1. Introduction
The Information and Communication Technology (ICT) sector has been a significant contributor to the global economy. According to a report by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)(The Economic Impact of ICT, 2004), the ICT sector has become a key driver of economic growth over the past decade. The rapid diffusion of the Internet, of mobile and of broadband networks all demonstrate how pervasive this technology has become.
The introduction of 5G technology has been a significant milestone in the field of telecommunications. It has not only revolutionized the way we communicate but also has the potential to transform the global economy. According to a report by PwC (Chow & Tandetzki, 2030), the introduction of 5G technology could add US$1.3tn to global GDP by 2030 in five sectors—healthcare, smart utilities, consumer and media, industrial manufacturing, and financial services. The report also estimates that the introduction of 5G technology could create up to 2.3 million jobs in Europe.
The potential benefits of 5G technology are not limited to Europe. A report by Analysys Mason highlights the potential economic benefits of 5G in emerging markets (Stewart et al., 2022). The report suggests that most countries are expected to generate overall economic benefits (GDP) three-to-seven times higher than the incremental cost of extending coverage. The report also estimates that 5G mobile broadband can generate consumer surplus between USD 1-10 billion per country 2020–35.
In developing countries, the adoption of 5G technology is expected to differ from that in developed regions. According to a report by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)(United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, n.d.), the digital divide between developed and developing countries is widening, the article suggests that the adoption of 5G technology in developing countries will be driven by the need to provide basic services such as healthcare, education, and financial services to underserved populations, while In developed countries, the adoption of 5G technology is expected to be driven by the need to improve existing services and create new ones.
In recent years, Egypt has embarked on a transformative journey towards digital empowerment. The convergence of technological advancements, policy reforms, and societal aspirations has set the stage for a profound shift in how Egypt approaches its economic challenges. This research aims to explore the pivotal role of 5G technology in this context and its potential to catalyze inclusive development.
“Digital Egypt” initiative stands as a testament to the country’s commitment to digital transformation. Launched to simplify access to government services, expand digital infrastructure, and foster innovation, this initiative has already begun reshaping the landscape of service delivery. By leveraging technology, Egypt aims to enhance citizen engagement, improve efficiency, and create new opportunities for economic growth.
2. Justification
This Research analysis is crucial for understanding how 5G adoption in Egypt, as an emerging market, aligns with broader economic trends and potential benefits. From enabling smart cities and efficient logistics to empowering small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), the adoption of 5G technology has the potential to revolutionize Egypt’s economy, 5G can drive productivity, attract investment, and create jobs. By analyzing the economic impact, we can uncover pathways for sustainable growth.
our research stands as a strategic initiative to comprehend, evaluate, and strategically position Egypt within the evolving landscape of global technological advancements and economic opportunities. Also it seeks to unravel the synergies between 5G technology and Egypt’s economic growth. By doing so, we contribute to the ongoing dialogue on Egypt’s digital transformation journey.
In light of these developments, the research aims to explore the potential impact of 5G technology on Egypt’s GDP. The research will examine the potential of 5G technology and its impact on the economy of Egypt. Finally, the research will not only contribute to academic understanding but also offer practical recommendations for policymakers and stakeholders on how to maximize the benefits of 5G technology for the economy of Egypt.
3. Research Questions
Quantifying the 5G introduction Impact on Egypt’s GDP by simulating the 5G introduction in similar countries
How does GDP growth trajectory change with 5G adoption?
What are the relations between some specific indicators (5G population coverage, Network speed and spectrum allocation) with the GDP growth?
Can we establish a relationship between 5G introduction and Egypt’s GDP economic performance?
4. Research Objectives
The overarching goal of this research is to contribute to Egypt’s strategic vision for digital transformation by exploring the potential impact of 5G technology. Specifically, we aim to understand how 5G deployment can drive economic growth and simulate the impact on Egypt’s GDP.
-
a)
-
Assessing Economic Implications:
- o
Objective: Analyze the relation between 5G introduction & the associated impact on the GDP.
- o
Expected Outcome: Provide evidence-based insights for policymakers and stakeholders.
-
b)
-
Promoting Digital Infrastructure & technology innovation in Egypt:
- o
Objective: Simulate the 5G introduction impact on Egypt’s GDP.
- o
Expected Outcome: Recommend priorities for 5G introduction strategies to ensure successful launch for the 5G services.
By achieving these objectives, we aim to pave the way for Egypt’s successful transition into the 5G era, fostering inclusive development and sustainable progress.
5. Hypothesis
H1: There is a relationship between the 5G population coverage and the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
H2: There is a relationship between network speed and the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
H3: Efficient spectrum allocation contributes to the country’s economic growth
6. Literature Review
The development of ICT, including 5G services, can drive economic growth by creating new opportunities for young people and promoting the formation of economic projects. Additionally, investments in information and communication technologies, such as 5G, have been found to have a positive association with economic growth globally. According to Pwc (Chow & Tandetzki, 2030), Adoption of 5G will add $1.3 trillion to global GDP by 2030 where healthcare sector which will be the biggest contributor to the economic gains from 5G with potential to add over half a trillion dollars to global GDP, followed by the smart utilities management that will add US$330bn to global GDP by 2030 mainly through the following 3 use cases:
- a)
Enhanced smart meters & smart grids (US$209bn)
- b)
Better waste management & reduced solid waste (US$82bn)
- c)
Reduced water leakage (US$39bn)
The report addressed that 5G-powered consumer and media applications could add US$254bn to global GDP by 2030, also the 5G-powered industrial manufacturing will add US$134bn and in addition to the financial-services applications contribution with US$134bn
At the regional level, North America will experience the biggest percentage uplift to GDP from 5G, followed by Asia and Oceania and then by Europe, the Middle East and Africa (EMEA). In absolute dollar terms, North America also will rank highest, and Asia and Oceania are projected to outpace EMEA because of its larger overall economy. (The scale of a national economy will influence its absolute impact on global GDP: a 2% increase in the US economy is about six times the size in dollar terms of a 1.3% expansion in the Japanese economy.) Among the countries analyzed those with strong, modern industrial production sectors may benefit more than those that rely on service industries such as banking.
Another research comparing the ICT and economic growth in Developing (Niebel, n.d.), Emerging and Developed Countries confirms relationship between ICT capital and GDP growth with no statistically significant differences in output elasticities of ICT between country groups. There was no clear indication that developing and emerging countries gain more from ICT investments than developed economies.
In USA, 5G promises massive job and GDP growth (5G Promises Massive Job and GDP Growth in the US, n.d.) as it will become a foundation for innovation and transform many sectors of the US economy. Timely rollout of 5G services and strong talent pipeline are critical for economic benefits that will improve business operations and consumer experience across the country. Coordination between policymakers, regulators, and private sector is needed for smooth rollout to generate not only direct but also indirect economic impact and contribute to employment and new revenue streams calculated with 1.2 trillion to GDP and create 3 million to 3.6 million new jobs from 2020 to 2030.
In Canada, a report prepared by GSMA (5G and Economic Growth: An Assessment of GDP Impacts in Canada, 2020) evaluated that 5G has the potential to enable new applications and use cases that could deliver 150 billion in additional value to the Canadian economy in the period 2020–2040. Timely access to spectrum is crucial for the speed and quality of 5G rollout as Canada's current 5G spectrum policy may limit investment and consumer benefits. The report emphasis that aligning 5G spectrum policies with international best practices can boost GDP growth.
The model was built around two main pillars: the first assesses how different use cases – applications and new/upgraded industrial processes supported by 5G technology can boost productivity and benefit the economy, the second looks into the impact on productivity and economic growth of 5G-based technologies and their impact on productivity. Together, these two pillars allow the model to forecast the impact on each sector of the economy.
In Africa, As of September 2023, 27 operators in 16 markets in Africa had launched commercial 5G services (
GSMA 5G in Africa, n.d.). More markets are expected to follow soon, with operators in an additional 10 countries making a commitment to launch 5G in the coming years. 10 countries in Africa have assigned spectrum for 5G services to operators (
Table 1). Frequency bands below 3 GHz are being considered for 4G and 5G development in Africa. Also, The 700, 800, and 900 MHz bands can improve 4G and 5G coverage. while the 600 and 1500 MHz bands may provide capacity in the future.
Table 1.
G spectrum assignments in Africa.
Table 1.
G spectrum assignments in Africa.
In Tanzania, focused research examines the impact of ICT on GDP growth that confirms causal relationship between ICT infrastructure/access and GDP growth(Mwananziche et al., 2023). Mobile telephone subscription growth has a significant impact on economic growth, meanwhile some key variables may influence economic growth, for instance, human capital, trade openness, the level of urbanization, and infrastructure such as electricity supply. Policymakers should focus on creating a solid ICT infrastructure and boosting internet access. Tanzanian authorities should prioritize investing in ICT to ensure a technologically connected workforce.
Analysys Mason conducted a study on the economics benefits of 5G deployment in 15 emerging nations including Egypt comparing 2 scenarios for the 5G spectrum deployment (Stewart et al., 2022), Scenario 1 based on extending low-band 5G coverage & Scenario 2 based on extending mid-band 5G coverage, where scenario 1 results in economic benefits of USD1-3 billion per country, while extending mid-band coverage (Scenario 2) could result in economic benefits of USD5-12 billion per country.
Figure 1.
Cumulative net present value of economic benefits by 5G roll-out scenario (2020–35). Source: (Stewart et al., 2022).
Figure 1.
Cumulative net present value of economic benefits by 5G roll-out scenario (2020–35). Source: (Stewart et al., 2022).
Considering all these research findings collectively, there is a relation between 5G adoption, spectrum allocation and economic growth. However, the impact varies across regions and countries, emphasizing the importance of factors such as infrastructure readiness, regulatory policies, and timely access to spectrum.
Another area of debate could be the influence of various factors on economic growth such as the resources competency, educational level, openness for new 5G use cases and infrastructure such as electricity/fuel supply as well as the uncertainties associated with the long projections till 2030 & 2040.
Therefore, the implementation of 5G technology in Egypt and the associated impact on economic growth need to be assessed considering similar countries conditions and applying the proper regression and statistical measures to simulate the potential impact on Egypt’s GDP.
7. Research Methodology
- a)
Research Design:
This study adopts a quantitative research design to systematically investigate the impact of 5G introduction on Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Quantitative methods allow for the measurement and statistical analysis of the relationships between 5G variables and GDP.
- b)
Research Phenomenon:
The research phenomenon, denoted as Y, represents the economic impact of 5G technology on Egypt’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Specifically, it examines how the deployment and utilization of 5G networks influence Egypt’s overall economic growth by simulating similar countries.
- c)
Independent Factors:
The research independent factors, denoted as X1, X2 & X3, play a crucial role in shaping the economic impact of 5G in Egypt:
-
X1 5G Population Coverage: The extent to which the 5G network covers the population in Egypt. It represents the proportion of people who have access to 5G services
X2: Network Speed: The data transfer rate provided by networks, measured in megabits per second (Mbps). It reflects how quickly data can be transmitted and received
X3: Spectrum Allocation: The allocation and management of enough radio frequency spectrum can encourage and accelerate 5G rollout
Figure 2.
Modeling Overview.
Figure 2.
Modeling Overview.
- e)
Data Collection Method:
Secondary Data gathering the existing data from official reports, research papers and databases. Look for information on similar countries like Egypt including the GDP, ICT indices and technological indicators that are affecting the 5G introduction in these countries.
Table 2.
IDI 2023 scores.
Table 2.
IDI 2023 scores.
8. Research Analysis
Statistical analysis will include multiple linear regression analysis to examine the relationship between 5G population coverage, network speed, spectrum allocation, and GDP.
Data analysis will be conducted using IBM SPSS tool providing a robust statistical framework for drawing valid relations and conclusions.


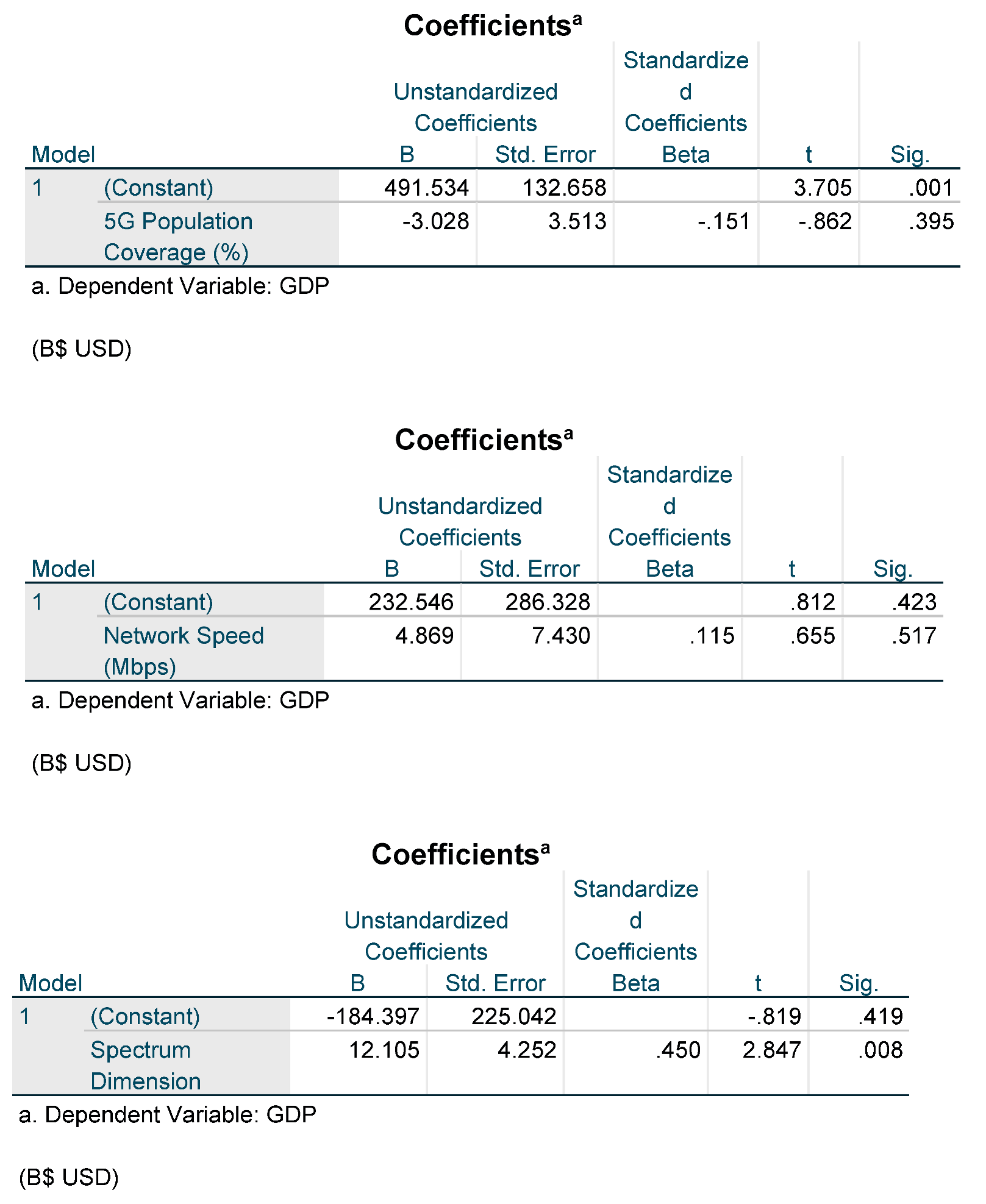
9. Discussion
There is no significant related relation between 5G population coverage and GDP as P value = 0.69 > 0.05, accordingly we will reject H1
There is no significant related relation between Network speed and GDP as P value = 0.383 > 0.05, accordingly we will reject H2
There is significant moderate positive relation between the spectrum allocation and GDP as P value < 0.05 & r =0.455 > 0.3, accordingly we will accept H3
By running multiple linear regression analysis considering the GDP (dependent variable) and 5G population coverage, Network speed & spectrum allocation (independent variable), there is a significant effect of spectrum allocation & 5G population coverage in the presence of the network speed on the GDP considering that:
o
P-value for the 5G population coverage = 0.005 < 0.05
o
P-value for the spectrum allocation = 0.000 < 0.05
Therefore the formula will be as the following:
GDP = -514.611 + 16.786 x Spectrum allocation – 10.674 x 5G Population Coverage
38.9% Variation in the GDP is due to change in the spectrum allocation, 5G population coverage in the presence of network speed variable.
10. Conclusion
The allocation of the 5G spectrum is anticipated to yield substantial economic benefit to Egypt, constituting a pivotal factor in ensuring the successful introduction of 5G. Particularly during the initial launch phase, it is imperative to consider conservative approach for the 5G population coverage at the beginning to prevent any adverse impact on the economic growth facilitated by the introduction of 5G. Additionally, careful selection of use cases and their associated coverage will play a crucial role in enabling stakeholders and the broader 5G ecosystem to realize significant GDP growth in Egypt.
11. Recommendations
the following recommendations are proposed for policymakers and stakeholders to ensure a successful introduction of 5G and maximize its positive impact on the country's GDP:
-
I.
-
Strategic Spectrum Allocation:
Develop and implement a comprehensive spectrum allocation strategy that aligns with international best practices.
Prioritize the allocation of frequency bands below specially in the mid-band for 5G development, considering their impact on coverage and capacity.
-
II.
-
Collaborative Policymaking:
Foster collaboration between policymakers, regulators, and the private sector to create a conducive environment for 5G deployment.
Establish clear and transparent regulatory frameworks that facilitate the timely rollout of 5G services and ensure a smooth transition.
-
III.
-
Investment in ICT Infrastructure:
Prioritize investments in ICT infrastructure, including robust connectivity and accessibility, to create a solid foundation for 5G deployment.
Focus on enhancing internet access to support the growth of digital services and applications.
-
IV.
-
Regional Considerations:
Take into account regional dynamics and collaboration, especially within the North African context, to optimize 5G strategies and share best practices.
Collaborate with neighboring countries and regional organizations to foster a harmonized approach to 5G adoption.
-
V.
-
Research and Development Initiatives:
Encourage research and development initiatives that explore innovative use cases and applications for 5G technology.
Support local businesses and startups in developing 5G-enabled solutions that can contribute to economic growth.
-
VI.
-
Education and Skill Development:
Invest in education and skill development programs to ensure a technologically competent workforce capable of leveraging 5G advancements.
Foster partnerships between academic institutions and industry to align educational programs with the needs of the evolving digital landscape.
-
VII.
-
Monitoring and Evaluation:
Implement mechanisms for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of 5G deployment, regularly assessing the economic impact and adjusting strategies as needed.
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of 5G initiatives and ensure they align with broader economic development goals.
-
VIII.
-
International Collaboration:
Engage in international collaboration and knowledge-sharing initiatives to stay abreast of global trends and advancements in 5G technology.
Participate in forums and partnerships that facilitate the exchange of best practices and lessons learned from other countries undergoing 5G adoption.
By incorporating these recommendations into policymaking and strategic planning, Egypt can position itself to harness the full potential of 5G technology. This holistic approach, addressing spectrum allocation, collaboration, infrastructure, regional dynamics, innovation, education, and ongoing evaluation, will contribute to a successful 5G introduction and foster sustainable economic growth.
References
-
5G and economic growth: an assessment of GDP impacts in Canada. (2020). www.gsmaintelligence.com.
-
5G Promises Massive Job and GDP Growth in the US. (n.d.).
- Chow, W., & Tandetzki, T. (2030). The global economic impact of 5G. Powering your tomorrow ATM 2 PwC The global economic impact of 5G.
-
GSMA 5G in Africa. (n.d.).
- Itu. (2023). The ICT Development Index 2023 International Telecommunication Union Development Sector.
- Mwananziche, J., Myovella, G., Karacuka, M., Haucap, J., & Moshi, G. (2023). Is digitalization a booster for economic growth in Africa? Short run and long run evidence from Tanzania. Telecommunications Policy, 47(10). [CrossRef]
- Niebel, T. (n.d.). ICT and Economic Growth-Comparing Developing, Emerging and Developed Countries. www.zew.de/en.
- Stewart, J., Lacour, H.-A., & Yi-Ju Chern, A. (2022). Future value of mobile in emerging markets. www.analysysmason.com.
-
Speedtest Intelligence,https://intelligence.speedtest.net.
-
GSMAi Sign in. (n.d.).https://data.gsmaintelligence.com/signin?returnPath=%2Fdata.
-
World Bank Open Data. https://data.worldbank.org.
-
World Bank Country and Lending Groups – World Bank Data Help Desk. (n.d.). World Bank Country and Lending Groups – World Bank Data Help Desk. https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups.
-
The Economic Impact of ICT. (2004). OECD. [CrossRef]
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. (n.d.). Digital economy report 2021 : cross-border data flows and development : for whom the data flow.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).











