Submitted:
22 January 2024
Posted:
23 January 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Material and Methods
Conclusions
References
- AASLD-IDSA. HCV Guidance: Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C 2016. Guidance produced by the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease and the Infectious Disease Society of America (AASLD-IDSA) covering recommendations for hepatitis C testing, clinical management and treatment. Available online: http://hcvguidelines.org/sites/default/files/HCV-Guidance_October_2016_a.pdf.
- Recommendations for prevention and control of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and HCV-related chronic disease. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. MMWR Recomm Rep. 1998;47(Rr-19):1–39. Recommendations from the Centers for the Disease Control and Prevention definng populations for risk-based testing of hepatitis C.
- Moyer VA. Screening for hepatitis C virus infection in adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(5):349–57. Hepatitis C testing recommendations for adults from the United States Preventive Services Task Force including risk-based testing and testing for adults born from 1945–1965. [CrossRef]
- Holmberg SD, Spradling PR, Moorman AC, Denniston MM. Hepatitis C in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(20):1859–61. Description of a care cascade integrating data from the Chronic Hepatitis Cohort Study and the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. [CrossRef]
- Viner K, Kuncio D, Newbern EC, Johnson CC. The continuum of hepatitis C testing and care. Hepatology. 2015;61(3):783–9. Description of an HCV continuum of care in a US urban center highlighting important areas where patients become lost at each stage.
- Koneru A, Nelson N, Hariri S, Canary L, Sanders KJ, Maxwell JF, et al. Increased Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Detection in Women of Childbearing Age and Potential Risk for Vertical Transmission - United States and Kentucky, 2011–2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(28):705–10. Analysis finding that the proportion of infants born to HCV-infected mothers increased 68% nationally and 124% in Kentucky.
- Kuncio DE, Newbern EC, Johnson CC, Viner KM. Failure to Test and Identify Perinatally Infected Children Born to Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Women. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(8):980–5. Analysis of surveillance data from the Philadelphia Department of Public Health finding a significiant number of women giving birth in Philadelphia tested positive for HCV but that most of their children were not tested for HCV. [CrossRef]
- Lambers FA, Prins M, Thomas X, Molenkamp R, Kwa D, Brinkman K, et al. Alarming incidence of hepatitis C virus re-infection after treatment of sexually acquired acute hepatitis C virus infection in HIV-infected MSM. AIDS. 2011;25(17):F21–7. [CrossRef]
- Martin TC, Martin NK, Hickman M, Vickerman P, Page EE, Everett R, et al. Hepatitis C virus reinfection incidence and treatment outcome among HIV-positive MSM. AIDS (London, England) 2013;27(16):2551–7. [CrossRef]
- Ingiliz P, Martin TC, Rodger A, Stellbrink HJ, Mauss S, Boesecke C, et al. HCV reinfection incidence and spontaneous clearance rates in HIV-positive men who have sex with men in Western Europe. J Hepatol. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Testing for HCV infection: an update of guidance for clinicians and laboratorians. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2013;62(18):362–5. Updated guidance for clinicians and laboratorians from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on diagnostic testing procedures for hepatitis C.
- Moyer VA. Screening for hepatitis C virus infection in adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(5):349–57. Hepatitis C testing recommendations for adults from the United States Preventive Services Task Force including risk-based testing and testing for adults born from 1945–1965. 1945. [CrossRef]
- Thomas DL, Seeff LB. Natural history of hepatitis C. Clin Liver Dis. 2005;9(3):383–98. vi. [CrossRef]
- Mack CL, Gonzalez-Peralta RP, Gupta N, Leung D, Narkewicz MR, Roberts EA, et al. NASPGHAN practice guidelines: Diagnosis and management of hepatitis C infection in infants, children, and adolescents. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;54(6):838–55. [CrossRef]
- Thein HH, Yi Q, Dore GJ, Krahn MD. Estimation of stage-specific fibrosis progression rates in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. Hepatology. 2008;48(2):418–31.
- Conteduca V, Sansonno D, Russi S, Pavone F, Dammacco F. Therapy of chronic hepatitis C virus infection in the era of direct-acting and host-targeting antiviral agents. J Infect. 2014;68(1):1–20. [CrossRef]
- Gomez J, Martell M, Quer J, Cabot B, Esteban JI. Hepatitis C viral quasispecies. J Viral Hepat. 1999;6(1):3–16. [CrossRef]
- Duffy S, Shackelton LA, Holmes EC. Rates of evolutionary change in viruses: patterns and determinants. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9(4):267–76. [CrossRef]
- Bukh J. The history of hepatitis C virus (HCV): Basic research reveals unique features in phylogeny, evolution and the viral life cycle with new perspectives for epidemic control. J Hepatol. 2016;65(1 Suppl):S2–s21. [CrossRef]
- Ly KN, Hughes EM, Jiles RB, Holmberg SD. Rising Mortality Associated With Hepatitis C Virus in the United States, 2003–2013. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(10):1287–8. Describes rising HCV-associated mortality in the United States from 2003–2013. During that time period, HCV-associated deaths surpassed 60 other nationally natofiable infectious conditions combined. [CrossRef]
- Allison RD, Tong X, Moorman AC, Ly KN, Rupp L, Xu F, et al. Increased incidence of cancer and cancer-related mortality among persons with chronic hepatitis C infection, 2006–2010. J Hepatol. 2015;63(4):822–8. Analysis of a cohort of HCV-infected persons that found the the incidence of liver cancer and many types of non-liver cancers were higher, and age at diagnosis and death younger, in patients with chronic HCV infection compared to the general population. [CrossRef]
- Alberti A, Chemello L, Benvegnù L. Natural history of hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 1999;31 Suppl 1:17–24. [CrossRef]
- Hoofnagle JH. Course and outcome of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002;36:S21–S29.
- Chen SL, Morgan TR. The natural history of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Int J Med Sci. 2006;3:47–52. [CrossRef]
- Chevaliez S, Pawlotsky JM. Virology of hepatitis C virus infection. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;26:381–389. [CrossRef]
- Saludes V, González V, Planas R, Matas L, Ausina V, Martró E. Tools for the diagnosis of hepatitis C virus infection and hepatic fibrosis staging. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:3431–3442. [CrossRef]
- Naveau S, Perlemuter G, Balian A. [Epidemiology and natural history of cirrhosis]. Rev Prat. 2005 Sep 30;55(14):1527-32.
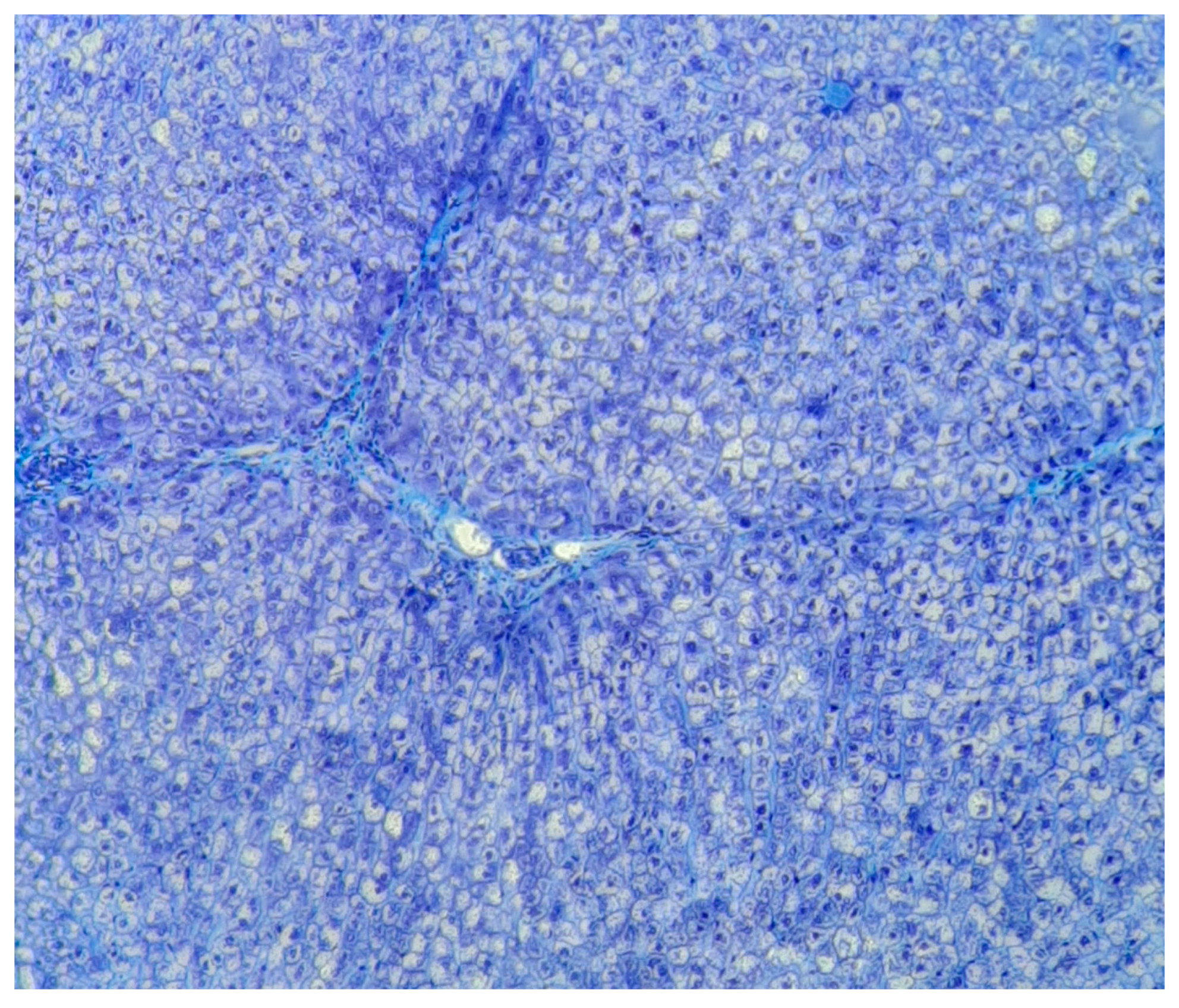
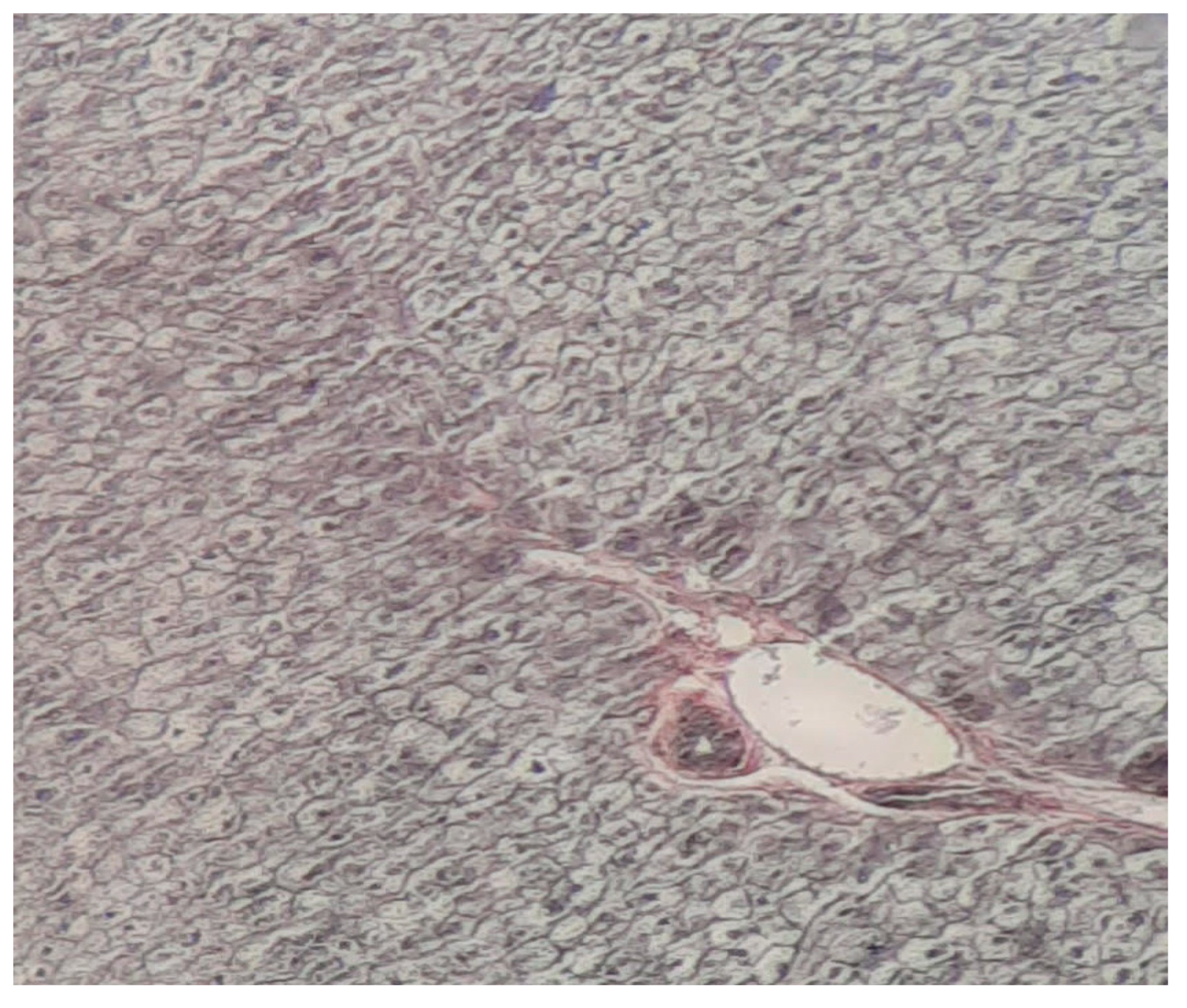
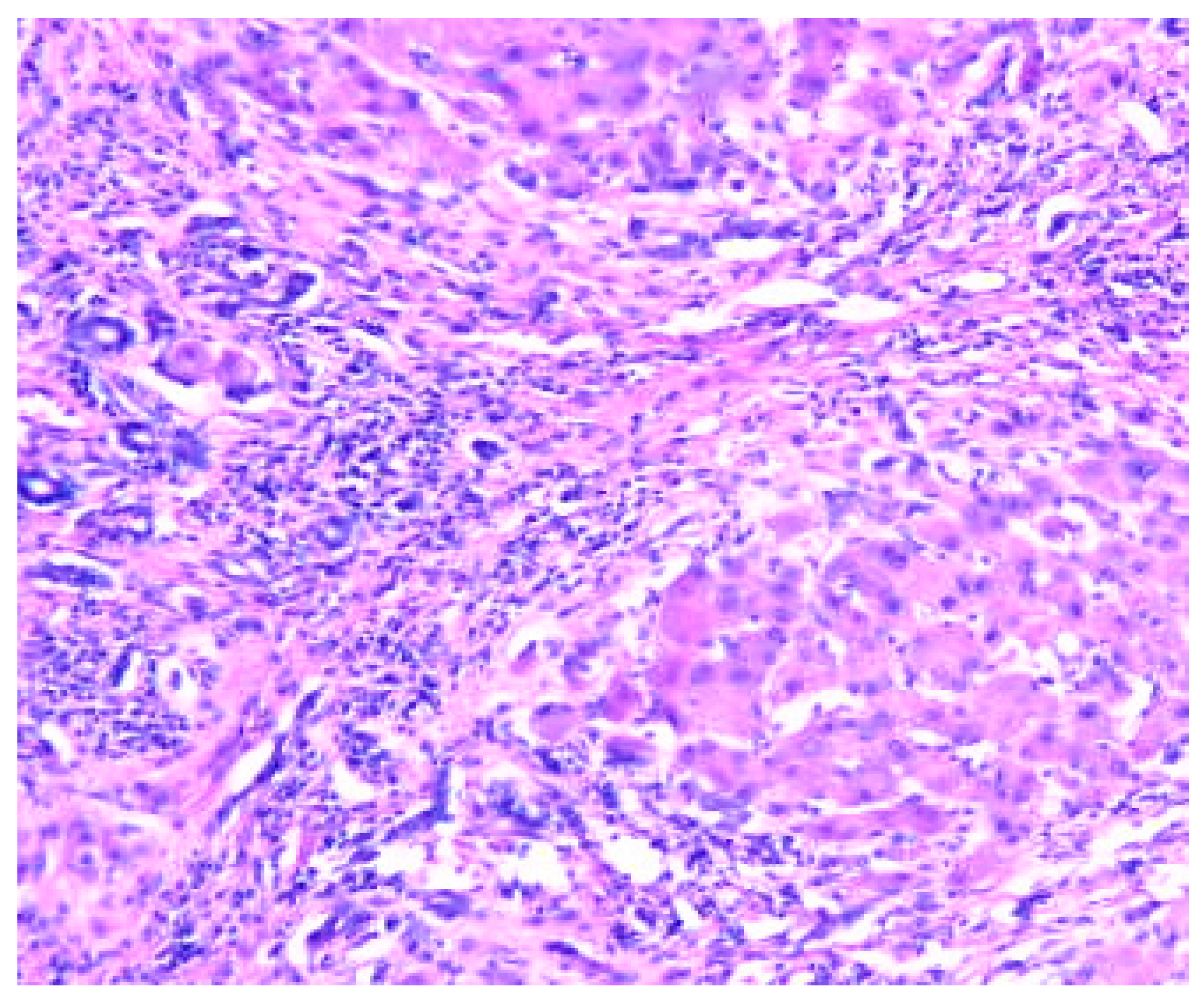

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



