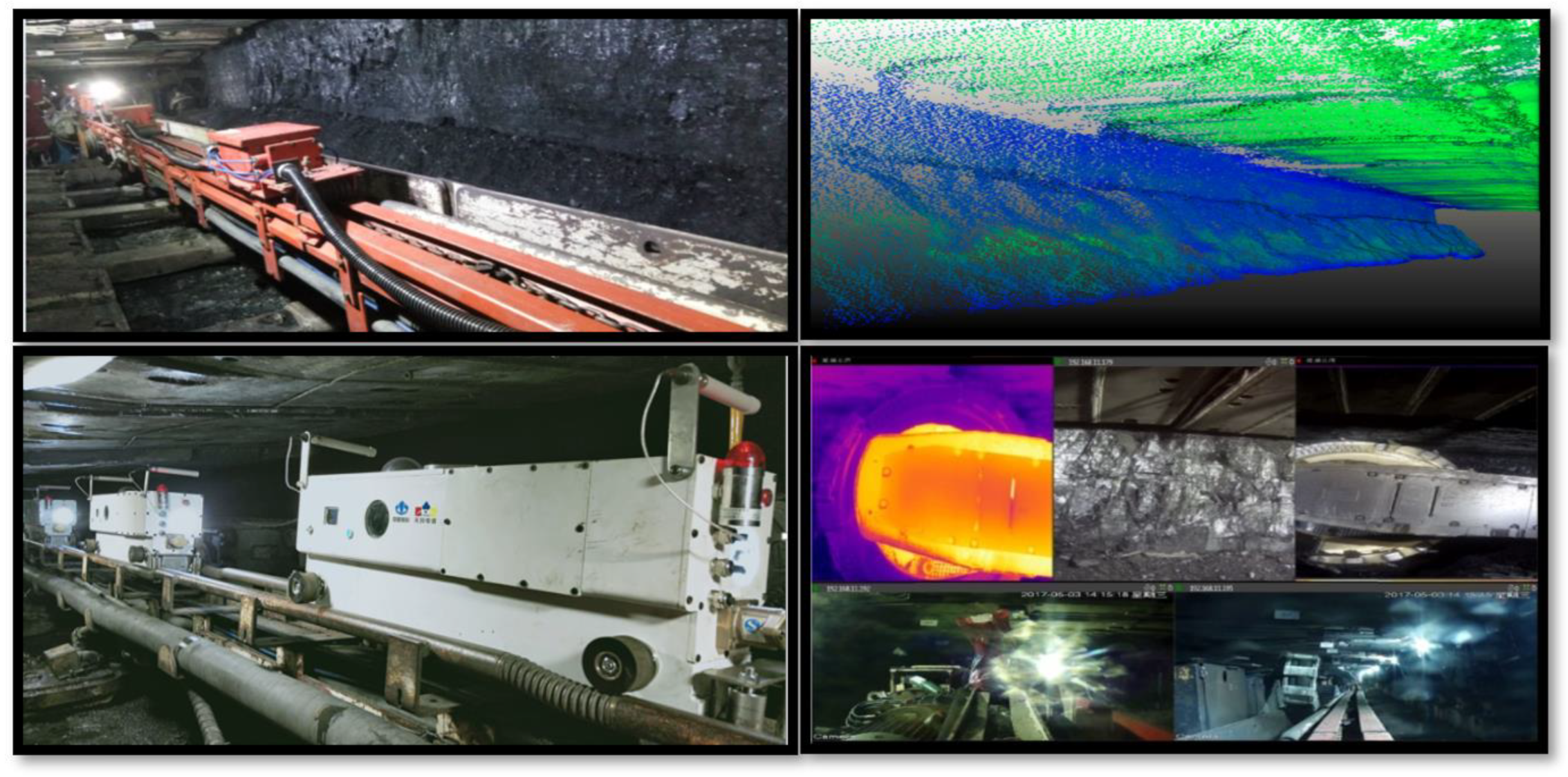
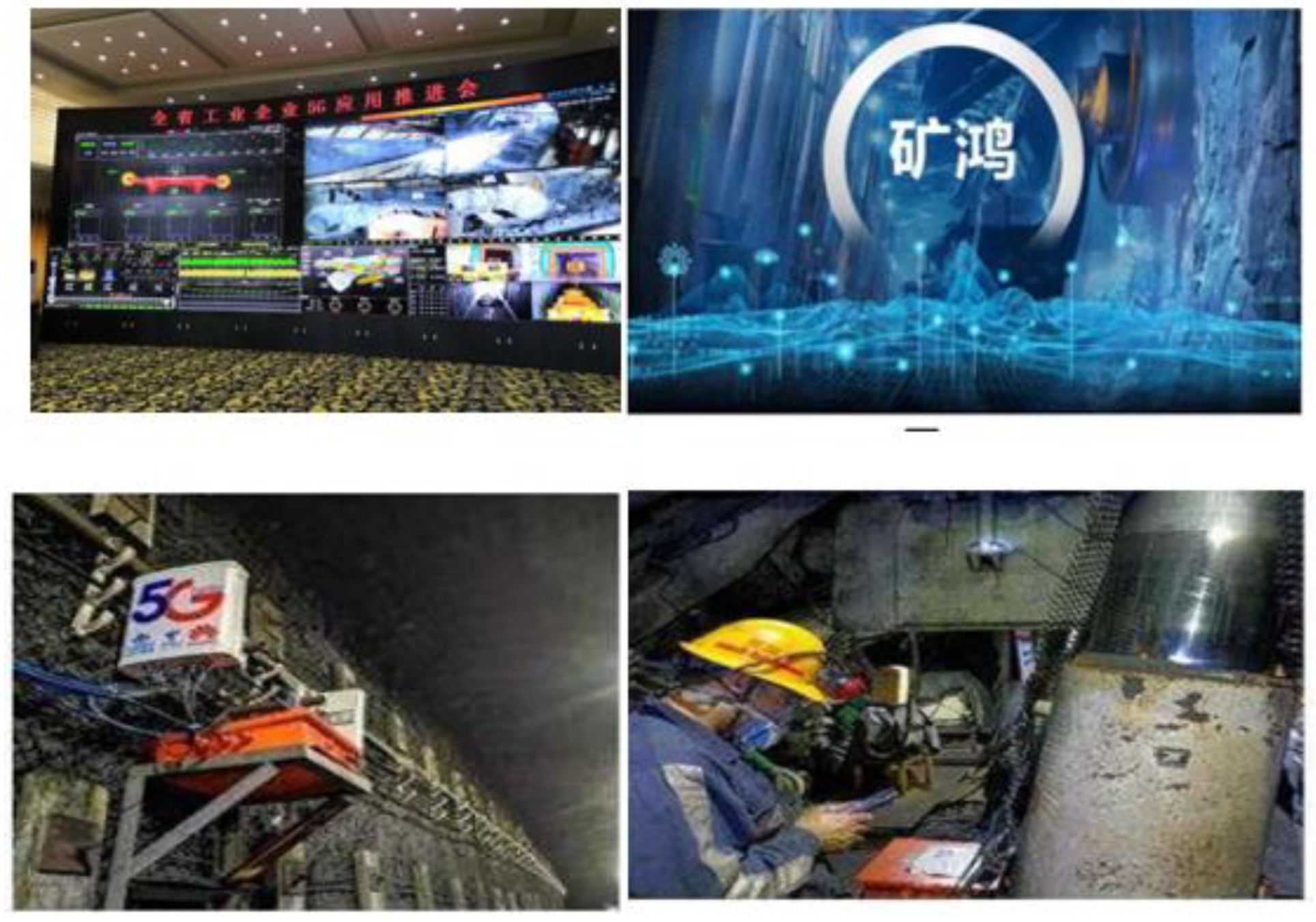
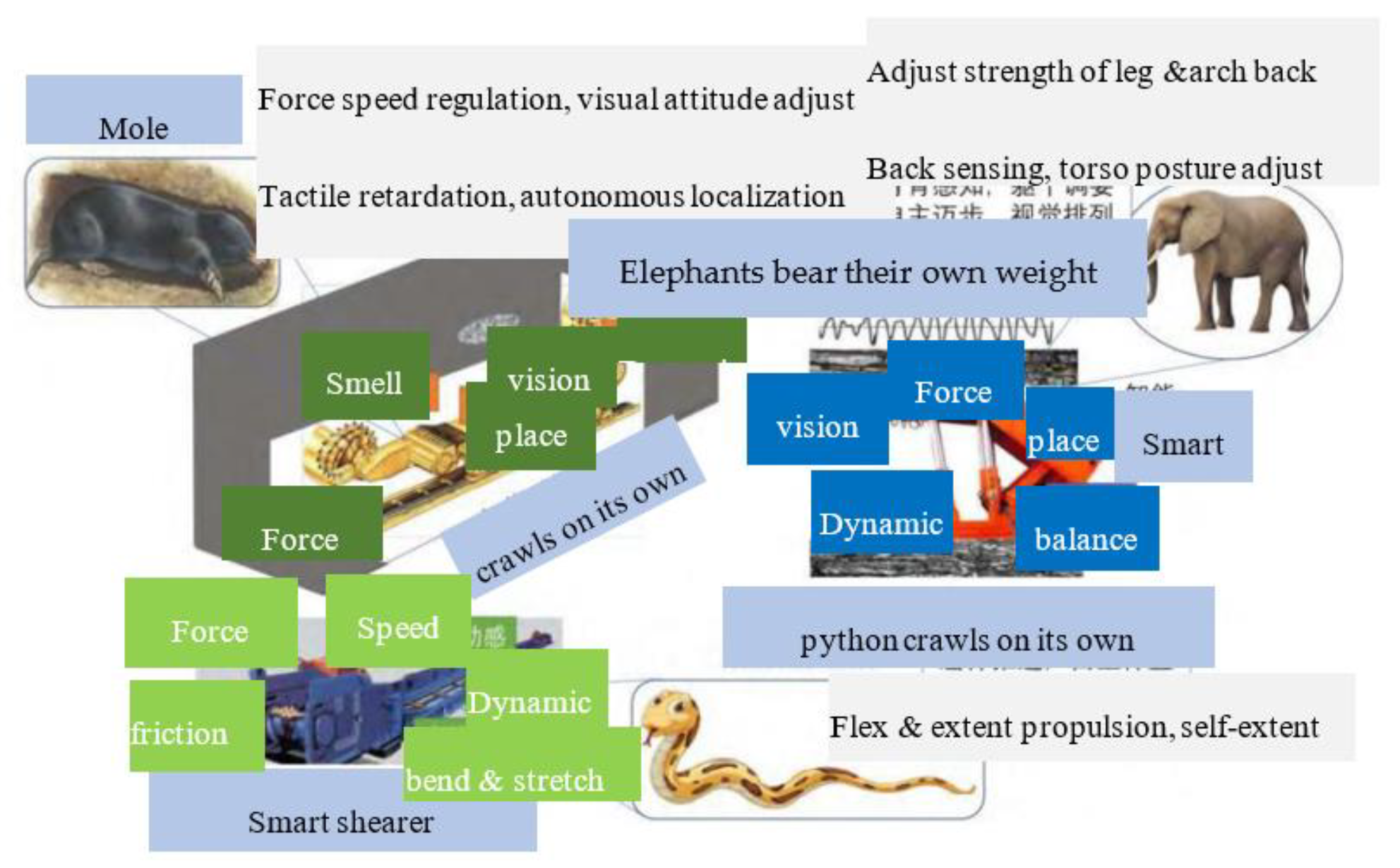
On the basis of technological breakthroughs in individual robots and successful research and development of individual robot equipment and systems, a reliability testing platform for coal mining robots and a remote intelligent operation and maintenance platform for robots have been proposed. Through reliability testing during the research and development process and online evaluation of the health status of application links, optimization design and iterative upgrading of various types of coal mining robots are achieved. At the same time, several intelligent coal mine system integration service enterprises have also developed a universal operating system for coal mine robots and a comprehensive control platform for all coal mine robots, thereby promoting the standardization, modularization, and industrial research and application of coal mine robots.
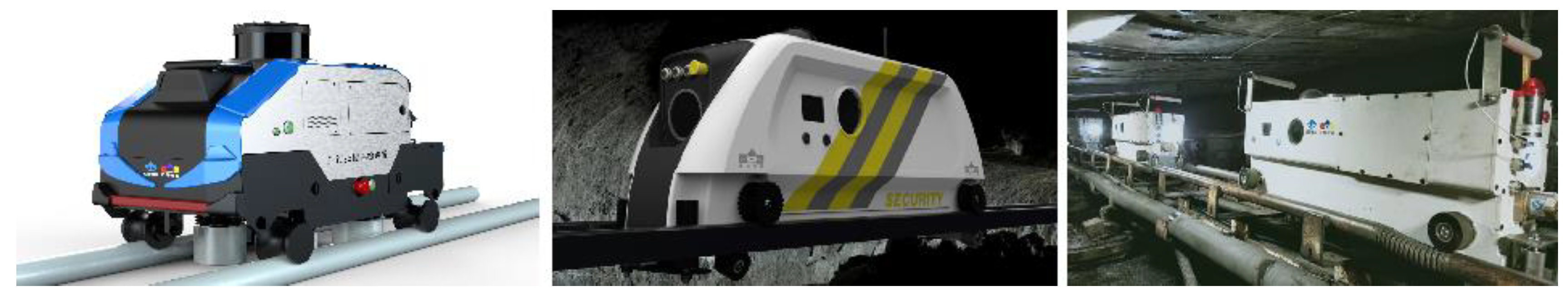
5.1. Application of inspection robots in intelligent mining control decision-making
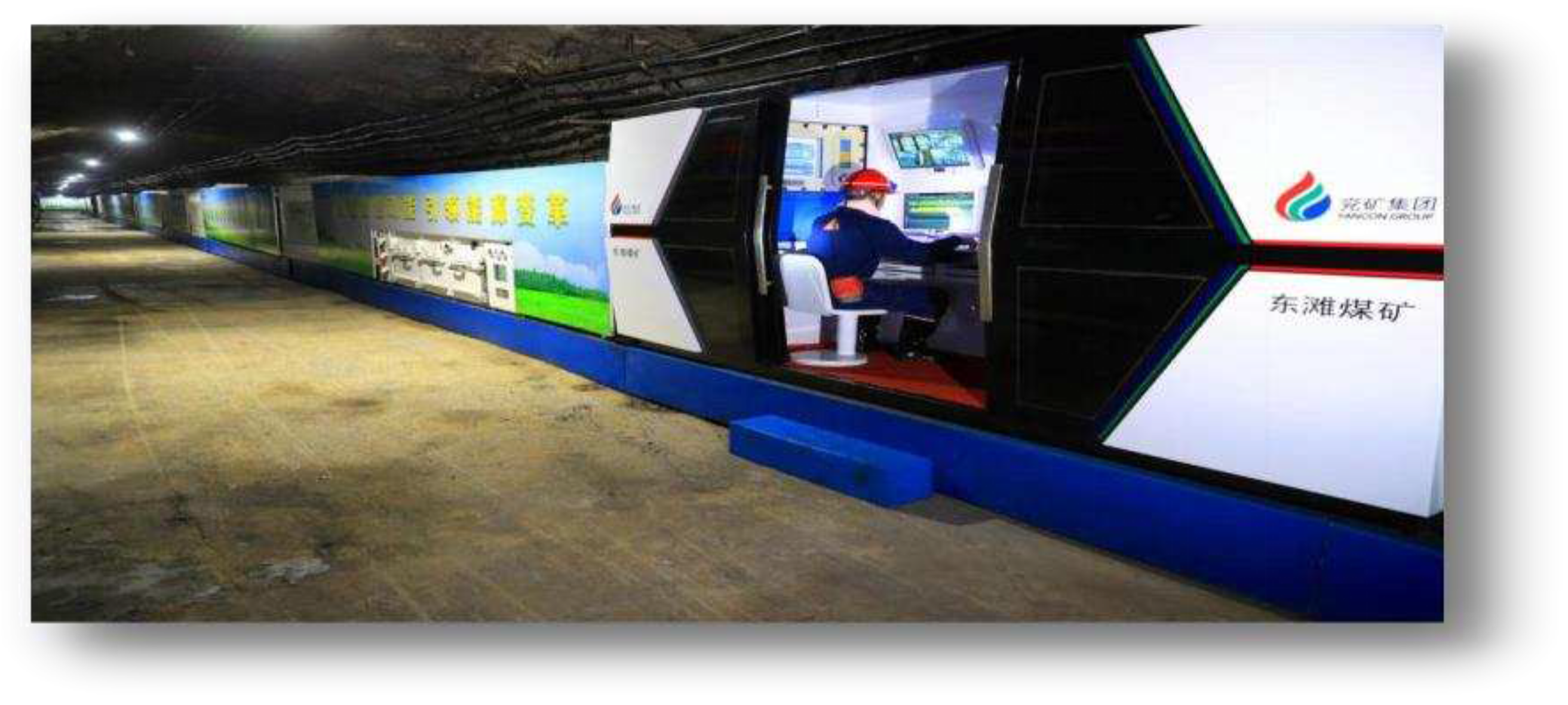
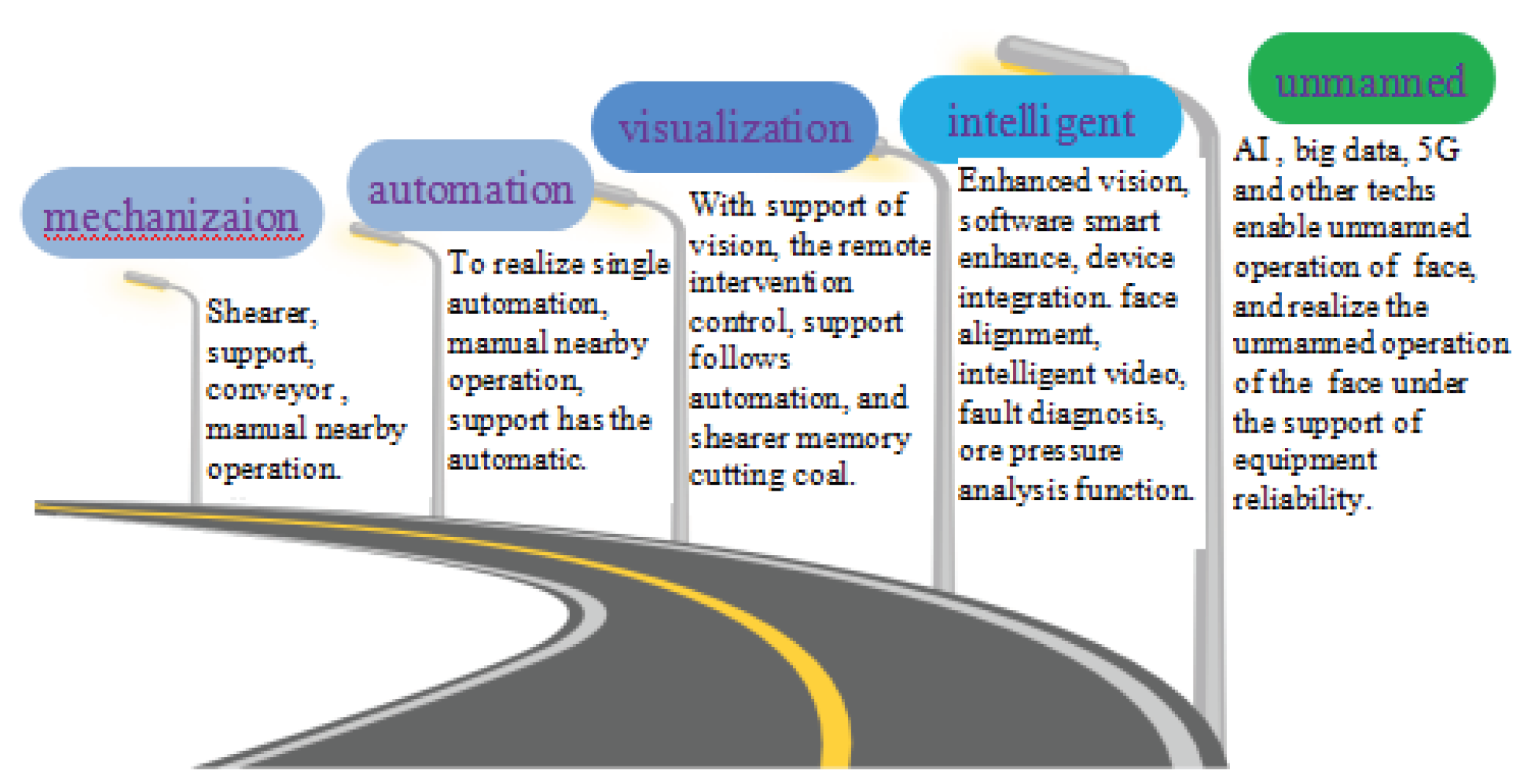
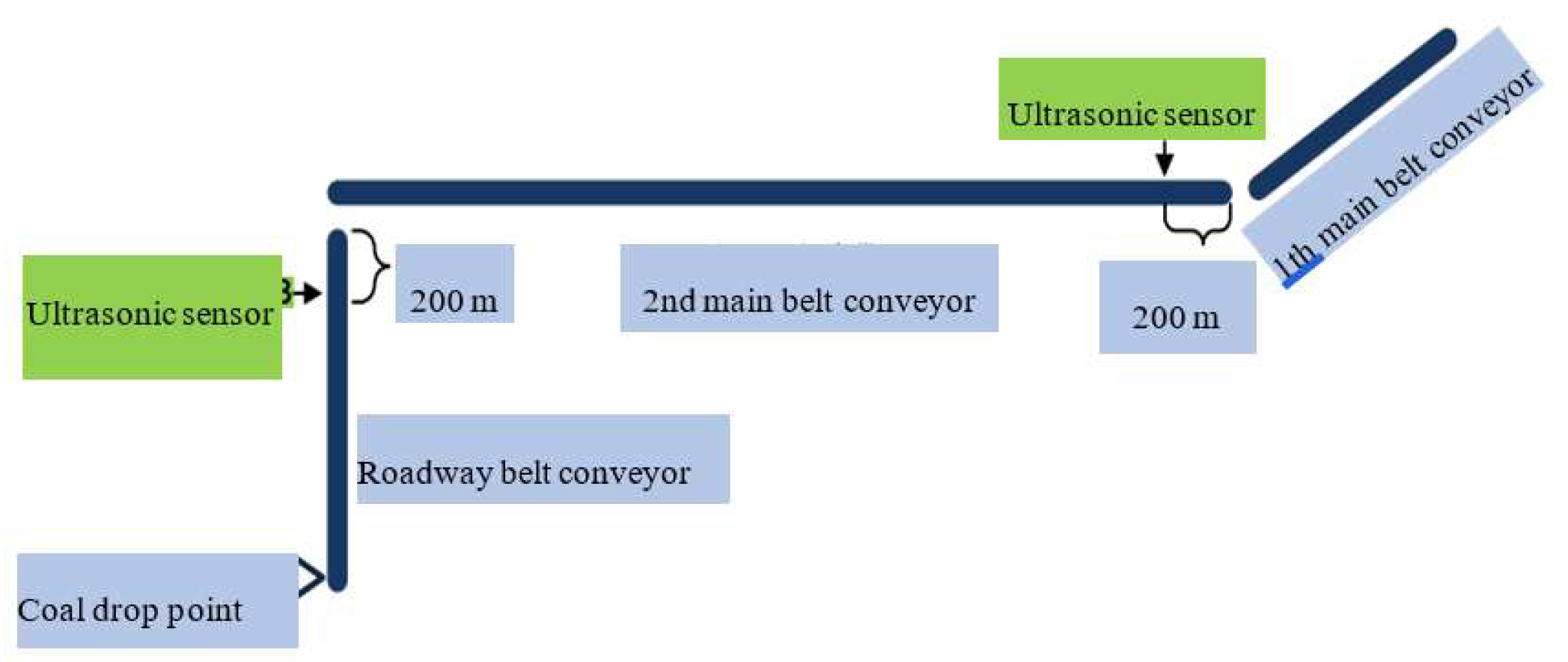
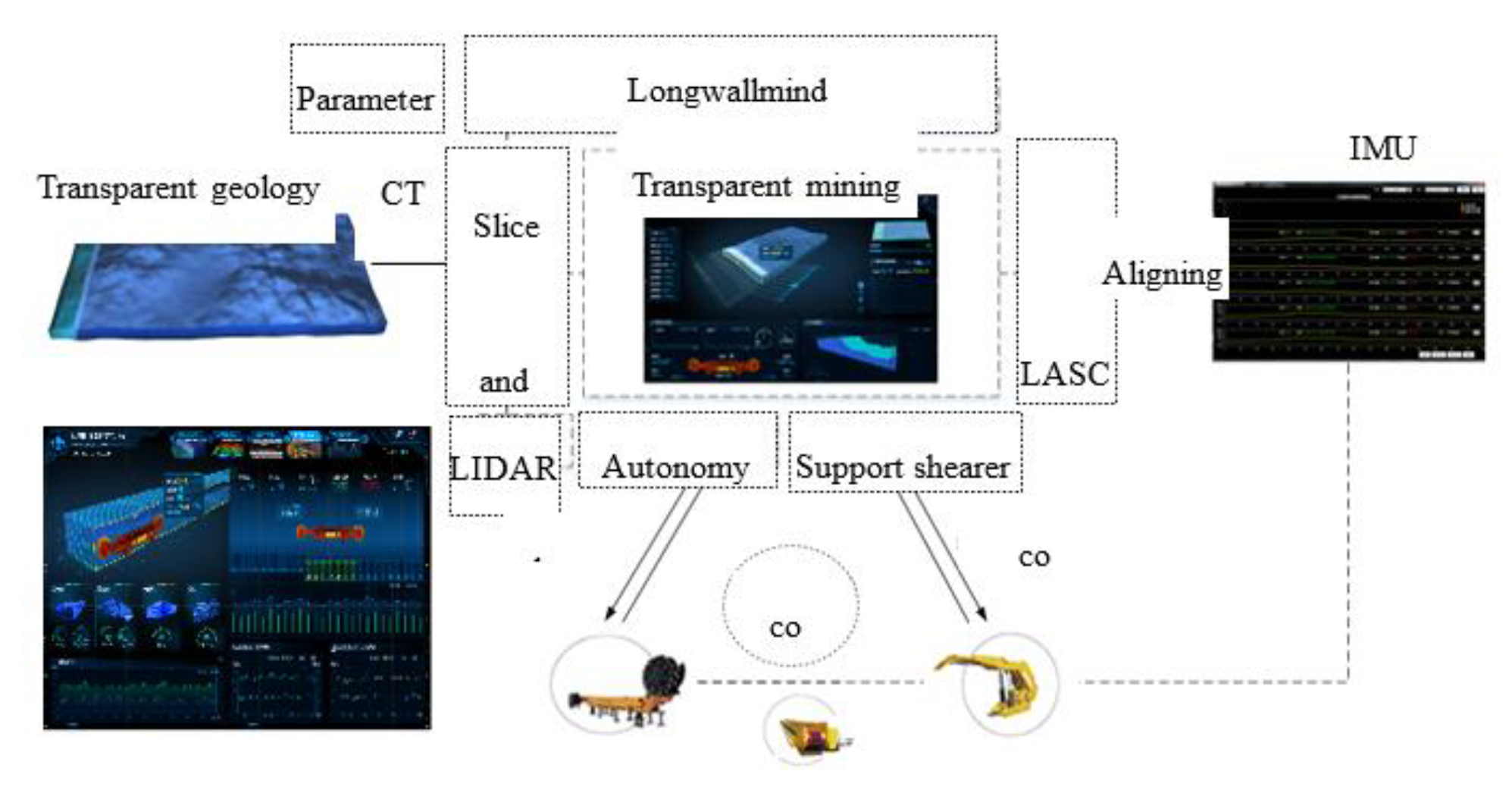
After nearly a decade of research and exploration, the current visual remote intervention mining mode has been the main mode of intelligent unmanned coal mining guided by various industry technologies, such as "unmanned operation, manned inspection", "visual immersion technology", and "transparent working face". Video monitoring technology is adopted for fully mechanized mining faces to extend human sight to the working face, freeing operators from harsh working faces to the monitoring center or ground sub controlling center. Based on real-time monitoring videos, the equipment of the fully mechanized mining face is centrally controlled, allowing the coal mining equipment of the fully mechanized mining face to possess robot characteristics. The intelligent adaptive mining mode is based on visual remote intervention technology and further enhances the development ideas of transparent mining by enhancing the capabilities of mining environment perception, intelligent decision-making, and equipment adaptive control.
Figure 12.
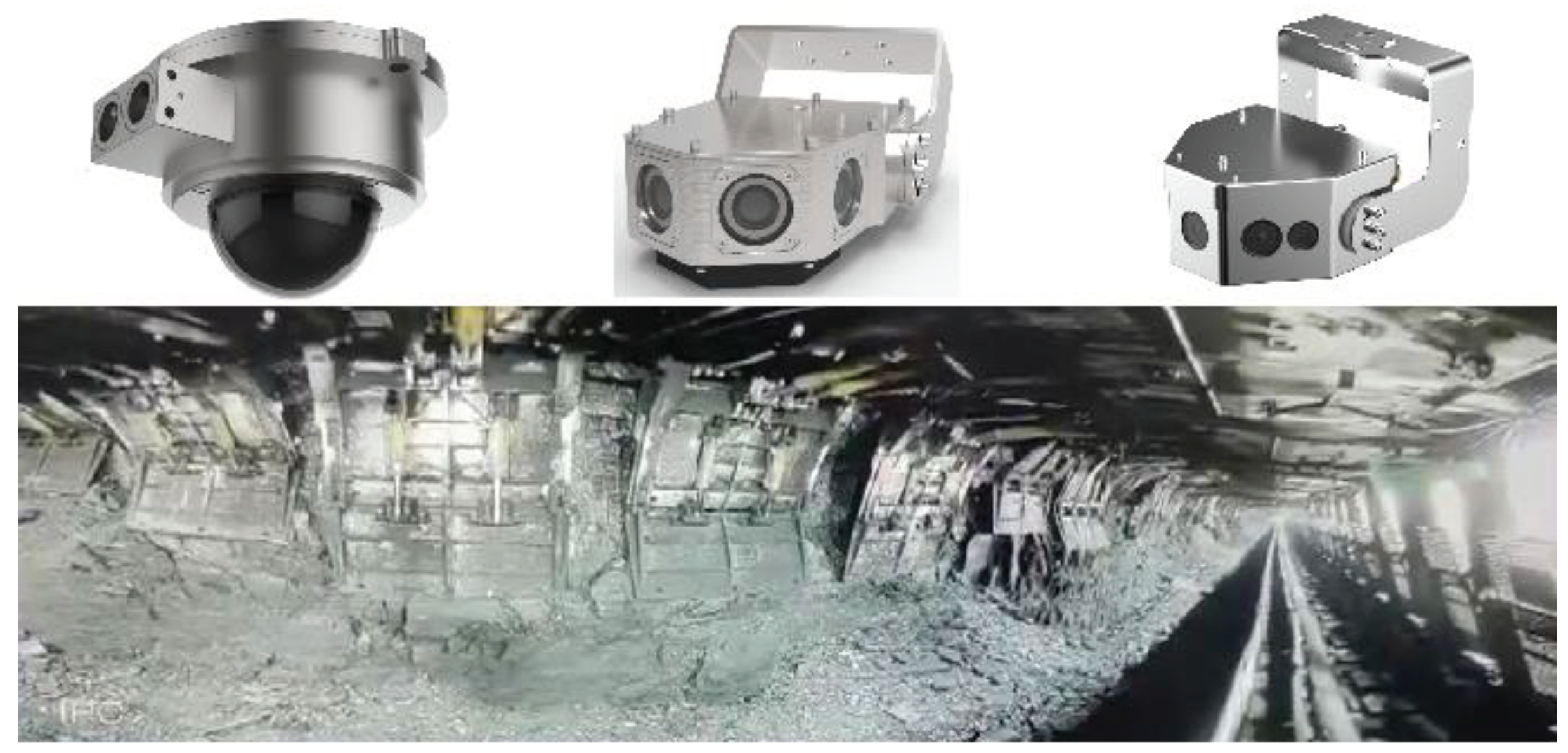
Fully mechanized mining inspection robot.
Figure 12.
Fully mechanized mining inspection robot.
The application scenarios mainly include the following aspects:
Coal mining robots can achieve greater flexibility and efficiency in remote operation and control, real-time monitoring and autonomous control, and achieve autonomous control in coal mining operations, including autonomous navigation, autonomous obstacle avoidance, and autonomous operation. Real-time monitoring and control have been achieved: robots need to monitor and control environmental parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and gas concentration, in real time during coal mining operations.
Figure 13.
Transparent geological model for a workface.
Figure 13.
Transparent geological model for a workface.
(2) Intelligent inspection: Realize the automation of robot inspection, including automatic inspection, intelligent obstacle avoidance, and fault warning, providing high-speed and stable communication support and allowing the robot to provide real-time feedback data from various equipment and sensors inside the coal mine to the control center for analysis and processing.
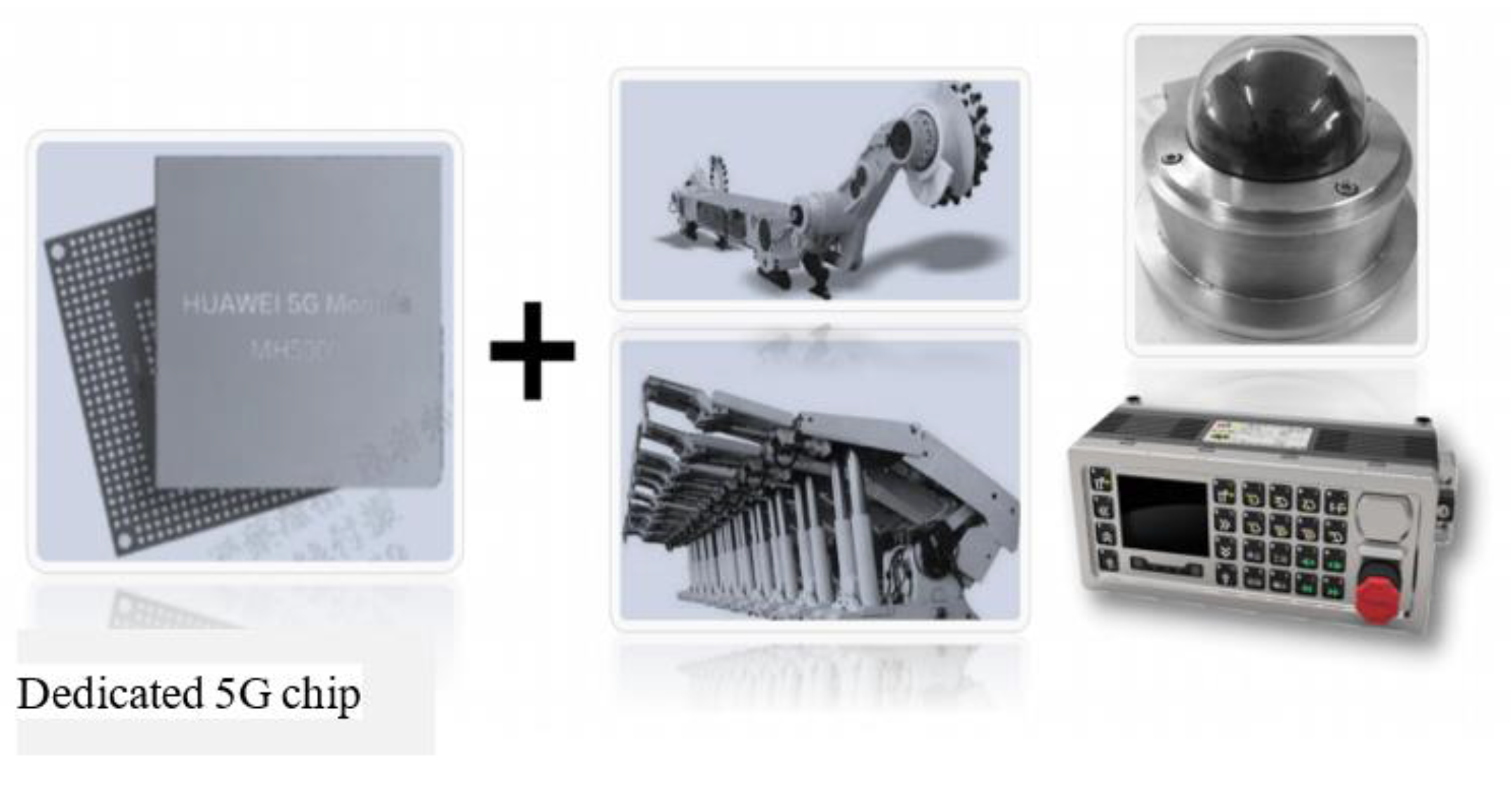
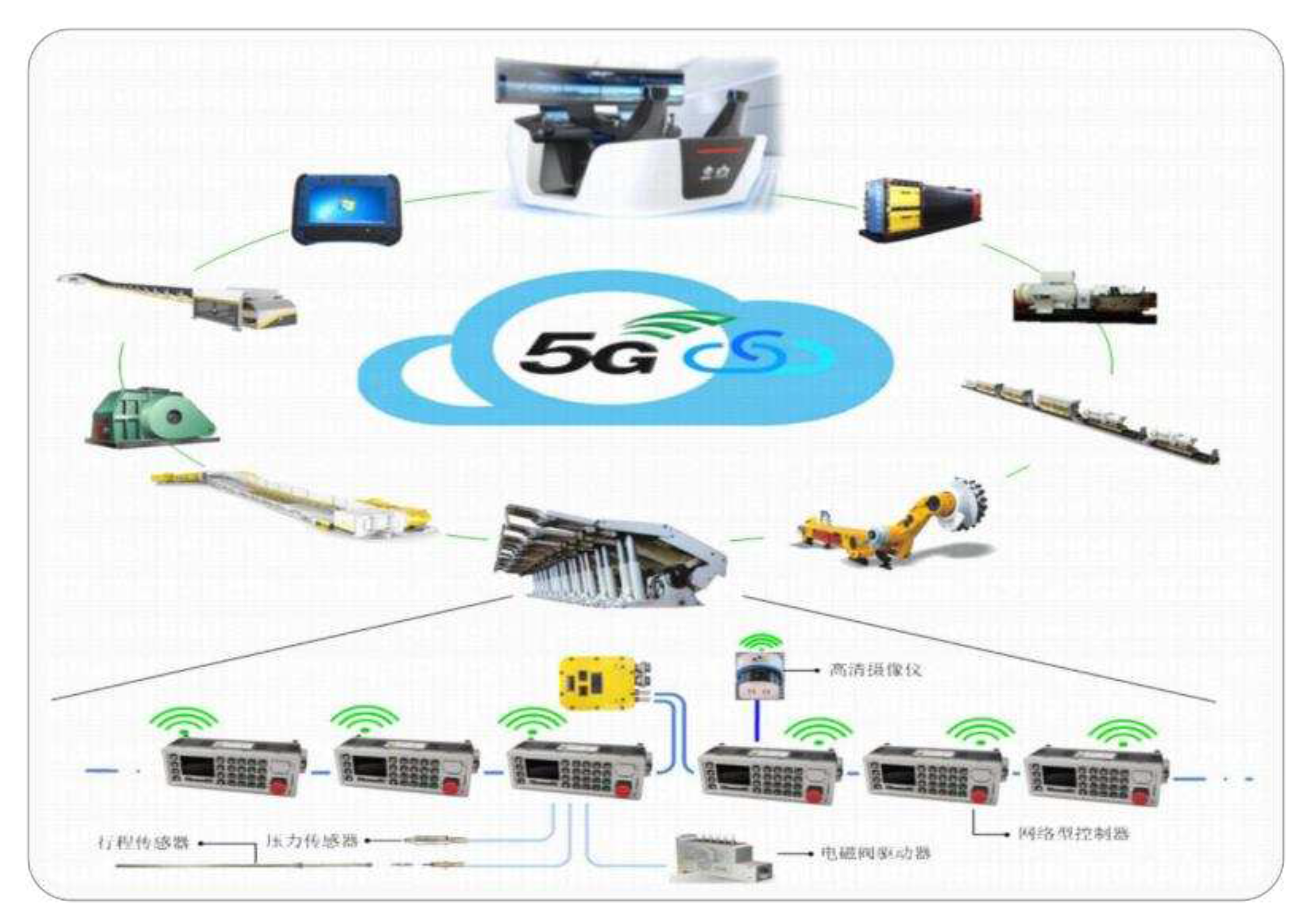
(3) Remote control and command: A network using 5G technology has a fast transmission speed and low latency, enabling remote control and control of robots, making coal mining more intelligent and automated, realizing more precise and fast remote commands, and communicating directly with on-site personnel through 5G technology to improve emergency response capabilities in emergency situations.
(4) Real-time monitoring and feedback: Autonomous path planning: Robots can cooperate with 5G networks to establish digital maps, achieve autonomous path planning and navigation, and improve transportation efficiency and accuracy.
(5) Data sharing: 5G technology can achieve data sharing among multiple robots, allowing different robots to collaborate and jointly complete coal mining tasks. The low latency communication capability and high reliability of 5G networks enable robots to perceive and control their movements and postures more accurately, improving job accuracy and safety.
(6) Internet of Things application: In fully mechanized mining faces, various devices can be connected through 5G technology to form the Internet of Things. In this way, centralized management and monitoring of the entire fully mechanized mining face can be achieved.
(7) Virtual reality technology: VR technology can provide miners with more realistic training and operating experience. The use of 5G technology can ensure the smoothness and stability of virtual reality images and improve training and operational effectiveness.
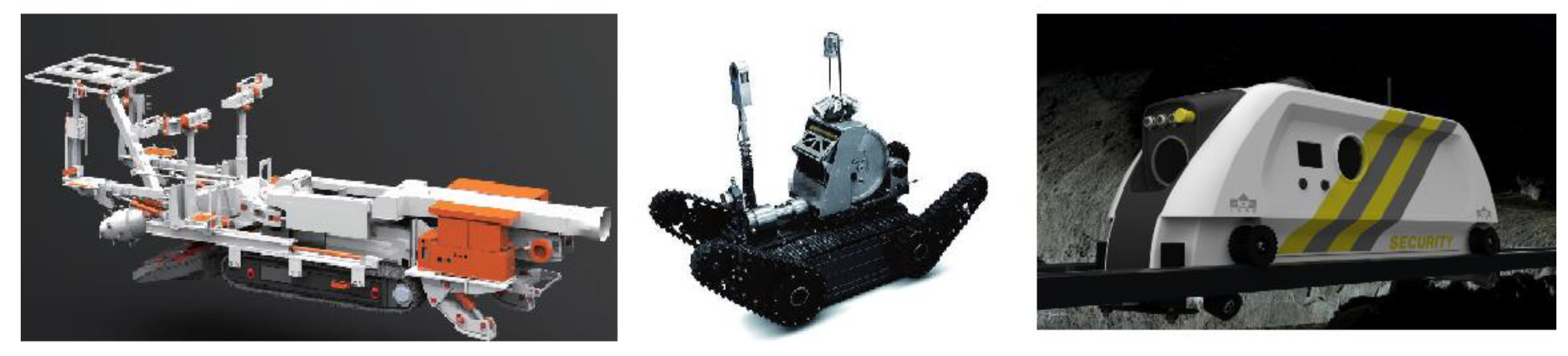
(8) Operation robots: Robots for special scenarios such as roof fall handling, advanced support, and safety detection are important auxiliary means for achieving intelligent mining.
Figure 14.
Future operation robots for coal mines.
Figure 14.
Future operation robots for coal mines.
5.2. Practice case
Moreover, the advanced automation system (ASA) and IMSC system developed by JOY in the U.S. have achieved the planning and cutting of coal cutters, significantly improving their work efficiency and programmable operational capabilities. The core of the support machine is still the electrohydraulic control system, while the transportation robot is controlled through real-time monitoring and coal flow balance.
Research on mining working faces in the CHN ENERGY Investment Group Shendong Mining Yujialiang Coal Mine, Shaanxi Coal Chemical Group Huangling Mining No.1 With respect to the coal mine, Tiandi Corporation Wangpo Coal Mine, and other coal mines, we have gained a deep understanding of the coal mining equipment and application situation of the working faces. Research has shown that encoders and rocker arm height sensors (swing angle sensors) are bottlenecks that restrict the intelligent application of shearers. Most domestic shearer manufacturers use angle sensors for rocker arm height measurements, with large errors of up to 5 cm; these sensors cannot support advanced functions such as remote control and coal cutting planning. Due to the installation of the shaft encoder outside the traveling box of the coal mining machine, the shaft encoder is easily damaged, which limits the application of coal mining machine positioning and inertial navigation. The collaboration and straightness control of support robots are key factors that constrain intelligence.
The following are successful cases of intelligent mining engineering practice in China:
(1) The Hongfa Mine in Yunnan. Intelligent mining at a height of 2.8 m has achieved an automation rate of 76% under complex geological conditions, with an average reduction of 30% (5 people) in the number of workers on the working face. By adopting automatic machines following operation, production efficiency has increased by more than 2%, achieving automatic, safe and efficient production with fewer or even unmanned machines following operations and fewer people on duty, effectively promoting the construction of intelligent mines.
(2) Face 11203 of the Ruifeng Mine. After debugging and putting into use in March 2020, the overall system was stable, with a low failure rate and normalized operation. Manual operation is not allowed in areas where conditions permit.
(3) Face 2209 (medium thick coal seam) of the Zikuang Yangjiacun Coal Mine in Zikuang. The average mining height is 2.3 m, and the working face length is 300 m. Automated cutting of triangular coal was realized, with an automation utilization rate of 70%. Usage effect: By using one centralized controller on the ground, the entire production system of the working face can be remotely controlled, reducing the number of people by more than 60% compared to the traditional fully mechanized working face of 12 in the past.
(4) Dongtan Mine 63-06 working face (large mining height). The mining height is 5.7 m, and the inclined length of the working face is 265 m, achieving the normalized application of intelligent support following operation. Usage effect: Each shift requires only 8 operators, including 1 scaffolding worker, 1 three-machine driver, 2 end workers, and 1 shift leader, reducing 8 people by 50%. Benchmarking project: The implementation of large-scale mining and normalized operation in the central and eastern regions has played a good demonstration role.
Figure 15.
Real scene of an intelligent working face in the Dongtan Coal Mine of Shandong Energy.
Figure 15.
Real scene of an intelligent working face in the Dongtan Coal Mine of Shandong Energy.
(5) Working face 4104 of the Yitai Baoshan Mine (thin coal seam). The mining height is 1.2-1.4 m, the minimum mining height is 1.25 m, and the inclined length of the working face is 240 m. Implementation situation: The intelligent operation of the working face equipment is normal, with a support and machine usage rate of up to 96.9%, an average daily coal cutting of 12 knives, and a daily production of 4500 tons. Application effect: The number of operators on the working face was reduced from 10-12 to 5-6, a reduction of more than 60%.
(6) Wangjialing Mine 12309 face (top coal caving). It was officially produced on August 23, 2019, and successfully implemented the application of four automatic coal caving technologies. The concept of "prerelease detection, identification during release, and postrelease monitoring" was developed. Application effect: Since the operation of the working face was normalized, the number of personnel in the first team of the Wangjialing Mine has been reduced from 100 to 75, a decrease of 24.8%. The project successfully passed the acceptance of the intelligent mining technology research project for top coal caving on July 9, 2020.
Figure 16.
Real view of the intelligent working face.
Figure 16.
Real view of the intelligent working face.
(7) Working face 8202 of the Tongxin Mine (top coal caving). The strike length is 2184.5 m, the inclined length is 200 m, the mining height is 3.9 m, the mining and drainage ratio is 1:2.91, and the coal seam dip angle is 1-2°. The normalization of the full face machine was achieved following automation and one click start stop, personnel were reduced, efficiency was increased, and production efficiency was increased by 10%.
(8) The 220704 working face of the Ningmei Zaoquan Coal Mine (with complex geological conditions). Basic situation: The length of the working face is 284.6 m, and the average mining height is 3.85 m. The problem of controlling the upward and downward movements of inclined working face equipment was solved, and an upward bottom sweeping knife and a downward top cutting knife were used for high-definition video. Application effect: A maximum of 13 coal cuts were achieved per day, and only one monitoring operator was placed on the working face.
(9) Dabaoding Coal Mine (large-angle complex coal seam). The average inclination angle is 26°, which is the first intelligent project in the southwest region with a large inclination angle. The authors achieved linkage between the anti-overturning oil cylinder of the support and the anti-slip oil cylinder of the scraper machine, thus achieving normalization of the following machine. Usage effect: The comprehensive mining team has a single shift of production workers, with only 3 people following the machine for inspection. On April 8, 2021, the "Intelligent System Project for Large Dip Complex Working Faces" of the Sichuan Coal Group successfully passed the acceptance meeting at the Dabaoding Mine project of the Panzhihua Coal Company.