Submitted:
31 January 2024
Posted:
01 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Robotic assembly task
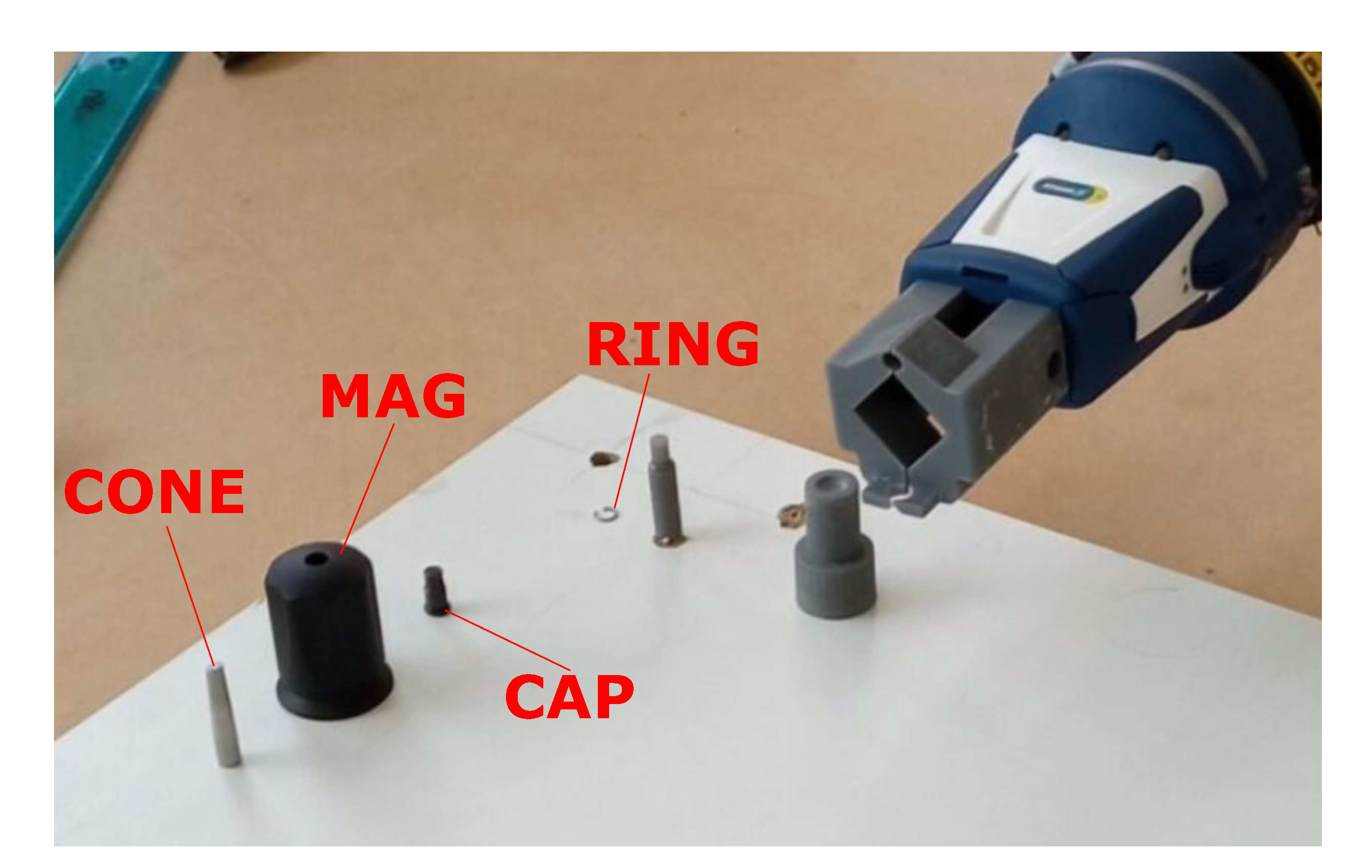
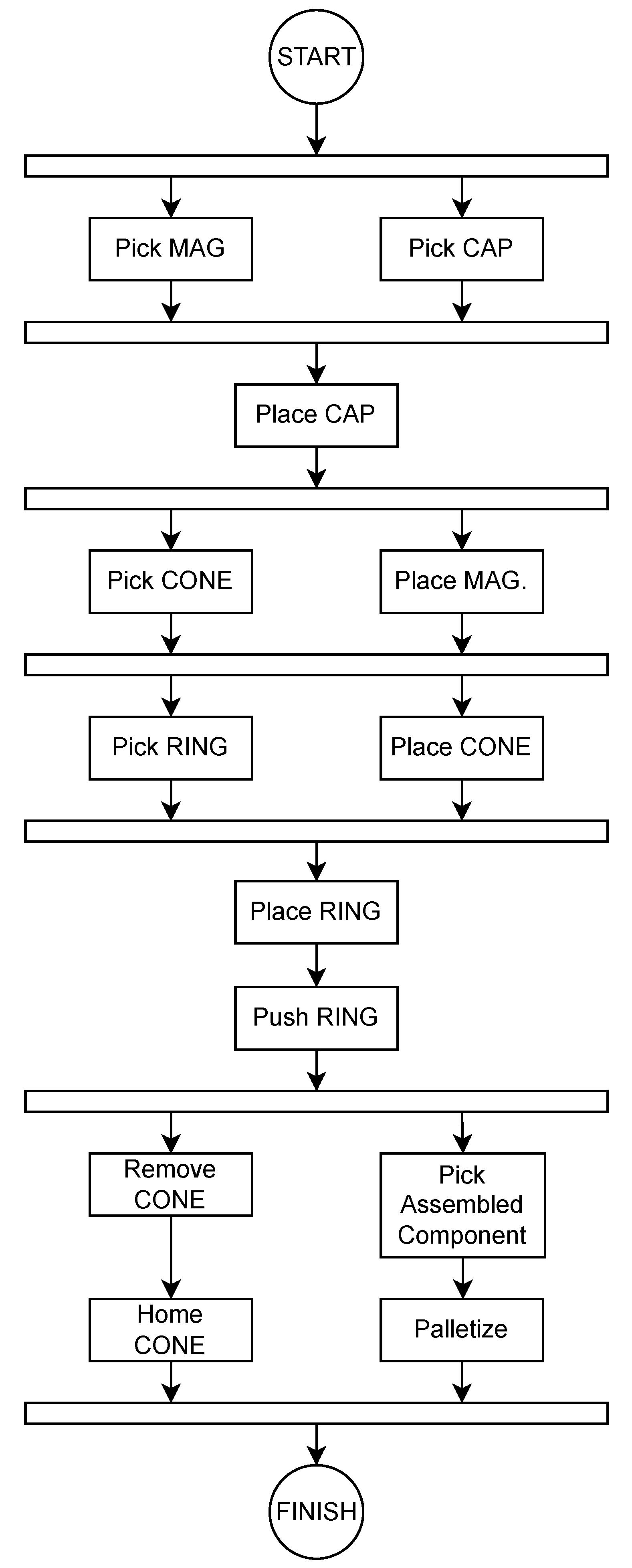
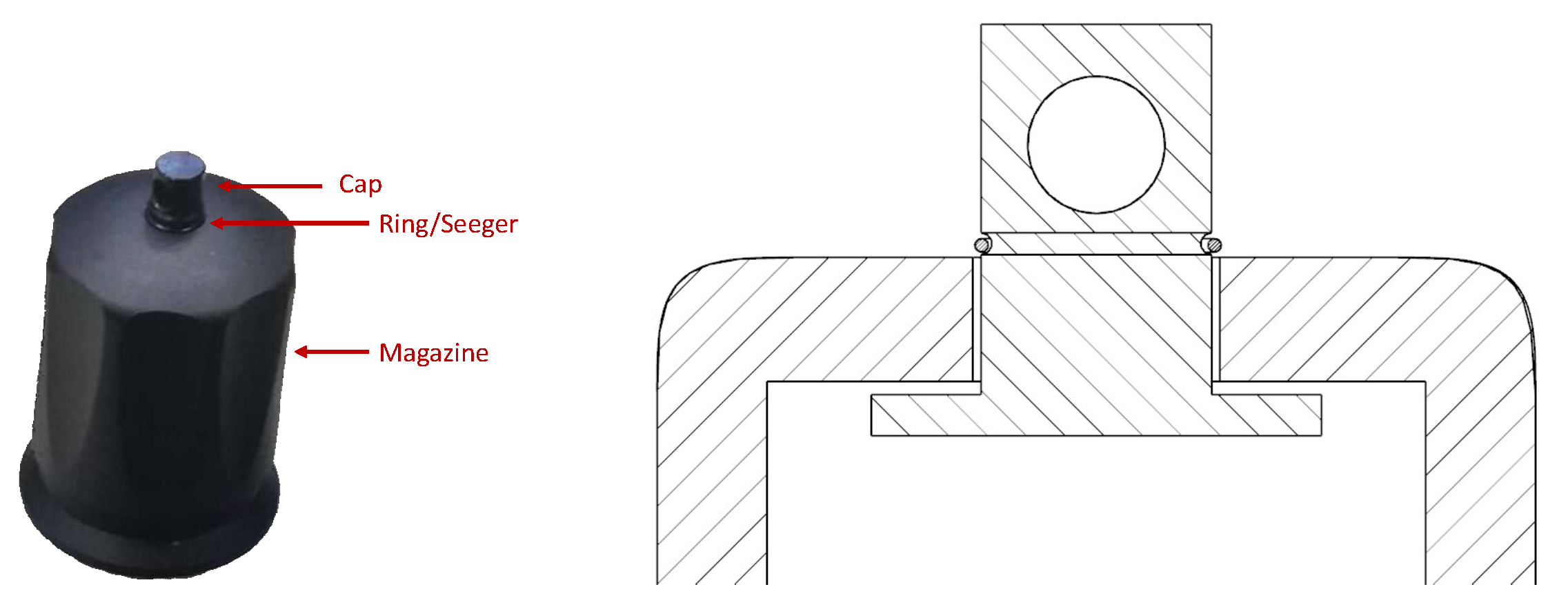
3. The Task to be Accomplished
- Pick and place the Cap
- Pick and place the Magazine
- Pick and place the Cone
- Pick and place the Ring
- Insert the Ring into its seat
- Remove the Cone from the piece and reposition it in its base

4. Tools and Methods
- Understanding customer requirements.
- Determining what tasks can be executed solely by the robot and which need automation.
- Identifying various tasks and figuring out their execution.
- Testing and evaluating functionality.
- Using the results to make modifications, greatly aided by 3D printing.
- Repeating this process until a satisfactory solution is achieved.
5. Results
5.1. Design of the fingers
5.1.1. Description of the functional parts of the fingers
5.2. Cycle time
6. Conclusion
- Shifting from manual to robotic assembly in this application is feasible but not advisable. It is important to consider redesigning products with robotic assembly in mind, incorporating specific design features to simplify robot training and facilitate easier assembly by robots.
- Slower operational speeds are crucial for maintaining precision in assembly tasks, particularly due to vibrations caused by motors in various configurations.
- The use of wait commands is essential to minimize vibrations and enhance the repeatability of the cycle.
- The introduction of vibrations during assembly, especially for handling rings, is suggested as a method to reduce interference and improve operational efficiency.
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
References
- Jain, A.; Jain, P.; Chan, F.T.; Singh, S. A review on manufacturing flexibility. International Journal of Production Research 2013, 51, 5946–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GUSTAVSSON, S.O. Flexibility and productivity in complex production processes. International Journal of Production Research 1984, 22, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovane, F.; Koren, Y.; Boër, C. Present and Future of Flexible Automation: Towards New Paradigms. CIRP Annals 2003, 52, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbani, A.; Molinari-Tosatti, L.; Pierpaoli, F. New frontiers for manufacturing in mass customization. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 5th Biannual World Automation Congress. TSI Press, WAC-02. [CrossRef]
- Mourtzis, D.; Doukas, M. , The Evolution of Manufacturing Systems: From Craftsmanship to the Era of Customisation. In Advances in Logistics, Operations, and Management Science; IGI Global, 2014; pp. 1–29. [CrossRef]
- Chammas, A.; Quaresma, M.; Mont’Alvão, C. A Closer Look on the User Centred Design. Procedia Manufacturing 2015, 3, 5397–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragança, S.; Costa, E.; Castellucci, I.; Arezes, P.M. , A Brief Overview of the Use of Collaborative Robots in Industry 4.0: Human Role and Safety. In Occupational and Environmental Safety and Health; Springer International Publishing, 2019; pp. 641–650. [CrossRef]
- Fager, P.; Sgarbossa, F.; Calzavara, M. Cost modelling of onboard cobot-supported item sorting in a picking system. International Journal of Production Research 2020, 59, 3269–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Makrini, I.; Elprama, S.A.; Van den Bergh, J.; Vanderborght, B.; Knevels, A.J.; Jewell, C.I.; Stals, F.; De Coppel, G.; Ravyse, I.; Potargent, J.; et al. Working with Walt: How a Cobot Was Developed and Inserted on an Auto Assembly Line. IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine 2018, 25, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safeea, M.; Neto, P.; Béarée, R. , The Third Hand, Cobots Assisted Precise Assembly. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing, 2019; pp. 454–457. [CrossRef]
- Barravecchia, F.; Mastrogiacomo, L.; Franceschini, F. A general cost model to assess the implementation of collaborative robots in assembly processes. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2023, 125, 5247–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, J.; Schlette, C.; Kjærgaard, M.B. Breaking Down the Energy Consumption of Industrial and Collaborative Robots: A Comparative Study. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 28th International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA). IEEE; 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshvarparast, A.; Battini, D.; Battaia, O.; Pirayesh, A. Collaborative robots in manufacturing and assembly systems: literature review and future research agenda. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giberti, H.; Abbattista, T.; Carnevale, M.; Giagu, L.; Cristini, F. A Methodology for Flexible Implementation of Collaborative Robots in Smart Manufacturing Systems. Robotics 2022, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Barthelmey, A.; Reckelkamm, T.; Kang, H.; Son, J. A Study on Human-Robot Collaboration based Hybrid Assembly System for Flexible Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the IECON 2019 - 45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society. IEEE; 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwani, F.; Asad, M.M.; Ibrahim, B. Collaborative Robots and Industrial Revolution 4. In 0 (IR 4.0). In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Emerging Trends in Smart Technologies (ICETST). IEEE; 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassmair, C.; Taylor, N. Human Robot Collaboration in Production Environments. 2014. 23rd IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication 2014 : Towards a Framework for Joint Action Workshop, IEEE RO-MAN 2014, Conference date: 25-08-2014. Through 29-08-2014. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, U.; Yang, E. Human–Robot Collaborations in Smart Manufacturing Environments: Review and Outlook. Sensors 2023, 23, 5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalos, G.; Karagiannis, P.; Dimitropoulos, N.; Andronas, D.; Makris, S. , Human Robot Collaboration in Industrial Environments. In Intelligent Systems, Control and Automation: Science and Engineering; Springer International Publishing, 2021; pp. 17–39. [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H. , Rapid Prototyping. In e-Design; Elsevier, 2015; pp. 743–786. [CrossRef]
- Shahrubudin, N.; Lee, T.; Ramlan, R. An Overview on 3D Printing Technology: Technological, Materials, and Applications. Procedia Manufacturing 2019, 35, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geonea, I.; Copilusi, C.; Dumitru, S.; Margine, A.; Rosca, A.; Tarnita, D. A New Exoskeleton Prototype for Lower Limb Rehabilitation. Machines 2023, 11, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciceri, M.; Gauterio, M.; Scaccabarozzi, S.; Paz, J.; Garcia-Carmona, R.; Aruanno, B.; Covarrubias, M. Rapid Prototyping in Engineering Education: Developing a Hand Exoskeleton for Personalized Rehabilitation. Computer-Aided Design and Applications. [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.Y.; Arif, Z.U.; Noroozi, R.; Hossain, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Umer, R. 3D/4D printing of cellulose nanocrystals-based biomaterials: Additives for sustainable applications. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2023, 251, 126287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albin, B.; Palpacelli, M.C. From Traditional Automation to Collaborative Robotics in Fine Robotic Assembly: a Case Study at i-Labs. In Proceedings of the 2023 I-RIM Conference. I-RIM, 2023. [In Press]. [Google Scholar]
- Bajrami, A.; Palpacelli, M.C. A Proposal for a Simplified Systematic Procedure for the Selection of Electric Motors for Land Vehicles with an Emphasis on Fuel Economy. Machines 2023, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, B.; Kempf, K. Opportunistic scheduling for robotic assembly. In Proceedings of the Proceedings. 1985 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Vol. 2; 1985; pp. 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.S.; Warnecke, H.J.; Gweon, D.G. Robotic assembly: a synthesizing overview. Robotica 1987, 5, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, M.A.R.; Nottensteiner, K.; Wedler, A.; Grunwald, G. Robotic Technologies for In-Space Assembly Operations. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, A.; Perry, G. Sensor-based robotic assembly systems: Research and applications in electronic manufacturing. Proceedings of the IEEE 1983, 71, 856–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicker, P.; Strip, D. Current research in robotics and automation-automated planning and programming for robotic batch mechanical assembly. Computer 1989, 22, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, D.O.; Stephanou, H.E. Micro and Mesoscale Robotic Assembly. Journal of Manufacturing Processes 2004, 6, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Fuhlbrigge, T.A. Integrated robotic system for high precision assembly in a semi-structured environment. Assembly Automation 2007, 27, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarić, A.; Xiao, J.; Shi, J. Reducing uncertainty in robotic surface assembly tasks based on contact information. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Workshop on Advanced Robotics and its Social Impacts; 2014; pp. 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Cabrera, M.; Lopez-Juarez, I.; Rios-Cabrera, R.; Corona-Castuera, J. Machine vision approach for robotic assembly. Assembly Automation 2005, 25, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BM MECCANICA - assembly line solution - Coni per guarnizione di diverse misure. https://www.bmmeccanica.com/prodotti/coni-per-guarnizioni-o-ring-di-diverse-misure/. Accessed: 2024-01-18.
- Dual-arm YuMi collaborative robot - ABB Group. https://new.abb.com/products/robotics/robots/collaborative-robots/yumi/dual-arm. Accessed: 2024-01-18.
- FANUC. CRX-10iA/L. https://www.fanuc.eu/it/it/robot/robot-filter-page/robot-collaborativi/crx-10ial, 2024. Accessed: 2024-01-19.
- Formlabs. Form 3. https://formlabs.com/it/3d-printers/form-3/, 2024. Accessed: 2024-01-19.
- SCHUNK. Co-act EGP-C Collaborating gripper for small components. https://schunk.com/gb/en/gripping-systems/parallel-gripper/co-act-egp-c/c/pgr_3995, n.d. SCHUNK. Co-act EGP-C Collaborating gripper for small components. https://schunk.com/gb/en/gripping-systems/parallel-gripper/co-act-egp-c/c/pgr_3995, n.d. Accessed: 2024-01-19.
- NX software including CAD and CAM | Siemens Software. https://plm.sw.siemens.com/en-US/nx/. Accessed: 2024-01-19.
- Formlabs. Software PreForm. https://formlabs.com/it/software/. Accessed: 2024-01-19.
- AlbinEV. Miscellaneous Projects. https://github.com/AlbinEV/miscellaneous_projects/tree/main/Progetto_1, 2024.
- Formlabs. Grey Resin | Formlabs. https://formlabs.com/it/negozio/materials/grey-resin/. Accessed: 2024-01-19.
- Bajrami, A.; Palpacelli, M.C. A Flexible Framework for Robotic Post-Processing of 3D Printed Components. In Proceedings of the Volume 7: 19th IEEE/ASME International Conference on Mechatronic and Embedded Systems and Applications (MESA). American Society of Mechanical Engineers, IDETC-CIE. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
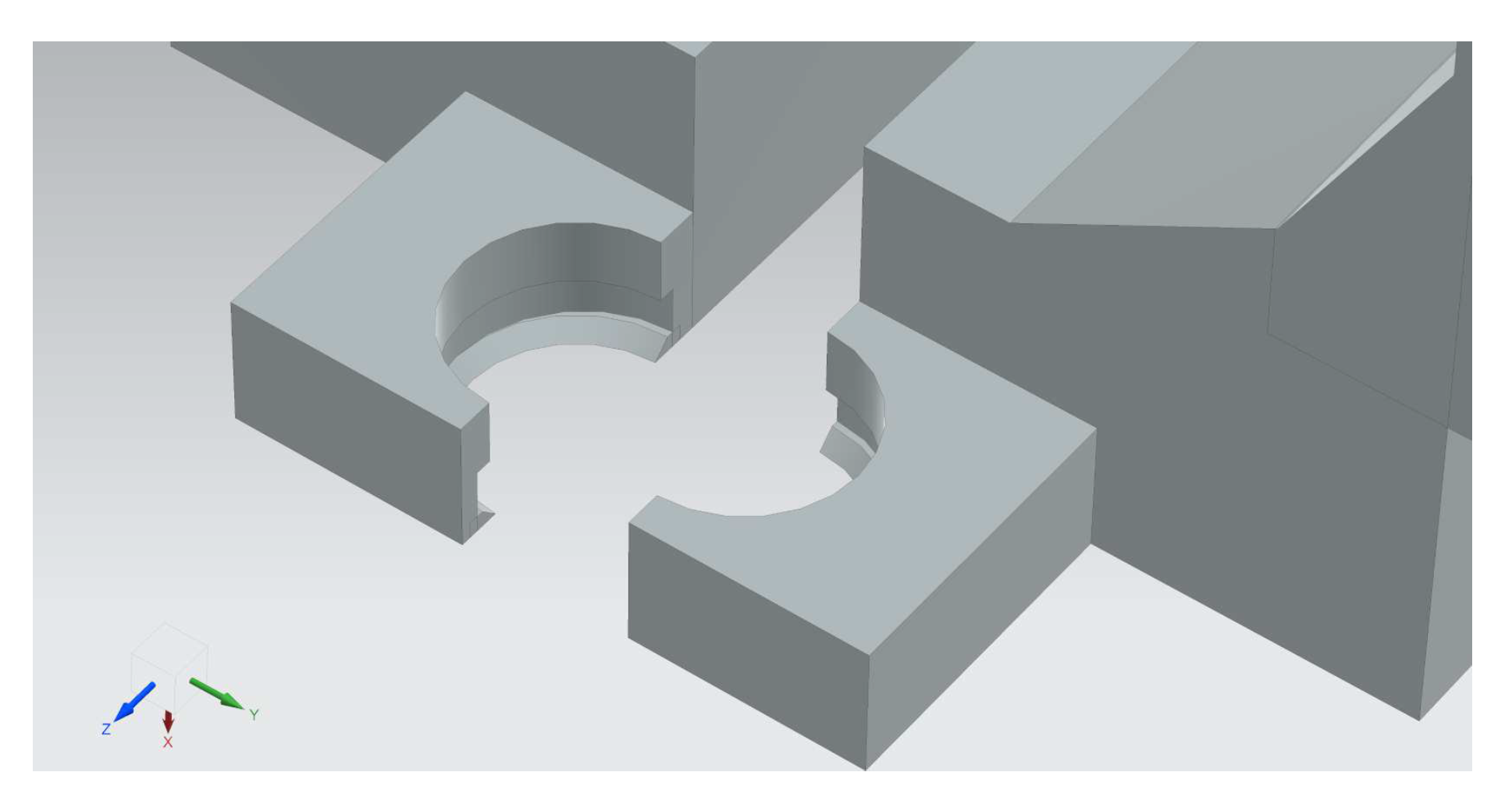
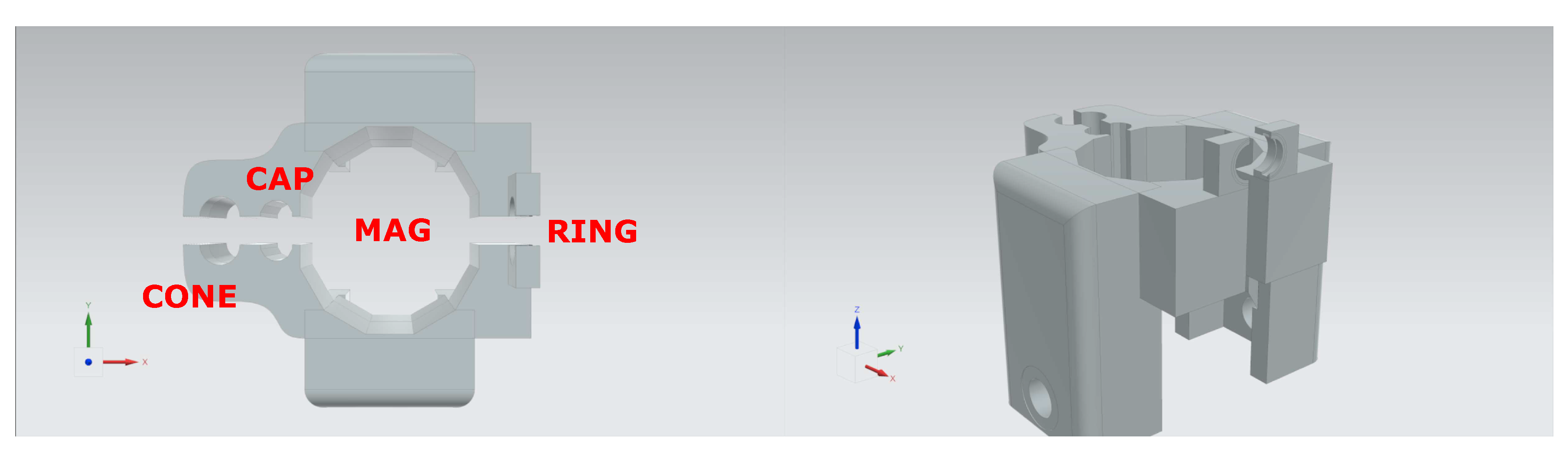

| Component | Shape and Function | Special Features |
|---|---|---|
| MAG Grip | Irregular cylindrical, decagonal shape | Adaptable to various positions |
| CAP Grip | Cylindrical with linear geometry | Ensures secure and universal grip |
| CONE Grip | Negative form, narrow at base | Prevents CONE from being pushed out |
| RING Grip | Triangular and elliptical internal space | Selects and grips small rings (Ø 9mm, thickness 0.7mm) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





