Submitted:
20 December 2023
Posted:
21 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
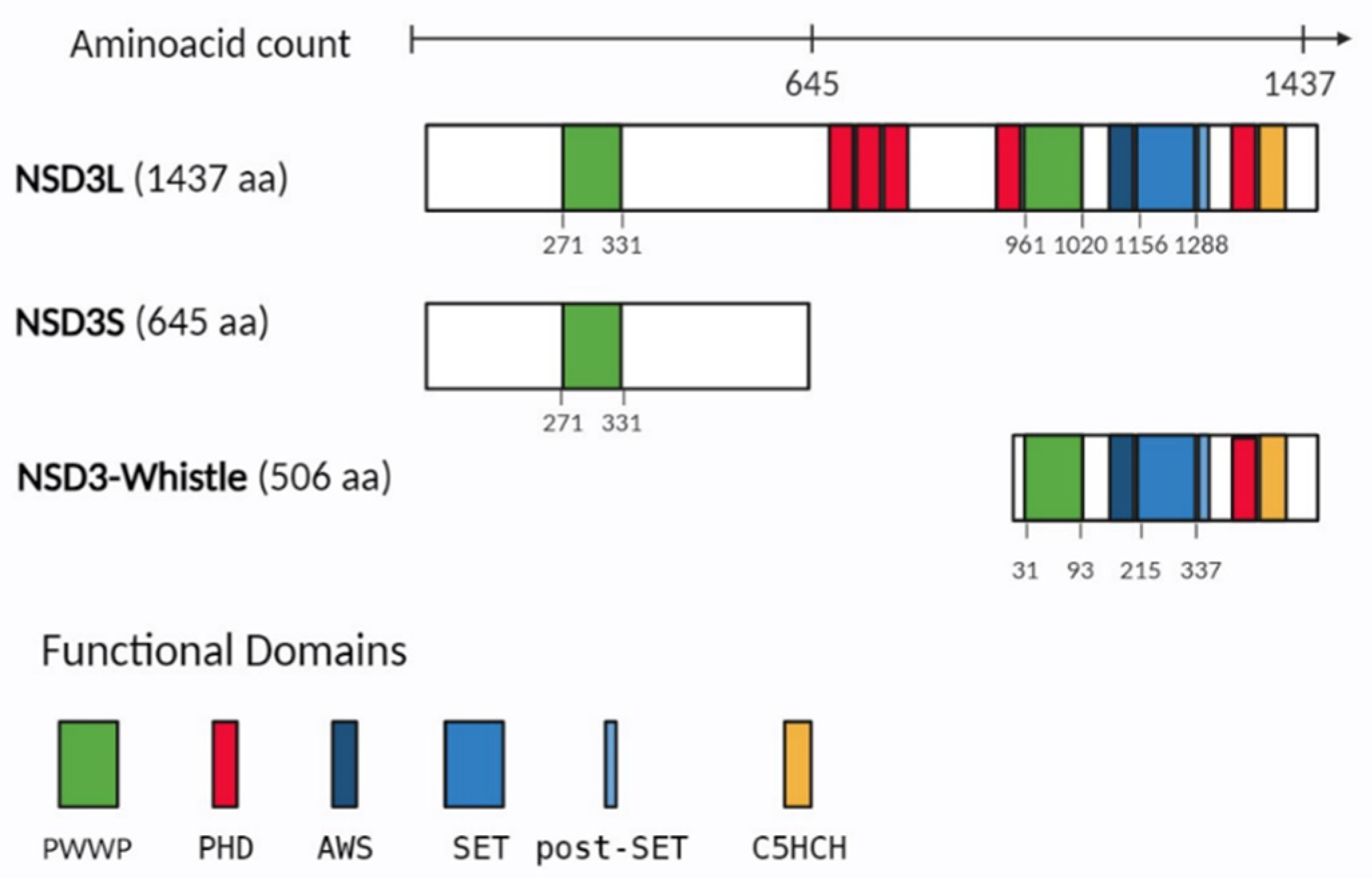
2. NSD3 protein structure
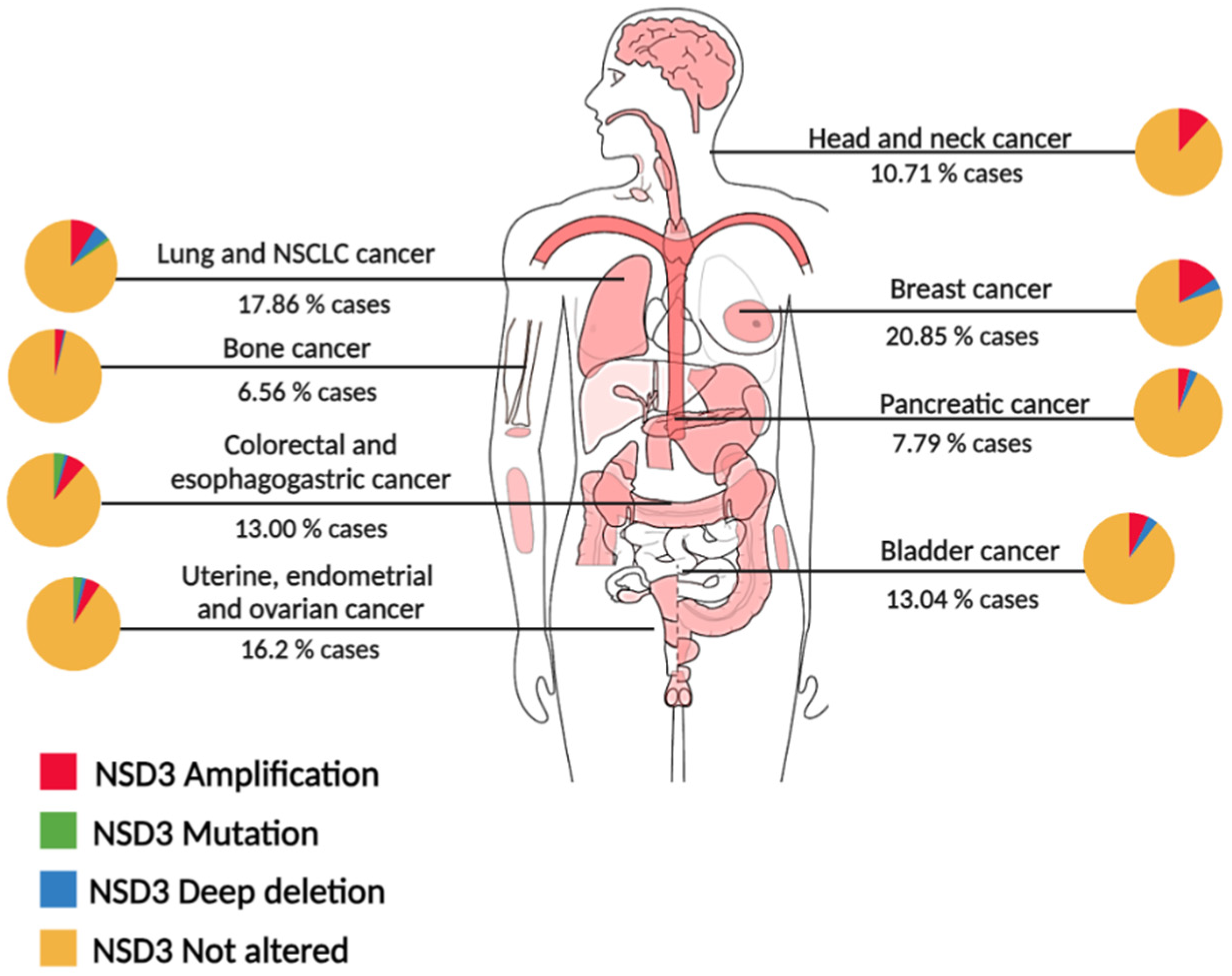
3. NSD3 alterations in cancer
3.1. Study of the amplicon 8p11-12: Chromothripsis
3.1.1. Amplification
3.1.2. Fusion proteins
3.1.3. Mutations
4. NSD3 involvement on cancer
4.1. Methyltransferase-dependent function of NSD3 in cancer
4.1.1. NOTCH pathway
4.1.2. MTOR pathway
4.1.3. EGFR pathway
4.1.4. IFN pathway
4.1.5. Cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) pathway
4.2. NSD3S isoform function as an adaptor protein
4.2.1. NSD3-NUT fusion
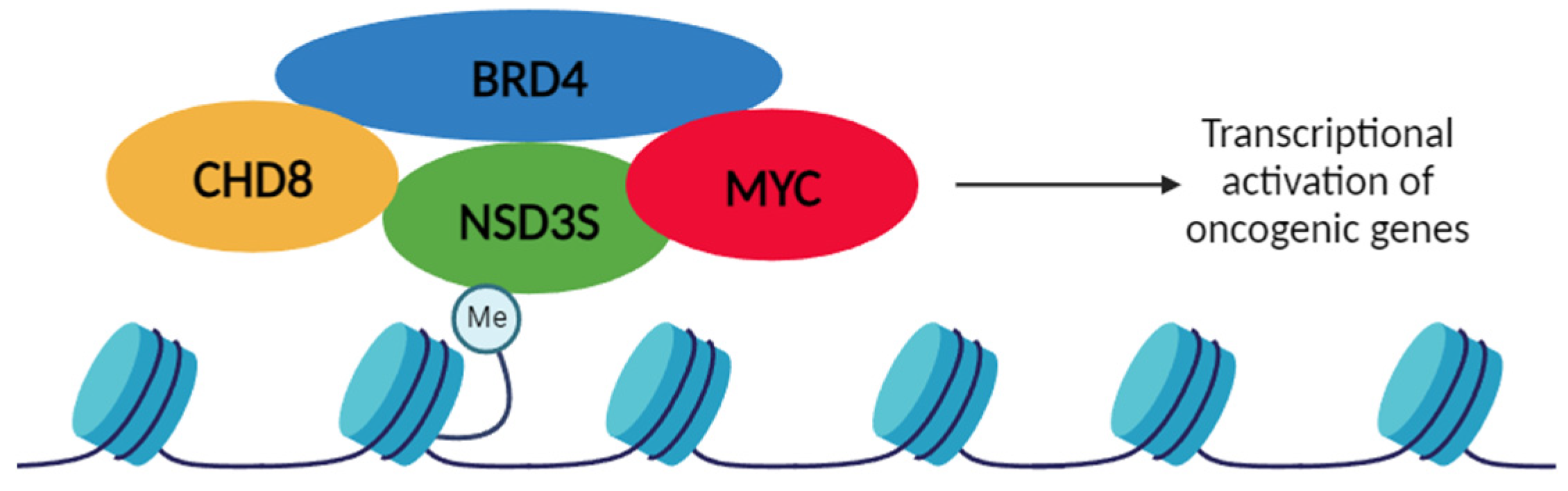
4.2.2. NSD3S-BRD4-CHD8 interactions
4.2.3. NSD3S-MYC interaction
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kornberg, R.D.; Lorch, Y. Twenty-Five Years of the Nucleosome, Fundamental Particle of the Eukaryote Chromosome. Cell 1999, 98, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barski, A.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.-Y.; Schones, D.E.; Wang, Z.; Wei, G.; Chepelev, I.; Zhao, K. High-Resolution Profiling of Histone Methylations in the Human Genome. Cell 2007, 129, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzarides, T. Histone Methylation in Transcriptional Control. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 2002, 12, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, M.; Di Luccio, E. Structural Insights into the Regulation and the Recognition of Histone Marks by the SET Domain of NSD1. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2011, 412, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Tian, W.; Yuan, G.; Deng, P.; Sengupta, D.; Cheng, Z.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Molecular Basis of Nucleosomal H3K36 Methylation by NSD Methyltransferases. Nature 2021, 590, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, J.; Coleman, K.; Tatton-Brown, K.; Hughes, H.E.; Temple, I.K.; Cole, T.R.P.; Rahman, N. Evaluation of NSD2 and NSD3 in Overgrowth Syndromes. Eur J Hum Genet 2005, 13, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauchmann, S.; Schwaller, J. NSD1: A Lysine Methyltransferase between Developmental Disorders and Cancer. Life 2021, 11, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyokawa, G.; Cho, H.-S.; Masuda, K.; Yamane, Y.; Yoshimatsu, M.; Hayami, S.; Takawa, M.; Iwai, Y.; Daigo, Y.; Tsuchiya, E.; et al. Histone Lysine Methyltransferase Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome Candidate 1 Is Involved in Human Carcinogenesis through Regulation of the Wnt Pathway. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 887-IN11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Kimball, S.; Liu, H.; Holowatyj, A.; Yang, Z.-Q. Genetic Alterations of Histone Lysine Methyltransferases and Their Significance in Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2466–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, S.F.; Gruel, N.; Nicolle, R.; Chapeaublanc, E.; Delattre, O.; Radvanyi, F.; Bernard-Pierrot, I. PPAPDC1B and WHSC1L1 Are Common Drivers of the 8p11-12 Amplicon, Not Only in Breast Tumors But Also in Pancreatic Adenocarcinomas and Lung Tumors. The American Journal of Pathology 2013, 183, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, C.; Geh, C.; Williams, V.; Heuckmann, J.M.; Menon, R.; Schneider, P.; Al-Kadhimi, K.; Dymond, M.; Smith, N.R.; Baker, D.; et al. Characterization of FGFR1 Locus in sqNSCLC Reveals a Broad and Heterogeneous Amplicon. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stec, I.; Van Ommen, G.-J.B.; Den Dunnen, J.T. WHSC1L1, on Human Chromosome 8p11.2, Closely Resembles WHSC1 and Maps to a Duplicated Region Shared with 4p16.3. Genomics 2001, 76, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angrand, P.-O.; Apiou, F.; Stewart, A.F.; Dutrillaux, B.; Losson, R.; Chambon, P. NSD3, a New SET Domain-Containing Gene, Maps to 8p12 and Is Amplified in Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Genomics 2001, 74, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Shi, Y. The Methyltransferase NSD3 Has Chromatin-Binding Motifs, PHD5-C5HCH, That Are Distinct from Other NSD (Nuclear Receptor SET Domain) Family Members in Their Histone H3 Recognition. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2013, 288, 4692–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zeng, H.; Lam, R.; Tempel, W.; Amaya, M.F.; Xu, C.; Dombrovski, L.; Qiu, W.; Wang, Y.; Min, J. Structural and Histone Binding Ability Characterizations of Human PWWP Domains. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rona, G.B.; Almeida, D.S.G.; Pinheiro, A.S.; Eleutherio, E.C.A. The PWWP Domain of the Human Oncogene WHSC1L1/NSD3 Induces a Metabolic Shift toward Fermentation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 54068–54081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, M.; Eberl, H.C.; Matarese, F.; Marks, H.; Denissov, S.; Butter, F.; Lee, K.K.; Olsen, J.V.; Hyman, A.A.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; et al. Quantitative Interaction Proteomics and Genome-Wide Profiling of Epigenetic Histone Marks and Their Readers. Cell 2010, 142, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stec, I.; Nagl, S.B.; van Ommen, G.-J.B. The PWWP Domain: A Potential Protein-Protein Interaction Domain in Nuclear Proteins Influencing Differentiation? FEBS Letters 2000. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, K.; Fraser, C.S.; Marunde, M.R.; Parker, M.M.; Sagum, C.; Burg, J.M.; Hall, N.; Popova, I.K.; Rodriguez, K.L.; Vaidya, A.; et al. Characterization of the Plant Homeodomain (PHD) Reader Family for Their Histone Tail Interactions. Epigenetics & Chromatin 2020, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, M.; Mevius, D.; Di Luccio, E. In Vitro Histone Lysine Methylation by NSD1, NSD2/MMSET/WHSC1 and NSD3/WHSC1L. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allali-Hassani, A.; Kuznetsova, E.; Hajian, T.; Wu, H.; Dombrovski, L.; Li, Y.; Gräslund, S.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; Schapira, M.; Vedadi, M. A Basic Post-SET Extension of NSDs Is Essential for Nucleosome Binding In Vitro. SLAS Discovery 2014, 19, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.-Q.; Liu, G.; Bollig-Fischer, A.; Giroux, C.N.; Ethier, S.P. Transforming Properties of 8p11-12 Amplified Genes in Human Breast Cancer. Cancer Research 2010, 70, 8487–8497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Ipsaro, J.J.; Shi, J.; Milazzo, J.P.; Wang, E.; Roe, J.-S.; Suzuki, Y.; Pappin, D.J.; Joshua-Tor, L.; Vakoc, C.R. NSD3-Short Is an Adaptor Protein That Couples BRD4 to the CHD8 Chromatin Remodeler. Molecular Cell 2015, 60, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irish, J.C.; Mills, J.N.; Turner-Ivey, B.; Wilson, R.C.; Guest, S.T.; Rutkovsky, A.; Dombkowski, A.; Kappler, C.S.; Hardiman, G.; Ethier, S.P. Amplification of WHSC1L1 Regulates Expression and Estrogen-independent Activation of ERα in SUM-44 Breast Cancer Cells and Is Associated with ERα Over-expression in Breast Cancer. Molecular Oncology 2016, 10, 850–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Kee, H.J.; Eom, G.H.; Choe, N.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.K.; Kook, H.; Kook, H.; Seo, S.B. Characterization of a Novel WHSC1-Associated SET Domain Protein with H3K4 and H3K27 Methyltransferase Activity. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2006, 345, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ICGC/TCGA Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes Consortium; Aaltonen, L.A.; Abascal, F.; Abeshouse, A.; Aburatani, H.; Adams, D.J.; Agrawal, N.; Ahn, K.S.; Ahn, S.-M.; Aikata, H.; et al. Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes. Nature 2020, 578, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.J.; Greenman, C.D.; Fu, B.; Yang, F.; Bignell, G.R.; Mudie, L.J.; Pleasance, E.D.; Lau, K.W.; Beare, D.; Stebbings, L.A.; et al. Massive Genomic Rearrangement Acquired in a Single Catastrophic Event during Cancer Development. Cell 2011, 144, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forment, J.V.; Kaidi, A.; Jackson, S.P. Chromothripsis and Cancer: Causes and Consequences of Chromosome Shattering. Nat Rev Cancer 2012, 12, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupina, K.; Goginashvili, A.; Cleveland, D.W. Scrambling the Genome in Cancer: Causes and Consequences of Complex Chromosome Rearrangements. Nat Rev Genet 2023. [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Ciriano, I.; Lee, J.J.-K.; Xi, R.; Jain, D.; Jung, Y.L.; Yang, L.; Gordenin, D.; Klimczak, L.J.; Zhang, C.-Z.; Pellman, D.S.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Chromothripsis in 2,658 Human Cancers Using Whole-Genome Sequencing. Nat Genet 2020, 52, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Xiong, T.; Li, S.; Bi, Y.; Kong, P.; Wang, F.; Cui, H.; Li, Y.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals Diverse Models of Structural Variations in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. The American Journal of Human Genetics 2016, 98, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parris, T.Z.; Rönnerman, E.W.; Engqvist, H.; Biermann, J.; Truvé, K.; Nemes, S.; Forssell-Aronsson, E.; Solinas, G.; Kovács, A.; Karlsson, P.; et al. Genome-Wide Multi-Omics Profiling of the 8p11-P12 Amplicon in Breast Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24140–24154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voutsadakis, I.A. 8p11.23 Amplification in Breast Cancer: Molecular Characteristics, Prognosis and Targeted Therapy. JCM 2020, 9, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard-Pierrot, I.; Gruel, N.; Stransky, N.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Reyal, F.; Raynal, V.; Vallot, C.; Pierron, G.; Radvanyi, F.; Delattre, O. Characterization of the Recurrent 8p11-12 Amplicon Identifies PPAPDC1B, a Phosphatase Protein, as a New Therapeutic Target in Breast Cancer. Cancer Research 2008, 68, 7165–7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner-Ivey, B.; Smith, E.L.; Rutkovsky, A.C.; Spruill, L.S.; Mills, J.N.; Ethier, S.P. Development of Mammary Hyperplasia, Dysplasia, and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma in Transgenic Mice Expressing the 8p11 Amplicon Oncogene NSD3. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2017, 164, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satpathy, S.; Krug, K.; Jean Beltran, P.M.; Savage, S.R.; Petralia, F.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Dou, Y.; Reva, B.; Kane, M.H.; Avanessian, S.C.; et al. A Proteogenomic Portrait of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell 2021, 184, 4348–4371.e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonon, G.; Wong, K.-K.; Maulik, G.; Brennan, C.; Feng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Khatry, D.B.; Protopopov, A.; You, M.J.; Aguirre, A.J.; et al. High-Resolution Genomic Profiles of Human Lung Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005, 102, 9625–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; McGee, J.; Chen, X.; Doman, T.N.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hamm, N.; Ma, X.; Higgs, R.E.; Bhagwat, S.V.; et al. Identification of Druggable Cancer Driver Genes Amplified across TCGA Datasets. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Flores, N.M.; Hausmann, S.; Lofgren, S.M.; Kharchenko, V.; Angulo-Ibanez, M.; Sengupta, D.; Lu, X.; Czaban, I.; Azhibek, D.; et al. Elevated NSD3 Histone Methylation Activity Drives Squamous Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2021, 590, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, R.; La Starza, R.; Veronese, A.; Aventin, A.; Schwienbacher, C.; Vallespi, T.; Negrini, M.; Martelli, M.F.; Mecucci, C. NUP98 Is Fused to the NSD3 Gene in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Associated with t(8;11)(P11.2;P15). Blood 2002, 99, 3857–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketani, T.; Taki, T.; Nakamura, H.; Taniwaki, M.; Masuda, J.; Hayashi, Y. NUP98–NSD3 Fusion Gene in Radiation-Associated Myelodysplastic Syndrome with t(8;11)(P11;P15) and Expression Pattern of NSD Family Genes. Cancer Genetics and Cytogenetics 2009, 190, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avenarius, M.R.; Miller, C.R.; Arnold, M.A.; Koo, S.; Roberts, R.; Hobby, M.; Grossman, T.; Moyer, Y.; Wilson, R.K.; Mardis, E.R.; et al. Genetic Characterization of Pediatric Sarcomas by Targeted RNA Sequencing. The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics 2020, 22, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, C.A.; Rahman, S.; Walsh, E.M.; Kühnle, S.; Grayson, A.R.; Lemieux, M.E.; Grunfeld, N.; Rubin, B.P.; Antonescu, C.R.; Zhang, S.; et al. NSD3–NUT Fusion Oncoprotein in NUT Midline Carcinoma: Implications for a Novel Oncogenic Mechanism. Cancer Discovery 2014, 4, 928–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Kurabe, N.; Ohnishi, I.; Yasuda, K.; Aoshima, Y.; Naito, M.; Tanioka, F.; Sugimura, H. NSD3-NUT-Expressing Midline Carcinoma of the Lung: First Characterization of Primary Cancer Tissue. Pathology - Research and Practice 2015, 211, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agaimy, A.; Tögel, L.; Stoehr, R.; Meidenbauer, N.; Semrau, S.; Hartmann, A.; Mantsopoulos, K. NSD3-NUTM1-Rearranged Carcinoma of the Median Neck/Thyroid Bed Developing after Recent Thyroidectomy for Sclerosing Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma with Eosinophilia: Report of an Extraordinary Case. Virchows Arch 2021, 479, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Yang, J.; Lv, L.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L. Comprehensive Genetic Profiling of Six Pulmonary Nuclear Protein in Testis Carcinomas with a Novel Micropapillary Histological Subtype in Two Cases. Human Pathology 2021, 115, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zeng, Z.; Han, J.; Zhu, Q. NSD3, a Member of Nuclear Receptor-Binding SET Domain Family, Is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker for Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Medicine 2023, 12, 10961–10978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xie, J.; Cai, S.; Wang, Q.; Feng, Z.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, W.; Ye, Z. Elevated Expression of Nuclear Receptor-Binding SET Domain 3 Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Cell Growth. Cell Death Dis 2021, 12, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.; Barbera, A.J.; Xu, Y.; Rutenberg, M.; Leonor, T.; Bi, Q.; Lan, F.; Mei, P.; Yuan, G.-C.; Lian, C.; et al. Human LSD2/KDM1b/AOF1 Regulates Gene Transcription by Modulating Intragenic H3K4me2 Methylation. Molecular Cell 2010, 39, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques-Fricke, B.T.; Roffers-Agarwal, J.; Hussein, A.O.; Yoder, K.J.; Gearhart, M.D.; Gammill, L.S. Profiling NSD3-Dependent Neural Crest Gene Expression Reveals Known and Novel Candidate Regulatory Factors. Developmental Biology 2021, 475, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques-Fricke, B.T.; Gammill, L.S. Neural Crest Specification and Migration Independently Require NSD3-Related Lysine Methyltransferase Activity. MBoC 2014, 25, 4174–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Min, J. Structure and Function of the Nucleosome-Binding PWWP Domain. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2014, 39, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-M.; Kee, H.-J.; Choe, N.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kook, H.; Kook, H.; Seo, S.-B. The Histone Methyltransferase Activity of WHISTLE Is Important for the Induction of Apoptosis and HDAC1-Mediated Transcriptional Repression. Experimental Cell Research 2007, 313, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.-Y.; Park, M.K.; Choi, H.-J.; An, H.W.; Park, Y.-U.; Choi, H.-J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.-Y.; Son, T.; Lee, H.; et al. NSD3-Induced Methylation of H3K36 Activates NOTCH Signaling to Drive Breast Tumor Initiation and Metastatic Progression. Cancer Research 2021, 81, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto, E.; Loewith, R.; Schmidt, A.; Lin, S.; Rüegg, M.A.; Hall, A.; Hall, M.N. Mammalian TOR Complex 2 Controls the Actin Cytoskeleton and Is Rapamycin Insensitive. Nat Cell Biol 2004, 6, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thedieck, K.; Polak, P.; Kim, M.L.; Molle, K.D.; Cohen, A.; Jenö, P.; Arrieumerlou, C.; Hall, M.N. PRAS40 and PRR5-Like Protein Are New mTOR Interactors That Regulate Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Jackson, M.W.; Wang, B.; Yang, M.; Chance, M.R.; Miyagi, M.; Gudkov, A.V.; Stark, G.R. Regulation of NF-κB by NSD1/FBXL11-Dependent Reversible Lysine Methylation of P65. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2010, 107, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Guo, L.; Duan, Z.J.; Tepper, C.G.; Xue, L.; Chen, X.; Kung, H.-J.; Gao, A.C.; Zou, J.X.; Chen, H.-W. Histone Methyltransferase NSD2/MMSET Mediates Constitutive NF-κB Signaling for Cancer Cell Proliferation, Survival, and Tumor Growth via a Feed-Forward Loop. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2012, 32, 3121–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloura, V.; Vougiouklakis, T.; Zewde, M.; Deng, X.; Kiyotani, K.; Park, J.-H.; Matsuo, Y.; Lingen, M.; Suzuki, T.; Dohmae, N.; et al. WHSC1L1-Mediated EGFR Mono-Methylation Enhances the Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Oncogenic Activity of EGFR in Head and Neck Cancer. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 40664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Yi, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, C. Downregulation of NSD3 (WHSC1L1) Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Migration via ERK1/2 Deactivation and Decreasing CAPG Expression in Colorectal Cancer Cells. OTT 2019, Volume 12, 3933–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Heylbroeck, C.; Pitha, P.M.; Hiscott, J. Virus-Dependent Phosphorylation of the IRF-3 Transcription Factor Regulates Nuclear Translocation, Transactivation Potential, and Proteasome-Mediated Degradation. Molecular and Cellular Biology 1998, 18, 2986–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Hata, N.; Asagiri, M.; Nakaya, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Tanaka, N. Positive Feedback Regulation of Type I IFN Genes by the IFN-inducible Transcription Factor IRF-7. FEBS Letters 1998, 441, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Xu, X.; Xie, B.; Zhao, Y.; Li, N.; Cao, X. The Methyltransferase NSD3 Promotes Antiviral Innate Immunity via Direct Lysine Methylation of IRF3. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2017, 214, 3597–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Marti, T.M.; Dorn, P.; Schmid, R.A.; Peng, R.-W.; Shu, Y. Dissecting the Immunological Profiles in NSD3-Amplified LUSC through Integrative Multi-Scale Analyses. Cancers 2022, 14, 4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-S.; Min, K.-W.; Kim, D.-H.; Son, B.-K.; Kwon, M.-J.; Hong, S.-M. High WHSC1L1 Expression Reduces Survival Rates in Operated Breast Cancer Patients with Decreased CD8+ T Cells: Machine Learning Approach. JPM 2021, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saloura, V.; Vougiouklakis, T.; Zewde, M.; Kiyotani, K.; Park, J.-H.; Gao, G.; Karrison, T.; Lingen, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Hamamoto, R. WHSC1L1 Drives Cell Cycle Progression through Transcriptional Regulation of CDC6 and CDK2 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42527–42538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Cho, H.; Toyokawa, G.; Kogure, M.; Yamane, Y.; Iwai, Y.; Hayami, S.; Tsunoda, T.; Field, H.I.; Matsuda, K.; et al. The Histone Methyltransferase Wolf–Hirschhorn Syndrome Candidate 1-like 1 (WHSC1L1) Is Involved in Human Carcinogenesis. Genes Chromosomes & Cancer 2013, 52, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.R.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, H.J.; Baek, M.; Bae, S.; Soh, J.W.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.S. Cyclin G1 Overcomes Radiation-Induced G2 Arrest and Increases Cell Death through Transcriptional Activation of Cyclin B1. Cell Death Differ 2006, 13, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, H.; Rachmin, I.; Yissachar, N.; Cohen, S.; Amiel, A.; Haffner, R.; Lavi, L.; Motro, B. Nek7 Kinase Targeting Leads to Early Mortality, Cytokinesis Disturbance and Polyploidy. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4046–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Piao, L.; Zhuang, M.; Qiu, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, M.; Ren, D. Silencing of Histone Methyltransferase NSD3 Reduces Cell Viability in Osteosarcoma with Induction of Apoptosis. Oncology Reports 2017, 38, 2796–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eot-Houllier, G.; Magnaghi-Jaulin, L.; Bourgine, G.; Smagulova, F.; Giet, R.; Watrin, E.; Jaulin, C. The Histone Methyltransferase NSD3 Contributes to Sister Chromatid Cohesion and to Cohesin Loading at Mitotic Exit. Journal of Cell Science 2023, 136, jcs261014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynoird, N.; Schwartz, B.E.; Delvecchio, M.; Sadoul, K.; Meyers, D.; Mukherjee, C.; Caron, C.; Kimura, H.; Rousseaux, S.; Cole, P.A.; et al. Oncogenesis by Sequestration of CBP/P300 in Transcriptionally Inactive Hyperacetylated Chromatin Domains. EMBO J 2010, 29, 2943–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, D.B.; Rueckert, J.; Cornea, V.; Lee, C.Y.; Dueber, J.; Bocklage, T. Thyroid Carcinoma with NSD3::NUTM1 Fusion: A Case with Thyrocyte Differentiation and Colloid Production. Endocr Pathol 2022, 33, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barletta, J.A.; Gilday, S.D.; Afkhami, M.; Bell, D.; Bocklage, T.; Boisselier, P.; Chau, N.G.; Cipriani, N.A.; Costes-Martineau, V.; Ghossein, R.A.; et al. NUTM1-Rearranged Carcinoma of the Thyroid: A Distinct Subset of NUT Carcinoma Characterized by Frequent NSD3-NUTM1 Fusions. American Journal of Surgical Pathology 2022, 46, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Sowa, M.E.; Ottinger, M.; Smith, J.A.; Shi, Y.; Harper, J.W.; Howley, P.M. The Brd4 Extraterminal Domain Confers Transcription Activation Independent of pTEFb by Recruiting Multiple Proteins, Including NSD3. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2011, 31, 2641–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Bengsch, F.; Svoronos, N.; Rutkowski, M.R.; Bitler, B.G.; Allegrezza, M.J.; Yokoyama, Y.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Bradner, J.E.; Conejo-Garcia, J.R.; et al. BET Bromodomain Inhibition Promotes Anti-Tumor Immunity by Suppressing PD-L1 Expression. Cell Reports 2016, 16, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ivanov, A.A.; Su, R.; Gonzalez-Pecchi, V.; Qi, Q.; Liu, S.; Webber, P.; McMillan, E.; Rusnak, L.; Pham, C.; et al. The OncoPPi Network of Cancer-Focused Protein–Protein Interactions to Inform Biological Insights and Therapeutic Strategies. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 14356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Pecchi, V.; Kwan, A.K.; Doyle, S.; Ivanov, A.A.; Du, Y.; Fu, H. NSD3S Stabilizes MYC through Hindering Its Interaction with FBXW7. Journal of Molecular Cell Biology 2020, 12, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Lee, A.-Y.; Lai, H.-T.; Zhang, H.; Chiang, C.-M. Phospho Switch Triggers Brd4 Chromatin Binding and Activator Recruitment for Gene-Specific Targeting. Molecular Cell 2013, 49, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaiah, B.N.; Mu, J.; Akman, B.; Uppal, S.; Weissman, J.D.; Cheng, D.; Baranello, L.; Nie, Z.; Levens, D.; Singer, D.S. MYC Protein Stability Is Negatively Regulated by BRD4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2020, 117, 13457–13467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parris, T.Z.; Kovács, A.; Hajizadeh, S.; Nemes, S.; Semaan, M.; Levin, M.; Karlsson, P.; Helou, K. Frequent MYC Coamplification and DNA Hypomethylation of Multiple Genes on 8q in 8p11-P12-Amplified Breast Carcinomas. Oncogenesis 2014, 3, e95–e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Lan, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, A.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, X.; Cao, Z.; et al. NSD2 Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis through Methylating and Activating STAT3 Protein. Oncogene 2021, 40, 2952–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrell, C.M.; Dorsam, S.T.; Ohta, H.; Humphries, R.K.; Derynck, M.K.; Haqq, C.; Largman, C.; Lawrence, H.J. Activation of Stem-Cell Specific Genes by HOXA9 and HOXA10 Homeodomain Proteins in CD34 + Human Cord Blood Cells. STEM CELLS 2005, 23, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttcher, J.; Dilworth, D.; Reiser, U.; Neumüller, R.A.; Schleicher, M.; Petronczki, M.; Zeeb, M.; Mischerikow, N.; Allali-Hassani, A.; Szewczyk, M.M.; et al. Fragment-Based Discovery of a Chemical Probe for the PWWP1 Domain of NSD3. Nat Chem Biol 2019, 15, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, A.; Du, W.; Huang, Y.; Wu, F.; Yu, L.; Li, J.; Wen, C.; et al. Discovery of a Potent and Selective Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) Degrader of NSD3 Histone Methyltransferase. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2022, 239, 114528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Hwang, I.; Kim, S.H.; Chung, H.W.; Ji, M.; Moon, S.; Park, H.; Kong, G.; Hur, W. Identification of Novel Class Inhibitors of NSD3 Methyltransferase Showing a Unique, Bivalent Binding Mode in the SET Domain. Chem Biol Drug Des 2023, 102, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



