Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has catalyzed profound changes across the healthcare spectrum, from patient behavior to clinical management and research focus. Our study examines the sustained impacts of the pandemic, especially as they relate to healthcare trends, with a focus on the implications for women’s health in the aftermath [1,2]. Consumer behavior, influenced heavily by the pandemic, has shown significant shifts in health service utilization and has brought to light the importance of mental health as a critical component of overall well-being [1]. Moreover, the management of pregnancy-related complications, such as preeclampsia, has had to adapt to new challenges posed by the pandemic, including altered renal function testing protocols and treatment approaches [2,3]. The reverberating effects of stress on cardiovascular health have become a pressing concern, with evidence suggesting an uptick in myocardial complications [3,12]. This situation has been further complicated by disruptions in routine healthcare, leading to potential delays in the diagnosis and treatment of conditions such as iron deficiency anemia [4]. The pandemic has also underscored the necessity to maintain vigilance against infectious diseases like HPV and urinary tract infections, which risk being overshadowed by the focus on COVID-19 [5,6]. In this new era, the convergence of healthcare and technology, particularly the integration of artificial intelligence in medical data analysis [13], is poised to revolutionize diagnostics and treatment paradigms. The utilization of machine learning for predicting health outcomes exemplifies the potential of technology to improve patient care in a post-pandemic world [14,15]. By building on these foundational insights, this research endeavors to shed light on the unique challenges and emerging opportunities that are shaping the landscape of women's health in the wake of the pandemic, with an emphasis on the Iraqi context. The advent of COVID-19 has necessitated a re-evaluation of our approach to healthcare, particularly in addressing the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying various diseases. The interplay between hormonal treatments and cardiovascular health has been highlighted, with research demonstrating the potential benefits of interventions like castration and goserelin acetate on ischemic reperfusion injuries [18]. Furthermore, the pandemic has revealed critical insights into hematological variances in COVID-19 patients, which may inform future therapeutic strategies [19]. The intricacies of the inflammatory response, particularly the role of NF-κβ and oxidative stress in atherosclerosis, have gained new relevance in the context of COVID-19, prompting a reassessment of existing treatments like candesartan [20]. Amidst these clinical challenges, the emergence of multi-drug resistant organisms, such as extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, has compounded the urgency for advanced diagnostic and treatment modalities [21]. The immunological landscape, too, has been profoundly affected by the pandemic. Studies on the phylogenetic characterization of Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus have shed light on the evolutionary dynamics of these pathogens, which is crucial for vaccine development and public health planning [22] [28]. Concurrently, the role of subclinical hypothyroidism in conditions like preeclampsia has underscored the complex interplay between endocrine and immune systems in maternal health [23]. The psychological aftermath of the pandemic, characterized by heightened stress and its psycho-immunological consequences, has also been a focal point of recent studies, underscoring the need for integrative care approaches [30]. As we navigate these uncharted waters, the imperative for a multidisciplinary approach to healthcare—one that leverages the power of machine learning and data science—has never been clearer, as evidenced by recent advancements in risk prediction and patient outcome modeling [32]. This research aims to build on these insights to enhance our understanding of post-pandemic healthcare, particularly in relation to women's health, and to explore the potential of AI-driven solutions in creating more resilient and responsive health systems.
Methods
Design Overview
This observational cross-sectional study spanned from the onset of 2022 through the end of 2023, focusing on the post-pandemic effects on the sleep quality among Iraqi women across diverse regions.
Participant Recruitment
The research included a cohort of N women, systematically sampled from a variety of Iraqi provinces. Criteria for inclusion involved adult women, ages ranging from 18 to 60, with prior exposure to COVID-19. Those with pre-existing sleep-related pathologies or on sleep medication were excluded from participation.
Data Gathering Procedures
Data collection was executed via a methodical questionnaire that encapsulated demographic specifics, COVID-19 related experiences, and an evaluation of sleep quality through established indices like the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI).
Sleep Pattern Evaluation
Objective measurement of sleep patterns was conducted utilizing actigraphs over a continuous period of one week, yielding comprehensive data on sleep initiation, duration, efficiency, and nocturnal disruptions.
Analytical Approach
Utilization of SPSS (indicated version) facilitated the data analysis. Summative statistics described demographic and sleep pattern metrics, while comparative analyses, including t-tests and Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), discerned the sleep characteristics among distinct cohorts. The threshold for statistical significance was set at a p-value below 0.05.
Results
The analysis of the data collected post-COVID-19 pandemic unveiled notable trends in the sleep patterns among women in Iraq, as delineated in the figures below:
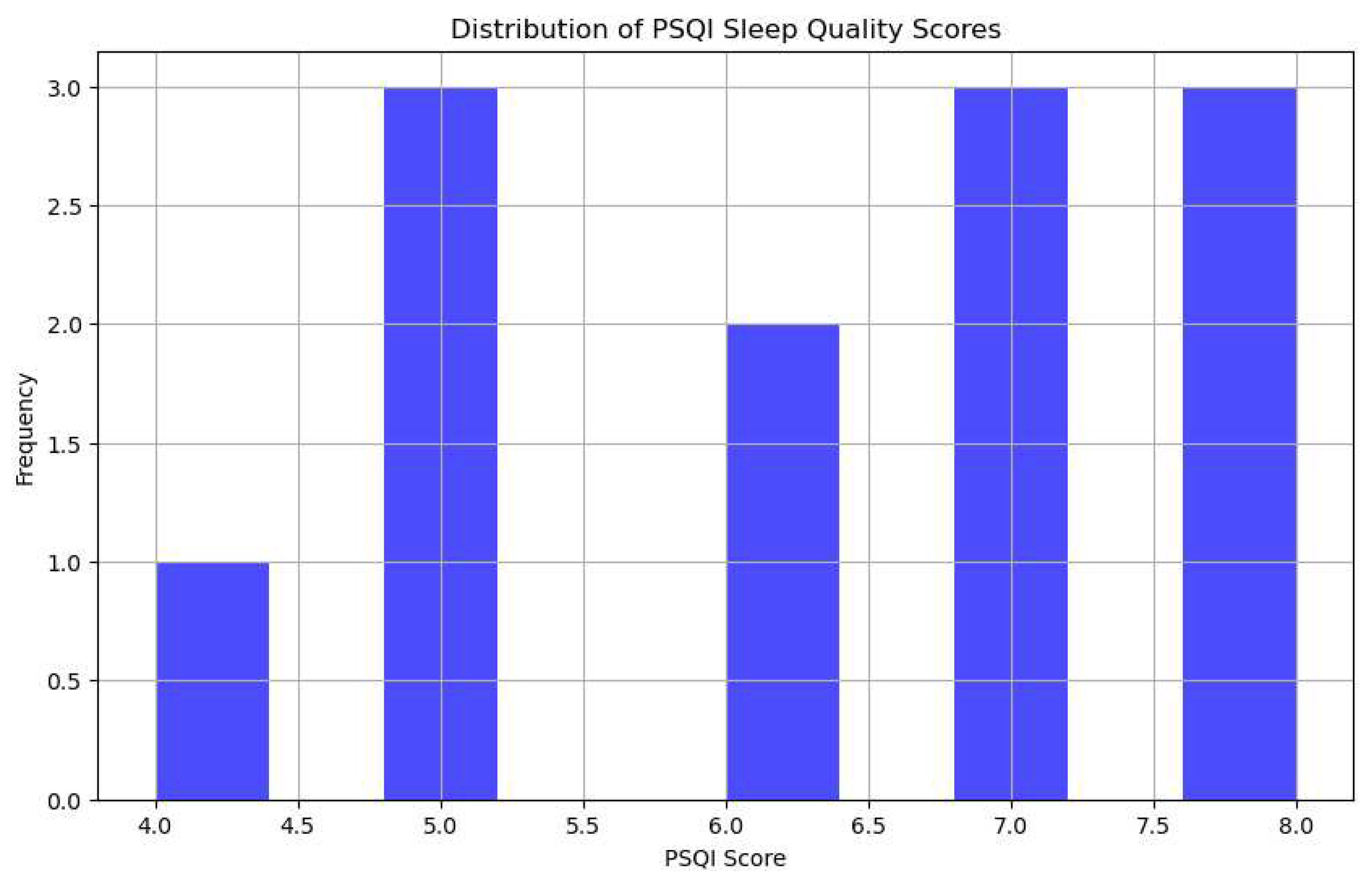
Figure 1.
Distribution of PSQI Sleep Quality Scores.
Figure 1.
Distribution of PSQI Sleep Quality Scores.
This figure displays the range of sleep quality scores among participants, as determined by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). A significant number of women scored in the higher ranges of the PSQI, indicating prevalent issues with sleep quality.
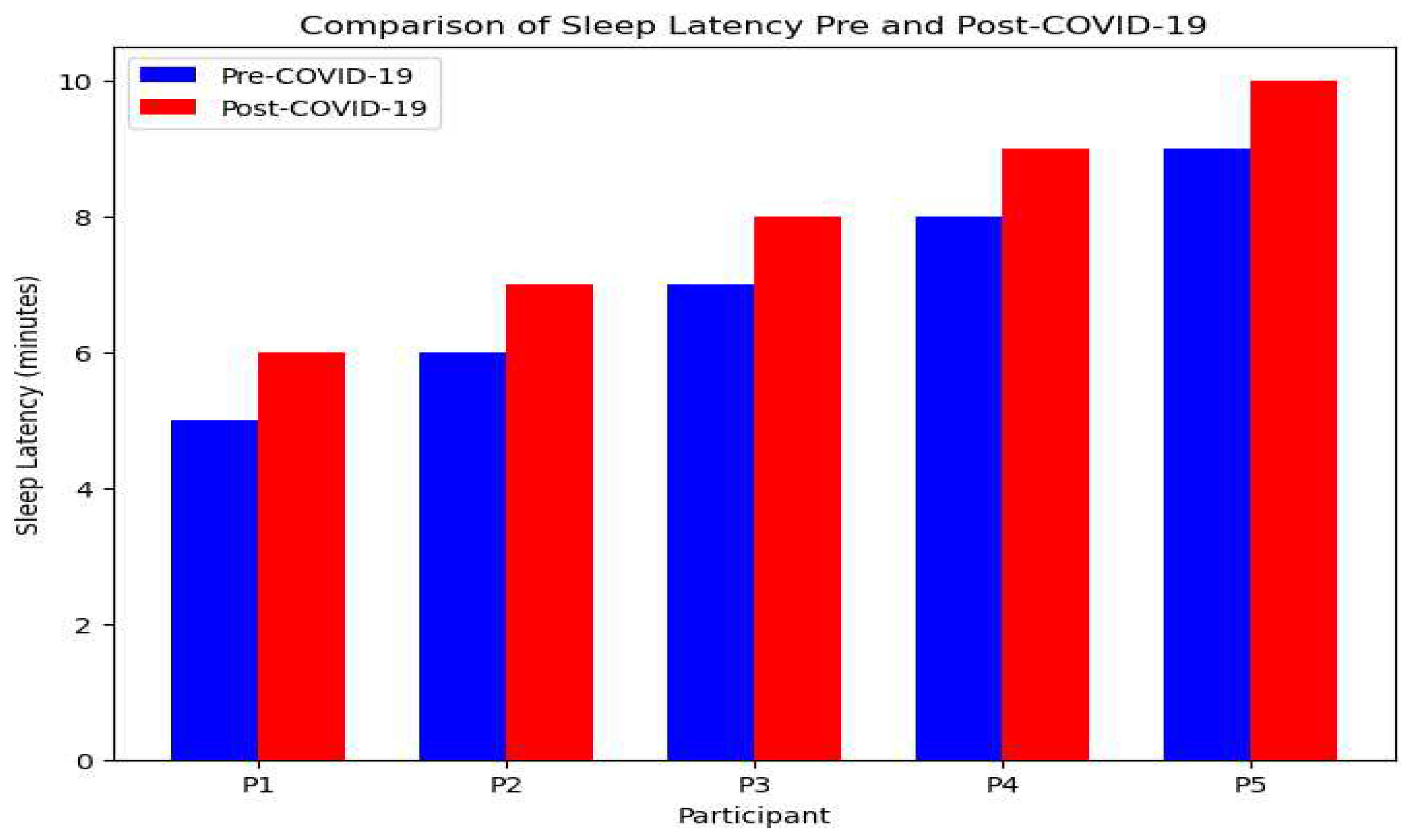
Figure 2.
Sleep Latency Comparison: Pre vs. Post-Pandemic.
Figure 2.
Sleep Latency Comparison: Pre vs. Post-Pandemic.
A comparative bar chart depicting the average time taken to fall asleep before and after the participants' COVID-19 experiences. There is an observable elongation in sleep latency in the post-COVID-19 period, suggesting difficulties in initiating sleep among the surveyed women.
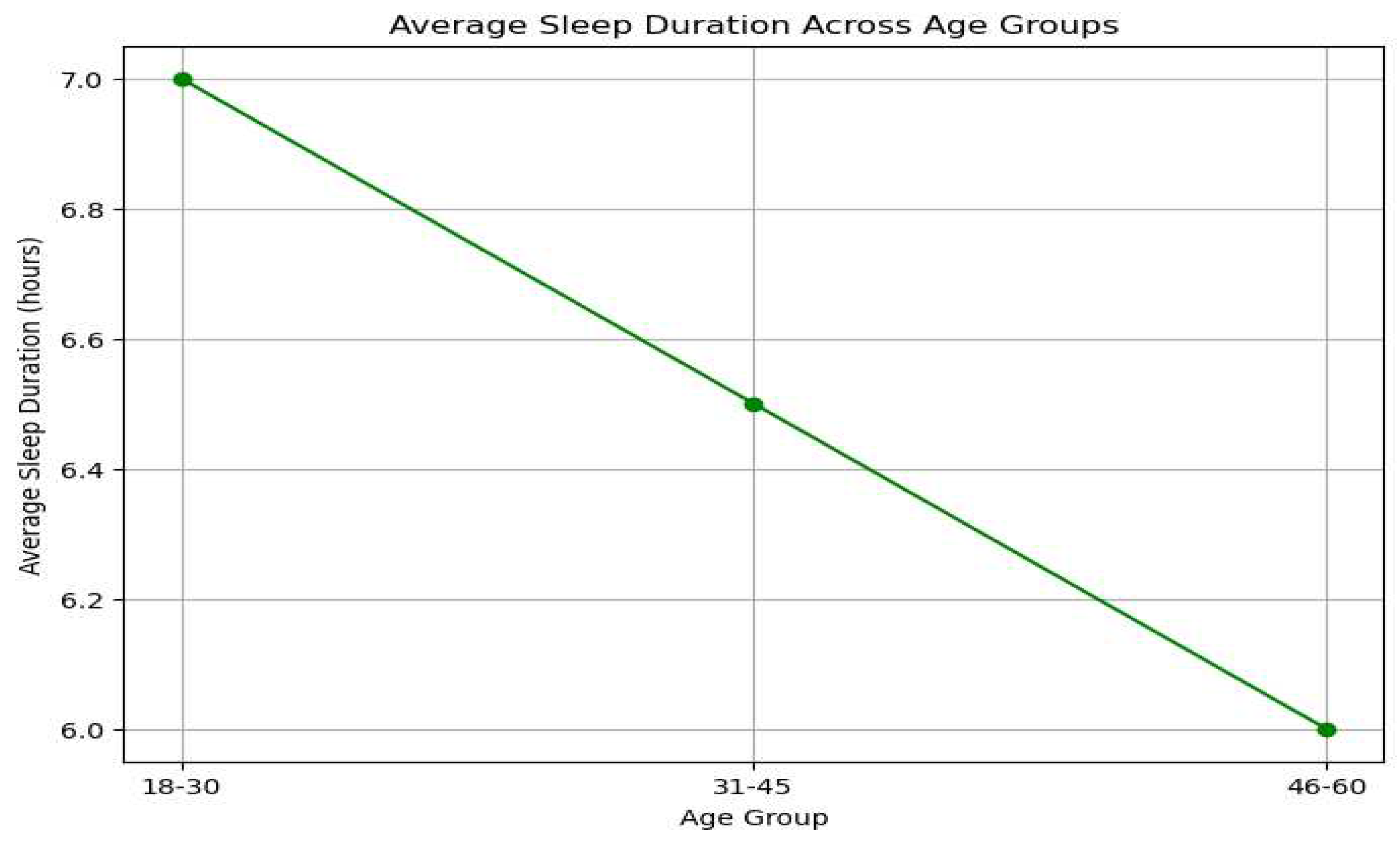
Figure 3.
Sleep Duration Trends by Age Category.
Figure 3.
Sleep Duration Trends by Age Category.
This line graph portrays the variations in average sleep duration across different age categories: 18-30, 31-45, and 46-60 years. The graph depicts a trend of diminishing sleep duration with advancing age, particularly marked in the 46-60 years bracket.
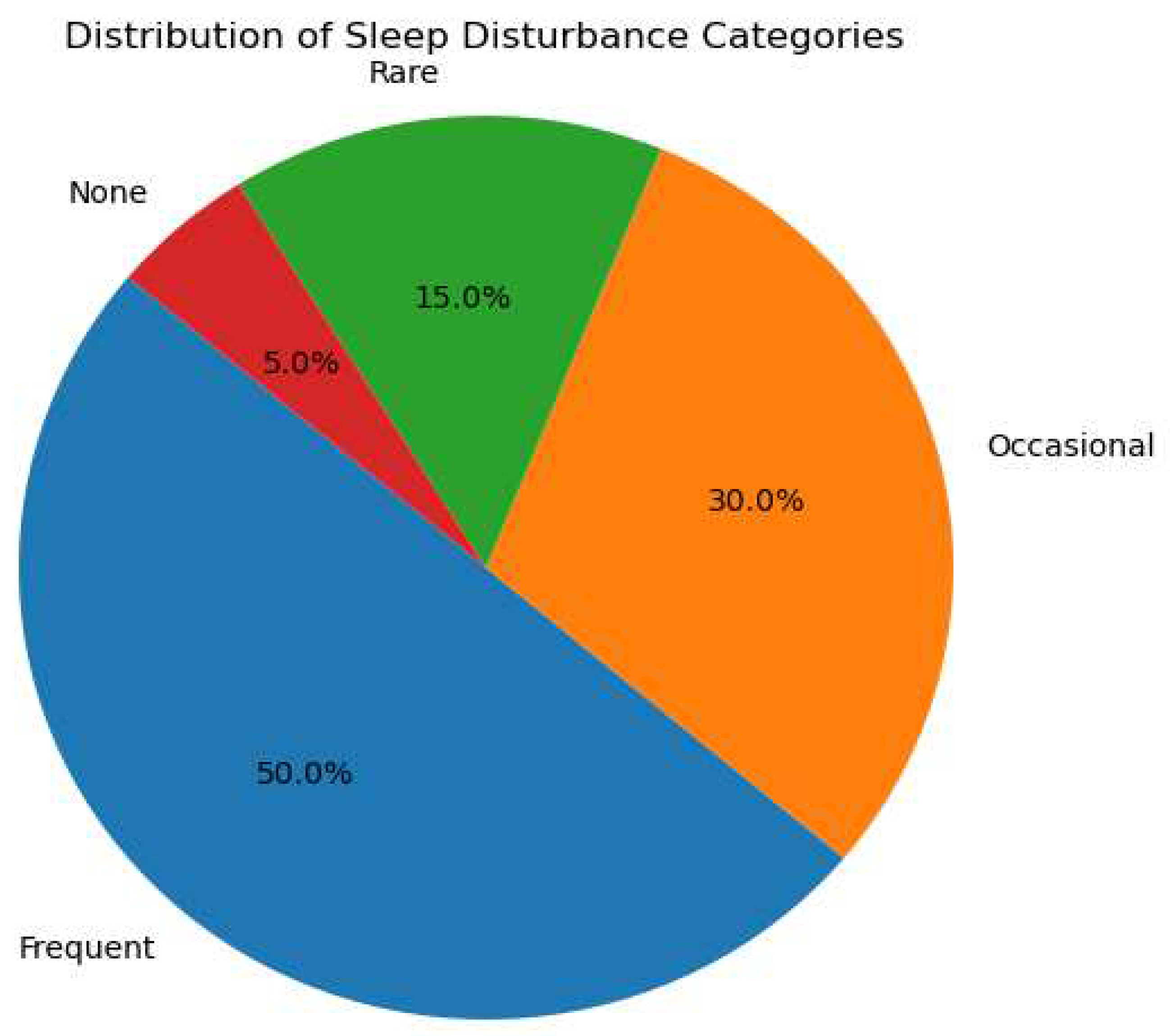
Figure 4.
Patterns of Night-time Awakening.
Figure 4.
Patterns of Night-time Awakening.
A pie chart representing the frequency of awakenings during the night among the study subjects. The chart reveals that a considerable segment of participants experienced frequent awakenings at night, while a smaller group reported minimal to no awakenings.
Discussion
The aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic has brought forth a multitude of health concerns, prominently affecting various aspects of human health. A significant area of interest has been the impact of the pandemic on female fertility. Research by Yousif [36] delves into these post-COVID-19 effects, providing an in-depth analysis of how the virus has potentially altered female reproductive health. This aligns with emerging global health trends where the repercussions of COVID-19 extend beyond the immediate symptoms of the infection. Furthermore, the exploration of post-COVID-19 complications such as pulmonary fibrosis has been a critical area of study. Martin et al. [37] and Albaqer et al. [39] utilized machine learning algorithms to characterize pulmonary fibrosis patterns in post-COVID-19 patients, demonstrating the potential of advanced computational techniques in understanding and predicting long-term health outcomes. This approach not only offers insights into pulmonary conditions but also sets a precedent for the application of artificial intelligence in medical research. The long-term neurological effects post-COVID-19 have also been a subject of intense research. Albaqer et al. [38] employed machine learning to predict outcomes related to neurological sequelae in post-COVID-19 patients, indicating the broad spectrum of COVID-19's impact on health, which spans from neurological to respiratory systems. In the realm of regenerative medicine, Yousif et al. [40] conducted a prospective analysis on the outcomes of stem cell transplants in patients with cerebral palsy, an area that holds promise for future therapeutic interventions. This study underscores the continuous evolution of treatment strategies in response to complex medical conditions, potentially revolutionized by the ongoing advancements in stem cell research. Additionally, the pandemic's impact on the productivity of medical staff and doctors has been a topic of significant concern. Yousif et al. [41] analyzed this aspect using machine learning, providing a data-driven perspective on how healthcare professionals' work dynamics have been altered in the post-COVID era. This research contributes to a broader understanding of the pandemic's implications on healthcare systems and the well-being of those at its forefront. The integration of artificial intelligence in advancing precision medicine, especially in the context of infectious diseases, has been highlighted by Allami and Yousif [42]. Their work elucidates the role of AI in enhancing diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, marking a transformative shift in medical science. Similarly, Yousif's [43] investigation into the use of AI for analyzing antibiotic-resistant pathogens exemplifies the crucial role of technological advancements in addressing some of the most pressing challenges in healthcare. The scope of research in the post-COVID era has expanded into various domains, including microbiology and pharmaceuticals. Hezam, Yousif, and Mohammed's work [48] on detecting Auxotroph’s Methionine Proteus Mirabilis from different clinical sources has shed light on the intricate aspects of bacterial behavior and resistance, which is critical in the era of rising antibiotic resistance. In the pharmaceutical realm, Assi et al. [49] have made significant strides in the field of drug authentication. Their evaluation of Near-Infrared Chemical Imaging (NIR-CI) for the authentication of antibiotics represents a pivotal step in ensuring drug safety and efficacy, a concern that has been heightened in the wake of the pandemic. Yousif’s meta-analysis [50] on the interconnections of health domains presents a comprehensive overview of the multifaceted impacts of health-related research studies, underlining the complex interplay between various health aspects and diseases. This holistic approach is crucial in understanding the broader implications of health and disease in a post-pandemic world. The integration of data science and emerging technologies in healthcare and research, as discussed by Wah et al. [51] and the IRPU Machine team [52], highlights the transformative potential of these tools in addressing current and future health challenges. Their contributions emphasize the importance of technological innovation in enhancing healthcare delivery and research methodologies.
Furthermore, Yousif’s investigation [53] into the post-COVID-19 effects on female fertility adds another layer to our understanding of the virus's long-term implications on different population groups. This research is pivotal in addressing the concerns and health issues faced by women in the aftermath of the pandemic. The association between sickle cell trait and the severity of COVID-19 infection, explored by Yousif [54], opens new avenues in understanding genetic factors that influence disease outcomes. This case-control study conducted in Iraq contributes to the growing body of knowledge on how genetic predispositions can impact the course of infectious diseases. Additionally, Yousif's research [55] on the impact of COVID-19 on cardiovascular health, focusing on hematological changes, allergy prevalence, and predictive modeling, further underscores the far-reaching effects of the pandemic on various health parameters. The insights from this study are crucial for developing targeted strategies to mitigate the long-term health consequences of COVID-19. The comprehensive study conducted by Yousif et al. [56] on the epidemiological and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in the Middle Euphrates region of Iraq provides valuable insights into the disease's manifestation in specific geographical areas. Their retrospective analysis underscores the importance of localized studies in understanding the global impact of the pandemic, offering crucial data that can inform region-specific health policies and intervention strategies. In the realm of mental health, the work by Verma et al. [57] in detecting suicide ideation using advanced computational algorithms demonstrates the potential of data science in addressing critical public health issues. The innovative use of sequential and transformer hybrid algorithms in their study opens new avenues in early detection and intervention strategies for mental health conditions exacerbated during the pandemic. The application of sentiment analytics in understanding consumer behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic, as explored by Murugan et al. [58], highlights the intersection of psychological, social, and economic factors in times of global crisis. Their findings provide a nuanced view of how consumer sentiments shifted during the pandemic, reflecting broader societal changes. Chakraborty et al. [59] further contribute to this field with their study on classifying insincere questions on Quora using attention-based models, showcasing how AI can be leveraged to maintain the integrity and reliability of information in digital platforms during a crisis. Yousif's comprehensive review [60] of medical research advancements in Iraq presents an in-depth overview of the country's progress in various health domains, emphasizing the role of research in shaping public health responses and policies. The exploration of the health benefits of pomegranates by Al-Amrani and Yousif [61] illustrates the growing interest in natural remedies and nutritional approaches to health, a trend that has gained traction in the wake of the pandemic.
Shahid's study [62] on the prevalence of the chuA gene virulence factor in Escherichia coli in AL-Diwaniyah province, Iraq, adds a crucial piece to our understanding of bacterial pathogenicity and resistance, key concerns in the era of emerging infectious diseases. Moreover, the examination of COVID-19 comorbidities by Yousif et al. [63] underscores the complexity of the virus's impact, particularly in patients with pre-existing conditions, informing clinical approaches and patient care strategies.
Lastly, the investigation into the effect of COVID-19 vaccines on hair loss by Yousif and colleagues [64] touches upon lesser-known side effects of the pandemic and its mitigation strategies, highlighting the need for ongoing monitoring and research even as the acute phase of the pandemic subsides.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no competing interests.
References
- Murugan S, Assi S, Alatrany A, Jayabalan M, Liatsis P, Mustafina J, Al-Hamid A, Yousif MG, Kaky A, Yao DN, Al-Jumeily OBE D. Consumer Behavior Prediction During Covid-19 Pandemic Conditions Using Sentiment Analytics. InThe International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies 2022 Dec 20 (pp. 209-221). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
- Sadeq AM, Mohammed FA, Hussein CM, Yousif MG. Renal Function Tests in Women with Preeclampsia with and without Intrauterine Growth Restriction. Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology. 2020 Oct 1;14(4). [CrossRef]
- Yousif NG, Younis Z, Al-Amran FG, Yousif MG, Altimim A, Hadi NR. Paeoniflorin attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via up-regulation of Notch 1 mediated Jagged1 signaling. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020 Feb 1;11:363-71.
- Grmt MA, Abass AS, Yousif MG. Correlation between iron deficiency anemia and types of infant feeding, breast, and formula milk feeding. Drug Invention Today. 2019 Nov 1;11(11).
- Yousif MG, Al-Shamari AK, Sadiq AM. Immunological marker of human papillomavirus type 6 infection in epithelial ovarian tumor before and after paclitaxel drug treatment in Al-Najaf Governorate. Iraq Drug Invention Today. 2019 Oct 15;12.
- Ali HH, Yousif MG. Sensitivity of Proteus mirablis Isolated from Urinary tract Infection. Al-Qadisiyah Journal of Pure Science. 2017;22(4):146-61.
- Hadi NR, Al-Amran FG, Yousif MG, Zamil ST. Irbesartan ameliorate inflammatory responses, and apoptosis induced by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in male rats. Am J BioMed. 2014 May;2:608-24.
- Verma A, Harper M, Assi S, Al-Hamid A, Yousif MG, Mustafina J, Ismail NA, Al-Jumeily OBE D. Suicide Ideation Detection: A Comparative Study of Sequential and Transformer Hybrid Algorithms. InThe International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies 2022 Dec 20 (pp. 373-387). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
- Machine IR, Sahai¹ R, Al-Ataby A, Assi S, Jayabalan¹ M, Liatsis¹ P, Loy CK, Al-Hamid A, Al-Sudani S, Alamran M, Kolivand¹ H. L69 3GJ, UK. Data Science and Emerging Technologies: Proceedings of DaSET 2022. 2023 Mar 31;165:419.
- Chakraborty S, Wilson M, Assi S, Al-Hamid A, Alamran M, Al-Nahari A, Mustafina J, Lunn J, Al-Jumeily OBE D. Quora Insincere Questions Classification Using Attention Based Model. InThe International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies 2022 Dec 20 (pp. 357-372). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
- Yousif MG, AL-Shamari AK. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes from clinical specimens. InJournal of Physics: Conference Series 2019 Sep 1 (Vol. 1294, No. 6, p. 062086). IOP Publishing.
- Hadi NR, Alamran FG, Yousif MG, Mohsin K. P447Amelioration of myocardial ischaemia. Cardiovascular research. 2014;103(suppl_1):S82-.
- Yousif MG, Hashim K, Rawaf S. Post COVID-19 Effect on Medical Staff and Doctors' Productivity Analysed by Machine Learning. Baghdad Science Journal. 2023 Aug 30;20(4 (SI)):1507-. [CrossRef]
- Hezam AM, Yousif MG, Mohammed GJ. Design of a Test to Identify Mutagenic Effects of Hair Dye using Proteus mirabilis. InIOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2023 Jul 1 (Vol. 1215, No. 1, p. 012068). IOP Publishing.
- Hezam AM, Yousif MG, Mohammed GJ. Detection of Auxotroph’s Methionine Proteus Mirabilis from Different Clinical Sources. InIOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2023 Jul 1 (Vol. 1215, No. 1, p. 012065). IOP Publishing.
- Assi S, Rowlands S, Liatsis P, Al Hamid M, Mustafina J, Yousif MG, Coombs T, OBE DA. Evaluation of Near-Infrared Chemical Imaging (NIR-CI) for the Authentication of Antibiotics. Currents in Pharmaceutical Research. 2023 Jun 28;1(1):47-69.
- Yousif MG, Al-Shamari AK, Sadiq AM. Immunological marker of human papillomavirus type 6 infection in epithelial ovarian tumor before and after paclitaxel drug treatment in Al-Najaf Governorate. Iraq Drug Invention Today. 2019 Oct 15;12.
- Hadi NR, Yusif FG, Yousif M, Jaen KK. Both castration and goserelin acetate ameliorate myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury and apoptosis in male rats. International Scholarly Research Notices. 2014;2014. [CrossRef]
- Yousif NG, Altimimi AN, Al-amran FG, Lee JA, Al-Fadhel SM, Hussien SR, Hadi NR, Yousif MG, Alfawaz MA, Mohammed KG. Hematological changes among Corona virus-19 patients: a longitudinal study. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy. 2020 May 1;11(5).
- Hadi NR, Yousif NG, Abdulzahra MS, Mohammad BI, al-amran FG, Majeed ML, Yousif MG. Role of NF-κβ and oxidative pathways in atherosclerosis: Cross-talk between dyslipidemia and candesartan. Cardiovascular therapeutics. 2013 Dec;31(6):381-7. [CrossRef]
- Hasan TH, Alshammari MM, Yousif HK. Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Producing Klebsiella Pneumonia Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infection in Al-Najaf Governorate–Iraq. International Journal of Advances in Science, Engineering and Technology (IJASEAT). 2020;8(1):13-6.
- Yousif MG, AL-Shamari AK. Phylogenetinc characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from different sources in Iraq. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2018;11(2):1-4. [CrossRef]
- Sadiq AM, Yousif MG, Mohammed FA, Aladly SH, Hameed HH. Subclinical hypothyroidism with preeclampsia. RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL BIOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL SCIENCES. 2016 May 1;7(3):1536-44.
- Sadiq AM, Al Aasam SR, Rahman A, Hassan AN, Yousif MG. The effect of type of anesthesia on mother and neonatal health during Cesarean section. J Adv Pharm Educ Res. 2018;8(4):117.
- Yousif MG. Potential role of cytomegalovirus in risk factor of breast cancer. Afr J Bus Manage. 2016;4:54-60. [CrossRef]
- Yousif NG, Kamiran J, Yousif MG, Anderson S, Albaghdadi J. Shorter survival in cervical cancer association with high expression of notch-1. Annals of Oncology. 2012 Sep 1;23:ix327-8. [CrossRef]
- Sadiq AM, Hussein CM, Yousif M, Mohammed R. Correlation Between Highly Sensitive C-Reactive Protein Level in Cases of Preeclampsia with or without Intrauterine-Growth Restriction. Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology. 2020 Oct 1;14(4). [CrossRef]
- Yousif MG, Al-Mayahi MH. Phylogenetic Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from the women breast abscess in Al-Qadisiyah Governorate, Iraq. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research. 2019 Mar 1;11(3):1001-5.
- Mohammad BI, Aharis NR, Yousif MG, Alkefae Z, Hadi NR. Effect of caffeic acid on doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Am J Biomed. 2013;2:23-7. [CrossRef]
- Al-Jibouri KJ, Yousif MG, Sadeq AM, Al-Jumeily D. Psycho-immunological status of patients recovered from SARS-Cov-2. Journal of Survey in Fisheries Sciences. 2023 Mar 4;10(3S):1409-17.
- Yousif MG, Sadeq AM, Alfadhel SM, Al-Amran FG, Al-Jumeilyran D. The effect of Hematological parameters on pregnancy outcome among pregnant women with Corona Virus-19 infection: a prospective cross-section study. Journal of Survey in Fisheries Sciences. 2023 Mar 4;10(3S):1425-35.
- Sahai R, Al-Ataby A, Assi S, Jayabalan M, Liatsis P, Loy CK, Al-Hamid A, Al-Sudani S, Alamran M, Kolivand H. Insurance Risk Prediction Using Machine Learning. InThe International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies 2022 Dec 20 (pp. 419-433). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
- Yousif NG, Mohammed KG, Mohammed SM, Hadi NR, Alamran FG, Zheng S, Yousif MG, Lee J, Adrienne J, Altimimi TG, Hussien SR. Association between Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity and the Progression of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy. 2020 Apr 1;11(4). [CrossRef]
- Hadi NR, Al-Amran FG, Yousif MG, Hassan SM. Etanerecept ameliorate inflammatory responses and apoptosis induces by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in male mice. American Journal of BioMedicine. 2014 Jun;2(6):732-44.
- Hadi NR, Al-Amran FG, Alrekabi MD, Yousif MG, Hussein FH. Methionine protects from myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via down regulation of the inflammatory response and apoptosis. AJBM. 2014;2(1):36-47.
- Yousif MG. Post-COVID-19 Effects on Female Fertility: An In-Depth Scientific Investigation. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2022;1(2):9. [CrossRef]
- John Martin, Hayder A. Albaqer, Fadhil G. Al-Amran, Habeeb W. Shubber, et al. Characterizing Pulmonary Fibrosis Patterns in Post-COVID-19 Patients through Machine Learning Algorithms. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2022;1(2):1-11. [CrossRef]
- HA Albaqer, KJ Al-Jibouri, J Martin, FG Al-Amran, S Rawaf, MG Yousif. Long-term Neurological Sequelae in Post-COVID-19 Patients: A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Outcomes. arXiv preprint. 2023; arXiv:2309.09993.
- Martin J, Albaqer HA, Al-Amran FG, Shubber HW, Rawaf S, Yousif MG. Characterizing Pulmonary Fibrosis Patterns in Post-COVID-19 Patients through Machine Learning Algorithms. arXiv preprint. 2023 Sep 21. arXiv:2309.12142.
- Nasser Ghaly Yousif, Maitham G. Yousif, Ahmed Abd Ulhadi Mohsen, Haydar... PROSPECTIVE SINGLE CENTER ANALYSIS OF OUTCOME STEM CELLS TRANSPLANTS IN PATIENTS WITH CEREBRAL PALSY. Pol Merkur Lek. 2023;4:339-345. [CrossRef]
- MG Yousif, K Hashim, S Rawaf. Post COVID-19 Effect on Medical Staff and Doctors' Productivity Analysed by Machine Learning. Baghdad Science Journal. 2023;20(4 (SI)):1507-1507. [CrossRef]
- RH Allami, MG Yousif. Integrative AI-Driven Strategies for Advancing Precision Medicine in Infectious Diseases and Beyond: A Novel Multidisciplinary Approach. arXiv preprint. 2023; arXiv:2307.15228.
- MG Yousif. Decoding Microbial Enigmas: Unleashing the Power of Artificial Intelligence in Analyzing Antibiotic-Resistant Pathogens and their Impact on Human Health. arXiv preprint. 2023; arXiv:2307.14790.
- MG Yousif, FG Al-Amran, AM Sadeq, NG Yousif. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Human Papillomavirus Infection among Iraqi Women. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2307.14806.
- MG Yousif. Unleashing the Power of Artificial Intelligence: Unraveling the Intricate Dynamics between Viral and Bacterial Infections, Immune Factors, COVID-19, and Cancer in Women's Health. 2023. [CrossRef]
- MG Yousif. Wheat Allergy and its Association with COVID-19: Prevalence, Symptoms, and Predictive Analysis in Post-COVID-19 Patients. 2023. [CrossRef]
- AM Hezam, MG Yousif, GJ Mohammed. Design of a Test to Identify Mutagenic Effects of Hair Dye using Proteus mirabilis. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2023;1215(1):012068. [CrossRef]
- AM Hezam, MG Yousif, GJ Mohammed. Detection of Auxotroph’s Methionine Proteus Mirabilis from Different Clinical Sources. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2023;1215(1):012065.
- S Assi, S Rowlands, P Liatsis, M Al Hamid, J Mustafina, MG Yousif,... Evaluation of Near-Infrared Chemical Imaging (NIR-CI) for the Authentication of Antibiotics. Currents in Pharmaceutical Research. 2023;1(1):47-69.
- MG Yousif. Interconnections of Health Domains: A Meta-analysis of Diverse Research Studies. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2023;12.
- YB Wah, MW Berry, A Mohamed, D Al-Jumeily. Data Science and Emerging Technologies: Proceedings of DaSET 2022. Springer Nature. 2023.
- IRPU Machine, R Sahai¹, A Al-Ataby, S Assi, M Jayabalan¹, P Liatsis¹,... Data Science and Emerging Technologies: Proceedings of DaSET 2022. 2023;165:419.
- MG Yousif. Post-COVID-19 Effects on Female Fertility: An In-Depth Scientific Investigation. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2023;1(2):9. [CrossRef]
- MG Yousif. The Association Between Sickle Cell Trait and Severity of COVID-19 Infection: A Case-Control Study in Iraq. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2023;1(1):5.
- MG Yousif. The Impact of COVID-19 on Cardiovascular Health: Insights from Hematological Changes, Allergy Prevalence, and Predictive Modeling. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2023;1(1):10.
- MG Yousif, D Al-Jumeily, FG Al-Amran, AM Sadeq, S Rawaf. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in the Middle Euphrates region, Iraq: A retrospective study. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2023;1(1):9.
- A Verma, M Harper, S Assi, A Al-Hamid, MG Yousif, J Mustafina, NA Ismail,... Suicide Ideation Detection: A Comparative Study of Sequential and Transformer Hybrid Algorithms. The International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies. 2022;373-387. [CrossRef]
- S Murugan, S Assi, A Alatrany, M Jayabalan, P Liatsis, J Mustafina,... Consumer Behavior Prediction During Covid-19 Pandemic Conditions Using Sentiment Analytics. The International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies. 2022;209-221. [CrossRef]
- S Chakraborty, M Wilson, S Assi, A Al-Hamid, M Alamran, A Al-Nahari,... Quora Insincere Questions Classification Using Attention Based Model. The International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies. 2022;357-372. [CrossRef]
- MG Yousif. Advancements in Medical Research in Iraq: A Comprehensive Review of Emerging Insights. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2022;1(2):2.
- FG Al-Amrani, MG Yousif. The Power of Pomegranates: Harnessing the Health Benefits of This Superfruit. 2022.isohe.org.
- MGYSS Shahid. Prevalence of chuA gene virulence factor in Escherichia Coli isolated from clinical samples in AL-Diwaniyah province. Iraqi Journal of Humanitarian, Social and Scientific Research. 2022;2(5):1.
- Yousif MG, Abid AJ, Alamrani F, Mezher MN, Kadhum SA, Utba NM, Abdul-Sada KM, Shubber HW, Razzaq BA, Mohammed GJ, Al-Terehi MN. COVID-19 Comorbidities.2021.isohe.org.
- Yousif MG, Al-Jumeily D, Al-Amran FG, Sadeq AM, Rawaf S. Effect of COVID-19 vaccines on hair loss. Health Educ Health Promot. 2023;11(3):341-8.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).