1. Introduction
Magnesium is one of the most common elements on the planet with a content of about 2% in the earth’s crust. Magnesium is characterized by high specific rigidity and strength, while being light in weight. In this regard, magnesium is used in many industries. The large production and growing consumption of magnesium has led to a greatly increasing volume of magnesium waste, which has extremely negative impacts on the environment. Magnesium waste in the form of chips is regularly generated during the mechanical processing of castings and sheets, while about 30% of magnesium is lost in the form of scrap. In this regard, it is important to resort to magnesium recycling to manage the use of primary magnesium. Hydride dispersion of magnesium waste to produce magnesium hydride is considered as a potential direction for processing magnesium waste. This approach allows to process magnesium waste of any shape and size without restrictions on quantity with magnesium hydride as a final product.
Magnesium hydride is one of the most well-known metals with the hydrogen storage capacity of about 7.6 wt.%. Magnesium proves itself as one of the candidates for its use in hydrogen storage systems. Despite all its advantages, it has a sufficiently high hydrogen yield temperature – about 400
oC due to its high stability, which is reflected in a sufficiently high enthalpy of hydride formation. The microstructure of the material is constantly being improved during high-energy milling [
1,
2,
3], which contributes to obtaining a homogeneous microstructural material [
4]. Milling in a planetary ball mill not only improves the microstructure of the material during milling process, but also destroys the oxide film on the magnesium surface, which allows accelerating the kinetics of the sorption/desorption reaction.
Further attempts were made to develop suitable catalysts, which led to a rapid absorption and desorption time of hydrogen (2 min at a temperature of 300°C) for magnesium hydride [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. Numerous experiments have been carried out with attempts to change the enthalpy of hydride formation using the chemical composition of the alloy. The most prominent representative is Mg
2NiH
4 [
14]. In the course of various studies, new methods for the synthesis of magnesium-based hydrides and magnesium hydride with reduced reaction enthalpy and increased capacity have been developed [
15,
16,
17]. Consequently, many efforts have been made to improve the performance of such hydride-forming metals through a variety of activation techniques and the addition of catalysts.
Several attempts have been made to improve the kinetics of the surface. For this purpose, various additives were used, among which platinum group metals, such as nickel [
18,
19], hydride–forming – Ce, New Brunswick, Ti [
20], low-temperature hydrides of the LaNi5 type [
21,
22,
23], non-hydride-forming by the type of iron, cobalt and chromium, positively affecting the kinetics of sorption of magnesium-based hydrides [
24,
25], as well as metal oxides [
8]. Three-dimensional transition metalloids and oxides could change and significantly improve the sorption kinetics [
9,
10,
13,
26].
The most promising of the known metals, mentioned before, for hydrogen storage in the bound state is magnesium. It is most commonly used in various studies, observing its interaction with hydrogen and improving its sorption and desorption characteristics with various catalysts. Many studies have considered and investigated various metals as additives such as nickel [
37,
38], cobalt [
39], iron [
40], titanium [
41], vanadium [
42], copper [
43], palladium [
44], fluorides and so on [
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51].
All the studies were aimed at establishing the nature of the interaction of magnesium with hydrogen in the presence of the above catalysts. Despite this variety of studies, the problem of high stability of the metal-hydride bond and, consequently, high temperature of hydrogen desorption from the material remains relevant to this day. At the same time, in similar studies [
34,
38,
42,
52,
53,
54], the question of finding the optimal ratio between the acceptable hydrogen yield temperature and the maximum hydrogen content by mass often arises. Also, the size of the added particles plays an important role, which does not allow to achieve the desired result. Particle size factor of added catalyst powders plays a key role in the process of hydrogen desorption from magnesium hydride and affects the process temperature. The choice of the optimal catalyst particle size is based on the required desorption kinetics and uniformity of catalyst distribution over the material volume. To improve the efficiency of the process of hydrogen desorption from magnesium hydride, researchers are studying various ways to modify this material. One possible solution is the addition of aluminum. Aluminum has a number of properties that make it attractive for use as an additive to magnesium hydride. First, it is highly active in reactions with hydrogen, which can accelerate the process of hydrogen release from MgH2. Secondly, aluminum has low cost and availability, making it a cost-effective option for industrial scale use. One of the main issues associated with the addition of aluminum to magnesium hydride is the effect of this process on the hydrogen desorption temperature. Since magnesium hydride has high stability of hydrogen bonds, i. e. high desorption temperature, there are some solutions to reduce it, and consequently to reduce the activation energy of desorption: additional grinding in a planetary ball mill, addition of catalysts, varying the synthesis parameters, etc.
In the study of Doppiu S. et al. nanocrystalline magnesium-nickel hydride MgH2, the grains (crystallites) of which have a size of about 11-12 nm, was used. It was synthesized in a magnetic mill by controlled mechanical milling of magnesium powder with the addition of various forms of nickel-lead powder obtained by decomposition of nickel carbonyl from 0.5 to 2 wt%. The powder catalysts used were designated as micro-Ni, submicro-Ni and nano-Ni, respectively. Based on the data obtained, nano-Ni was found to be the most effective catalyst with the property of significantly increasing the rate of hydrogen uptake by magnesium to form hydride. At addition of 0.5 wt% of nano-nickel catalyst powder the rate of hydrogen absorption increases approximately twice in comparison with pure magnesium.
The LiMg(AlH
4)
3 hydride used in the study [
55], is able to release about 7.2 wt.% of the total amount of hydrogen during the two-step thermal decomposition reaction. The authors indicate that the first temperature peak was observed at 120 degrees Celsius and the second at 160 degrees Celsius. The decomposition process of MgD2 is explained by thermodynamic destabilization due to the formation of Al
xMg
y phases. The experimentally detected decomposition modes of Li-Mg alanate are presumably related to the enthalpy of decomposition, since the contaminated or accelerated LiMgAlH
6 intermediate may participate more actively in the thermal decomposition reaction at lower temperatures. Whereas pure LiMgAlH
6, which has kinetic barriers, requires higher temperatures to initiate the two-step decay during the exothermic reaction.
Jinzhe Lyu et. al evaluated the hydrogen accumulation properties of Mg and Mg-Al hydrides. The authors found several key points in their study: 10 at. % aluminum coating accelerates hydrogen desorption by a factor of 10 and has a higher hydrogen content compared to Mg coating, Mg-10 at.% Al exhibits a temperature decrease of 17 degrees Celsius. The temperature decrease is due to the weakening of the Mg-H bond. In the study, the authors also suggested that this behaviour of the aluminum substrate is due to discontinuous growth on the polyimide base. Aluminum forms island-like islands that do not form an alloy with magnesium and serve as heterogeneous nucleation centres to trap hydrogen atoms.
C.X. Shang et al. demonstrated in their study powder mixtures based on magnesium hydride with doping of 8 mol% aluminum, nickel, iron, titanium, copper and niobium. According to the results, the heat of formation obtained during thermally stimulated desorption at 300oC, the MgH2-8 mol% Al system had a heat of formation -28.36 kJ/mol, compared to magnesium hydride -75.99 kJ/mol. The extent of the effect of increasing the desorption rate and interaction with hydrogen decreases from Ni, Al, Fe, Nb, Ti to Cu.
On this basis, a number of studies have been carried out to determine the effect of the size of the added particles on the kinetics of sorption and desorption reactions. The same was carried out in this study - nanosized aluminum powder produced by the method of electric explosion of wires (EEW) was used and its effect on the hydrogen yield temperature from the composite was determined. In this work, EEW-aluminum powder obtained on the basis of Tomsk Polytechnic University acts as such an additive [
56,
57]. The EEW method for producing nanopowders, in fact, combines the characteristics of dispersing methods - destruction of the conductor under the action of electricity and methods of vaporization and condensation - most of the material of the conductor during the electric pulse explosion passes into the gas phase. And in this case, the amount of metal turned into vapor is determined by the amount of energy injected into the conductor. One of the advantages of electric explosive technology is its flexibility - it allows to produce nanopowders of metals, alloys, intermetallides and chemical compounds with nonmetals using the same equipment. In the production of nanopowders of metals, alloys and intermetallic substances, inert gases, especially argon, are usually used as a gas medium. Nanopowders produced in such an environment are pyrophoric, i. e. they easily burn in contact with oxygen. To prevent this effect, they are passivated by slow oxidation with air components or by applying a special coating to their surface. It is important to note that the properties of nanopowders produced by the electroexplosion method strongly depend not only on the electrical parameters of their production, but also on the conditions of passivation.
The method of EEW is widely used to obtain nano-sized metal powders, including from wire after operation. This powder has a core-metal structure, the shell is an oxide film, which allows it to be used to improve the properties of a composite based on magnesium hydride.
2. Materials and Methods
In this work, magnesium hydride powder was obtained by the method of hydride dispersion of pure (99%) magnesium chips. Particle size of obtained powder is up to 300 microns. Fine aluminum powder was produced from aluminum wire after operation by the method of electric explosion of wires. The Division of Experimental Physics at Tomsk Polytechnic University developed a Gas Reaction Automated Machine (GRAM) to prepare magnesium hydride and study the accumulation of hydrogen in it.
An initial activation of magnesium was carried out using a planetary ball mill to increase its surface area and improve its interaction with hydrogen in the GRAM complex. The ratio of the mass of balls to the mass of magnesium powder in milling jars was 10:1. Synthesis of the samples was also carried out using this equipment for 2 hours in argon atmosphere with a ball-to-powder mass ratio of 20:1. All parameters were selected on the basis of previous studies, including those carried out at the Division of Experimental Physics by our research group.
Preparation of samples and their loading into milling jars was carried out in argon atmosphere (99.9% purity) using a leak-proof glove box SPEKS GB 02M ("Spectroscopic Systems", Russia). The mass content of hydrogen was analyzed using RHEN602 instrument (LECO Corporation, USA). The microstructure of the obtained materials was investigated using a TESCAN VEGA 3 SBU microscope (Tescan Orsay Holding a.s., Czech Republic), and the elemental composition was analyzed by energy dispersive spectroscopy (X-Max 50, Oxford Instruments plc., UK). The phase composition of the materials was studied by X-ray diffraction in the angle range of 5-90o (XRD-7000S, Shimadzu, Japan). High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images were obtained using JEM-2100F (JEOL, Japan).
3. Results and discussions
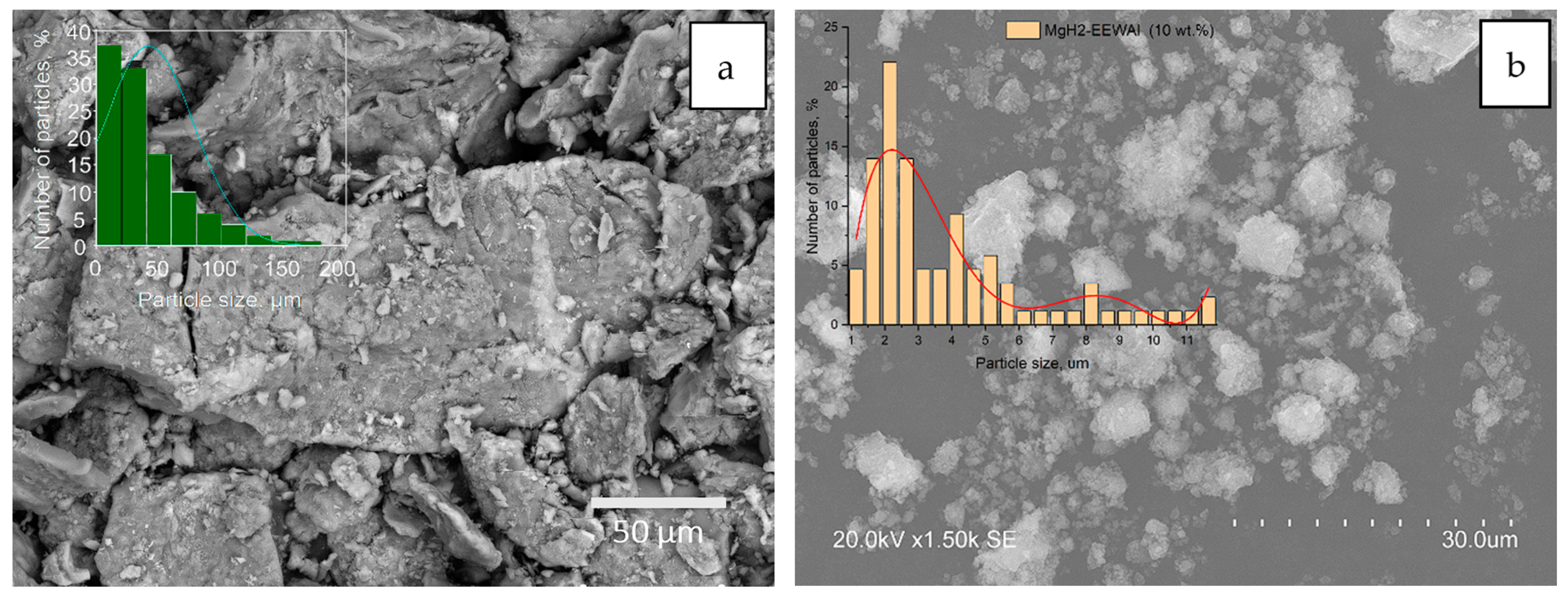
The microstructure and X-ray diffraction patterns of magnesium hydride and composite are shown in
Figure 1. The obtained experimental data indicate a positive effect in the reduction of particle size in the synthesis process in a planetary ball mill. A change in microstructure is demonstrated, which in turn, based on previous studies, also had a positive effect on the desorption characteristics of the material. The energy dispersive analysis shown in
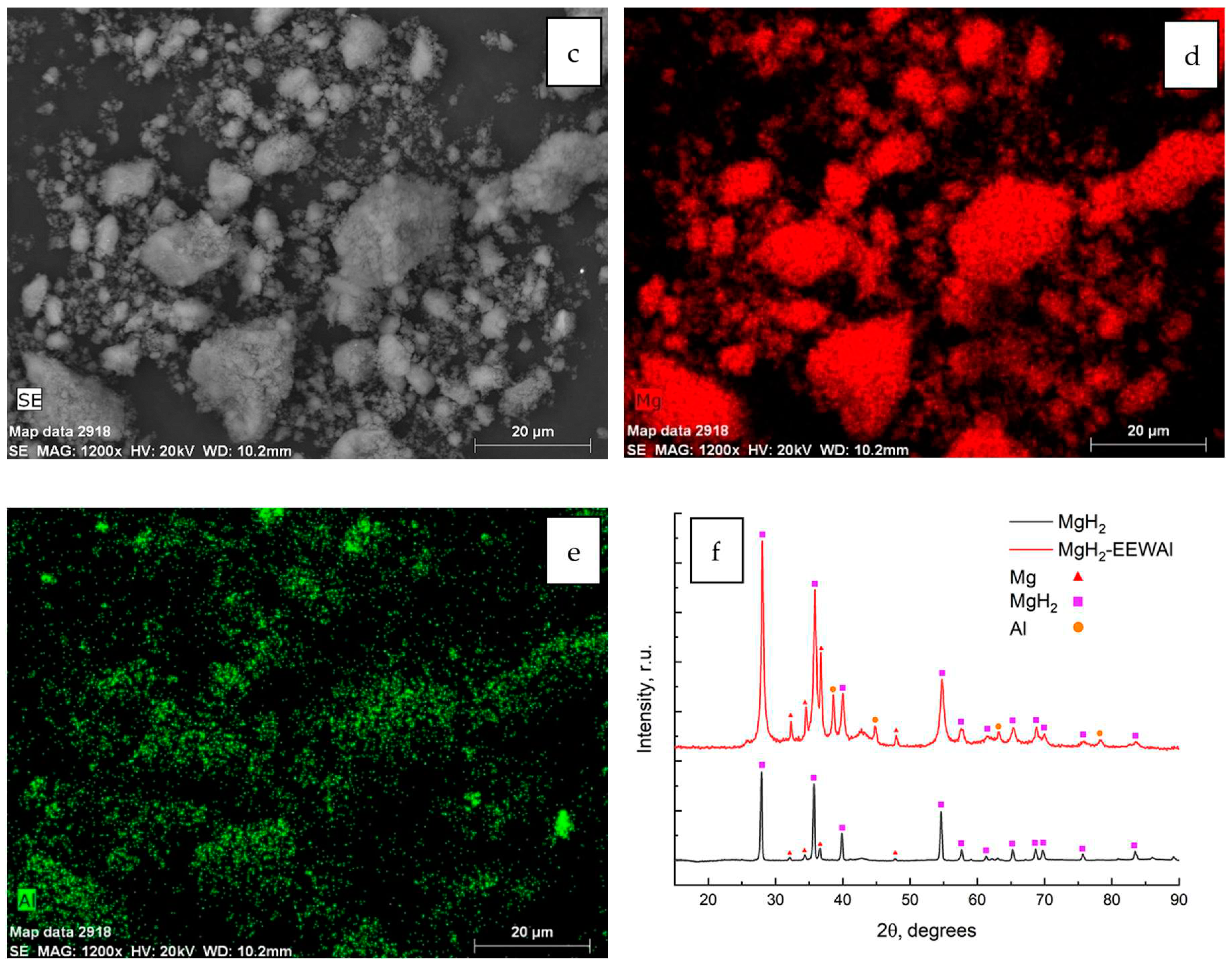
Figure 1 (c-e) allowed us to create distribution maps of elements on the surface of the sample. During this analysis, the scattered X-rays recorded when the sample was exposed to the electron beam allowed the identification of the elements present in the material. Elemental mapping during energy dispersive analysis provided information on the micro- and nanostructure of the material, its chemical composition, and the spatial distribution of elements on the sample surface.
X-ray diffraction analysis on the sample surface allowed the identification of the phases present in the materials. Diffraction patterns of the materials are typical for the obtained samples. The observed phases are mainly magnesium hydride, magnesium and aluminum phases. The synthesis of the materials resulted in an increase in the micro strains of the material, which is a consequence of the method used to produce the composite.
After obtaining samples by scanning electron microscopy, the size of magnesium hydride particles was found to be about 150 μm and agglomerates reaching about 200 μm in size (
Figure 1, a). The selected rotational speed of the grinding bowls allowed to obtain magnesium hydride particles of smaller size. (
Figure 1, f) clearly shows that most of the phase composition is magnesium hydride with a small amount of magnesium phase. Particle size reduction using a planetary ball mill is an important process in the field of materials science. The benefits of particle size reduction using a planetary ball mill include the ability to produce materials with improved physical, chemical and mechanical properties by increasing the specific surface area of the particles, as well as creating nanostructured materials with unique properties.
Scanning electron microscopy study showed a significant decrease in the size of the composite particles up to 11 µm (
Figure 1, b), which indicates the optimally selected parameters of synthesis of the materials - 900 rpm for 2 hours. The elemental composition of the composite is mainly magnesium hydride with uniformly distributed EEW aluminum powder particles on magnesium (
Figure 1, c-e). At the same time, analysis of the phase composition of the materials did not reveal the presence of extraneous elements. The diffraction patterns show characteristic peaks observed at appropriate diffraction angles in the range of angles 5-90
o.
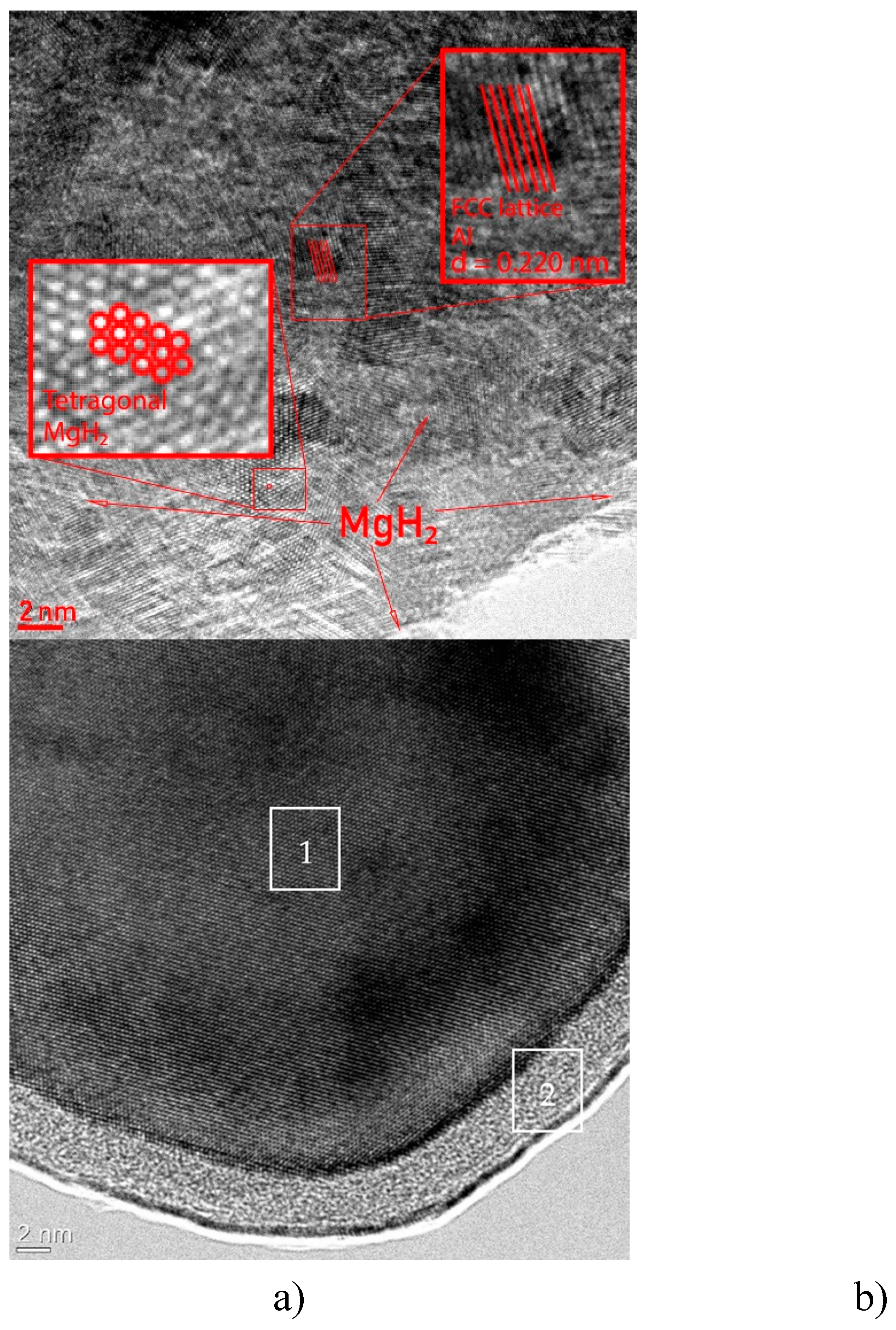
TEM micrographs of the MgH
2-EEWAl sample (10 wt.%) and separate particle of Al are shown on the
Figure 2. The method of transmission electron microscopy allowed to specify crystal structures of synthesized materials.
The structure of the composite obtained by synthesis in a planetary ball mill is shown in
Figure 2 (a) and it can be observed how the aluminum and magnesium hydride atoms are distributed in the volume. Aluminum has FCC lattice while magnesium hydride has a tetragonal rutile type lattice. According to microscopy data, the aluminum nanoparticle (Fig. 2, b) is a homogeneous metal core 1, covered with a homogeneous protective passivating oxide-hydroxide shell 2. The figure clearly shows the structures of the components of this composite. The interplane distance for aluminum was experimentally obtained equal to 0.220 nm (theoretical 0.202 nm). Presumably, this structure of magnesium hydride and aluminum hydride allows for weaker Mg-H bonds and promotes faster decomposition of magnesium hydride.
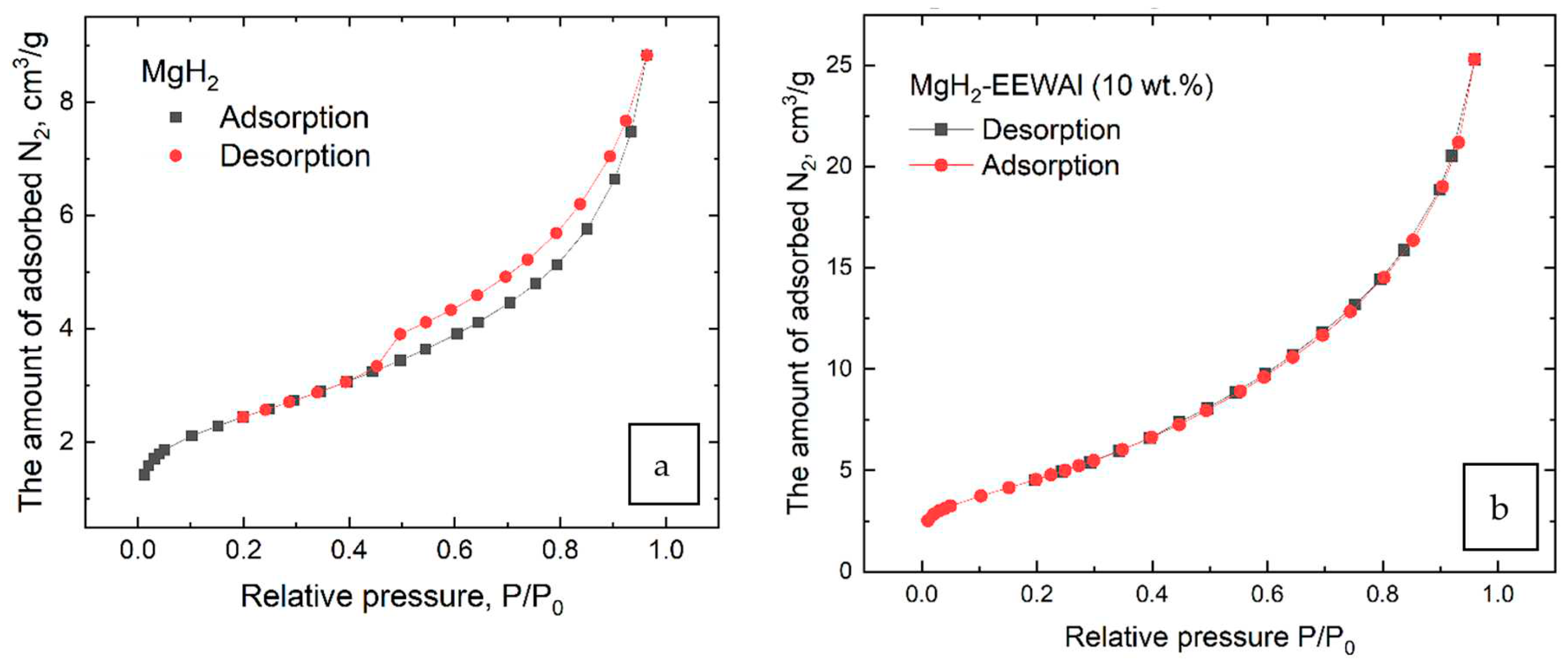
Further, the volumetric and structural characteristics of the material were evaluated using BET surface analysis. The method proposed by Brunauer, Emmett and Teller (BET) is a widely used method for determining the specific surface area of materials. This method is based on measuring the volume of gas absorbed by a material at different relative pressures and then analysing this data using the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller equation. The BET equation describes the relationship between the volume of gas absorbed and the relative pressure in the pores of the material. It takes into account that gas molecules will preferentially adsorb on the pore surface of the material, resulting in an increase in the volume of absorbed gas as the relative pressure increases. Using the BET equation, the specific surface area of the material can be calculated based on measured data on the volume of absorbed gas at different relative pressures. This parameter is an important parameter because the specific surface area of a material affects its chemical, physical and technological properties. The BET method provides information on the structure of porous materials, their surface area and properties, which is important for the development of new materials and optimisation of production processes.
As mentioned earlier in the text, the additional milling process in the planetary ball mill helped to significantly increase the surface area of the materials in order to improve their interaction with hydrogen, for which a corresponding BET analysis was performed to confirm this statement (
Figure 3).
During the BET analysis, it was found that the surface area was increased from 8.5 to 17.5 m2/g. The co-milling of magnesium and aluminum hydride particles in a planetary ball mill is a process of mechanical milling of materials under the action of friction and impact forces. This process results in a reduction in particle size and an increase in particle surface area. Magnesium hydride and aluminum are highly reactive, and grinding these materials together in the mill results in an increase in the surface area of each particle. This in turn increases the availability of active sites for chemical reactions such as hydrogenation or oxidation. Increasing the surface area of magnesium and aluminum hydride particles can be useful in various industrial processes such as the production of composite materials, catalysts or energy intensive systems.
Thermal Stimulated Desorption (TSD) is an experimental technique used to study the properties of materials, particularly composites. In the process of thermally stimulated desorption, the sample is heated, which promotes the desorption (release) of gases that have been absorbed by the material while it has been exposed to a specific environment. The basic principle of the method is that the gases absorbed by the material are released from heating temperatures, allowing their characteristics to be studied and their concentration quantified. This provides information on the absorption of gases, the structure of the material, its chemical stability, and the effect of various influences on its properties.
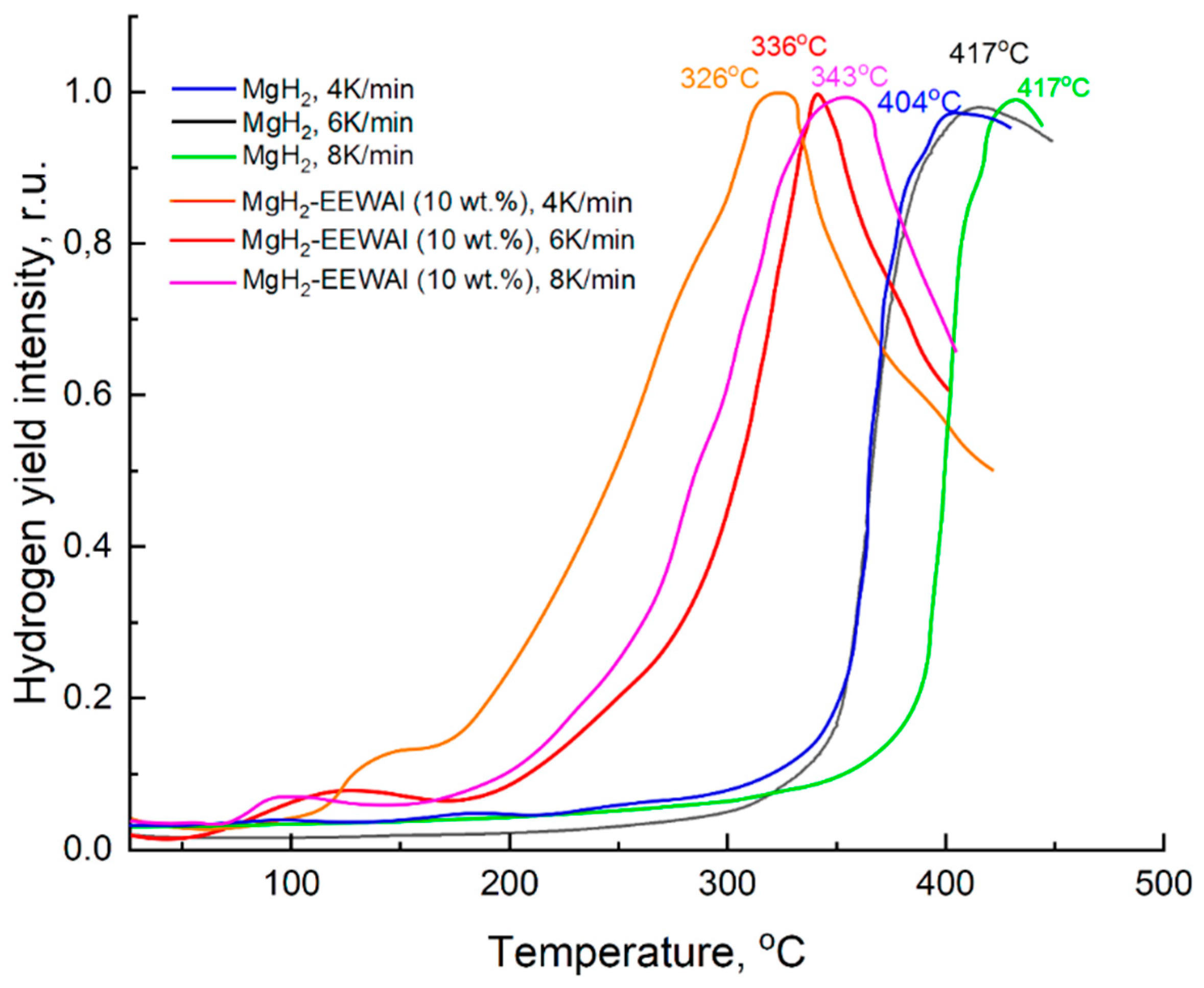
According to the results of the thermally stimulated desorption (TSD) (
Figure 4), it was demonstrated that the largest amount of hydrogen released was at a temperature of about 336
oC at a heating rate of 6 K/min. In comparison with pure magnesium hydride, the difference in desorption temperatures is 81 degrees. This decrease in temperature is presumably due to its structural and phase changes during the co-milling process in a planetary ball mill, as a consequence of the catalytic effect of aluminum and its ability to destabilize Mg-H bonds.
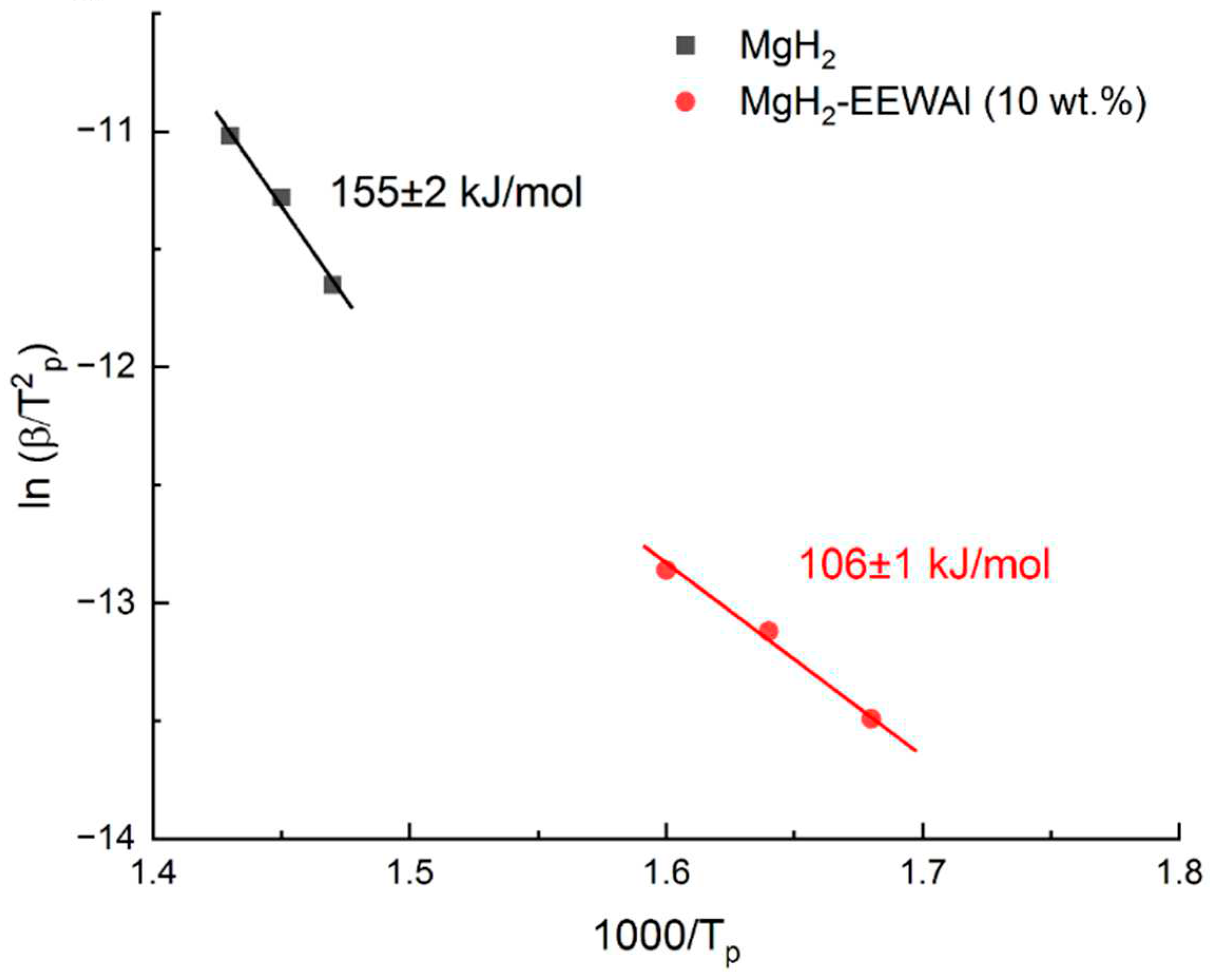
Presumably, the decrease in the desorption temperature was influenced by the catalytic effect of the addition of aluminum powder produced by the electric explosion of wires method. At the same time, the temperature of the beginning of the hydrogen release turned out to be about 117oC, and the maximum was 336oC. There is also an effect from the joint milling of synthesized materials, which made it possible to reduce the particle size and thereby reduce the activation energy of desorption. Based on the results of thermally stimulated desorption, the desorption activation energy was calculated, presented below. The Kissinger method is an overwhelmingly popular way of estimating the activation energy of thermally stimulated processes. The essence of the method is to remove these desorption curves at different heating rates (in this case – 4, 6, 8 K/min), resulting in peak shifts. The temperature values at peaks at different heating rates are taken, a calculation is performed to construct in Arrhenius coordinates (1000/Tp from ln(β/T2p)) and the angular coefficient (A) is determined, which gives the activation energy (Ed).
Table 1 shows the calculation of the angular coefficient for calculating the activation energy using the Kissinger method.
Based on the obtained values of temperature maxima at different heating rates, a recalculation was performed for the construction in Arrhenius coordinates (
Figure 5) and the angular coefficient A was found, which will then be applied in calculating the activation energy.
where А – angular coefficient, R – universal gas constant,
β- heating rate,
Tp - the temperature of the peak hydrogen yield.
Based on the above equation, it becomes possible to determine the activation energy of desorption. Further, Arrhenius curves were constructed (
Figure 5), which also allowed us to estimate this energy.
After plotting, the angular coefficient was found and the activation energy was calculated by formula 1, which is shown for each of the materials in
Table 2.
The data obtained show a significant decrease in the activation energy of desorption, which is due to the catalytic effect of the addition of aluminum obtained by the electric wire explosion method.
According to the calculation results, it is clearly showed that there is a decrease in the energy. Difference between the initial magnesium hydride and the composite is 49 kJ/mol. Presumably, nanoscale particles of aluminum produced by the electric explosion of wires method can reduce the activation energy due to joint milling in a planetary ball mill and changes in the structure of magnesium hydride itself. This achieves a catalytic and synergistic effect in reducing the desorption temperature by 100 degrees. The shift of the temperature peak of hydrogen desorption from magnesium hydride is presumably related to structural and phase changes in the obtained composite during co-milling. The catalytic effect that was shown in this work is a base for further studies related to this type of additives. In the future it is planned to vary the fraction of grinding balls, synthesis parameters and the amount of added material to establish the regularities of composite behavior.
4. Conclusions
In this article, we used magnesium chips to produce magnesium hydride and aluminum wire after use to produce nano-sized aluminum powder. The composite MgH2–10 wt.%EEWAl was synthesized by ball milling using obtained magnesium hydride and aluminum nanosized powder. The microstructure and hydrogenation/dehydrogenation properties of the composite MgH2–10 wt.%EEWAl and the effect of EEWAl on the hydrogen properties of Mg/MgH2 were determined. Using scanning electron microscopy, it was shown that the composite consists of MgH2 particles with a uniform distribution of aluminum nanoparticles on their surface. The average particle size of the composite is about 1.5 microns. Based on the experimental results, the addition of nanoscale aluminum powder improved the desorption characteristics of MgH2. The addition of aluminum powder produced by the electric explosion of wires method made it possible to reduce the desorption temperature to 336oC at heating rate 6 K/min in comparison with conventional magnesium hydride, the hydrogen yield temperature of which was 417oC. This is presumably due to the catalytic effect in reducing the activation energy (ΔEd = 49 kJ/mol) of desorption, which in turn allowed to significantly reduce the temperature. The beginning of the hydrogen release occurred at a temperature of about 117oC. The mass content of hydrogen in the composite was 5.5 wt.%. The results obtained make it possible to expand the possibility of using magnesium and aluminum waste for hydrogen energy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.N.K.; validation, A.A.K.; resources, V.N.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.K.; writing—review and editing, V.N.K., A.V.M.; supervision, V.N.K.; project administration, V.N.K.; funding acquisition, V.N.K. and A.V.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Governmental Program, Grant № FSWW-2023-0005.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- R. Schulz: S. Boily, L. Zaluski, A. Zaluska, P. Tessier, J.O. Stro¨m-Olsen, Innovations in Metallic Materials (1995) 529.
- Schulz R. et al. Recent developments in the applications of nanocrystalline materials to hydrogen technologies //Materials Science and Engineering: A. – 1999. – Т. 267. – №. 2. – С. 240-245. [CrossRef]
- Zaluska A., Zaluski L., Ström–Olsen J. O. Nanocrystalline magnesium for hydrogen storage //Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 1999. – Т. 288. – №. 1-2. – С. 217-225. [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana C. Mechanical alloying and milling //Progress in materials science. – 2001. – Т. 46. – №. 1-2. – С. 1-184. [CrossRef]
- Liang G. et al. Hydrogen desorption kinetics of a mechanically milled MgH2+ 5at.% V nanocomposite //Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2000. – Т. 305. – №. 1-2. – С. 239-245. [CrossRef]
- Huot J., Liang G., Schulz R. Mechanically alloyed metal hydride systems //Applied Physics A. – 2001. – Т. 72. – С. 187-195. [CrossRef]
- Grigorova E. et al. Effect of additives on the hydrogen sorption properties of mechanically alloyed composites based on Mg and Mg2Ni //International journal of hydrogen energy. – 2005. – Т. 30. – №. 10. – С. 1099-1105. [CrossRef]
- Oelerich W., Klassen T., Bormann R. Metal oxides as catalysts for improved hydrogen sorption in nanocrystalline Mg-based materials //Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2001. – Т. 315. – №. 1-2. – С. 237-242. [CrossRef]
- Barkhordarian G., Klassen T., Bormann R. Fast hydrogen sorption kinetics of nanocrystalline Mg using Nb2O5 as catalyst //Scripta materialia. – 2003. – Т. 49. – №. 3. – С. 213-217. [CrossRef]
- Barkhordarian G., Klassen T., Bormann R. Effect of Nb2O5 content on hydrogen reaction kinetics of Mg //Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2004. – Т. 364. – №. 1-2. – С. 242-246. [CrossRef]
- Bogdanović B., Schwickardi M. Ti-doped alkali metal aluminium hydrides as potential novel reversible hydrogen storage materials //Journal of alloys and compounds. – 1997. – Т. 253. – С. 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Gutfleisch O. et al. Hydrogen sorption properties of Mg–1 wt.% Ni–0.2 wt.% Pd prepared by reactive milling //Journal of alloys and compounds. – 2005. – Т. 404. – С. 413-416. [CrossRef]
- Hanada N. et al. Remarkable improvement of hydrogen sorption kinetics in magnesium catalyzed with Nb2O5 //Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2006. – Т. 420. – №. 1-2. – С. 46-49. [CrossRef]
- Reilly Jr J. J., Wiswall Jr R. H. Reaction of hydrogen with alloys of magnesium and nickel and the formation of Mg2NiH4 //Inorganic chemistry. – 1968. – Т. 7. – №. 11. – С. 2254-2256. [CrossRef]
- G. Barkhordarian, T. Klassen, R. Bormann. International patent application, Publ. No. WO2006063627.
- Vajo J. J., Skeith S. L., Mertens F. Reversible storage of hydrogen in destabilized LiBH4 //The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. – 2005. – Т. 109. – №. 9. – С. 3719-3722. [CrossRef]
- Barkhordarian G. et al. Unexpected kinetic effect of MgB2 in reactive hydride composites containing complex borohydrides //Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2007. – Т. 440. – №. 1-2. – С. L18-L21. [CrossRef]
- Stepanov A. et al. Hydriding properties of mechanical alloys Mg Ni //Journal of the Less Common Metals. – 1987. – Т. 131. – №. 1-2. – С. 89-97. [CrossRef]
- O. Gutfleisch, N. Schlorke-deBoer, A.S. Pratt, A. Walton, J. Speight, I.R. Harris, A. Zu¨ttel, J. Alloy. Compd. 356– 357 (2003) 598–602. [CrossRef]
- Ivanov E. et al. Magnesium mechanical alloys for hydrogen storage //Journal of the Less common Metals. – 1987. – Т. 131. – №. 1-2. – С. 25-29. [CrossRef]
- Terzieva M., Khrussanova M., Peshev P. Hydriding and dehydriding characteristics of Mg-LaNi5 composite materials prepared by mechanical alloying //Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 1998. – Т. 267. – №. 1-2. – С. 235-239. [CrossRef]
- Liang G. Synthesis and hydrogen storage properties of Mg-based alloys //Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2004. – Т. 370. – №. 1-2. – С. 123-128. [CrossRef]
- Gross K. J. et al. Mechanically milled Mg composites for hydrogen storage: the relationship between morphology and kinetics //Journal of alloys and compounds. – 1998. – Т. 269. – №. 1-2. – С. 259-270. [CrossRef]
- Konstanchuk I. G. et al. The hydriding properties of a mechanical alloy with composition Mg-25% Fe //Journal of the Less Common Metals. – 1987. – Т. 131. – №. 1-2. – С. 181-189. [CrossRef]
- Liang G. et al. Catalytic effect of transition metals on hydrogen sorption in nanocrystalline ball milled MgH2–Tm (Tm= Ti, V, Mn, Fe and Ni) systems //Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 1999. – Т. 292. – №. 1-2. – С. 247-252. [CrossRef]
- Huot J. et al. Structure of nanocomposite metal hydrides //Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2002. – Т. 330. – С. 727-731. [CrossRef]
- Jain I. P., Lal C., Jain A. Hydrogen storage in Mg: a most promising material // International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. – 2010. – Vol. 35. – N. 10. – P. 5133–5144. [CrossRef]
- E. Rivard, M. Trudeau, K. Zaghib, Hydrogen storage for mobility: a review, Materials, 2019, 12(12), 1-22 (1973). [CrossRef]
- J. Lyu, R. R. Elman, L. A. Svyatkin, V. N. Kudiiarov, Theoretical and Experimental Research of Hydrogen Solid Solution in Mg and Mg-Al System, Materials, 2022, 15(5), 1-13 (1667), doi:. [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J., Kudiiarov, V., & Lider, A. (2022). Experimentally Observed Nucleation and Growth Behavior of Mg/MgH2 during De/Hydrogenation of MgH2/Mg: A Review. Materials, 15(22), 8004. [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J., Elman, R., Svyatkin, L., & Kudiiarov, V. (2022). Theoretical and Experimental Studies of Al-Impurity Effect on the Hydrogenation Behavior of Mg. Materials, 15(22), 8126. [CrossRef]
- Ruse, E., Buzaglo, M., Pevzner, S., Pri-Bar, I., Skripnyuk, V. M., Rabkin, E., & Regev, O. (2017). Tuning Mg hydriding kinetics with nanocarbons. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 725, 616-622. [CrossRef]
- Ruse, E., Pevzner, S., Bar, I. P., Nadiv, R., Skripnyuk, V. M., Rabkin, E., & Regev, O. (2016). Hydrogen storage and spillover kinetics in carbon nanotube-Mg composites. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41(4), 2814-2819. [CrossRef]
- Popilevsky L, Skripnyuk VM, Beregovsky M, Sezen M, Amouyal Y, Rabkin E. Hydrogen storage and thermal transport properties of pelletized porous Mg-2 wt.% multiwall carbon nanotubes and Mg-2 wt.% graphite composites. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2016;41:14461–74. [CrossRef]
- Oelerich W., Klassen T., Bormann R. Metal oxides as catalysts for improved hydrogen sorption in nanocrystalline Mg-based materials // Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2001. – Vol. 315. – N. 1–2. – P. 237–242. [CrossRef]
- Milošević S. et al. Fast hydrogen sorption from MgH2–VO2 (B) composite materials // Journal of Power Sources. – 2016. – Vol. 307. – P. 481–488. [CrossRef]
- Polanski M., Bystrzycki J. Comparative studies of the influence of different nano-sized metal oxides on the hydrogen sorption properties of magnesium hydride // Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2009. – Vol. 486. – N. 1–2. – P. 697–701. [CrossRef]
- Shao H. et al. Preparation and hydrogen storage properties of nanostructured Mg–Ni BCC alloys // Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2009. – Vol. 477. – N. 1–2. – P. 301–306. [CrossRef]
- Liu H. et al. Recent advances in hydrogen storage of MgH2 doped by Ni // IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. – IOP Publishing, 2019. – Vol. 267. – N. 2. – Article number 022042. [CrossRef]
- Shao H. et al. Synthesis and hydrogen storage behavior of Mg–Co–H system at nanometer scale // Journal of Solid State Chemistry. – 2004. – Vol. 177. – N. 10. – P. 3626–3632. [CrossRef]
- Pukazhselvan D. et al. Dehydrogenation properties of magnesium hydride loaded with Fe, Fe− C, and Fe− Mg additives // ChemPhysChem. – 2017. – Vol. 18. – N. 3. – P. 287–291. [CrossRef]
- Zhou C. et al. Roles of Ti-based catalysts on magnesium hydride and its hydrogen storage properties // Inorganics. – 2021. – Vol. 9. – N. 5. – Article number 36. [CrossRef]
- Ren C. et al. Hydrogen storage properties of magnesium hydride with V-based additives // The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. – 2014. – Vol. 118. – N. 38. – P. 21778–21784. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y. et al. Magnesium nanoparticles with Pd decoration for hydrogen storage // Frontiers in Chemistry. – 2020. – Vol. 7. – Article number 949. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y. et al. Effect of novel La-based alloy modification on hydrogen storage performance of magnesium hydride: First-principles calculation and experimental investigation // Journal of Power Sources. – 2022. – Vol. 551. – Article number 232187. [CrossRef]
- Spassov T. et al. Mg–Ni–RE nanocrystalline alloys for hydrogen storage // Materials Science and Engineering: A. – 2004. – Vol. 375. – P. 794–799. [CrossRef]
- Jangir M. et al. Catalytic effect of TiF4 in improving hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 // International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. – 2016. – Vol. 41. – N. 32. – P. 14178–14183. [CrossRef]
- Park H. R. et al. Hydrogen Sorption of Pure Mg and Niobium (V) Fluoride-Added Mg Alloys Prepared by Planetary Ball Milling in Hydrogen // Korean Journal of Metals and Materials. – 2016. – Vol. 54. – N. 12. – P. 916–924. [CrossRef]
- Lin H. J. et al. Enhanced hydrogen desorption property of MgH2 with the addition of cerium fluorides // Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2015. – Vol. 645. – P. S392-S396. [CrossRef]
- Malka I. E., Czujko T., Bystrzycki J. Catalytic effect of halide additives ball milled with magnesium hydride // International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. – 2010. – Vol. 35. – N. 4. – P. 1706–1712. [CrossRef]
- Malka I. E. et al. A study of the ZrF4, NbF5, TaF5, and TiCl3 influences on the MgH2 sorption properties // International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. – 2011. – Vol. 36. – N. 20. – P. 12909–12917. [CrossRef]
- Wu C. Z. et al. Effect of carbon/noncarbon addition on hydrogen storage behaviors of magnesium hydride // Journal of Alloys and Compounds. – 2006. – Vol. 414. – N. 1–2. – P. 259–264. [CrossRef]
- Rahmalina D. et al. Experimental Evaluation for the Catalytic Effect of Nickel in Micron Size on Magnesium Hydride //WSEAS Transactions on Applied and Theoretical Mechanics. – 2021. – Т. 16. – С. 293-302. [CrossRef]
- Varin R. A. et al. Catalytic effects of various forms of nickel on the synthesis rate and hydrogen desorption properties of nanocrystalline magnesium hydride (MgH2) synthesized by controlled reactive mechanical milling (CRMM) //Journal of alloys and compounds. – 2007. – Т. 432. – №. 1-2. – С. 217-231. [CrossRef]
- Grove H. et al. Decomposition of lithium magnesium aluminum hydride //international journal of hydrogen energy. – 2011. – Т. 36. – №. 13. – С. 7602-7611. Grove H. et al. Decomposition of lithium magnesium aluminum hydride //international journal of hydrogen energy. – 2011. – Т. 36. – №. 13. – С. 7602-7611. [CrossRef]
- Nazarenko O. B. et al. Features of physico-chemical properties of nanopowders and nanomaterials: Textbook (Vulture Sibrums). – 2012.
- Influence of Short-Pulse Microwave Radiation on Thermochemical Properties Aluminum Micropowder / A. V. Mostovshchikov, F. A. Gubarev, O. B. Nazarenko, A. N. Pestryakov // Materials . — 2023 . — Vol. 16, iss. 3 . — [951, 9 p.] . — Title screen. — [References: 26 tit.]. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).