4.1. Stakeholders’ View on Living Culture Festival, Circular Economy and Smart Tourism Village.
Kenderan Village is located in Tegallalang District, Gianyar Regency, Bali Province, has an area of approximately 7.18 km2 and is at an altitude of approximately 600 meters above sea level. Kenderan Village has superior village potential in the form of Artificial Resource Potential which includes agriculture, cultural arts, tourism, and economy. During the management of the tourism sector, there have been several problems, namely, the physical condition of village resources, the seasonal calendar, and local village institutional problems. Based on the problems, potential challenges and limitations faced by Kenderan Village, a vision for Kenderan Village Development for 2015-2020 was established, namely “The realization of a Prosperous, Just and Prosperous Kenderan Village Community Based on Agriculture Imbued with Tri Hita Karana”.
Table 6.
FGD Results.
| Stake Holders |
Expert Opinion |
Focus |
| Head of Rural Area Empowerment, Department of PMD Gianyar |
To support Kenderan village, the local residential government will provide policy and budget especially for managing waste, improving people’s welfare, and facilitate SME business growth |
Supporting tourism village |
| Secretary of Cooperative Office |
Support event that can activate local participation in SME business and propose idea that Temple can become the hub for local community’s activities |
Use temple to support local business and SMEs |
| Digital Ambassador of Gianyar Region |
Provide digital access for community business and coordination |
Digital accessibility |
| Religious Leader |
The potential for Temple to become agent of change, center of religious life, economic, socio-cultural and conservation activities, as well as piloting program for Smart and Circular Economy based Tourism Village development. |
Improve the role of temple in community’s daily productive lives |
| Village Leader |
Tourism villages build excellence/uniqueness in order to win the competition |
Focus on economic and welfare gain from tourism or creative industry |
| Tourism Group Leader |
Tri Hita Karana philosophy, circular economy and living culture festival as means for tourist village differentiation |
Local wisdom and events for developing thematic tourism |
| Environmentalist |
The people lack of sustainable awareness and practices. Free plastic usage and sustainable practice campaign at Tegalalang. During pandemic working together with donators/local phylantrophists hold exchange 1 kg of waste with 1 kg of rice. |
Sustainable awareness for destination preservation |
| Tourism Business Group Leader |
Local wisdom, local produce, creativity (tourism packages also integrated local businesses are urgently required) |
Local business enhancement |
| Creative Industry Leader |
Implement more sustainable products by implementing planning one tree for every use of one log. |
Sustainable practice to increase business |
| Village owned enterprises (BUMDES) |
Utilizing local festivals as means to activate, promote, and improve informal economy and SMEs |
Improve business and local welfare. |
Based on information from
Table 5 above, Kenderan Village has already realized the role of tourism sector for their welfare and that their religion, unique culture and way of life could become their valuable tourism resource. The locals also believe that their religious activities can be designed into creative festivals that shows their living traditions and become calendar of events that will attract international tourists to their villages as the festival still showing the genuine tradition.
While community leaders have realized the importance of conserving the nature and managing waste by promoting several conservation activities such as exchange the household waste into rice as certain group collected donation during covid-19 as well as supported by their philosophy of Tri Hita Karana which means respect three pillars of life, the relationship with Gods, humankind, and the environment they live in. However, the temple is still becoming the source of offering waste that the locals throw into the creek. Through the FGD, the locals have a strong belief that should Kenderan Village has a big tendency to be able to implement circular economy by making the practice as their village positioning and branding, while making the temple as the agent of change through the religious leader’s cause to change the way the locals manage waste and return to the Balinese philosophy, Tri Hita Karana, especially to respect next generation and their living habitats. Through FGD it is also sought that temple can be the center and the pilot of circular economy implementation, while festival as the lever to communicate and promote their commitments in active sustainable development program in Kenderan Village. Tourism destinations around the world utilize events and festivals as means for economic development and destination marketing by tourism destinations around the world [
70], as well as enhance tourist experience at the destinations [
71], while could also be employed in order to promote sustainability [
72].
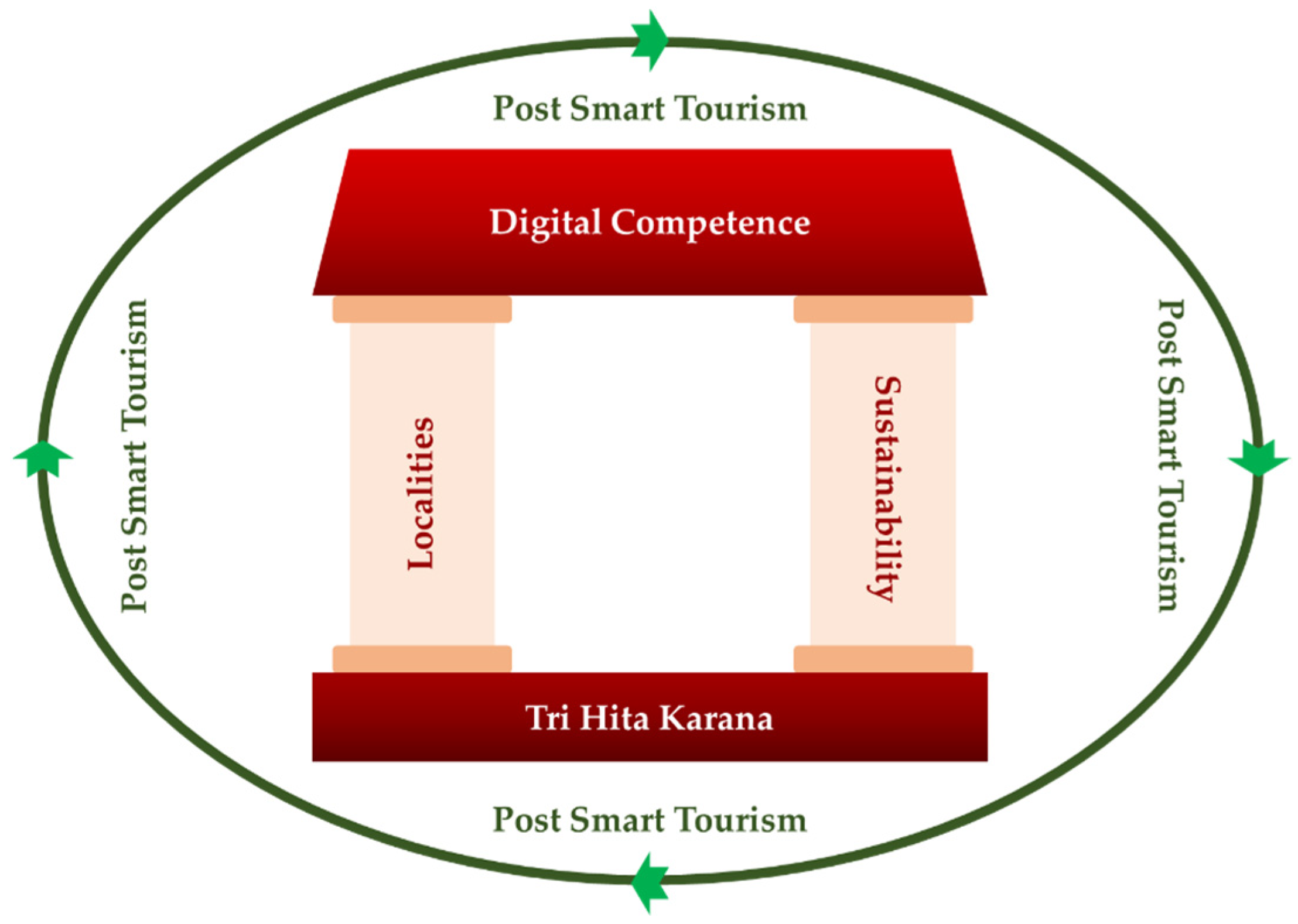
From the FGD data collection, we can identify that in order to be a successful smart tourism village in Kenderan cannot only rely on technology innovation alone but employ technology as enabler or tools to make the tourism village accessible and co create experience. To create smart tourism village, Kenderan Village should identify local context, in this context Tri Hita Karana, which also comply with the value of sustainable practice represented by BE.
Figure 3.
Qualitative Model of Post Smart Tourism Destination for Kenderan Village.
Figure 3.
Qualitative Model of Post Smart Tourism Destination for Kenderan Village.
To ensure the diffusion of idea to the locals, get collective acceptance and support inclusion, Kenderan Village should design their temple as the generator and agent of change, so that tourism village differentiation can be deeply experienced by all human’s senses while technology adoption could become new digital accessibility for tourists and all stakeholders to co-create the demanded experience. This concept is relevant with the ideas that developing sustainable tourism destination including its spatial planning, especially rural tourism, should be based on each destination’s unique attraction resources and local wisdom [
73,
74] while technology supports tourism value chain ecosystem [
27,
75,
76,
77].
To make Kenderan Village an inclusive and innovative tourism destination, several steps need to be taken into consideration, including efforts to form a team that has a variety of skills and expertise needed to plan and implement the transformation of Kenderan Village. Next, it is necessary to carry out a feasibility study to determine the potential and needs of the village and create a strategic plan that includes short-term and long-term goals, as well as how to achieve them. Involvement of local communities, regional government, business actors and other related parties in the planning and decision-making process is needed for village development. Ensure that infrastructure and services in the village meet the needs of all types of visitors including those with physical limitations including accessibility, disability-friendly accommodation and training programs for local communities. It is important to provide training and support for local communities in adopting technology including the use of smartphones, online booking platforms and other digital tools that will enable them to engage in the digital tourism industry. Utilize social media, websites and online booking platforms to market Kenderan Village and ensure information about attractions, accommodation and activities is available online. Consider engaging in activities that allow tourists to interact with local communities and understand their culture including craft workshops, lectures on local history, or other cultural events. With these steps, Kenderan Village has a great opportunity to become an agent of change that integrates tourist village differentiation with technology adoption, creating a unique and inclusive tourism destination.
4.2. Quantitative Analysis
The level of absolute fit with RMSEA of this research model shows <0.05 indicating the level of fit of the model in the excellent category. Goodness of Fit Indices (GFI) and Adjusted Goodness of Fit Ind ex (AGFI) > 0.80, and Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) and RMR values are smaller than 0.05, so it can be concluded that the research model is in accordance with empirical conditions. The Chi-Square value of this study with degrees of freedom with p value> 0.05, according to the Chi-Square index, the fit of this research model is very good [
69]. The measurement model explains the relationship between each construct and the indicators where the values are used to test validity and reliability. This analysis can be explained by the value of discriminant validity, loading factor, construct validity and composite reliability. Construct validity is explained by the factor loading value. Composite reliability and Cronbach Alpha are used to see the reliability or level of reliability of dimensions in measuring research variables. Analysis of the relationship between indicator variables and their latent variables is referred to as the measurement equation which is displayed as follows.
The table above shows the results of first order construct measurement for variables with factor loading (λ) > 0.50 with prob < 0.05, meaning that the indicator has good enough validity to explain the latent construct [
78]. The results show that six variables have valid dimensions and indicators with count> t table at α = 0.05. The Construct Reliability (CR) value shows that all dimensions and indicators have a fairly high consistency with a value > 0.7. Discriminant validity is explained by the square root value of average variance extracted (AVE). The recommended value is above 0.5. and the results show that the AVE> 0.5. So in general that the indicators and dimensions reflect all latent variables. The t statistics for hypothesis testing on the operational variables shows that all antecedent variables, namely digital competence, circular economy and creative events significantly affect the independent variable, post smart tourism consecutively 0.044; 0.270, and 0.300 as seen in
Table 8 below.
Table 7.
Measurement Model Testing Results.
Table 7.
Measurement Model Testing Results.
| Variable |
Indicators |
Code |
Standardized Loading (l) |
t |
Prob. |
Construct Reliability (CR) |
Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
| Creative Events |
Tangible Environment |
CE1 |
0,87 |
9,60 |
0,000 |
0,96 |
0,78 |
| Social Cohesion |
CE2 |
0,9 |
9,98 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Innovative Novel Concept |
CE3 |
0,89 |
9,78 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Sense of Professionalism |
CE4 |
0,88 |
9,73 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Local Wisdom Content |
CE5 |
0,89 |
9,85 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Special Performance |
CE6 |
0,87 |
9,62 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Tourism Circular Economy |
Preservation of Resources |
TCE1 |
0,69 |
- |
- |
0,93 |
0,73 |
| Green Technology Adoption |
TCE2 |
0,89 |
6,03 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Environmental Stewardship |
TCE3 |
0,78 |
5,6 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Waste Management |
TCE4 |
0,94 |
6,16 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Sustainable Environment |
TCE5 |
0,95 |
6,19 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Digital Competence |
Information Handling |
DC1 |
0,89 |
- |
- |
0,95 |
0,81 |
| Social Networking |
DC2 |
0,89 |
7,30 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Content Creation |
DC3 |
0,92 |
7,48 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Safety Concern |
DC4 |
0,91 |
7,45 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Post Smart Tourism |
Digital Experience |
Smart1 |
0,82 |
- |
- |
0,93 |
0,74 |
| Smart Business Ecosystem |
Smart2 |
0,88 |
7,20 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Technological Infrastructure |
Smart3 |
0,87 |
7,15 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Interactive Communication |
Smart4 |
0,85 |
7,04 |
0,000 |
|
|
| Real Time Information |
Smart5 |
0,87 |
7,18 |
0,000 |
|
|
Table 8.
Hypothesis Testing.
Table 8.
Hypothesis Testing.
| No |
Hypothesis |
Coeff. Estimate |
Standard error |
t-stat |
Prob. |
R2 |
| 1 |
Digital Competence → Post Smart Tourism |
0,440* |
0,120 |
3,800 |
0,000 |
0,194 |
| 2 |
Tourism Circular Economy → Post Smart Tourism |
0,270* |
0,110 |
2,390 |
0,018 |
0,073 |
| 3 |
Creative Events → Post Smart Tourism |
0,300* |
0,130 |
2,240 |
0,026 |
0,090 |
| 4 |
Creative Events → Digital Competence |
0,660* |
0,095 |
6,930 |
0,000 |
0,436 |
| 5 |
Creative Events → Tourism Circular Economy |
0,690* |
0,120 |
5,900 |
0,000 |
0,476 |
| 6 |
Creative Events → Tourism Circular Economy → Post Smart Tourism |
0,186** |
0,083 |
2,257 |
0,025 |
0,186 |
| 7 |
Creative Events → Digital Competence → Post Smart Tourism |
0,290** |
0,090 |
3,243 |
0,001 |
0,290 |
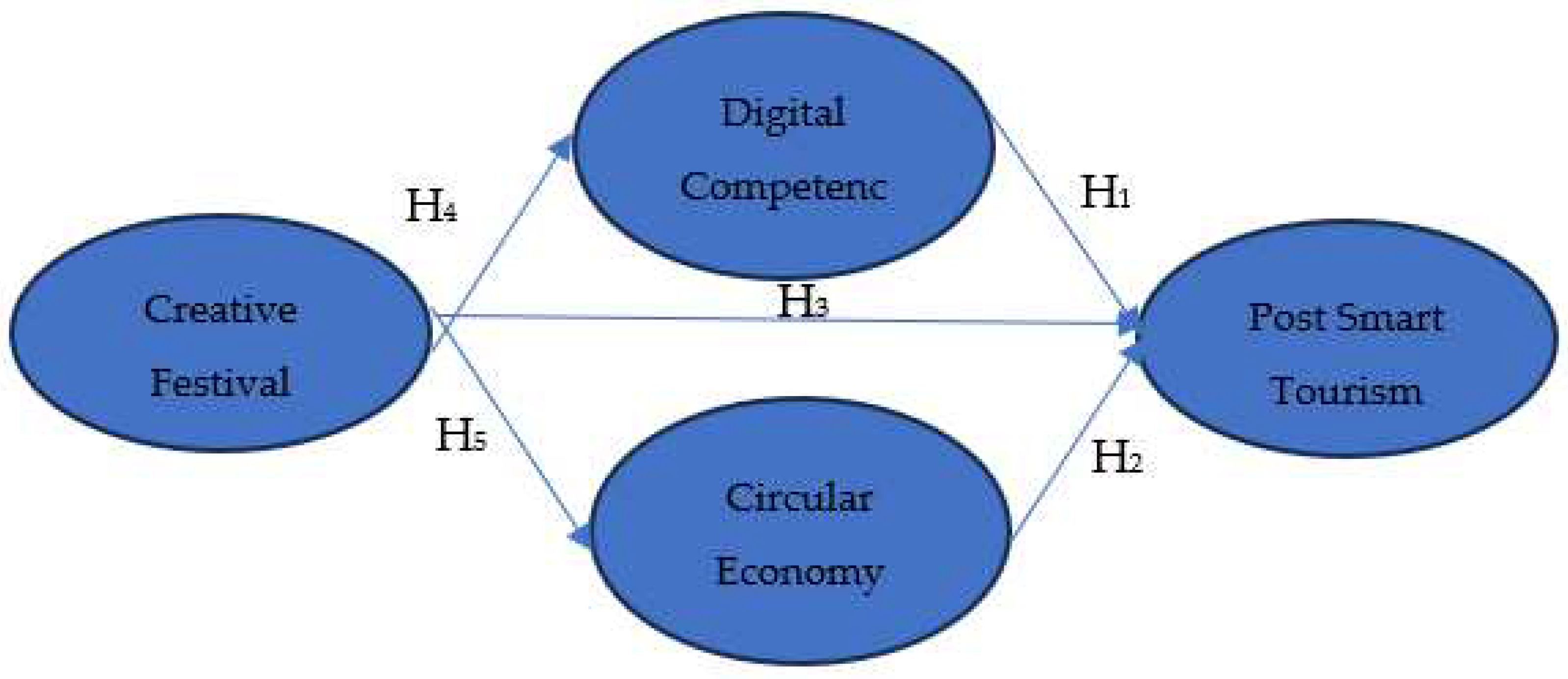
Each hypothesis testing explanation as follows. Hypothesis 1 (H1), digital competence has a significant effect on post smart tourism. Digital competency has a direct coefficient of 0.440 and significant on Post Smart Tourism with prob. 0.000 <α (0.05), so hypothesis 1 is accepted. Digital competency has a positive effect on post smart tourism with an estimated value of 0.440, meaning that if digital competency increases by one unit, then post smart tourism also increases by 44%. The R2 value of 0.194 means that post smart tourism is influenced by digital competency by 19.4%, the rest is influenced by other variables.
Hypothesis 2 (H2), tourism circular economy has a significant effect on post smart tourism. Tourism circular economy has a direct coefficient of 0.270 and significant on post smart tourism with prob. 0.018 <α (0.05), so hypothesis 2 is accepted. Tourism circular economy has a positive effect on post smart tourism with an estimated value of 0.270, meaning that if circular economy increases by one unit, then post smart tourism also increases by 27%. R2 value of 0.073 means that post smart tourism is influenced by tourism circular economy by 7.3%, the rest is influenced by other variables.
Hypothesis 3 (H3) Creative event has a significant effect on post smart tourism destination. Creative event has a direct coefficient of 0.300 and significant on post smart tourism destination with prob. 0.026 <α (0.05), so hypothesis 3 is accepted. Creative event has a positive effect on post smart tourism with an estimated value of 0.300, meaning that if creative event increases by one unit, then post smart tourism destination also increases by 30%. The R2 value of 0.090 means that post smart tourism is influenced by creative event by 9%, the rest is influenced by other variables.
Hypothesis 4 (H4), creative event has a significant effect on digital competence. Creative event has a direct coefficient of 0.660 and significant on digital competency with prob. 0.000 <α (0.05), so hypothesis 4 is accepted. Creative event has a positive effect on digital competency with an estimated value of 0.660, meaning that if creative event increases by one unit, then digital competency also increases by 66%. The R2 value of 0.436 means that digital competency is influenced by creative event by 43.6%, the rest is influenced by other variables.
Hypothesis 5 (H5), creative event has a significant effect on tourism circular economy. Creative event has a direct coefficient of 0.690 and significant on tourism circular economy with prob 0.000 <α (0.05), so hypothesis 5 is accepted. Creative event has a positive effect on tourism circular economy with an estimated value of 0.69, meaning that if creative event increases by one unit, then tourism circular economy also increases by 69%. R2 value of 0.476 means that tourism circular economy is influenced by creative event by 47%, the rest is influenced by other variables.
Based on the hypothesis test above, it can be concluded that the direct influence can be felt if a tourist village has a creative event, it will have a direct impact on 3 variables, namely tourism circular economy, smart tourism and digital competency. For significant influence there are tourism circular economy and digital competency variables where the percentage of influence of each variable reaches 69% and 66%. While the influence on the post smart tourism variable is only 30%. Mediating effects of tourism circular economy and digital competence to post smart tourism. Creative event has an indirect coefficient of 0.186 and significant to smart tourism through tourism circular economy with prob. 0.025 < α (0.05). Based on the sobel test conducted, the t statistic is 2.257, meaning that tourism circular economy can mediate the effect of creative event on smart tourism because 2.257> 1.98 (t table) with an indirect effect of 18.6%. Creative event has an indirect coefficient of 0.290 and significant to smart tourism through digital competency with prob. 0.001 < α (0.05). Based on the sobel test conducted, a t statistic of 3.243 was obtained, meaning that digital competency can mediate the effect of creative event on smart tourism because 3.243> 1.98 (t table) with an indirect effect of 29%.
After knowing the direct effect and indirect effect, the total effect is described as follows. Total effect (influence and indirect) of creative events on post smart tourism through tourism circular economy: 0,300 + 0.186 = 0,486—48,6%. Total effect (influence and indirect) of creative events on post smart tourism through digital competency: 0,300 + 0,290 = 0,590—59%. Based on the analysis of direct and indirect impacts, digital competence has the greatest impact on post smart tourism. Where digital competence also has an influence on the implementation of creative events and tourism circular economy. In the 4 indicators owned by digital competence (information handling skills, social networking capability, content creation skills, and safety concern), content creation skills have the greatest relationship of 0.92 or 92% to the organization of creative events, tourism circular economy and post smart tourism.
Figure 4.
Structural Model Analysis.
Figure 4.
Structural Model Analysis.
4.3. Post-Smart Tourism Village Model
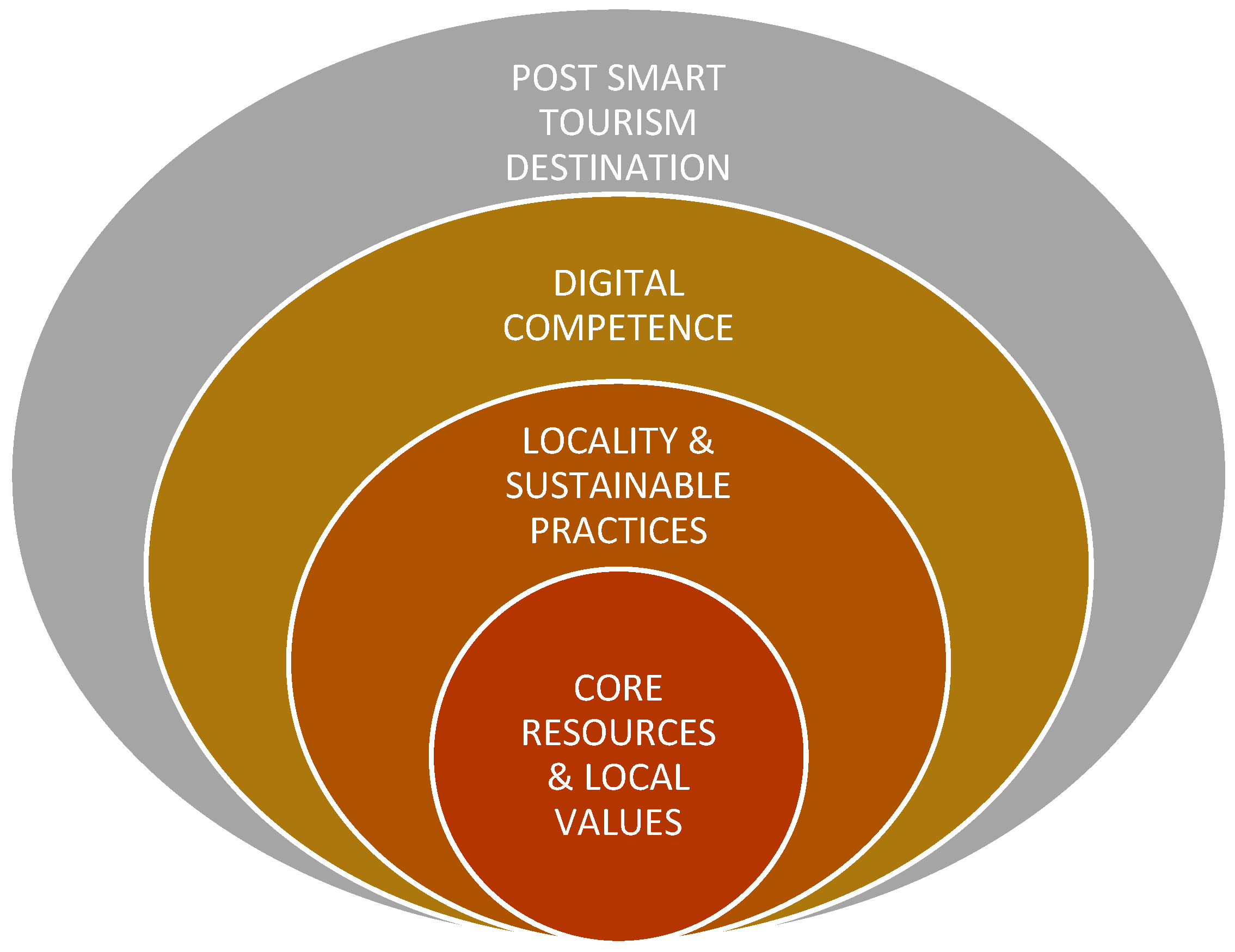
The triangulation of qualitative and quantitative research shows that the tourism core resources and destination’s components become the most important factors to be explored and developed with the local value, the uniqueness and differentiation aspects of the post smart tourism model, that locality aspects and sustainability practice are used in order to ensure the development of competitive and sustainable smart tourism destination model.
Figure 5.
Model Post-Smart Tourism.
Figure 5.
Model Post-Smart Tourism.
The model proposed is quite similar to the model proposed by Coca-Stefaniak [
13] regarding post smart tourism. In Kenderan, the local value, the spiritual ideology Tri Hita Karana would strengthen the application of sustainable development, as it proposes a balance between God, man and nature, while digital competence will become enabler to make the destination accessible for tourists as well able to encourage stakeholder co create experience. The existence of creative events can invite various parties or new stakeholders to help accelerate and activate tourist villages not only to create smart tourism destination but also encourage the implementation of digitalization and circular economy that will form an ecosystem whose implementation considers natural, human and social capital as essential components for developing sustainable local and planet friendly destinations. Kenderan Living Culture Festival 2022 is an example of creative event organized by involving various groups, seen from the participants who contribute through Village UMKM stands that show agricultural products, carving products; local arts and cultural performances; gathering of environmental communities, academics, local village governments and other villages. If Kenderan Tourism Village can be persistent, then a resilient and sustainable Circular Economy Ecosystem can be realized. However, (CE360 Alliance, 2020) also mentioned that the process of transforming into a village that carries CE is an iterative project that needs to be supported starting from the trial and error process, then continuing to develop and strive for continuous improvement. To be successful, any changes made must consider the business context, external trends, desired market position, target customers, core capabilities, strengths and weaknesses of the village. In line with the definition of circular economy (CE) according to (CE360 Alliance, 2020) which is a deliberately designed socio-economic system inspired by natural systems, regenerative human and natural capital that works long term for all stakeholders. The high influence of creative events is due to external trends, namely the demand from today’s travelers who have a lot of interest in tranquility, comfort and meaningful travel. Revealed by (CE360 Alliance, 2020) that today’s travelers want to experience life like a local of the tourist attractions they visit, tend to look for the characteristics or uniqueness of the place, take a trip that is transformative, participatory and has a specific purpose such as Melukat spiritual tourism which boomed during the pandemic, etc. When connected to smart tourism and digital competency, it is related to the self-existence of millennial and gen Z tourists. Which, this generation of tourists prefers trips that can and have the aim of “Showing/showing off” to their peers or followers on social media so that access to information on a tourist attraction or the aesthetics and appearance of a tourist attraction that is “instagrammable” and can be “tagged” in its location is needed especially if it can be manifested through an attractive Event. As the village also promote its local values and locality aspects, then the tourist village will be able to gain its competitive advantage more sustainable as locality is the most valuable, rare, inimitable and hard to be substitute as the main exploration in placemaking of tourist destination.
To ensure the support and active participation of the event, Kenderan Village can encourage temple to take active role not only as center of community activities and venue but also as an agent to encourage community to empower themselves in cultural preservation and implement the philosophy of Tri Hita Karana in daily local people’s lives but also diffused the circular economy innovation including the initial use of renewable energy. The dominance of the influence of creative events is also accompanied by other demand trends mentioned by (CE360 Alliance, 2020), namely the increase in domestic travel interest after covid-19 due to the discovery of local attractions and local culture in less crowded destinations. This increases the pride of travelers who can enjoy local attractions and culture in a more private and discreet manner. Therefore, creative events also need to consider targeting tourists who are not only for large audiences, but also those who prefer privacy, where these people are usually willing to pay more.