Submitted:
27 December 2023
Posted:
29 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Synaptic densities
2.2. Statistical Methods
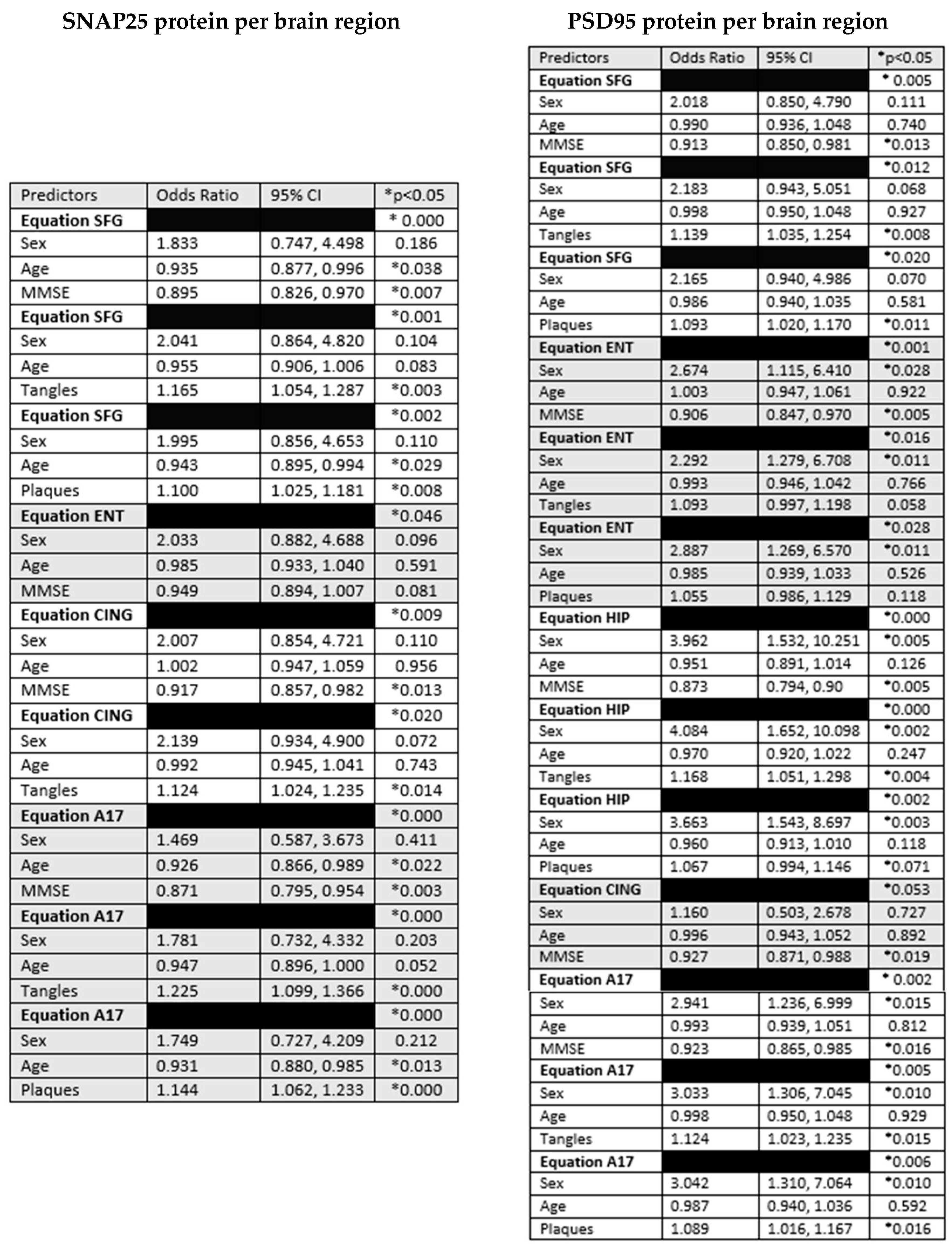
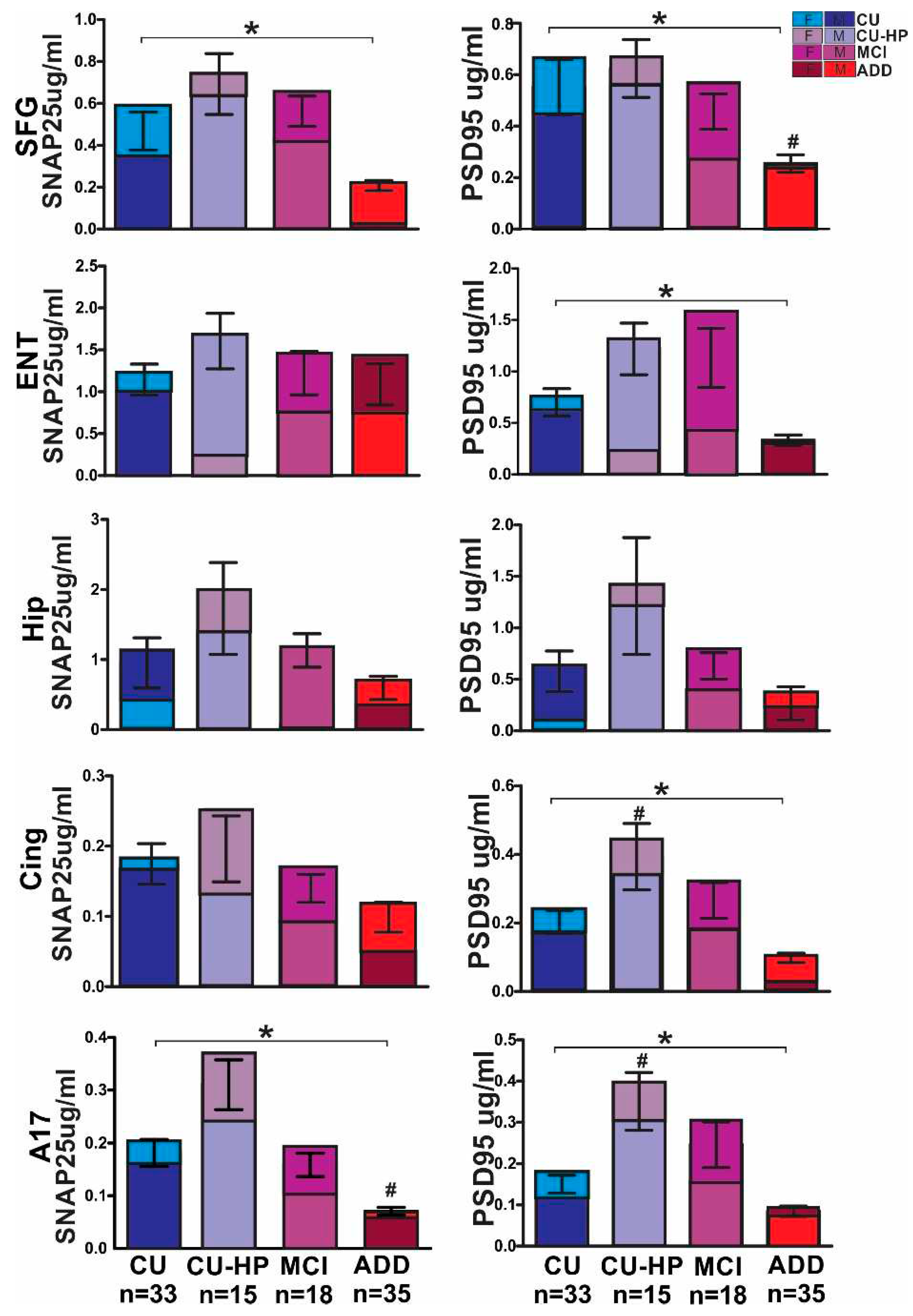
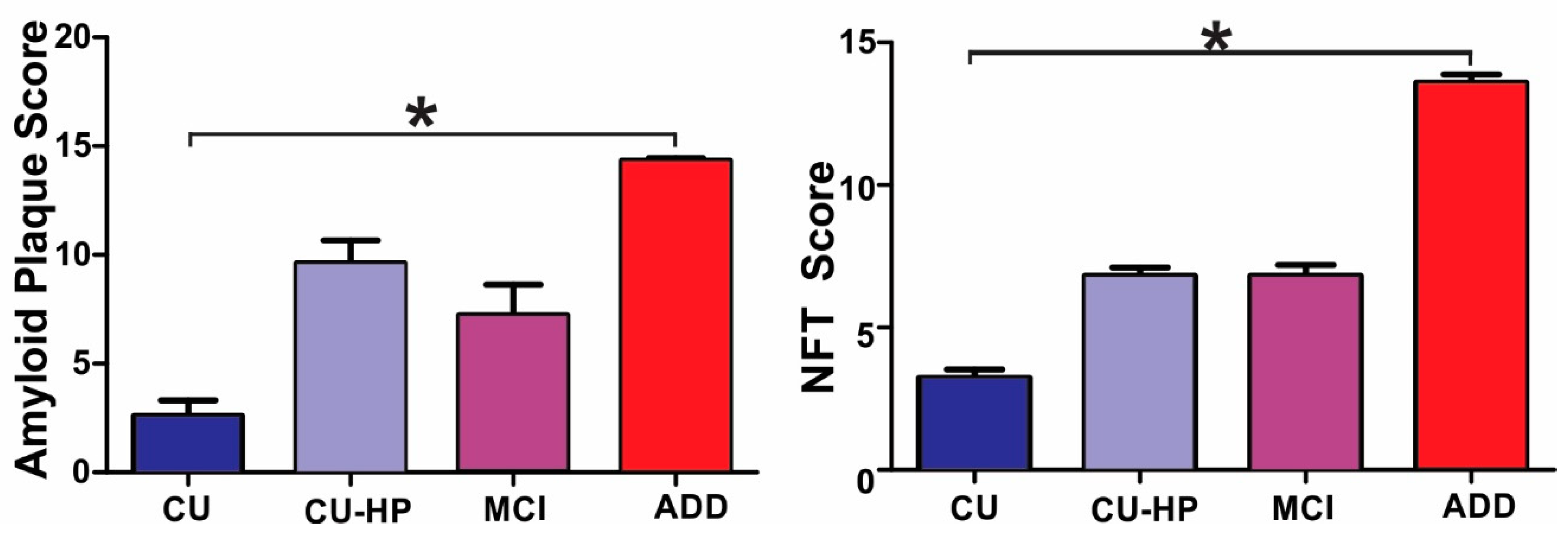
3. Results
4. Discussion
References
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, B.M.; Anderson, J.M. A quantitative study of cerebral atrophy in old age and senile dementia. J. Neurol. Sci. 1981, 50, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheff, S.W.; Neltner, J.H.; Nelson, P.T. Is synaptic loss a unique hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschall, P.E.; Ajmo, J.M.; Eakin, A.K.; Howell, M.D.; Mehta, H.; Bailey, L.A. Panel of synaptic protein ELISAs for evaluating neurological phenotype. Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 201, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, R.; King, V.G.; Wirenfeldt, M.; Vinters, H.V. Synapse loss in dementias. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecca, A.P.; O'Dell, R.S.; Sharp, E.S.; Banks, E.R.; Bartlett, H.H.; Zhao, W.; Lipior, S.; Diepenbrock, N.G.; Chen, M.K.; Naganawa, M.; Toyonaga, T. Synaptic density and cognitive performance in Alzheimer’s disease: A PET imaging study with [(11) C]UCB-J. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 18, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakkenberg, B.; Pelvig, D.; Marner, L.; Bundgaard, M.J.; Gundersen, H.J.G.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Regeur, L. Aging and the human neocortex. Exp. Gerontol. 2003, 38, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelvig, D.P.; Pakkenberg, H.; Regeur, L.; Oster, S.; Pakkenberg, B. Neocortical glial cell numbers in Alzheimer’s disease. A stereological study. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2003, 16, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regeur, L.; Jensen, G.B.; Pakkenberg, H.; Evans, S.; Pakkenberg, B. No global neocortical nerve cell loss in brains from patients with senile dementia of Alzheimer’s type. Neurobiol. Aging 1994, 15, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filon, J.R.; Intorcia, A.J.; Sue, L.I.; Arreola, E.V.; Wilson, J.; Davis, K.J.; Sabbagh, M.N.; Belden, C.M.; Caselli, R.J.; Adler, C.H.; et al. Gender Differences in Alzheimer Disease: Brain Atrophy, Histopathology Burden, and Cognition. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology 2016, 75, 748–754. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, M.; Yin, X.; Chen, K.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, D. The role of pathological tau in synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s diseases. Transl. Neurodegener. 2021, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, S.A.; Spires-Jones, T.L.; Durrant, C.S. The physiological roles of tau and Abeta: implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathology and therapeutics. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 417–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spires-Jones, T.L.; Hyman, B.T. The intersection of amyloid beta and tau at synapses in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2014, 82, 756–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Serra, R.; Alonso-Nanclares, L.; Cho, K.; Giese, K.P. Emerging insights into synapse dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzioras, M.; McGeachan, R.I.; Durrant, C.S.; Spires-Jones, T.L. Synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 19, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Christian, K.M.; Song, H.; Ming, G.-L. Synaptic dysfunction in complex psychiatric disorders: from genetics to mechanisms. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henstridge, C.M.; Pickett, E.; Spires-Jones, T.L. Synaptic pathology: A shared mechanism in neurological disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 28, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.; Jambrina, E.; Li, J.; Marston, H.; Menzies, F.; Phillips, K.; Gilmour, G. Targeting the Synapse in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccioni, G.; Mango, D.; Saidi, A.; Corbo, M.; Nisticò, R. Targeting Microglia-Synapse Interactions in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, R.E.; Naganawa, M.; Toyonaga, T.; Koohsari, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, M.-K.; Matuskey, D.; Finnema, S.J. Imaging of Synaptic Density in Neurodegenerative Disorders. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63 (Suppl. 1), 60S–67S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-K.; Mecca, A.P.; Naganawa, M.; Finnema, S.J.; Toyonaga, T.; Lin, S.-F.; Najafzadeh, S.; Ropchan, J.; Lu, Y.; McDonald, J.W.; et al. Assessing Synaptic Density in Alzheimer Disease With Synaptic Vesicle Glycoprotein 2A Positron Emission Tomographic Imaging. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.G.; Sue, L.I.; Walker, D.G.; Roher, A.E.; Lue, L.; Vedders, L.; Connor, D.J.; Sabbagh, M.N.; Rogers, J. The Sun Health Research Institute Brain Donation Program: description and experience, 1987-2007. Cell Tissue Bank 2008, 9, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Sue, L.I.; Serrano, G.; Shill, H.A.; Walker, D.G.; Lue, L.; Roher, A.E.; Dugger, B.N.; Maarouf, C.; et al. Arizona Study of Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders and Brain and Body Donation Program. Neuropathology 2015, 34, 354–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montine, T.J.; Phelps, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; Cairns, N.J.; Dickson, D.W.; Duyckaerts, C.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; Mirra, S.S.; et al. National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease: a practical approach. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallyas, F. An argyrophil III method for the demonstration of fibrous neuroglia. Acta Morphol. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1981, 29, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Demonstration of amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary changes in whole brain sections. Brain Pathol. 1991, 1, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Arai, T.; Nonaka, T.; Kametani, F.; Yoshida, M.; Hashizume, Y.; Beach, T.G.; Buratti, E.; Baralle, F.; Morita, M.; et al. Phosphorylated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, T.G.; White, C.L.; Hamilton, R.L.; Duda, J.E.; Iwatsubo, T.; Dickson, D.W.; Leverenz, J.B.; Roncaroli, F.; Buttini, M.; Hladik, C.L.; et al. Evaluation of alpha-synuclein immunohistochemical methods used by invited experts. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 116, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Dohmae, N.; Kawashima, A.; Masliah, E.; Goldberg, M.S.; Shen, J.; Takio, K.; Iwatsubo, T. alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirra, S.S.; Heyman, A.; McKeel, D.; Sumi, S.M.; Crain, B.J.; Brownlee, L.M.; Vogel, F.S.; Hughes, J.P.; Belle, G.V.; Berg, L.; Participating CERAD Neuropathologists The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD). Part II. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1991, 41, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aging, N.I.O. Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. The National Institute on Aging, and Reagan Institute Working Group on Diagnostic Criteria for the Neuropathological Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 1997, 18 (Suppl. 4), S1–S2. [Google Scholar]
- Hyman, B.T.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer disease from the National Institute on Aging and the Reagan Institute Working Group on diagnostic criteria for the neuropathological assessment of Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 56, 1095–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirra, S.S. The CERAD neuropathology protocol and consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: a commentary. Neurobiol. Aging 1997, 18 (Suppl. 4), S91–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, F.; Corradini, I.; Morini, R.; Fossati, G.; Menna, E.; Pozzi, D.; Pacioni, S.; Verderio, C.; Bacci, A.; Matteoli, M. Reduced SNAP-25 alters short-term plasticity at developing glutamatergic synapses. EMBO Rep. 2013, 14, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, G.; Morini, R.; Corradini, I.; Antonucci, F.; Trepte, P.; Edry, E.; Sharma, V.; Papale, A.; Pozzi, D.; Defilippi, P.; et al. Reduced SNAP-25 increases PSD-95 mobility and impairs spine morphogenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivisäkk, P.; Carlyle, B.C.; Sweeney, T.; Quinn, J.P.; Ramirez, C.E.; Trombetta, B.A.; Mendes, M.; Brock, M.; Rubel, C.; Czerkowicz, J.; Graham, D. Increased levels of the synaptic proteins PSD-95, SNAP-25, and neurogranin in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, A.A.; Gao, W.J. PSD95: A synaptic protein implicated in schizophrenia or autism? Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 82, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nelson, C.D.; Li, X.; Winters, C.A.; Azzam, R.; Sousa, A.A.; Leapman, R.D.; Gainer, H.; Sheng, M.; Reese, T.S. PSD-95 is required to sustain the molecular organization of the postsynaptic density. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6329–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.; El-Husseini, A. Excitation Control: Balancing PSD-95 Function at the Synapse. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2008, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honer, W.G. Pathology of presynaptic proteins in Alzheimer’s disease: more than simple loss of terminals. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 1047–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlo, S.; Spampinato, S.F.; Sortino, M.A. Early compensatory responses against neuronal injury: A new therapeutic window of opportunity for Alzheimer’s Disease? CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeKosky, S.T.; Ikonomovic, M.D.; Styren, S.D.; Beckett, L.; Wisniewski, S.; Bennett, D.A.; Cochran, E.J.; Kordower, J.H.; Mufson, E.J. Upregulation of choline acetyltransferase activity in hippocampus and frontal cortex of elderly subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Ann. Neurol. 2002, 51, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Nanclares, L.; Gonzalez-Soriano, J.; Rodriguez, J.R.; DeFelipe, J. Gender differences in human cortical synaptic density. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2008, 105, 14615–14619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyer, M.M.; Phillips, L.L.; Neigh, G.N. Sex Differences in Synaptic Plasticity: Hormones and Beyond. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pinilla, E.; Ordóñez, C.; del Valle, E.; Navarro, A.; Tolivia, J. Regional and Gender Study of Neuronal Density in Brain during Aging and in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| DX (n) | Age (SD) | Gender (M:F) | PMI (SD) | Brain weight (SD) |
MMSE (SD) |
Total plaques | Thal stage | Total tangle | Braak stage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CU (33) | 83 (7)* | 17:16 | 3 (1) | 1211 (123)* | 29 (1) | 3 (4)* | 1 (2)* | 3 (2)* | 2 (.8)* | |
| CU-HP (15) | 92 (6)# | 7:8 | 4 (3) | 1203 (128) | 28 (2) | 10 (4)# | 3 (1)# | 7 (1)# | 4 (0)# | |
| MCI (18) | 90 (7)# | 7:11 | 4 (2) | 1149 (87) | 26 (3) | 7 (6) | 2 (2)# | 7 (2)# | 4 (.4)# | |
| ADD (35) | 82 (8) | 20:15 | 3 (1) | 1089 (125)# | 15 (8) | 14 (1)# | 5 (.6)# | 14 (2)# | 6 (.5)# | |
| SNAP25 | MMSE | Age | Total tangles | Total plaques | PSD95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal | 0.29 ** | 0.18 (NS) | -0.213 ** | -0.292 ** | 0.655 *** |
| Entorhinal | 0.26 * | 0.22 * | -0.050 | -0.081 | 0.737 *** |
| Hippocampus | 0.16 (NS) | 0.12 (NS) | -0.085 | -0.062 | 0.698 *** |
| Cingulate | 0.39 *** | 0.18 (NS) | -0.294 ** | -.286 ** | 0.629 *** |
| A17 | 0.49 *** | 0.32 ** | -0.430 *** | -0.445 *** | 0.674 *** |
| PSD95 | |||||
| Frontal | 0.31 ** | 0.06 (NS) | -.0267 * | -0.213 * | |
| Entorhinal | 0.41 *** | 0.20 * | -0.191 * | -0.233 * | |
| Hippocampus | 0.43 *** | 0.20 * | -0.324 ** | -0.307 ** | |
| Cingulate | 0.32 ** | 0.19 (NS) | -0.257 ** | -0.260 ** | |
| A17 | 0.33 ** | 0.22 * | -0.231 ** | -0.291 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





