Blood Adv 2022, 6, 5132–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, N.J.; Muftuoglu, M.; Ong, F.; Nasr, L.; Macaron, W.; Montalban-Bravo, G.; Alvarado, Y.; Basyal, M.; Daver, N.; Dinardo, C.D.; et al. A phase 1/2 study of azacitidine, venetoclax and pevonedistat in newly diagnosed secondary AML and in MDS or CMML after failure of hypomethylating agents. J Hematol Oncol 2023, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarlock, K.; Liu, X.; Minard, C.G.; Isikwei, E.A.; Reid, J.M.; Horton, T.M.; Fox, E.; Weigel, B.J.; Cooper, T. Feasibility of pevonedistat combined with azacitidine, fludarabine, cytarabine in pediatric relapsed/refractory AML: Results from COG ADVL1712. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, M.R.; Crimmins, M.A.; Yetz-Aldape, J.; Kriz, R.; Kelleher, K.; Herrmann, S. The cloning of CD70 and its identification as the ligand for CD27. J Immunol 1994, 152, 1756–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riether, C.; Schurch, C.M.; Buhrer, E.D.; Hinterbrandner, M.; Huguenin, A.L.; Hoepner, S.; Zlobec, I.; Pabst, T.; Radpour, R.; Ochsenbein, A.F. CD70/CD27 signaling promotes blast stemness and is a viable therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. J Exp Med 2017, 214, 359–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flieswasser, T.; Van den Eynde, A.; Van Audenaerde, J.; De Waele, J.; Lardon, F.; Riether, C.; de Haard, H.; Smits, E.; Pauwels, P.; Jacobs, J. The CD70-CD27 axis in oncology: The new kids on the block. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2022, 41, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riether, C.; Pabst, T.; Hopner, S.; Bacher, U.; Hinterbrandner, M.; Banz, Y.; Muller, R.; Manz, M.G.; Gharib, W.H.; Francisco, D.; et al. Targeting CD70 with cusatuzumab eliminates acute myeloid leukemia stem cells in patients treated with hypomethylating agents. Nat Med 2020, 26, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorabi, A.M.; Hajighasemi, S.; Kiaie, N.; Gheibi Hayat, S.M.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Johnston, T.P.; Sahebkar, A. The pivotal role of CD69 in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 2020, 111, 102453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angenendt, L.; Woste, M.; Mikesch, J.H.; Arteaga, M.F.; Angenendt, A.; Sandmann, S.; Berdel, W.E.; Lenz, G.; Dugas, M.; Meshinchi, S.; et al. Calcitonin receptor-like (CALCRL) is a marker of stemness and an independent predictor of outcome in pediatric AML. Blood Adv 2021, 5, 4413–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruedigam, C.; Bagger, F.O.; Heidel, F.H.; Paine Kuhn, C.; Guignes, S.; Song, A.; Austin, R.; Vu, T.; Lee, E.; Riyat, S.; et al. Telomerase inhibition effectively targets mouse and human AML stem cells and delays relapse following chemotherapy. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 15, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstovsek, S.; Manshouri, T.; Smith, F.O.; Giles, F.J.; Cortes, J.; Estey, E.; Kantarjian, H.; Keating, M.; Jeha, S.; Albitar, M. Telomerase activity is prognostic in pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia: Comparison with adult acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2003, 97, 2212–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwe, S.P.; Huang, F.; Kolb, E.A.; Gopalakrishnapillai, A. Imetelstat Induces Leukemia Stem Cell Death in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient-Derived Xenografts. J Clin Med 2022, 11, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





