2.1. Enterprise Digital Transformation and Green Technology Innovation
Green technological innovation, also known as environmentally friendly technological innovation, is a collective term for management and technological innovations aimed at environmental protection. It encompasses innovations in various aspects, including product design, green materials, green processes, green equipment, green recycling and treatment, and green packaging (Aguilera-Caracuel and Ortiz-de-Mandojana, 2013). With sustainable development as its core value, green technological innovation utilizes technological and managerial innovations as driving mechanisms to achieve modern technological innovation through environmental protection and energy conservation (Alder et al., 2012). Through green technological innovation, companies can improve the efficiency of raw material and energy utilization (Braun and Wield, 2007), reduce resource utilization costs, and minimize environmental costs (Omonijo and Yunsheng, 2022), thereby lowering operational expenses and gaining a competitive edge in the market competition(Porter and Linde, 1995). In the development of manufacturing companies, green technological innovation, as a new type of technological innovation that simultaneously considers environmental protection and green economic development(Berrone et al., 2013), plays an increasingly important role.
This study considers the factors influencing green technological innovation in companies, which can be categorized into external factors and internal factors. External factors primarily include the financing environment (Lin and Ma, 2022), economic conditions (Li et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2023), market environment (Cleff and Rennings, 1999), and policy environment (Ren et al., 2021), among others. However, the impact of external factors is holistic rather than specific to individual companies. Therefore, this study chooses to empirically investigate the more heterogeneous internal factors.
Internal factors encompass characteristics specific to the company itself, digital capabilities, information acquisition and sharing capabilities, resource allocation capabilities, among others. For instance, company size is a key internal factor determining technological innovation (Feng and Ma, 2020). Company size represents capital accumulation and serves as the foundation and capability for innovation activities (Stock et al., 2002). This implies that larger companies can provide stable resource inputs for technological innovation. Furthermore, green innovation requires the integration of resource consumption and manufacturing system information, as well as the integration of knowledge across different technological domains both within and outside the company (Cui et al., 2020). The company's information acquisition and sharing capabilities can effectively improve resource allocation efficiency, thereby promoting green technological innovation.
Based on the analysis above, the impact of digital transformation on green technological innovation in companies can be mainly reflected in the following two aspects. On one hand, digital transformation can help companies "reduce costs and increase efficiency," optimize resource utilization, and enhance innovation investment. Technological innovation in companies requires a substantial input of resources (Zhou et al., 2017), including stable human and capital investments. The problem of "market failure" caused by its risk uncertainty and externalities leads to private benefits being smaller than social benefits for companies, reducing their motivation for innovation. Therefore, insufficient innovation drive and weak R&D investment are challenges that hinder technological innovation in companies (Hartono and Kusumawardhani, 2019). Digital transformation in companies can improve their ability to perceive the external environment and acquire different resources (Xue et al., 2022), thereby helping them efficiently integrate and obtain internal and external resources. The emergence of intelligent manufacturing and robotic production can liberate some labor, enabling them to shift to more creative and specialized work, thus improving the efficiency of existing human capital utilization (Demartini et al., 2019). Moreover, digital transformation not only helps companies achieve intelligent operations and cost reduction in organizational management but also enhances efficiency and productivity. Digital transformation enables companies to achieve intelligent operations throughout the entire process, from research and development to production and sales, optimizing products and services in-depth, which is beneficial for reducing operating costs (Agarwal et al., 2010) and alleviating the shortage of R&D innovation funding.
On the other hand, digital transformation can enhance a company's capability to acquire, integrate, and share information, thereby increasing innovation opportunities. Compared to general technological innovation, green innovation related to a company's production and low-carbon management processes requires the integration of resource consumption, environmental impact, and manufacturing system information, which places higher demands on the company's information-sharing capability (Feng et al., 2022).
Based on the analysis of aggregated massive data, digital transformation can facilitate efficient information flow, intelligent analysis, and feedback (Verhoef et al., 2021), which fully meets the requirements of information-sharing capability in companies. It helps companies improve efficiency and seize innovation opportunities based on the acquired information. Building upon the above analysis, the following hypothesis is proposed:
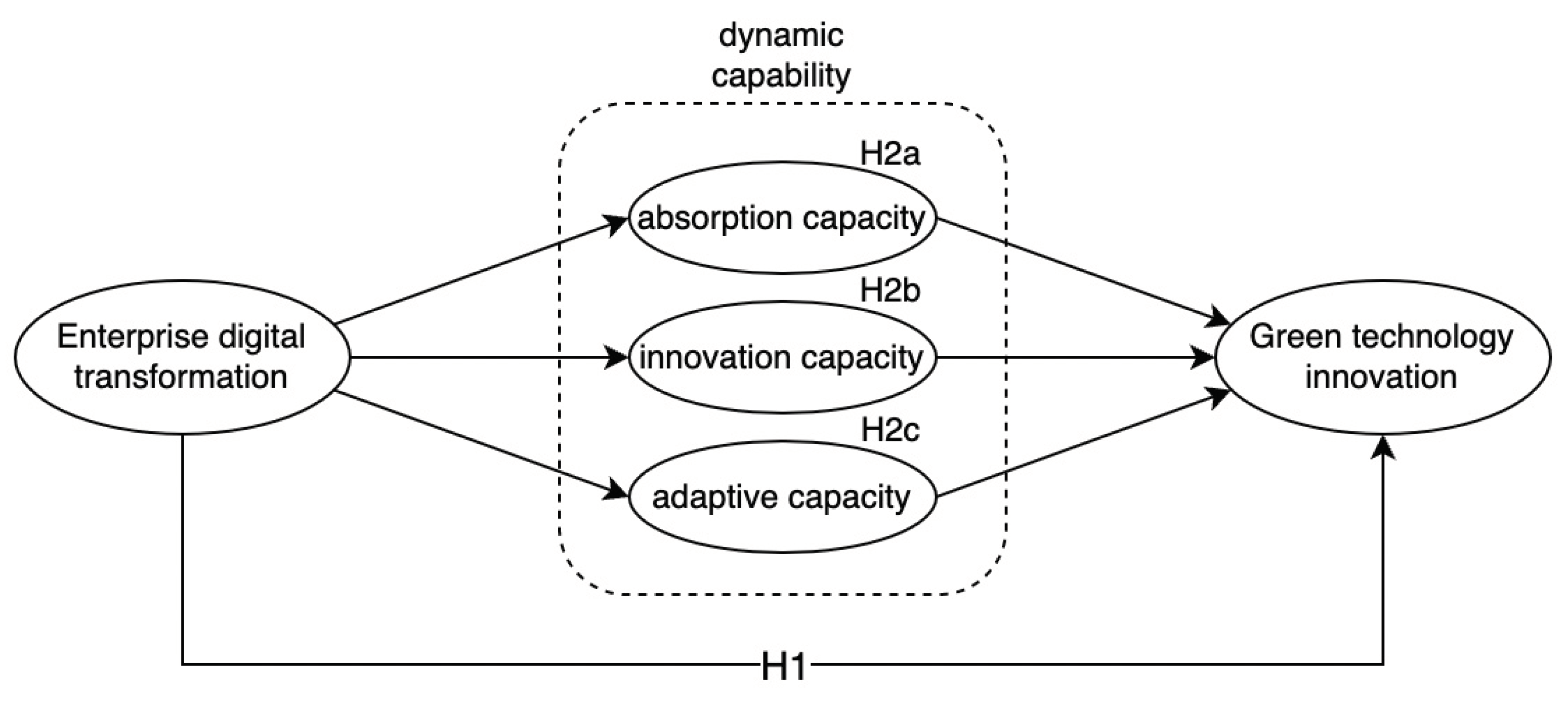
H1: Digital transformation in companies has a positive impact on green technological innovation.
2.2. The Mediating Role of Dynamic Capabilities
Although existing research has shown that digital transformation in companies has a promoting effect on green technological innovation, the specific mechanisms of its impact have not been fully clarified. The digital technology has driven diverse changes in production, innovation, and business models (Hanelt et al., 2021) further intensifying competition among companies. Enhancing competitiveness remains an important issue for companies. According to the dynamic capabilities theory, companies should generate a new capability by integrating, building, and reconfiguring internal and external resources, enabling them to adapt quickly to the business environment and form their own competitive advantage (Teece, 2007). In the context of digital transformation, data is an important resource for value creation in companies (Verhoef et al., 2021). Digitization brings various capabilities to companies, including leveraging digital technology applications such as cloud computing, big data, and artificial intelligence to enhance their technological advantages, as well as efficient integration, analysis, and integration of acquired data information resources, known as information integration capabilities (Günther et al., 2017). This further promotes the development of a company's dynamic capabilities. By utilizing the dynamic capabilities brought by digital transformation, companies can more flexibly respond to the current economic environment and the incentivized market competition, ensuring that they can seize innovation opportunities and promote technological progress in the digital economy era. Previous research has explored the role of dynamic capabilities in various aspects such as firm innovation performance (Zhou et al., 2017), digital circular business models (Eechoud and Ganzaroli, 2023), and competitive advantage (Ferreira et al., 2020). However, it has not extensively investigated the mechanisms through which dynamic capabilities influence the level of green technological innovation in companies.
Currently, there is no unified standard for classifying dynamic capabilities. This study draws on the research of Wang and Ahmed (2007), ZhaoFeng et al. (2016), and others, combined with practical considerations, to divide dynamic capabilities into absorptive capacity, innovation capacity, and adaptability. Absorptive capacity refers to the ability of a company to identify, acquire, and integrate external knowledge, and ultimately transform it into its own innovation advantage (Zahra and George, 2002). Innovation capacity refers to the ability of a company to develop new products or technologies. Adaptability, on the other hand, refers to the ability of a company to flexibly respond to changes in the market environment and optimize its resource allocation (Vogel and Güttel, 2013).
The impact of digital transformation on a company's dynamic capabilities is reflected in several aspects. Firstly, digital transformation helps companies absorb and utilize new knowledge, enhancing their absorptive capacity. In the era of the digital economy, data has become an important production factor, and the information contained in processed data holds immense value for companies (Sagiroglu and Sinanc, 2013). Through digital transformation, companies can establish a learning organization, continuously learn and improve by collecting and analyzing large-scale data, thus facilitating the identification and acquisition of valuable new knowledge. Additionally, digital transformation provides real-time feedback and evaluation mechanisms, enabling companies to timely understand their strengths and weaknesses, thereby enhancing their learning and continuous improvement capabilities.
Secondly, digital transformation can optimize a company's innovation model and enhance its innovation capacity. By leveraging digital technologies and platforms, companies can innovate products and services more rapidly, implement new business models (Vaska et al., 2021), and expand into new market areas. Through collaboration with other companies, research institutions, and startups, as well as the sharing of resources and knowledge, companies can quickly access new technologies, innovations, and market opportunities (Faria et al., 2010). This open innovation model and collaborative network provide broader development space for a company's innovation capacity.
Lastly, digital transformation drives efficiency improvement and resource optimization in companies, enhancing their adaptability. The application of digital technology enhances a company's market perception, resource integration, and organizational collaboration capabilities (Warner and Wäger, 2019), enabling companies to swiftly perceive the external environment and respond accordingly. Data-driven decision-making also enhances a company's sensitivity to environmental changes and response speed (Provost and Fawcett, 2013), strengthening its adaptability. Through data analysis and insights, companies can gain a more accurate understanding of market demand, customer behavior, and competitive dynamics, thus making more astute decisions.
The enhancement of dynamic capabilities such as absorptive capacity, innovation capability, and adaptability enables companies to quickly identify and adapt to changing market demands and environmental pressures. In green technology innovation, companies need to continuously track and understand new trends and requirements in areas such as environmental protection, sustainable development, and energy efficiency (Su et al., 2022). Companies with strong dynamic capabilities possess agility and flexibility (Zhou et al., 2017), allowing them to promptly adjust their technology research and development direction, product design, and production processes to meet the needs of green technology innovation.
Furthermore, the company's dynamic capabilities are closely related to innovation. Green technology innovation requires companies to have exploratory thinking and innovative abilities (Huang et al., 2022), constantly exploring new technologies and solutions to reduce environmental burdens, improve resource utilization efficiency, and enhance ecological benefits. The company's dynamic capabilities promote green technology innovation by facilitating knowledge sharing within the organization, stimulating employees' creative thinking, and fostering an innovative culture (Liao et al., 2009).
Moreover, green technology innovation demands efficient resource integration, including technology, capital, talent, and market resources. Companies with strong dynamic capabilities proactively seek and integrate relevant resources (Teece, 2007) and apply them in the process of green technology innovation. For example, companies can establish collaborative relationships with suppliers, partners, and research institutions to share technology and knowledge and jointly carry out green technology innovation projects.
Lastly, technological innovation is an ongoing learning and adaptation process. Green technology innovation often involves knowledge and information about new technologies, markets, and regulations (Guo et al., 2018). Companies need to have stronger learning capabilities to timely update and apply new knowledge to maintain competitiveness. A company's dynamic capabilities facilitate the acquisition, transformation, and application of knowledge (Nielsen, 2006), assisting companies in continuous improvement and enhancement of green technology innovation.
Based on the previous analysis, digital transformation of companies can enhance the dynamic capabilities of absorptive capacity, innovation capability, and adaptability. Companies with high dynamic capabilities can facilitate information acquisition and knowledge transformation, strengthen their understanding and cognition of green technology innovation, and convert acquired information into valuable knowledge (Nieves and Haller, 2014). This knowledge can then be applied in the process of green technology innovation, thereby driving innovation occurrence and implementation. Additionally, companies with high dynamic capabilities can establish close collaborative relationships with suppliers, partners, and research institutions, sharing technology and knowledge, and forming collaborative networks and innovation ecosystems. Such companies can share risks, engage in collaborative learning and co-innovation, and accelerate the progress and application of green technology innovation.
Lastly, company's dynamic capabilities enable organizations to possess flexibility and agility (Teece, 2007), allowing them to timely adjust resource allocation, organizational structure, and business processes to adapt to changing market demands and environmental pressures. This flexibility and agility enable companies to better address uncertainties and risks in green technology innovation, swiftly adjust their technology research and development direction, product design, and production processes to meet the needs of green technology innovation.
In conclusion, dynamic capabilities play an intermediary role in the impact of digital transformation on green technology innovation within companies. Based on the aforementioned analysis, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H2a: Absorptive capacity plays an intermediary role in the impact of digital transformation on green technology innovation within companies.
H2b: Innovation capability plays an intermediary role in the impact of digital transformation on green technology innovation within companies.
H2c: Adaptability plays an intermediary role in the impact of digital transformation on green technology innovation within companies.
The theoretical model of this study is shown in
Figure 1.