Submitted:
05 January 2024
Posted:
08 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
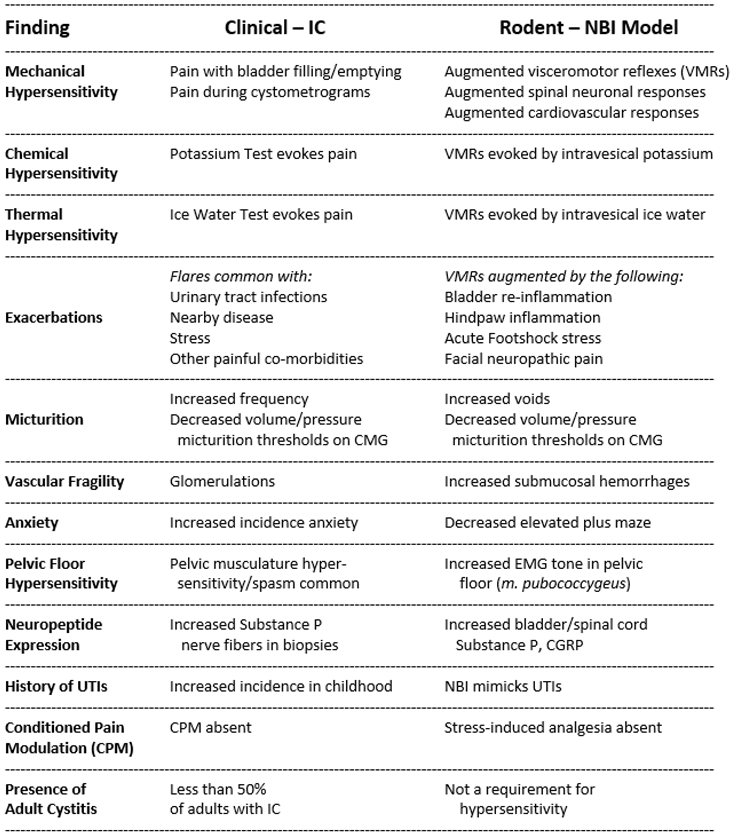
Introduction
Conclusions
Material and Methods
Common methodology
Funding Information
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
Ethics Statements
References
- Abreu-Mendes P, Costa A, Charrua A, Almeida Pinto R, Cruz F. The role of urinary VEGF in observational studies of BPS/IC patients: a systematic review. Diagnostics (Basel) 2022; 12:1037. [CrossRef]
- Afari N, Buchwald D, Clauw D, Hong B, Hou X, Krieger JN, Mullins C, Stephens-Shields AJ, Gasperi M, Williams DA; MAPP Research Network. A MAPP network case-control study of urological chronic pelvic pain compared with nonurological pain conditions. Clin J Pain 2020; 36:8-15. [CrossRef]
- Akiyama Y and Hanno P. Phenotyping of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Int J Urol 2019; 1: 17-19. [CrossRef]
- Al-Chaer ED, Kawasaki M, Pasricha TJ. A new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development. Gastroenterology 2000; 119: 1276-128. [CrossRef]
- Applebaum AE, Vance WH, Coggeshall RE. Segmental localization of sensory cells that innervate the bladder. J Comp Neurol 1980; 192:203-209. [CrossRef]
- Archer AC, DeBerry JJ, DeWitte C, Ness TJ. Neonatal cystitis makes adult female rat urinary bladders more sensitive to low concentration microbial antigens. Res Rep Urol 2023; 15: 531-539. [CrossRef]
- Ball CL, Ness TJ and Randich A. Opioid blockade and inflammation reveal estrous cycle effects on visceromotor reflexes evoked by bladder distension. J Urol 2010; 184: 1529-1535. [CrossRef]
- Beggs S, Currie G, Salter MW, Fitzgerald M, Walker SM. Priming of adult pain responses by neonatal pain experience: maintenance by central neuroimmune activity. Brain 2012; 135:404-417. [CrossRef]
- Blatt LK, Lashinger ES, Laping NJ and Su X. Evaluation of pressor and visceromotor reflex responses to bladder distension in urethane anesthetized rats. Neurourol Urodyn 2009; 28: 442-446. [CrossRef]
- Bullones Rodríguez MÁ, Afari N, Buchwald DS; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Working Group on Urological Chronic Pelvic Pain. Evidence for overlap between urological and nonurological unexplained clinical conditions. J Urol 2013; 189(1 Suppl): S66-74.
- Butler RK, Finn DP. Stress-induced analgesia. Prog Neurobiol 2009; 88: 184-202. [CrossRef]
- Castroman P, Ness TJ. Vigor of visceromotor responses to urinary bladder distension in rats increases with repeated trials and stimulus intensity. Neurosci Letts 2001; 306:97-100. [CrossRef]
- Clemens JQ, Clauw DJ, Kreder K, Krieger JN, Kusek JW, Lai HH, Rodriguez L, Williams DA, Hou X, Stephens A, Landis JR; MAPP Research Network. Comparison of baseline urological symptoms in men and women in the MAPP research cohort. J Urol 2015; 193:1554-1558. [CrossRef]
- Clemens JQ, Meenan RT, O’Keeffe Rosetti MC, Gao SY, Calhoun EA. Prevalence and incidence of interstitial cystitis in a managed care population. J Urol 2005; 173: 98-102. [CrossRef]
- Clemens JQ, Mullins C, Ackerman AL, Bavendam T, van Bokhoven A, Ellingson BM, Harte SE, Kutch JJ, Lai HH, Martucci KT, Moldwin R, Naliboff BD, Pontari MA, Sutcliffe S, Landis JR; MAPP Research Network Study Group. Urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome: insights from the MAPP Research Network. Nat Rev Urol. 2019; 16:187-200. [CrossRef]
- Clodfelder-Miller B, DeBerry JJ, Ness TJ. Urothelial bladder afferents selectively project to L6/S1 levels and are more peptidergic than those projecting to the T13/L1 levels in female rats. Heliyon 2023; 2023: e18495. [CrossRef]
- Clodfelder-Miller BJ, Kanda H, Gu J, Creighton JR, Ness TJ and Deberry JJ. Urothelial bladder afferent neurons in the rat are anatomically and neurochemically distinct from non-urothelial afferents. Brain Res 2018; 1689: 45-53. [CrossRef]
- Clodfelder-Miller B, Ness TJ and DeBerry JJ. Neonatal bladder inflammation results in adult female mouse phenotype with increased frequency and nociceptive responses to bladder filling. Front Syst Neurosci. 2022; 16: 858220. [CrossRef]
- Deberry JJ, Ness TJ, Robbins MT, Randich A. Inflammation-induced enhancement of the visceromotor reflex to urinary bladder distention: Modulation by endogenous opioids and the effects of early-in-life experience with bladder inflammation. J Pain 2007; 8:914-23. [CrossRef]
- Deberry JJ, Randich A., Shaffer A., Robbins M, and Ness TJ. Neonatal bladder inflammation produces functional changes and alters neuropeptide content in bladders of adult female rats. J Pain 2010; 11:247-255. [CrossRef]
- DeBerry JJ, Robbins MT, Ness TJ The amygdala central nucleus is required for acute stress-induced bladder hyperalgesia in a rat visceral pain model. Brain Res 2015; 1606:77-85. [CrossRef]
- DeGroat WC, Araki I, Vizzard MA. Developmental and injury induced plasticity in the micturition reflex pathway. Behav Brain Res 1998: 92: 127-140. [CrossRef]
- Deutsch G, Deshpande H, Frölich MA, Lai HH, Ness TJ. Bladder distension increases blood flow in pain related brain structures in subjects with interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2016; 196: 902-10. [CrossRef]
- Deutsch G, Deshpande H, Lai HH, Kutch JJ, Ness TJ. Cerebral perfusion and sensory testing results differ in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome patients with and without fibromyalgia: a site-specific MAPP Network study. J Pain Res 2021; 14: 3887-3895. [CrossRef]
- Ding X, Liang Y-J, Su L, Liao F-Ff, ang D, Tai J, Xing G-G. BDNF contributes to the neonatal incision-induced facilitation of spinal long-term potentiation and the exacerbation of incisional pain in adult rats. Neuropharm 2018; 137: 114-132. [CrossRef]
- Farmer MA, Huang L, Martucci K, Yang CC, Maravilla KR, Harris RE, Clauw DJ, Mackey S, Ellingson BM, Mayer EA, Schaeffer AJ, Apkarian AV; MAPP Research Network. Brain white matter abnormalities in female interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: A MAPP Network Neuroimaging Study. J Urol.2015; 194:118-26. [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald M, Koltzenberg M. The functional development of descending inhibitory pathways in the dorsolateral funiculus of the newborn rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1986; 389: 261-270. [CrossRef]
- Gold MS, Zhang L, Wrigley DL, Traub RJ. Prostaglandin E(2) modulates TTX-RI(Na) in rat colonic sensory neurons. J Neurophysiol 2002; 88:1512-1522. [CrossRef]
- Griffith JW, Stephens-Shields AJ, Hou X, Naliboff BD, Pontari M, Edwards TC, Williams DA, Clemens JQ, Afari N, Tu F, Lloyd RB, Patrick DL, Mullins C, Kusek JW, Sutcliffe S, Hong BA, Lai HH, Krieger JN, Bradley CS, Kim J, Landis JR. Pain and urinary symptoms should not be combined into a single score: psychometric findings from the MAPP Research Network. J Urol 2016; 195: 949-54. [CrossRef]
- Gupta A, Bhatt RR, Naliboff BD, Kutch JJ, Labus JS, Vora PP, Alaverdyan M, Schrepf A, Lutgendorf S, Mayer EA; MAPP Research Network. Impact of early adverse life events and sex on functional brain networks in patients with urological chronic pelvic pain syndrome (UCPPS): A MAPP Research Network study. PLoS One 2019;14: e0217610. [CrossRef]
- Gupta P, Gallop R, Spitznagle T, Lai H, Tu F, Krieger JN, Clemens JQ, Bradley CS, Yang C, Sutcliffe S, Moldwin R, Kreder K, Kutch J, Rodriguez LV. Is pelvic floor muscle tenderness a distinct urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome phenotype? Findings from the MAPP Research Network symptom pattern study. J Urol 2022; 208: 341-349. [CrossRef]
- Harte SE, Schrepf A, Gallop R, Kruger GH, Lai HHH, Sutcliffe S, Halvorson M, Ichesco E, Naliboff BD, Afari N, Harris RE, Farrar JT, Tu F, Landis JR, Clauw DJ; MAPP Research Network. Quantitative assessment of nonpelvic pressure pain sensitivity in urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a MAPP Research Network study. Pain 2019; 160: 1270-1280. [CrossRef]
- Hsieh C-T, Lee Y-J, Dai X, Ojeda NB, Lee HJ, Tien L-T, Fan L-W. Systemic lipopolysaccharide-induced pain sensitivity and spinal inflammation were reduced by minocycline in neonatal rats. Int J Mol Sci 2018; 19:2947. [CrossRef]
- Huang L, Kutch JJ, Ellingson BM, Martucci KT, Harris RE, Clauw DJ, Mackey S, Mayer EA, Schaeffer AJ, Apkarian AV, Farmer MA; MAPP Research Network. Brain white matter changes associated with urological chronic pelvic pain syndrome: multisite neuroimaging from a MAPP case-control study. Pain 2016; 157: 2782-2791. [CrossRef]
- Ji N-N, Meng Q-X, Wang Y, Zhou Z-M, Song Y, Hua R, Zhang Y-M. Microglia-derived TNF-a inhibiting GABAergic neurons in the anterior lateral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis precipitates visceral hypersensitivity induced by colorectal distension in rats. Neurobio Stress 2022; 18: 100449. [CrossRef]
- Kairys AE, Schmidt-Wilcke T, Pulu T, Ichesco E, Labus JS, Martucci K, Farmer MA, Ness TJ, Deutsch G, Mayer EA, Mackey S, Apkarian AV, Maravilla K, Clauw DJ, Harris RE. Increased brain gray matter in the primary somatosensory cortex is associated with increased pain and mood disturbance in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. J Urol. 2015; 193:131-7. [CrossRef]
- Kanda H, Clodfelder-Miller BJ, Gu JG, Ness TJ, DeBerry JJ. Electrophysiological properties of lumbosacral primary afferent neurons innervating urothelial and non-urothelial layers of mouse urinary bladder. Brain Res 2016; 1648:81-9. [CrossRef]
- Kannampalli P, Babygirija R, Zhang J, Poe MM et al. Neonatal bladder inflammation induces long-term visceral pain and altered responses of spinal neurons in adult rats. Neuroscience 346: 349-364, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick LA, Kutch JJ, Tillisch K, Naliboff BD, Labus JS, Jiang Z, Farmer MA, Apkarian AV, Mackey S, Martucci KT, Clauw DJ, Harris RE, Deutsch G, Ness TJ, Yang CC, Maravilla K, Mullins C, Mayer EA. Alterations in resting state oscillations and connectivity in sensory and motor networks in women with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. J Urol 2014; 192: 947-55. [CrossRef]
- Krieger JN, Stephens AJ, Landis JR, Clemens JQ, Kreder K, Lai HH, Afari N, Rodríguez L, Schaeffer A, Mackey S, Andriole GL, Williams DA; MAPP Research Network. Relationship between chronic nonurological associated somatic syndromes and symptom severity in urological chronic pelvic pain syndromes: baseline evaluation of the MAPP study. J Urol 2015;193: 1254-62. [CrossRef]
- Kutch JJ, Ichesco E, Hampson JP, Labus JS, Farmer MA, Martucci KT, Ness TJ, Deutsch G, Apkarian AV, Mackey SC, Klumpp DJ, Schaeffer AJ, Rodriguez LV, Kreder KJ, Buchwald D, Andriole GL, Lai HH, Mullins C, Kusek JW, Landis JR, Mayer EA, Clemens JQ, Clauw D, Harris RE, MAPP Research Network. Brain signature and functional impact of centralized pain: a multidisciplinary approach to the study of chronic pelvic pain (MAPP) network study. Pain 2017; 158:1979-1991. [CrossRef]
- Lai HH, Gardner V, Ness TJ, Gereau RW 4th. Segmental hyperalgesia to mechanical stimulus in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome - evidence of central sensitization. J Urol 2014; 191:1294-9. [CrossRef]
- Lai H, Gereau RW 4th, Luo Y, O'Donnell M, Rudick CN, Pontari M, Mullins C, Klumpp DJ. Animal models of urologic chronic pelvic pain syndromes: findings from the multidisciplinary approach to the study of chronic pelvic pain research network. Urology 2015; 85: 1454-65. [CrossRef]
- Lai HH, Jemielita T, Sutcliffe S, Bradley CS, Naliboff B, Williams DA, Gereau RW 4th, Kreder K, Clemens JQ, Rodriguez LV, Krieger JN, Farrar JT, Robinson N, Landis JR; MAPP Research Network. Characterization of whole-body pain in urological chronic pelvic pain syndrome at baseline: A MAPP Research Network Study. J Urol 2017; 198: 622-631. [CrossRef]
- Lai HH, Krieger JN, Pontari MA, Buchwald D, Hou X, Landis JR; MAPP Research Network. Painful bladder filling and painful urgency are distinct characteristics in men and women with urological chronic pelvic pain syndromes: A MAPP Research Network Study. J Urol 2015; 194: 1634-41. [CrossRef]
- Lai HH, Newcomb C, Harte S, Appleby D, Ackerman AL, Anger JT, Nickel JC, Gupta P, Rodriguez LV, Landis JR, Clemens JQ; MAPP Research Network. Comparison of deep phenotyping features of UCPPS with and without Hunner lesion: A MAPP-II Research Network Study. Neurourol Urodyn 2021; 40: 810-818. [CrossRef]
- Lai HH, North CS, Andriole GL, Cupps L, Song D, Ness TJ, Hong BA. Urological symptoms in a subset of patients with urological chronic pelvic pain syndrome and a polysymptomatic, polysyndromic pattern of presentation. J Urol 2014; 191: 1802-7. [CrossRef]
- LaPrairie JL, Murphy AZ. Female rats are more vulnerable to the long-term consequences of neonatal inflammatory injury. Pain 2007; 132: S124-S133. [CrossRef]
- Lutgendorf SK, Zia S, Luo Y, O'Donnell M, van Bokhoven A, Bradley CS, Gallup R, Pierce J, Taple BJ, Naliboff BD, Quentin Clemens J, Kreder KJ, Schrepf A. Early and recent exposure to adversity, TLR-4 stimulated inflammation, and diurnal cortisol in women with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: A MAPP research network study. Brain Behav Immun 2023; 111: 116-123. [CrossRef]
- Mazeaud C, Rigaud J, Levesque A et al. Stratification of patients with interstitial cystitis-bladder pain syndrome according to the anatomical bladder capacity. Urology 2019; 123: 87-92. [CrossRef]
- Miranda A, Mickle A, Bruckert M et al. NMDA receptor mediates chronic visceral pain induced by neonatal noxious somatic stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol 2014; 744: 28-35. [CrossRef]
- Miranda A, Mickle A, Schmidt J, Zhang Z et al. Neonatal cystitis-induced colonic hypersensitivity in adult rats: a model of viscero-visceral convergence. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2011; 23: 683-e281. [CrossRef]
- Moriarty O, Harrington L, Beggs S, Walker SM. Opioid analgesia and the somatosensory memory of neonatal surgical injury in the adult rat. Br J Anaesth 2018; 121: 314-324. [CrossRef]
- Moriarity O, Tu Y, Sengar AS, Salter MW, Beggs S, Walker SM. Priming of adult incision response by early-life injury: neonatal microglial inhibition has persistent but sexually dimorphic effects in adult rats. J Neurosci 2019; 39: 3081-3093. [CrossRef]
- Mukerji G, Waters J, Chessell IP, Bountra C, Agarwal SK, Anand P. Pain during ice water test distinguishes clinical bladder hypersensitivity from overactivity disorders. BMC Urol 2006; 6: 31. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Castroman P. Evidence for two populations of rat spinal nociceptive neurons excited by urinary bladder distension. Brain Res 2001; 923:147-156. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Castroman PJ, Randich A. Acute bladder inflammation differentially affects spinal visceral nociceptive neurons. Neurosci Lett 2009; 467:150-4. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Clodfelder-Miller B, McNaught J, Miller DE and Su X. Benzodiazepines suppress neuromodulatory effects of pudendal nerve stimulation on rat bladder nociception. Anesth Analg, 2020; 130:1077-1084. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Clodfelder-Miller B, McNaught J, Miller DE and Su X. Neuromodulatory effects of pudendal nerve stimulation on bladder hypersensitivity are present in opioid-pretreated rats" Reg Anesth Pain Med 2019; 44: 1015-1020. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, DeWitte C, DeBerry JJ. Spinal neurochemical mechanisms of acute stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity in healthy rats. Neurosci Letts 2022; 770: 136401. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, DeWitte C, DeBerry JJ, Hart MP, Clodfelder-Miller B, Gu JG, Ling J, Randich A. A model in female rats with phenotypic features similar to interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Front Pain Res 2021; 7: 791045. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, DeWitte C, DeBerry JJ, Randich A. Neonatal bladder inflammation alters the role of the central amygdala in hypersensitivity produced by acute footshock stress in adult female rats. Brain Res. 2018; 1698: 99-105. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, DeWitte C, McNaught J, Clodfelder-Miller B and Su X. Spinal mechanisms of pudendal nerve stimulation-induced inhibition of bladder hypersensitivity in rats. Neurosci Letts 2018; 686: 181-185. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, DeWitte C, Randich A. Neonatal cystitis leads to alterations in spinal corticotropin releasing factor receptor-type 2 content and function in adult rats following bladder re-inflammation. Brain Res 2022; 1788: 147927. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, DeWitte C, Randich A. The double insult of neonatal cystitis plus adult somatic inflammation results in corticotropin releasing factor Type II receptor-dependent bladder hypersensitivity in female rats. J Pain 2022; 23: 2167-2178. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, DeWitte C, Robbins MT and DeBerry JJ. Neonatal cystitis alters mechanisms of stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity in rats. Neurosci Letts 2022; 778: 136617. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Gebhart GF. Colorectal distension as a noxious visceral stimulus: physiologic and pharmacologic characterization of pseudaffective reflexes in the rat. Brain Res 1988; 450:153-169. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Gebhart GF. Interactions between visceral and cutaneous nociception. I. Noxious cutaneous stimuli inhibit visceral nociceptive neurons and reflexes. J Neurophysiol 1991; 66:20-28. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1991.66.1.20. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Gebhart GF. Acute inflammation differentially alters the activity of two classes of rat spinal visceral nociceptive neurons. Neurosci Lett 2000; 281:131-134. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Gebhart GF. Inflammation enhances reflex and spinal neuron responses to noxious visceral stimulation in rats. Am J Physiol 2001; 280: G649-G657. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Lewis-Sides A, Castroman P. Characterization of pressor and visceromotor reflex responses to bladder distension in rats: sources of variability and effect of analgesics. J Urol 2001; 165: 968-974.
- Ness TJ, Lloyd LK, Fillingim RB. An endogenous pain control system is altered in subjects with interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2014; 191: 364-70. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, McNaught J, Clodfelder-Miller B, Su X. Medications used to treat bladder disorders may alter effects of neuromodulation. Neurourol Urodyn 2020; 39:1313-1320. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Richter HE, Varner RE, Fillingim RB. A psychophysical study of discomfort produced by repeated filling of the urinary bladder. Pain 1998; 76: 61-69. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Powell-Boone T, Cannon R, Lloyd LK, Fillingiim RB. Psychophysical evidence of hypersensitivity in subjects with interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2005; 173: 1983-1987. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Randich A. Which spinal cutaneous nociceptive neurons are inhibited by intravenous lidocaine in the rat? Reg Anesth Pain Med 2006; 31: 248-253. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Randich A. Neonatal bladder inflammation alters activity of adult rat spinal visceral nociceptive neurons. Neurosci Lett 2010; 472: 210-214. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Randich A, Nelson DE, Su X. Screening and optimization of nerve targets and parameters reveals inhibitory effect of pudendal stimulation on rat bladder hypersensitivity. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2016; 41: 737-743. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ, Randich A, Su X, DeWitte C and Hildebrand K. Systemic and intrathecal baclofen produce bladder antinociception in rats. BMC Urology 2021; 21: 139. [CrossRef]
- Ness TJ and Su X. Parametric assessment of spinal cord stimulation on bladder pain-like responses in rats. Neuromodulation 2022; 25: 1134-1140.
- Nickel JC, Stephens A, Landis JR, Mullins C, van Bokhoven A, Anger JT, Ackerman AL, Kim J, Sutcliffe S, Krol JE, Sen B, Hammond J, Ehrlich GD; Multidisciplinary Approach to the Study of Chronic Pelvic Pain (MAPP) Research Network. Urinary fungi associated with urinary symptom severity among women with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS). World J Urol 2020; 38: 433-446.
- Otsuji J, Hayashi Y, Hitomi S, Soma C, Soma K, Shibuta I, Iwata K, Shirakawa T, Shinoda M. Decreased PPARgamma in the trigeminal spinal subnucleus caudalis due to neonatal injury contributes to incision-induced mechanical allodynia in female rats. Sci Reps 2022; 12: 19314. [CrossRef]
- Overholt, TL, Matthews CA, Evans RJ, BaDLANI g, Ahn C, Simon T, Walker SJ. Small fiber polyneuropathy is associated with non-bladder-centric interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome patients. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg 2021; 27: 581-585. [CrossRef]
- Pang X, Marchand J, Sant GR, Kream RM, Theoharides TC. Increased number of substance P positive nerve fibers in interstitial cystitis. J Urol 1995; 75: 744-750.
- Parsons CL. Potassium sensitivity test. Tech Urol 1996. 2:171-173.
- Park JS, Jung HD, Cho YS, Jin MH, Hong CH. Neonatal bladder irritation is associated with vanilloid receptor TRPV1 expression in adult rats. Int Neurourol J 2018; 22: 169-176. [CrossRef]
- Pattinson D and Fitzgerald M. The neurobiology of infant pain: development of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission in the spinal dorsal horn. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2004; 29: 36-44. [CrossRef]
- Peters KM, Killinger KA and Ibrahim IA. Childhood symptoms and events in women with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Urology 2009; 73: 258-62. [CrossRef]
- Pierce J, Harte SE, Afari N, Bradley CS, Griffith JW, Kim J, Lutgendorf S, Naliboff BD, Rodriguez LV, Taple BJ, Williams D, Harris RE, Schrepf A. Mediators of the association between childhood trauma and pain sensitivity in adulthood: a MAPP Research Network analysis. Pain 2023; 164: 1995-2008.
- Plair A, Evans RJ, Langefeld CD, Matthews CA, Badlani G, Walker SJ. Anesthetic bladder capacity is a clinical biomarker for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome subtypes. J Urol 2021 158: 74-80. [CrossRef]
- Randich A, DeWitte C, DeBerry JJ, Robbins MT, and Ness TJ. Lesions of the central amygdala and ventromedial medulla reduce bladder hypersensitivity produced by acute but not chronic foot shock. Brain Res 2017; 1675: 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Randich A, Mebane H, Deberry JJ, Ness TJ. Rostral ventral medulla modulation of the visceromotor reflex evoked by urinary bladder distension in female rats. J Pain 2008; 9: 920-926. [CrossRef]
- Randich A, Mebane H, Ness TJ. Ice water testing reveals hypersensitivity in adult rats that experienced neonatal bladder inflammation: Implications for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2009; 182: 337-42. [CrossRef]
- Randich A, Uzzell TW, Cannon RS and Ness TJ. Inflammation and enhanced nociceptive responses to bladder distension produced by intravesical zymosan in the rat. BMC Urol 2006; 6:2. [CrossRef]
- Randich A, Uzzell TW, DeBerry JJ and Ness TJ. Neonatal urinary bladder inflammation produces adult bladder hypersensitivity. J Pain 2006; 7: 469-79. [CrossRef]
- Robbins MT, DeWitte C, Ness TJ. Stress-induced bladder hypersensitivity: effect of corticotropin releasing factor receptors assessed by spinal neurophysiology and neurochemistry. Neuropharmacology 2023; 224: 109369. [CrossRef]
- Robbins MT, Ness TJ. Footshock-induced urinary bladder hypersensitivity: role of spinal corticotrophin-releasing factor receptors. J Pain 2008; 9: 991-998.
- Robbins MT, Uzzell TW, Aly S and Ness TJ. Visceral nociceptive input to the area of the medullary lateral reticular nucleus ascends in the lateral spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 2005; 381: 329-333. [CrossRef]
- Robbins MT, Uzzell TW, Aly S, and Ness TJ. Characterization of thalamic neuronal responses to urinary bladder distension, including the effect of acute spinal lesions in the rat. J Pain 2006; 7: 218-224.
- Ruda MA, Ling QD, Hohmann AG, Peng YB, Tachibana T. Altered nociceptive neuronal circuits after neonatal peripheral inflammation. Science. 2000; 289:628-31. [CrossRef]
- Schachar JS, Evans RJ, Parks GE, Zambon J, Badlani G, Walker SJ. Histological evidence supports low anesthetic bladder capacity as a marker of a bladder-centric disease subtype ininterstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Int Urogynecol J 2019; 30: 1863-1870.
- Schrepf A, Naliboff B, Williams DA, Stephens-Shields AJ, Landis JR, Gupta A, Mayer E, Rodriguez LV, Lai H, Luo Y, Bradley C, Kreder K, Lutgendorf SK; MAPP Research Network. Adverse childhood experiences and symptoms of urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome: A Multidisciplinary Approach to the Study of Chronic Pelvic Pain Research Network Study. Ann Behav Med 2018; 52: 865-877.
- Schwaller F and Fitzgerald M. The consequences of pain in early life: injury-induced plasticity in developing pain pathways. Eur J Neurosci 2014; 39: 344-352. [CrossRef]
- Sengupta JN, Pochiraju S, Kannampalli P, Bruckert M, Addya S, Yadav P, Miranda AM, Shaker R, Banerjee B. MicroRNA-mediated GABA Aa-1 receptor subunit down-regulation in adult spinal cord following neonatal cystitis-induced chronic visceral pain in rats. Pain 2013; 154: 59-70.
- Shaffer AD. “Early-in-Life Bladder Inflammation Alters Cappa-Opioid Modulation of Inflammatory Bladder Pain” All ETDs from UAB. 2012; 2938. Available online: https://digitalcommons.library.uab.edu/etd-collection/2938.
- Shaffer AD, Ball CL, Robbins MT, Ness TJ and Randich A. Effects of acute adult and early-in-life bladder inflammation on bladder neuropeptides in adult female rats. BMC Urol 2011; 11: 18. [CrossRef]
- Shaffer AD, Ness TJ, Randich A. Early-in-life bladder inflammation alters U50,488H but not morphine-induced inhibition of visceromotor responses to urinary bladder distension. Neurosci Lett 2013; 534:150-154. [CrossRef]
- Shaffer AD, Ness TJ, Robbins MT, Randich A. Early in life bladder inflammation alters opioid peptide content in the spinal cord and bladder of adult female rats. J Urol 2013; 189:352-358. [CrossRef]
- Smith C, Nordstrom E, Sengupta JN, Miranda A. Neonatal gastric suctioning results in chronic visceral and somatic hyperalgesia: role of corticotropin releasing factor. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2007; 19: 692-699. [CrossRef]
- Stephens-Shields AJ, Lai HH, Landis JR, Kreder K, Rodriguez LV, Naliboff BD, Afari N, Sutcliffe S, Moldwin R, Griffith JW, Clemens JQ, Bradley CS, Quallich S, Gupta P, Harte SE, Farrar JT. Clinically important differences for pain and urinary symptoms in urological chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a MAPP Network study. J Urol 2023; 209: 1132-1140.
- Sutcliffe S, Colditz GA, Goodman MS, Pakpahan R, Vetter J, Ness TJ, Andriole GL, Lai HH. Urological chronic pelvic pain syndrome symptom flares: characterisation of the full range of flares at two sites in the Multidisciplinary Approach to the Study of Chronic Pelvic Pain (MAPP) Research Network. BJU Int 2014;114: 916-25. [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe S, Colditz GA, Pakpahan R, Bradley CS, Goodman MS, Andriole GL, Lai HH. Changes in symptoms during urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome symptom flares: findings from one site of the MAPP Research Network. Neurourol Urodyn 2015; 34: 188-95.
- Talluri B, Hoelzel F, Medda BK, Terashvili, Sanvanson P, Shaker R, Banerjee A, Sengupta JN, Banerjee B. Identification and characterization of rostral ventromedial medulla neurons synaptically connected to the urinary bladder afferents in female rats with or without neonatal cystitis. J Comp Neurol 2022; 530: 1129-1147.
- Tullus K, Shaikh N. Urinary tract infections in children. Lancet 2020; 395:1659–1668.
- Vega-Avelaira D, Ballesteros JJ, Lopez-Garcia JA. Inflammation-induced hyperalgesia and spinal microglia reactivity in neonatal rats. Eur J Pain 2013; 17: 1180-1188. [CrossRef]
- Vega-Avelaira D, McKelvey R, Hathway G, Fitzgerald M. The emergence of adolescent onset pain hypersensitivity following neonatal nerve injury. Mol Pain 2012; 8: 30. [CrossRef]
- Vizzard MA. Alterations in spinal cord Fos protein expression induced by bladder stimulation following cystitis. Am J Physiol 2000; 278: R1027-R1039. [CrossRef]
- Wilson ML and Gaido L. Laboratory diagnosis of urinary tract infections in adult patients. Med Micro 2004; 38: 1150-1158. [CrossRef]
- Woodworth D, Mayer E, Leu K, Ashe-McNalley C, Naliboff BD, Labus JS, Tillisch K, Kutch JJ, Farmer MA, Apkarian AV, Johnson KA, Mackey SC, Ness TJ, Landis JR, Deutsch G, Harris RE, Clauw DJ, Mullins C, Ellingson BM; MAPP Research Network. Unique microstructural changes in the brain associated with urological chronic pelvic pain syndrome (UCPPS) revealed by diffusion tensor MRI, super-resolution track density imaging, and statistical parameter mapping: A MAPP Network Neuroimaging Study. PLoS One 2015;10: e0140250. [CrossRef]
- Xu L, Gebhart GF. Characterization of mouse lumbar splanchnic and pelvic nerve urinary bladder mechanosensory afferents. J Neurophysiol 2008; 99: 244-253. [CrossRef]
- Zhang G, Yu L, Chen Z-Y, Zhu J-S, Hua R, Qin X, Cao J-L, Zhang Y-M. Activation of corticotropin-releasing factor neurons and microglia in paraventricular nucleus precipitates visceral hypersensitivity induced by colorectal distension in rats. Brain Behav Immun 2016; 55: 93-104. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Yu J, Kannampalli P, Nie L et al. MicroRNA-mediated downregulation of potassium-chloride-cotransporter and vesicular GABA transporter expression in spinal cord contributes to neonatal cystitis-induced visceral pain in rats. Pain 2017; 158: 2461-2474. [CrossRef]
- Zhang G, Zhao B-X, Hua R, Kang J, Shao B-M, Carbonaro TM, Zhang Y-M. Hippocampal microglial activation and glucocorticoid receptor down-regulation precipitate visceral hypersensitivity induced by colorectal distension in rats. Neuropharm 2016; 102: 295-303. [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann M. Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 1983; 16: 109-110. [CrossRef]
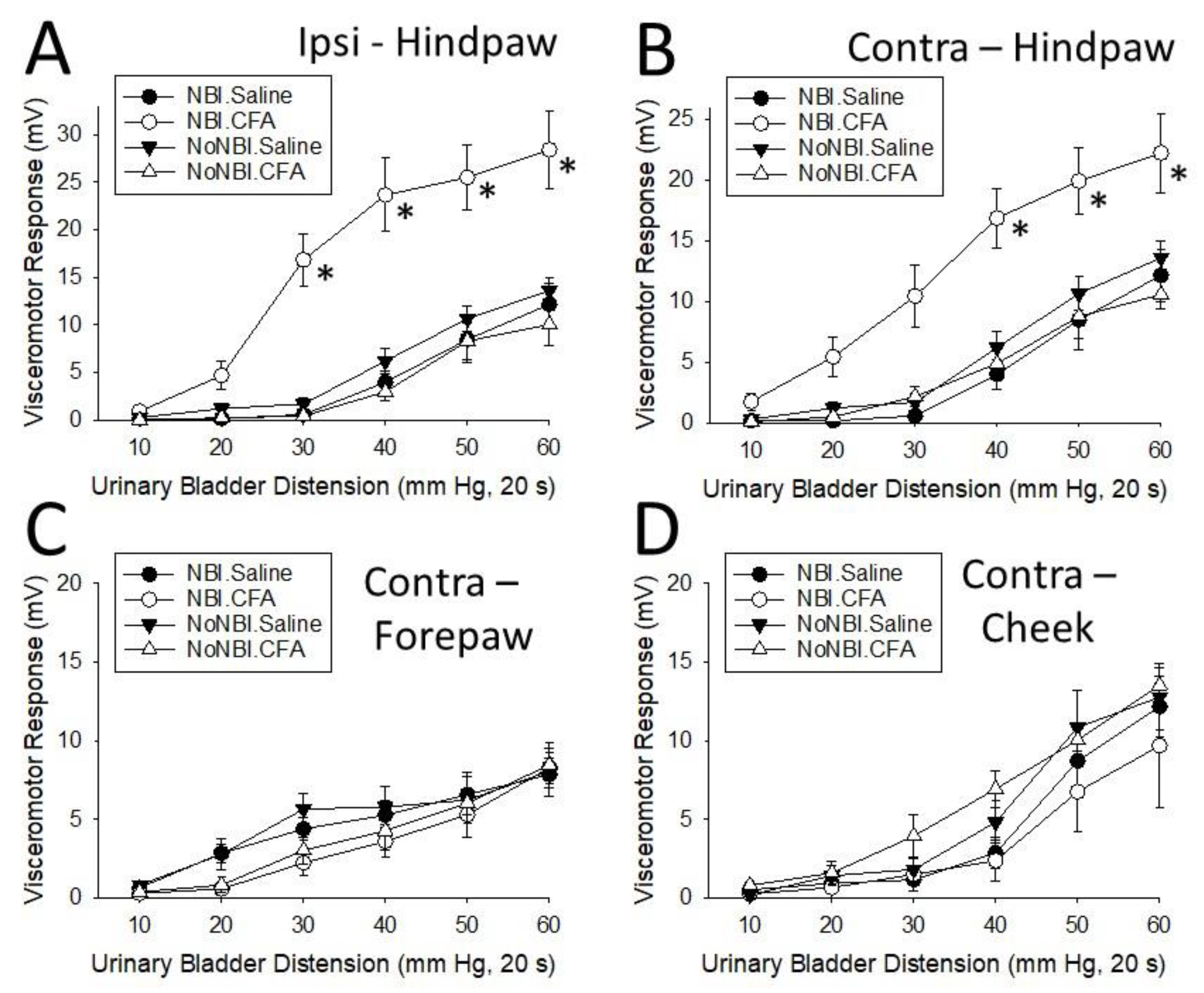
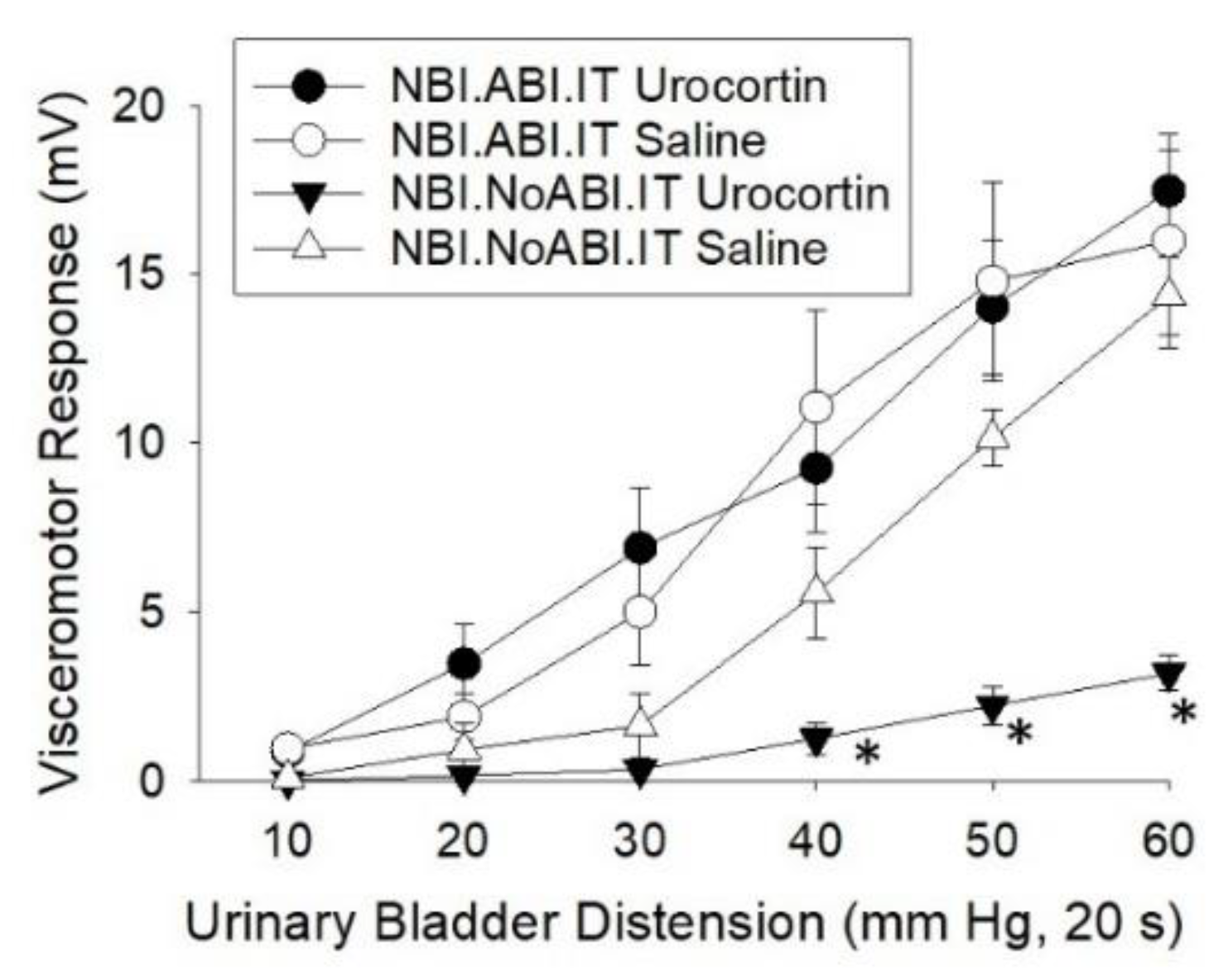
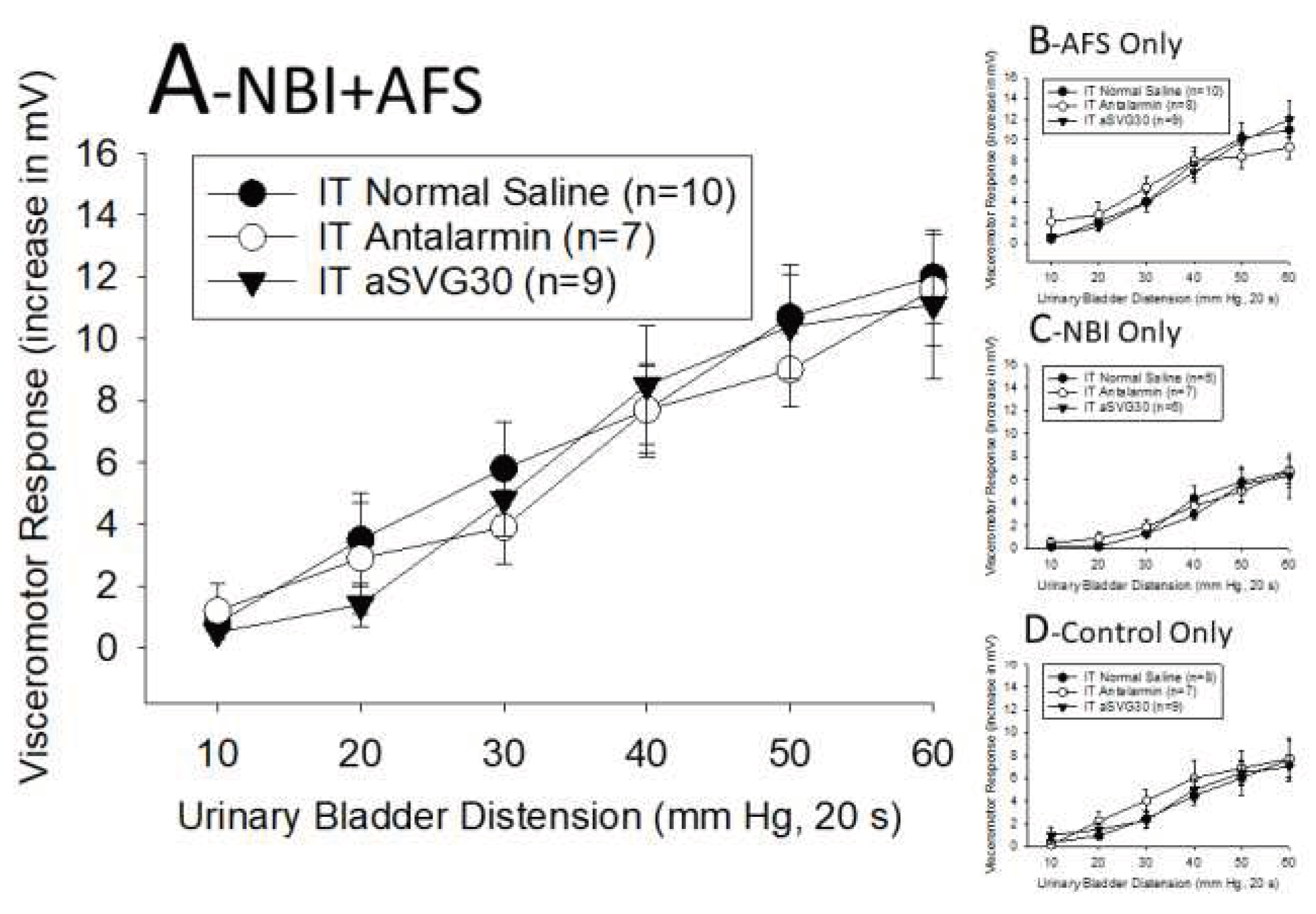
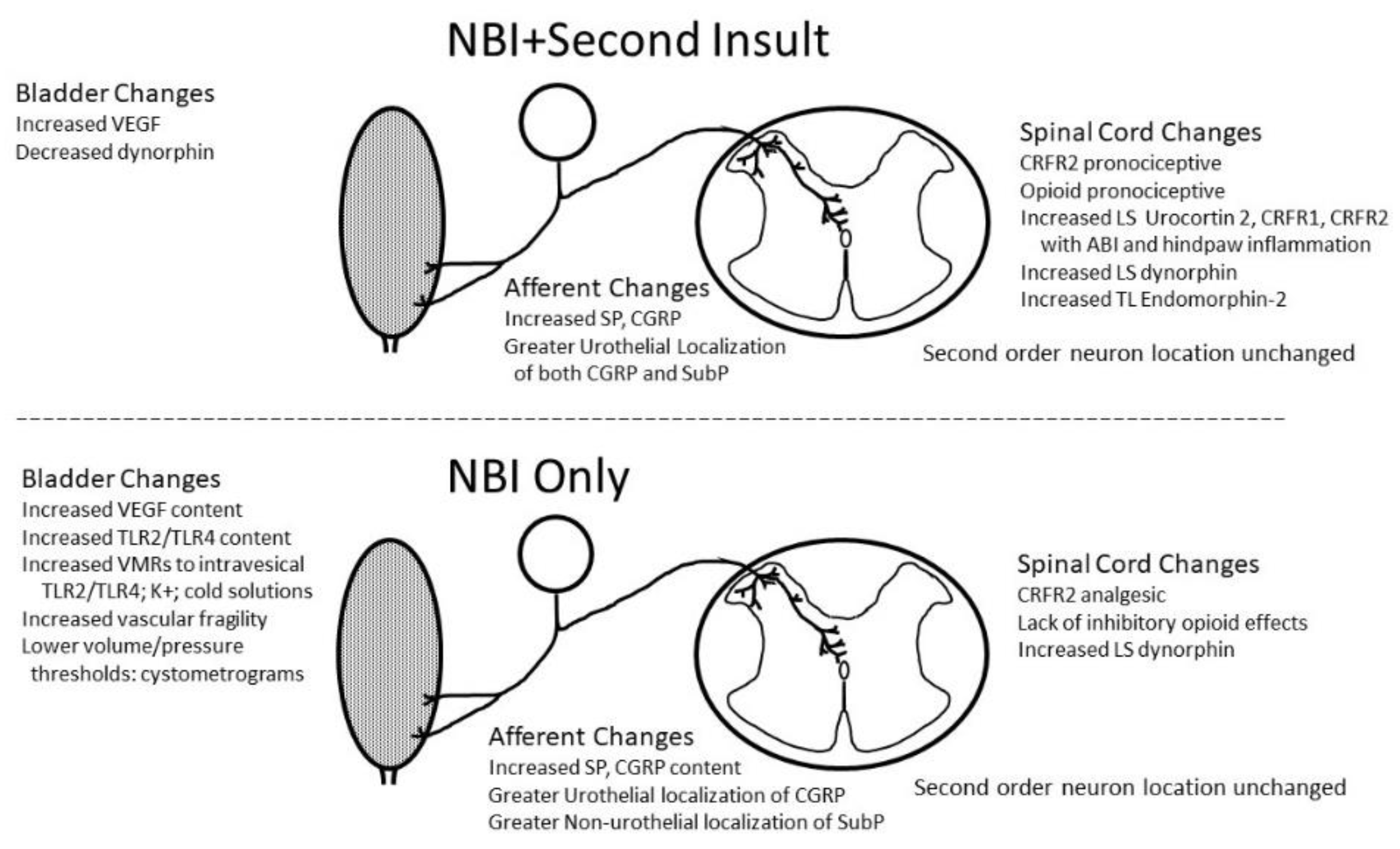
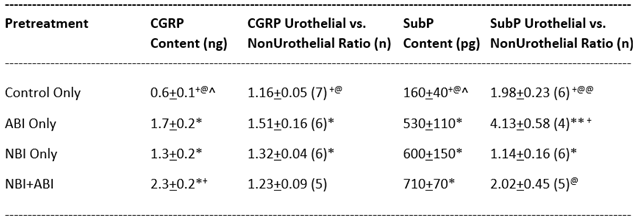
| SERUM/PLASMA | Control Only | NBI Only | NBI+ABI | ABI only | |
| Dynorphin108 [% Control Only mean] (n) | 100 + 5 (14) | 104 + 6 (16) | 107 + 6 (15) | 100 + 6 (16) | |
| Beta Endorphin108 [% Control Only mean] (n) | 100 + 7 (14) | 90 + 6 (16) | 98 + 5 (15) | 85 + 5 (16) | |
| WHOLE BLADDER | Control Only | NBI Only | NBI+ABI | ABI only | |
| TLR26 [ng/mg protein] (n) | 163 + 18 (8) | 289 + 51* (8) | n.m. | n.m. | |
| TLR46 [ng/mg protein] (n) | 8 + 1 (8) | 17 + 3** (8) | n.m. | n.m. | |
| Dynorphin108 [ng/mg protein] (n) | 0.39 + 0.03 (4) | 0.46 + 0.04 (5) | 0.32 + 0.02* (7) | 0.42+0.02 (7) | |
| VEGF [pg/mg protein] (n) | 51.4 + 3.3 (9) | 52.0 + 5.7 (9) | 62.3 + 2.3* (9) | 62.0 + 3.5* (8) | |
| SPINAL CORD | Level | Control Only | NBI Only | NBI+ABI | ABI only |
| TLR26 [ng/mg protein] (n) | TL | 669 + 121 (6) | 869 + 67 (5) | n.m. | n.m. |
| LS | 508 + 80 (6) | 511 + 104 (6) | n.m. | n.m. | |
| TLR46 [ng/mg protein] (n) | TL | 4.2 + 0.7 (6) | 4.4 + 0.7 (5) | n.m. | n.m. |
| LS | 1.7 + 0.3 (6) | 2.5 + 0.8 (6) | n.m. | n.m. | |
| Dynorphin108 [ng/mg protein] (n) | TL | 0.28+0.03 (6) | 0.30 + 0.01 (6) | 0.28 + 0.01 (8) | 0.24 + 0.02 (7) |
| LS | 0.17 + 0.02 (5) | 0.27 + 0.01* (6) | 0.26 + 0.02* (8) | 0.18 + 0.01 (7) | |
| Endomorphin-2108 [ng/mg protein] (n) | TL | 1.31 + 0.03 (6) | 1.18 + 0.06 (6) | 0.92 + 0.10* (8) | 1.32 + 0.11 (7) |
| LS | 1.61 + 0.16 (5) | 1.79 + 0.18 (6) | 1.76 + 0.07 (8) | 1.73 + 0.04 (7) | |
| CRFR164 [ng/mg protein] (n) | LS | 1.40 + 0.17 (8) | 1.56 + 0.07 (8) | 2.39 + 0.23** (8) | 1.72 + 0.13 (8) |
| CRFR264 [ng/mg protein] (n) | LS | 1.42 + 0.21 (8) | 1.83 + 0.07 (8) | 3.37 + 0.62** (8) | 1.83 + 0.31 (8) |
| CRF Peptide64 [ng/mg protein] (n) | LS | 27 + 12 (8) | 11 + 4 (8) | 99 + 41 | 291 + 114* (8) |
| Urocortin64 [ng/mg protein] (n) | LS | 5.1 + 0.5 | 6.5 + 0.9 | 7.5 + 0.8* | 5.5 + 0.2 |
| SPINAL CORD | Level | Control Only | NBI Only | NBI+CFA | CFA Only |
| CRFR165 [ng/mg protein] (n) | LS | 2.23 + 0.10 (5) | 2.53 + 0.18 (5) | 2.87 + 0.14* (5) | 2.50 + 0.04 95) |
| CRFR265 [ng/mg protein] (n) | LS | 1.53 + 0.08 (5) | 2.15 + 0.09** (5) | 2.37 + 0.10** (5) | 1.93 + 0.07* (5) |
| SPINAL CORD | Level | Control Only | NBI Only | NBI+AFS | AFS Only |
| CRFR1 [ng/mg protein] (n) | LS | 2.53 + 0.14 (5) | 1.90 + 0.05 (5) | 2.13 + 0.16 (5) | 2.41 + 0.15 (5) |
| CRFR2 [ng/mg protein] (n) | LS | 1.99 + 0.13 (5) | 1.58 + 0.04* (5) | 1.62 + 0.06* (5) | 1.91 + 0.13 (5) |
| L5 Lateral Dorsal Horn | Not Distended | Distended | L6 Lateral Dorsal Horn | Not Distended | Distended | S1 Lateral Dorsal Horn | Not Distended | Distended |
| Control Only | 1.60 + 0.39 | 3.63 + 0.59* | Control Only | 2.71 + 0.46 | 4.88 + 0.65* | Control Only | 2.21 + 0.33 | 2.17 + 0.63 |
| ABI Only | 2.25 + 0.68 | 3.77 + 0.89 | ABI Only | 3.54 + 1.33 | 4.19 + 1.30 | ABI Only | 1.21 + 0.42 | 1.54 + 0.28 |
| NBI Only | 3.69 + 0.99 | 4.44 + 0.42 | NBI Only | 3.13 + 0.30 | 7.36 + 1.03* | NBI Only | 2.09 + 0.92 | 2.86 + 0.95 |
| NBI+ABI | 2.69 + 0.62 | 4.34 + 0.14* | NBI+ABI | 4.00 + 1.95 | 4.83 + 0.40 | NBI+ABI | 2.23 + 1.29 | 1.75 + 0.34 |
| L5 Medial Dorsal Horn | Not Distended | Distended | L6 Medial Dorsal Horn | Not Distended | Distended | S1 Medial Dorsal Horn | Not Distended | Distended |
| Control Only | 9.11 + 0.83 | 13.06 + 4.22 | Control Only | 8.42 + 1.30 | 17.73 + 2.78* | Control Only | 4.88 + 1.11 | 4.17 + 2.28 |
| ABI Only | 13.61 + 3.66 | 13.50 + 3.03 | ABI Only | 11.88 + 4.34 | 11.29 + 3.36 | ABI Only | 3.56 + 1.43 | 2.12 + 0.84 |
| NBI Only | 9.92 + 3.75 | 20.25 + 0.69* | NBI Only | 10.42 + 3.42 | 18.98 + 4.21 | NBI Only | 4.42 + 1.25 | 6.44 + 3.00 |
| NBI+ABI | 10.79 + 1.52 | 12.46 + 1.46 | NBI+ABI | 10.86 + 3.28 | 12.83 + 1.20 | NBI+ABI | 5.81 + 4.45 | 3.38 + 1.06 |
| L5 Spinal Nucleus | Not Distended | Distended | L6 Parasympathetic Nucleus | Not Distended | Distended | S1 Parasympathetic Nucleus | Not Distended | Distended |
| Control Only | 0.75 + 0.14 | 6.46 + 1.97* | Control Only | 3.78 + 1.48 | 12.42 + 1.40* | Control Only | 1.44 + 0.25 | 4.81 + 1.64 |
| ABI Only | 1.04 + 0.25 | 4.46 + 0.74* | ABI Only | 1.96 + 0.59 | 8.40 + 2.67 | ABI Only | 0.90 + 0.20 | 2.40 + 0.47* |
| NBI Only | 0.46 + 0.38 | 5.98 + 1.41* | NBI Only | 1.42 + 0.92 | 6.96 + 1.93* | NBI Only | 0.79 + 0.29 | 3.77 + 1.28 |
| NBI+ABI | 0.94 + 0.17 | 6.34 + 1.64* | NBI+ABI | 2.29 + 0.78 | 6.75 + 1.63* | NBI+ABI | 1.11 + 0.52 | 3.46 + 1.49 |
| L5 Dorsal Commissure | Not Distended | Distended | L6 Dorsal Commissure | Not Distended | Distended | S1 Dorsal Commissure | Not Distended | Distended |
| Control Only | 4.73 + 1.40 | 23.40 + 4.99* | Control Only | 4.82 + 0.88 | 23.00 + 3.87* | Control Only | 3.50 + 0.68 | 6.00 + 1.96 |
| ABI Only | 7.92 + 2.16 | 17.82 + 3.52* | ABI Only | 5.23 + 2.09 | 13.79 + 3.21* | ABI Only | 2.35 + 0.98 | 3.13 + 1.27 |
| NBI Only | 4.13 + 0.13 | 24.71 + 4.99* | NBI Only | 2.29 + 0.79 | 16.21 + 1.78* | NBI Only | 1.46 + 0.21 | 8.02 + 1.90* |
| NBI+ABI | 5.73 + 1.19 | 17.02 + 3.82* | NBI+ABI | 4.65 + 1.12 | 14.21 + 4.68* | NBI+ABI | 2.55 + 1.73 | 5.23 + 2.72 |
|
*effect of distension; p<0.05 Bold indicates significant difference from “Not Distended” measure |
Data represents Mean + SEM Fos+ nuclei | |||||||
|
Repeated Final Columns for Reviewers – formatting issues with conversion S1 Lateral Dorsal Horn |
Not Distended | Distended | ||||||
| Control Only | 2.21 + 0.33 | 2.17 + 0.63 | ||||||
| ABI Only | 1.21 + 0.42 | 1.54 + 0.28 | ||||||
| NBI Only | 2.09 + 0.92 | 2.86 + 0.95 | ||||||
| NBI+ABI | 2.23 + 1.29 | 1.75 + 0.34 | ||||||
| S1 Medial Dorsal Horn | Not Distended | Distended | ||||||
| Control Only | 4.88 + 1.11 | 4.17 + 2.28 | ||||||
| ABI Only | 3.56 + 1.43 | 2.12 + 0.84 | ||||||
| NBI Only | 4.42 + 1.25 | 6.44 + 3.00 | ||||||
| NBI+ABI | 5.81 + 4.45 | 3.38 + 1.06 | ||||||
| S1 Parasympathetic Nucleus | Not Distended | Distended | ||||||
| Control Only | 1.44 + 0.25 | 4.81 + 1.64 | ||||||
| ABI Only | 0.90 + 0.20 | 2.40 + 0.47* | ||||||
| NBI Only | 0.79 + 0.29 | 3.77 + 1.28 | ||||||
| NBI+ABI | 1.11 + 0.52 | 3.46 + 1.49 | ||||||
| S1 Dorsal Commissure | Not Distended | Distended | ||||||
| Control Only | 3.50 + 0.68 | 6.00 + 1.96 | ||||||
| ABI Only | 2.35 + 0.98 | 3.13 + 1.27 | ||||||
| NBI Only | 1.46 + 0.21 | 8.02 + 1.90* | ||||||
| NBI+ABI | 2.55 + 1.73 | 5.23 + 2.72 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





