Submitted:
20 December 2023
Posted:
20 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
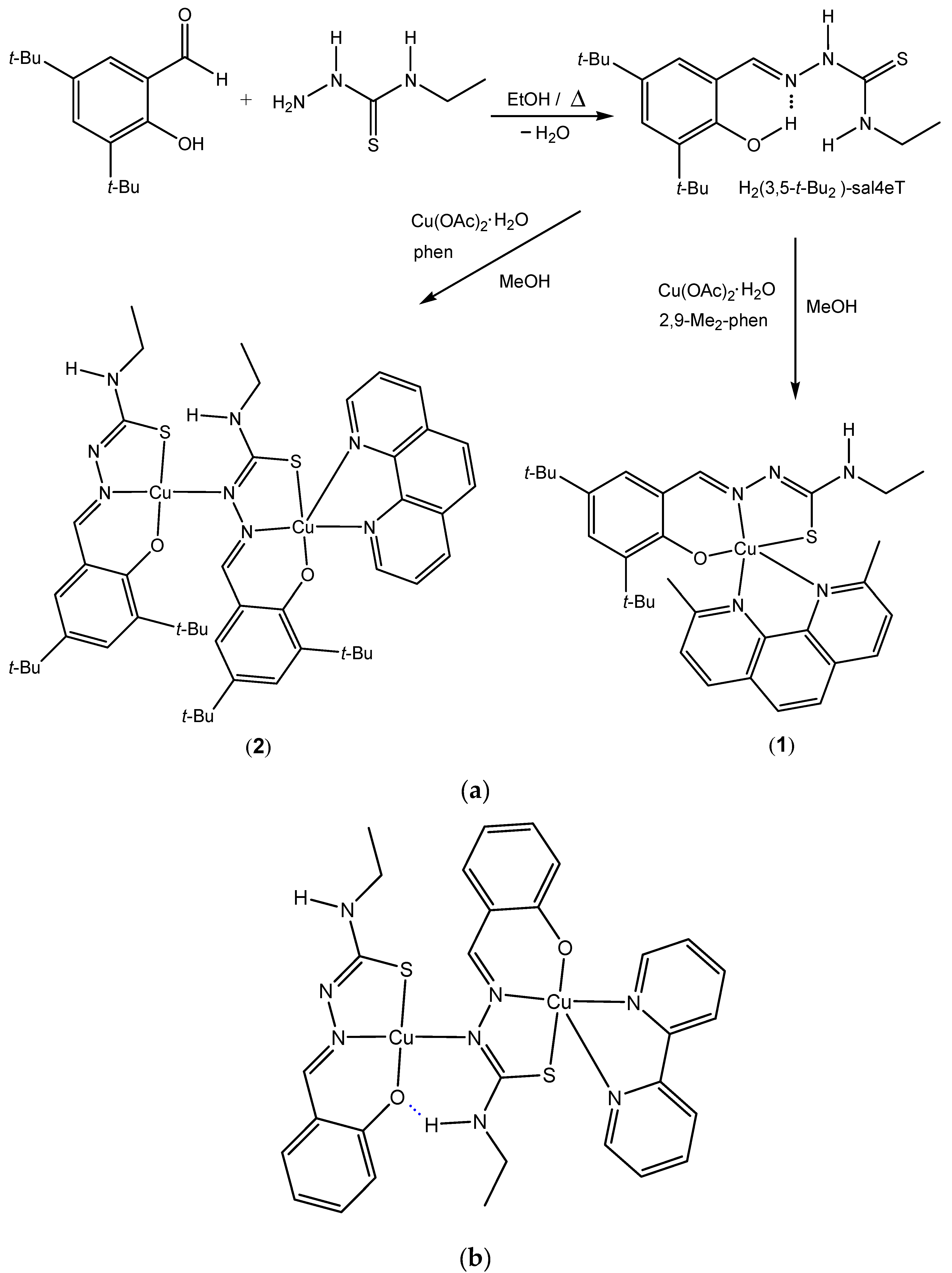
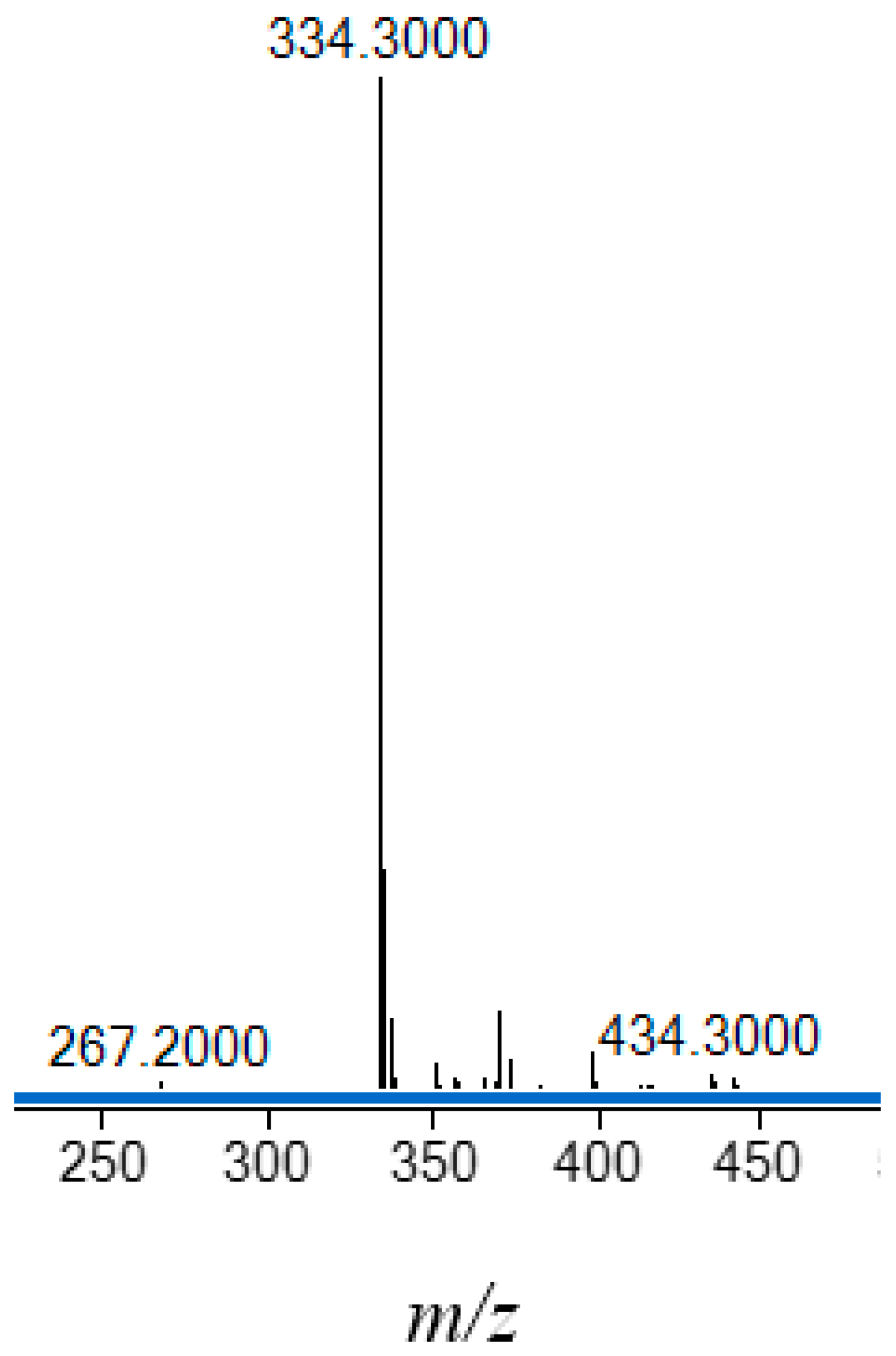
2.1. Synthesis and Chemical Identification of the Thiosemicarbazone Ligand
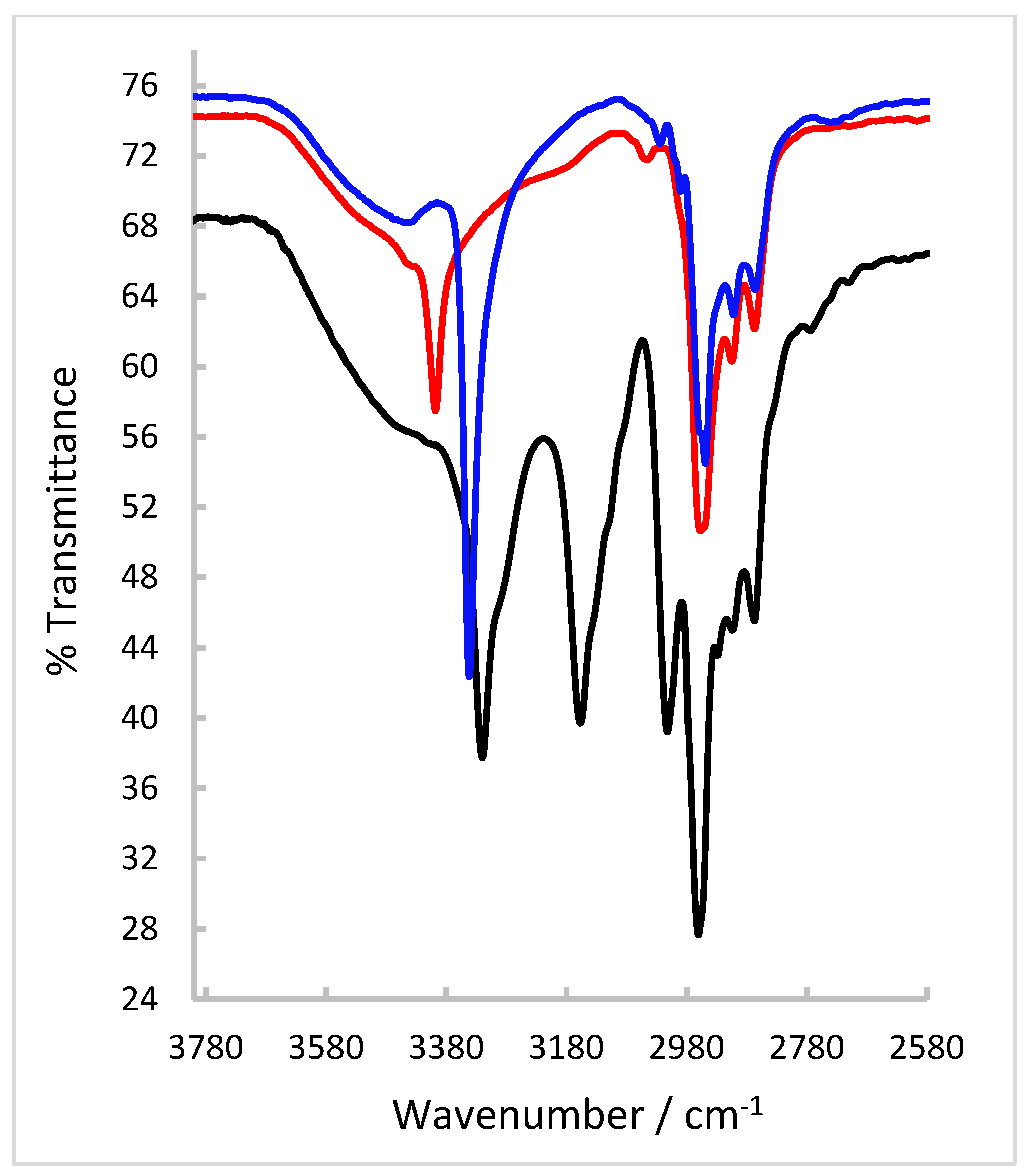
2.2. FT-IR and NMR Spectroscopic Characterization of the Thiosemicarbazone Ligand
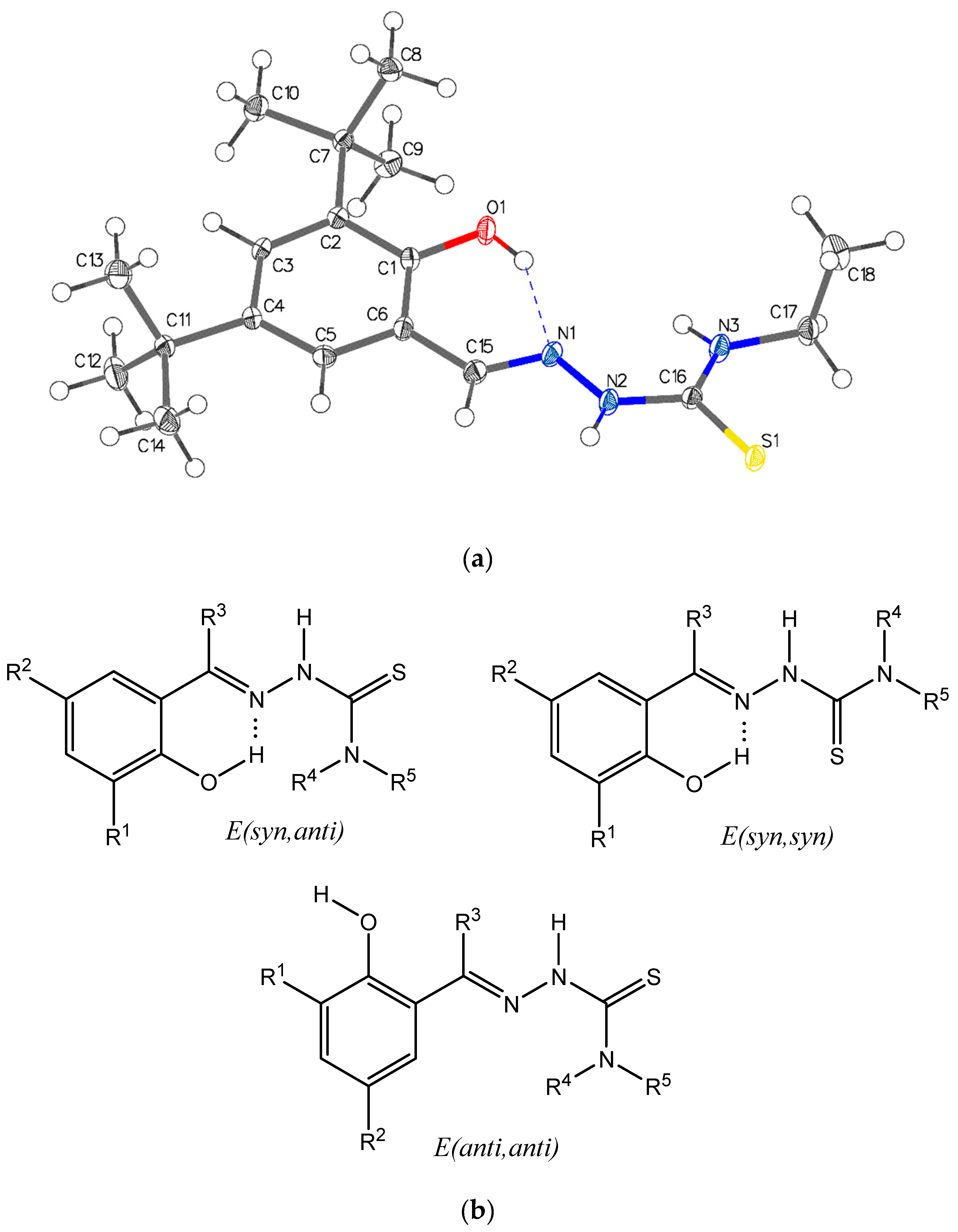
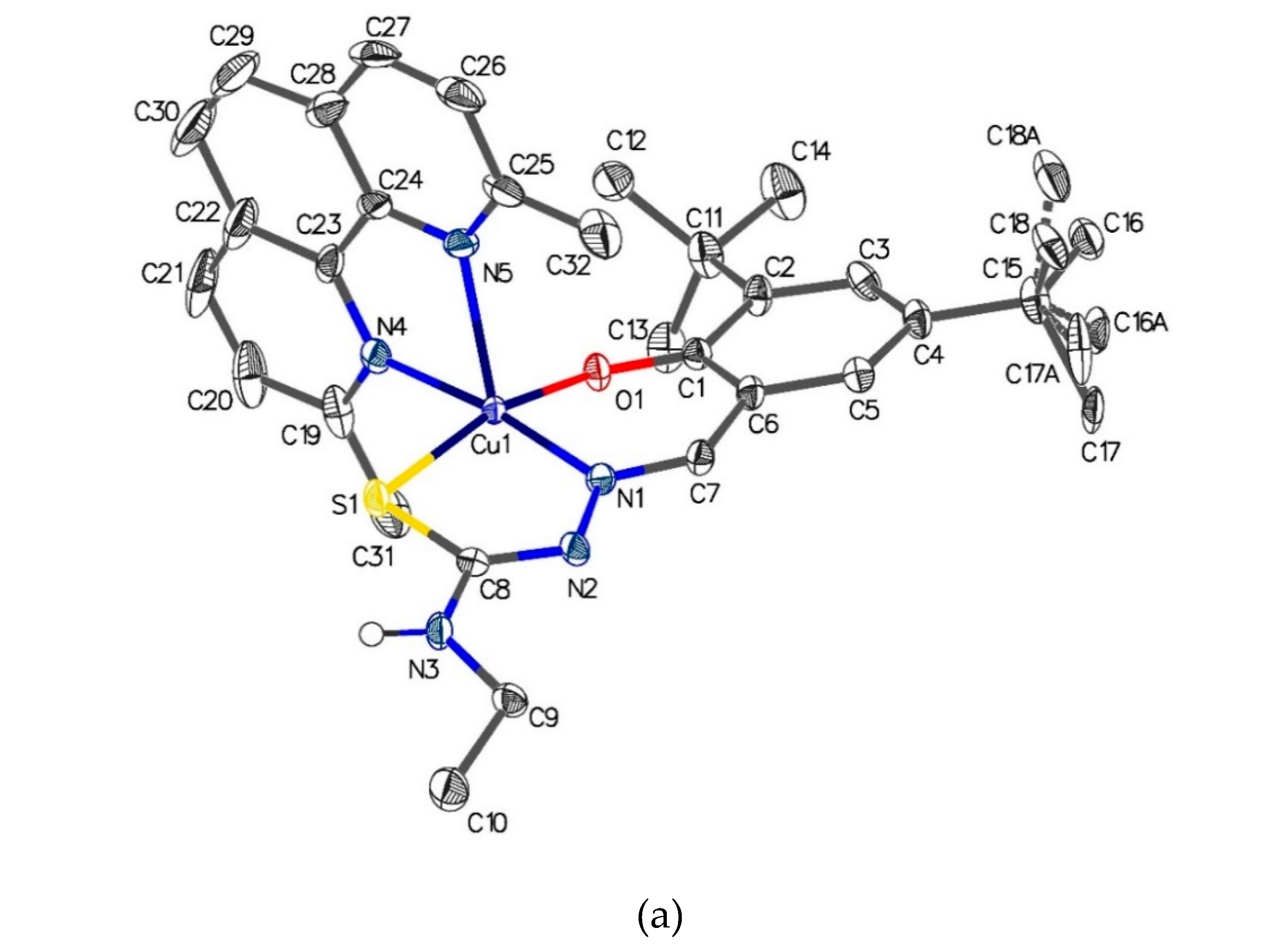
2.3. Single-Crystal X-ray Structure Determination of the Thiosemicarbazone Ligand
2.4. Synthesis and Chemical Identification of the Copper(II) Thiosemicarbazone Complexes
2.5. FT-IR Spectroscopy and Magnetic Susceptibility Measurements
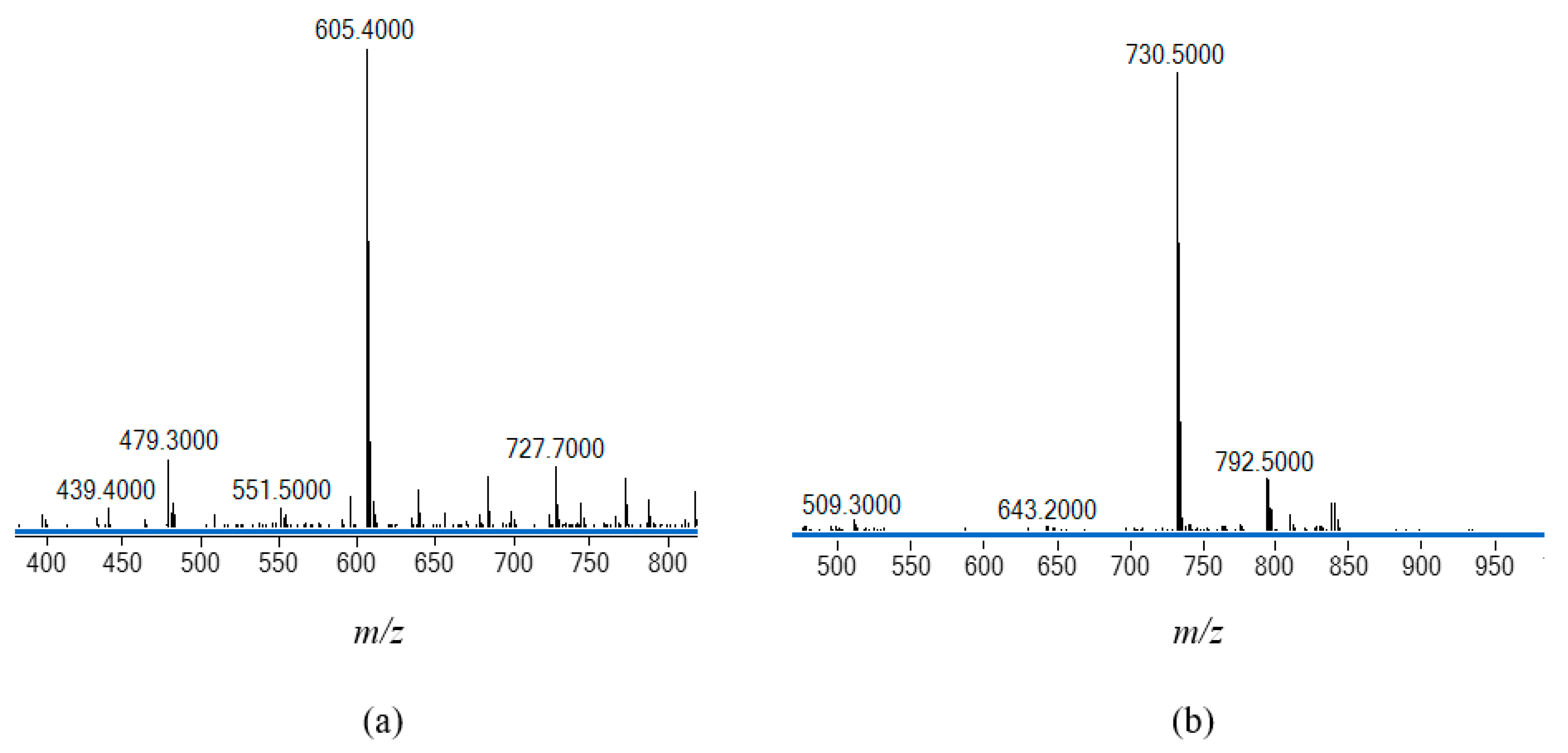
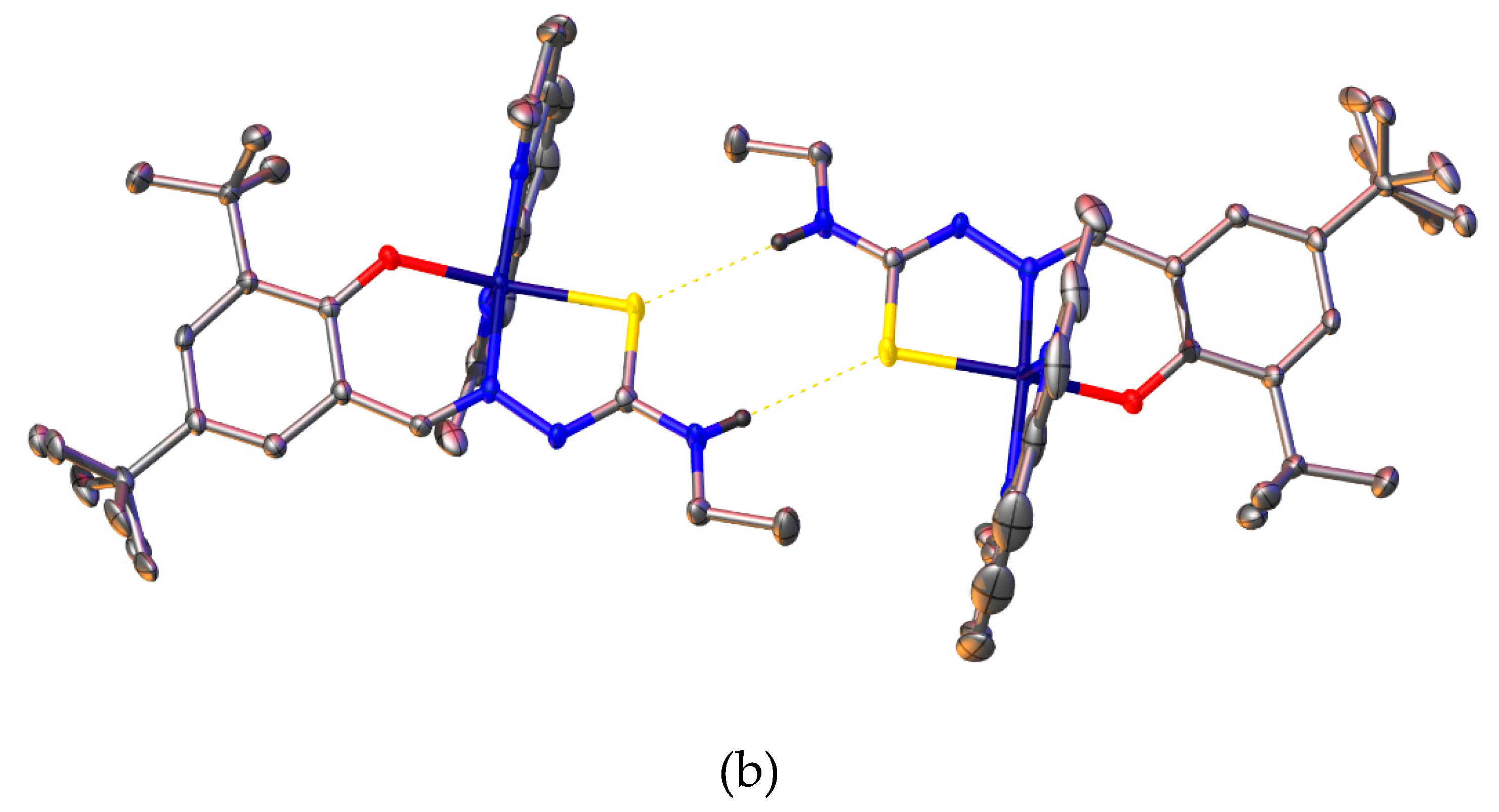
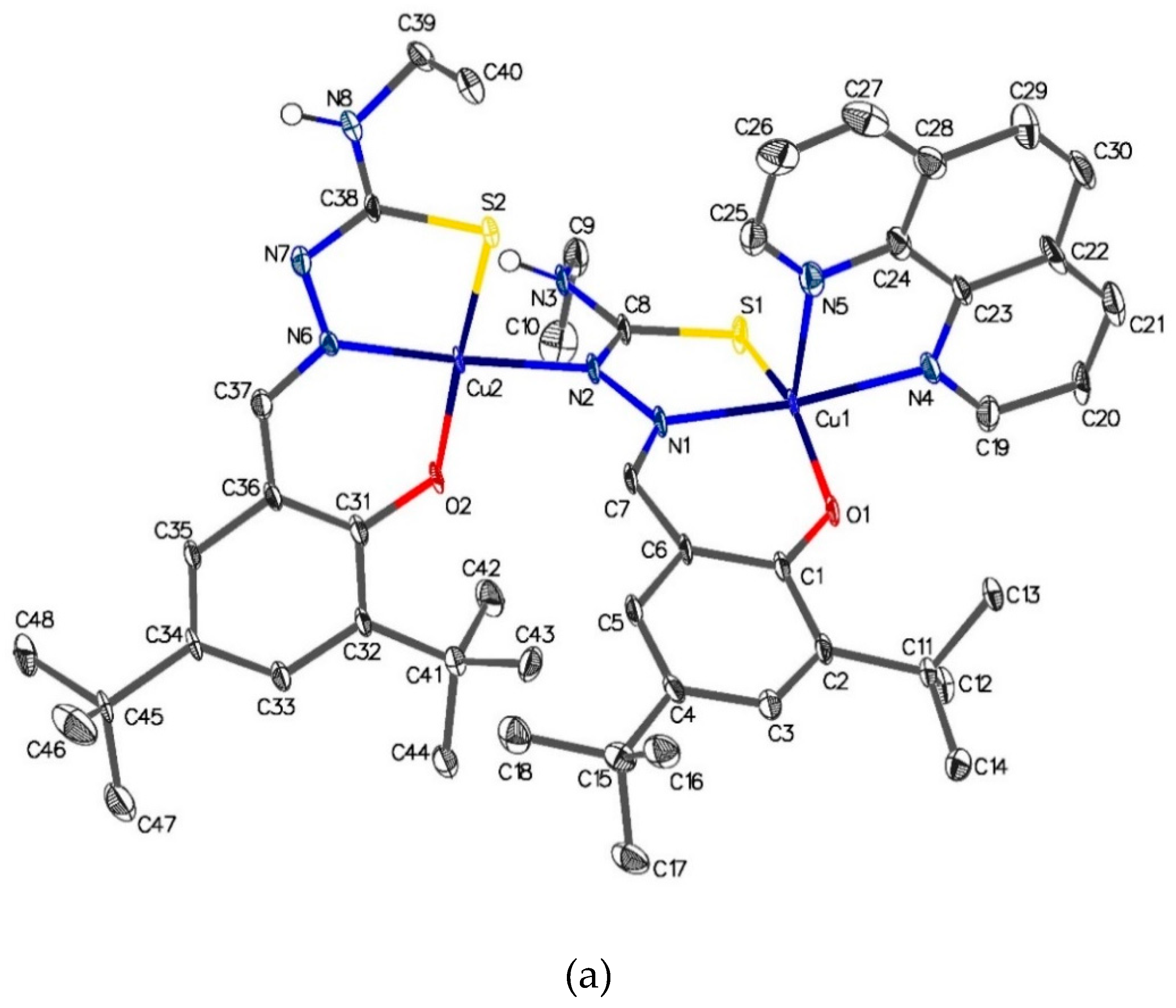
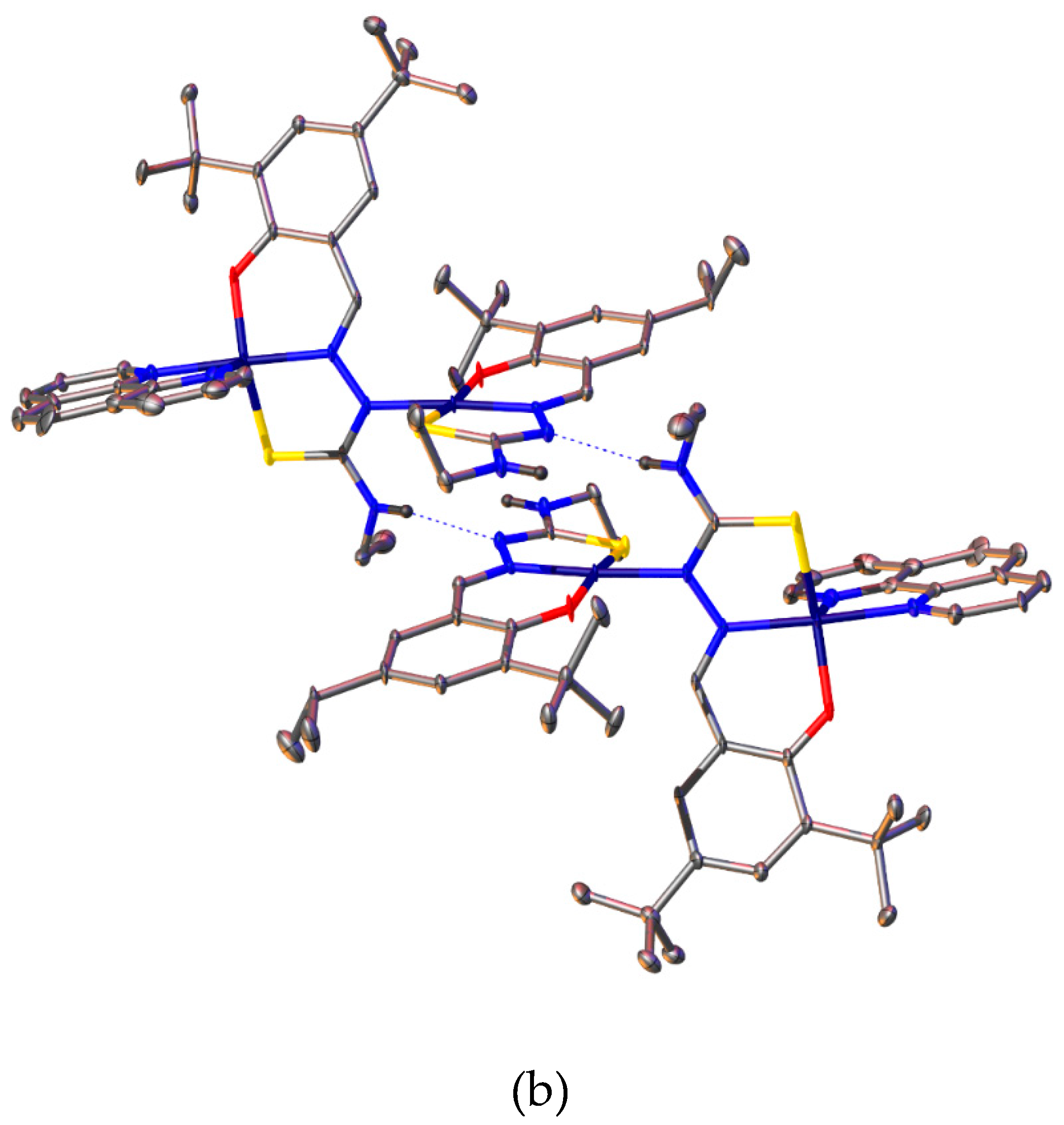
2.6. Single-Crystal X-ray Analyses of the Ternary Copper(II) Complexes
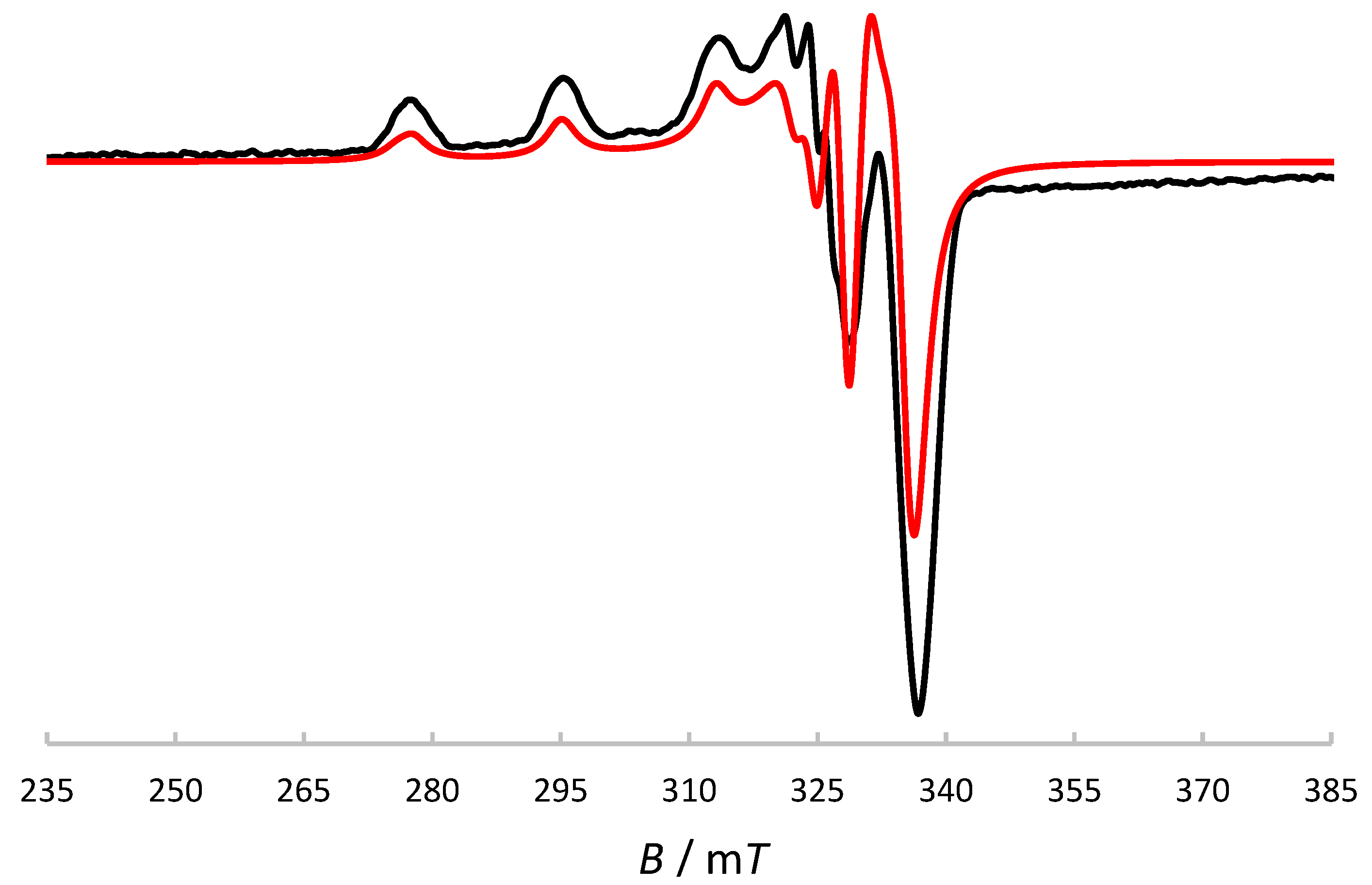
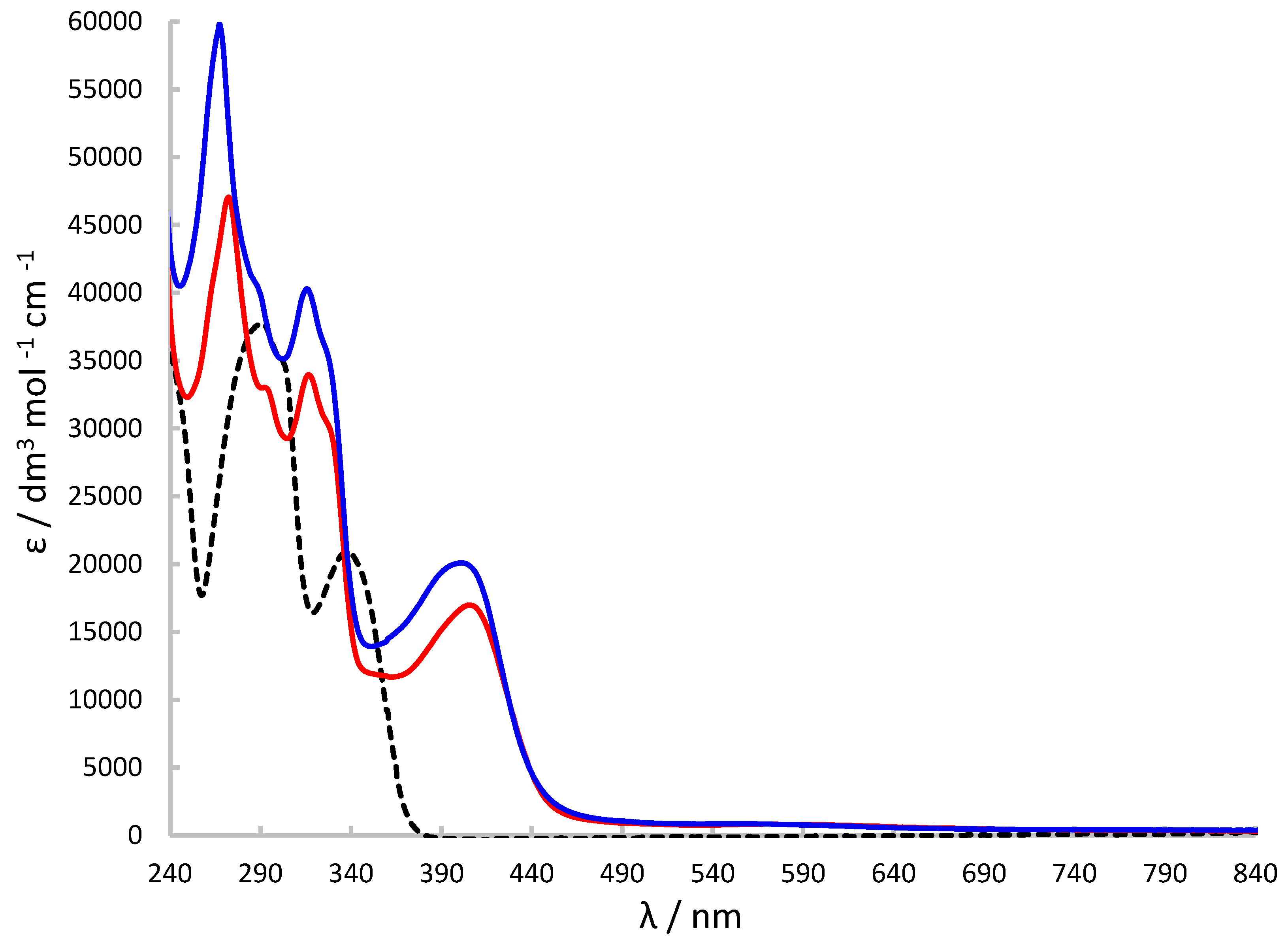
2.7. X-Band ESR and UV-Visible Spectroscopic Characterisation
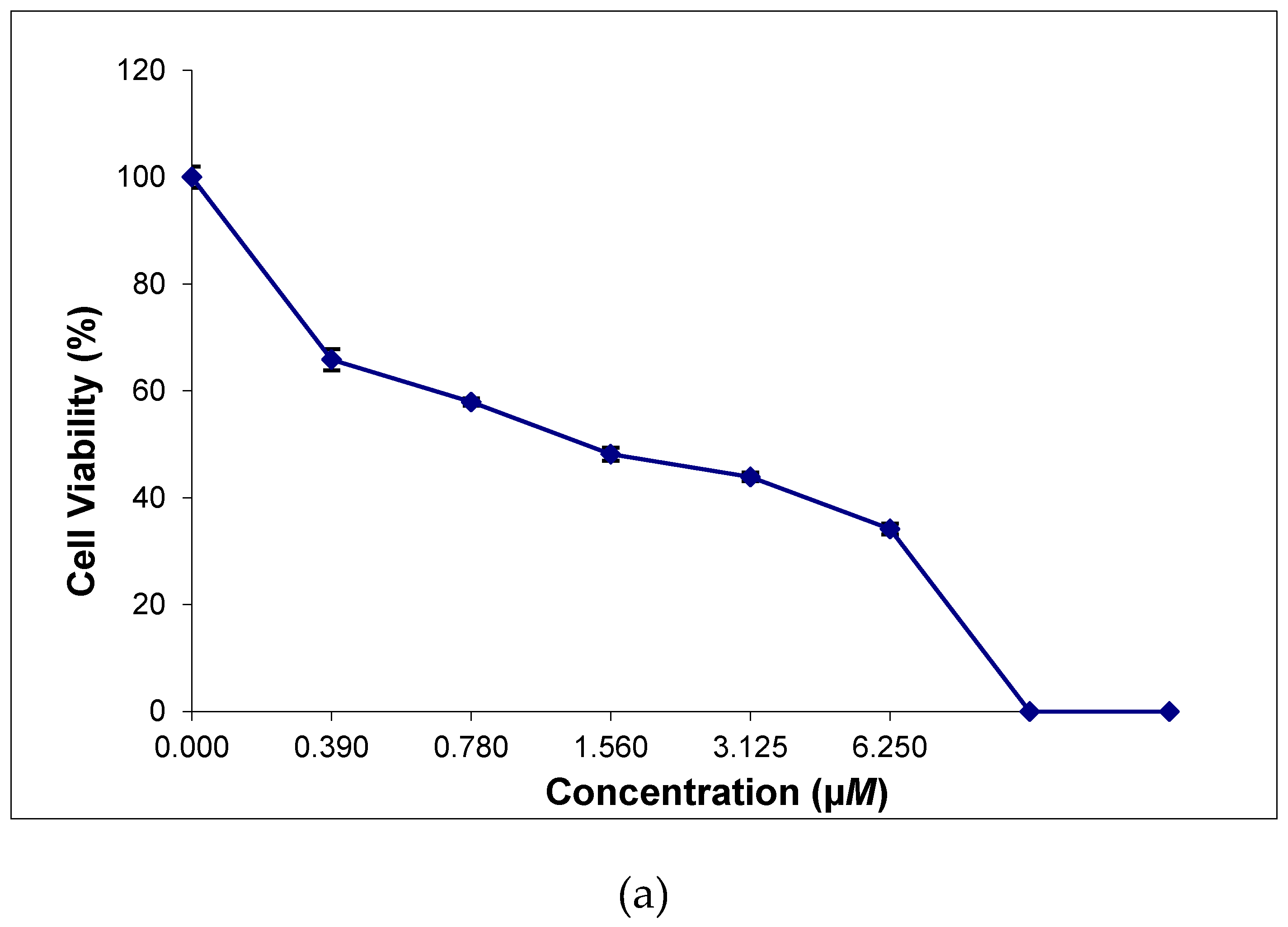
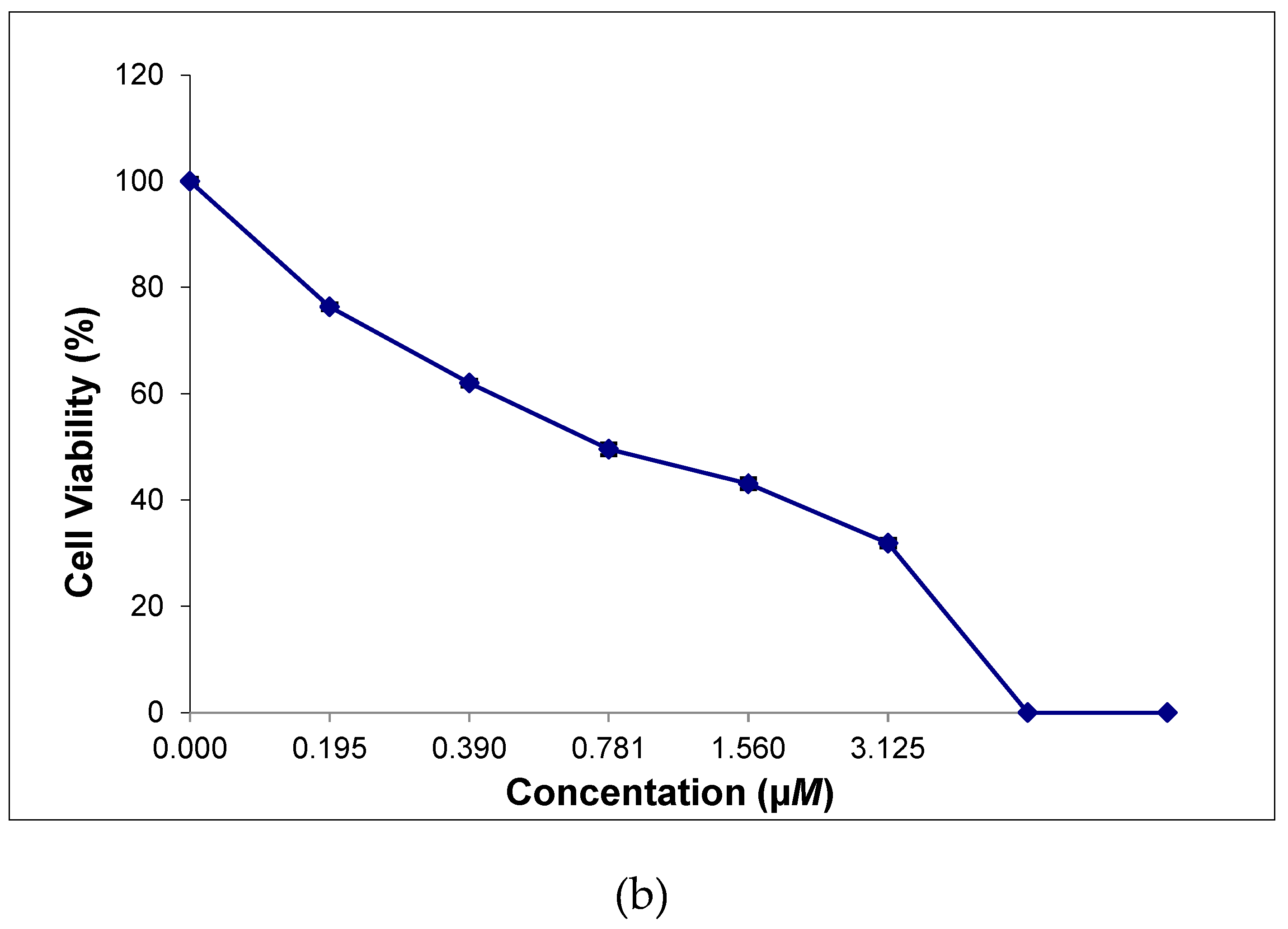
2.8. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of the Thiosemicarbazone Ligand and the Ternary Copper(II) Complexes
3. Conclusion
4. Experimental
4.1. Materials and Physical Techniques
4.2. Synthesis of H2(3,5-t-Bu2)-sal4eT
4.3. Synthesis of [Cu{(3,5-t-Bu2)-sal4eT}(2,9-Me2-phen)] (1)
4.4. Synthesis of [Cu2{(3,5-t-Bu2)-sal4eT}2(phen)] (2)
4.5. Investigation of Anticancer Activity
4.5.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.5.2. Cytotoxicity Evaluation by the MTT Assay
Supplementary Materials
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lobana, T.S.; Sharma, R.; Bawa, G.; Khanna, S. Bonding and structure trends of thiosemicarbazone derivatives of metals – an overview. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 977–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasis, L.; Demertzis, M.A.; Yadav, P.N.; Kovala-Demertzi, D.; Prentjas, C.; Castiñeiras, A.; Skoulika, S.; West, D.X. Palladium(II) and platinum(II) complexes of 2-hydroxyacetophenone N(4)-ethylthiosemicarbazone – crystal structure and description of bonding properties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2004, 357, 4113–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gou, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, K.; Qi, J.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, S.; Liang, H.; Yang, F. Four copper(II) compounds synthesized by anion regulation: structure, anticancer function and anticancer mechanism. Eur. J. Med. Chem, 2016, 121, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobana, T.S.; Kumari, P.; Bitcher, R.; Jasinski, J.P.; Golen, J.A. Metal derivatives of thiosemicarbazones: crystal and molecular structures of mono- and dinuclear copper(II) complexes with N1-substituted salicylaldehyde rhiosemicarbazones. Z. Anorg. Allg Chem. 2012, 638, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobana, T.S.; Kumari, P.; Castiñeiras, A.; Butcher, R.J. The effect of C-2 substituents of salicyladehyde-based thiosemicarbazones on the synthesis, spectroscopy, structures, and fluorescence of nickel(II) complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 3557–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Lobana, S.T.; Butcher, R.J.; Castiñeiras, A.; Zeller, M. The effect of substituents at C2/N1 atoms of salicylaldehyde and 2-hydroxyacetophenone-based thiosemicarbazones on the nature of nickel(II) complexes with 1,10-phenanthroline and terpyridine as co-ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 482, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiras-Gabián, G.; Vázquez-López, M.; Abram, U. Dimeric rhenium(I) carbonyl complexes with thiosemicarbazone backbone. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2004, 630, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Yao, Q.; Tian, L.; Wang, Y. Piperidylthiosemicarbazones Cu(II) complexes with a high anticancer activity by catalysing hydrogen peroxide to degrade DNA and promote apoptosis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Liang, S.; Gou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, F.; Liang, H. Synthesis of four binuclear copper(II) complexes: structure, anticancer properties and anticancer mechanism. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 96, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.-Y.; Wu, B.-M.; Mak, T.C.W. ; Synthesis and structural characterization of new quadridentate N3S-compound di-2-pyridyl ketone thiosemicarbazone and its binuclear copper(II) complexes. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1996, 3485–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovejoy, D.B.; Richardson, D.R. Novel “hybrid” iron chelators derived from aroylhydrazones and thiosemicarbazones demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against tumor cells. Blood 2002, 100, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Richardson, D.R. Novel di-pyridyl-derived iron chelators with marked and selective antitumor activity: in vitro and in vivo assessment. Blood, 2004, 104, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, D.R.; Sharpe, P.C.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Senaratne, D.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Islam, M.; Bernhardt, P.V. Dipyridyl thiosemicarbazone chelators with potent and selective antitumour activity form iron complexes with redox activity. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6510–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinowski, D.S.; Yu, Y.; Sharpe, P.C.; Islam, M.; Liao, Y.-T.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Kumar, N.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Richardson, D.R. Design, synthesis, and characterization of novel iron chelators: structure-activity relationships of the 2-benzoylpyridine thiosemicarbazone series and their 3-nitrobenzoyl analogues as potent antitumor agents. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 3716–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, D.R.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Richardson, V.; Sharpe, P.C.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Islam, M.; Bernhardt, P.V. 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones are potent iron chelators and antiproliferative agents: redox activity, iron complexation and characterization of their antitumor activity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, P.J.; Sharpe, P.C.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Richardson, D.R. Novel thiosemicarbazones of the ApT and DpT series and their copper complexes: identification of pronounced redox activity and characterization of their antitumor activity. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5759–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, C.; Punnia-Moorthy, G.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Jansson, P.J.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Sharpe, P.C.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Richardson, D.R. Halogenated 2´-benzoylpyridine thiosemicarbazone (XBpT) chelators with potent and selective anti-neoplastic activity: relationship to intracellular redox activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6936–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovejoy, D.B.; Sharp, D.M.; Seebacher, N.; Obeidy, P.; Prichard, T.; Stefani, C.; Basha, M.T.; Sharpe, P.C.; Jansson, P.J.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Richardson, D.R. Novel second-generation di-2-pyridylketone thiosemicarbazones show synergism with standard chemotherapeutics and demonstrate potent activity against lung cancer xenografts after oral and intravenous administration in vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7230–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, C.; Jansson, P.J.; Gutierrez, E.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Richardson, D.R.; Kalinowski, D.S. Alkyl substituted 2´-benzoylpyridine thiosemicarbazone chelators with potent and selective anti-neoplastic activity: novel ligands that limit methemoglobin formation. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohui, K.; Afanasenko, E.; Bacher, F.; Ting, R.L.X.; Zafar, A.; Blanco-Cabra, N.; Torrents, E.; Dömötör, O.; May, N.V.; Darvasiova, D.; Enyedy, E.A.; Popović-Bijelić, A.; Reynisson, J.; Rapta, P.; Babak, M.V.; Pastorin, G.; Arion, V.B. New water-soluble copper(II) complexes with morpholine-thiosemicarbazone hybrids: insights into the anticancer and antibacterial mode of action. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Li, M.-X. Synthesis, characterization, and biological activity of cadmium(II) and antimony(III) complexes based on 2-acetylpyrazine thiosemicarbazones. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 530, 120671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savir, S.; Liew, J.W.K.; Vythilingam, I.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Tan, C.H.; Sim, K.S.; Lee, V.S.; Maah, M.J.; Tan, K.W. Nickel(II) complexes with plyhydroxybenzaldehyde and O,N,S tridentate thiosemicarbazone ligands: synthesis, cytotoxicity, antimalarial activity, and molecular docking studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1242, 130815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Argüelles, M.C.; López-Silva, E.C.; Sanmartín, J.; Pelagatti, P.; Zani, F. Copper complexes of imidazole-2-, pyrrole-2- and indol-3-carbaldehyde thiosemicarbazones: inhibitory activity against fungi and bacteria. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genova, P.; Varadinova, T.; Matesanz, A.I.; Marinova, D.; Souza, P. Toxic effects of bis(thiosemicarbazone) compounds and its palladium(II) complexes on herpes simplex virus growth. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 197, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaküҫük-İyidoğan, A.; Taşdemir, D.; Oruҫ-Emre, E.E.; Balzarini, J. Novel platinum(II) and palladium(II) complexes of thiosemicarbazones derived from 5-substitutedthiophene-2-carbaldehydes and their antiviral and cytotoxicity activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 5616–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, K.; Buchanan, R.M.; Grapperhaus, C.A. Antifungal activity of thiosemicarbazones, bis(thiosemicarbazones), and their metal complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 225, 111620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanye, S.D.; Smith, G.S.; Lategan, C.; Smith, P.J.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Chibale, K. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of gold(I) thiosemicarbazone complexes for antimalarial activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Shiota, Y.; Kariyazaki, A.; Kanegawa, S.; Yoshizawa, K.; Sato, O. Heterometallic FeIII/K coordination polymer with a wide thermal hysteretic spin transition at room temperature. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovala-Demertzi, D.; Yadav, P.N.; Demertzis, M.A.; Jasiski, J.P.; Andreadaki, F.J.; Kostas, I.D. First use of a palladium complex with a thiosemicarbazone ligand as catalyst precursor for the Heck reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 2923–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungwirth, U.; Kowol, C.R.; Keppler, B.K.; Hartinger, C.G.; Berger, W.; Heffeter, P. Anticancer Activity of Metal Complexes: Involvement of Redox Processes. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1085–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.; Chaudhary., M. Synthesis, crystal structure, computational study and anti-virus effect of mixed ligand copper(II) complex with ONS donor Schiff base and 1,10-phenanthroline. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1246, 131246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambalavanan, P.; Palani, K.; Ponnuswamy, M.N. Crystal structure of [1-(2-phenyloxyN[N-cyclohexylthiouryl)] ethylamine-(1,10-phenanthrolinyl)]copper(II). Cryst. Res. Technol. 2002, 37, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.D.; Reddy, P.A.N.; Nethaji, M.; Chakravarty, A.R. Ternary copper(II) complexes of thiosemicarbazones and heterocyclic bases showing N3OS coordination as models for the type-2 centers of copper monooxygenases. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2003, 349, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.M.; Naik, A.D.; Nethaji, M.; Chakravarty, A.R. Synthesis, crystal structure and photo-induced DNA cleavage activity of ternary copper(II)-thiosemicarbazone complexes having heterocyclic bases. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2004, 357, 2315–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobana, T.S.; Indoria, S.; Jassal, A.K.; Kaur, H.; Arora, D.S.; Jasinski, J.P. Synthesis, structures, spectroscopy and antimicrobial properties of complexes of copper(II) with salicylaldehyde N-substituted thiosemicarbazones and 2,2´-bipyridine or 1,10-phenanthroline. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 76, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indoria, S.; Lobana, T.S.; Kauer, H.; Arora, D.S.; Randhawa, B.S.; Jassal, A.K.; Jasinski, J.P. Synthesis and structures of 5-methoxysalicyladehyde thiosemicarbazonates of copper(II): molecular spectroscopy, ESI-mass studies and antimicrobial activity. Polyhedron, 2016, 107, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobana, T.S.; Indoria, S.; Sood, S.; Arora, D.S.; Randhawa, B.S.; Garcia-Santos, I.; Smolinski, V.A.; Jasinski, J.P. Synthesis of 5-nitrosalicylaldehyde-N-substituted thiosemicarbazonates of copper(II): molecular structures, spectroscopy, ESI-mass studies and antimicrobial activity. Inorg. Chim Acta 2017, 46, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainscough, E.W.; Brodie, A.M.; Ranford, J.D.; Waters, J.M. Reaction of nitrogen and sulphur donor ligands with the antitumour complex [{CuL(MeCO2)}2] (HL = 2-formylpyridine thiosemicarbazone) and the single-crystal X-ray structureof [CuL(bipy)]ClO4 (bipy = 2,2´-bipyridine). J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1991, 1737–1742.
- Kartikeyan, R.; Murugan, D.; Ajaykamal, T.; Varadhan, M.; Rangasamy, L.; Velusamy, M.; Palaniandavar, M.; Rajendiran, V. Mixed ligand copper(II)-diimine complexes of 2-formylpyridine-N4-phenylthiosemicarbazone: diimine co-ligands tune the in vitro nanomolar cytotoxicity. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 9148–9169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreeja, P.B.; Kurup, M.R.P.; Kishore, A.; Jasmin, C. Spectral characterization, X-ray structure and biological investigations of copper(II) ternary complexes of 2-hydroxyacetophenone 4-hydroxybenzoic acid hydrazone and heterocyclic bases, Polyhedron 2004, 23, 575–581.
- Reddy, P.A.N.; Santra, B.K.; Nethji, M.; Chakravarty, A.R. Metal-assisted light-induced DNA cleavage activity of 2-(methylthio)phenylsalicyladimine Shiff base copper(II) complexes having planar heterocyclic bases. J. Inorg, Biochem. 2004, 98, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.R.; Shilpa, A.; Raju, N.; Raghavaiah, P. Synthesis, structure, DNA binding and cleavage properties of ternary amino acid Schiff base-phen/bipy Cu(II) complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2011, 105, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li. A.; Liu, Y.-H.; Yuan, L.-Z.; Ma, Z.-Y.; Zhao, C.-L.; Xie, C.-Z.; Bao, W.-G.; Xu, J.-Y. Association of structural modifications with bioactivity in three new copper(II) complexes of Schiff base ligands derived from 5-chlorosalicylaldehyde and amino acids. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 146, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendiran. ; karthik, R.; Palaniandavar, M.; Stoeckli-Evans, H.; Periasamy, V.S.; Akbarsha, M.A.; Srinag, B.S.; Krishnamurthy, H. Mixed-ligand copper(II)-phenolate complexes: effect of coligand on enhanced DNA and protein binding, DNA cleavage, and anticancer activity. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 8208–8221. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, P.A.N.; Nethaji, M.; Chakravarty, A.R. Synthesis, crystal structures and properties of ternary copper(II) complexes having 2,2´-bipyridine and amino acid salicylaldiminates as models for the type-2 sites in copper oxidases. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2002, 337, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, N.; Sithambaresan, M.; Kurup, M.R.P. Spectral studies of copper(II) complexes of tridentate acylhdrazone ligands with heterocyclic compounds as coligands: X-ray crystal structure of one acylhydrazone copper(II) complex. Spectrochim. Acta Part A, 2011, 79, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, L.L.; Ranford, J.O.; Robinson, W.T.; Svensson, J.O.; Tan, A.L.C.; Wu, D. Model for the reduced Schiff base intermediate between amino acids and pyridoxal: copper(II) complexes of N-(2-hdroxybenzyl)amino acids with nonpolar side chains and the crystal structures of [Cu(N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-D,L-alanine)(phen·H2 O and [Cu(N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-D,L-alanine)(imidazole)]. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 6466–6472. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernal, M.; García-Vázquez, J.A.; Romero, J.; Gómez, C.; Durán, M.L.; Sousa, A.; Sousa-Pedrares, A.; Rose, D.J.; Maresca, K.P.; Zubieta, J. Electrochemical synthesis of cobalt, nickel, zinc and cadmium complexes with N[(2-hydroxyphenyl)methylidine]-N´-tosylbenzene-1,2-diamine. The crystal structures of {1,10-phenanthroline)[N-2-oxophenyl)methylidine]-N-tosylbenzene-1,2-diaminato}nickel(II) and {1,10-phenanthroline)[N-2-oxophenyl)methylidine]-N´-tosylbenzene-1,2-diaminato}copper(II). Inorg. Chim. Acta 1999, 295, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.-Z.; Meng, Z.-X.; Liu, B.L.; Cai, G.-L.; Zhang, C.-L.; Wang, X.-Y. Novel tumor chemotherapeutic agents and tumor radio-imaging agents: potential tumor pharmaceuticals of ternary copper(II) complexes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2005, 8, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.A.N.; Nethaji, M.; Chakravarty, A.R. Hydrolytic cleavage of DNA by ternary amino acid Schiff base copper(II) complexes having planar heterocyclic ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, L.; Liu, G.; Xu, T.; Wang, D. Synthesis, crystal structure and DNA-binding properties of a new copper(II) complex with L-valine Schiff base and 1,10-phenanthroline. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 986, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labisbal, E.; Garcia-Vazquez, Romero, J.; Picos, S.; Sousa, A.; Castiñeiras, A.; Maichle-Mössmer. Electrochemical synthesis and structural characterization of nickel(II) and copper(II) complexes of tridentate Schiff bases: molecular structure and the five-coordinated copper(II) complex: 1,10-phenanthroline {2-[2-oxyphenyl)iminomethyl]phenolato}copper(II). Polyhedron 1995, 14, 663–670.
- Sharma, M.; Ganeshpandian, M.; Majumder, M.; Tamilarasan, A.; Sharma, M.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Islam, N.S.; Palaniandavar, M. Octahedral copper(II)-diimine complexes of triethylenetetramine: effect of stereochemical fluxionality and ligand hydrophobicity on CuII/CuI redox, DNA binding and cleavage, cytotoxicity and apoptosis-inducing ability. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 8282–8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.H.; Kong, K.C.; Von,S.T.; Balraj, P.; Jensen, P.; Thirthagiri, E.; Hamada, H.; Chikira, M. Synthesis, characterization, DNA-binding stuídy and anticancer properties of ternary metal(II) complexes of edda and an intercalating ligand. Dalton Trans. 2008, 447–454.
- Selvakumar, B.; Rajendiran, V.; Maheswari, P.U.; Stoeckli-Evans, H.; Palaniandavar, M. Structures, spectra, and DNA-binding properties of mixed ligand copper(II) complexes of iminodiacetic acid: the novel role of diamine co-ligands on DNA conformation and hydrolytic and oxidative double strand DNA cleavage. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-T.; Moubaraki, B.; Murray, K.S.; Vittal, J.J. Synthesis, characterization and properties of ternary copper(II) complexes containing reduced Schiff base N-(2-hdroxybenzyl)-amino acids and 1,10-phenanthroline. Dalton Trans. 2003, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.T.; Moubaraki, B.; Murray, K.S.; Ranford, J.D.; Vittal, J.J. Interconversion of a monomer and two coordination polymers of a copper(II)-reduced Schiff base ligand-1,10-phenanthroline complex based on hydrogen- and coordinative-bonding. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 5934–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.A.N.; Nethaji, M.; Chakravarty, A.R. Ternary mononuclear and ferromagnetically coupled dinuclear copper(II) complexes of 1,10-phenanthroline and N-salicylidine-2-methoxyaniline that show supramolecular self-organization. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 2318–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoga, D.; Szklarzewicz, J.; Stadnicka, K.; Shongwe, M.S. Iron(III) complexes with a biologically relevant aroylhydrazone: crystallographic evidence for coordination versatility. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 9042–9044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; El-Saied, F.A.; Shakdofa, M.M.E.; Karnik, S.; Jaragh-Alhadad, L.A. Synthesis and characterization of thiosemicarbazone metal complexes: crystal structure, and proliferation activity against breast (MCF7) and lung (A549) cancers. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1274, 134485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latheef, L.; Manoj, E.; Kurup, M.R.P. Salicylaldehyde 4,4’-(hexane-1,6-diyl)-thiosemicarbazone. Acta Cryst. 2006, C62, o16–o18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, D.; Mazumdar, S.K.; Banerjee, T.; Ghosh, S.; Mak, T.C.W. Structure of salicylaldehyde thiosemicarbazone. Acta Cryst. 1988, C44, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrdoljak, V.; Cindrić, M.; Milić, D.; Matcović-Ćalogović, D.; Novak, P.; Kamenar, B. Synthwsis of five new molybdenum(VI) thiosemicarbazonato complexes. Crystal structures of salicylaldehyde and 3-methoxysalicylaldehyde 4-methylthiosemicarbazones and their molybdenum(VI) complexes. Polyhedron 2005, 24, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labisbal, E.; Haslow; K. D.; Sousa-Pedrares, Valdés-Martínez, J.; Hernández-Ortega, S.; West, D.X. Copper(II) and nickel(II) complexes of 5-methyl-2-hydroacetophenone N(4)-substituted thiosemicarbazones. Polyhedron 2003, 22, 2831–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowol, C.R.; Reisner, E.; Chiorescu, I.; Arion, V.B.; galanski, M.; Deubel, D.V.; Keppler, B.K. An electrochemical study of antineoplatic gallium, iron, and ruthenium with redox noninnocent α-N-heterocyclic chalcogensemicarbazones. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 11032–11047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, D.X.; Bain, G.A.; Butcher, R.J.; Jasinski, J.P.; Li, Y.; Pozdniakiv, R.Y.; Valdés-Martínez, J.; Toscano, R.A.; Hernández-Ortega, S. Structural studies of three isomeric forms of heterocyclic N(4)-substituted thiosemicarbazones and two nickel(II) complexes. Polyhedron 1996, 15, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowol, C.R.; Eichinger, R.; Jakupec, M.A.; Galanski, M.S.; Arion, V.B.; Keppler, B.K. Effect of metal ion complexation and chalcogen donor identity on the antiproliferative activity of 2-acetylpyridine N,N-dimethyl(chalcogen)semicarbazones. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2007, 101, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, A.; Abdul Razak, I. , Chantrapromma, S.; Fun, H.-K.; Philip, V.; Sreekanth, A.; Kurup, M.R.P. Di-2-pyridyl ketone N4,N4-(butane-1,4-diyl)thiosemicarbazone. Acta Cryst. 2002, C58, 0652–o654. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, V.; Suni, V.; Kurup, M.R.P. Di-2-pyridyl ketone 4-methyl-4-phenylthiosemicarbazone. Acta Cryst. 2004, C60, o856–o858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geary, W.J. The use of conductivity measurements in organic solvents for the characterisation of coordination compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1971, 7, 81–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, V.; Manoj, E.; Kurup, M.R.P.; Nethaji, M. [Di-2-pyridyl ketone N4,N4-(butane-1,4-diyl)thiosemicarbazonato-κ3N,N´S]dioxovanadium(V). Acta Cryst. 2005, C61, m488–m490. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Saiz, P.; García-Tojal, J.; Mendia, A.; Donnadieu, B.; Lezama, L.; Pizarro, J.L.; Arriortua, M.I.; Rojo, T. Coordination modes in a tridentate NNS (thiosemicarbazonato)copper(II) system containing oxygen-donor coligands – structures of [{Cu(L)(X)}2] (X = formato, propionato, nitrito). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shongwe, M.S.; Al-Kharousi, H.N.R.; Adams, H.; Morris, M.J.; Bill, E. Unprecedented [V2O]6+ Core of a centrosymmetric thiosemicarbazonato dimer: spontaneous deoxygenation of oxovanadium(IV). Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, A.W.; Rao, T.N.; Reedijk, J.; van Rijn, J. , Verschoor, G.C. Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of copper(II) compounds containing nitrogen-sulphur donor ligands: the crystal and molecular structure of aqua[1,7-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol-2´-yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane]copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1984, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, P.V.; Sharpe, P.C.; Islam, M.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Richardson, D.R. Iron chelators, of the dipyridylketone thiosemicarbazone class: precomplexation, and transmetalation effects on anticancer activity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, O.P. Crystal and molecular structure of tris-(1,10-phenanthroline)copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton, 1973; 1237–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Burčák,M. ; Potočňák, I.; Baran, P.; Jäger, L. Low-dimensional compounds containing cyano groups. X. (Dicyanamido-κN1)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N´)copper(II) perchlorate. Acta Cryst. 2004, C60, m601–m604. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Powell, D.R.; Houser, R.P. Structural variation in copper(I) complexes with pyridylmethylamide ligands: structural analysis with a new four-coordinate geometry index, τ4. Dalton Trans., 2007, 955–964.
- Tei, L.; Blake, A.J.; Lippolis, V.; Wilson, C.; Schröder, M. Methanolysis of nitrile-functionalised pendant arm derivatives of 1,4,7-triazacyclononane upon coordination to CuII. Dalton Trans. 2003, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.-Y.; Liao, S.; Wanner, M.; Fiedler, J.; Zhang, C.; Kang, B.-S.; Kaim, W. The copper(I)/copper(II) transition in complexes with 8-alkylthioquinoline based multidentate ligands. Dalton Trans. 2003, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubbs, K.J.; Fuller, A.L.; Bennett, B.; Arif, A.M.; Makowska-Grzyska, M.M.; Berreau, L.M. Evaluation of the influence of a thioether substituent on the solid state and solution properties of N3S-ligated copper(II) complexes. Dalton Trans. 2003, 3111–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Li, A.; Shao, J.; Xie, C.-Z.; Song, X.-Q.; Bao, W.-G.; Xu, J.-Y. Four Cu(II) complexes based on antitumour chelators: synthesis, structure, DNA binding/damage, HSA interaction and enhanced cytotoxicity. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 8036–8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, P.; Zeng, P.; Lu, J.; Chen, H.; Liao, X.; Yang, N. New oxidovanadium complexes incorporating thiosemicarbazones and 1,10-phenanthroline dervatives as DNA cleavage, potential anticancer agents, and hydroxyl radical scavenger. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2015, 86, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruker, SADABS, Bruker Axs Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA 2016.
- Krause, L.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Sheldrick, G.M.; D. Stalke, D. J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2015, 48, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT - Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71 (Md), 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42(2), 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | H2(3,5-t-Bu2)-sal4eT | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C18H29N3OS | C32H39CuN5OS | C48H62Cu2N8O2S2 |
| Molar mass (g mol–1) | 335.50 | 605.28 | 974.25 |
| T (K) | 100 | 99.99 | 100.01 |
| Crystal system | monoclinic | monoclinic | triclinic |
| Space group | P21/c | P21/n | P |
| a (Å) | 18.4754(14) | 8.5924(3) | 11.3898(6) |
| b (Å) | 9.2040(7) | 18.5809(6) | 13.1195(8) |
| c (Å) | 11.5714(9) | 19.4132(6) | 16.6701(10) |
| α (°) | 90 | 90 | 78.980(2) |
| β (°) | 95.517(2) | 100.451(2) | 89.824(2) |
| γ (°) | 90 | 90 | 83.661(3) |
| V (Å3) | 1958.6(3) | 3047.99(17) | 2429.7(2) |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| ρcalc (g cm–3) | 1.138 | 1.319 | 1.332 |
| μ (mm–1) | 0.173 | 1.904 | 2.241 |
| F(000) | 728.0 | 1276.0 | 1024.0 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.500 × 0.200 × 0.150 | 0.240 × 0.120 × 0.080 | 0.508 × 0.207 × 0.040 |
| Radiation (λ/ Å) | MoKα (λ = 0.71073) | CuKα (λ = 1.54178) | CuKα (λ = 1.54178) |
| 2Θ range (°) | 4.43 – 57.282 | 6.638 – 133.168 | 5.402 – 133.766 |
| Reflections collected | 37828 | 19602 | 30501 |
| Rint | 0.0661 | 0.0918 | 0.0708 |
| GOF on F2 | 1.051 | 1.044 | 1.189 |
| R1, wR2 [I≥2σ (I)] | 0.0403, 0.0909 | 0.0513, 0.1235 | 0.1083, 0.3568 |
| R1, wR2 [all data] | 0.0607, 0.1010 | 0.0749, 0.1378 | 0.1180, 0.3692 |
| C16-S1 | 1.7029(14) |
| C1-O1 | 1.3605(16) |
| N1-N2 | 1.3854(16) |
| C15-N1 | 1.2904(19) |
| C16-N2 | 1.3499(18) |
| C15-N1-N2 | 113.66(12) |
| N2-C16-N3 | 118.40(13) |
| N2-C16-S1 | 117.87(11) |
| N3-C16-S1 | 123.72(11) |
| [Cu{(3,5-t -Bu2)-sal4eT}(2,9-Me2-1,10-phen)] (1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu(1)-S(1) | 2.2823(9) | S(1)-C(8) | 1.739(3) |
| Cu(1)-O(1) | 1.934(2) | N(2)-C(8) | 1.313(4) |
| Cu(1)-N(1) | 1.959(3) | N(1)-N(2) | 1.400(4) |
| Cu(1)-N(4) | 2.057(3) | N(1)-C(7) | 1.296(4) |
| Cu(1)-N(5) | 2.308(3) | N(3)-C(8) | 1.357(4) |
| O(1)-Cu(1)-N(1) | 91.55(10) | N(1)-Cu(1)-N(4) | 172.64(11) |
| N(1)-Cu(1)-S(1) | 84.77(8) | N(1)-Cu(1)-N(5) | 109.81(11) |
| O(1)-Cu(1)-N(4) | 90.08(10) | N(4)-Cu(1)-S(1) | 91.76(7) |
| O(1)-Cu(1)-N(5) | 98.14(10) | N(5)-Cu(1)-S(1) | 97.38(7) |
| O(1)-Cu(1)-S(1) | 164.38(8) | N(4)-Cu(1)-N(5) | 77.04(11) |
| [Cu2{(3,5-t-Bu2)-sal4eT}2(phen)] (2) | |||
| Cu(1)-S(1) | 2.266(3) | Cu(2)-S(2) | 2.231(3) |
| Cu(1)-O(1) | 1.908(7) | Cu(2)-O(2) | 1.888(7) |
| Cu(1)-N(1) | 1.952(8) | Cu(2)-N(2) | 2.017(8) |
| Cu(1)-N(4) | 2.039(8) | Cu(2)-N(6) | 1.940(8) |
| Cu(1)-N(5) | 2.276(9) | N(6)-C(37) | 1.310(12) |
| S(1)-C(8) | 1.737(9) | S(2)-C(38) | 1.746(9) |
| N(2)-C(8) | 1.322(13) | N(7)-C(38) | 1.316(12) |
| N(1)-C(7) | 1.301(13) | N(6)-N(7) | 1.391(11) |
| N(1)-N(2) | 1.381(11) | N(8)-C(38) | 1.353(13) |
| O(1)-Cu(1)-N(1) | 93.7(3) | N(5)-Cu(1)-S(1) | 102.9(2) |
| N(1)-Cu(1)-S(1) | 85.2(2) | N(4)-Cu(1)-N(5) | 77.7(3) |
| O(1)-Cu(1)-N(4) | 89.7(3) | O(2)-Cu(2)-N(2) | 88.1(3) |
| O(1)-Cu(1)-N(5) | 104.6(3) | O(2)-Cu(2)-N(6) | 94.2(3) |
| O(1)-Cu(1)-S(1) | 152.4(2) | N(2)-Cu(2)-N(6) | 176.3(3) |
| N(1)-Cu(1)-N(4) | 172.2(4) | S(2)-Cu(2)-N(2) | 91.8(2) |
| N(1)-Cu(1)-N(5) | 94.6(3) | S(2)-Cu(2)-N(6) | 86.3(2) |
| N(4)-Cu(1)-S(1) | 95.1(2) | S(2)-Cu(2)-O(2) | 172.1(3) |
| IC50 / µM | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compound | HeLa | MCF-7 |
| H(3,5-t-Bu2)-sal4eT | >100 | >100 |
| [Cu{3,5-t-Bu2)-sal4eT}(2,9-Me2-phen)] (1) | 1.35 ± 0.11 | >100 |
| [Cu2{3,5-t-Bu2)-sal4eT}2(phen)] (2) | >100 | 0.73 ± 0.06 |
| Docetaxel | 60.70 ± 5.13 | 92.54 ± 7.99 |
| Paclitaxel | 15.84±1.28 | >100 |
| Cisplatin | 13.28 ± 3.84 [82] | 13.36 ± 1.25 [83] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





