Submitted:
01 February 2024
Posted:
02 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
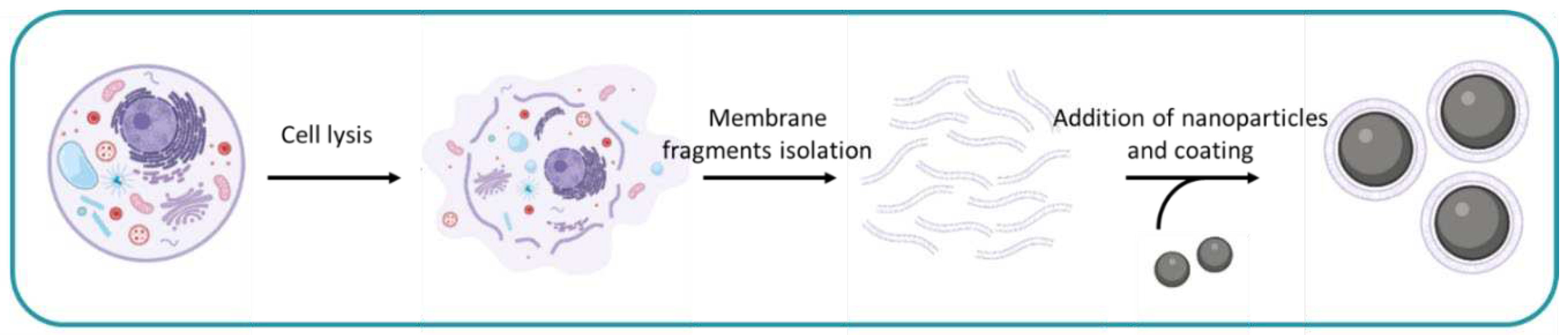
1. Introduction
2. General Procedure
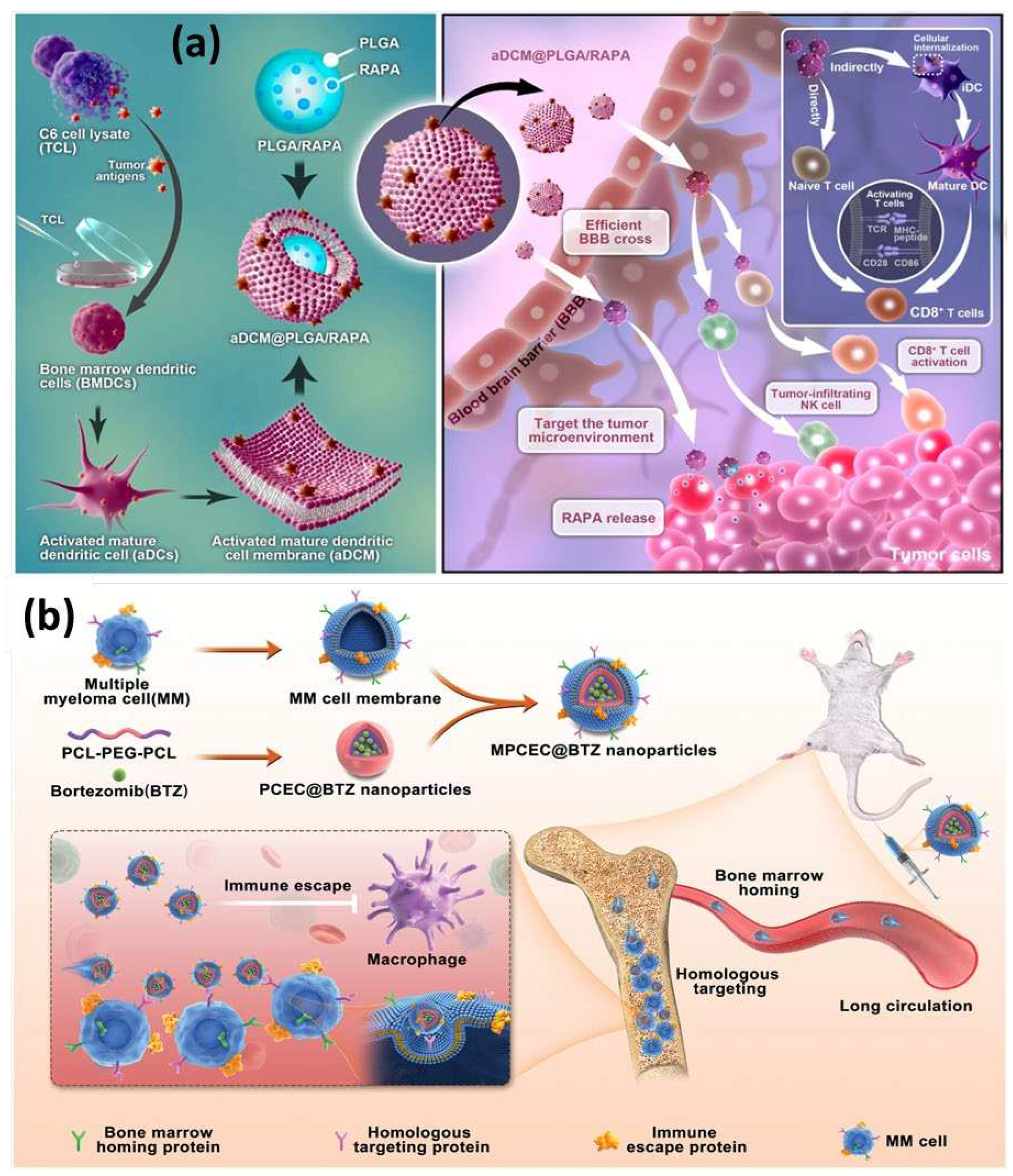
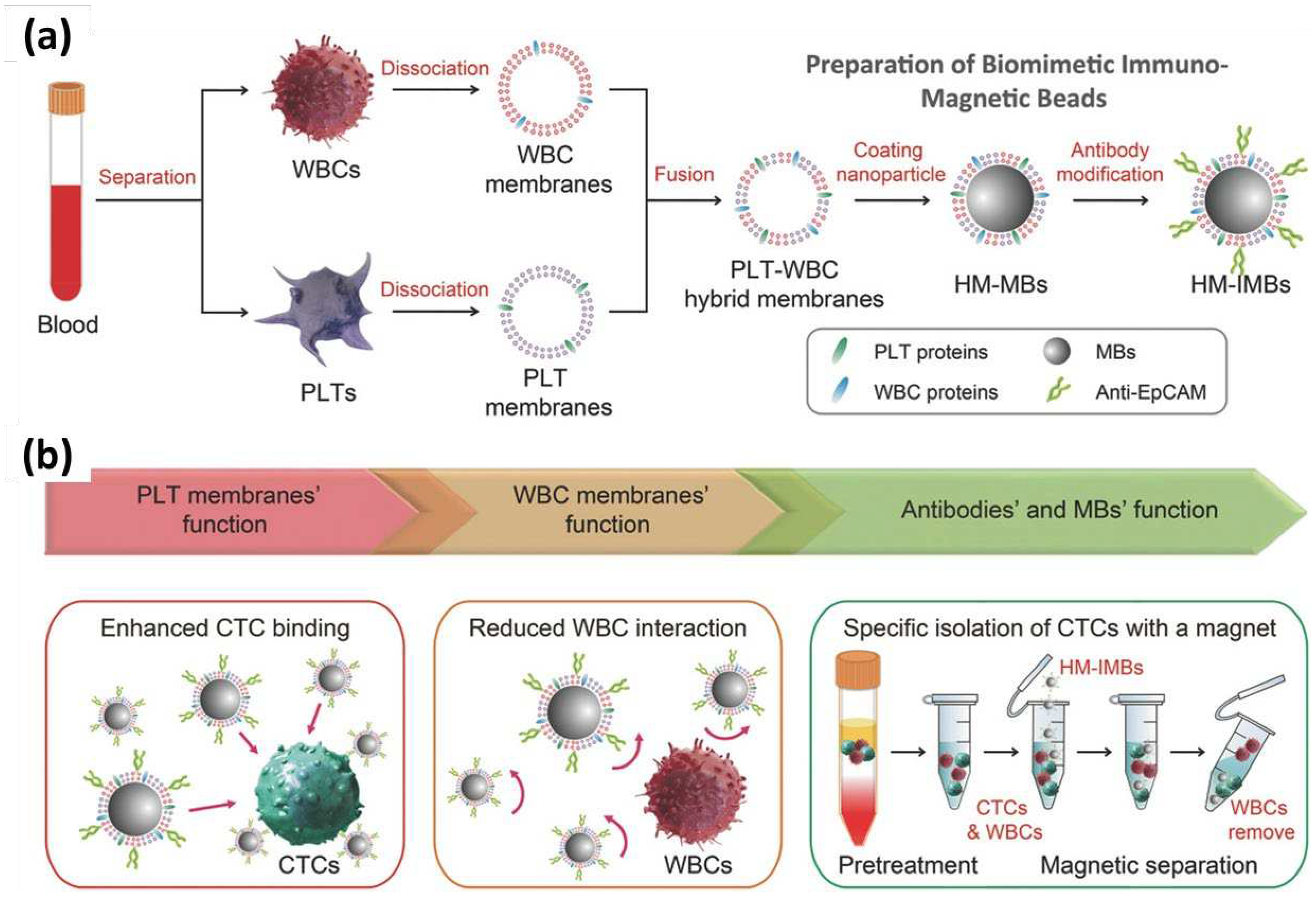
3. Membrane Donor Cells
| Donor cell | Cell lines | Application | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cervical and ovarian cancer | HeLa | Homologous targeting | [22,23,24,25] | |
| Multiple myeloma | ARD, KMS11, 5TGM1 | [26] | ||
| Melanoma | B16-F10, MDA-MB-435 | [12,27,28,29,30,31,32,33] | ||
| Leukemia | CHRF-288-11, C1498, RAW264.7, THP-1, Jurkat, HL-60 | [24,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] | ||
| Breast cancer | 4T1, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468 | [6,38,41,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57] | ||
| Colon carcinoma | CT-26 | [24,59] | ||
| Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | CAL 27, SCC7 | [60,61,62,63] | ||
| Lung cancer | NCI-H460, A549 | [55,64] | ||
| Glioma | GL261, C6, U87MG | [65,66] | ||
| Glioblastoma | U251 | [67,68] | ||
| Prostate cancer | RM-1 | [69] | ||
| Liver cancer | HepG2 | [70] | ||
| Fibroblasts | NIH 3T3 | [50,104] | ||
| Embryonic kidney cells | HEK293 | [105] | ||
| Vaginal endothelial cells | VK2/E6E7 | [106] | ||
| Neural stem cells | Primary cells | [107] | ||
| Microglia | HMC3 | [68] | ||
| Keratinocytes | Hacat | [108] | ||
| Mesenchymal stem cells | Primary cells | [96,97,98,99,100] | ||
| Neuroblastoma | Neuro-2a | Neurotoxin capture | [58] | |
| Erythrocytes | Primary cells | Cancer tissue targeting | [19,30,47,49,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90] | |
| Avoidance of immune recognition | ||||
| Leukocytes | Primary cells | [71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,88,91,92,93,94,95] | ||
| Platelets | Primary cells | Cancer cell binding ability | [49,72,85,86,101,102,103] |
4. Fragmentation of Cell Membranes
4.1. Hypotonic Lysis
4.2. Homogenization
4.3. Freeze-Thaw
4.4. Sonication
4.5. Other Methods
4.6. Summary
5. Membrane Fragments Isolation
5.1. Centrifugation
5.2. Gradient
5.3. Washing
5.4. Other Methods
5.5. Summary
6. Nanoparticle Cores
6.1. Cargoes Loaded into the Particles.
6.2. Summary
7. Membrane Coating of Nanoparticles
7.1. Coating after Vesicle Formation
7.2. Sonication
7.3. Extrusion
7.4. Sonication-Extrusion
7.5. Summary
8. Discussion
9. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfram, J.; Ferrari, M. Clinical Cancer Nanomedicine. Nano Today 2019, 25, 85–98. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S. Advantages of Nanomedicine in Cancer Therapy: A Review. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2023, 6, 22594–22610. [CrossRef]
- Aftab, S.; Shah, A.; Nadhman, A.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Aysıl Ozkan, S.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Shukla, S.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Nanomedicine: An Effective Tool in Cancer Therapy. Int J Pharm 2018, 540, 132–149. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Zhang, P.; Meng, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Luo, X.; Gao, M. Recent Advancements in Biocompatible Inorganic Nanoparticles towards Biomedical Applications. Biomater Sci 2018, 6, 726–745. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.Q.; Li, X.; Dai, H.W. Hybrid Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles: A Multifunctional Biomimetic Platform for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Acta Biomater 2020, 112, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Dai, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Xi, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Qian, K.; Guo, S.; Zhu, C.; et al. Cancer-Cell-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles with a Yolk-Shell Structure Augment Cancer Chemotherapy. Nano Lett 2020, 20, 936–946. [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.; Tavares, A.J.; Dai, Q.; Ohta, S.; Audet, J.; Dvorak, H.F.; Chan, W.C.W. Analysis of Nanoparticle Delivery to Tumours. Nature Reviews Materials 2016 1:5 2016, 1, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M. Debugging Nano–Bio Interfaces: Systematic Strategies to Accelerate Clinical Translation of Nanotechnologies. Trends Biotechnol 2018, 36, 755–769. [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.H.; Kroll, A. V.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L. Cell Membrane Coating Nanotechnology. Advanced Materials 2018, 30, 1706759. [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.M.J.; Fang, R.H.; Wang, K.C.; Luk, B.T.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Dehaini, D.; Nguyen, P.; Angsantikul, P.; Wen, C.H.; Kroll, A. V.; et al. Nanoparticle Biointerfacing by Platelet Membrane Cloaking. Nature 2015 526:7571 2015, 526, 118–121. [CrossRef]
- Kroll, A. V.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Biointerfacing and Applications of Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles. Bioconjug Chem 2017, 28, 23–32. [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.H.; Hu, C.M.J.; Luk, B.T.; Gao, W.; Copp, J.A.; Tai, Y.; O’Connor, D.E.; Zhang, L. Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Anticancer Vaccination and Drug Delivery. Nano Lett 2014, 14, 2181–2188. [CrossRef]
- Oroojalian, F.; Beygi, M.; Baradaran, B.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Shahbazi, M.A. Immune Cell Membrane-Coated Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Small 2021, 17, 2006484. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Lin, J.; Chew, S.Y. Neural Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Targeted and Enhanced Uptake by Central Nervous System Cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021, 13, 55840–55850. [CrossRef]
- Luk, B.T.; Zhang, L. Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Journal of Controlled Release 2015, 220, 600–607. [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles: Research Advances. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 625–641. [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Cheng, P.; Pu, K.; Zhen, X.; Cheng, P.; Pu, K. Recent Advances in Cell Membrane–Camouflaged Nanoparticles for Cancer Phototherapy. Small 2019, 15, 1804105. [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Park, W.; Park, S. Bin; Rhim, W.K.; Han, D.K. Recent Trends in Cell Membrane-Cloaked Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Applications. Methods 2020, 177, 2–14. [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.M.J.; Zhang, L.; Aryal, S.; Cheung, C.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Erythrocyte Membrane-Camouflaged Polymeric Nanoparticles as a Biomimetic Delivery Platform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 10980–10985. [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Su, J.; Ran, W.; Zhang, P.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Li, Y. Preparation and Application of Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2575–2592. [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Rudnitzki, F.; Hüttmann, G.; Zhang, Z.; Rahmanzadeh, R. Important Factors for Cell-Membrane Permeabilization by Gold Nanoparticles Activated by Nanosecond-Laser Irradiation. Int J Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 5659–5672. [CrossRef]
- Soprano, E.; Migliavacca, M.; López-Ferreiro, M.; Pelaz, B.; Polo, E.; del Pino, P. Fusogenic Cell-Derived Nanocarriers for Cytosolic Delivery of Cargo inside Living Cells. J Colloid Interface Sci 2023, 648, 488–496. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, F.; Hou, W.; Wang, Y.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Y. Cancer Cell Membrane-Enveloped Dexamethasone Normalizes the Tumor Microenvironment and Enhances Gynecologic Cancer Chemotherapy. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 16703–16714. [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bai, X.; Martikainen, M.V.; Kårlund, A.; Roponen, M.; Xu, W.; Hu, G.; Tasciotti, E.; Lehto, V.P. Cell Membrane Coating Integrity Affects the Internalization Mechanism of Biomimetic Nanoparticles. Nature Communications 2021 12:1 2021, 12, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ji, M.; Wang, Q.; He, N.; Li, Y. Ca2+ Signaling Modulation Using Cancer Cell Membrane Coated Chitosan Nanoparticles to Combat Multidrug Resistance of Cancer. Carbohydr Polym 2020, 238, 116073. [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Chu, B.; Wei, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, D.; Huang, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, M.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Cancer-Cell-Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Therapy of Multiple Myeloma Based on Bone Marrow Homing. Advanced Materials 2022, 34, 2107883. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhi, S.; Ou, J.; Gao, J.; Zheng, L.; Huang, M.; Du, S.; Shi, L.; Tu, Y.; Cheng, K. Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticle Co-Loaded with Photosensitizer and Toll-like Receptor 7 Agonist for the Enhancement of Combined Tumor Immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kroll, A. V; Fang, R.H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wei, X.; Lai Yu, C.; Gao, J.; Luk, B.T.; Dehaini, D.; Gao, W.; et al. Nanoparticulate Delivery of Cancer Cell Membrane Elicits Multiantigenic Antitumor Immunity. Advanced Materials 2017, 29, 1703969. [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Adjuvant Nanoparticles with Mannose Modification for Effective Anticancer Vaccination. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5121–5129. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dong, H.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, K.; Dai, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. Erythrocyte-Cancer Hybrid Membrane Camouflaged Hollow Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles for Prolonged Circulation Life and Homotypic-Targeting Photothermal/Chemotherapy of Melanoma. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5241–5252. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Krishnan, N.; Zhou, J.; Chekuri, S.; Wei, X.; Kroll, A. V; Lai Yu, C.; Duan, Y.; Gao, W.; Fang, R.H.; et al. Engineered Cell-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles Directly Present Tumor Antigens to Promote Anticancer Immunity. Advanced Materials 2020, 32, 2001808. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Mohapatra, A.; Zhou, J.; Holay, M.; Krishnan, N.; Gao, W.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Virus-Mimicking Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Cytosolic Delivery of mRNA. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2022, 61, e202113671. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, C.; You, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. Bacterial Vesicle-Cancer Cell Hybrid Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Tumor Specific Immune Activation and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020, 12, 41138–41147. [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Jin, M.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Lu, Q. Macrophage Membrane-Coated Liposomes as Controlled Drug Release Nanocarriers for Precision Treatment of Osteosarcoma. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2022, 5, 18396–18408. [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.C.; Sterin, E.H.; Day, E.S. Membrane-Wrapped Nanoparticles for Enhanced Chemotherapy of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2022, 8, 4439–4448. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gong, H.; Mohapatra, A.; Heo, J.; Gao, W.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Genetically Engineered Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Dexamethasone to Inflamed Lungs. Sci Adv 2021, 7, 7820–7836. [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ren, M.; He, P.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, S. Genetically Engineered Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Antibacterial and Immunoregulatory Dual-Function Treatment of Ligature-Induced Periodontitis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2023, 11, 1113367. [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, S.; Xian, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, S.; Xian, Y. Multivalent Aptamer Functionalized Ag2S Nanodots/Hybrid Cell Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanobioprobe for the Ultrasensitive Isolation and Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells. Adv Funct Mater 2020, 30, 1909781. [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, E.; Yu, Y.; Krishnan, N.; Silva-Ayala, D.; Fang, R.H.; Griffiths, A.; Gao, W.; et al. Extending the In Vivo Residence Time of Macrophage Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles through Genetic Modification. Small 2023, 2305551. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, C.; Ma, B.; Liu, Z.; Du, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, N.; Huang, X.; Ou, L. Genetically Engineered Cell Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for High-Performance Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells. Adv Funct Mater 2023, 2304426. [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Yu, X.; You, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, R.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Yuan, Y. Macrophage-Cancer Hybrid Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Targeting Lung Metastasis in Breast Cancer Therapy. J Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Dou, C.; Xia, Y.; Li, B.; Zhao, M.; Yu, P.; Zheng, Y.; El-Toni, A.M.; Atta, N.F.; Galal, A.; et al. Neutrophil-like Cell-Membrane-Coated Nanozyme Therapy for Ischemic Brain Damage and Long-Term Neurological Functional Recovery. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2263–2280. [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Pan, L.; Qian, S.; Yang, X.; Pan, L.; Chi, R.; Chen, J.; Pan, J.; Shi, C. Antimicrobial Peptide Nanoparticles Coated with Macrophage Cell Membrane for Targeted Antimicrobial Therapy of Sepsis. Mater Des 2023, 229, 111883. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Lv, B.; Lin, Z.; Chu, X.; Xiong, Y.; Knoedler, S.; Cao, F.; Lin, C.; Chen, L.; Yu, C.; et al. Neddylation Suppression by a Macrophage Membrane-Coated Nanoparticle Promotes Dual Immunomodulatory Repair of Diabetic Wounds. Bioact Mater 2024, 34, 366–380. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, M.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Q. Macrophage Membrane-Decorated MnO2 Nanozyme Catalyzed the Scavenging of Estradiol for Endometriosis Treatment. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2024, 233, 113633. [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.A.; Wilkins, D.E.; Dang, M.N.; Hoover, E.C.; Aboeleneen, S.B.; Day, E.S. Cancer Cell Membrane Wrapped Nanoparticles for the Delivery of a Bcl-2 Inhibitor to Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol Pharm 2023, 20, 3895–3913. [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, W.X.; Zhou, Z.L.; Lv, Q.Y.; Cui, H.F. Thermosensitive Biomimetic Hybrid Membrane Camouflaged Hollow Gold Nanoparticles for NIR-Responsive Mild-Hyperthermia Chemo-/Photothermal Combined Tumor Therapy. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2022, 5, 5113–5125. [CrossRef]
- Holay, M.; Zhou, J.; Park, J.H.; Landa, I.; Ventura, C.J.; Gao, W.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Organotropic Targeting of Biomimetic Nanoparticles to Treat Lung Disease. Bioconjug Chem 2022, 33, 586–593. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Yao, X.; Sung, S.; Pang, Z.; Yang, W. Erythrocyte-Cancer Hybrid Membrane-Camouflaged Melanin Nanoparticles for Enhancing Photothermal Therapy Efficacy in Tumors. Biomaterials 2019, 192, 292–308. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, S.; Ding, B.; Qu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Sun, Y.; Fang, H.; Long, Y.; Zhang, R.; et al. Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Rare Earth Doped Nanoparticles for Tumor Surgery Navigation in NIR-II Imaging Window. Chemical Engineering Journal 2020, 385, 123959. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cai, H.; Li, Z.; Ren, L.; Ma, X.; Zhu, H.; Gong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gu, Z.; Luo, K. A Tumor Cell Membrane-Coated Self-Amplified Nanosystem as a Nanovaccine to Boost the Therapeutic Effect of Anti-PD-L1 Antibody. Bioact Mater 2023, 21, 299–312. [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, F.; Yan, D.; Han, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Zhong Tang, B.; Cui, J.; Zhang, F.; Yan, D.; et al. “Trojan Horse” Phototheranostics: Fine-Engineering NIR-II AIEgen Camouflaged by Cancer Cell Membrane for Homologous-Targeting Multimodal Imaging-Guided Phototherapy. Advanced Materials 2023, 35, 2302639. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Jing, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, C.; Xiao, G.; Wang, S.; Liang, X.; Dou, Y.; Ding, Z.; Zhu, Y.; et al. 4T1 Cell Membrane-Derived Biodegradable Nanosystem for Comprehensive Interruption of Cancer Cell Metabolism. Chinese Chemical Letters 2023, 34, 108161. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, T.; He, T.; Li, Y.; Yin, S. Cancer Cell Membrane–Encapsulated Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Tumor Immuno-Photothermal Therapy. Chemical Engineering Journal 2023, 463, 142495. [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Xie, W.; Wang, M.; Wang, P.; Li, Q.; Cheng, J.; Yan, M.; Xia, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, G. Cancer Cell Membrane-Camouflaged CuPt Nanoalloy Boosts Chemotherapy of Cisplatin Prodrug to Enhance Anticancer Effect and Reverse Cisplatin Resistance of Tumor. Mater Today Bio 2024, 24, 100941. [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Shukla, R.P.; Yadav, K.; Singh, N.; Marwaha, D.; Gautam, S.; Bakshi, A.K.; Rai, N.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, D.; et al. Dacarbazine-Primed Carbon Quantum Dots Coated with Breast Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomes for Improved Breast Cancer Therapy. Journal of Controlled Release 2024, 365, 43–59. [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Gómez Martínez, M.; Happonen, E.; Qian, J.; Gómez Vallejo, V.; Jorge Mendazona, H.; Jokivarsi, K.; Scaravilli, M.; Latonen, L.; Llop, J.; et al. A PEG-Assisted Membrane Coating to Prepare Biomimetic Mesoporous Silicon for PET/CT Imaging of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int J Pharm 2024, 123764. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ai, X.; Duan, Y.; Xian, N.; Fang, R.H.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L. Neuronal Cellular Nanosponges for Effective Detoxification of Neurotoxins. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19145–19154. [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.F.; Chen, Y.; Zou, M.Z.; Li, C.X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.J.; Cheng, S.X.; Zhang, X.Z. Homotypic Targeted Photosensitive Nanointerferer for Tumor Cell Cycle Arrest to Boost Tumor Photoimmunotherapy. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 18555–18567. [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Yu, G.T.; Meng, Q.F.; Bu, L.L.; Tian, R.; Lin, L. Sen; Deng, H.; Yang, W.; Zan, M.; Ding, J.; et al. Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Personalized Therapy in Patient-Derived Xenograft Models. Adv Funct Mater 2019, 29, 1905671. [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.L.; Rao, L.; Yu, G.T.; Chen, L.; Deng, W.W.; Liu, J.F.; Wu, H.; Meng, Q.F.; Guo, S.S.; Zhao, X.Z.; et al. Cancer Stem Cell-Platelet Hybrid Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Photothermal Therapy of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Adv Funct Mater 2019, 29, 1807733. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, Z.; Pan, Q.; Bai, Y.; Yu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Z.; Pan, Q.; Yu, M.; et al. Targeted Therapy of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Cancer Cell Membrane Coated Co-Fc Nanoparticles Via Autophagy Inhibition. Adv Funct Mater 2023, 33, 2300235. [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Wu, Q.; You, Y.; Lan, Z.; Zou, K.L.; Cheng, G.W.; Chen, H.; Han, Y.H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Microwave-Responsive Gadolinium Metal-Organic Frameworks Nanosystem for MRI-Guided Cancer Thermotherapy and Synergistic Immunotherapy. Bioact Mater 2024, 33, 532–544. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ke, J.; Jia, H.; Ren, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C. Cancer Cell Membrane Coated PLGA Nanoparticles as Biomimetic Drug Delivery System for Improved Cancer Therapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2023, 222, 113131. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Dai, L.; Yu, J.; Cao, H.; Bao, Y.; Hu, J.J.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Sofia, A.; Chen, H.; et al. Tumor Microenvironment Targeting System for Glioma Treatment via Fusion Cell Membrane Coating Nanotechnology. Biomaterials 2023, 295, 122026. [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Shen, W.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C. Preparation of C6 Cell Membrane-Coated Doxorubicin Conjugated Manganese Dioxide Nanoparticles and Its Targeted Therapy Application in Glioma. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2023, 180, 106338. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.N.; Miranda, R.R.; Moreno, N.S.; Pincela Lins, P.M.; Leite, C.M.; Leite, A.E.T.; Machado, T.R.; Cataldi, T.R.; Labate, C.A.; Reis, R.M.; et al. Using Design of Experiments (DoE) to Optimize Performance and Stability of Biomimetic Cell Membrane-Coated Nanostructures for Cancer Therapy. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2023, 11, 1120179. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Mu, N.; Ding, Y.; Huang, R.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; Chen, T. Tumor Microenvironment Targeting for Glioblastoma Multiforme Treatment via Hybrid Cell Membrane Coating Supramolecular Micelles. Journal of Controlled Release 2024, 366, 194–203. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dong, S.; Wu, J.; Lv, X.; Yang, N.; Wei, Q.; Wang, C.; Chen, J. Surgically Derived Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated R837-Loaded Poly(2-Oxazoline) Nanoparticles for Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2023, 15, 7878–7886. [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, M.J.C.; Lin, K.S.; Weng, M.T.; Kunene, S.C.; Lin, Y.S.; Lin, Y.T. Synthesis and Characterization of Silica Nanoparticles from Rice Ashes Coated with Chitosan/Cancer Cell Membrane for Hepatocellular Cancer Treatment. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 228, 487–497. [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Quattrocchi, N.; Van De Ven, A.L.; Chiappini, C.; Evangelopoulos, M.; Martinez, J.O.; Brown, B.S.; Khaled, S.Z.; Yazdi, I.K.; Enzo, M.V.; et al. Synthetic Nanoparticles Functionalized with Biomimetic Leukocyte Membranes Possess Cell-like Functions. Nature Nanotechnology 2012 8:1 2012, 8, 61–68. [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Meng, Q.F.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yu, G.T.; Li, A.; Ma, W.; Zhang, N.; Guo, S.S.; Zhao, X.Z.; et al. Platelet–Leukocyte Hybrid Membrane-Coated Immunomagnetic Beads for Highly Efficient and Highly Specific Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells. Adv Funct Mater 2018, 28, 1803531. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, K.; Li, C.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Q.; He, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Macrophage-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Tumor-Targeted Chemotherapy. Nano Lett 2018, 18, 1908–1915. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, M.; Du, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.; Han, Y.; Yan, F.; Shi, Z.; Feng, S. Tumor-Associated-Macrophage-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Improved Photodynamic Immunotherapy. Nano Lett 2021, 21, 5522–5531. [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, W.; Li, S.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Multimodal Enzyme Delivery and Therapy Enabled by Cell Membrane-Coated Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticles. Nano Lett 2020, 20, 4051–4058. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fan, W.; Ling, Y.; Wen, J.; Li, J.; Peng, Z.; Jin, M. Renal Clearable BiOI Nanodots with M1 Macrophage Membrane Coating for Enhanced Radiotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mater Des 2023, 227, 111777. [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Hou, X.; Wei, Z.; Liu, D.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, K. Macrophage Membrane-Coated SN-38-Encapsulated Liposomes for Efficient Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2024, 91, 104904. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Miao, X.; Bo, S.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y. Macrophage Membrane-Coated Self-Assembled Curcumin Nanoparticle Missile for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2024, 91, 105237. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Fan, Z.; Lemons, P.K.; Cheng, H. A Facile Approach to Functionalize Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1012–1022. [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, L.; Chen, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, D.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, X. Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanocarriers with Biomimetic Deformability of Erythrocytes for Ultralong Circulation and Enhanced Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6527–6540. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Akiva, E.; Meyer, R.A.; Yu, H.; Smith, J.T.; Pardoll, D.M.; Green, J.J. Biomimetic Anisotropic Polymeric Nanoparticles Coated with Red Blood Cell Membranes for Enhanced Circulation and Toxin Removal. Sci Adv 2020, 6. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, X.; Huang, R.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Xiang, X.; Chen, W.; Nie, X.; et al. Erythrocyte Membrane Camouflaged Graphene Oxide for Tumor-Targeted Photothermal-Chemotherapy. Carbon N Y 2019, 146, 660–670. [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.H.; Hu, C.M.J.; Chen, K.N.H.; Luk, B.T.; Carpenter, C.W.; Gao, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.E.; Lu, W.; Zhang, L. Lipid-Insertion Enables Targeting Functionalization of Erythrocyte Membrane-Cloaked Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8884–8888. [CrossRef]
- Luk, B.T.; Fang, R.H.; Hu, C.M.J.; Copp, J.A.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Dehaini, D.; Gao, W.; Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, L. Safe and Immunocompatible Nanocarriers Cloaked in RBC Membranes for Drug Delivery to Treat Solid Tumors. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1004–1011. [CrossRef]
- Dehaini, D.; Wei, X.; Fang, R.H.; Masson, S.; Angsantikul, P.; Luk, B.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, M.; Jiang, Y.; Kroll, A. V; et al. Erythrocyte–Platelet Hybrid Membrane Coating for Enhanced Nanoparticle Functionalization. Advanced Materials 2017, 29, 1606209. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, X.; Midgley, A.C.; Liu, Q.; Kang, H.; Wu, J.; Khalique, A.; Qian, M.; et al. Biomimetic Design of Artificial Hybrid Nanocells for Boosted Vascular Regeneration in Ischemic Tissues. Advanced Materials 2022, 34, 2110352. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fang, H.; Liu, Q.; Gai, Y.; Yuan, L.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Hou, Y.; Gao, M.; Lan, X. Red Blood Cell Membrane-Coated Upconversion Nanoparticles for Pretargeted Multimodality Imaging of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Biomater Sci 2020, 8, 1802–1814. [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Huang, B.; Li, M.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Su, J. Neutrophil-Erythrocyte Hybrid Membrane-Coated Hollow Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles for Targeted and Photothermal/ Anti-Inflammatory Therapy of Osteoarthritis. Compos B Eng 2022, 237, 109855. [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Lang, T.; Zheng, C.; Yan, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, R.; Huang, X.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Yin, Q. Promote Intratumoral Drug Release and Penetration to Counteract Docetaxel-Induced Metastasis by Photosensitizer-Modified Red Blood Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticle. Adv Funct Mater 2023, 33, 2212109. [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Li, Y.; Long, H.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, F.; Li, M.; Wu, C.; Liu, Z. Cell Membrane-Camouflaged DOX-Loaded β-Glucan Nanoparticles for Highly Efficient Cancer Immunochemotherapy. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 225, 873–885. [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Kuang, L.; Yin, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Wang, B.; Dong, Z.; Wang, W.; Yin, T.; et al. Tumor-Antigen Activated Dendritic Cell Membrane-Coated Biomimetic Nanoparticles with Orchestrating Immune Responses Promote Therapeutic Efficacy against Glioma. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 2341–2355. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; You, Y.; Xie, L.; Tong, S.; Chen, Y.; Liang, K.; Zhou, S.; Li, F.; et al. Neutrophil-Biomimetic “Nanobuffer” for Remodeling the Microenvironment in the Infarct Core and Protecting Neurons in the Penumbra via Neutralization of Detrimental Factors to Treat Ischemic Stroke. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2022, 14, 27743–27761. [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Zhu, Q.; Wei, D.; Feng, J.; Yao, J.; Jiang, T.; Song, Q.; Wei, X.; Chen, H.; Gao, X.; et al. Nanoparticles Coated with Neutrophil Membranes Can Effectively Treat Cancer Metastasis. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1397–1411. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L. Fucoidan-Loaded, Neutrophil Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles Facilitate MRSA-Accompanied Wound Healing. Mater Des 2023, 227, 111758. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, L.; Tu, F.; Rui, X.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, R. Neutrophil Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles Exhibit Increased Antimicrobial Activities in an Anti-Microbial Resistant K. Pneumonia Infection Model. Nanomedicine 2023, 48, 102640. [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Lu, J.; Jiao, D. Stem Cell Membrane Vesicle–Coated Nanoparticles for Efficient Tumor-Targeted Therapy of Orthotopic Breast Cancer. Polym Adv Technol 2019, 30, 1051–1060. [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Villicana, C.; Barati, D.; Freeman, P.; Luo, Y.; Yang, F. Stem Cell Membrane-Coated Microribbon Scaffolds Induce Regenerative Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses in a Critical-Size Cranial Bone Defect Model. Advanced Materials 2023, 35, 2208781. [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, M.; Huang, J.; Jin, X.; Zhu, C.; Lv, M.; Yang, N.; Chen, S.; Shao, M.; et al. Nucleus-Targeting Manganese Dioxide Nanoparticles Coated with the Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Membrane for Cancer Cell Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2023, 15, 10541–10553. [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Wu, Z.; Yi, X.; Hui, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Tengjisi; Wang, H.; Brooks, A.; Wang, H.; et al. Nanoparticle Elasticity Regulates the Formation of Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles and Their Nano-Bio Interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2214757120. [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, S.; Tabasi, H.; Zahiri, M.; Abnous, K.; Mohammad Taghdisi, S.; Nekooei, S.; Nekooei, N.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Surface Engineering of Hollow Gold Nanoparticle with Mesenchymal Stem Cell Membrane and MUC-1 Aptamer for Targeted Theranostic Application against Metastatic Breast Cancer. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2023, 187, 76–86. [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Gong, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, W.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Targeted Gene Silencing in Vivo by Platelet Membrane-Coated Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticles. Sci Adv 2020, 6. [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xie, W.; Zan, H.M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Dong, W. Platelet Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery and Local Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Orthotopic Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Mater Chem B 2020, 8, 4648–4659. [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Wu, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Fan, W.; Mou, X.; Cai, Y.; Yang, X. Platelet Membrane-Coated Bio-Nanoparticles of Indocyanine Green/Elamipretide for NIR Diagnosis and Antioxidant Therapy in Acute Kidney Injury. Acta Biomater 2024, 173, 482–494. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Rao, P.; Qian, H.; Shi, Y.; Chen, S.; Lan, J.; Mu, D.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X.; Deng, C.; et al. Regulatory Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes Cell Membrane Coated Nanoparticles: A Novel Targeted Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Advanced Science 2023, 10, 2204998. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Sun, S.; Wang, P.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M.; Chen, J.; Wu, R.; Zhang, J.; et al. Genetically Engineering Cell Membrane-Coated BTO Nanoparticles for MMP2-Activated Piezocatalysis-Immunotherapy. Advanced Materials 2023, 35, 2300964. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yin, Q.; Tian, D.; Yang, X.; Liu, S.; Sun, X.; Chen, Q.; Fang, B.; Liang, H.; Li, L.; et al. Vaginal Epithelial Cell Membrane-Based Phototherapeutic Decoy Confers a “Three-in-One” Strategy to Treat against Intravaginal Infection of Candida Albicans. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 12160–12175. [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, M.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, Q. Multiscale NIR-II Imaging-Guided Brain-Targeted Drug Delivery Using Engineered Cell Membrane Nanoformulation for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 5033–5046. [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, G.; Dang, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, S. Genetically Engineered Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles with High-Density Customized Membrane Receptor for High-Performance Drug Lead Discovery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2023, 15, 52150–52161. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kim, S.G.; Blenis, J. Cell Metabolism Perspective Rapamycin: One Drug, Many Effects. Cell Metab 2014, 19, 373–379. [CrossRef]
- Luk, B.T.; Jack Hu, C.M.; Fang, R.H.; Dehaini, D.; Carpenter, C.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L. Interfacial Interactions between Natural RBC Membranes and Synthetic Polymeric Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2730–2737. [CrossRef]
- Mornet, S.; Lambert, O.; Duguet, E.; Brisson, A. The Formation of Supported Lipid Bilayers on Silica Nanoparticles Revealed by Cryoelectron Microscopy. Nano Lett 2005, 5, 281–285. [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, X.; Feng, N. Red Blood Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanoparticles: A Novel Drug Delivery System for Antitumor Application. Acta Pharm Sin B 2019, 9, 675–689. [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Han, G.M.; Wang, D.X.; Liu, D. Bin; Liu, A.A.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.L.; Yuan, L.; Kong, D.M. Red Blood Cell Membrane Biomimetic Nanoprobes for Ratiometric Imaging of Reactive Oxygen Species Level in Atherosclerosis. Chemical Engineering Journal 2024, 479, 147515. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, K.; Pan, Y.; Rao, L.; Luo, G. Engineered Cell Membrane-Derived Nanoparticles in Immune Modulation. Advanced Science 2021, 8, 2102330. [CrossRef]
- Angsantikul, P.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L. Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles As an Emerging Antibacterial Vaccine Platform. Vaccines 2015, Vol. 3, Pages 814-828 2015, 3, 814–828. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, G. Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Bacterial Infection. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 2022, 14, e1825. [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Wang, S.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, M.S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L. Emerging Approaches to Functionalizing Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 941–955. [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, N.; Peng, F.X.; Mohapatra, A.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Genetically Engineered Cellular Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Biomaterials 2023, 296, 122065. [CrossRef]

| Lysis buffer used 1 | References |
|---|---|
| Tris-HCl-based hypotonic buffers | [6,12,24,26,28,31,32,35,39,46,51,52,55,57,60,64,65,69,71,74,91,92,93,99,104,106,107,108] |
| PBS-based hypotonic buffers | [22,47,63,80,81,86,87,89,90,98] |
| HEPES-based hypotonic buffers | [23,49,72] |
| EGTA-based hypotonic buffers | [36,58] |
| NaHCO3-based buffers | [40,66] |
| Double distilled water | [94] |
| Unspecified hypotonic buffers | [25,27,33,34,37,42,43,47,50,59,62,67,68,76,85,88,95,97] |
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Hypotonic lysis | Maintains membrane characteristics Compatible with downstream applications |
Typically necessitates a combination with other techniques to obtain the fragments. |
| Homogenization | Maintains membrane characteristics |
Typically necessitates a combination with other techniques to obtain the fragments |
| Freeze-thaw | Simplicity | Potential damage to temperature-sensitive membrane proteins Impact on the activity of sensitive enzymes Cryoconcentration |
| Sonication | Fastest method | Potential damage to temperature-sensitive membrane proteins Generation of free radicals |
| Nanoparticles | Size range (nm) | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLGA | 50-300 | Drug loading | [12,19,23,28,29,31,32,36,39,41,44,46,48,58,64,65,67,79,81,83,84,85,86,91,92,93,94,95,96,103,104] |
| Polystyrene | 100-200 | [22] | |
| PCEC | 50-150 | [26] | |
| MPEG-PLGA | 50-150 | [27] | |
| PCN-224 | 50-150 | [59] | |
| PEG-PLGA | 25-150 | [35,107] | |
| PEGDA | 100-150 | [80] | |
| Gelatin | 50-100 | [60] | |
| Poly(β-amino ester) | - | [73] | |
| ZIF-8 MOF | 100-300 | [51,75,101] | |
| Spherical nonporous SiO2 nanoparticles | 50-150 | [24] | |
| Mesoporous silica nanoparticles | 150-200 | [6] | |
| Colloidal silica nanoparticles | 200-250 | [99] | |
| Porous silica | 150-200 | [57] | |
| Chitosan-silica nanoparticles | 100-200 | [25,70] | |
| Nanoporous silica | - | [71] | |
| Silk fibroin | 100-150 | [37] | |
| Graphene oxide | 150-200 | [82] | |
| Magnetic beads | 50-150 | [72] | |
| Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles | 50-450 | [38] | |
| Heparan sulfate | 100-200 | [89] | |
| PMBEOx-COOH | 25-75 | [69] | |
| Curdlan | 50-150 | [90] | |
| PFC | 150-200 | [106] | |
| Pluronic F127 nanomicelles | 50-250 | [54] | |
| Liposomes | 100-150 | [34,77] | |
| CB[7]-PEG-Ce6 polymer | 100-200 | [68] | |
| Polydopamine-fructose-curcumin nanoparticles | 100-200 | [78] | |
| Hollow gold nanoparticles | 100-200 | Chemo/Photothermal therapy | [47,100] |
| Hollow copper sulfide nanoparticles | 150-250 | [30] | |
| Polypyrrole | 100-150 | [102] | |
| Melanin nanoparticles | 200-250 | Photothermal therapy | [49] |
| Fe3O4 nanoparticles | 50-250 | [40,61] | |
| Hollow polydopamine | 150-200 | [33] | |
| DHTDP | 50-150 | [52] | |
| BiOI nanodots | 5-10 | Radiotherapy | [76] |
| NaYF4:Yb,Er nanoparticles | 50-100 | Photodynamic therapy | [74] |
| NaYF4:Nd5@NaYF4 | 100-200 | Imaging | [50] |
| NaGdF4:Yb,Tm nanoparticles | 100-150 | [87] | |
| Gd MOF | 150-200 | [63] | |
| MPBzyme | 100-200 | Ischemic stroke therapy | [42] |
| Co-Fc MOF | 250-300 | ROS production | [62] |
| BTO nanoparticles | 50-150 | [105] | |
| MnO2 | 25-150 | [45,66,98] | |
| IrO2 | 50-150 | [53] | |
| CuPt nanoalloys | 25-50 | [55] | |
| Fucose-based CQDs | 5-10 | [56] | |
| Gelatin microribbon scaffolds | 200-300 | Bone regeneration | [97] |
| AMPNP | 50-100 | Antibacterial function | [69] |
| Load | Use/Function | Nanoparticles | Bioactive loading | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dexamethasone | Anti-inflammatory drug Chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy |
PLGA | 2-10% 3 | [23,36,48] |
| Hollow copper sulfide | 45.52% 2 | [88] | ||
| Doxorubicin | Chemotherapy | NPS | - | [71] |
| HGNPs | 31-37% 3 | [47,100] | ||
| PEG-PLGA | 14.2±2.4% 1 | [35] | ||
| PEGDA | 15% 3 | [80] | ||
| GO | 42.9% 3 | [82] | ||
| DCuS | 87.7% 1 | [30] | ||
| PLGA | 9-10% 1 | [41,84] | ||
| Mesosporous silica | - | [6] | ||
| Liposome | 40% 3 | [34] | ||
| Chitosan-silica | 18-33% 3 | [25,70] | ||
| Polypyrrole | - | [102] | ||
| MnO2 | 40-70% 3 | [66] | ||
| Curdlan | - | [90] | ||
| Paclitaxel | PLGA | 4-16% 2 | [64,96] | |
| Poly(β-amino ester) | 9.88% 3 | [73] | ||
| MnO2 | - | [98] | ||
| Cisplatin (Pt) | Gelatin nanoparticles | 12.55% 3 | [60] | |
| Docetaxel | Heparan sulfate | 9-10% 2 | [89] | |
| Dacarbazine | Fucose-based CQDs | - | [56] | |
| SN-38 | Liposomes | 5.54+-0.73% 1 | [77] | |
| MTIC | (CB[7]-PEG-Ce6) | 5.42% 3 | [68] | |
| KLA peptide | Induces apoptosis | PLGA | - | [95] |
| Temozolomide | Alkylating agent | PLGA | 8% 3 | [65] |
| Epirubicin | Immunogenic cell death inducer | ZIF-8 | - | [51] |
| Bortezomib | Proteasome inhibitor | PCEC | 2.87±0.51% 3 | [26] |
| Carfilzomib | Proteasome inhibitor | PLGA | 3.74±0.28% 3 | [93] |
| ABT-737 | Bcl-2 inhibitor | PLGA | 5-10% 1 | [46] |
| Rapamycin | Specific inhibitor of the mTOR signaling pathway [109] | PLGA | 11.39% 2 | [91] |
| TPI-1 | Inhibitor of the downstream effector molecule SHP-1 | Liposome | 40% 3 | [34] |
| Mefuparib hydrochloride | poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor | Mesoporous silica | - | [6] |
| Hydroxychloroquine | Autophagy inhibitor | Co-Fc | 12,81±4.21% 3 | [62] |
| NLG919 | IDO-1 enzyme inhibitor | Pluronic F127 | 5.08% 3 | [54] |
| aPD-1 | PD-1 inhibitor | Gd-MOF | - | [63] |
| MLN4924 | Neddylation inhibitor | PLGA | 10% 3 | [44] |
| R837 | Antagonist against TLR-7 | PLGA | 8% 1 | [29] |
| PMBEOx-COOH | 6.1% 3 | [69] | ||
| L-γ-glutamyl-p-nitroanilide (GPNA) | Glutamine transporter antagonist (Glycolysis inhibition) |
IrO2 | - | [53] |
| Bexarotene | hydrophobic retinoid X receptor (RXR) antagonist | PEG-PLGA | 43.24% 3 | [107] |
| siCdk4 | Knocks down Cdk4 | PCN-224 | 1.3 μg/mg | [59] |
| siRNASur | Knocks down Survivin | ZIF-8 | - | [101] |
| Ca2+ targeting siRNA | Knocks down the expression Ca2+ channels | Chitosan-silica | 1.12% 3 | [25] |
| mRNA transcripts for EGFP and CLuc | Silence EGGP and CLuc | PLGA | 1 μg/mg | [32] |
| L-7 | Immune adjuvant | MPEG-PLGA | 2.69% 3 | [27] |
| CpG oligodeoxynucleotide 1826 | Immunological adjuvant that triggers the maturation of antigen-presenting cells | PLGA | 1 nmol/mg | [28] |
| TCPP | Photosensitizer | MPEG-PLGA | 4.84% 3 | [27] |
| Indocyanine green (ICG) | Photothermal agent | Graphene oxide | 10.7% 3 | [82] |
| Pluronic F127 | 10.26% 3 | [54] | ||
| PLGA | - | [103] | ||
| Glucose oxidase | Mediators of the cascade generation of ROS | ZIF-8 | - | [51] |
| Hemin | - | |||
| Calcitriol | Anti-metastasis agent | Heparan sulfate | 2.92±0.16% 2 | [89] |
| Cannabidiol | Neuroprotective product | PLGA | 3.9±0.2% 3 | [92] |
| Elamipretide | Antioxidant | PLGA | - | [103] |
| hySF | Vascular regeneration | PLGA | - | [86] |
| BMP-2 | Boosting bone regeneration | Gelatin microribbon scaffolds | - | [97] |
| Minocycline hydrochloride | Antimicrobial agent | Silk fibroin | 7.86% 3 | [37] |
| LMWF | Anti methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus | PLGA | 4.7% 1 | [94] |
| Biphosphonate | Chelator for 89Zr radiolabeling | Porous silicon | - | [57] |
| Ag2S nanodots | Biosensing and bioimaging | Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles | - | [38] |
| AgAuSe quantum dots | Bioimaging | PEG-PLGA | 10% 3 | [107] |
| Uricase | PoC study | MOF | - | [75] |
| DiI | Fluorophore, PoC study | Hollow dopamine | - | [33] |
| Fe3O4 | - | [40] | ||
| SiO2 | - | [99] | ||
| DiD | PLGA | 0.2% 1 | [81] | |
| DiR | 0.1% 1 | [39] | ||
| DiO | 0.1% 1 | |||
| Hollow polydopamine | - | [33] | ||
| IR780 | AMPNP | - | [43] |
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Sonication | Allows the fusion of multiple cell membranes from different cell types Favors right-side out orientation of the membranes |
Potential damage to temperature-sensitive membrane proteins Generation of free radicals |
| Extrusion | Allows the creation of multi-layer structures Does not denature proteins |
Can cause a reduction in drug loading It is not applicable for irregularly shaped nanoparticles |
| Sonication-extrusion | Combines the advantages of both | Retains the disadvantages of both, except the inability to coat irregularly shaped nanoparticles |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





