Submitted:
07 February 2024
Posted:
07 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
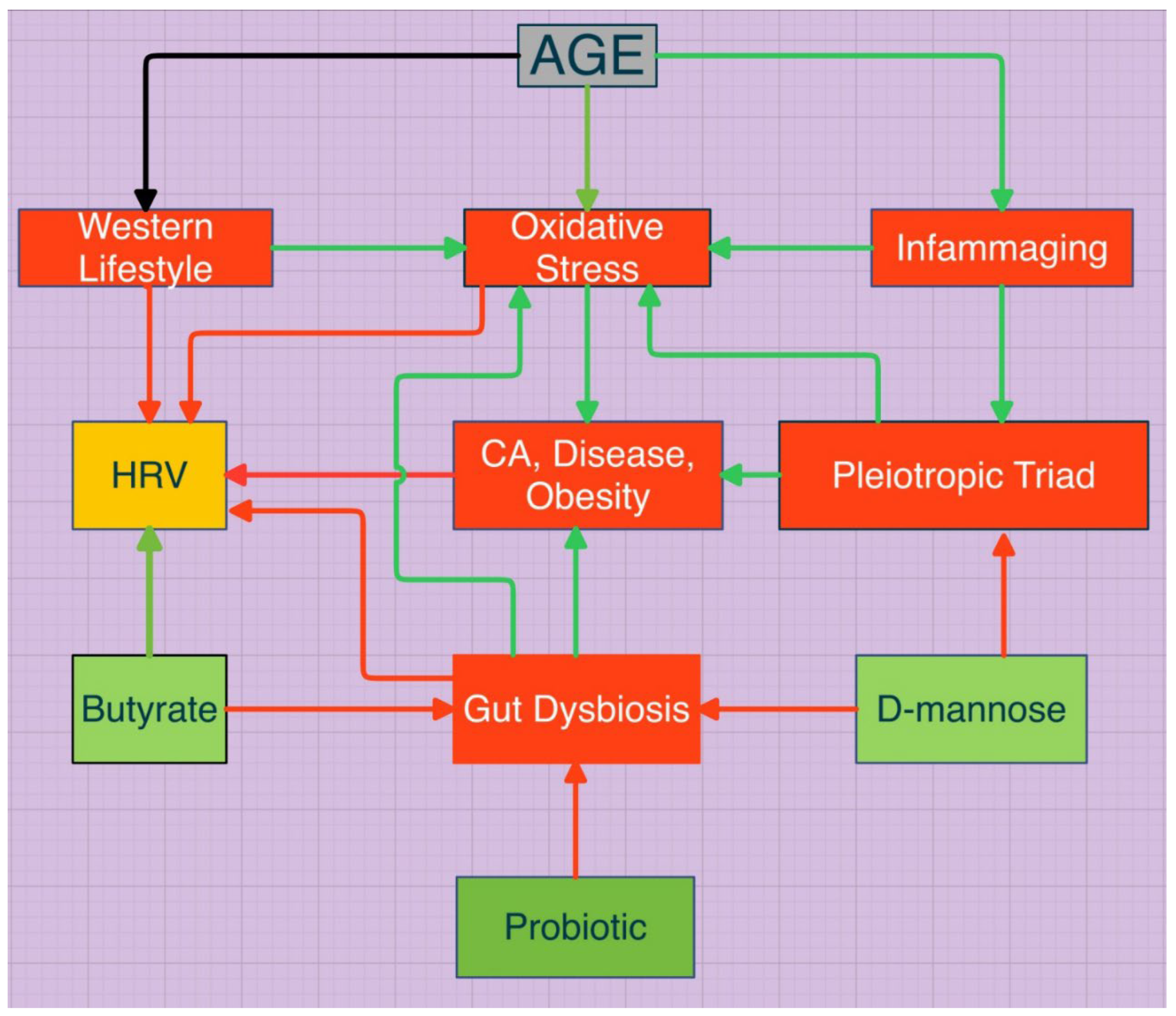
1. Oxidative Stress and Gut Dysbiosis
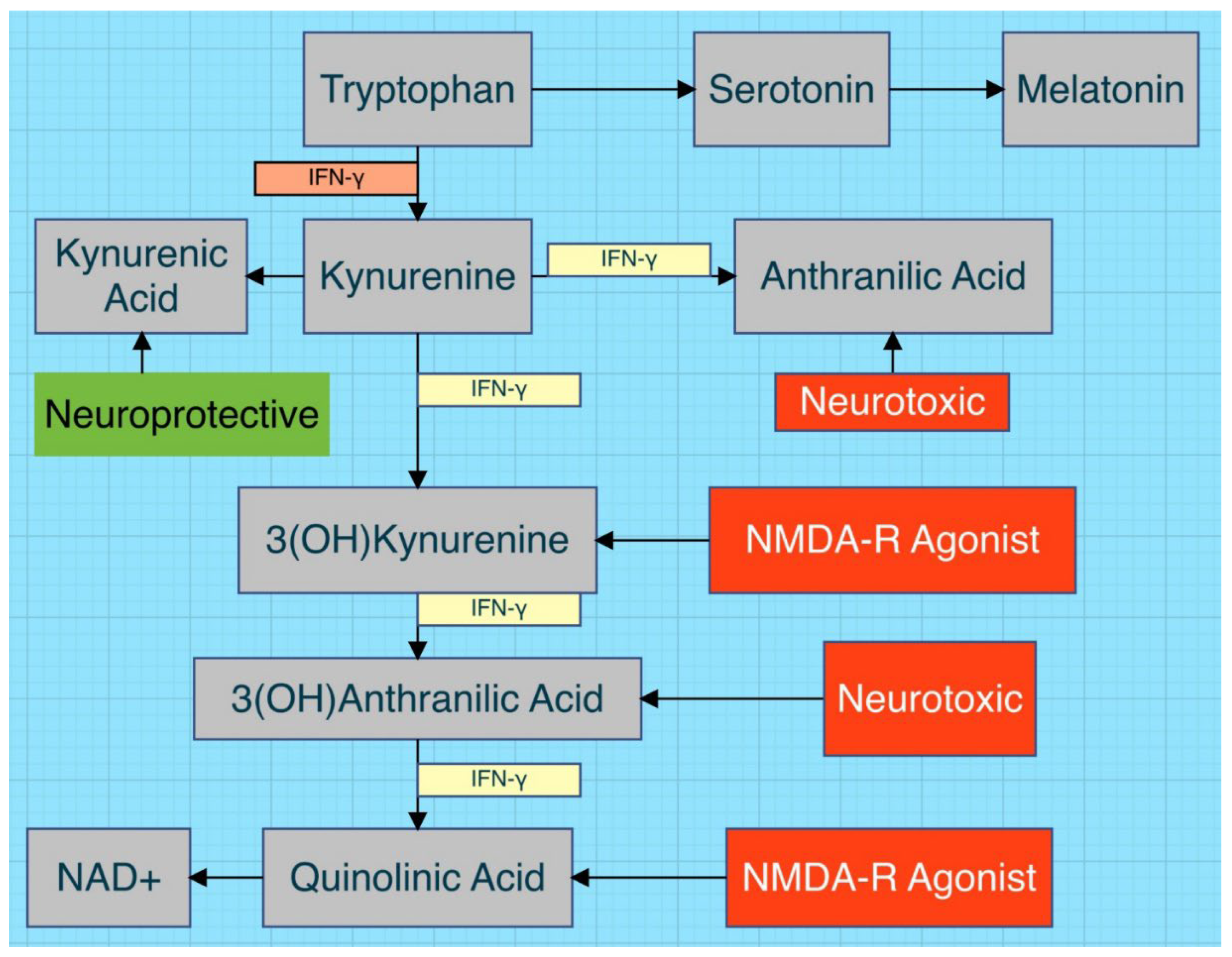
2. Altered Tryptophan Metabolism (ATM) and KTR
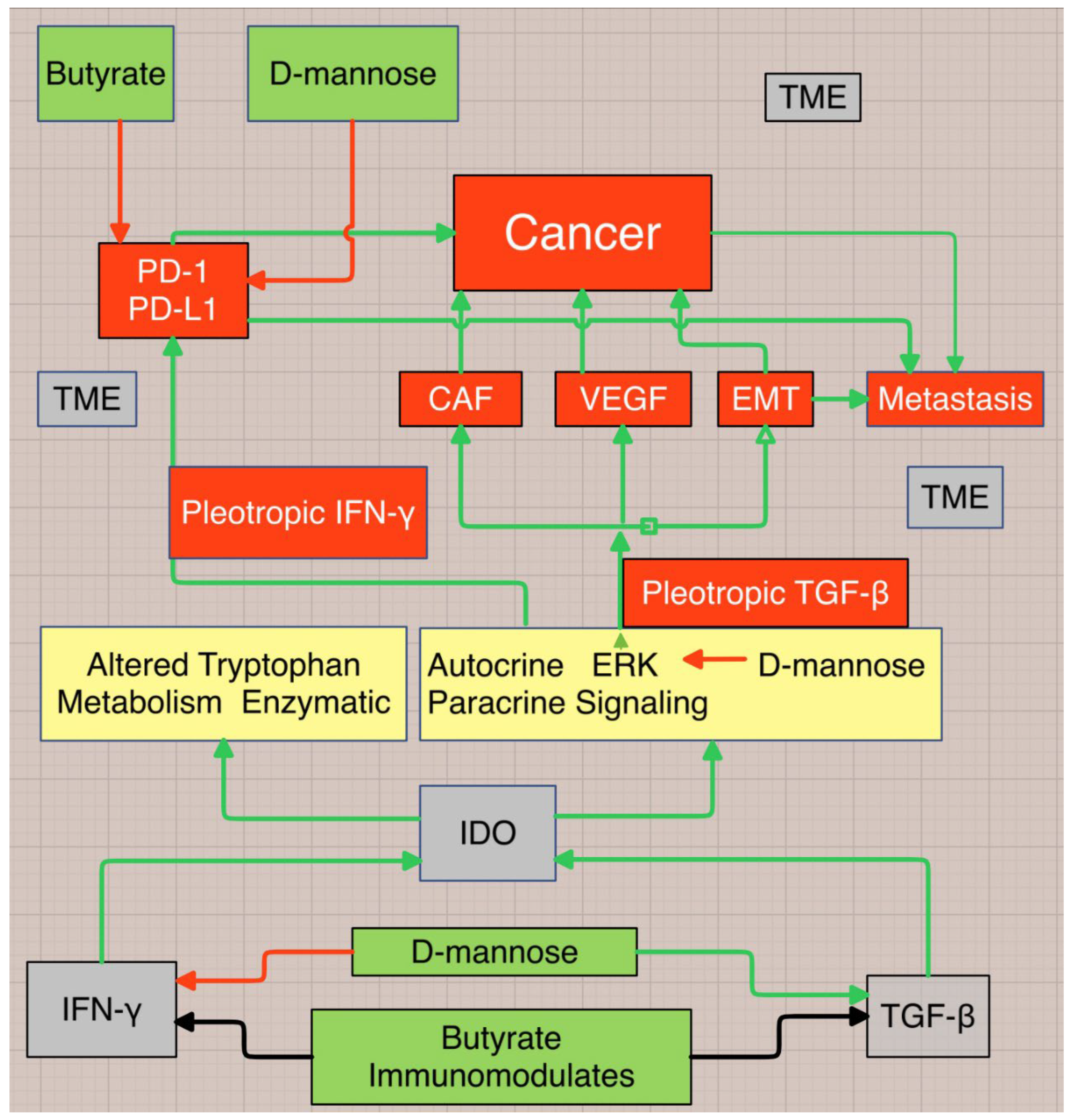
3. IFN-γ and TGF-β
4. GPCR
A. GPCR and SARS Cov2
B. GPCR and Gut Dysbiosis
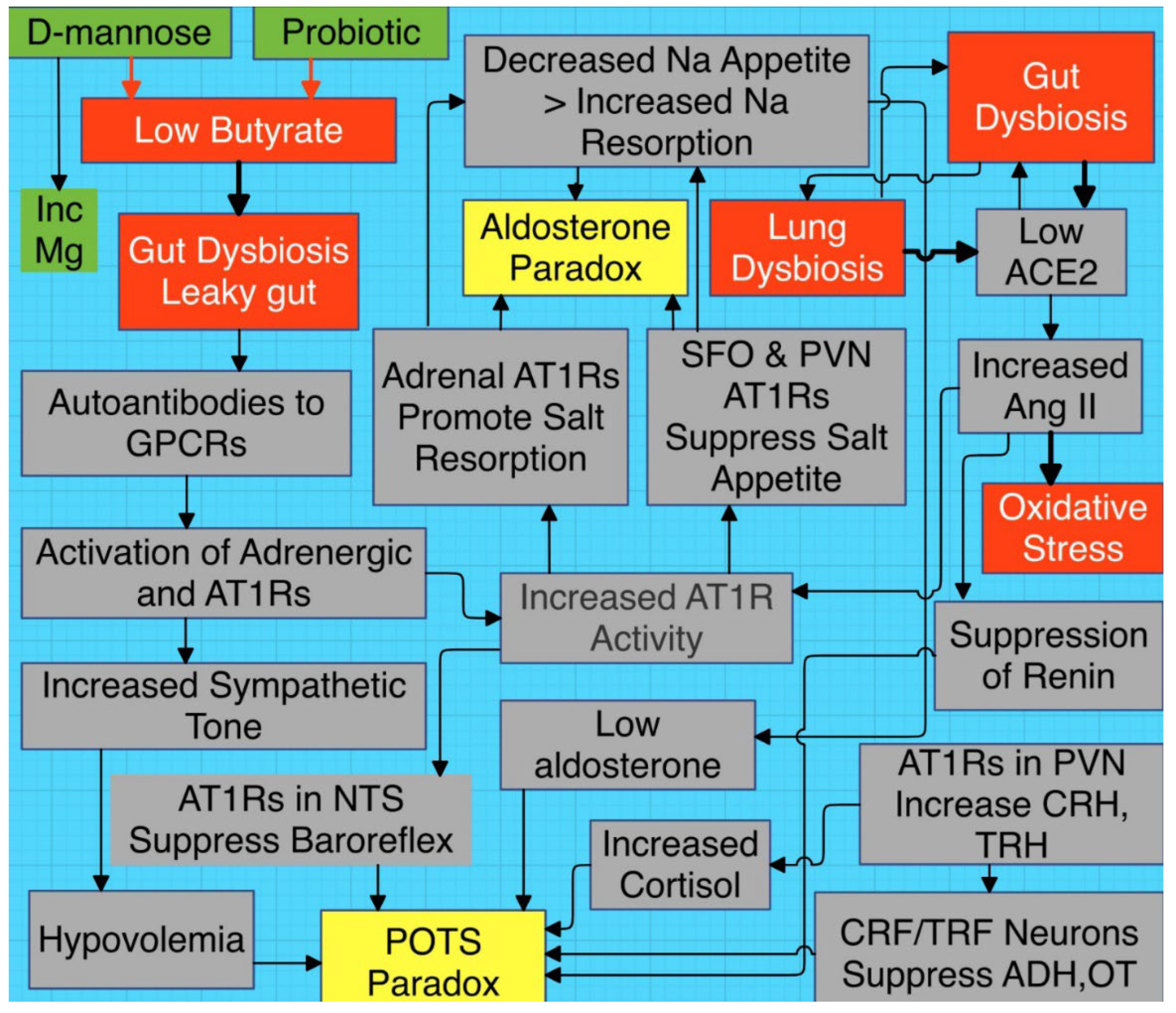
5. HRV and the Triple Play
A. HRV
B. Triple Play
Conclusion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flaherty RL, Owen M, Fagan-Murphy A, Intabli H, Healy D, Patel A, et al. Glucocorticoids induce production of reactive oxygen species/reactive nitrogen species and DNA damage through an iNOS mediated pathway in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Mar 24;19(1):35. [CrossRef]
- Yang HL, Li MM, Zhou MF, Xu HS, Huan F, Liu N, et al. Links Between Gut Dysbiosis and Neurotransmitter Disturbance in Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Depressive Behaviours: the Role of Inflammation. Inflammation. 2021 Dec;44(6):2448-2462. [CrossRef]
- Shandilya S, Kumar S, Kumar Jha N, Kumar Kesari K, Ruokolainen J. Interplay of gut microbiota and oxidative stress: Perspective on neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. J Adv Res. 2021 Sep 17;38:223-244. [CrossRef]
- den Besten G, van Eunen K, Groen AK, Venema K, Reijngoud DJ, Bakker BM. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J Lipid Res. 2013 Sep;54(9):2325-40. [CrossRef]
- Liu H, Wang J, He T, Becker S, Zhang G, Li D, Ma X. Butyrate: A Double-Edged Sword for Health? Adv Nutr. 2018 Jan 1;9(1):21-29. [CrossRef]
- Ridler, C. Acetate promotes obesity via a gut–brain–β-cell axis. Nat Rev Endocrinol 12, 436 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Lin HV, Frassetto A, Kowalik Jr EJ, Nawrocki AR, Lu MM, Kosinski JR, et al. (2012) Butyrate and Propionate Protect against Diet-Induced Obesity and Regulate Gut Hormones via Free Fatty Acid Receptor 3-Independent Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 7(4): e35240. [CrossRef]
- Psichas, A. Sleeth, M., Murphy, K. et al. The short chain fatty acid propionate stimulates GLP-1 and PYY secretion via free fatty acid receptor 2 in rodents. Int J Obes 39, 424–429 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Yadav H, Lee JH, Lloyd J, Walter P, Rane SG. Beneficial metabolic effects of a probiotic via butyrate-induced GLP-1 hormone secretion. J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 30;288(35):25088-25097. [CrossRef]
- Bose S, Ramesh V, Locasale JW. Acetate Metabolism in Physiology, Cancer, and Beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2019 Sep;29(9):695-703. [CrossRef]
- Grignon, S.; Deslauriers, J. (2015). The Reciprocal Effects of Oxidative Stress and Glutamate Neurotransmission. Medicine, Biology. [CrossRef]
- Baj A, Moro E, Bistoletti M, Orlandi V, Crema F, Giaroni C. Glutamatergic Signaling Along The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 25;20(6):1482. [CrossRef]
- Sas K, Szabó E, Vécsei L. Mitochondria, Oxidative Stress and the Kynurenine System, with a Focus on Ageing and Neuroprotection. Molecules. 2018; 23(1):191. [CrossRef]
- Benech N, Rolhion N, Sokol H. Tryptophan metabolites get the gut moving. Cell Host Microbe. 2021 Feb 10;29(2):145-147. [CrossRef]
- Roager, H.M. Licht, T.R. Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease. Nat Commun 9, 3294 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Zhou Y, Chen Y, He H, Peng M, Zeng M, Sun H. The role of the indoles in microbiota-gut-brain axis and potential therapeutic targets: A focus on human neurological and neuropsychiatric diseases. Neuropharmacology. 2023 Nov 15;239:109690. [CrossRef]
- Liu JJ, Ching J, Wee HN, Liu S, Gurung RL, Lee J, et al., Subramaniam T, Sum CF, Sharma K, Kestenbaum BR, Lim SC. Plasma Tryptophan-Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites and Risk for Progression to End-Stage Kidney Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2023 Dec 1;46(12):2223-2231. [CrossRef]
- Ye X, Li H, Anjum K, Zhong X, Miao S, Zheng G, Liu W, Li L. Dual Role of Indoles Derived From Intestinal Microbiota on Human Health. Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 17;13:903526. [CrossRef]
- Gietl M, Burkert F, Seiwald S, Böhm A, Hofer S, Gostner JM, et al. Interferon-gamma Mediated Metabolic Pathways in Hospitalized Patients During Acute and Reconvalescent COVID-19. Int J Tryptophan Res. 2023 Feb 13;16:11786469231154244. [CrossRef]
- Booij, L., Swenne, C.A., Brosschot, J.F., Haffmans, P.M., Thayer, J.F., & van der Does, A.J. (2006). Tryptophan Depletion Affects Heart Rate Variability and Impulsivity in Remitted Depressed Patients with a History of Suicidal Ideation. Biological Psychiatry, 60, 507-514. [CrossRef]
- Zahar S, Schneider N, Makwana A, Chapman S, Corthesy J, Amico M, et al. Dietary tryptophan-rich protein hydrolysate can acutely impact physiological and psychological measures of mood and stress in healthy adults. Nutr Neurosci. 2023 Apr;26(4):303-312. [CrossRef]
- Gáspár R, Halmi D, Demján V, Berkecz R, Pipicz M, Csont T. Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites as Potential Clinical Biomarkers in Coronary Artery Disease. Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 8;12:768560. [CrossRef]
- Lund A, Nordrehaug JE, Slettom G, Solvang SH, Pedersen EK, Midttun Ø, et al. Plasma kynurenines and prognosis in patients with heart failure. PLoS One. 2020 Jan 10;15(1):e0227365. [CrossRef]
- Marx, W. McGuinness, A.J., Rocks, T. et al. The kynurenine pathway in major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of 101 studies. Mol Psychiatry 26, 4158–4178 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Heylen A, Vermeiren Y, Kema IP, van Faassen M, van der Ley C, Van Dam D, et al. Brain Kynurenine Pathway Metabolite Levels May Reflect Extent of Neuroinflammation in ALS, FTD and Early Onset AD. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(4):615. [CrossRef]
- Chen P, Geng X. Research progress on the kynurenine pathway in the prevention and treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2225800. [CrossRef]
- Lovelace MD, Varney B, Sundaram G, Lennon MJ, Lim CK, Jacobs K, et al. Recent evidence for an expanded role of the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism in neurological diseases. Via Neuropharmacology. 2017 Jan;112(Pt B):373-388. [CrossRef]
- Ala, M. The footprint of kynurenine pathway in every cancer: a new target for chemotherapy. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 5;896:173921. [CrossRef]
- Mangoni AA, Zinellu A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism in rheumatic diseases. Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 23;14:1257159. [CrossRef]
- Eryavuz Onmaz, D. Tezcan, D., Yilmaz, S. et al. Altered kynurenine pathway metabolism and association with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus. Amino Acids 55, 1937–1947 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Eller, S.K. Däubener, W. (2015). Role of Kynurenine Pathway in Infections. In: Mittal, S. (eds) Targeting the Broadly Pathogenic Kynurenine Pathway. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Darcy CJ, Davis JS, Woodberry T, McNeil YR, Stephens DP, Yeo TW, Anstey NM. An observational cohort study of the kynurenine to tryptophan ratio in sepsis: association with impaired immune and microvascular function. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21185. [CrossRef]
- Fadhilah F, Indrati AR, Dewi S, Santoso P. The Kynurenine/Tryptophan Ratio as a Promising Metabolomic Biomarker for Diagnosing the Spectrum of Tuberculosis Infection and Disease. Int J Gen Med. 2023 Nov 28;16:5587-5595. [CrossRef]
- Lionetto L, Ulivieri M, Capi M, De Bernardini D, Fazio F, Petrucca A, et al. Increased kynurenine-to-tryptophan ratio in the serum of patients infected with SARS-CoV2: An observational cohort study. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021 Mar 1;1867(3):166042. [CrossRef]
- Jin B, Singh R, Ha SE, Zogg H, Park PJ, Ro S. Pathophysiological mechanisms underlying gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with COVID-19. World J Gastroenterol. 2021 May 21;27(19):2341-2352. [CrossRef]
- Croitoru-Lamoury J, Lamoury FMJ, Caristo M, Suzuki K, Walker D, Takikawa O, et al. (2011) Interferon-γ Regulates the Proliferation and Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Activation of Indoleamine 2,3 Dioxygenase (IDO). PLoS ONE 6(2): e14698. [CrossRef]
- Chouraki V, Preis SR, Yang Q, Beiser A, Li S, Larson MG, et al. Association of amine biomarkers with incident dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in the Framingham Study. Alzheimers Dement. 2017 Dec;13(12):1327-1336. [CrossRef]
- Strober W, Kelsall B, Fuss I, Marth T, Ludviksson B, Ehrhardt R, Neurath M. Reciprocal IFN-gamma and TGF-beta responses regulate the occurrence of mucosal inflammation. Immunol Today. 1997 Feb;18(2):61-4. [CrossRef]
- Gauthier T, Chen W. IFN-γ and TGF-β, Crucial Players in Immune Responses: A Tribute to Howard Young. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2022 Dec;42(12):643-654. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9917322/. [CrossRef]
- Elkoshi, Z. Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases: A Tale of Two Immunological Opposites? Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 25;13:821598. [CrossRef]
- Stoff R, Wolf Y, Boursi B. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation as a Cancer Therapeutic. Cancer J. 2023 Mar-Apr 01;29(2):102-108. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Liu M, Zhao M, Li P, Gao C, Fan X, Cai G, Lu Q, Chen X. Fecal microbiota transplantation for the management of autoimmune diseases: Potential mechanisms and challenges. J Autoimmun. 2023 Dec;141:103109. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Yang, F., Zhang, S. et al. Genetic and environmental factors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and promising therapeutic intervention via fecal microbiota transplantation. npj Parkinsons Dis. 7, 70 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamed, E.F. Ibrahim, M.N., Mostafa, N.E. et al. Role of interferon gamma in SARS-CoV-2-positive patients with parasitic infections. Gut Pathog 13, 29 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Cremoni M, Allouche J, Graça D, Zorzi K, Fernandez C, Teisseyre M, et al. Low baseline IFN-γ response could predict hospitalization in COVID-19 patients. Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 26;13:953502. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Gomes, M. Kruglov, A., Durek, P. et al. SARS-CoV-2 in severe COVID-19 induces a TGF-β-dominated chronic immune response that does not target itself. Nat Commun 12, 1961 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. A potential treatment of COVID-19 with TGF-β blockade. Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Apr 21;16(11):1954-1955. [CrossRef]
- Wang XF, Wang HS, Wang H, Zhang F, Wang KF, Guo Q, et al. The role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) in immune tolerance: focus on macrophage polarization of THP-1 cells. Cell Immunol. 2014 May-Jun;289(1-2):42-8. [CrossRef]
- Pallotta MT, Rossini S, Suvieri C, Coletti A, Orabona C, Macchiarulo A, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1): an up-to-date overview of an eclectic immunoregulatory enzyme. FEBS J. 2022 Oct;289(20):6099–6118. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. IDO: more than an enzyme. Nat Immunol 12, 809–811 (2011). [CrossRef]
- Ye Z, Yue L, Shi J, Shao M, Wu T. Role of IDO and TDO in Cancers and Related Diseases and the Therapeutic Implications. J Cancer. 2019 Jun 2;10(12):2771-2782. [CrossRef]
- Chung JY, Chan MK, Li JS, Chan AS, Tang PC, Leung KT, et al. TGF-β Signaling: From Tissue Fibrosis to Tumor Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 15;22(14):7575. [CrossRef]
- Sri-Ngern-Ngam K, Keawvilai P, Pisitkun T, Palaga T. Upregulation of programmed cell death 1 by interferon gamma and its biological functions in human monocytes. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Oct 17;32:101369. [CrossRef]
- Jorgovanovic D, Song M, Wang L, Zhang Y. Roles of IFN-γ in tumor progression and regression: a review. Biomark Res. 2020 Sep 29;8:49. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Han, F., Du, Y. et al. Hypoxic microenvironment in cancer: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Sig Transduct Target Ther 8, 70 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Numata Y, Akutsu N, Ishigami K, Koide H, Wagatsuma K, Motoya M, Sasaki S, Nakase H. Synergistic effect of IFN-γ and IL-1β on PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 May 5;30:101270. [CrossRef]
- Ehanire T, Ren L, Bond J, Medina M, Li G, Bashirov L, et al. Angiotensin II stimulates canonical TGF-β signaling pathway through angiotensin type 1 receptor to induce granulation tissue contraction. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015 Mar;93(3):289-302. [CrossRef]
- Pujantell M, Skenteris NT, Claussen JM, Grünhagel B, Thiele RJ, Altfeld M. Sex-dependent differences in type I IFN-induced natural killer cell activation. Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 15;14:1277967. [CrossRef]
- Castenmiller C, Keumatio-Doungtsop BC, van Ree R, de Jong EC, van Kooyk Y. Tolerogenic Immunotherapy: Targeting DC Surface Receptors to Induce Antigen-Specific Tolerance. Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 19;12:643240. [CrossRef]
- Angioni R, Sánchez-Rodríguez R, Viola A, Molon B. TGF-β in Cancer: Metabolic Driver of the Tolerogenic Crosstalk in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers. 2021; 13(3):401. [CrossRef]
- Hu ZJ, Xu J, Yin JM, Li L, Hou W, Zhang LL, et al. Lower Circulating Interferon-Gamma Is a Risk Factor for Lung Fibrosis in COVID-19 Patients. Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 29;11:585647. [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N. Transforming growth factor-β in tissue fibrosis. J Exp Med. 2020 Feb 13;217(3):e20190103. [CrossRef]
- Ong CH, Tham CL, Harith HH, Firdaus N, Israf DA. TGF-β-induced fibrosis: A review on the underlying mechanism and potential therapeutic strategies. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 15;911:174510. [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Marques O, Moll G, Catar R, Preuß B, Bankamp L, Pecher AC, et al. Autoantibodies targeting G protein-coupled receptors: An evolving history in autoimmunity. Report of the 4th international symposium. Autoimmun Rev. 2023 May;22(5):103310. [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Marques, O. Halpert, G., Schimke, L.F. et al. Autoantibodies targeting GPCRs and RAS-related molecules associate with COVID-19 severity. Nat Commun 13, 1220 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Wallukat G, Hohberger B, Wenzel K, Fürst J, Schulze-Rothe S, Wallukat A, et al. Functional autoantibodies against G-protein coupled receptors in patients with persistent Long-COVID-19 symptoms. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021;4:100100. [CrossRef]
- Riemekasten G, Petersen F, Heidecke H. What Makes Antibodies Against G Protein-Coupled Receptors so Special? A Novel Concept to Understand Chronic Diseases. Front Immunol. 20. [CrossRef]
- Gunning, W.T., III; Stepkowski, S.M.; Kramer, P.M.; Karabin, B.L.; Grubb, B.P. Inflammatory Biomarkers in Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome with Elevated G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Autoantibodies. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 623 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loebel M, Grabowski P, Heidecke H, Bauer S, Hanitsch LG, Wittke K, et al. Antibodies to β adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors in patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. Brain Behav Immun. 2016 Feb;52:32-39. [CrossRef]
- Malkova AM, Shoenfeld Y. Autoimmune autonomic nervous system imbalance and conditions: Chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, silicone breast implants, COVID and post-COVID syndrome, sick building syndrome, post-orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, autoimmune diseases and autoimmune/inflammatory syndrome induced by adjuvants. Autoimmun Rev. 2023 Jan;22(1):103230. [CrossRef]
- Arjun S Yadaw, David K Sahner, Hythem Sidky, Behdad Afzali, Nathan Hotaling, Emily R Pfaff, et al. Preexisting Autoimmunity Is Associated With Increased Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using Data From the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C), Clinical Infectious Diseases, Volume 77, Issue 6, 15 September 2023, Pages 816–826. [CrossRef]
- Klein, J. Wood, J., Jaycox, J.R. et al. Distinguishing features of long COVID identified through immune profiling. Nature 623, 139–148 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, H. Ambreen, S., Raziq, H., & Hayyat, A. (2021). Comparison of cortisol levels in patients with vasovagal syncope and postural tachycardia syndrome. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences, 38(1). [CrossRef]
- Jing Lin, Huacai Zhao, Jie Shen, Fuyong Jiao, Salivary Cortisol Levels Predict Therapeutic Response to a Sleep-Promoting Method in Children with Postural Tachycardia Syndrome (2017) The Journal of Pediatrics. 191:91-95. [CrossRef]
- Laurin JKH, Oyewunmi OA, Garland EM, Gamboa A, Nwazue VC, Paranjape SY, et al. Adrenal gland response to adrenocorticotropic hormone is intact in patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Auton Neurosci. 2023 Sep;248:103105. [CrossRef]
- Catherine, J. Hutchings, Markus Koglin & Fiona H. Marshall (2010) Therapeutic antibodies directed at G protein-coupled receptors, mAbs, 2:6, 594-606. [CrossRef]
- Hazell GG, Hindmarch CC, Pope GR, Roper JA, Lightman SL, Murphy D, et al. G protein-coupled receptors in the hypothalamic paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei--serpentine gateways to neuroendocrine homeostasis. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2012 Jan;33(1):45-66. [CrossRef]
- Liu Q, Mak JWY, Su Q, et al. Gut microbiota dynamics in a prospective cohort of patients with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome Gut 2022;71:544-552. [CrossRef]
- Alenazy MF, Aljohar HI, Alruwaili AR, Daghestani MH, Alonazi MA, Labban RS, et al. Gut Microbiota Dynamics in Relation to Long-COVID-19 Syndrome: Role of Probiotics to Combat Psychiatric Complications. Metabolites. 2022; 12(10):912. [CrossRef]
- Pundir P, Kulka M. The role of G protein-coupled receptors in mast cell activation by antimicrobial peptides: is there a connection? Immunol Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;88(6):632-40. [CrossRef]
- Paavola KJ, Sidik H, Zuchero JB, Eckart M, Talbot WS. Type IV collagen is an activating ligand for the adhesion G protein-coupled receptor GPR126. Sci Signal. 2014 Aug 12;7(338):ra76. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scisignal.20053473. [CrossRef]
- Salzer I, Ray S, Schicker K, Boehm S. Nociceptor Signaling through ion Channel Regulation via GPCRs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2488. [CrossRef]
- McFadyen JD, Stevens H, Peter K. The Emerging Threat of (Micro)Thrombosis in COVID-19 and Its Therapeutic Implications. Circ Res. 2020 Jul 31;127(4):571-587. [CrossRef]
- Offermanns, S. Activation of platelet function through G protein-coupled receptors. Circ Res. 2006 Dec 8;99(12):1293-304. [CrossRef]
- Thakur N, Ray AP, Sharp L, Jin B, Duong A, Pour NG, et al. Anionic phospholipids control mechanisms of GPCR-G protein recognition. Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 13;14(1):794. [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.E. Feng, A., Meng, W. et al. New-onset IgG autoantibodies in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Nat Commun 12, 5417 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Natalini, J.G. Singh, S. & Segal, L.N. The dynamic lung microbiome in health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol 21, 222–235 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Sencio V, Machado MG, Trottein F. The lung-gut axis during viral respiratory infections: the impact of gut dysbiosis on secondary disease outcomes. Mucosal Immunol. 2021 Mar;14(2):296-304. [CrossRef]
- Hamming I, Timens W, Bulthuis ML, Lely AT, Navis G, van Goor H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J Pathol. 2004 Jun;203(2):631-7. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z. Yang, Z., Wang, Y., Zhou, F., Li, S., Li, C., Li, L., Zhang, W., & Li, X. (2021). Recent advance of ACE2 and microbiota dysfunction in COVID-19 pathogenesis. Heliyon, 7. [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.A. Schrevens, S., van Dijck, P. et al. Fungal G-protein-coupled receptors: mediators of pathogenesis and targets for disease control.Nat Microbiol 3, 402–414 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Chambers, PW (2023), The Candida Covid Connection: Preexisting Candida Overgrowth and Gut Dysbiosis Drives Long Covid, J. Neuroscience and Neurological Surgery, 13(7). [CrossRef]
- Kumwenda P, Cottier F, Hendry AC, Kneafsey D, Keevan B, Gallagher H, et al. Estrogen promotes innate immune evasion of Candida albicans through inactivation of the alternative complement system. Cell Rep. 2022 Jan 4;38(1):110183. [CrossRef]
- Zaongo SD, Ouyang J, Isnard S, Zhou X, Harypursat V, Cui H, et al. Candida albicans can foster gut dysbiosis and systemic inflammation during HIV infection. Gut Microbes. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2167171. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Ebinger, J.E., Mostafa, R. et al. Paradoxical sex-specific patterns of autoantibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Transl Med 19, 524 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T. et al. Sex differences in immune responses that underlie COVID-19 disease outcomes Nature 588, 315–320 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Pujantell M, Altfeld M. Consequences of sex differences in Type I IFN responses for the regulation of antiviral immunity Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 16;13:986840. [CrossRef]
- Bousoik E, Montazeri Aliabadi H. Do We Know Jack About JAK? A Closer Look at JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Front Oncol. 2018 Jul 31;8:287. [CrossRef]
- Zhou X, Guan Z, Jin X, Zhao J, Chen G, Ding J, et al. Reversal of alopecia areata, osteoporosis follow treatment with activation of Tgr5 in mice. Biosci Rep. 2021 Jul 30;41(7):BSR20210609. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary PK, Kim S. An Insight into GPCR and G-Proteins as Cancer Drivers. Cells. 2021 Nov 24;10(12):3288. [CrossRef]
- Jiang Z, Rajamanickam S, Justice NJ. Local Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Signaling in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus. J Neurosci. 2018 Feb 21;38(8):1874-1890. [CrossRef]
- Jiang Z, Rajamanickam S, Justice NJ. CRF signaling between neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) coordinates stress responses. Neurobiol Stress. 2019 Aug 10;11:100192. [CrossRef]
- Herhaus B, Thesing G, Conrad R, Petrowski K. Alterations in heart rate variability and pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha in individuals with panic disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2023 Apr;322:115107. [CrossRef]
- Thanou, A. Stavrakis, S., Dyer, J.W. et al. Impact of heart rate variability, a marker for cardiac health, on lupus disease activity. Arthritis Res Ther18, 197 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Jones DR, Smyth JM, Engeland CG, Sliwinski MJ, Russell MA, Sin NL, et al. Affect variability and inflammatory markers in midlife adults. Health Psychol. 2020 Aug;39(8):655-666. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Lin, Y. Tumor necrosis factor and cancer, buddies or foes?. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29, 1275–1288 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Rébé C, Ghiringhelli F. Interleukin-1β and Cancer. Cancers. 2020; 12(7):1791. [CrossRef]
- Kumari N, Dwarakanath BS, Das A, Bhatt AN. Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):11553-11572. [CrossRef]
- Williams DP, Koenig J, Carnevali L, Sgoifo A, Jarczok MN, Sternberg EM, Thayer JF. Heart rate variability and inflammation: A meta-analysis of human studies. Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Aug;80:219-226. [CrossRef]
- Cooper TM, McKinley PS, Seeman TE, Choo TH, Lee S, Sloan RP. Heart rate variability predicts levels of inflammatory markers: Evidence for the vagal anti-inflammatory pathway. Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Oct;49:94-100. [CrossRef]
- Steffen PR, Bartlett D, Channell RM, Jackman K, Cressman M, Bills J, Pescatello M. Integrating Breathing Techniques Into Psychotherapy to Improve HRV: Which Approach Is Best? Front Psychol. 2021 Feb 15;12:624254. [CrossRef]
- Hartmann R, Schmidt FM, Sander C, Hegerl U. Heart Rate Variability as Indicator of Clinical State in Depression. Front Psychiatry. 2019 Jan 17;9:735. [CrossRef]
- Koch C, Wilhelm M, Salzmann S, Rief W, Euteneuer F. A meta-analysis of heart rate variability in major depression. Psychological Medicine. 2019;49(12):1948-1957. [CrossRef]
- Arakaki X, Arechavala RJ, Choy EH, Bautista J, Bliss B, Molloy C, et al. The connection between heart rate variability (HRV), neurological health, and cognition: A literature review. Front Neurosci. 2023 Mar 1;17:1055445. [CrossRef]
- Liu KY, Elliott T, Knowles M, Howard R. Heart rate variability in relation to cognition and behavior in neurodegenerative diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. 2022 Jan;73:101539. [CrossRef]
- Benjamin BR, Valstad M, Elvsåshagen T, Jönsson EG, Moberget T, Winterton A, et al. Heart rate variability is associated with disease severity in psychosis spectrum disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Dec 20;111:110108. [CrossRef]
- Kloter E, Barrueto K, Klein SD, Scholkmann F, Wolf U. Heart Rate Variability as a Prognostic Factor for Cancer Survival - A Systematic Review. Front Physiol. 2018 May 29;9:623. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y, Koshy, S, Hui, D, Palmer, JL, Shin, K, Bozkurt, Mehtap, et al. Prognostic Value of Heart Rate Variability in Patients With Cancer. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology 32(6):p 516-520, December 2015. [CrossRef]
- Kubota Y, Chen LY, Whitsel EA, Folsom AR. Heart rate variability and lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Ann Epidemiol. 2017 Oct;27(10):619-625.e2. [CrossRef]
- Musialik-Łydka A, Sredniawa B, Pasyk S. Heart rate variability in heart failure. Kardiol Pol. 2003 Jan;58(1):10-6. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14502297/. [CrossRef]
- Lees T, Shad-Kaneez F, Simpson AM, Nassif NT, Lin Y, Lal S. Heart Rate Variability as a Biomarker for Predicting Stroke, Post-stroke Complications and Functionality. Biomark Insights. 2018 Jul 18;13:1177271918786931. [CrossRef]
- Buitrago-Ricaurte N, Cintra F, Silva GS. Heart rate variability as an autonomic biomarker in ischemic stroke. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2020 Nov;78(11):724-732. [CrossRef]
- Benichou T, Pereira B, Mermillod M, Tauveron I, Pfabigan D, Maqdasy S, et al. Heart rate variability in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2018 Apr 2;13(4):e0195166. [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, EB, Chambless, LE, Liao, D, Prineas, RJ, Evans, GW, Rosamond, WD, et al. Diabetes, Glucose, Insulin, and Heart Rate Variability: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Diabetes Care 1 March 2005; 28 (3): 668–674. [CrossRef]
- Hirten RP, Danieletto M, Tomalin L, Choi KH, Zweig M, Golden E, et al. Use of Physiological Data From a Wearable Device to Identify SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Symptoms and Predict COVID-19 Diagnosis: Observational Study J Med Internet Res 2021;23(2):e26107. [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.L.G. Vieira, L.d.P., Dias, L.S. et al. Impact of long COVID on the heart rate variability at rest and during deep breathing maneuver. Sci Rep 13, 22695 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Suh H-W, Kwon C-Y, Lee B. Long-Term Impact of COVID-19 on Heart Rate Variability: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. Healthcare. 2023; 11(8):1095. [CrossRef]
- Mooren, F.C. Böckelmann, I., Waranski, M. et al. Autonomic dysregulation in long-term patients suffering from Post-COVID-19 Syndrome assessed by heart rate variability. Sci Rep 13, 15814 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Garis, G. Haupts, M., Duning, T. et al. Heart rate variability and fatigue in MS: two parallel pathways representing disseminated inflammatory processes. Neurol Sci 44, 83–98. 44. [CrossRef]
- Novikova DS, Popkova TV, Panafidina TA, Il’ina AE, Kliukvina NG, Markelova EI, et al. Clinical significance of heart rate variability in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ter Arkh. 2008;80(9):68-72. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19555041/.
- Ingegnoli F, Buoli M, Antonucci F, Coletto LA, Esposito CM, Caporali R. The Link Between Autonomic Nervous System and Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Bench to Bedside. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Dec 7;7:589079. [CrossRef]
- Windham BG, Fumagalli S, Ble A, et al. The Relationship between Heart Rate Variability and Adiposity Differs for Central and Overall Adiposity. Journal of Obesity. 2012;2012:149516. [CrossRef]
- Farah BQ, Prado WL, Tenório TR, Ritti-Dias RM. Heart rate variability and its relationship with central and general obesity in obese normotensive adolescents. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2013 Jul-Sep;11(3):285-90. [CrossRef]
- Yadav RL, Yadav PK, Yadav LK, Agrawal K, Sah SK, Islam MN. Association between obesity and heart rate variability indices: an intuition toward cardiac autonomic alteration - a risk of CVD. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2017 Feb 17;10:57-64. [CrossRef]
- Rastović M, Srdić-Galić B, Barak O, Stokić E. Association between anthropometric measures of regional fat mass and heart rate variability in obese women. Nutr Diet. 2017 Feb;74(1):51-60. [CrossRef]
- Rose, S. Bennuri, S.C., Davis, J.E. et al. Butyrate enhances mitochondrial function during oxidative stress in cell lines from boys with autism.Transl Psychiatry 8, 42 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Rode, J, Yang, L, König, J, Hutchinson, AN, Wall, R, Venizelos, N, et al. Butyrate Rescues Oxidative Stress-Induced Transport Deficits of Tryptophan: Potential Implication in Affective or Gut-Brain Axis Disorders. Neuropsychobiology 27 May 2021; 80 (3): 253–263. [CrossRef]
- Gao K, Mu CL, Farzi A, Zhu WY. Tryptophan Metabolism: A Link Between the Gut Microbiota and Brain. Adv Nutr. 2020 May 1;11(3):709-723. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui MT, Cresci GAM. The Immunomodulatory Functions of Butyrate. J Inflamm Res. 2021 Nov 18;14:6025-6041. [CrossRef]
- Tsubokawa M, Nishimura M, Mikami T, Ishida M, Hisada T, Tamada Y. Association of Gut Microbial Genera with Heart Rate Variability in the General Japanese Population: The Iwaki Cross-Sectional Research Study. Metabolites. 2022; 12(8):730. [CrossRef]
- Domuschiev, I. The relationship between Heart Rate Variability (HRV) and gut microbiota Mar 2023 ResearchGate https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369356948.
- Fusco W, Lorenzo MB, Cintoni M, Porcari S, Rinninella E, Kaitsas F, et al. Short-Chain Fatty-Acid-Producing Bacteria: Key Components of the Human Gut Microbiota. Nutrients. 2023; 15(9):2211. [CrossRef]
- Coppola S, Avagliano C, Calignano A, Berni Canani R. The Protective Role of Butyrate against Obesity and Obesity-Related Diseases. Molecules. 2021; 26(3):682. [CrossRef]
- Peng K, Dong W, Luo T, Tang H, Zhu W, Huang Y, et al. Butyrate and obesity: Current research status and future prospect. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 24;14:1098881. [CrossRef]
- van Deuren T, Blaak EE, Canfora EE. Butyrate to combat obesity and obesity-associated metabolic disorders: Current status and future implications for therapeutic use. Obes Rev. 2022 Oct;23(10):e13498. [CrossRef]
- Ridler, C. Acetate promotes obesity via a gut–brain–β-cell axis. Nat Rev Endocrinol 12, 436 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Schug, Z. Vande Voorde, J., Gottlieb, E. The metabolic fate of acetate in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 16, 708–717 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Baothman, O.A. Zamzami, M.A., Taher, I. et al. The role of Gut Microbiota in the development of obesity and Diabetes. Lipids Health Dis 15, 108 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Ma Y, Chen C. Prebiotic Functions of Mannose Oligosaccharides Revealed by Microbiomic and Metabolomic Analyses of Intestinal Digesta (P20-017-19). Curr Dev Nutr. 2019 Jun 13;3(Suppl 1):nzz040.P20-017-19. [CrossRef]
- Dong, L. Xie, J., Wang, Y. et al. Mannose ameliorates experimental colitis by protecting intestinal barrier integrity. Nat Commun 13, 4804 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Zhang W, Cheng H, Gui Y, Zhan Q, Li S, Qiao W, et al. Mannose Treatment: A Promising Novel Strategy to Suppress Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 27;12:756920. [CrossRef]
- Sharma V, Smolin J, Nayak J, Ayala JE, Scott DA, Peterson SN, et al. Mannose Alters Gut Microbiome, Prevents Diet-Induced Obesity, and Improves Host Metabolism. Cell Rep. 2018 Sep 18;24(12):3087-3098. [CrossRef]
- Haensel A, Mills PJ, Nelesen RA, Ziegler MG, Dimsdale JE. The relationship between heart rate variability and inflammatory markers in cardiovascular diseases. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2008 Nov;33(10):1305-12. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I, Snijder, MB, Twisk, JWR, van Mechelen, W, Kemper, HCG, Seidell, JC, et al. Central Fat Mass Versus Peripheral Fat and Lean Mass: Opposite (Adverse Versus Favorable) Associations with Arterial Stiffness? The Amsterdam Growth and Health Longitudinal Study, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, Volume 89, Issue 6, 1 June 2004, Pages 2632–2639. [CrossRef]
- Cabral M, Bangdiwala SI, Severo M, Guimarães JT, Nogueira L, Ramos E. Central and peripheral body fat distribution: Different associations with low-grade inflammation in young adults? Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2019 Sep;29(9):931-938. [CrossRef]
- Xiao P, Hu Z, Lang J, Pan T, Mertens RT, Zhang H, et al. Mannose metabolism normalizes gut homeostasis by blocking the TNF-α-mediated proinflammatory circuit. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023 Feb;20(2):119-130. [CrossRef]
- Torretta S, Scagliola A, Ricci L, Mainini F, Di Marco S, Cuccovillo I, et al. D-mannose suppresses macrophage IL-1β production. Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 11;11(1):6343. [CrossRef]
- Guo L, Hou Y, Song L, Zhu S, Lin F, Bai Y. D-Mannose Enhanced Immunomodulation of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells via Inhibiting IL-6 Secretion. Stem Cells Int. 2018 Sep 9;2018:7168231. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Gao Y, Lin T. Expression of interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in non-small cell lung cancer and its relationship with the occurrence and prognosis of cancer pain. Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Dec;10(12):12759-12766. [CrossRef]
- Yoshida N, Ikemoto S, Narita K, Sugimura K, Wada S, Yasumoto R, et al. Interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1beta in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2002 May 6;86(9):1396-400. [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.N. Giles, J.T. & Liao, K.P. Shared inflammatory pathways of rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol 19, 417–428 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Lambertsen KL, Biber K, Finsen B. Inflammatory cytokines in experimental and human stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012 Sep;32(9):1677-98. [CrossRef]
- Zorena K, Jachimowicz-Duda O, Ślęzak D, Robakowska M, Mrugacz M. Adipokines and Obesity. Potential Link to Metabolic Disorders and Chronic Complications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(10):3570. [CrossRef]
- Liu C, Feng X, Li Q, Wang Y, Li Q, Hua M. Adiponectin, TNF-α and inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine. 2016 Oct;86:100-109. [CrossRef]
- Ishijima T, Nakajima K. Inflammatory cytokines TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 are induced in endotoxin- stimulated microglia through different signaling cascades. Sci Prog. 2021 Oct;104(4):368504211054985. [CrossRef]
- Möller, B. Villiger, P.M. Inhibition of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Springer Semin Immun 27, 391–408 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Mikos H, Mikos M, Rabska-Pietrzak B, Niedziela M. The clinical role of serum concentrations of selected cytokines: IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 in diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD) in children. Autoimmunity. 2014 Nov;47(7):466-72. [CrossRef]
- Dhanalakshmi, M. Sruthi, D., Jinuraj, K.R. et al. Mannose: a potential saccharide candidate in disease management. Med Chem Res 32, 391–408 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Nan F, Sun Y, Liang H, Zhou J, Ma X, Zhang D. Mannose: A Sweet Option in the Treatment of Cancer and Inflammation. Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 13;13:877543. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Jiang N, Ping J, Xu L. TGF-β1-induced autophagy activates hepatic stellate cells via the ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med. 2021 Jan;47(1):256-266. [CrossRef]
- Fang Z, Meng Q, Xu J, Wang W, Zhang B, Liu J, et al. Signaling pathways in cancer-associated fibroblasts: recent advances and future perspectives. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023 Jan;43(1):3-41. [CrossRef]
- Xie L, Law BK, Chytil AM, Brown KA, Aakre ME, Moses HL. Activation of the Erk pathway is required for TGF-beta1-induced EMT in vitro. Neoplasia. 2004 Sep-Oct;6(5):603-10. [CrossRef]
- Xu J, Liu X, Jiang Y, Chu L, Hao H, Liua Z, Verfaillie C, Zweier J, Gupta K, Liu Z. MAPK/ERK signalling mediates VEGF-induced bone marrow stem cell differentiation into endothelial cell. J Cell Mol Med. 2008 Dec;12(6A):2395-406. [CrossRef]
- Zhang R, Yang Y, Dong W, Lin M, He J, Zhang X, et al. D-mannose facilitates immunotherapy and radiotherapy of triple-negative breast cancer via degradation of PD-L1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Feb 22;119(8):e2114851119. [CrossRef]
- Rha, MS. Shin, EC. Activation or exhaustion of CD8+ T cells in patients with COVID-19. Cell Mol Immunol 18, 2325–2333 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Gulley JL, Schlom J, Barcellos-Hoff MH, Wang XJ, Seoane J, Audhuy F, et al. Dual inhibition of TGF-β and PD-L1: a novel approach to cancer treatment. Mol Oncol. 2022 Jun;16(11):2117-2134. [CrossRef]
- Young HA, Benton D. Heart-rate variability: a biomarker to study the influence of nutrition on physiological and psychological health? Behav Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;29(2 and 3-Spec Issue):140-151. [CrossRef]
- Karzon R, Jackson A, Lloyd I, Hall A, Lee L. The Role of Nutraceuticals in the Prevention and/or Treatment of COVID-19: An Umbrella Review. CANDJ [Internet]. 2023 Dec. 28 [cited 2024 Feb. 6];30(4):66-80 https://candjournal.ca/index.php/candj/article/view/165. [CrossRef]
- Souza PBd, de Araujo Borba L, Castro de Jesus L, Valverde AP, Gil-Mohapel J, Rodrigues ALS. Major Depressive Disorder and Gut Microbiota: Role of Physical Exercise. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):16870. [CrossRef]
- Reginato E, Azzolina D, Folino F, Valentini R, Bendinelli C, Gafare CE, et al. Dietary and Lifestyle Patterns are Associated with Heart Rate Variability. J Clin Med. 2020 Apr 14;9(4):1121. [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Vicente A, Hernando D, Santos-Lozano A, Rodríguez-Romo G, Vicente-Rodríguez G, Pueyo E, et al. Heart Rate Variability and Exceptional Longevity. Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 17;11:566399. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




