1. Introduction
As a natural product, the nutritional and medicinal value of honey has been recognized since the ancient civilizations. Currently there has been great interest of honey by the researchers, medical community and public dealers. Honey is an antiseptic agent for the treatment of illnesses such as ulcers, bedsores, and other skin infections that result from burns and injuries [
1,
2]. As an antibiotic, honey is very effective on infections that have not been cured with any authenticated antibiotics. The astonishing effect of honey in clearing infections quickly and helping healing was stated in numerous research findings on its antibacterial activity [
3].
The honey antioxidant is varying due to some reasons including botanical sources foraged by the bees, seasonal and environmental contributions, and harvesting methods [
4,
5]. The entire characteristic of honey antioxidant results from many bioactive substances. However, the phenolic profile is well known to contribute largely to the total honey antioxidant activity [
6,
7].
The antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of honey are largely affected by the honey polyphenols, flavonoids, peptides/proteins, di-carbonyls and hydrogen peroxide. Antioxidants substance of honey is found in high levels. These substances include enzymatic and non-enzymatic ones such as catalase, phenolic acids, flavonoids, carotenoids, organic acids, ascorbic acid, amino acids, proteins, and Millard reaction products [
4,
5,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. Honey phenolic compounds vary according to its botanical/geographical origin, honeybee race, climate conditions and factors such as the honey harvest, treatment, and storage [
15].
A comparative study was performed to determine the efficacy, antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant of four honey types from different botanical/geographical origins. Although there are many reports on the antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of honey, the current study enriches our knowledge of antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of honey in the light of its phenolic and flavonoid contents. It might also be a new intervention utilization of a safe (none cytotoxic) nutraceutical, which can contribute to the management of chronic diseases commonly associated with oxidative stress.
2. Results
2.1. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity
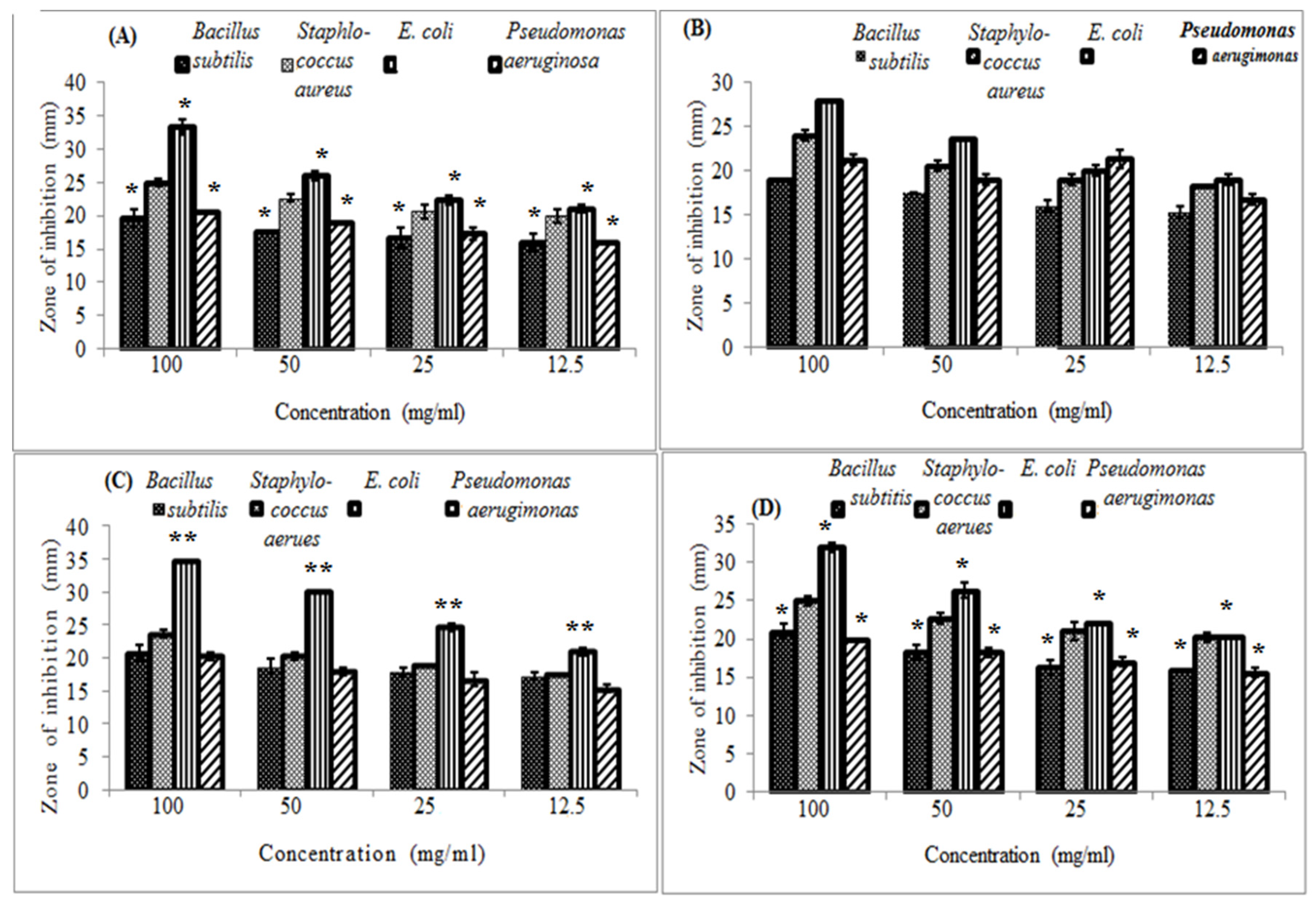
In the present study, all investigated honeys were active against the tested pathogens. A
. seyal honey, in all concentrations, significantly (
p ˂ 0.05) had positive effects on B.
subtilis, E.
coli, and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It was most active against E
. coli giving maximum growth inhibition diameter of 33.3 mm (
Figure 1A). Similarly
, Zizuphus honey was significantly (
p ˂ 0.01) active against E
. coli giving maximum growth inhibition diameter of 34.7 mm (
Figure 1C). Its activity was almost the same as for the rest of the tested bacteria.
Cucurbita honey also was significantly (
p ˂ 0.05) active against B
. subtilis, E
. coli and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (
Figure 1D). Only, A
. nilotica honey showed steady and similar activity on all the tested bacteria (
Figure 1B). No statistically significant differences were observed between
Zizuphus and
Cucurbita honeys (
p = 0.157) and between A
. seyal and A
. nilotica honeys (
p = 0.247) in their overall antibacterial activities (
Table 1). It can be noticed that all the investigated floral honeys have almost constant antibacterial activity (˷25 mm) against
Staphylococcus aureus (
Figure 1A, B, and C, D). It is also important to note that E
. coli was resistant to the standard antibiotic tested (
supplementary material Table S1) while it was the most susceptible candidate to the all investigated floral honeys (
Figure 1A, B, C, and D).
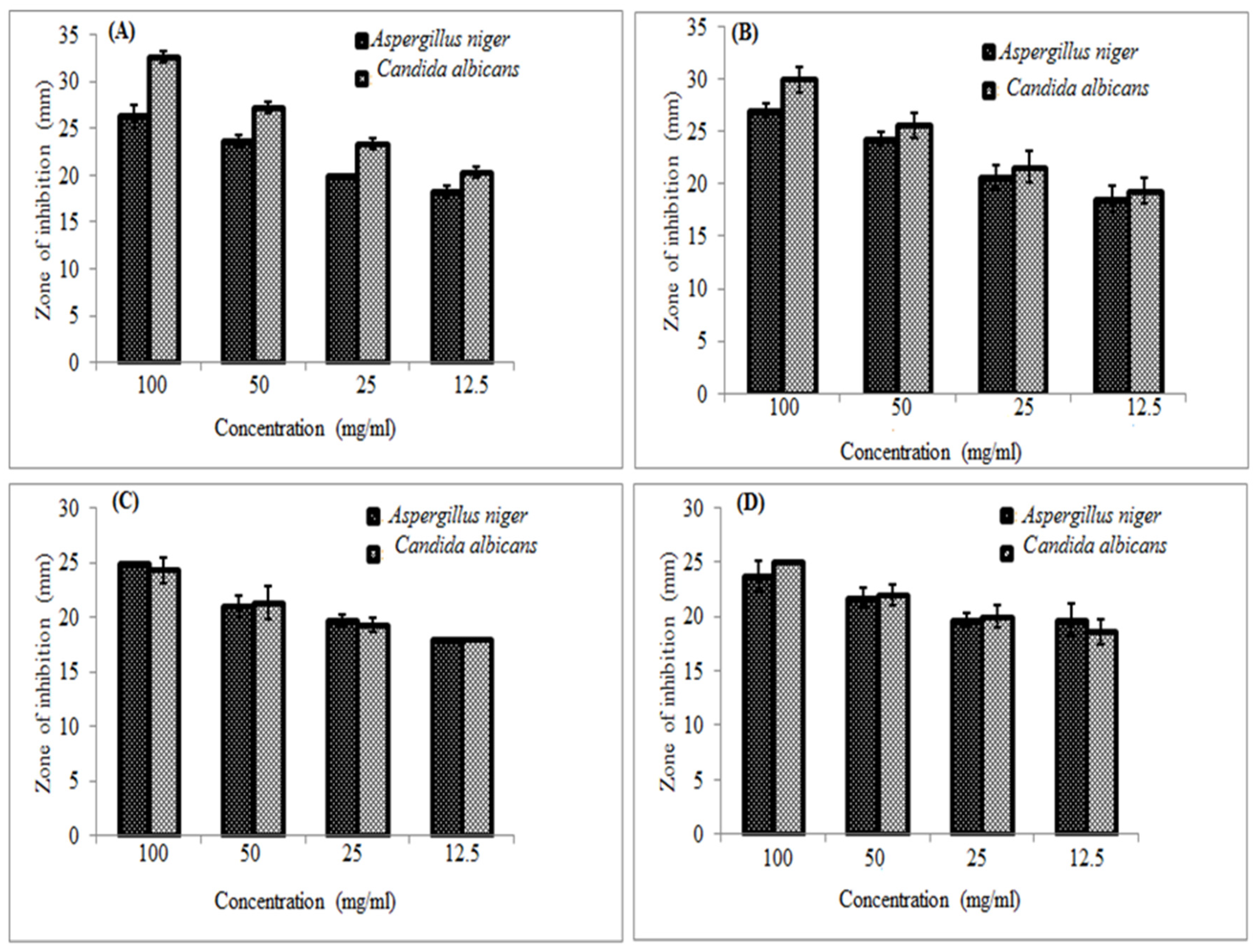
Figure 2 shows the antifungal activity of honeys. All the assayed honey types have shown similar activities against
Candida albicans and
Spergillus niger. None of the honey types has expressed statistical significance variations.
2.2. Scavenging Activity, Total Flavonoid and Total Phenol Contents
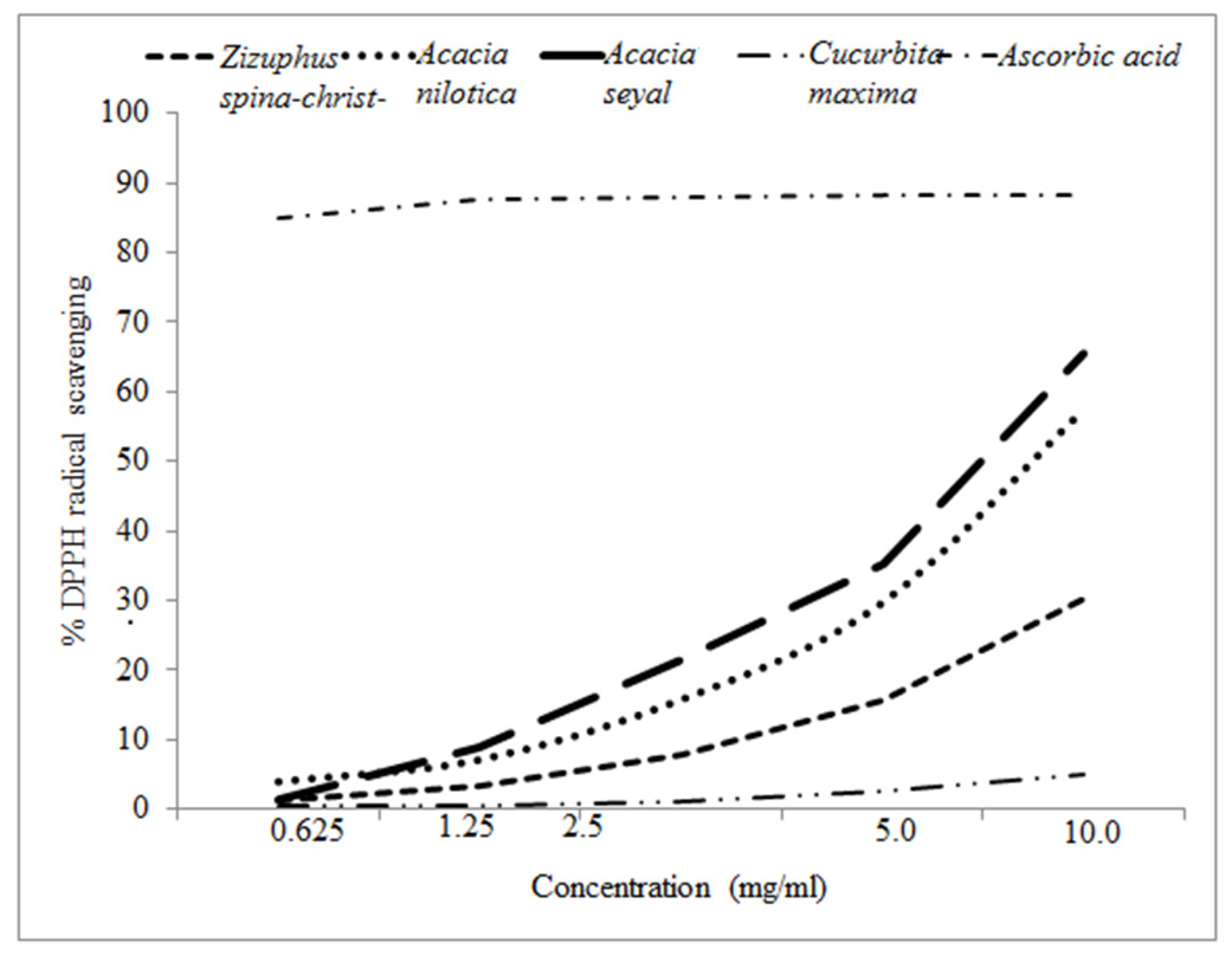
The scavenging activity of the different floral honeys was presented in
Figure 3. The IC
50 varied greatly between the samples,
Acacia seyal honey was the most active (IC
50 = 6.68 mg/ml) followed by
Acacia nilotica (IC
50 = 9.08 mg/ml) and
Ziziphus (IC
50 = 72.31 mg/ml).
Cucrbita honey was not active in DPPH inhibition (
Table 2). The total phenol varied from 5.75 to 67.95 mg GAE/100 g respectively; in
cucurbita and
Acacias honey types. The two varieties of
Acacia have shown no significant difference (
p ˂ 0.01) between them in the phenol contents (
Table 2). The total flavonoid contents were similar 0.15 mg QE/100 g in
Zizuphus and
Cucurbita honeys. They varied from 0. 57-0. 50 mg QE/100 g in A
. nilotica and A
. seyal honeys respectively (
Table 2).
2.3. Cytotoxicity of Honey
As results show, the LD
50 from Brine shrimp lethality bioassay was ˃ 1000 µg/ml indicating no cytotoxicity. Thus all the studied honey types are safe compared to the positive control vincristine sulfate which show LD
50 ˃ 249 (
Table 3).
3. Discussion
3.1. Antimicrobial Activity
It is common to find a plethora of evidence of incorporating traditional folks into the modern medicine [
16]. Globally, honey has gained reputation in classical medicine for its potential of defeating several illnesses [
17]. The activity of honey against bacterial and fungi has extensively been documented in many scientific reports [
18,
19].
The obtained antibacterial activity results in the present study came in line with the findings of other reports [
20,
21] who tested the antibacterial activity of honey against many bacteria such as E.
coli,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and
Staphylococcus aureus. Also, results in this investigation have shown that the differences in the antibacterial activity depend on the botanical origin of the honey, unlike, Al-Waili
et al. (2013) [
22] who stated that there were non-significant differences between different varieties of honey against pathogens.
The current result concerning antifungal activity was again, corroborative to the finding of Al-Waili
et al. (2013) [
22]. However, according to their results,
Acacia’s honeys were the lowest in their activity to suppress
Candida albicans while,
Acacias honeys were very effective against
Candida albicans in this study (
Figure 2A & B). This could attribute to the different geographical locations of the tested samples of honey in both studies.
Acacia seyal gave growth inhibition diameter of (32.7 mm) against
Candida albicans even this result is comparable to the result obtained by the standard antifungal drug tested for comparing the results (
supplementary material Table S2).
3.2. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity, Flavonoid and Total Phenol Contents
The phytochemical composition, antioxidant compounds and hydrogen peroxide are among the compounds responsible for the bactericidal and bacteriostatic activity of honey [
21]. Also supplementary proteinaceous compounds generated by the indigenous bacteria in the honey bee guts prior to honey ripening and royal jelly proteins in honey render additional antimicrobial activity to honey [
23,
24].
The obtained antioxidant activity result in this paper was clearly in disagreement with the previous antioxidant capacities reported by Idris
et al. (2011) for some Sudanese honeys [
25]. They reported higher antioxidant capacity for
Zizuphus honey than A
. seyal and A
. nilotica honeys. They employed the phosphatidylcholine peroxidation method while the current study used DPPH-radical scavenging method. The explanation for this disagreement may be attributed to the existence of different anti-oxidative ways exploited by the different kinds of honey. However, the IC
50 values recorded here are corresponding to those reported by Meda
et al. (2005) [
26]. The total phenols and flavonoids demonstrated in this work are similar to the finding of other authors [
5,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31].
3.3. Cytotoxicity of Honey
The cytotoxicity of the investigated 12 honey samples by Brine shrimp lethality bioassay indicated that cytotoxic activity was not reported, and therefore the entirely studied honey samples are safe for living cells. Similar finding was reported by Mohammed
et al. (2019) [
32].
Cucurbita and
Ziziphus honeys demonstrated strong antimicrobial activity though
Cucurbita was inactive and
Ziziphus was poor in the antioxidant capacities. This could support the notion that “the level of phenolic compounds present in honey is not always responsible for its antioxidant activity” [
4,
31]. And this in turn supports the hypothesis “that honeys had additional antimicrobial activity arising from unknown substances” [
30,
31] which should be addressed by research in the future. The
Cucurbita species are known to have antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. Therefore, these plant species have been given great interest in the last years due to their use in multiple applications [
33]. Our findings clearly show the merit antimicrobial activities of honey produced from the
Cucurbita plant, which reflects the fact, that natural honey contains the properties of its botanical origin. However, the weakness of the
Cucurbita and
Ziziphus honeys to the antioxidant properties may suggest that honey is not necessary to express all the properties of its botanical origin.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling
Twelve samples of honey of different botanical/geographical origins were randomly collected from apiaries during the season 2000/2021. The samples were labeled from (1- 12) and then stored under laboratory conditions (20 °C) waiting for analysis.
4.2. The Antimicrobial Activity Assays
The cup-plate agar diffusion assay was applied according to Kavanagh (1972) [
34] with some minor modifications. The antibacterial activity of the honey samples was assayed against two Gram-positive bacteria
Bacillus subtilis (NCTC 8236) and
Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923) and two Gram-negative bacteria
Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 27853). Standardized bacterial stock suspension (108 - 109 CFU/ml) was thoroughly mixed with molten sterile nutrient agar (1:100 ml) which was kept at 45°C. Then 20 ml aliquots of the inoculated nutrient agar were distributed into sterile Petri-dish plates. Four cups of (10 mm in diameter) were made using a sterile cork borer (No. 4) and the agar discs were removed. Then after, each cup was filled with 0.1 ml of sample and allowed to diffuse at room temperature for 2 h. The plates were then incubated in an upright position at 37°C for 18 h. Two replicates were carried out for each honey sample against each of the bacterium. The diameters of the resultant growth inhibition zones were measured and averaged.
The same method was employed for the antifungal test against two fungi strains Aspergillus niger (ATCC 9763) and Candida albicans (ATCC 7596). However, instead of nutrient agar; Sabouraud dextrose agar was used as inoculation media. The inoculated medium was incubated at 25°C for two days for Candida albicans and three days for Aspergillus niger.
4.3. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
Free radical scavenging DPPH (1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl) was applied to the samples according to the method described by Kumaran and Karunakaran (2007) [
35]. Honey solutions (10-100 µg/ml) were mixed with 0.4 mM DPPH in methanol (2.0:1.0 ml). The mixture was shaken vigorously and kept in dark at room temperature for 30 min. Blank solutions were prepared with each sample (2.0 honey: 1.0 ml methanol) while the negative control was 1.0 ml of 0.4 mM DPPH solution plus 2.0 ml methanol. L- Ascorbic acid was used as positive control. The absorbance of the assay mixture (in triplicates) was measured at 515 nm against each blank with spectrophotometer. DPPH radical inhibition was calculated using the equation:
where Ao is the absorbance of the control, A1 is the absorbance of the tested sample. The IC
50 values were calculated from the plotted graph of DPPH radical scavenging activity against the concentration of the assayed sample.
4.4. Brine Shrimp Lethality Bioassay
The cytotoxicity of honey was assayed against Brine shrimps nauplii
Artemia salina (Ocean 90, USA) according to Meyer
et al. (1982) [
36]. Honey was dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) at three doses (1000, 100, and10 μg/mL). The honey solutions were then added to the pre-marked vials containing 30.0 live Brine shrimp nauplii in 5.0 ml simulated sea water (38.0 g of sea salt in one liter of distilled water). After 24 h, the vials were inspected using magnifying glass and the number of survived nauplii in each vial was counted. Nauplii were considered dead if they did not show any observable internal or external movement during 30.0 seconds. The number of the dead nauplii in each treatment was compared to the dead nauplii in the control. DMSO and vincristine sulfate were used respectively as negative control and reference standard.
4.5. Total Phenol Content
Total phenols were determined using a modified method of the Folin–Ciocalteu [
37]. Honey samples were mixed with distilled water (5.0 g: 50.0 ml) and filtered through Whatman No. 1. The resultant solution was mixed with 0.2 N Folin–Ciocalteu (0.5: 2.5 ml) (Sigma– Aldrich Chemie, Steinheim- Germany) for 5.0 min and 2.0 ml of Na
2CO
3 solution (75.0 g/l) were added. All samples were incubated at room temperature in the dark for 2 h, the absorbance of the mixture was read at 760 nm against blank solution containing methanol instead of honey. A calibration curve was developed using a stock solution of Gallic acid (Sigma– Aldrich Chemie, Steinheim, Germany) 1.0 mg/ml was prepared by further dilutions. The linearity of the curve was (R
2 = 0.998). The mean of triplicate readings was used, and the total phenol content was expressed as mg of Gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/100 g of honey.
4.6. Total Flavonoids
Total flavonoids were determined as described by Kim
et al. (2003) [
38] with little modification. Firstly, honey solution (1.0 mg/ml) was prepared and mixed with 0.3 ml of 5 % NaNO
2. Then 0.3 ml 10% AlCl
3 was added after 5 minutes. Prepared honey samples were mixed and after six minutes neutralized with 2 ml (1 M NaOH) solution. The absorbance of the mixture was read at 510 nm and quantification was performed using a standard curve. The titration curve was developed using different concentrations (5-114 μg/ml) of quercetin. The curve was linear (R
2 = 0.989). The results (triplicates) were expressed as quercetin equivalent (QE)/100 g honey.
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Data were entered and plotted using Microsoft Excel 2010. Statistical Package for Social Science (version 16, SPSS Corporation, Chicago, IL) was applied to determine: One-way ANOVA, Student's t-test, and Duncan's multiple range test (DMRT) for means comparison.
5. Conclusions
In general, this study corroborates the known antimicrobial activity of honey [
39] and furtherly demonstrates that
Acacia seyal and
Acacia nilotica honeys were the most active antioxidants. In addition, the results proved that
Cucurbita and
Ziziphus honeys have strong antimicrobial activity though being poor in their antioxidant capacities. We also can conclude that honey may have additional antimicrobial activity arising from unknown substances, which should be addressed by research in the future.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1. The antibacterial activity of the reference antibiotics against the standard bacteria. Table S2. The antifungal activity of the reference antibiotics against the standard fungi.
Author Contributions
SM and WK are the principle and co investigators of the project, respectively. AK did the majority of the laboratory works. SM provided statistical analysis of the data and drafted the manuscript. MA, KK, MM, BA and HG validated the results, revised the manuscript and facilitated the financial support.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of the Scientific Research at King Khalid University, grant number RGP.1/342/43.
Data Availability Statement
Competing Interests
the authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cilia, G.; Fratini, F.; Marchi, M.; Sagona, S.; Turchi, B.; Adamchuk, L.; Felicioli, A.; Kačániová, M. Antibacterial Activity of Honey Samples from Ukraine. Vet Sci. 2020, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoone, P.; Oluwadun, A.; Warnock, M.; Fyfe, L. Honey: A Therapeutic Agent for Disorders of the Skin. Cent Asian J Glob Health 2016, 5, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.D.; Mandal, S. Honey: its medicinal property and antibacterial activity. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2011, 1, 154–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauliuc, D.; Dranca, F.; Oroian, M. Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolic Content, Individual Phenolics and Physicochemical Parameters Suitability for Romanian Honey Authentication. Foods 2020, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dżugan, M.; Tomczyk, M.; Sowa, P.; Grabek-Lejko, D. Antioxidant Activity as Biomarker of Honey Variety. Molecules 2018, 23, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halagarda, M.; Groth, S.; Popek, S.; Rohn, S.; Pedan, V. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Profile of Selected Organic and Conventional Honeys from Poland. Antioxidants Basel. 2020, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianciosi, D.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Afrin, S.; Gasparrini, M.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Manna, P. P.; Zhang, J.; Bravo, L.L.; Martínez Flórez, S.; Agudo, T. P.; et al. Phenolic Compounds in Honey and Their Associated Health Benefits: A Review. Molecule 2018, 23, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yayinie, M.; Atlabachew, M.; Tesfaye, A.; Hilluf, W.; Reta, C.; Alemneh, T. Polyphenols, flavonoids, and antioxidant content of honey coupled with chemometric method: geographical origin classification from Amhara region, Ethiopia. Int J Food Prop. 2020, 25, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Sajid, M.; Azim, M.K. Isolation of 62 kDa protein with antioxidant activity from natural honey. JCSP. 2014, 36, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Gasparrini, M.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Mazzoni, L.; Giampieri, F. The Composition and Biological Activity of Honey: A Focus on Manuka Honey. Foods 2014, 3, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarghandian, S.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samini, F. Honey and Health: A Review of Recent Clinical Research. Pharmacognosy Res. 2017, 9, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azman, K.F.; Aziz, C.B.A.; Zakaria, R.; Ahmad, A.H.; Shafin, N.; Ismail, C.A.N. Tualang Honey: A Decade of Neurological Research. Molecules 2021, 26, 5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Baig, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Liaqat, S.; Fatima, S.; Jabeen, S.; Shamim, N.; Othman, N.H. Honey as a Potential Natural Antioxidant Medicine: An Insight into Its Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018, 83, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, A.; Pehlivan, T. Antioxidant activities of some monofloral honey types produced across Turkey. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018, 25, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.E.A. Factors Affecting the Physicochemical Properties and Chemical Composition of Bee’s Honey. Food Rev Int. 2022, 38, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaerjani, W.M.A.; Abu-Melha, S.; Alshareef, R.M. H.; Al-Farhan, B.S.; Ghramh, H.A.; Al-Shehri, B. M.A.; Bajaber, M.A.; Khan, K. A.; Alrooqi, M.M.; Modawe, G.A.; et al. Biochemical Reactions and Their Biological Contributions in Honey. Molecules 2022, 27, 4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, A.; Zollman, C.; Lee, R. Herbal medicine. West J Med. 2001, 175, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molan, P. Why honey is effective as a medicine. Bee World 2001, 82, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Waili, N.A. Investigating the antimicrobial activity of natural honey and its effect on the pathogenic bacterial infection of surgical wounds and conjunctiva. J Med Foods 2004, 7, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, V.M.; Cooper, R.A.; Molan, P.C. (2005) The antibacterial activity of honey against coagulase-negative Staphylococci. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005, 56, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R. A.; Molan, P.C.; Harding, K.G. The sensitivity to honey of Gram-positive cocci of clinical significance isolated from wounds. J Appl Microbiol. 2002, 93, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Waili, N.; Al Ghamdi, A.; Ansari, M. J.; Al-Attal, Y. Al-Mubarak, A.; Salom, K. Differences in Compositions of Honey Samples and their Impact on the Antimicrobial activities against Drug Multiresistant Bacteria and Pathogenic Fungi. Arch Med Res. 2013, 44, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willix, D.J.; Molan, P.C.; Harfoot, C.G. A comparison of the sensitivity of wound-infecting species of bacteria to the antibacterial activity of Manuka honey and other honey. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992, 73, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Churey, J.J.; Worobo, R.W. Antimicrobial activity of bacterial isolates from different floral sources of honey. Int J Food Microbiol. 2008, 126, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idris, Y.M.A.; Mariod, A.A.; Hamad, S.I. Physicochemical Properties, Phenolic Contents and Antioxidant Activity of Sudanese Honey. Int J Food Prop. 2011, 14, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meda, C.E.; Romito, M.; Millogo, J.; Nacoulma, O.G. Determination of the total phenolic, flavonoid and proline contents in Burkina Fasan honey, as well as their radical scavenging activity. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuçuk, M.; Kolayl, S.; Karaoglu, S.; Ulusoy, S.; Baltacı, C.; Candan, F. Biological activities and chemical composition of three honeys of different types from Anatolia. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasa, M. ; Candiracci, M.; Accorsi, A.; Piacentini, M.P.; Albertini, M.C.; Piatti, E. Raw Millefiori honey is packed full of antioxidants. Food Chem. 2005, 97, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlil, I.M.; Mahaneem, M.; Jamalullail, S.M.S.; Alam, N.; Sulaiman, S.A. Evaluation of Radical Scavenging Activity and Color Intensity of Nine Malaysian Honeys of Different Origin. JAS 2011, 3, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachman, J.; Orsák, M.; Hejtmánková, A.; Kovářová, E. Evaluation of antioxidant activity and total phenolics of selected Czech honeys. LWT – Food Sci Technol, 2010; 43, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al, M.L.; Daniel, D.; Moise, A.; Bobis, O.; Laslo, L.; Bogdanov, S. Physico-chemical and bioactive properties of different floral origin honeys from Romania. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A; Kabbashi, AS.; Koko, W.S.; Ansari, M.J.; Adgaba, N.; Al-Ghamdi, A. In vitro activity of some natural honeys against Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia labilia trophozoites. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2019, 26, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Capanoglu, E.; Adrar, N.; Catalkaya, G.; Shaheen, S.; Jaffer, M.; Giri, L.; Suyal, R.; Jugran, A.K.; Calina, D.; et al. Cucurbits Plants: A Key Emphasis to Its Pharmacological Potential. Molecules 2019, 24, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, F. Analytical Microbiology II. Academic Press Pub., New York and London, 1971.
- Kumaran, A.; Karunakkaran, R.J. In vitro antioxidant activities of methanol extracts of five Phyllanthus species from India. LWT – Food Sci Technol 2007, 40, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.N.; Ferrigni, N.R.; Putnam, J.E.; Jacobsen, L.B.; Nichols, D.E.; McLaughlin, J. L. (1982) Brine shrimp: a convenient general bioassay for active plant constituents. Planta Med 1982, 45, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagent. Am J Enol Viticult 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.O.K.; Lee, S.W.; Jeong, C.Y. Antioxidant capacity of phenolic phytochemicals from various cultivars of plums. Food Chem 2003, 81, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundo, M.A.; Padilla-Zakour, O.I.; Worobo, R. W. Growth inhibition of foodborne pathogens and food spoilage organisms by select raw honeys. Int J Food Microbiol. 2004, 97, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).