Submitted:
30 December 2023
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Background of Green Economy Transition in Cambodia
3.1. Definitions
3.2. Green Economy under Green Growth Secretariat of MoE (Before Oct 2012)
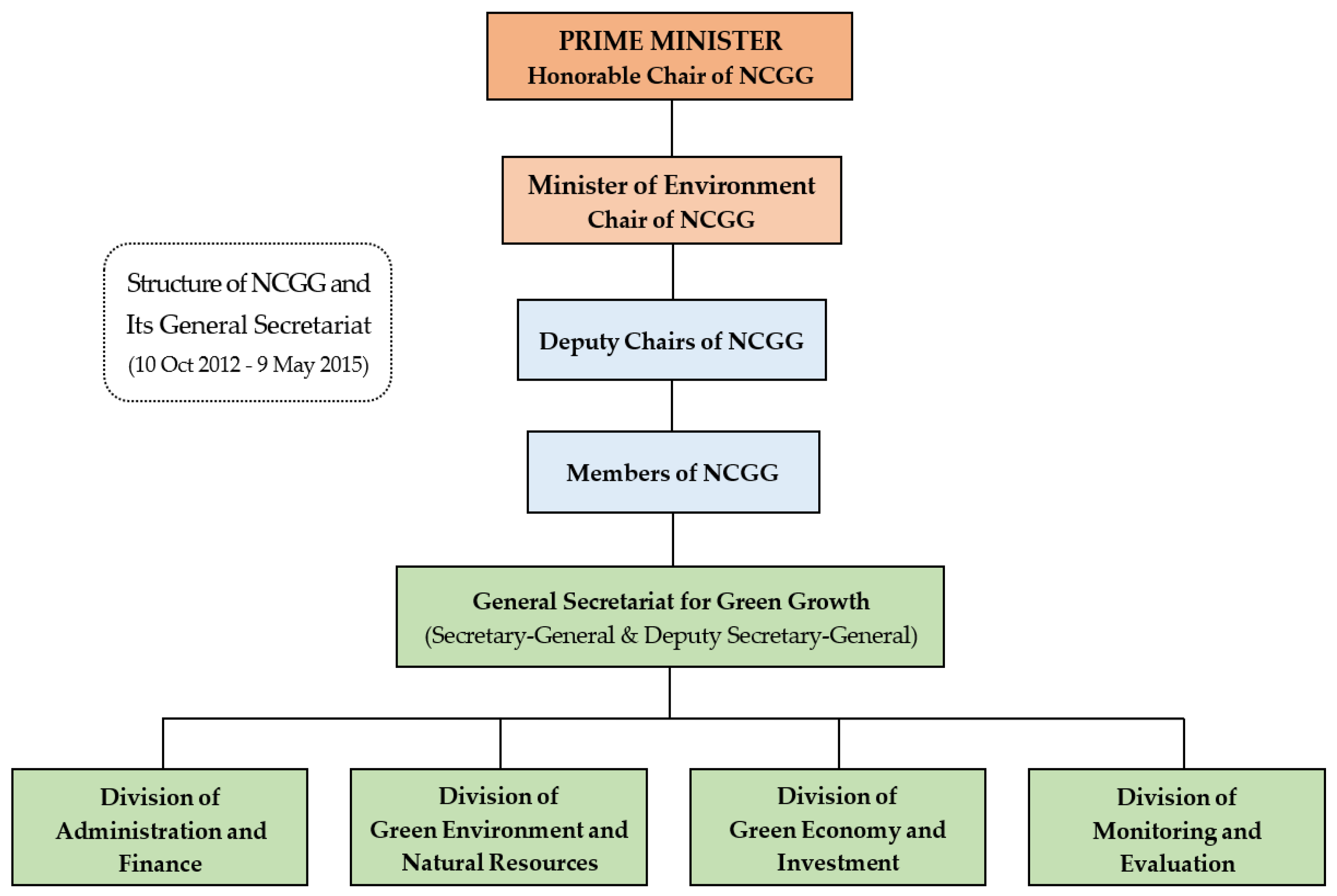
3.3. Green Economy under the General Secretariat of NCGG (Oct 2012–May 2015)
3.3.1. Institutional Structures
3.3.2. National Policy and Strategic Plan
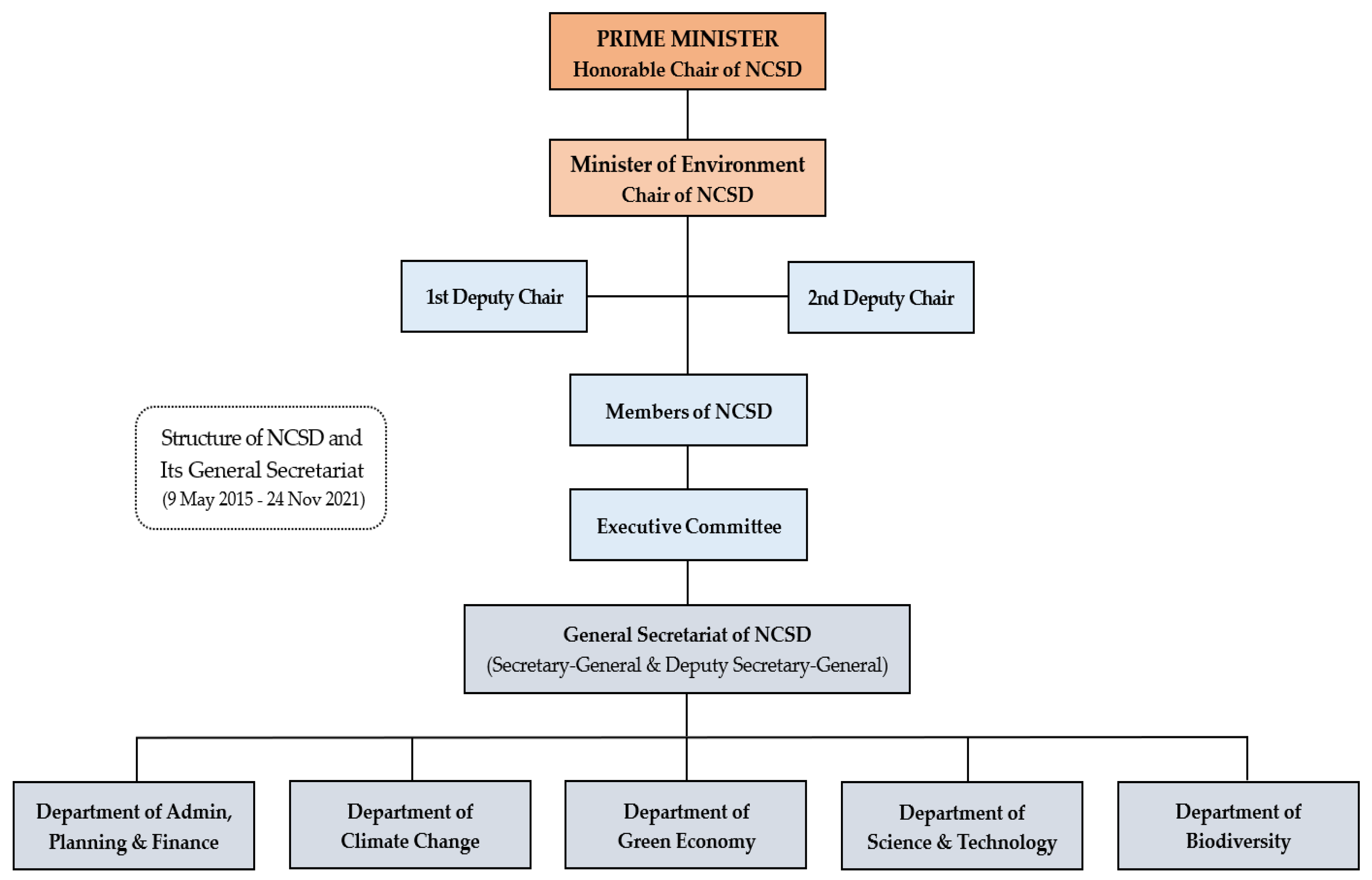
3.4. Green Economy under the General Secretariat of NCSD (May 2015 - Nov 2021)
3.4.1. Institutional Integration
3.4.2. NCSD Roles and Duties
- Formulating, directing, and evaluating policies, strategic plans, action plans, legal instruments, programs, and projects related to sustainable development;
- Promoting mainstreaming of sustainable development into relevant policies, legal instruments, strategic plans, action plans, programs, and projects in collaboration with relevant line ministries and agencies;
- Mobilizing resources for implementation of policies, legal instruments, strategic plans, action plans, programs, and projects related to sustainable development;
- Establishing and fostering partnerships with development partners, private sector, academia, other relevant stakeholders aimed at supporting sustainable development;
- Encouraging and promoting the research study, education, training, exchange of technologies and dissemination relevant to sustainable development;
- Proposing the national positions and strategies for participating in international agreements, meetings and negotiations relevant to sustainable development;
- Reviewing and giving approval on national communications under the multilateral environmental agreements to which Cambodia is a party;
- Managing the government information and communications relevant to sustainable development;
- Leading, managing and facilitating the works related to green economy, climate change, biodiversity conservation and biosafety; and
- Implementing any other duties assigned to it by the Royal Government of Cambodia.
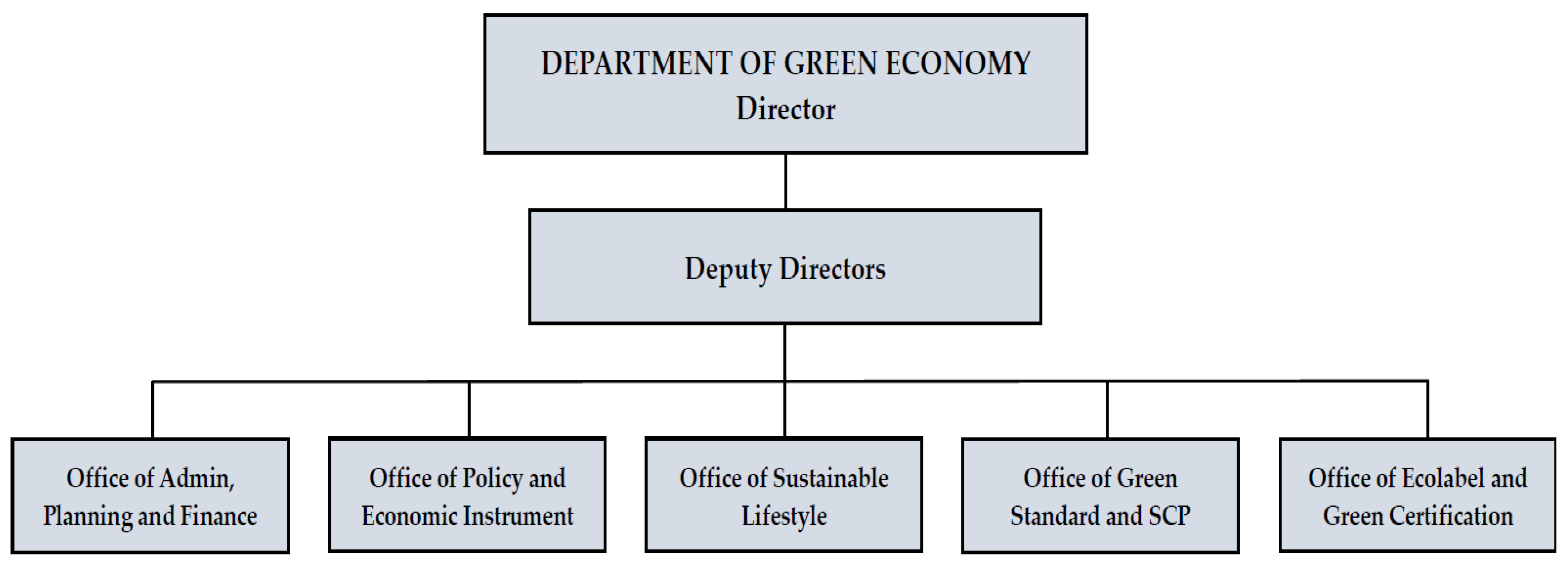
3.4.3. Department of Green Economy
- Coordinating and implementing legal documents, policies, strategic plan, action plan, programs, and project for supporting the green economy pathway as well as monitoring and evaluation and annual report;
- Coordinating research in related impacts and benefits of development activities to sustainable development dimensions: Economy, environment, society and culture;
- Coordinating natural capital accounting and measuring green domestic products;
- Coordinating feasibility study and establishing pollution-based payment principal mechanism and payment for environmental service and coordinating, monitoring, and evaluating the implementation of agreed mechanism;
- Coordinating research and establishing supporting tool system for decision making such as impact assessment, multicriterial analysis, cost-benefit analysis to contribute to modification or establishment of legal documents, policies, strategic plan, action plan, programs, and projects;
- Researching and developing the policies and the mechanisms related to sustainable consumption and production, such as eco-label and green certification, green public procurement, and monitoring and evaluation of the agreed mechanism;
- Building and strengthening the cooperation with partners, civil society organization, private sector, academic institute and other stakeholders to promote green economy development;
- Disseminating and mobilizing resources for the implementation of agreed policies.
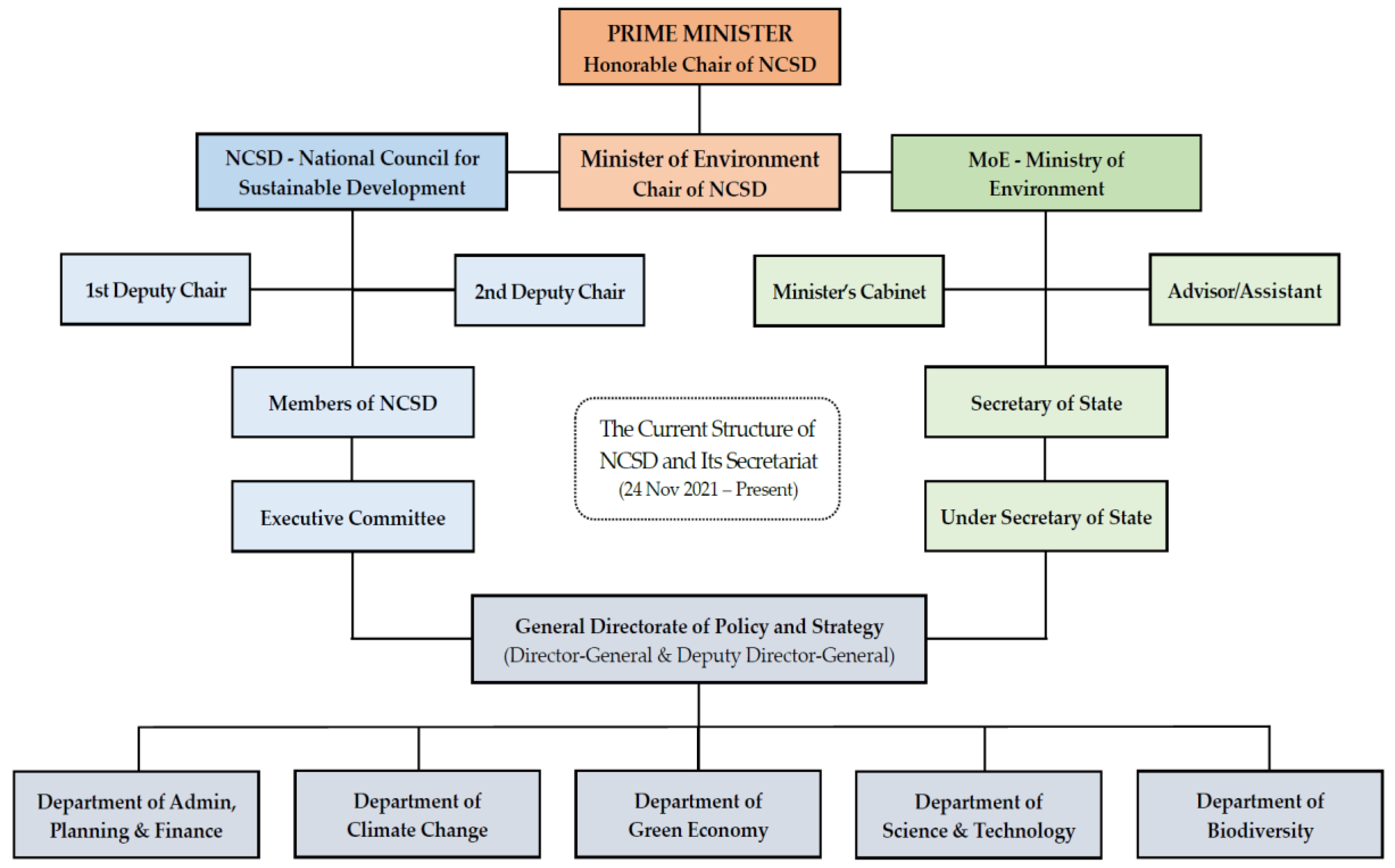
3.5. Green Economy under General Directorate of Policy and Strategy (Nov 2021–Present)
3.5.1. Secretariat Refunctioning
3.5.2. Members of NCSD and Structure of Department of Green Economy
4. Progress of Green Economic Development in Cambodia
4.1. The Code and Policies Supporting Green Economy Transition
4.2. Pentagonal Strategy Phase I of the Royal Government of Cambodia
4.3. SWOT Analysis
4.3.1. Strengths
- Cambodia has high economic growth with political stability;
- RGC’s Rectangular Strategy Four-Phase and Pentagonal Strategy Phase I have strongly supported green economy and low-carbon development;
- Cambodia has a strong responsible institution for promoting green economy and sustainable development for both policy-making and technical/implementing levels (Inter-Ministerial Council, Operating Secretariat, and Technical Department);
- Members of the National Council for Sustainable Development (NCSD) are Secretary of State levels from all RGC’s ministries and relevant committees—good for cross-sector policy making, coordination, and consultation. All Governors of the Capital and Provincial Administrations are also its members—good for implementation of the work at sub-national levels;
- Cambodia has significantly developed regulations and policies for supporting green economy transition, particularly the environmental code, new law on investment, green growth policy, carbon neutrality strategy, etc.
- Ministries and relevant institutions, as well as capital and provincial administrations (NCSD members) have been developing/integrating green economy/green growth principles in their development plan;
- Cambodia has been strongly supported by development partners, for example, UN PAGE Agencies: UNIDO, UNDP, UNITAR, ILO, and UNEP; GGGI; EU; etc.;
- Many relevant stakeholders have been supporting green economic development in Cambodia, which means that not only the government, but also private companies, business, academia, and civil societies have been supporting green economy;
- Public awareness on environmental issues, including climate change, clean and green development, and green economy and sustainable development has been largely started at all national and sub-national levels (nationwide) [42].
4.3.2. Weaknesses
- Cambodia is still lack of human/technical and financial resources for green economic development;
- Capacities of national institutions, especially sub-national institutions for integrating green economy/green growth principles into their development plan are still limited;
- Procedures for integrating green economic mechanisms into relevant sectors are still facing difficulties and challenging;
- Cambodia is still weak in R&D and science-based decision making; still limited in science and technology;
- Green growth/green economic development is not a common practice (needed strong commitments, efforts, and good understanding) [42].
4.3.3. Opportunities
- There are highly increasing in global and regional interests on low-carbon and green economic development;
- Green growth/green economic development principles have always been integrated into the national development plans, and clearly addressed in the RGC’s Pentagonal Strategy Phase I;
- RGC has increased priority and targets in the National Development Plan for green economy and sustainable development;
- Cambodian livelihoods have improved—a right time to strengthening public and/or citizen’s involvements in environmental protection;
- Cambodia officially became a member of the UN Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE) and has been implementing the five-year workplan, supported by five joint UN Agencies [43];
- Cambodia developed green and sustainable city strategic plan for the capital and seven secondary cities, with identified a list of 48 priority projects for green growth and circular economy promotion [42].
4.3.4. Threats
- There is still limited in understanding of green economy and growth and sustainable development;
- Some existing policies and priorities are conflicting with green economy and green growth policy;
- Some of key economic sectors are also confronting with green growth and green economy principles;
- There is still limited in capacities of national government institutions for coordinating cross-cutting sector works;
- Green growth/green economy policy and project implementations are facing with impacts of climate change and global crisis [42].
5. Conclusions
5.1. Summary and Conclusions
5.2. General Recommendations
- Cambodia should invest more on research and development (R&D) in green growth and green economic development, particularly on green technology and innovation, renewable energies, and energy generation from municipal solid wastes.
- Green growth and green economic development are needed technological skills for creating alternative or renovating new resources; therefore, the government should support its young officials to pursue a master’s or PhD degree in these fields;
- National and international investments should take high considerations on negative impacts of investment projects on the environment and public health, such as the quality of life and natural environment and resources.
- All relevant stakeholders should be contributing to and involving in green activities and sustainability or related projects because joining hands together we can achieve a clean, green, and sustainable development.
- Education ministry should increase green or environmental curriculum in order to make students widely known about green concepts and activities—this is good for them to think and act clean, green, and sustainable in everyday life.
5.3. Recommendations for DGE
- DGE should prepare educational documents or guidebooks in to help improving the understanding of the publics, especially students, on environmental-friendly or green activities in everyday life;
- DGE should create the media programs to promote national activities and raise awareness on clean, green, and sustainable activities and citizens’ involvement via television programs, YouTube, Facebook, etc.
- DGE should have a group of trainers to provide training on green economy concepts, such as “Think Green, Act Green” to the students from primary school to university levels, and to local officials and local communities.
- DGE should collaborate with research institutions to conduct research on renewable energies, energy generation from municipal wastes, green technology, etc.
- DGE should cooperate with research institutions to provide some courses relating to green growth/green economy for sharing experiences, exchange projects, and skill development, as well as providing places for students to intern or volunteer.
- DGE should involve students from universities and institutions in dissemination workshops, capacity development programs, green growth and green economy seminars, and other national green growth programs.
- DGE should create an R&D office for coordinating the research and development on clean and renewable energies, energy generation from municipal solid wastes, green technology, green buildings, green industry, etc.
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | Title (Note) | Year |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | National Green Growth Roadmap [1] (published online in December 2009 and printed book in March 2010) |
2009 |
| 2 | Cambodia Climate Change Alliance [44] (led by MoE and supported by EU, Denmark, Sweden, and UNDP) |
2010 |
| 3 | Memorandum of Understanding on Green Growth Cooperation [32] (first MoU with GGGI signed in March 2011) |
2011 |
| 4 | Royal Decree on the Establishment of National Council for Green Growth [4] (replaced by Royal Decree [6]) |
2012 |
| 5 | Sub-decree on Organization and Functioning of General Secretariat of NCGG [33] (replaced by Sub-decree [8]) |
2012 |
| 6 | National Policy on Green Growth [5] (approved by the Government on 1 March 2013 in the full cabinet meeting) |
2013 |
| 7 | National Strategic Plan on Green Growth 2013-2030 [28] | 2013 |
| 8 | Cambodia Climate Change Strategic Plan 2014-2023 [45] | 2014 |
| 9 | Royal Decree on the Establishment of the National Council for Sustainable Development (NCSD) [6] | 2015 |
| 10 | Sub-decree on Organization and Functioning of General Secretariat of NCSD [8] (repealed by Sub-decree [10]) |
2015 |
| 11 | Prakas on Organization and Functioning of Department of Green Economy [9] (repealed by Prakas [35]) |
2015 |
| 12 | Green City Strategic Planning Methodology: A Guide for the Development of a Green City Strategic Plan [13] | 2016 |
| 13 | Memorandum of Understanding on Continuous Green Growth Cooperation [46] | 2016 |
| 14 | Phnom Penh Green City Strategic Plan 2017–2026 and List of Priority Green City Investment Projects [47] | 2017 |
| 15 | Phnom Penh Sustainable City Plan 2018–2030 [48] | 2018 |
| 16 | Green Growth Potential Assessment: Cambodia Country Report [49] | 2018 |
| 17 | Economic, Social and Environmental Impacts of Greening the Industrial Sector [50] | 2018 |
| 18 | Cambodia: De-risking Renewable Energy Investment [51] | 2019 |
| 19 | Guidelines and Certification Standards for Green Buildings in Cambodia [52] | 2019 |
| 20 | Sustainable City Strategic Plan 2020-2030 for Seven Secondary Cities [53] | 2020 |
| 21 | Full Economic Appraisal of the Potentials of Solar PV Energy in Cambodia [54] | 2020 |
| 22 | Royal Decree on the Amendment of the Royal Decree on the Establishment of NCSD [34] | 2021 |
| 23 | Sub-decree on Organization and Functioning of the Ministry of Environment [10] | 2021 |
| 24 | Prakas on Organization and Functioning of the Offices under the Departments of the General Directorate of Policy and Strategy [35] |
2021 |
| 25 | New Law on Investment [55] (indicating encouragements/incentives for environmental-friendly investments) |
2021 |
| 26 | Stocktaking and Analytical Options for Green Buildings in Cambodia [56] | 2021 |
| 27 | Guideline on Green Office and Green Event and Evaluation Mechanism [57] | 2021 |
| 28 | Cambodia’s Long-Term Strategy for Carbon Neutrality [37] | 2021 |
| 29 | Circular Economy Strategy and Action Plan [38] | 2021 |
| 30 | Cambodia’s Roadmap for Sustainable Consumption and Production 2022-2035 [39] | 2022 |
| 31 | Memorandum of Understanding on Continuous Green Growth Cooperation [58] | 2022 |
| 32 | UN Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE) [43] | 2022 |
| 33 | National Energy Efficiency Policy 2022-2030 [59] | 2022 |
| 34 | Environment and Natural Resources Code of Cambodia [36] | 2023 |
| 35 | New Law on Public Procumbent [60] (indicating green public procumbent–GPP–promotion) | 2023 |
| 36 | Pentagonal Strategy for Growth, Employment, Equity, Efficiency, and Sustainability [40] | 2023 |
| 37 | Circular Strategy on Environment 2023-2028 [61] | 2023 |
| 38 | Draft Sub-decree on Ecolabel [62] | 2023 |
| 39 | Draft Cambodia’s Guidelines and Certification for Green Buildings (CamGCGB) [63] | 2023 |
| 40 | Draft NCSD Decision on the Establishment of the National Steering Committee (NSC) for the United Nations Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE) in Cambodia [64] |
2023 |
References
- Ministry of Environment. The National Green Growth Roadmap. 2009. Available online: https://policy.asiapacificenergy.org/node/477 (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Essam, Y.M.; Shannon, W.; Gary, K. 2013. Making Growth Green and Inclusive: The Case of Cambodia - Green Growth Papers; OECD Publishing: Paris, France; Volume 9.
- Kwon. S. 2013. Promoting a New Paradigm of Economic Growth and Environmental Sustainability; the Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI): Seoul, South Korea.
- Ministry of Royal Palace. 2012. The Royal Decree on the Establishment of the National Council for Green Growth; the Ministry of Royal Palace: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Royal Government of Cambodia. 2013. The National Policy on Green Growth; Office of the Council of Ministers: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Ministry of Royal Palace. 2015. The Royal Decree on the Establishment of the National Council for Sustainable Development; the Ministry of Royal Palace: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- National Council for Sustainable Development. Introduction to the National Council for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://ncsd.moe.gov.kh/ncsd/about-ncsd (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Royal Government of Cambodia. 2015. The Sub-decree on Organization and Functioning of General Secretariat of the National Council for Sustainable Development; the Office of the Council of Ministers: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Ministry of Environment. 2015. The Prakas on Organization and Functioning of the Department of Green Economy; the Ministry of Environment: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Royal Government of Cambodia. 2021. The Sub-decree on Organization and Functioning of the Ministry of Environment; the Office of the Council of Ministers: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Chan, P. 2019. Cambodian Green Economy – 2nd Edition; Lambert Academic Publishing: Chisinau, Moldova, European Union.
- Chan, P. 2016. A Study on the Mechanism of Green Economic Development in Cambodia. Master’s Thesis; the Build Bright University: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- NCSD; GGGI. 2016. Green City Strategic Planning Methodology: A Guide for the Development of a Green City Strategic Plan; the National Council for Sustainable Development: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- NCSD; GGGI. 2017. The Phnom Penh Green City Strategic Plan 2017–2026 and List of Priority Green City Investment Projects for Phnom Penh; the National Council for Sustainable Development: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Chan, P.; Lee, M.H. 2019. Developing Sustainable City Indicators for Cambodia through Delphi Processes of Panel Surveys. Sustainability, 11, 3166. [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.; Lee, M.-H. 2019. Prioritizing Sustainable City Indicators for Cambodia. Urban Sci., 3, 104. [CrossRef]
- Chan, P. The Development and Prioritization of Consensus Sustainable City Indicators for Cambodia. Ph.D. Thesis, the Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, P. 2020. Assessing Sustainability of the Capital and Emerging Secondary Cities of Cambodia Based on the 2018 Commune Database. Data, 5, 79. [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.; Gulbaram, K.; Schuetze, T. 2023. Assessing Urban Sustainability and the Potential to Improve the Quality of Education and Gender Equality in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. Sustainability, 15, 8828. [CrossRef]
- UNCDF; FSFM; MEF. 2022. Development of INFF Finance Strategy in Cambodia; Frankfurt School of Finance & Management: Frankfurt, Germany.
- Cambodia Development Resource Institute. 2023. PAGE Policy Scoping Study in Cambodia; Cambodia Development Resource Institute: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Mattessich, P.W.; Monsey, B.R. 1992. Collaboration: What Makes It Work: A Review of Research Literature on Factors Influencing Successful Collaboration; Amherst H. Wilder Foundation: North Saint Paul, MN, USA.
- Snyder, H. 2019. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res., 104, 333–339. [CrossRef]
- Chan, P. 2021. Child-Friendly Urban Development: Smile Village Community Development Initiative in Phnom Penh. World, 2, 505-520. [CrossRef]
- Chan, P. 2022. An Empirical Study on Data Validation Methods of Delphi and General Consensus. Data, 7, 18. [CrossRef]
- Chan, P. 2022. The Consensus Planning and Design Criteria for Sustainable Buildings in Cambodia. Preprints (MDPI), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Towards a Green Economy: Pathways to Sustainable Development and Poverty Eradication. 2011. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/126GER_synthesis_en.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- National Council for Green Growth. The National Strategic Plan on Green Growth 2013–2030. 2013. Available online: https://policy.asiapacificenergy.org/ru/node/2806 (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- OECD. Green Growth and Sustainable Development. 2011. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/greengrowth/ (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- World Commission on Environment and Development. 1987. From One Earth to One World: An Overview; Oxford University Press: Oxford, United Kingdom.
- Chan, P. 2016. Cambodian Green Economy – 1st Edition; Department of Green Economy: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Lee, H.H. 2012. GGGI’s Green Growth Program in the Perspective of Development Impact Assessment – Slide Presentation; the Global Green Growth Institute: Seoul, South Korea.
- Royal Government of Cambodia. 2012. The Sub-decree on Organization and Functioning of General Secretariat of the National Council for Green Growth; the Office of the Council of Ministers: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Ministry of Royal Palace. 2021. The Royal Decree on the Amendment of the Royal Decree on Organization and Functioning of the National Council for Sustainable Development; the Ministry of Royal Palace: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Ministry of Environment. 2021. Prakas on Organization and Functioning of the Offices under the Departments of the General Directorate of Policy and Strategy; the Ministry of Environment: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Ministry of Royal Palace. 2023. The Royal Kram to Endorse the Environment and Natural Resources Code of Cambodia; the Ministry of Royal Palace: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- National Council for Sustainable Development. 2021. Cambodia’s Long-Term Strategy for Carbon Neutrality; the National Council for Sustainable Development: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- National Council for Sustainable Development. 2021. Circular Economy Strategy and Action Plan; the National Council for Sustainable Development: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Ministry of Environment; SWITCH-Asia. 2022. Cambodia’s Roadmap for Sustainable Consumption and Production 2022-2035; General Directorate of Policy and Strategy: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Royal Government of Cambodia. 2023. Pentagonal Strategy for Growth, Employment, Equity, Efficiency, and Sustainability; the Office of the Council of Ministers: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Royal Government of Cambodia. 2023. Introducing the “Pentagonal Strategy–Phase I” and the “Key Measures of the Royal Government for the Seventh Legislature of the National Assembly” by Samdech Hun Manet, Prime Minister of Cambodia at the First Plenary Session of the Council of Ministers; Peace Palace, 24th August 2023.
- Chan, P. Understanding Green Economic Development in Cambodia. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual Macroeconomic Conference on “Climate Risks and Green Economy Transition”, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 8 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- The United Nations Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE): 2022 Annual Report. Available online: https://www.un-page.org/2022-annual-report/ (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Ferguson, A.; Sin, S. 2014. Cambodia Climate Change Alliance (CCCA) - Final Report - June 2014; Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency: Stockholm, Sweden.
- Royal Government of Cambodia. 2014. Cambodia Climate Change Strategic Plan 2014-2023; Office of the Council of Ministers: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- GGGI. Cambodia and GGGI Extend Green Growth Partnership for Next 5 Years. 2016. Available online: https://gggi.org/cambodia-and-gggi-extend-green-growth-partnership-for-next-5-years/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Chan, P. 2019. Sustainable City Assessment Indicators for Cambodia: Relevance, Development and Application; Lambert Academic Publishing: Chisinau, Moldova, European Union.
- NCSD; GGGI. Phnom Penh Sustainable City Plan 2018–2030. 2018. Available online: https://ncsd.moe.gov.kh/resources/document/sustainable-city-plan-phnom-penh-2018-2030en (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- GGGI. 2018. Green Growth Potential Assessment: Cambodia Country Report; GGGI Cambodia Office: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- GGGI. 2018. The Economic, Social and Environmental Impacts of Greening the Industrial Sector; GGGI Cambodia Office: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- UNDP. 2019. Cambodia: De-risking Renewable Energy Investment; the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP): New York, USA.
- Nop, S. 2019. Guidelines and Certification for Green Buildings in Cambodia (2nd MKCF); Ministry of Environment: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- NCSD; GGGI. 2020. Sustainable City Strategic Plan 2020-2030 for Seven Secondary Cities. Available online: https://gggi.org/report/sustainable-city-strategic-plan-2020-2030-for-seven-secondary-cities-en/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- UNDP. 2020. Full Economic Appraisal of the Potentials of Solar PV Energy in Cambodia; the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP): New York, USA.
- Ministry of Royal Palace. 2021. The Royal Kram to Endorse the New Law on Investment of Cambodia; the Ministry of Royal Palace: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- General Secretariat of the National Council for Sustainable Development. 2021. Stocktaking and Analytical Options for Green Buildings in Cambodia; Ministry of Environment: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Department of Green Economy. 2021. Guideline on Green Office and Green Event and Evaluation Mechanism; the Ministry of Environment: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- GGGI. Green Growth Cooperation in Cambodia Deepened. 2022. Available online: https://gggi.org/green-growth-cooperation-in-cambodia-deepened/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Royal Government of Cambodia. 2022. National Energy Efficiency Policy 2022-2030; Office of the Council of Ministers: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Ministry of Royal Palace. 2023. The Royal Kram to Endorse the New Law on Public Procumbent; the Ministry of Royal Palace: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Ministry of Environment. 2023. The Circular Strategy on Environment 2023-2028; the Ministry of Environment: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Department of Green Economy. 2023. Draft Sub-decree on Eco-label; the Ministry of Environment: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Department of Green Economy. 2023. Draft Cambodia’s Guidelines and Certification for Green Buildings (CamGCGB); the Ministry of Environment: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
- Department of Green Economy. 2023. Draft NCSD Decision on the Establishment of National Steering Committee for UN PAGE in Cambodia; the National Council for Sustainable Development: Phnom Penh, Cambodia.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).