Submitted:
15 December 2023
Posted:
18 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
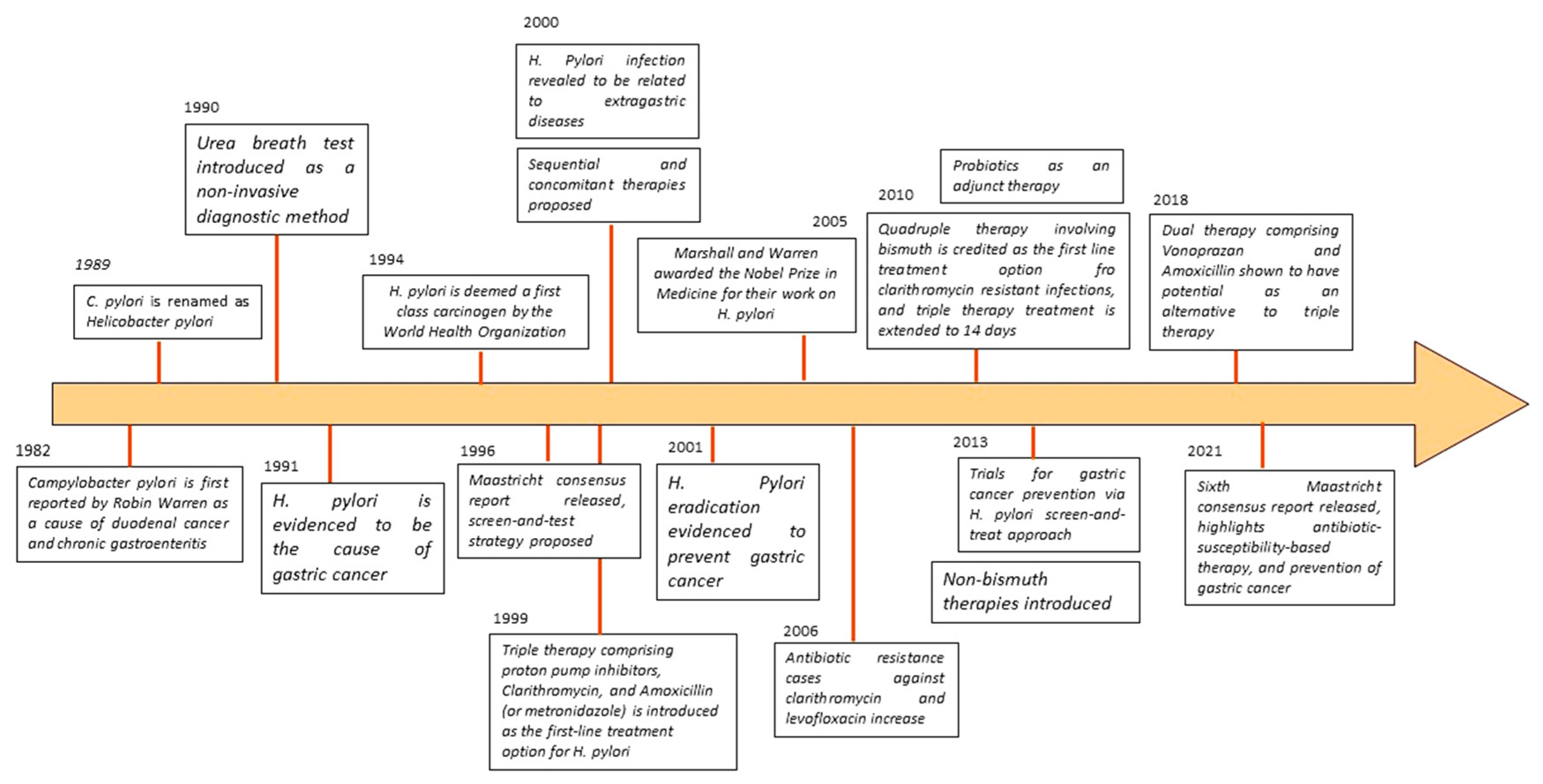
1. Introduction
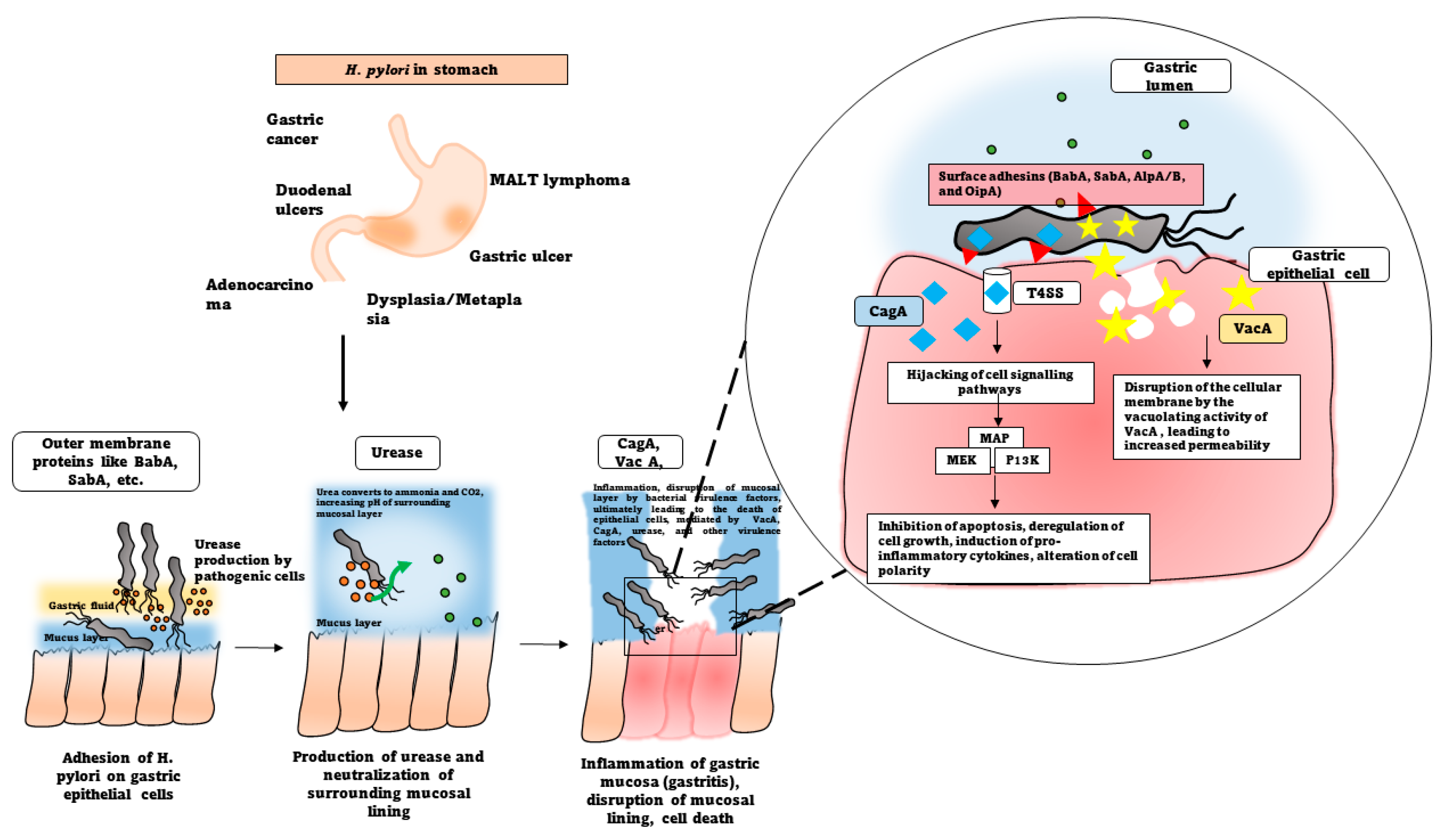
2. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori
2.1. Molecular Mechanisms of Infection
2.1.1. Attachment and Colonisation
2.1.2. Production of virulence factors
2.1.3. CagA and VacA
2.1.4. Urease production
2.2. Immune system modulation and induction of inflammatory responses
2.3. Modulation of Mucin Production
3. Disease Associations
4. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori Infections
4.1. Non-invasive tests
4.1.1. Serological Assays
4.1.2. Urea Breath Test (UBT)
4.1.3. Stool Antigen Test (SAT)
4.2. Invasive tests
4.2.1. Histology
4.2.2. Culture examinations
| Diagnostic test | Sensitivity | Specificity | Advantages/Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urea breath test (UBT) | >95% | >95% |
Advantages: Gold standard in many clinical diagnoses, Cost-effective, reliable, simple, non-invasive, can be used for confirming eradication of infection Disadvantages: May give false negatives in presence of other urease producing bacteria and Helicobacter species. Low accuracy under conditions of gastritis and gastric malignancies, requires a high load of bacteria in the specimen. Requires expensive equipment. |
[96, 83] |
| Stool Antigen test (SAT) | 96% | 97% |
Advantages: Cost-effective, simple, rapid, doesn’t require expensive instruments Disadvantages: It may give false negatives under low bacterial count, and accuracy is affected by recent intake of PPI and CAM, not useful for post-eradication confirmation |
[87, 86] |
| Serological tests | 85% | >80% |
Advantages: Inexpensive, can be employed for patients who have recently undergone triple therapy. Only test not affected by PPI intake or use of antibiotics Disadvantages: Unreliable for ongoing infections, cannot be used to confirm eradication |
[74] |
| Rapid urease test (RUT) | 80-90% | 93-100%. |
Advantages: Rapid, inexpensive, simple Disadvantages: Invasive, requires additional confirmatory tests, accuracy affected by intake of PPI and antibiotics |
[45] |
| Culture | 70-90% | 100% |
Advantages: Gold standard for confirmation, can be used to ascertain antibiotic sensitivity Disadvantages: Elaborate, time-consuming, expensive, requires specific expertise in microbiology |
[97] |
| Histopathology | >95% | 99% | Advantages: Gold standard in routine clinical diagnostics, provides additional information about associated pathologies, extremely sensitive and specific | [88] |
| Molecular methods (PCR) | 96% | 98% |
Sensitive even at very low bacterial counts Disadvantages: Expensive, requires sophisticated equpiments, may give false positive results |
[75] |
4.2.3. Molecular and Genetic Markers
5. Treatment Strategies
5.1. Antibiotic therapy and selection of antibiotics
5.2. Proton pump inhibitors
5.3. The rising issue of Antibiotic Resistance
6. Future Directions
6.1. Challenges and Opportunities
6.2. Advancements in Research
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Warren, J.R.; Marshall, B. Unidentified Curved Bacilli on Gastric Epithelium in Active Chronic Gastritis. Lancet 1983, 1, 1273–1275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krienitz, W. Ueber Das Auftreten von Spirochäten Verschiedener Form Im Mageninhalt Bei Carcinoma Ventriculi. DMW - Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 1906, 32, 872–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroblewski, L.E.; Peek, R.M.; Wilson, K.T. Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Cancer: Factors That Modulate Disease Risk. Clin Microbiol Rev 2010, 23, 713–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Moayyedi, P. Helicobacter pylori Infection in Functional Dyspepsia. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013, 10, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, I.W. Helicobacter pylori Infection: When Should It Be Treated? In Current Trends and Concerns in Infectious Diseases; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 81–102. ISBN 978-3-030-36966-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gravina, A.G.; Zagari, R.M.; De Musis, C.; Romano, L.; Loguercio, C.; Romano, M. Helicobacter pylori and Extragastric Diseases: A Review. World J Gastroenterol 2018, 24, 3204–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection - The Maastricht IV/ Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2012, 61, 646–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer.; World Health Organization. Schistosomes, Liver Flukes and Helicobacter pylori.; IARC, 1994; ISBN 9283212614.
- Farinha, P.; Gascoyne, R.D. Helicobacter pylori and MALT Lymphoma. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1579–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Belayneh, Y.M. Helicobacter pylori and Duodenal Ulcer: Systematic Review of Controversies in Causation. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 2019, 12, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Aldubaib, M.; Abalkhail, A.; Anagreyyah, S.; Anajirih, N.; Almuzaini, A.M.; Rawway, M.; Alfadhel, A.; Draz, A.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Infection: Current Status and Future Prospects on Diagnostic, Therapeutic and Control Challenges. Antibiotics 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikaru, H.; A, E.K.; L, M.A.; M, O.K.; H, M.M.; Eitaro, A. Helicobacter pylori Uses the TlpB Receptor To Sense Sites of Gastric Injury. Infect Immun 2019, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H. Role of Flagella in the Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori. Curr Microbiol 2017, 74, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Kamiya, S. Biofilm Formation by Helicobacter pylori and Its Involvement for Antibiotic Resistance. Biomed Res Int 2015, 2015, 914791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, N.R.; Hartung, M.L.; Müller, A. Life in the Human Stomach: Persistence Strategies of the Bacterial Pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nat Rev Microbiol 2013, 11, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, V.E. Helicobacter pylori and Its Role in Gastric Cancer. Microorganisms 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backert, S.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Fischer, W. Composition, Structure and Function of the Helicobacter pylori Cag Pathogenicity Island Encoded Type IV Secretion System. Future Microbiol 2015, 10, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HATAKEYAMA, M. Structure and Function of Helicobacter pylori CagA, the First-Identified Bacterial Protein Involved in Human Cancer. Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Series B 2017, 93, 196–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, X.; Tang, B.; Li, B.-S.; Xie, R.; Hu, C.-J.; Luo, G.; Qin, Y.; Dong, H.; Yang, S.-M. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factor CagA Promotes Tumorigenesis of Gastric Cancer via Multiple Signaling Pathways. Cell Communication and Signaling 2015, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusters, J.G.; van Vliet, A.H.M.; Kuipers, E.J. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 2006, 19, 449–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, S.; Mentis, A.F. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Helicobacter 2007, 12, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, B.; Lo Sardo, F.; Scalera, S.; Memeo, L.; Colarossi, C.; Mare, M.; Blandino, G.; Ciliberto, G.; Maugeri-Saccà, M.; Bon, G. Hippo Pathway Dysregulation in Gastric Cancer: From Helicobacter pylori Infection to Tumor Promotion and Progression. Cell Death Dis 2023, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cover, T.L.; Blanke, S.R. Helicobacter pylori VacA, a Paradigm for Toxin Multifunctionality. Nat Rev Microbiol 2005, 3, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foegeding, N.J.; Caston, R.R.; McClain, M.S.; Ohi, M.D.; Cover, T.L. An Overview of Helicobacter pylori VacA Toxin Biology. Toxins (Basel) 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, N.; Tay, A.C.Y.; Marshall, B.J.; Jain, U. Helicobacter pylori VacA, a Distinct Toxin Exerts Diverse Functionalities in Numerous Cells: An Overview. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincă, A.L.; Meliț, L.E.; Mărginean, C.O. Old and New Aspects of H. pylori-Associated Inflammation and Gastric Cancer. Children 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Hu, B. Immunological Perspective: Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastritis. Mediators Inflamm 2022, 2022, 2944156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.; Greenfield, L.K.; Bronte-Tinkew, D.; Capurro, M.I.; Rizzuti, D.; Jones, N.L. VacA Promotes CagA Accumulation in Gastric Epithelial Cells during Helicobacter pylori Infection. Sci Rep 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venerito, M.; Krieger, T.; Ecker, T.; Leandro, G.; Malfertheiner, P. Meta-Analysis of Bismuth Quadruple Therapy versus Clarithromycin Triple Therapy for Empiric Primary Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Digestion 2013, 88, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y. Mechanisms of Disease: Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010, 7, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, N.-C.; Oh, S.-T.; Sung, J.Y.; Cha, K.A.; Lee, M.H.; Oh, B.-H. Supramolecular Assembly and Acid Resistance of Helicobacter pylori Urease. Nat Struct Biol 2001, 8, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, H.L.; Mendz, G.L.; Hazell, S.L. Helicobacter pylori: Physiology and Genetics; 2001; ISBN 1555812139.
- Malfertheiner, P.; Camargo, M.C.; El-Omar, E.; Liou, J.-M.; Peek, R.; Schulz, C.; Smith, S.I.; Suerbaum, S. Helicobacter pylori Infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idowu, S.; Bertrand, P.P.; Walduck, A.K. Gastric Organoids: Advancing the Study of H. pylori Pathogenesis and Inflammation. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.-Y.; Sheu, B.-S.; Wu, J.-J. Helicobacter pylori Infection: An Overview of Bacterial Virulence Factors and Pathogenesis. Biomed J 2016, 39, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.R.; Winter, J.A.; Robinson, K. Differential Inflammatory Response to Helicobacter pylori Infection: Etiology and Clinical Outcomes. J Inflamm Res 2015, 8, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Elios, M.M.; Amedei, A.; Cappon, A.; Del Prete, G.; de Bernard, M. The Neutrophil-Activating Protein of Helicobacter pylori (HP-NAP) as an Immune Modulating Agent. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2007, 50, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeyaullah, Md.; AlShahrani, A.M.; Ahmad, I. Association of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Host Cytokine Gene Polymorphism with Gastric Cancer. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021, 2021, 8810620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.; Ceponis, P.J.M.; Lebel, S.; Huynh, H.; Sherman, P.M. Helicobacter pylori Activates Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression in Gastrointestinal Epithelial Cells. Infect Immun 2003, 71, 3496–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larussa, T.; Leone, I.; Suraci, E.; Imeneo, M.; Luzza, F. Helicobacter pylori and T Helper Cells: Mechanisms of Immune Escape and Tolerance. J Immunol Res 2015, 2015, 981328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, M.P.; D’Elios, M.M. Cytotoxic T Cells in H. pylori-Related Gastric Autoimmunity and Gastric Lymphoma. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010, 2010, 104918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes Victor, E. and Peniche, A.G. Helicobacter pylori Deregulates T and B Cell Signaling to Trigger Immune Evasion. In Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation: Induction, Resolution and Escape by Helicobacter pylori; Backert, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; pp. 229–265. ISBN 978-3-030-15138-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Patel, G.K.; Ghoshal, U.C. Helicobacter pylori-Induced Inflammation: Possible Factors Modulating the Risk of Gastric Cancer. Pathogens 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, T.J.; Scott, K.E.; Fox, J.G.; Hagen, S.J. Tight Junction Disruption: Helicobacter pylori and Dysregulation of the Gastric Mucosal Barrier. World J Gastroenterol 2015, 21, 11411–11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.Y.; Miftahussurur, M.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori as an Oncogenic Pathogen, Revisited. Expert Rev Mol Med 2017, 19, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wroblewski, L.E.; Peek, R.M.; Wilson, K.T. Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Cancer: Factors That Modulate Disease Risk. Clin Microbiol Rev 2010, 23, 713–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, P.; Valenzuela Valderrama, M.; Bravo, J.; Quest, A.F.G. Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Cancer: Adaptive Cellular Mechanisms Involved in Disease Progression. Front Microbiol 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoog, E.; Göteborgs universitet. Helicobacter Spp. Interactions with Mucins : Adhesion and Mucin Regulation of Pathogen Proliferation and Gene Expression; Department of Medical Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Institute of Biomedicine, Sahlgrenska Academy at University of Gothenburg, 2014; ISBN 9789162888718.
- Nazanin, N.; V, J.M.E.; Sukanya, R.; K, L.S. Helicobacter pylori Infection Impairs the Mucin Production Rate and Turnover in the Murine Gastric Mucosa. Infect Immun 2013, 81, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padra Médea and Benktander, J. and Benktander, J. and R.K. and L.S.K. Carbohydrate-Dependent and Antimicrobial Peptide Defence Mechanisms Against Helicobacter pylori Infections. In Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation: Induction, Resolution and Escape by Helicobacter pylori; Backert, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; ISBN 978-3-030-15138-6. [Google Scholar]
- Fock, K.M. Review Article: The Epidemiology and Prevention of Gastric Cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014, 40, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Cao, H.; Zhang, L.-H.; Xu, Z. Harnessing the CRISPR-Cas Systems to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance. Front Microbiol 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eusebi, L.H.; Zagari, R.M.; Bazzoli, F. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayali, S.; Manfredi, M.; Gaiani, F.; Bianchi, L.; Bizzarri, B.; Leandro, G.; Di Mario, F.; De’angelis, G.L. Helicobacter pylori, Transmission Routes and Recurrence of Infection: State of the Art. Acta Biomedica 2018, 89, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, S.F. The Clinical Evidence Linking <em>Helicobacter pylori</Em> to Gastric Cancer. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017, 3, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipponen, P.; Hyvärinen, H. Role of Helicobacter pylori in the Pathogenesis of Gastritis, Peptic Ulcer and Gastric Cancer. Scand J Gastroenterol 1993, 28, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zullo, A.; Hassan, C.; De Francesco, V.; Repici, A.; Manta, R.; Tomao, S.; Annibale, B.; Vaira, D. Helicobacter pylori and Functional Dyspepsia: An Unsolved Issue? World J Gastroenterol 2014, 8957–8963. [Google Scholar]
- Moayyedi P, S.S.D.J.J.D.B.H.A.I.M.O.R.W.S.R.A.B.C.; Forman, D. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori for Non-ulcer Dyspepsia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, D.; Bebb, J. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Peptic Ulcers. Medicine 2019, 47, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, M.; Reddy, K.M.; Marsicano, E. Peptic Ulcer Disease and Helicobacter pylori Infection. Mo Med 2018, 115, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ferro, A.; Peleteiro, B.; Malvezzi, M.; Bosetti, C.; Bertuccio, P.; Levi, F.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C.; Lunet, N. Worldwide Trends in Gastric Cancer Mortality (1980–2011), with Predictions to 2015, and Incidence by Subtype. Eur J Cancer 2014, 50, 1330–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatoon, J.; Rai, R.P.; Prasad, K.N. Role of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Cancer: Updates. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2016, 8, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégraud, F.; Bessède, E.; Varon, C. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastric Carcinoma. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2015, 21, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.G. Cellular and Molecular Aspects of Gastric Cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2006, 12, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polk, D.B.; Peek, R.M. Helicobacter pylori: Gastric Cancer and Beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 2010, 10, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, P.Y.; Aboul-Soud, M.A.M. From Inflammation to Gastric Cancer: Role of Helicobacter pylori. Oncol Lett 2017, 13, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalali, B.; Formichella, L.; Gerhard, M. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori: Changes towards the Future. Diseases 2015, 3, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, S.M.; Retnakumar, R.J.; Chouhan, D.; Devi, T.N.B.; Dharmaseelan, S.; Devadas, K.; Thapa, N.; Tamang, J.P.; Lamtha, S.C.; Chattopadhyay, S. Helicobacter pylori in Human Stomach: The Inconsistencies in Clinical Outcomes and the Probable Causes. Front Microbiol 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenova, I. Clinical Relevance of Helicobacter pylori Infection. J Clin Med 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chey, W.D.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Howden, C.W.; Moss, S.F. ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology | ACG 2017, 112.
- Shatila, M.; Thomas, A.S. Current and Future Perspectives in the Diagnosis and Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection. J Clin Med 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dore, M.P.; Pes, G.M. What Is New in Helicobacter pylori Diagnosis. An Overview. J Clin Med 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-K. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Current Options and Developments. World J Gastroenterol 2015, 21, 11221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Yamaoka, Y. Diagnostic Methods of Helicobacter pylori Infection for Epidemiological Studies: Critical Importance of Indirect Test Validation. Biomed Res Int 2016, 2016, 4819423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Pratap, C.B.; Jain, A.K.; Gulati, A.K.; Nath, G. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori: What Should Be the Gold Standard? World J Gastroenterol 2014, 20, 12847–12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, T.; Ganji, L. The Diagnostic Tests for Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2019, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Rengifo, D.F.; Mendoza, B.; Jaramillo, C.; Rodríguez-Urrego, P.A.; Vera-Chamorro, J.F.; Alvarez, J.; Delgado, M. del P.; Jimenez-Soto, L.F. Helicobacter pylori Culture as a Key Tool for Diagnosis in Colombia. The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries 2019, 13, 720–726. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Zhu, Y. Effect of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on Gastric Precancerous Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Helicobacter 2023, 28, e13013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbrink, P.; van Doorn, L.J. Serological Methods for Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Monitoring of Eradication Therapy. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 2000, 19, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siavoshi, F.; Saniee, P.; Khalili-Samani, S.; Hosseini, F.; Malakutikhah, F.; Mamivand, M.; Shahreza, S.; Sharifi, A.H. Evaluation of Methods for H. pylori Detection in PPI Consumption Using Culture, Rapid Urease Test and Smear Examination. Ann Transl Med 2015, 3. [CrossRef]
- Skrebinska, S.; Mégraud, F.; Bessède, E. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankararaman, S.; Moosavi, L. Urea Breath Test; 2023.
- Ferwana, M.; Abdulmajeed, I.; Alhajiahmed, A.; Madani, W.; Firwana, B.; Hasan, R.; Altayar, O.; Limburg, P.J.; Murad, M.H.; Knawy, B. Accuracy of Urea Breath Test in Helicobacter pylori Infection: Meta-Analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2015, 21, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowski, D.C.; van Zanten, S.V. Dyspepsia. Can Med Assoc J 2015, 187, 276–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, S.E. Helicobacter pylori Infection. New England Journal of Medicine 2019, 380, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoyama, T. Stool Antigen Tests for the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection. World J Gastroenterol 2013, 19, 8188–8191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, J.P.; de la Morena, F.; Abraira, V. Accuracy of Monoclonal Stool Antigen Test for the Diagnosis of H. pylori Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology | ACG 2006, 101.
- Ricci, C.; Holton, J.; Vaira, D. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori: Invasive and Non-Invasive Tests. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2007, 21, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, L.M.J.; Takwoingi, Y.; Siddique, S.; Selladurai, A.; Gandhi, A.; Low, B.; Yaghoobi, M.; Gurusamy, K.S. Non-Invasive Diagnostic Tests for Helicobacter pylori Infection. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S. Histopathologic Diagnosis of H. pylori Infection and Associated Gastric Diseases. In Helicobacter pylori; Kim, N., Ed.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2016; ISBN 978-981-287-706-2. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, R.; Sagar, M. Comparison of Different Histological Staining Methods for Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Gastric Biopsy. Cureus 2022. [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.F.; Genta, R.M.; Yardley, J.H.; Correa, P.; the Participants in the International Workshop on the Histopathology of Gastritis, H. 1994 Classification and Grading of Gastritis: The Updated Sydney System. Am J Surg Pathol1996; 20.
- Mărginean, C.O.; Meliț, L.E.; Săsăran, M.O. Traditional and Modern Diagnostic Approaches in Diagnosing Pediatric Helicobacter pylori Infection. Children 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zullo, A.; Hassan, C.; Lorenzetti, R.; Winn, S.; Morini, S. A Clinical Practice Viewpoint: To Culture or Not to Culture Helicobacter pylori. Digestive and Liver Disease 2003, 35, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschl, A.M.; Makristathis, A. Methods to Detect Helicobacter pylori: From Culture to Molecular Biology. Helicobacter 2007, 12, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurgalieva, Z.Z.; Conner, M.E.; Opekun, A.R.; Zheng, C.Q.; Elliott, S.N.; Ernst, P.B.; Osato, M.; Estes, M.K.; Graham, D.Y. B-Cell and T-Cell Immune Responses to Experimental Helicobacter pylori Infection in Humans. Infect Immun 2005, 73, 2999–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macin, S.; Alp, A.; Sener, B.; Sokmensuer, C.; Orhan, D.; Ozen, H.; Kav, T.; Akyon, Y. Comparison of Culture, Real- Time-PCR, ELISA, and Histopathological Examination Methods for Identification of Helicobacter pylori. Istanbul Medical Journal 2018, 19, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bénéjat, L.; Ducournau, A.; Lehours, P.; Mégraud, F. Real-Time PCR for Helicobacter pylori Diagnosis. The Best Tools Available. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantuya, B.; El Serag, H.B.; Saruuljavkhlan, B.; Azzaya, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Uchida, T.; Oyuntsetseg, K.; Oyunbileg, N.; Davaadorj, D.; Yamaoka, Y. Advantage of 16S RRNA Amplicon Sequencing in Helicobacter pylori Diagnosis. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, J.P.; González, L.; Calvet, X.; García, N.; López, T.; Roqué, M.; Gabriel, R.; Pajares, J.M. Proton Pump Inhibitor, Clarithromycin and Either Amoxycillin or Nitroimidazole: A Meta-Analysis of Eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000, 14, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokkas, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Malfertheiner, P.; Niv, Y.; Gasbarrini, A.; Leja, M.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.; Graham, D.Y. Comparative Effectiveness of Multiple Different First-Line Treatment Regimens for Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Network Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safavi, M.; Sabourian, R.; Foroumadi, A. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Current and Future Insights. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Gisbert, J.P. Optimizing Clarithromycin-Containing Therapy for Helicobacter pylori in the Era of Antibiotic Resistance. World J Gastroenterol 2014, 20, 10338–10347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.Y.; Fischbach, L. Helicobacter pylori Treatment in the Era of Increasing Antibiotic Resistance. Gut 2010, 59, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyanova, L.; Hadzhiyski, P.; Gergova, R.; Markovska, R. Evolution of Helicobacter pylori Resistance to Antibiotics: A Topic of Increasing Concern. Antibiotics 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y. Antibiotic Treatment for Helicobacter pylori : Is the End Coming? World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2015, 6, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.K.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Yang, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Shin, C.M.; Kim, S.E.; Lim, H.C.; Kim, J.H.; Nam, S.Y.; et al. Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Korea 2020. Gut Liver 2021, 15, 168–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luther, J.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Schoenfeld, P.S.; Moayyedi, P.; Vakil, N.; Chey, W.D. Empiric Quadruple vs. Triple Therapy for Primary Treatment OfHelicobacter pyloriInfection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Efficacy and Tolerability. Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology | ACG 2010, 105.
- Lin, T.F.; Hsu, P.I. Second-Line Rescue Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Where Are We Now? World J Gastroenterol 2018, 24, 4548–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essa, A.S.; Kramer, J.R.; Graham, D.Y.; Treiber, G. Meta-Analysis: Four-Drug, Three-Antibiotic, Non-Bismuth-Containing “Concomitant Therapy” Versus Triple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SACHS, G.; SHIN, J.M.; HOWDEN, C.W. Review Article: The Clinical Pharmacology of Proton Pump Inhibitors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006, 23, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Sachs, G. Pharmacology of Proton Pump Inhibitors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2008, 10, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Kandulski, A.; Venerito, M. Proton-Pump Inhibitors: Understanding the Complications and Risks. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017, 14, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, D.S.; Kim, D.; Peura, D.A. 25 Years of Proton Pump Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Qian, X.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Song, C.; Wu, S.; An, Y.; Yuan, R.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y. The Effect of Antibiotic Resistance on Helicobacter pylori Eradication Efficacy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotti Giuseppe and Cendron, L. Structural Aspects of Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Resistance. In Helicobacter pylori in Human Diseases: Advances in Microbiology, Infectious Diseases and Public Health Volume 11; Kamiya Shigeru and Backert, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; ISBN 978-3-030-21916-1. [Google Scholar]
- Savoldi, A.; Carrara, E.; Graham, D.Y.; Conti, M.; Tacconelli, E. Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance in Helicobacter pylori: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis in World Health Organization Regions. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keikha, M.; Karbalaei, M. Prevalence of Antibiotic Heteroresistance Associated with Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microb Pathog 2022, 170, 105720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Calvet, X. Update on Non-Bismuth Quadruple (Concomitant) Therapy for Eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 2012, 5, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.-C.; Chang, W.-L.; Chen, W.-Y.; Yang, H.-B.; Wu, J.-J.; Sheu, B.-S. Levofloxacin-Containing Triple Therapy to Eradicate the Persistent H. pylori after a Failed Conventional Triple Therapy. Helicobacter 2007, 12, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-I.; Tsai, F.-W.; Kao, S.-S.; Hsu, W.-H.; Cheng, J.-S.; Peng, N.-J.; Tsai, K.-W.; Hu, H.-M.; Wang, Y.-K.; Chuah, S.-K.; et al. Ten-Day Quadruple Therapy Comprising Proton Pump Inhibitor, Bismuth, Tetracycline, and Levofloxacin Is More Effective than Standard Levofloxacin Triple Therapy in the Second-Line Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology | ACG 2017, 112. [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-I.; Tsay, F.-W.; Kao, J.Y.; Peng, N.-J.; Chen, Y.-H.; Tang, S.-Y.; Kuo, C.-H.; Kao, S.-S.; Wang, H.-M.; Wu, I.-T.; et al. Tetracycline-Levofloxacin versus Amoxicillin-Levofloxacin Quadruple Therapies in the Second-Line Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Calvet, X.; O’Connor, A.; Mégraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A. Sequential Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Critical Review. J Clin Gastroenterol 2010, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, H.J. Forty Years of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Changes in Findings at Esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Helicobacter 2023, 28, e13026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-L.; Huang, H.-L.; Huang, B.-S.; Chen, P.-C.; Chen, C.-S.; Wang, H.-L.; Lin, P.-H.; Chieh, M.-S.; Wu, J.-J.; Yang, J.-C.; et al. Combination of OipA, BabA, and SabA as Candidate Biomarkers for Predicting Helicobacter pylori-Related Gastric Cancer. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 36442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarov, T.; Kiran, B.; Bagirova, M.; Allahverdiyev, A.M.; Abamor, E.S. An Overview of Nanotechnology-Based Treatment Approaches against Helicobacter pylori. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2019, 17, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Lao, Y.-H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yi, K.; Chen, Z.; Han, J.; Song, W.; Tao, Y.; Li, M. Combatting Helicobacter pylori with Oral Nanomedicines. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 9826–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, W.; Zhang, J.; Xia, X. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori: The Power of Nanosized Formulations. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortright, K.E.; Chan, B.K.; Koff, J.L.; Turner, P.E. Phage Therapy: A Renewed Approach to Combat Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestre, A.; Sathiya Narayanan, R.; Rivas, D.; John, J.; Abdulqader, M.A.; Khanna, T.; Chakinala, R.C.; Gupta, S. Role of Probiotics in the Management of Helicobacter pylori. Cureus 2022, 14, e26463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestrovic, A.; Perkovic, N.; Tonkic, A.; Sundov, Z.; Kumric, M.; Bozic, J. Personalized Approach in Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Antibiotics 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.Y. Transitioning of Helicobacter pylori Therapy from Trial and Error to Antimicrobial Stewardship. Antibiotics 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addissouky, T.A.; Wang, Y.; El Sayed, I.E.T.; Baz, A. El; Ali, M.M.A.; Khalil, A.A. Recent Trends in Helicobacter pylori Management: Harnessing the Power of AI and Other Advanced Approaches. Beni Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment option | Drugs employed | Duration of therapy | References |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Triple therapy (PPI+ two antibiotics) |
PPI, Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin (or Metronidazole) | 7 days | [119] |
| Bismuth Quadruple therapy (BQT) | PPI, bismuth, tetracycline, and metronidazole | 14 days | [29] |
| Levofloxacin-containing triple therapy | PPI, levofloxacin, amoxicillin | 14 days | [120] |
| Levofloxacin-amoxicillin quadruple therapy | PPI, bismuth, levofloxacin, amoxicillin | 10 days | [121] |
| Tetracycline-levofloxacin quadruple therapy | PPI, bismuth, levofloxacin, tetracycline | 10 days | [122] |
| Concomitant therapy (non-bismuth therapy) | PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and a nitrimidazole | [119] | |
| Sequential therapy (dual) | PPI and amoxicillin for 5 days, followed by triple therapy (PPI, clarithromycin, and tinidazole) for next 5 days | 10 days | [123] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





