Submitted:
20 January 2024
Posted:
22 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Ecological Zoning Method
2.2. Methods of Investigating Species Distribution and Composition
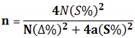
2.3. Data Processing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
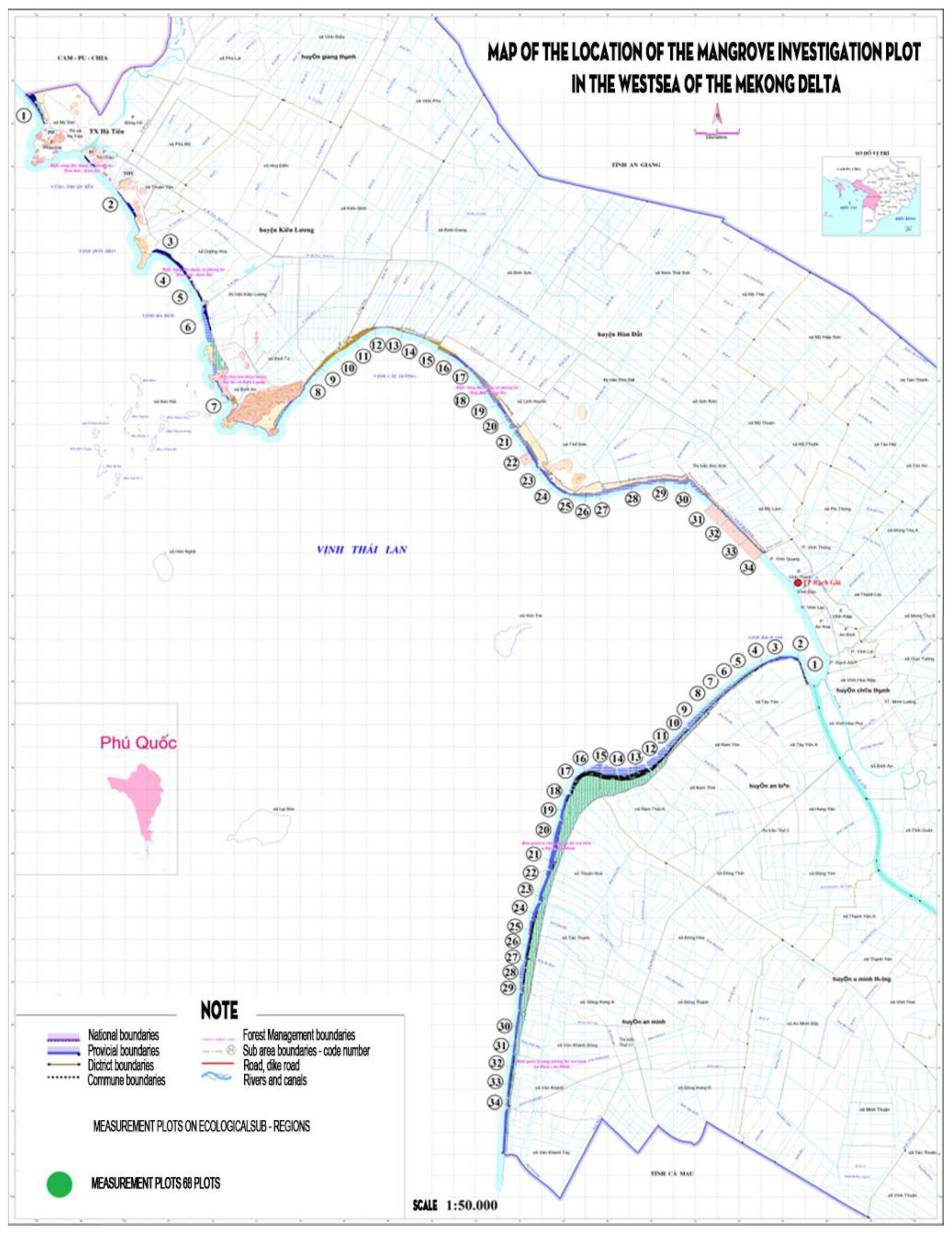
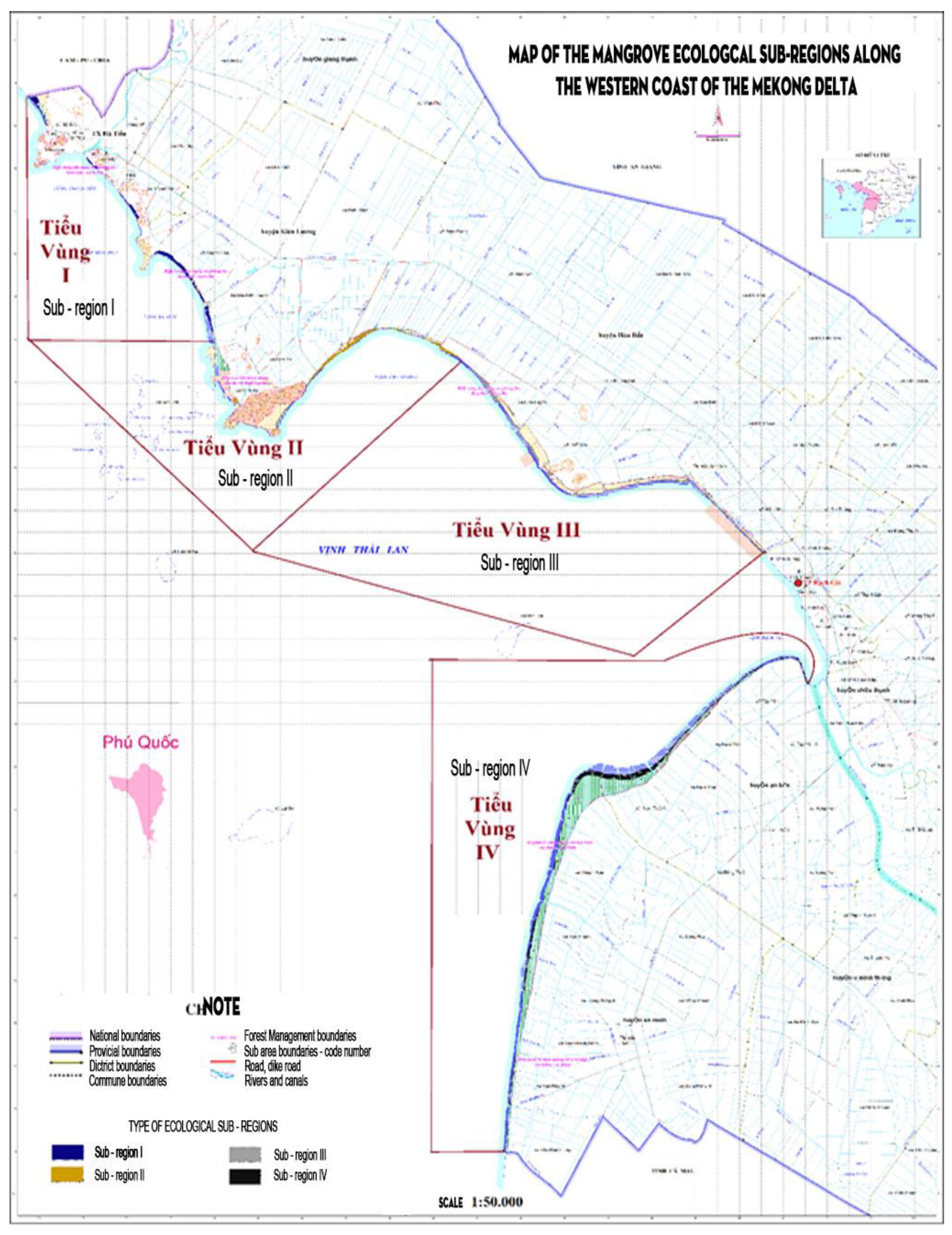
3.1. Results of Dividing Sub Region on Mangroves in the Western Mekong Delta
| TT | Families | Species | Local Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sonneratiaceae | Sonneratia caseolaris | Ban chua |
| 2 | Sonneratiaceae | Sonneratia ovate | Ban oi |
| 3 | Annonaceae | Annona reticulate | Binh bat |
| 4 | Combretaceae | Lumnitzera littorea | Coc do |
| 5 | Combretaceae | Lumnitzera racemosa | Coc trang |
| 6 | Rhizophoraceae | Rhizophora mucronata | Dung |
| 7 | Areecaceae | Nipa fruticans | Dua nuoc |
| 8 | Rhizophoraceae | Rhizophora apiculata | Duoc |
| 9 | Euphorbiaceae | Excoecaria agallocha | Gia |
| 10 | Avicenniaceae | Avicennia marina | Mam bien |
| 11 | Avicenniaceae | Avicennia officinalis | Mam den |
| 12 | Avicenniaceae | Avicennia alba | Mam trang |
| 13 | Rhizophoraceae | Bruguiera gymnorhiza | Vet du |
| 14 | Rhizophoraceae | Bruguiera cylindrical | Vet tru |
| 15 | Myrsinaceae | Aegiceras corniculatum | Su |
| 16 | Malvaceae | Hibiscus tiliaceus | Tra |
3.2. Species Structure of Mangroves in Sub-Regions of the Western Mekong Delta
- a.
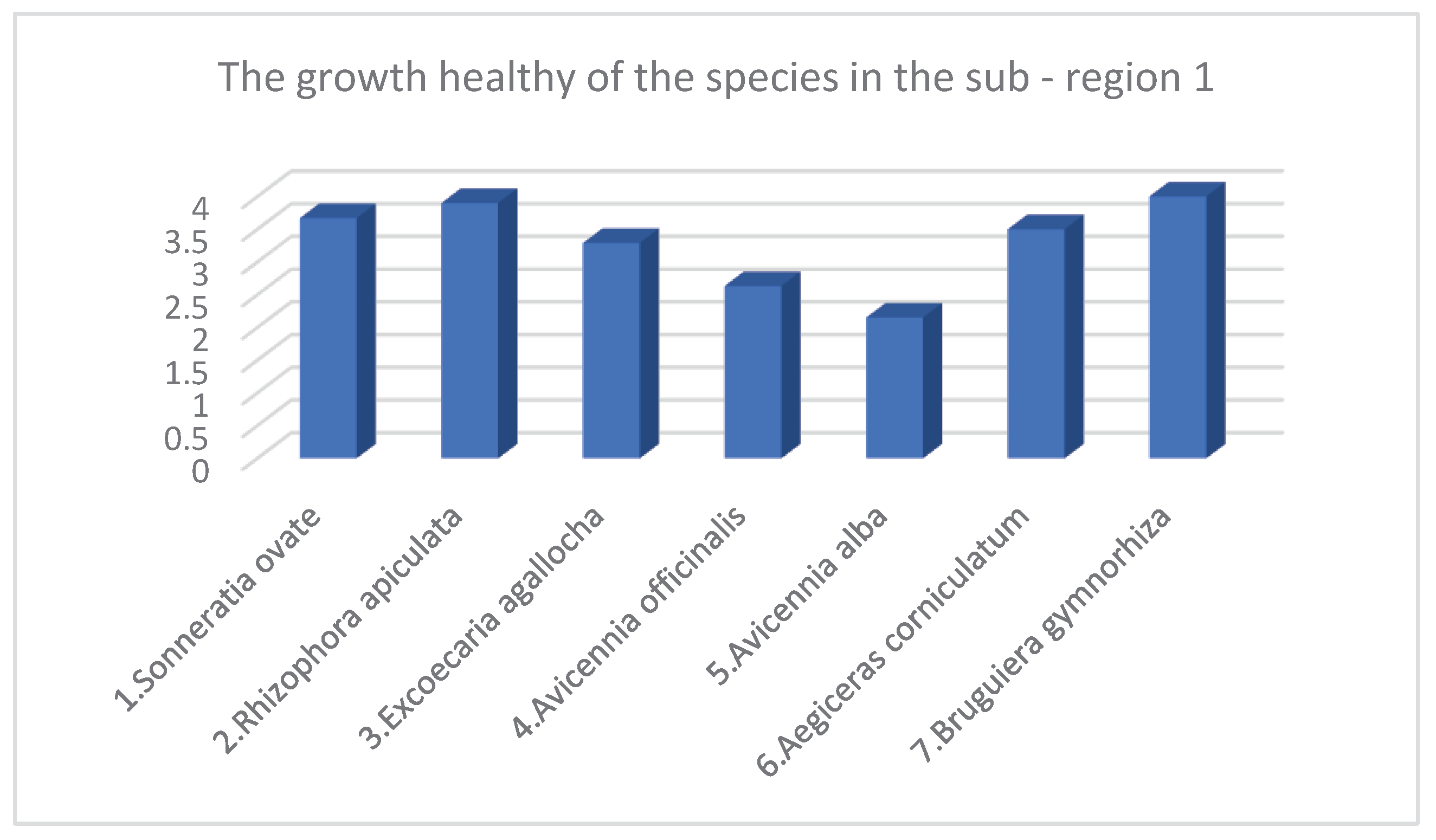
- Species structure of Mangroves in sub-region 1
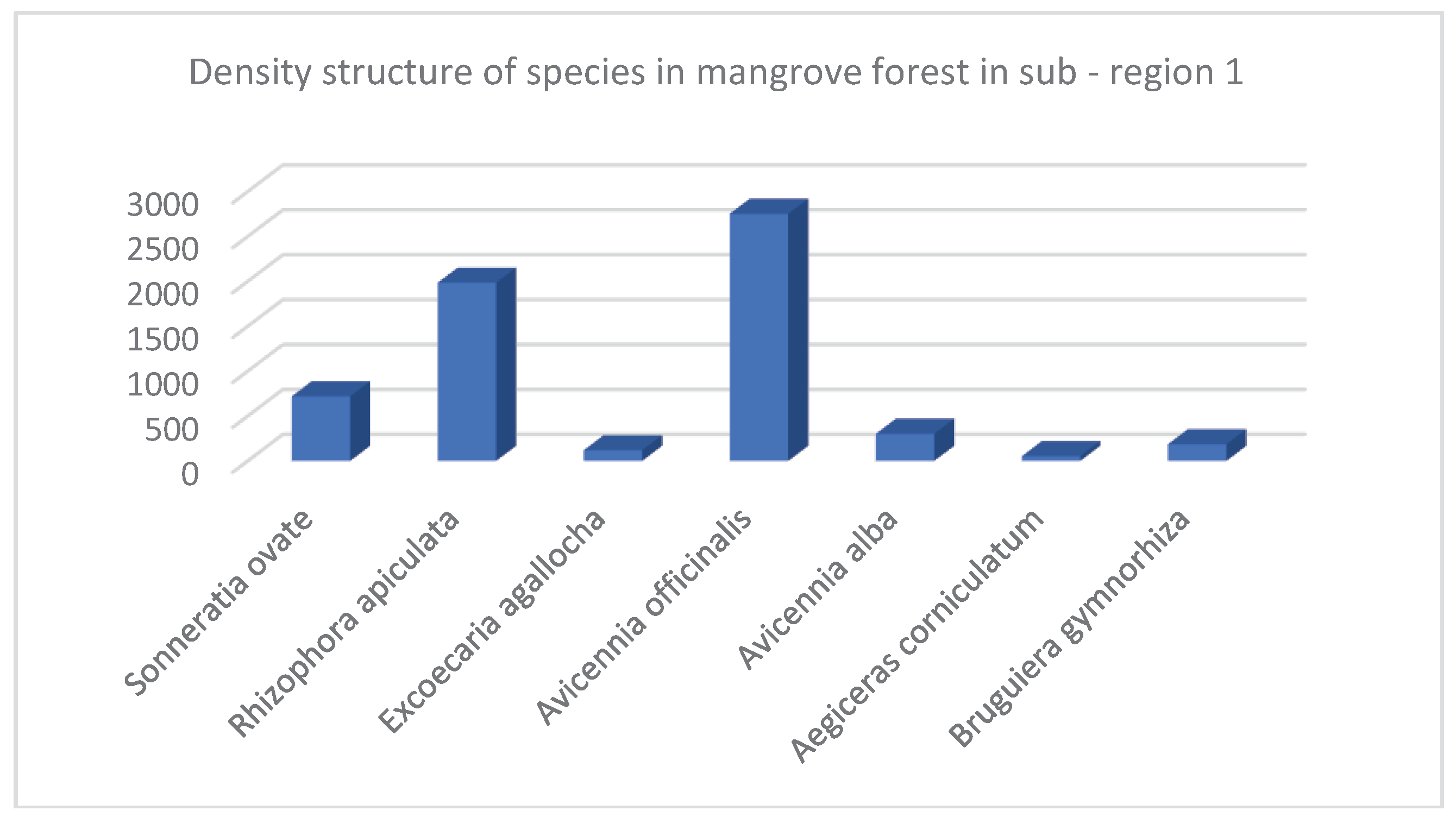
| No. | Species | Density Structure (Tree) | Species Ratio (%) | Average Height (Meter) | Average Diameter (Centimeter) | Canopy Structure (Square Meter m2) | Heathy Structure (1 …5) 1: Bad 5: Best |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
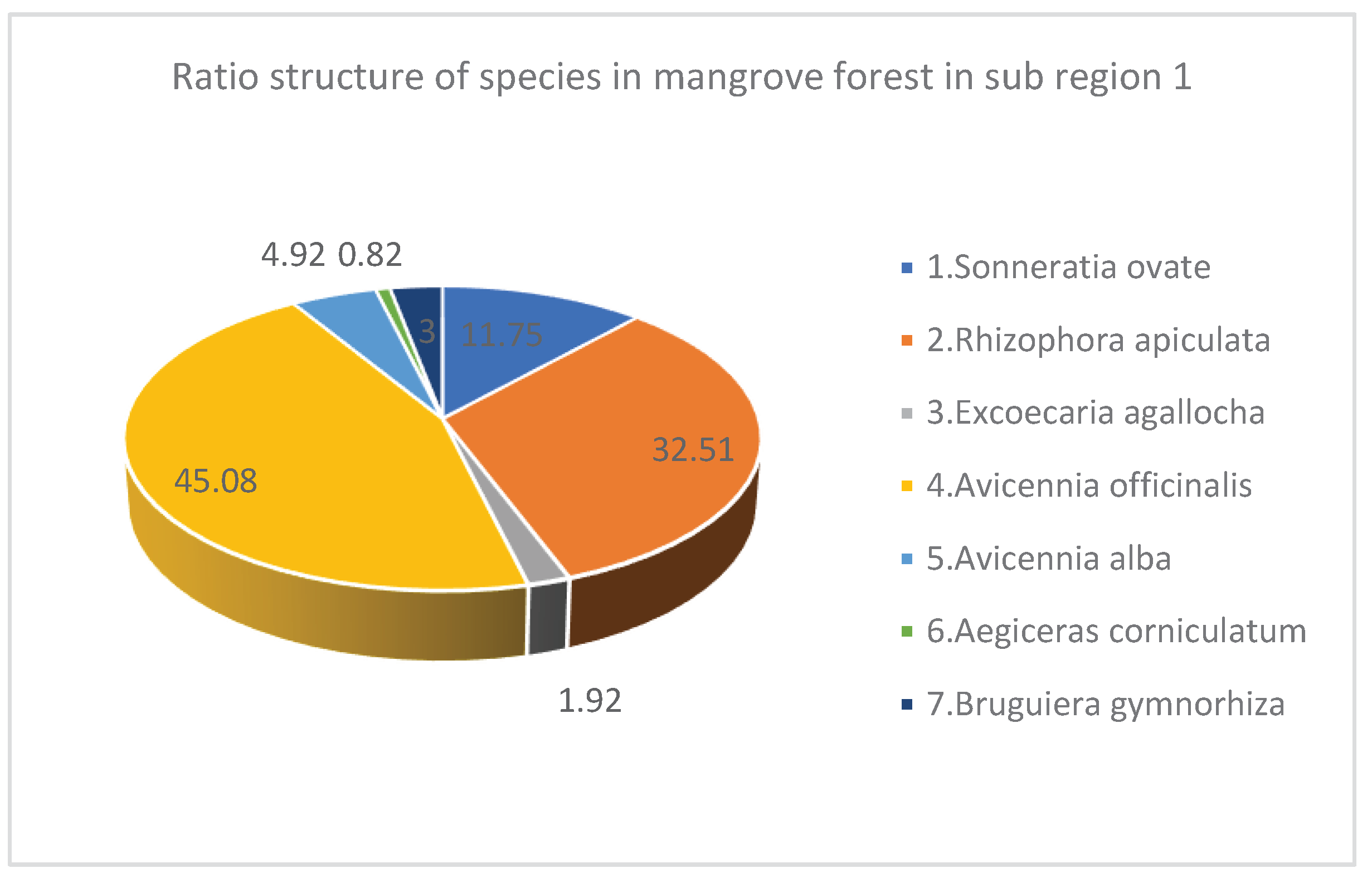
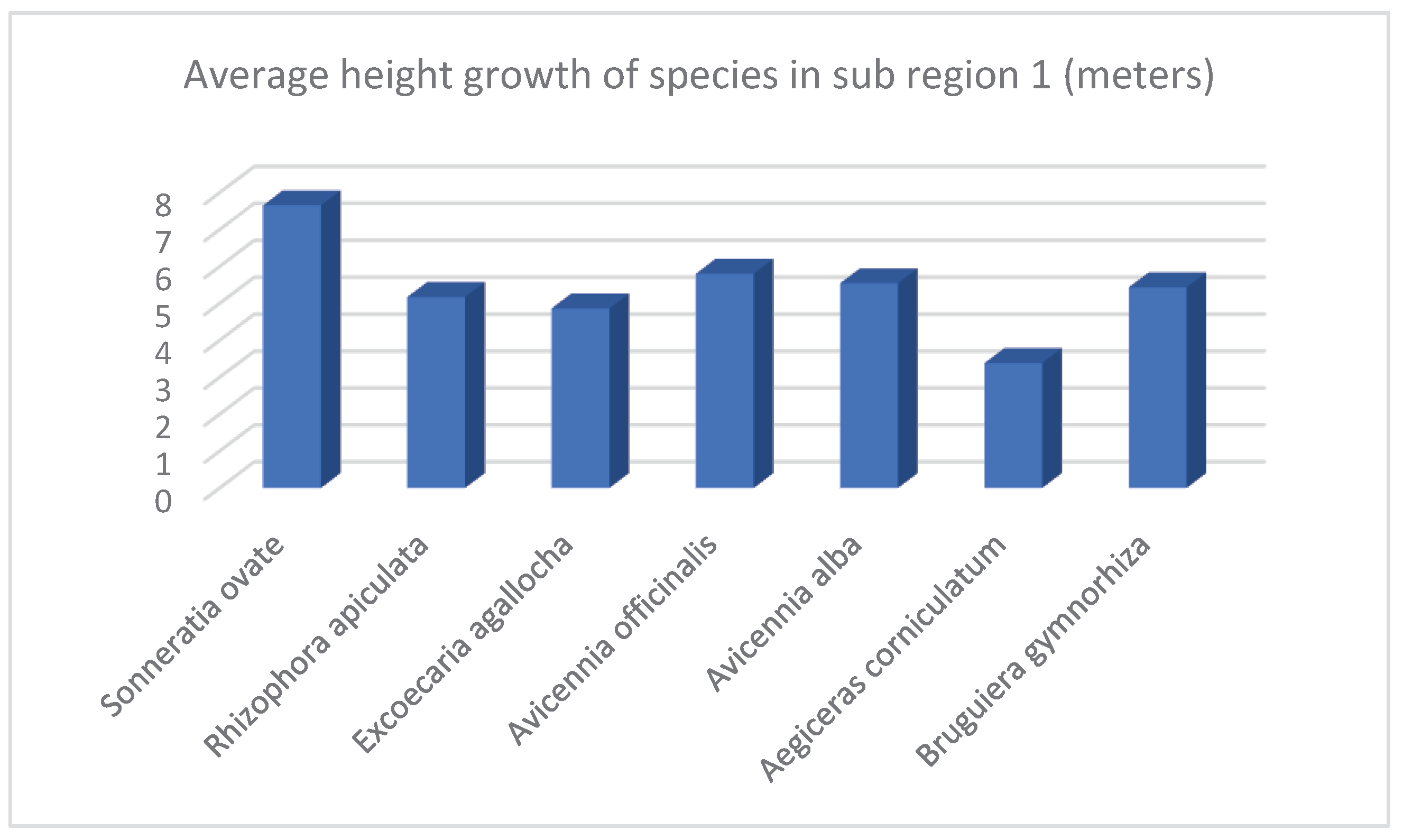
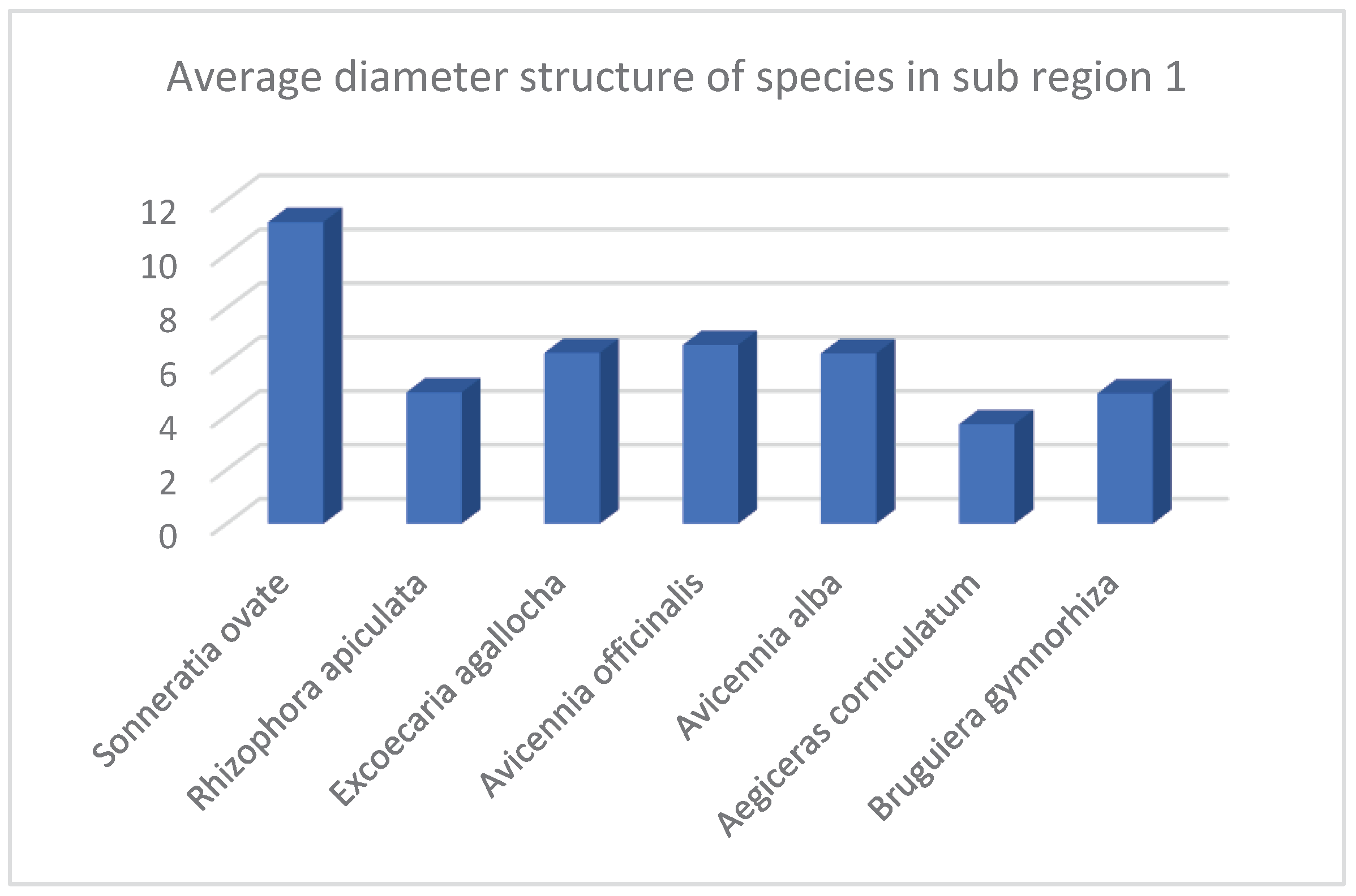
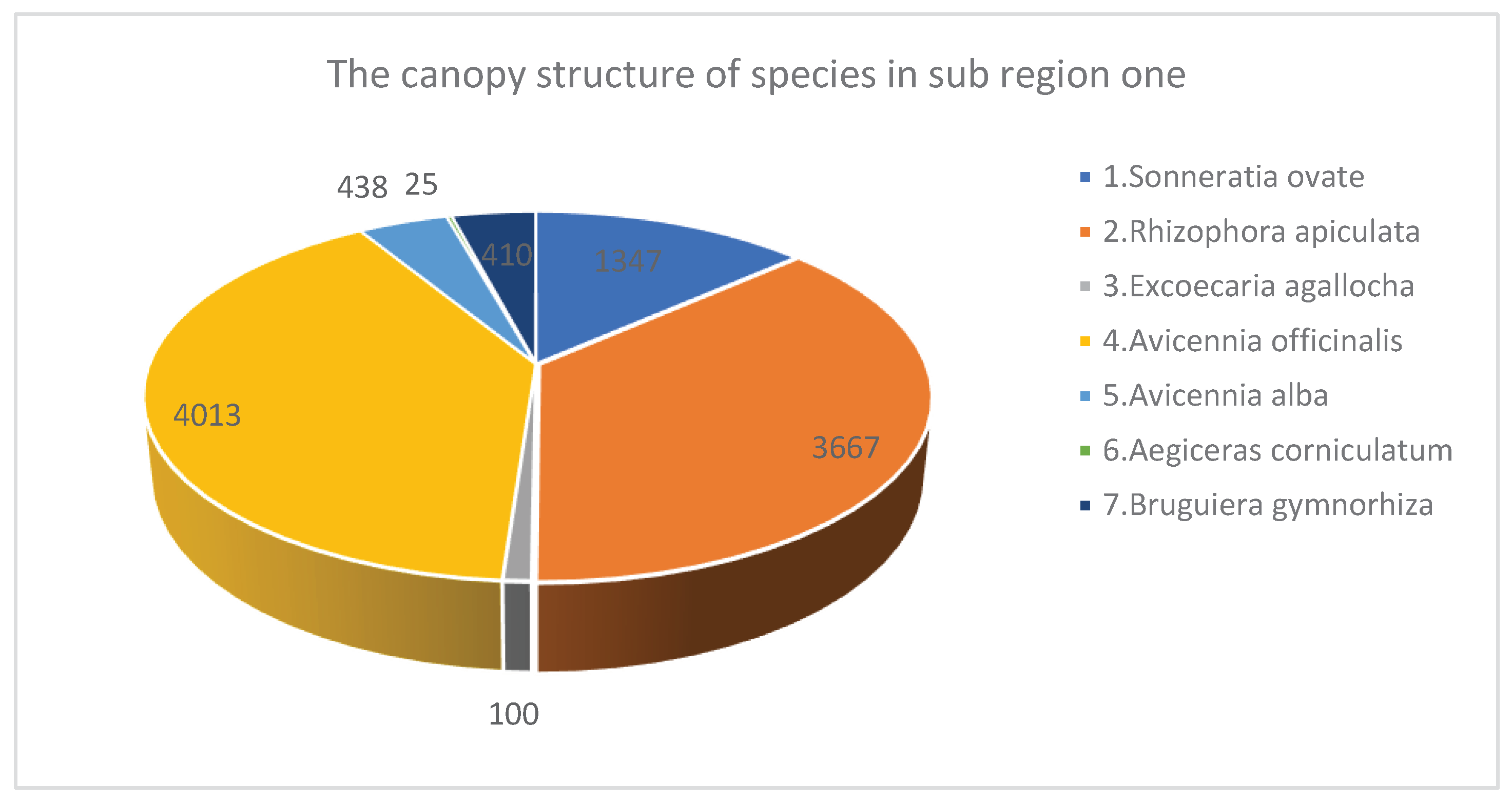
| 1 | Sonneratia ovate | 717 | 11.75 | 7.65 | 11.19 | 1347 | 3.67 |
| 2 | Rhizophora apiculata | 1983 | 32.51 | 5.17 | 4.87 | 3667 | 3.9 |
| 3 | Excoecaria agallocha | 117 | 1.92 | 4.86 | 6.43 | 100 | 3.29 |
| 4 | Avicennia officinalis | 2750 | 45.08 | 5.8 | 6.63 | 4013 | 2.63 |
| 5 | Avicennia alba | 300 | 4.92 | 5.54 | 6.32 | 438 | 2.15 |
| 6 | Aegiceras corniculatum | 50 | 0.82 | 3.38 | 3.69 | 25 | 3.5 |
| 7 | Bruguiera gymnorhiza | 183 | 3 | 5.43 | 4.38 | 410 | 4 |
| Total* / Average** | 6100* | 100* | 5.40** | 6.27** | 10000* | 3.31** |
| No. | Species | Density Structure (Tree) | Species Ratio (%) | Average Height (Meter) | Average Diameter (Centimeter) | Canopy Structure (Square Meter m2) | Heathy Structure (1 …5) 1: Bad 5: Best |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sonneratia caseolaris | 20 | 0.51 | 10.5 | 25.54 | 155 | 4 |
| 2 | Annona reticulate | 10 | 0.26 | 3.5 | 11.78 | 24 | 2 |
| 3 | Lumnitzera littorea | 50 | 1.28 | 3.17 | 5.22 | 16 | 2.33 |
| 4 | Lumnitzera racemosa | 110 | 2.81 | 4.55 | 5.64 | 70 | 3.02 |
| 5 | Rhizophora apiculata | 540 | 13.81 | 5.72 | 8.17 | 581 | 4.04 |
| 6 | Excoecaria agallocha | 740 | 18.93 | 5.37 | 6.42 | 943 | 3.51 |
| 7 | Avicennia officinalis | 1190 | 30.43 | 5.99 | 13.91 | 4773 | 3.92 |
| 8 | Avicennia alba | 820 | 20.97 | 7.85 | 12.35 | 2759 | 2.98 |
| 9 | Hibiscus tiliaceus | 90 | 2.30 | 5.99 | 10.75 | 202 | 2.78 |
| 10 | Bruguiera gymnorhiza | 260 | 6.65 | 5.47 | 8.08 | 322 | 3.78 |
| 11 | Aegiceras corniculatum | 80 | 2.05 | 3.72 | 5.45 | 155 | 4.31 |
| Total* / Average** | 3910* | 100* | 5.62** | 10.30** | 10000* | 3.33** |
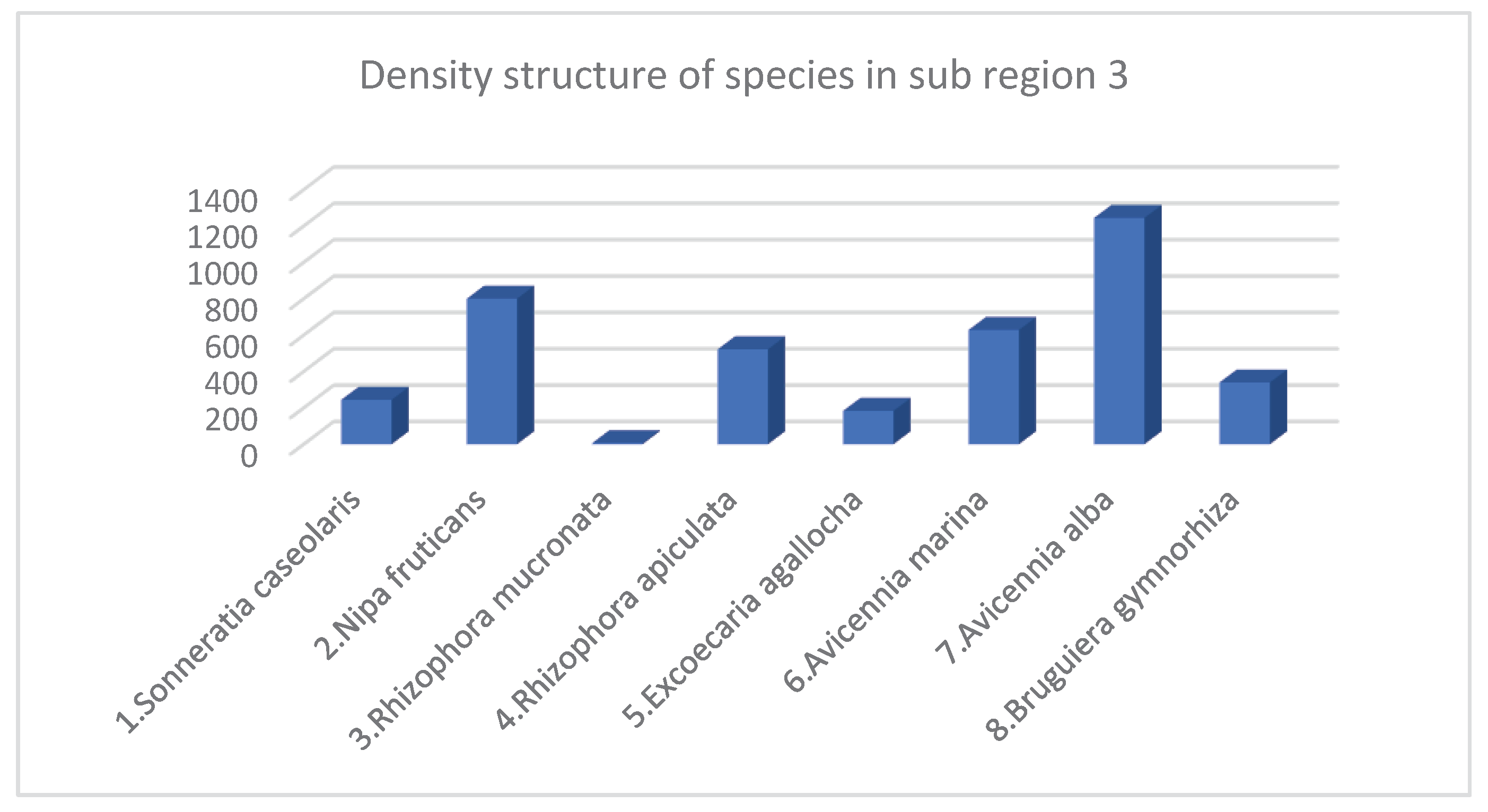
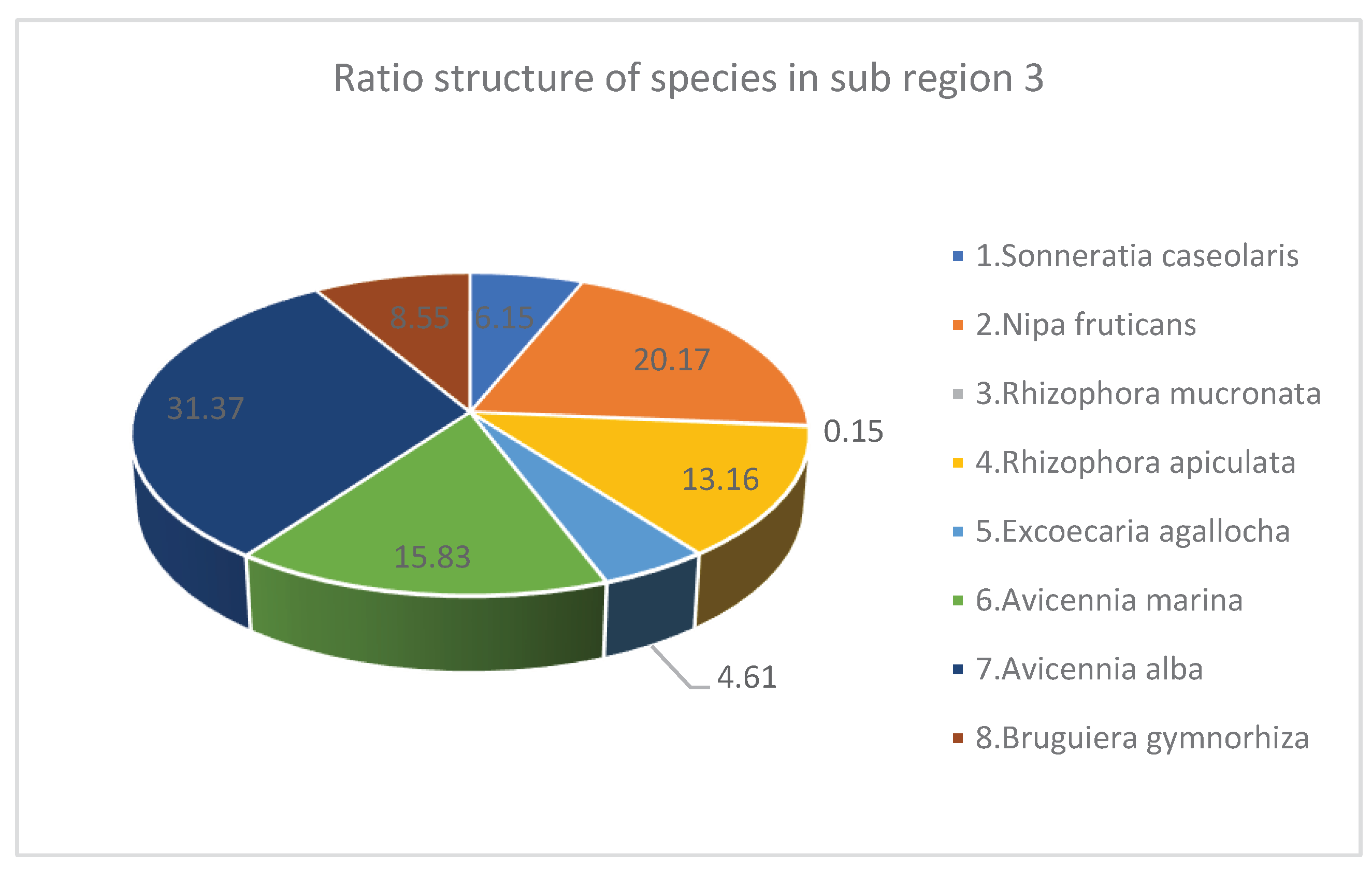
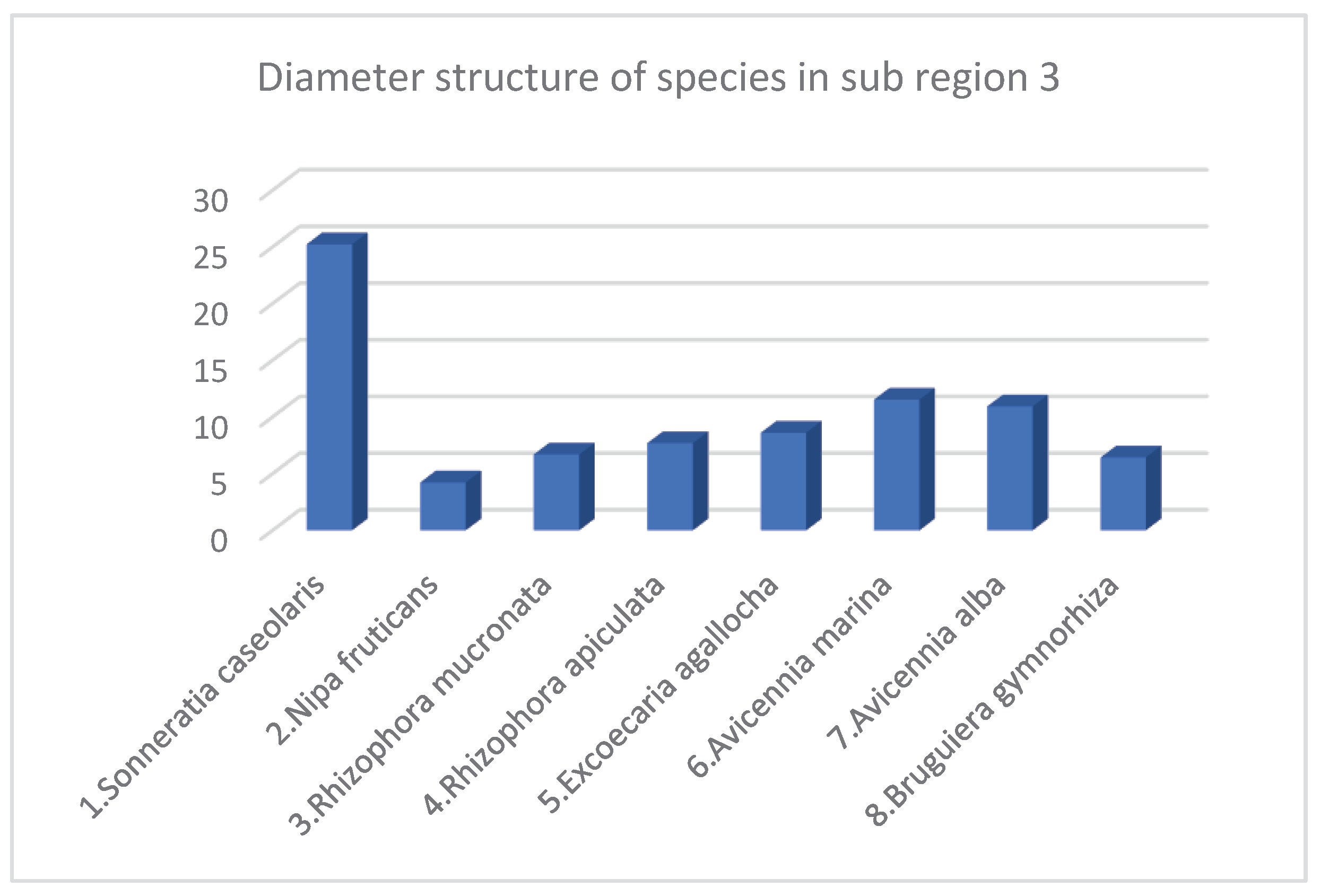
| No. | Species | Density Structure (Tree) | Species Ratio (%) | Average Height (meter) | Average Diameter (Centimeter) | Canopy Structure (Square Meter m2) | Heathy Structure (1 …5) 1: Bad 5: Best |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
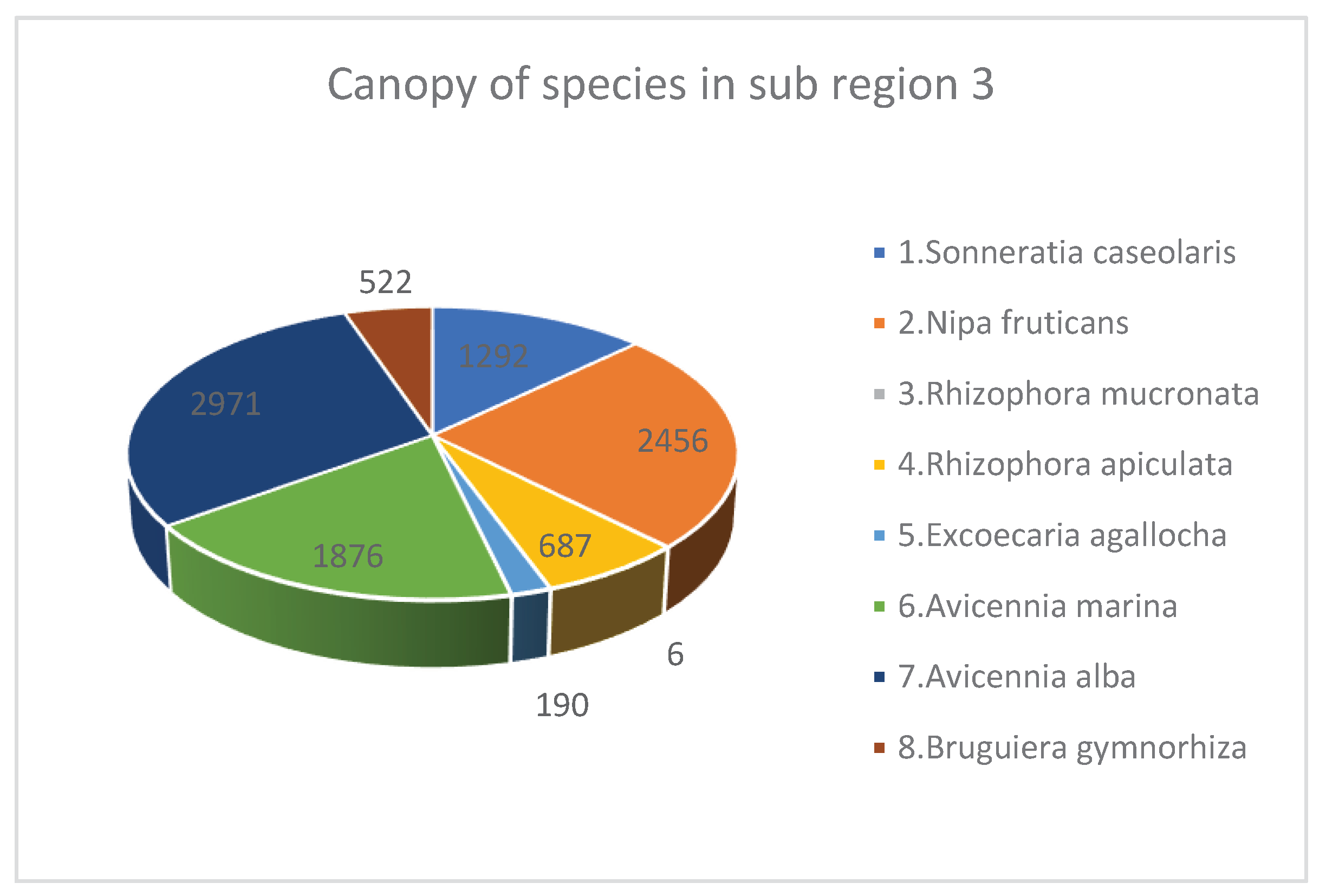
| 1 | Sonneratia caseolaris | 244 | 6.15 | 12.1 | 25.22 | 1292 | 3.34 |
| 2 | Nipa fruticans | 800 | 20.17 | 4.58 | Monocot | 2456 | 3.28 |
| 3 | Rhizophora mucronata | 6 | 0.15 | 8 | 6.68 | 6 | 3 |
| 4 | Rhizophora apiculata | 522 | 13.16 | 7.26 | 7.68 | 687 | 4.29 |
| 5 | Excoecaria agallocha | 183 | 4.61 | 6.83 | 8.6 | 190 | 3.33 |
| 6 | Avicennia marina | 628 | 15.83 | 8.18 | 11.52 | 1876 | 3.15 |
| 7 | Avicennia alba | 1244 | 31.37 | 7.6 | 10.92 | 2971 | 3.15 |
| 8 | Bruguiera gymnorhiza | 339 | 8.55 | 4.63 | 6.42 | 522 | 3.78 |
| Total* / Average** | 3966* | 100* | 7.40** | 10.16** | 10000* | 3.41** |
- b.
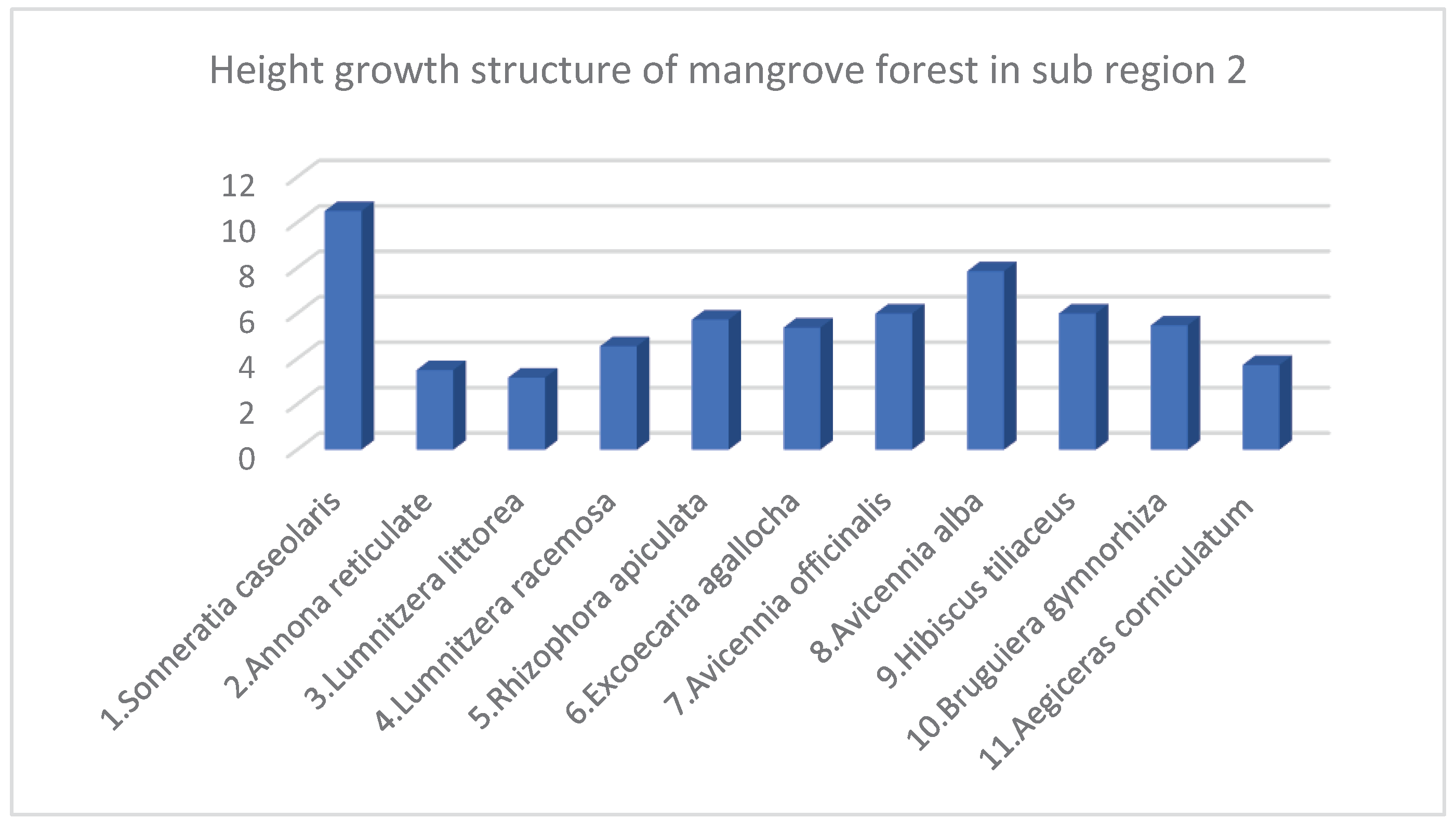
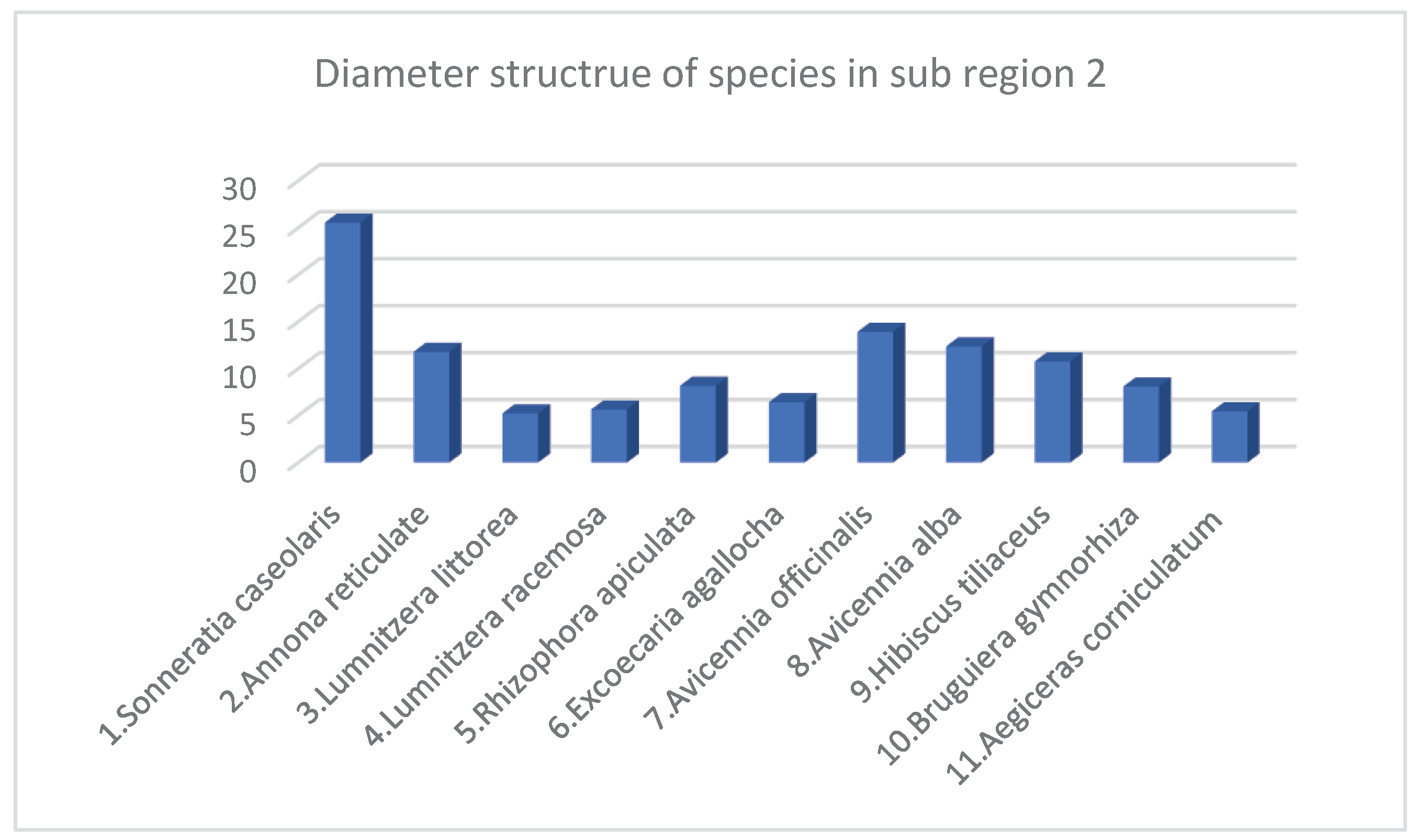
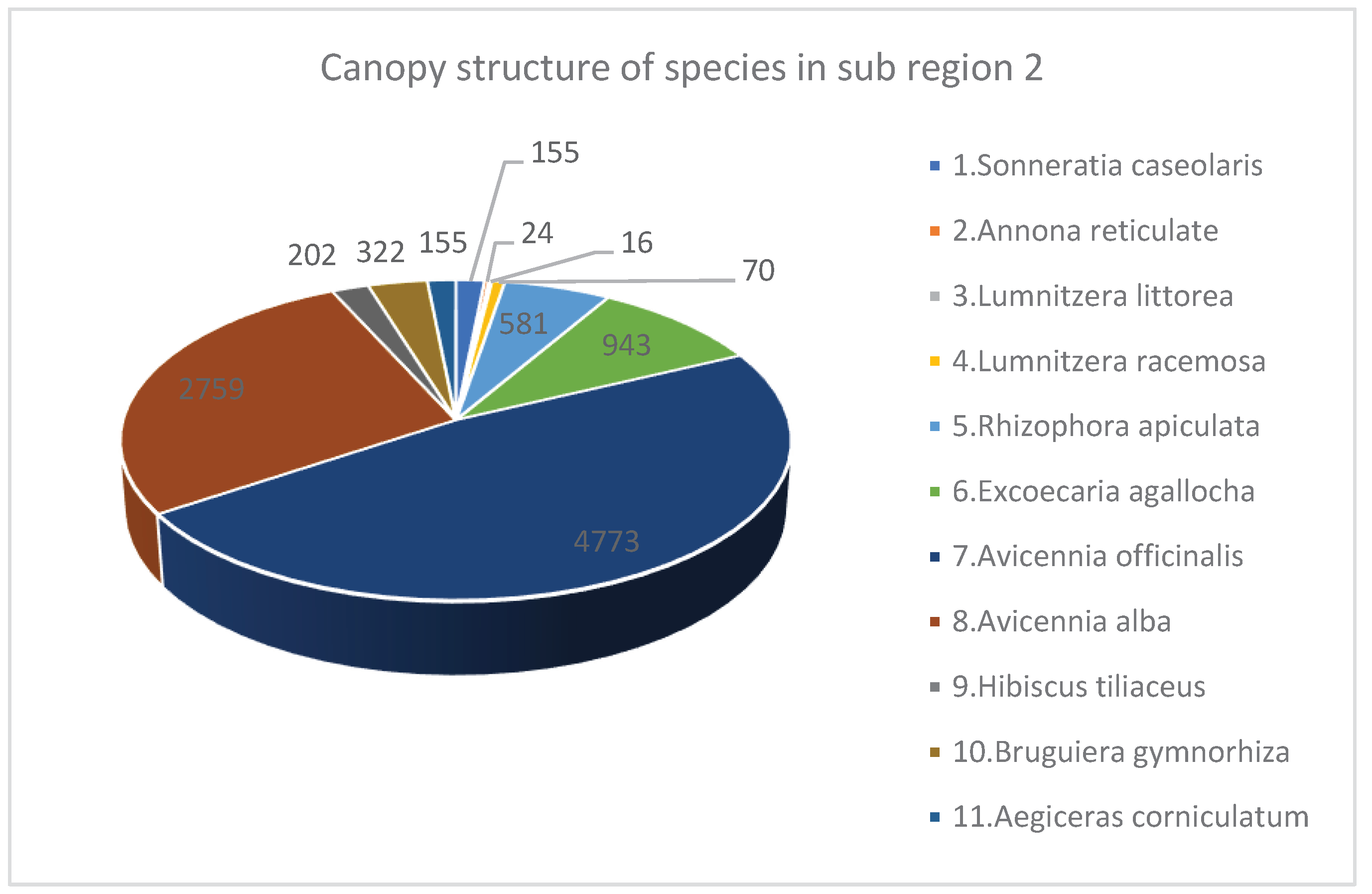
- Species structure of Mangroves in Sub region 2

| No. | Species | Density Structure (Tree) | Species Ratio (%) | Average Height (meter) | Average Diameter (Centimeter) | Canopy Structure (Square Meter m2) | Heathy Structure (1 …5) 1: Bad 5: Best |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
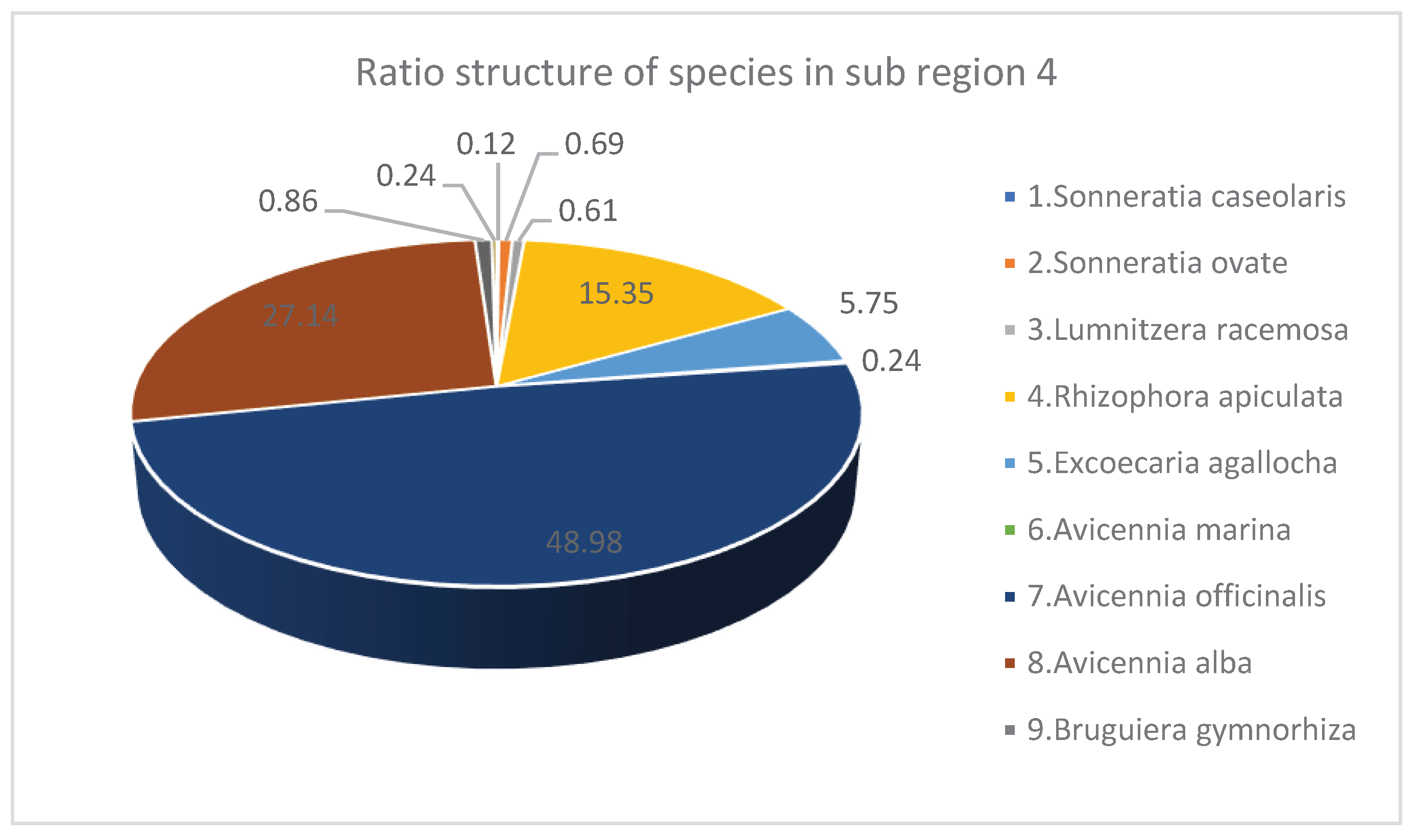
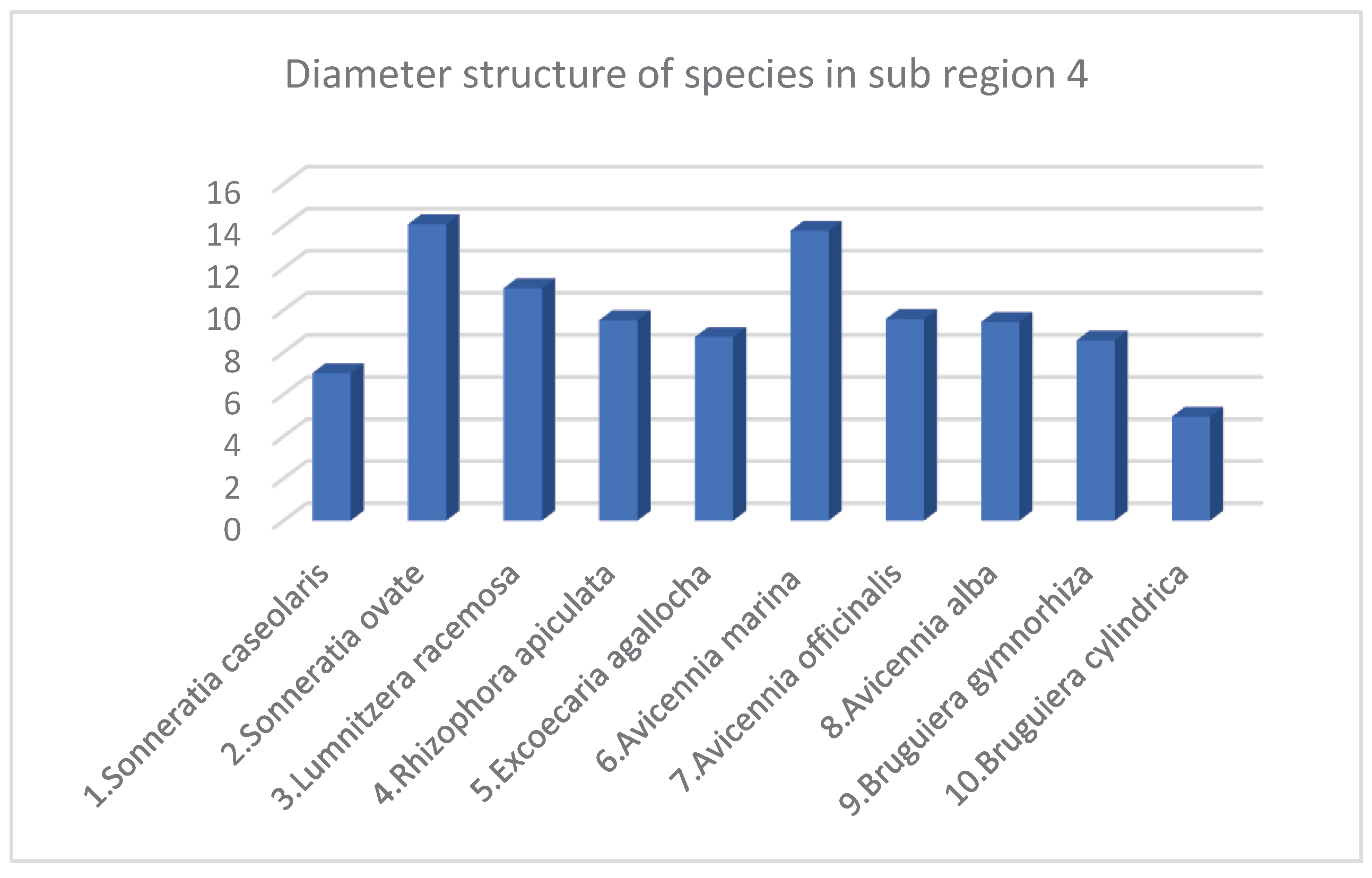
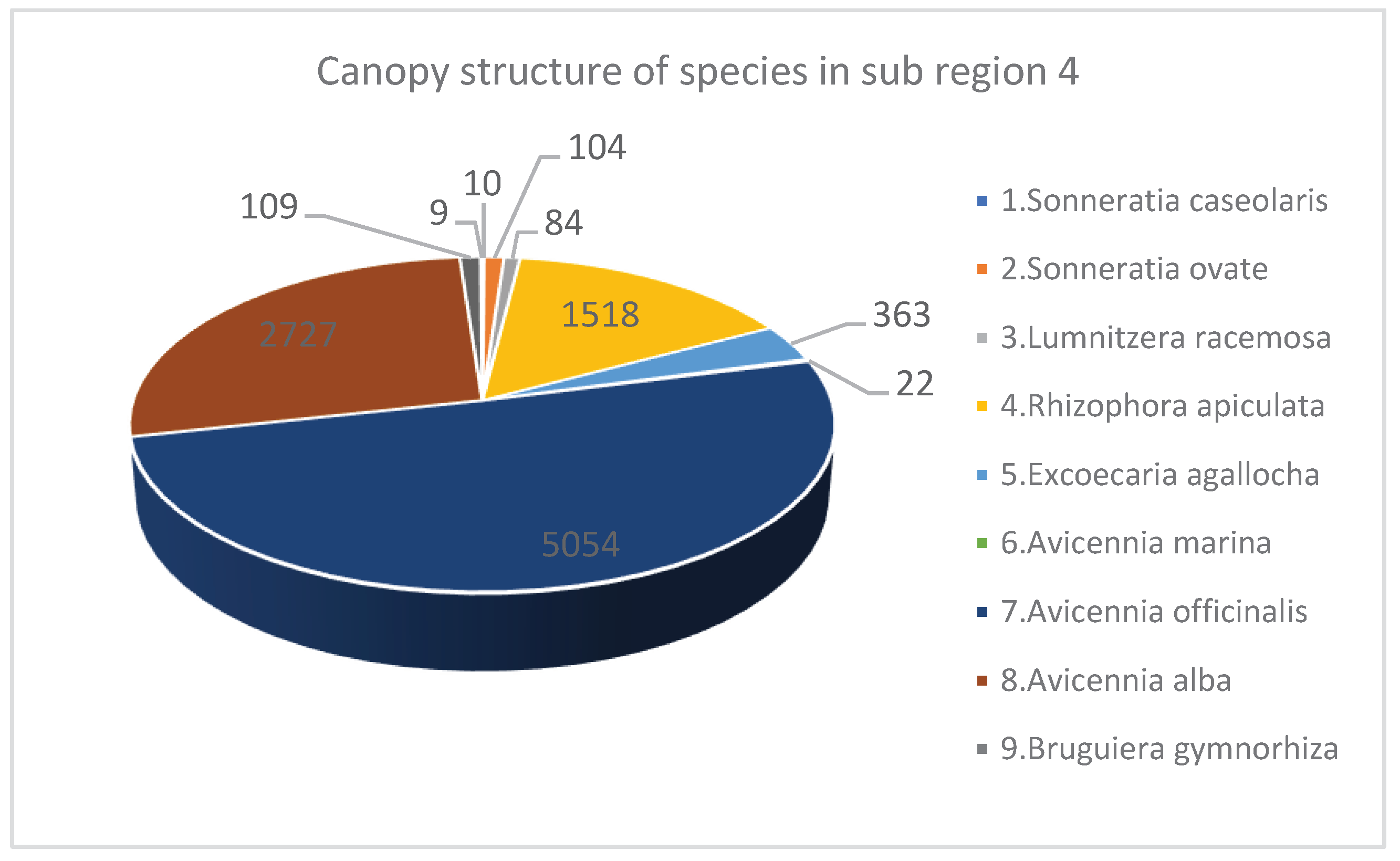
| 1 | Sonneratia caseolaris | 3 | 0.12 | 7.5 | 7 | 10 | 4 |
| 2 | Sonneratia ovate | 17 | 0.69 | 10.72 | 14.08 | 104 | 4 |
| 3 | Lumnitzera racemosa | 15 | 0.61 | 10.45 | 11.04 | 84 | 4 |
| 4 | Rhizophora apiculata | 376 | 15.35 | 9.07 | 9.52 | 1518 | 3.82 |
| 5 | Excoecaria agallocha | 141 | 5.75 | 6.9 | 8.72 | 363 | 3.76 |
| 6 | Avicennia marina | 6 | 0.24 | 10.85 | 13.77 | 22 | 3.5 |
| 7 | Avicennia officinalis | 1200 | 48.98 | 8.05 | 9.57 | 5054 | 3.47 |
| 8 | Avicennia alba | 665 | 27.14 | 7.6 | 9.43 | 2727 | 3.52 |
| 9 | Bruguiera gymnorhiza | 21 | 0.86 | 8.93 | 8.56 | 109 | 3.75 |
| 10 | Bruguiera cylindrica | 6 | 0.24 | 6.8 | 4.93 | 9 | 3.5 |
| Total* / Average** | 2450* | 100* | 8.69* | 9.66** | 10000* | 3.73** |

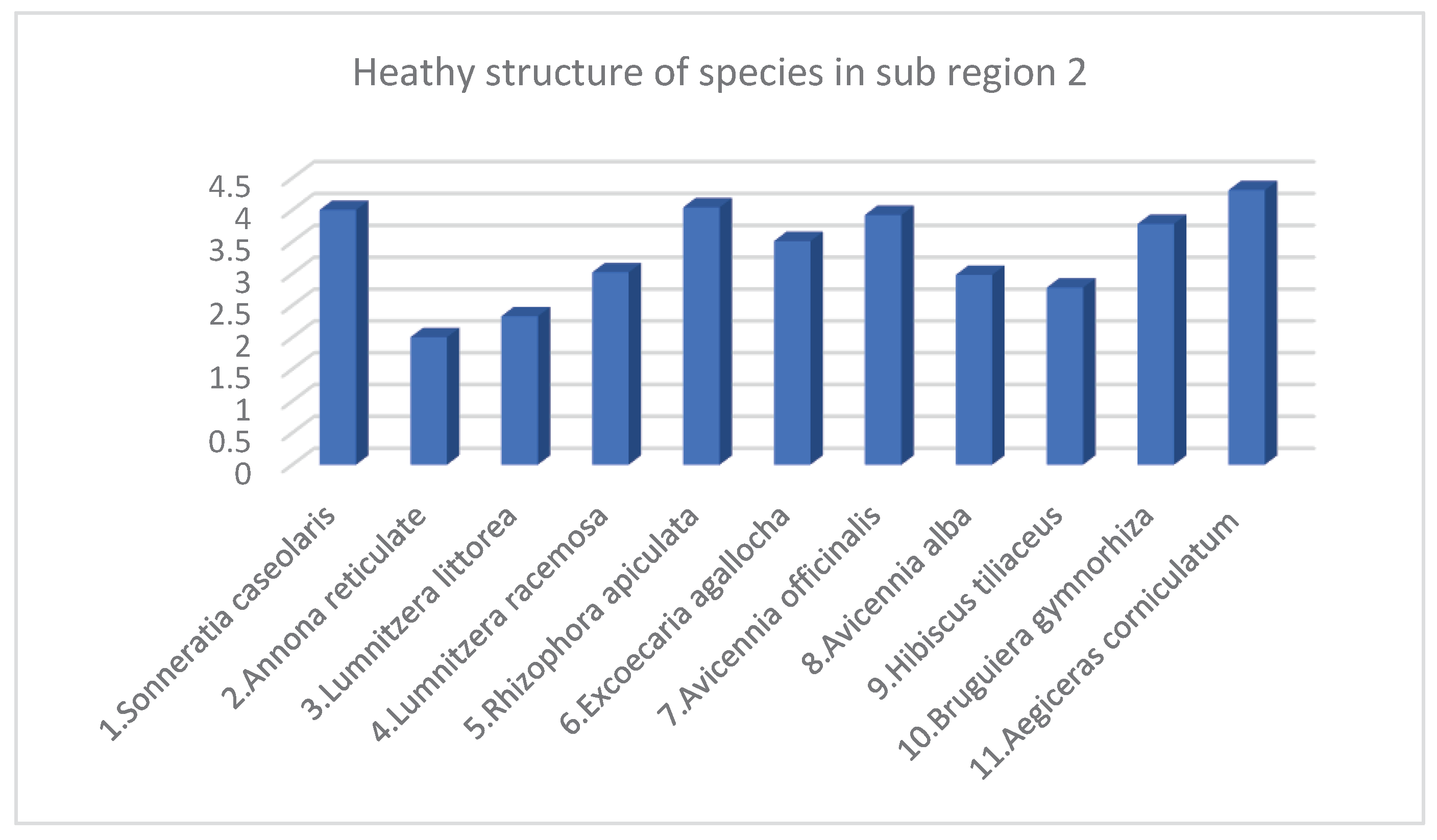
| No. | Species | Density Structure (Tree) | Species Ratio (%) | Average Height (Meter) | Average Diameter (Centimeter) | Canopy Structure (Square Meter m2) | Heathy Structure (1 …5) 1: Bad 5: Best |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sonneratia caseolaris | 91 | 2.07 | 9.44 | 17.24 | 541 | 3.78 |
| 2 | Sonneratia ovate | 110 | 2.50 | 10.72 | 14.08 | 304 | 3.65 |
| 3 | Annona reticulate | 2 | 0.05 | 3.5 | 11.78 | 6 | 2 |
| 4 | Lumnitzera littorea | 10 | 0.23 | 3.17 | 5.22 | 4 | 2.33 |
| 5 | Lumnitzera racemosa | 32 | 0.73 | 7.5 | 8.34 | 51 | 3.51 |
| 6 | Nipa fruticans | 128 | 2.91 | 4.58 | 4.21 | 526 | 3.28 |
| 7 | Rhizophora mucronata | 2 | 0.05 | 8.00 | 6.68 | 3 | 3 |
| 8 | Rhizophora apiculata | 1165 | 26.47 | 6.81 | 7.56 | 1809 | 4.01 |
| 9 | Excoecaria agallocha | 325 | 7.38 | 5.99 | 7.52 | 384 | 3.47 |
| 10 | Avicennia marina | 195 | 4.43 | 9.52 | 12.64 | 546 | 3.32 |
| 11 | Avicennia officinalis | 1006 | 22.86 | 6.61 | 10.04 | 2626 | 3.34 |
| 12 | Avicennia alba | 1116 | 25.36 | 7.15 | 9.75 | 2955 | 2.95 |
| 13 | Bruguiera gymnorhiza | 39 | 0.87 | 6.33 | 6.60 | 70 | 3.83 |
| 14 | Bruguiera cylindrical | 140 | 3.18 | 6.8 | 4.93 | 76 | 3.5 |
| 15 | Aegiceras corniculatum | 22 | 0.50 | 3.55 | 4.57 | 51 | 4.31 |
| 16 | Hibiscus tiliaceus | 18 | 0.41 | 5.99 | 10.75 | 48 | 2.78 |
| Total* / Average** | 4401 | 100 | 6.87 | 9.04 | 10000* | 3.28 |
- c.
- Species structure of Mangroves in Sub region 3


- d.
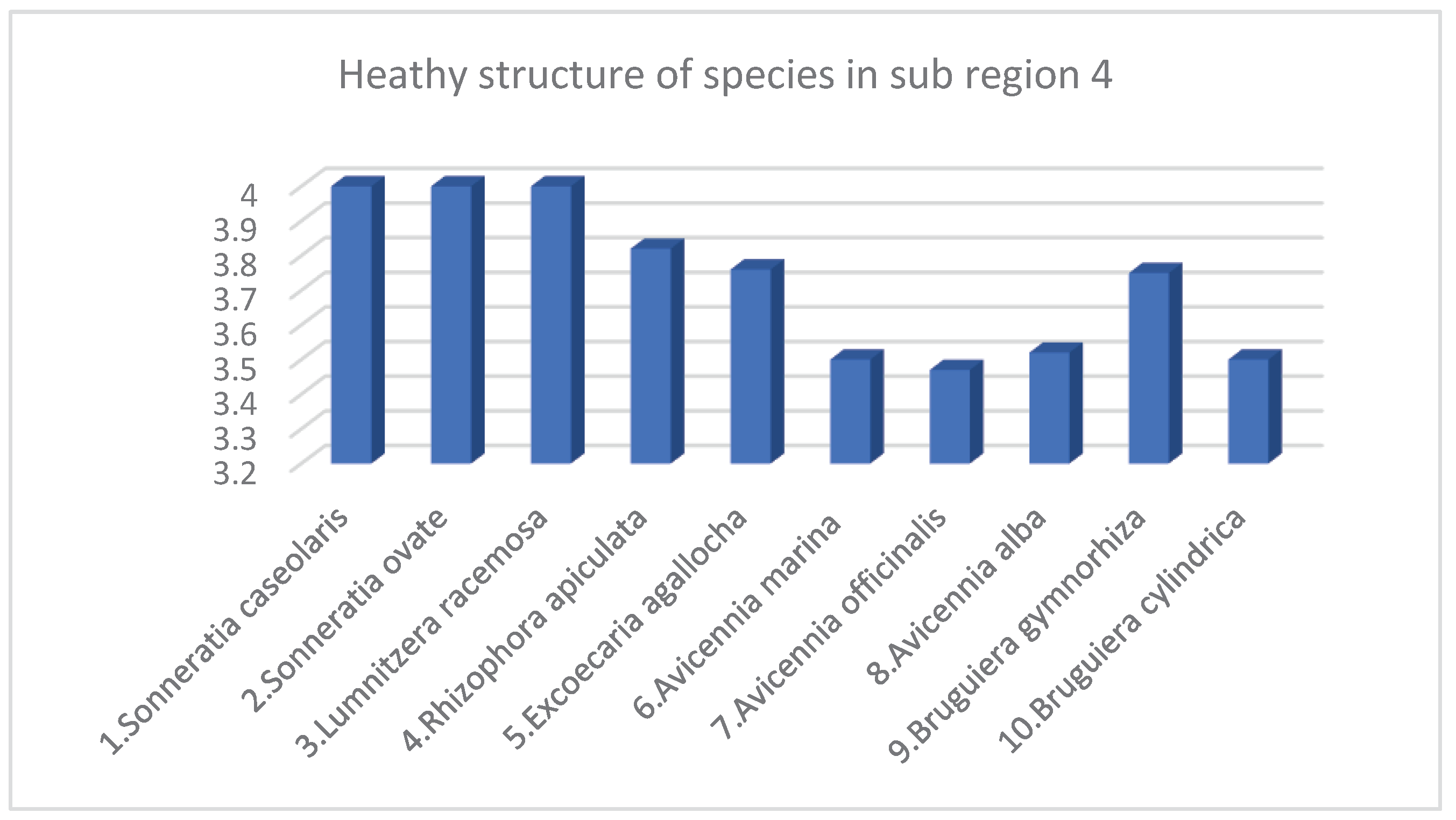
- Species struscture of Mangroves in Sub region 4


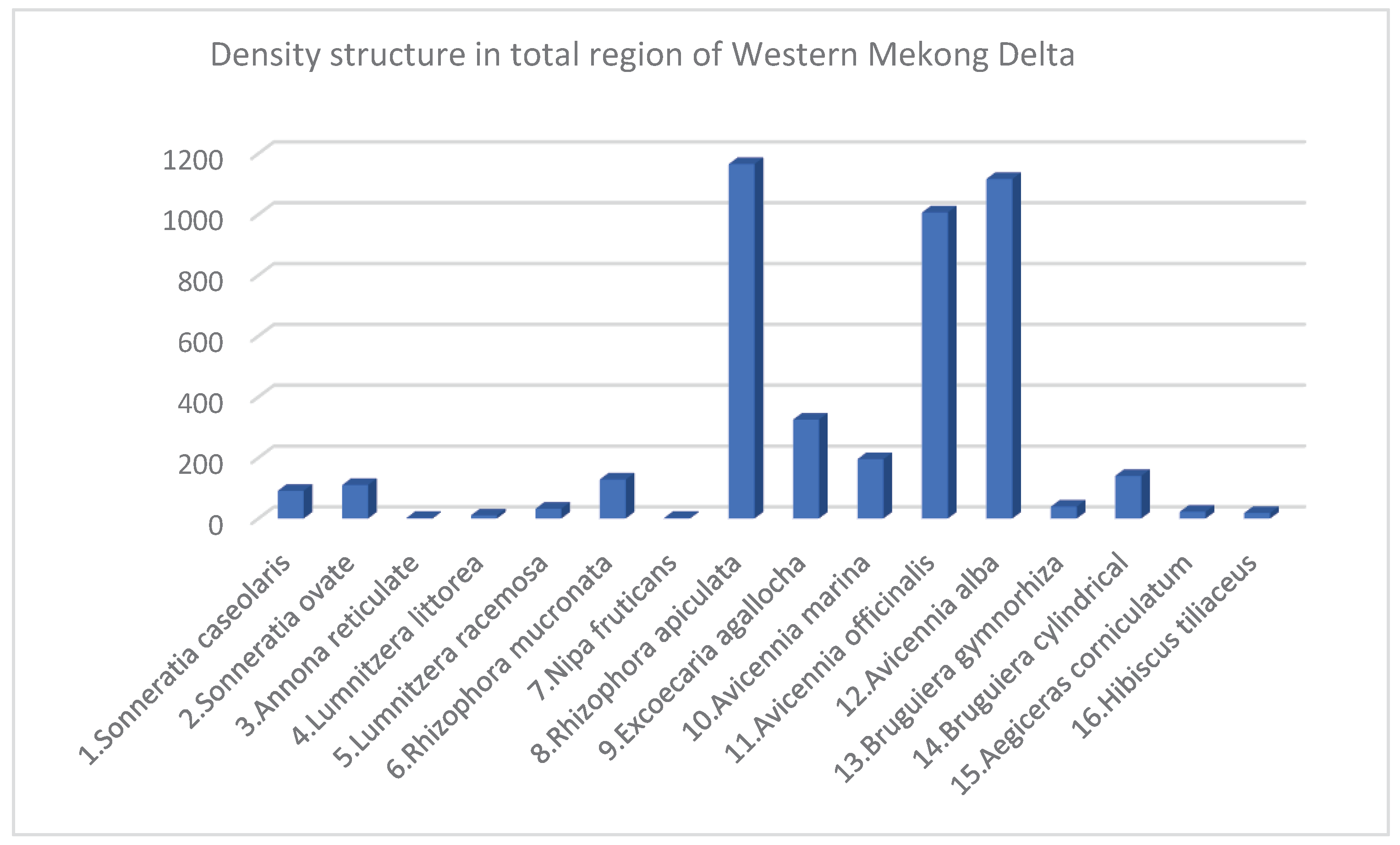
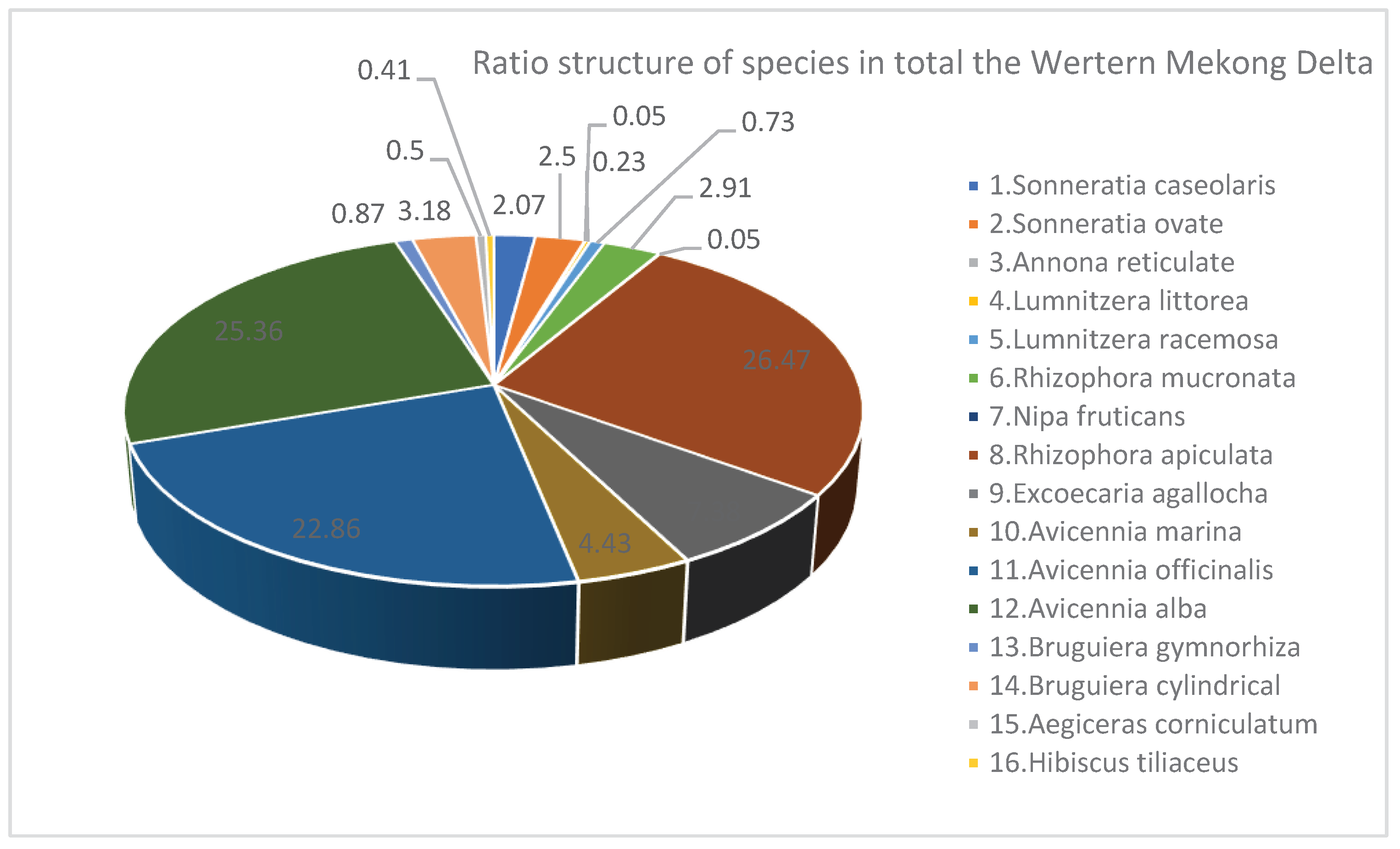
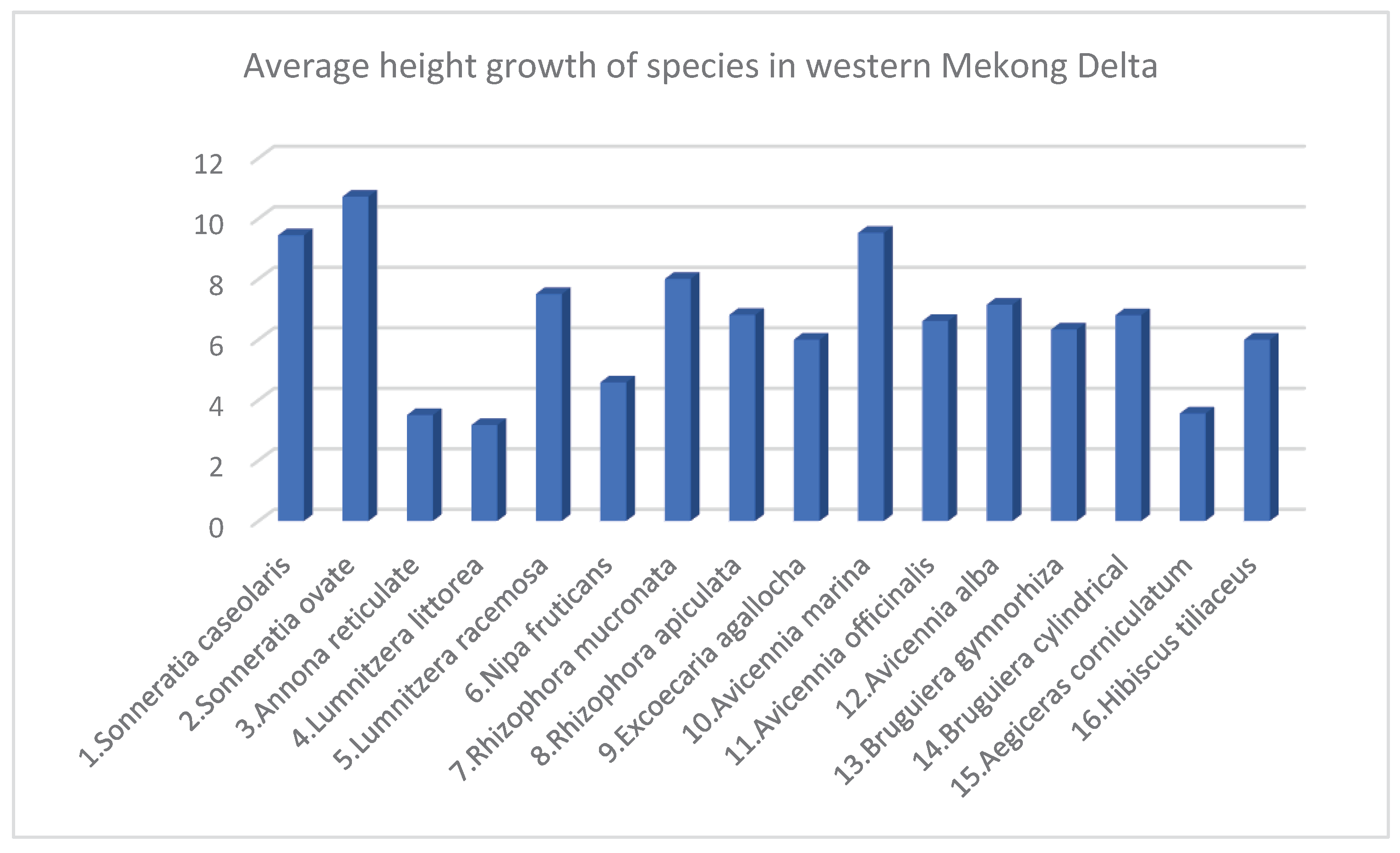
3.3. Species Structure of Mangroves in Eegion Western Mekong Delta
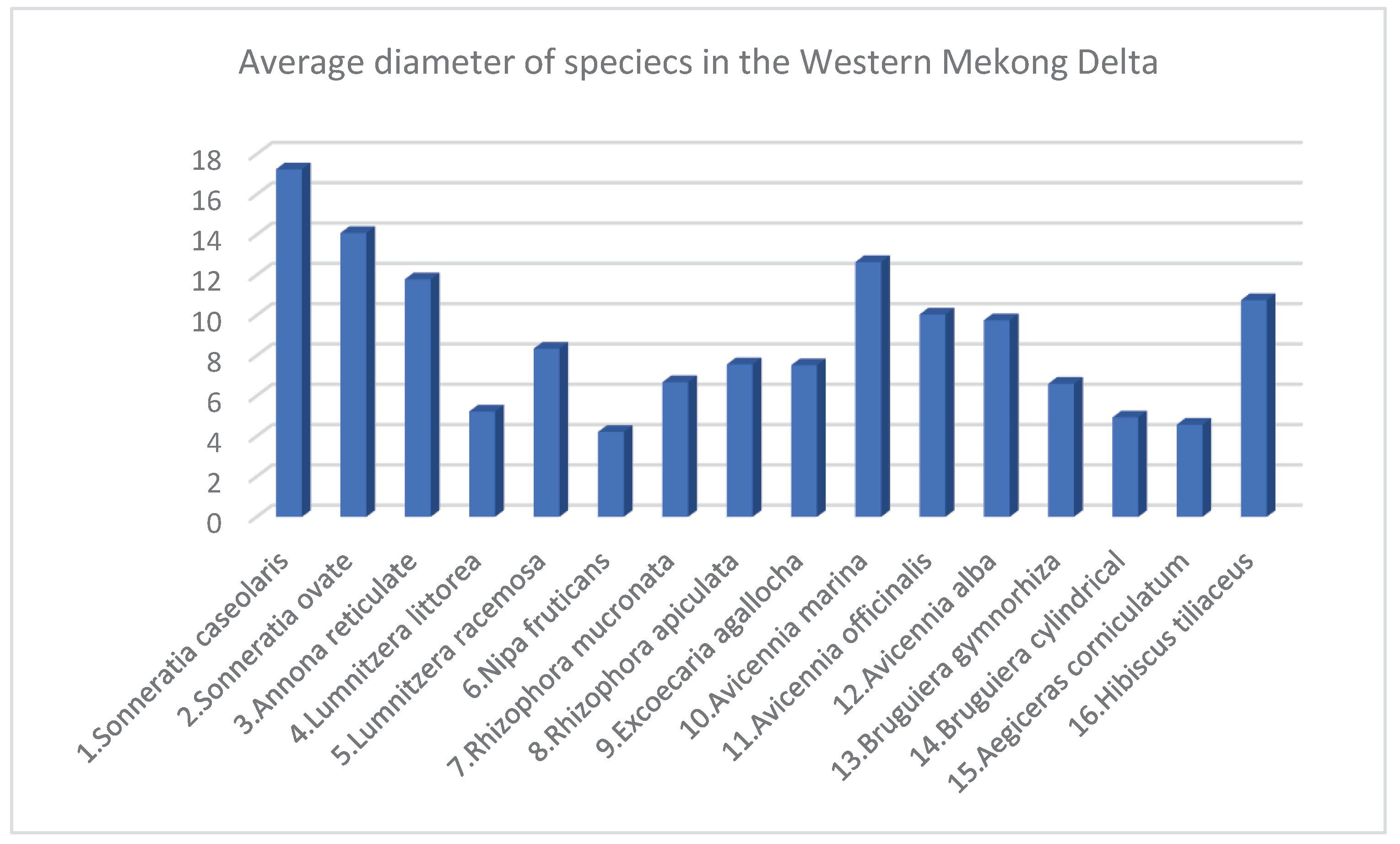
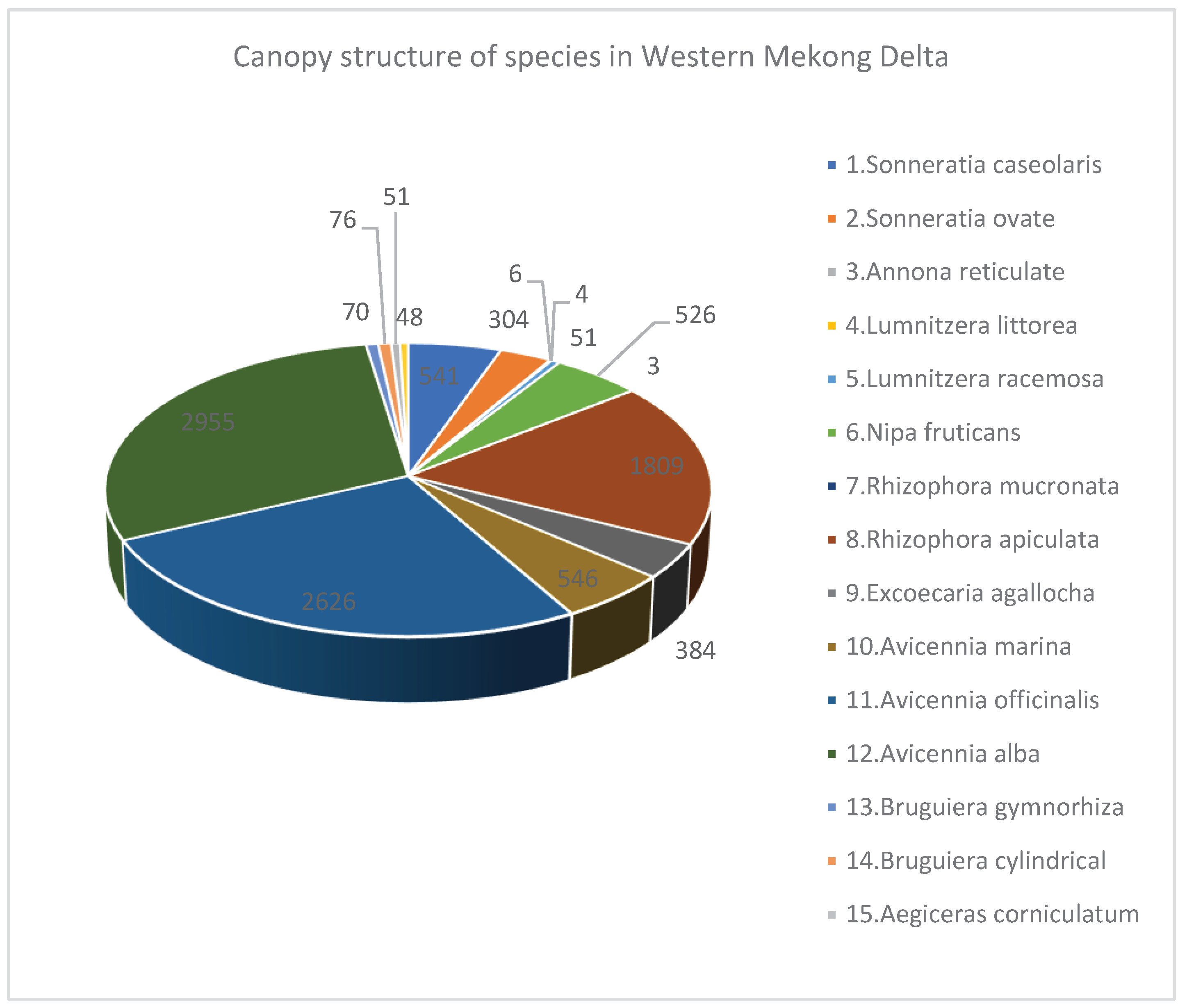
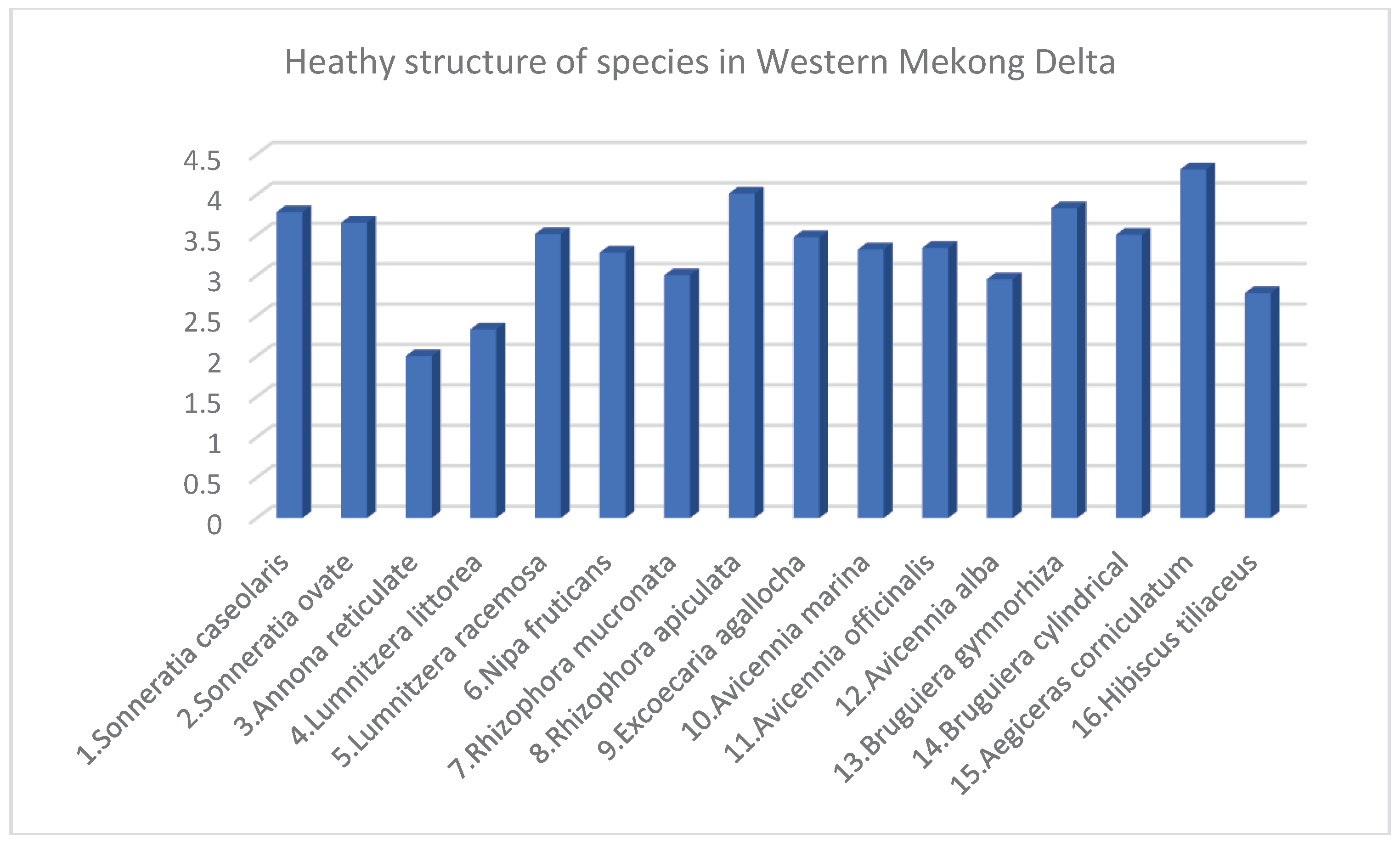
3.4. Discussions
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AHMAD Dwi Setyawan. Rhizophora mucronata as source of foods and medicines. Journal of Bonorowo Wetland 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ball, 1998. Ecophysiology of mangroves. Trees, 2(3): 129-142.(1998). [CrossRef]
- Bhavya Mehta, et al,. A review on a lesser known indian mangrove: Avicennia officinalis L. (Family: Ancanthaceae). International Journal of Green Pharmacy* January-Mar 2021*15(1)1 (2021). [CrossRef]
- DARD (Department of Agriculture and Rural Development of Kien Giang province). Kien Giang province mangrove belt restoration project for the period 2012 - 2016.(2012).
- DARD (Department of Agriculture and Rural Development of Kien Giang province). Report on Agriculture and Rural Development Planning in Kien Giang province for the period 2010 - 2020. (2010).
- Duke, N.C., 1992.1992. 42: 63-100.
- Fitri Budiyanto, et al. Exploring the Mangrove Fruit: From the Phytochemicals to Funtional Food Development and the Curent Progress in the Middle East. MDPI mdpi.com/1660 – 3397/20/5/303. 2022. Volume 20/ Isue 5. [CrossRef]
- GIZ Kien Giang. Conservation and development of Biosphere Reserve in Kien Giang province. 2012.
- GIZ. Remote sensing and mapping of mangrove forests. Research report in Kien Giang province. 2011.
- GIZ Mangrove forests in Kien Giang province biosphere reserve. Agricultural publisher. 2013.
- Ha Quoc Hung, Dang Trung Tan. Handbook of plants and trees of Ca Mau mangrove forest. Tran Ngoc Hy printing factory - Ca Mau. 1999.
- Henni Syawal, et al. Phytochemical analysis of Rhizophora apiculata leaf extract and its inhibitory action against Staphylococus aureus, Aeronomus hydrophyla and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. AACL Bioflux, 2020, Volume 13, Issue 4. http://www.bioflux.com.ro/aacl.
- Indah Rosulva, et al.,. Physico – chemical chracterization of Indonesian mangroves fruits species. Future of Food: Journal on Food, Agriculture and Society. 10(5) August 2022. [CrossRef]
- Jaryyal, et al. Glycemic Index Biscuirs Formulation of Pedada Flour (Sonneratia caseolaris) with Tubers Starch. The2nd International Joint Conference on Science and Technology (IJCST) 2017. IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Madhav Bhilave, et al. Formulation of Fish Feed Using Mangrove Leaves (Avicennia officinalis). Shivaji University, Kolhapur. 2016. Vol 9 (1) January – June 2016.BIONANO FRONTIER.
- Ngo Dinh Que, Pham Trong Thinh, Chu Van Cuong, Huynh Huu To, Nhu Van Ky, Ly Tho, Nguyen Van Thang, Vo Van Duc, Phan Tien Lam, Karyl Michael. Restore mangrove forests in coastal areas of Vietnam. Report on survey results in January 2012 of GIZ Kien Giang.
- Ngo Tran Vu. Improving methods and studying the genetic diversity of Avicennia (A. officialis L.) in Can Gio mangrove biosphere reserve using RAPD technique. Graduation thesis report at Ho Chi Minh City University of Agriculture and Forestry. Ho Chi Minh, 2007.
- Nguyen Hai Tuat. Mathematical statistics in forestry. Agricultural Publishing House, (1982).
- Nguyen Hai Tuat, Ngo Kim Khoi. Statistical processing of experimental research results in agriculture and forestry Nguyen Hai Tuat, Nguyen Ngoc Binh, 2005. (1996).
- Nguyen Hai Tuat, Nguyen Ngoc Binh. Exploiting and using SPSS to process data in forestry.(2005).
- Nguyen Xuan Niem, Le Thanh Viet, Huynh Huu To, Ly Minh Tai, Nguyen Thanh Hai, Pham Van Giau. Restoring mangrove forests in Kien Giang biosphere reserve in the context of climate change adaptation, (2017).
- Norm Duke. Australia’s Mangroves. Published by University of Queensland & Norman C. Duke Designed by Diana Kleine, 200 pages.(2006).
- Norm Duke. Mangrove forests in the Biosphere Reserve of Kien Giang province, Vietnam. Agricultural publisher. (2013).
- Phan Nguyen Hong et al. Vietnam's mangrove forests. Agriculture Publishing House. Hanoi. (1999).
- Quach Van Toan Em, Pham Van Ngot. Research on the growth of Red Toad (Lumnitzera Rittorea Voigt) with different salt regimes at the nursery stage (2007). Pages 297 - 304 in the bookRestore mangrove forests to cope with climate change towards sustainable development.
- Rahmat Kurniawan, et al. The cytotoxicity studies of phytosterrol discovered from Rhizophor apiculata against three human cancer cell lines. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science Vol. 13(01), pp 156-162, January, 2023. Exploiting non-timber forest producs for food. [CrossRef]
- S.K. Das, et al. Bioactivity guided isolation and structural characterization of the antidiabetic and antioxidant compound form bark extract of Avicennia oficinalis L. South African Journal of Botany, Volume 125, September, 2019. [CrossRef]
- SHEN Guan – yuan, et al. Optimization of Formula and Technology of Tabletting Candy of Avicennia marina Fruit. Vol. 40, No. 18, 2019. Scien and Technology of Food Industry. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Sumartini, et al. Brownies from Mangrove Fruit Flour: The Use of Variation of Flours As an Alternative to High Food Nutrition. Indonesian Food and Nutrition Progress, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Swagat Kumar Das, et, al. Pharmacological activities of leaf and bark extracts a medicinal mangrove plant Avicennia oficinalis L. Clinical Phytoscience, Volume 4, article number 13, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Thai Thanh Luom. Recovering and managing mangrove forests in the context of climate change in Kien Giang province, Proceedings of the National Conference, Can Gio, City. Ho Chi Minh, November 23 - 25, 2010.
- Truong Thi Nga, Phung Thi Bich Lam. Distribution of mangrove communities in Hon Dat district, Kien Giang province according to environmental factors.2007. Pages 279 - 284 in the book Restore mangrove forests to cope with climate change towards sustainable development.
- Vien Ngoc Nam. Using Primer software in calculating forest biodiversity indices. City University of Agriculture and Forestry. Ho Chi Minh 2011.
- Vu Tan Phuong, Nguyen Ngoc Lung, Do Dinh Sam, Nguyen Xuan Quat, Tran Viet Lien, Ngo Dinh Que, Tran Van Con, Nguyen Dinh Ky, Lai Vinh Cam, Do Huu Thu, Ngo Tien Giang, Hoang Viet Anh, Dinh Thanh Giang, Pham Ngoc Thanh. Forestry ecological zoning in Vietnam. Report of the Center for Forest Ecology and Environment of the Vietnam Academy of Forest Sciences. 2011.
- Wintah, et al. Mangrove Chocolate Food be Observed from the Nutrititional Values Found in the Coast of South West Aceh. E3S Web of Conferences 448, 03050 (2023). [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




