Submitted:
04 February 2024
Posted:
05 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Focused Question
2.2. Language
2.3. Literature Search and Dabatases
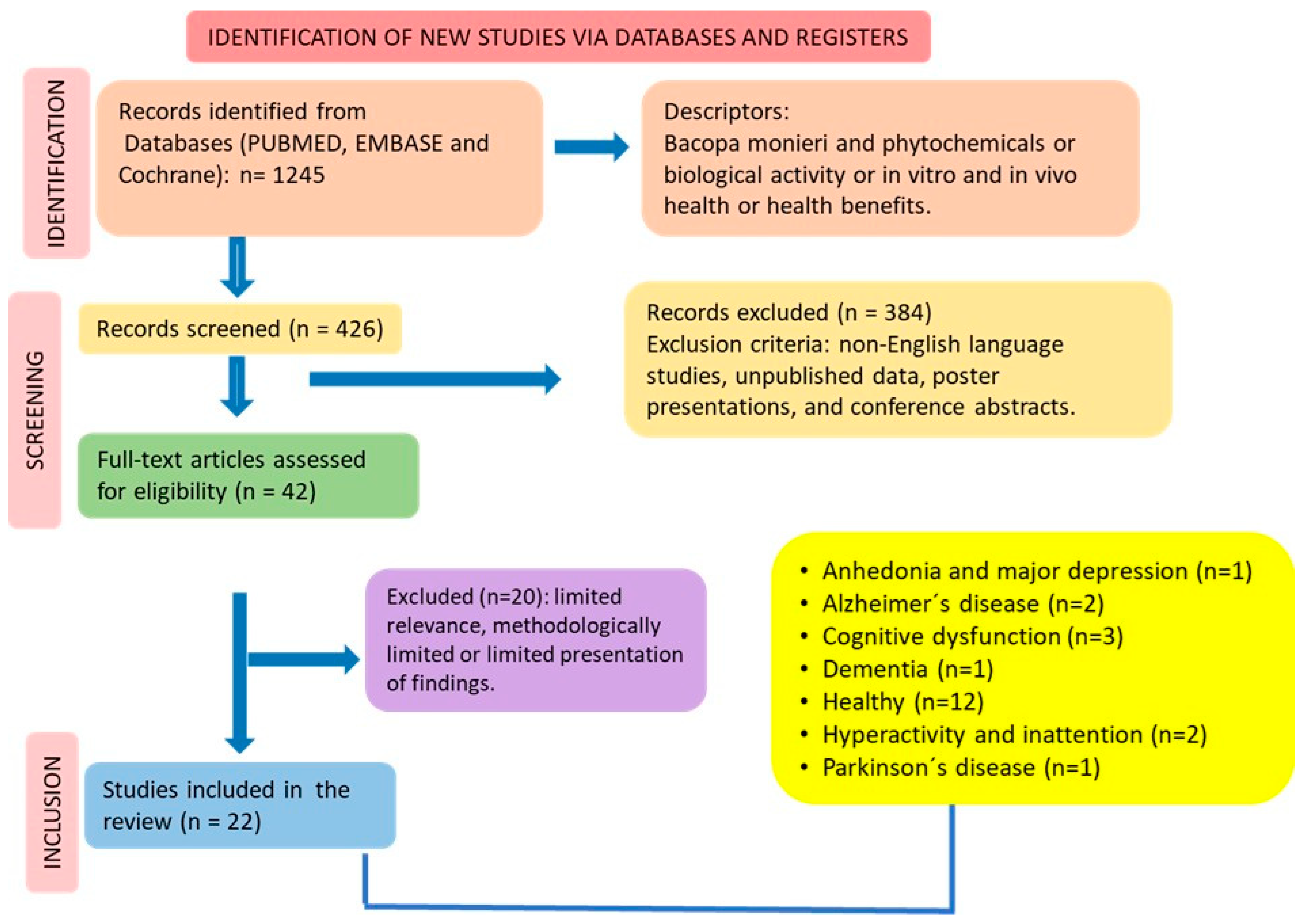
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Search and Selection of the Relevant Articles
2.7. Quality Assessment
3. Results
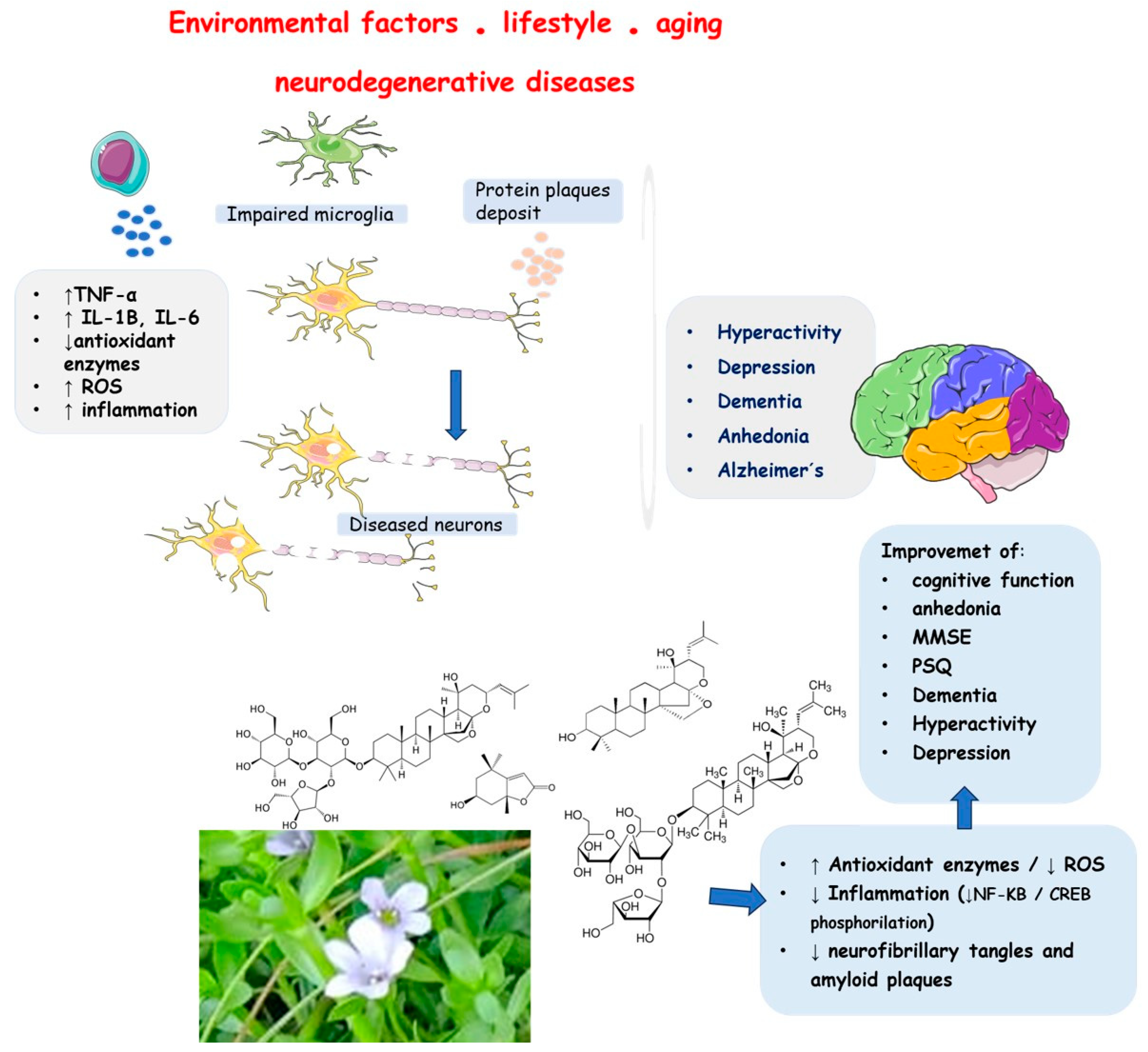
4. Discussion
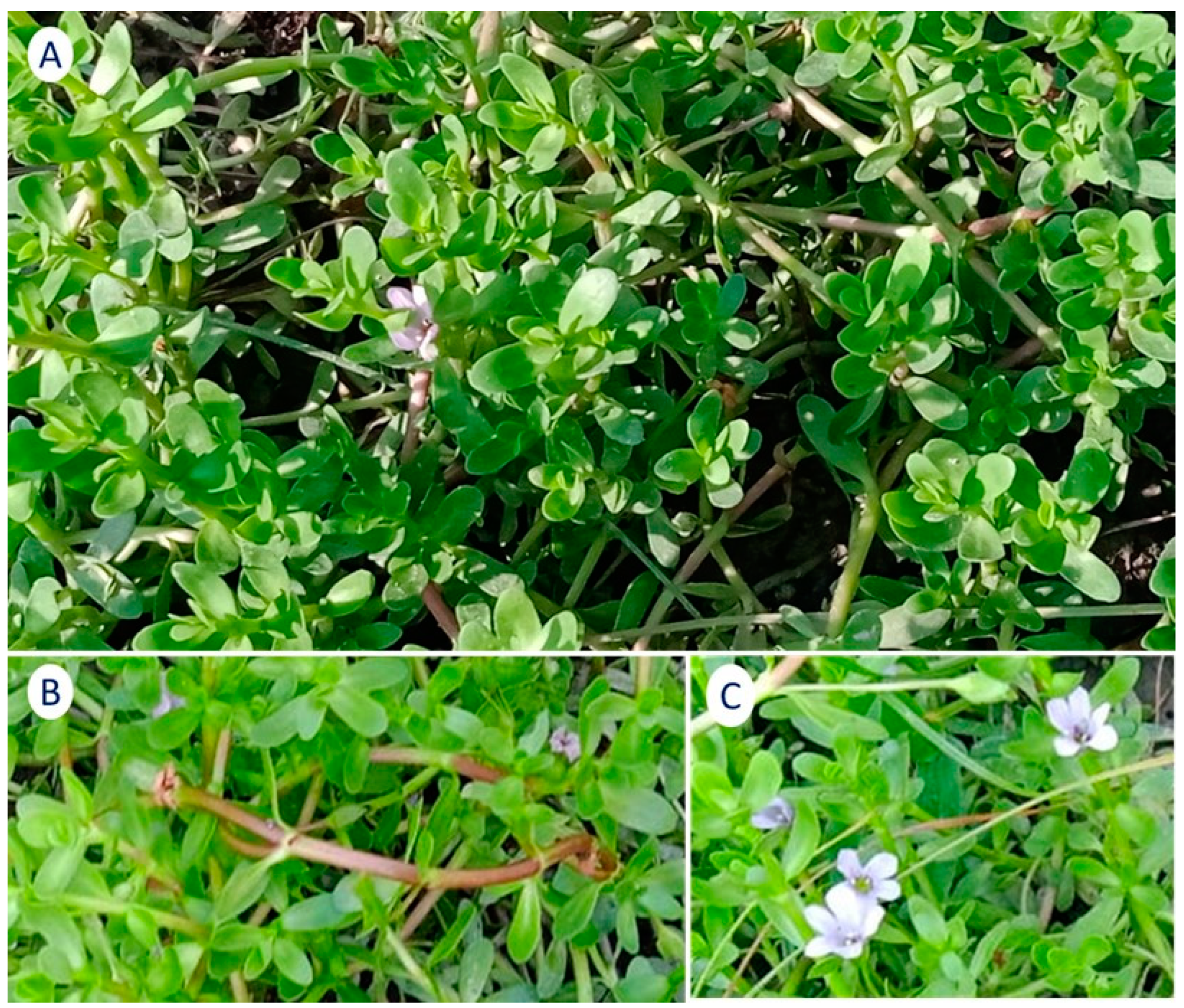
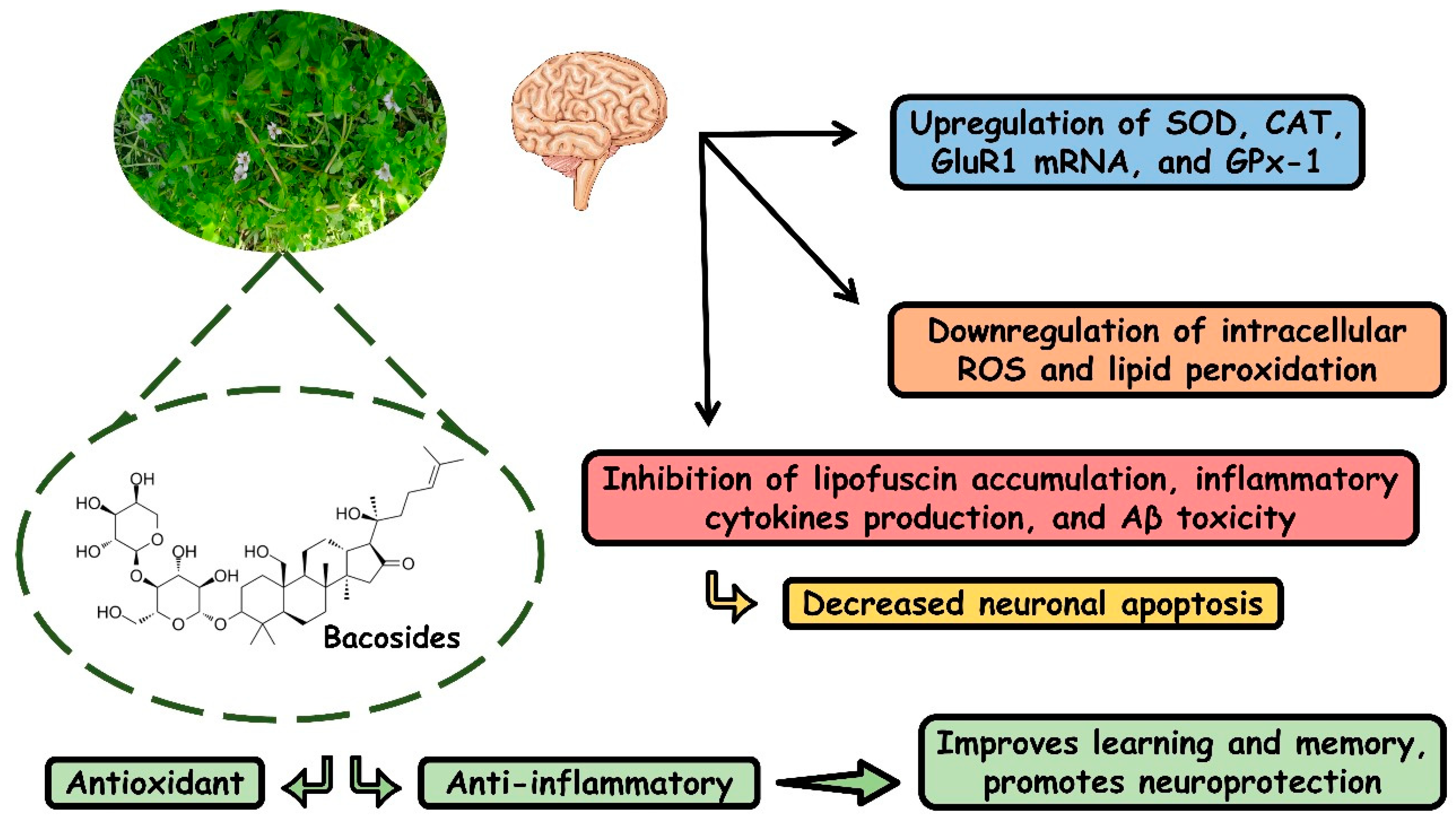
4.1. Bacopa Monnieri (BM)
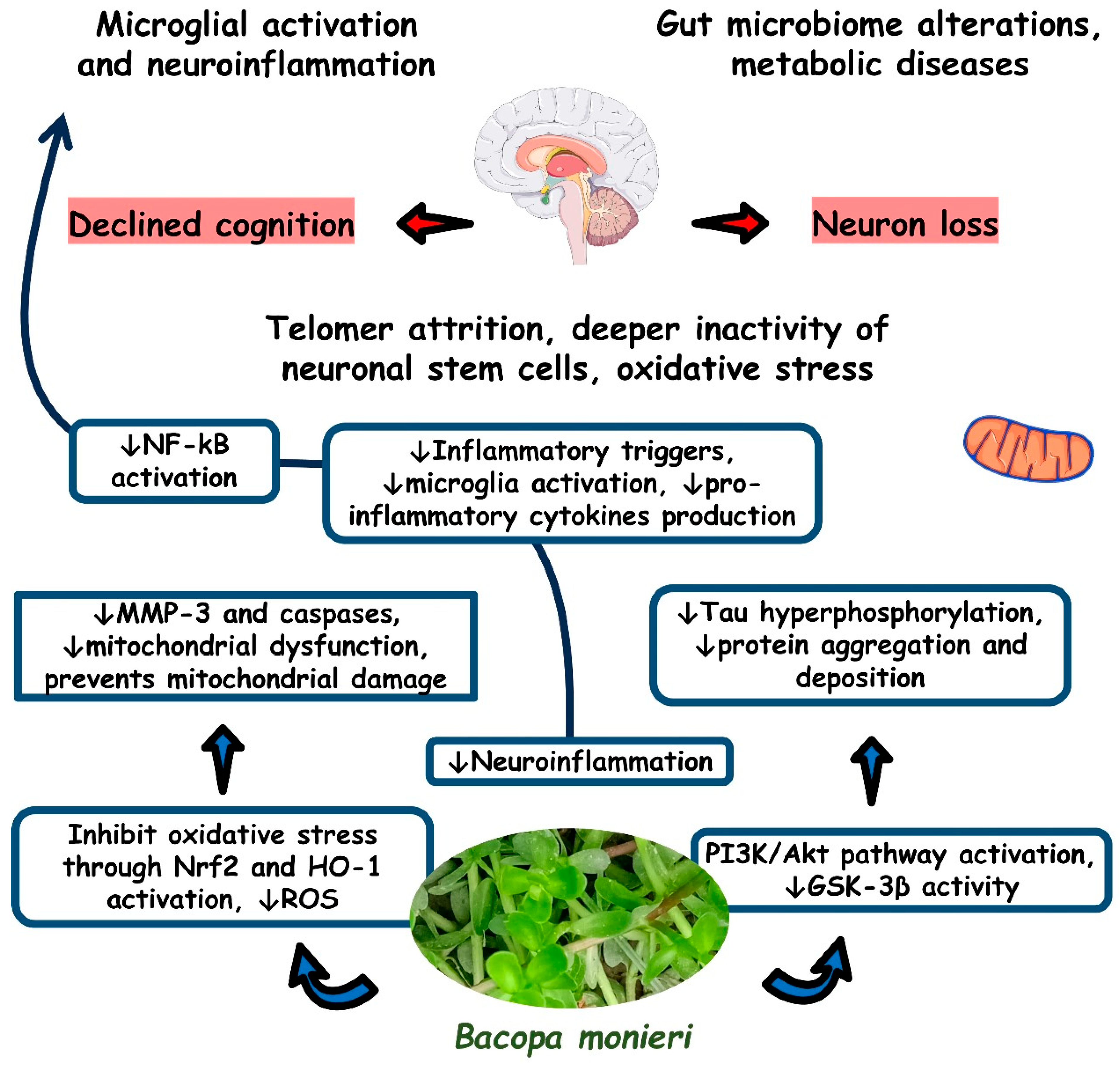
4.2. BM and Inflammation
4.3. BM and Oxidative Stress
4.4. BM and Mithocondrial Dysfunction
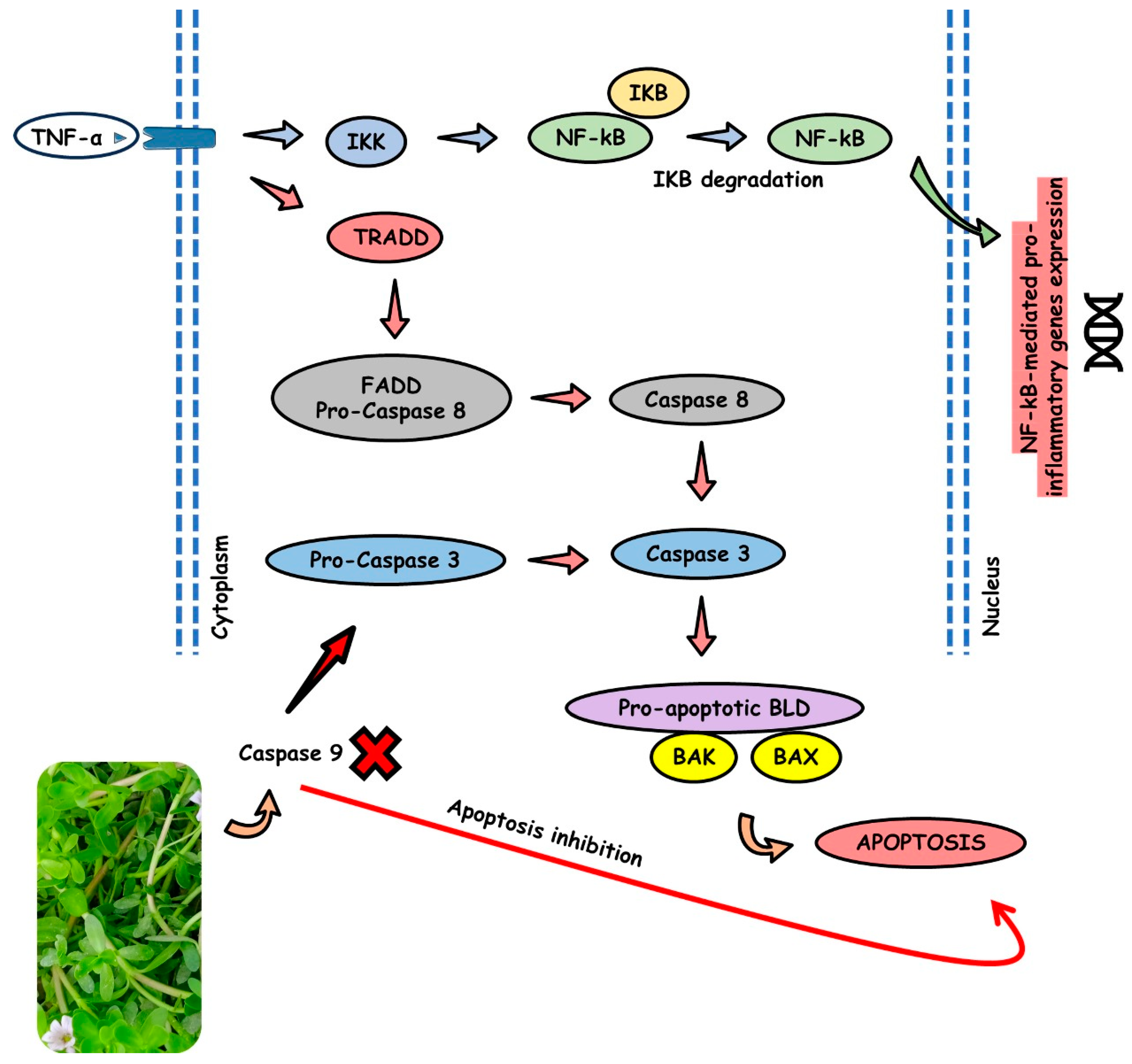
4.5. BM and Apoptosis
4.6. BM and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Evidence from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
4.7. BM and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Results of Clinical Trials
5. Safety
6. Conclusions, Strengths, Limitations, and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dalgaard, C.J.; Hansen, C.W.; Strulik, H. Physiological aging around the World. PloS One 2022, 17, e0268276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wen, Z. The mediating role of inflammaging between mitochondrial dysfunction and sarcopenia in aging: a review. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2023, 12, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ijaz, N.; Buta, B.; Xue, Q.L.; Mohess, D.T.; Bushan, A.; Tran, H.; Batchelor, W.; deFilippi, C.R.; Walston, J.D.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; et al. Interventions for Frailty Among Older Adults With Cardiovascular Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 482–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Nuncio, M.D.C.; Ziegler, T.R. Micronutrient status and protein-energy malnutrition in free-living older adults: a current perspective. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damluji, A.A.; Chung, S.E.; Xue, Q.L.; Hasan, R.K.; Moscucci, M.; Forman, D.E.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Batchelor, W.; Walston, J.D.; Resar, J.R.; Gerstenblith, G. Frailty and cardiovascular outcomes in the National Health and Aging Trends Study. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3856–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Ma, L. Inflammatory markers and physical frailty: towards clinical application. Immun. Ageing I A 2024, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orts-Cortés, M.I.; Cabañero-Martínez, M.J.; Meseguer-Liza, C.; Arredondo-González, C.P.; de la Cuesta-Benjumea, C.; Abad-Corpa, E. Effectiveness of nursing interventions in the prevention of falls in older adults in the community and in health care settings: A systematic review and meta-analysis of RCT. Enferm. Clin. (Engl. Ed. ). [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Peng, X.; Xie, L.; Dong, K.; Ma, D.; Xu, W.; Shi, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Yu, X.; Yang, Y. Importance of Bmal1 in Alzheimer's disease and associated aging-related diseases: Mechanisms and interventions. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montine, K.S.; Berson, E.; Phongpreecha, T.; Huang, Z.; Aghaeepour, N.; Zou, J.Y.; MacCoss, M.J.; Montine, T.J. Understanding the molecular basis of resilience to Alzheimer's disease. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1311157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Taruya, J.; Ito, H. Persistence of Kii amyotrophic lateral sclerosis after the 2000s and its characteristic aging-related tau astrogliopathy. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Chen, C. Editorial: Towards a mechanistic understanding of depression, anxiety, and their comorbidity: perspectives from cognitive neuroscience. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1268156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Vécsei, L. Integrating Armchair, Bench, and Bedside Research for Behavioral Neurology and Neuropsychiatry: Editorial. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Editorial of Special Issue 'Dissecting Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Diseases: Neurodegeneration and Neuroprotection'. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos-Rabal, P.; González-Fuentes, J.; Castro-Vázquez, L.; Lozano, M.V.; Rodríguez-Robledo, V.; Santander-Ortega, M.J.; Selva-Clemente, J.; Villaseca-González, N.; Del Mar Arroyo-Jiménez, M. Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Multidisciplinary Approach. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 3305–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Canteli, M.; Iadecola, C. Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Aging: JACC Focus Seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, B.; Sanlier, N. Alzheimer, Parkinson, dementia, and phytochemicals: insight review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitz, V.; Makarious, M.B.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Iwaki, H.; Singleton, A.B.; Nalls, M.; Heilbron, K.; Blauwendraat, C. Analysis of rare Parkinson's disease variants in millions of people. NPJ Park. Dis. 2024, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Exploring the Etiological Links behind Neurodegenerative Diseases: Inflammatory Cytokines and Bioactive Kynurenines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Spekker, E.; Polyák, H.; Tóth, F.; Vécsei, L. Mitochondrial Impairment: A Common Motif in Neuropsychiatric Presentation? The Link to the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic System. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, A.L.; Venkataraman, A. The Safety and Efficacy of Botanicals with Nootropic Effects. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1442–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Cao, G.; Zhao, D.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Yan, M. Ethnic, Botanic, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of the Acorus L. Genus: A Review. Mol. (Basel Switz. ) 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Bohár, Z.; Vécsei, L. Are Kynurenines Accomplices or Principal Villains in Dementia? Maintenance of Kynurenine Metabolism. Mol. (Basel Switz. ) 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, J.; Vengalasetti, Y.V.; Bredesen, D.E.; Rao, R.V. Neuroprotective Herbs for the Management of Alzheimer's Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.; Mosa, O.F.; Nawaz, A.; Hamdoon, A.A.E.; Elkhalifa, M.E.M.; Sadiq, A.; Ullah, F.; Ahmed, A.; Kabra, A.; Khan, H.; Murthy, H.C.A. Neuroprotective potentials of Lead phytochemicals against Alzheimer's disease with focus on oxidative stress-mediated signaling pathways: Pharmacokinetic challenges, target specificity, clinical trials and future perspectives. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2023, 124, 155272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, N.C.L.; Malta, S.M.; Franco, R.R.; Silva, H.C.G.; Silva, M.H.; Rodrigues, T.S.; de Oliveira, R.M.; Araújo, T.N.; Augusto, S.C.; Espindola, F.S.; Ueira-Vieira, C. Antioxidant and anti-Alzheimer's potential of Tetragonisca angustula (Jataí) stingless bee pollen. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Wang, Z.; Ming, Y.C.; Shen, L.; Ji, H.F. Are micronutrient levels and supplements causally associated with the risk of Alzheimer's disease? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 6665–6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, L.T.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.Q. Neuroprotective effect of the traditional decoction Tian-Si-Yin against Alzheimer's disease via suppression of neuroinflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 321, 117569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.; Parsaee, A.; Vasefi, M. Polyherbal and Multimodal Treatments: Kaempferol- and Quercetin-Rich Herbs Alleviate Symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease. Biology 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerom, J.P.; Madhukumar, S.; Nair, R.H.; Narayanan, S.P. Anti-amyloid potential of some phytochemicals against Aβ-peptide and α-synuclein, tau, prion, and Huntingtin protein. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Ordoñez, W.O.; Cajas-Salazar, N.; Velasco-Reyes, M.A. Genetic and epigenetic targets of natural dietary compounds as anti-Alzheimer's agents. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushma; Sahu, M.R.; Murugan, N.A.; Mondal, A.C. Amelioration of Amyloid-β Induced Alzheimer's Disease by Bacopa monnieri through Modulation of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and GSK-3β/Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, e2300245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukat, S.; Zia, M.A.; Uzair, M.; Attia, K.A.; Abushady, A.M.; Fiaz, S.; Ali, S.; Yang, S.H.; Ali, G.M. Bacopa monnieri: A promising herbal approach for neurodegenerative disease treatment supported by in silico and in vitro research. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, H.N. Biotechnological production of bacosides from cell and organ cultures of Bacopa monnieri. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brimson, J.M.; Brimson, S.; Prasanth, M.I.; Thitilertdecha, P.; Malar, D.S.; Tencomnao, T. The effectiveness of Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) Wettst. as a nootropic, neuroprotective, or antidepressant supplement: analysis of the available clinical data. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, P.; Gosukonda, J.S.; Sherman, S.H.; Joshee, N.; Gosukonda, R.M. Prediction of In vitro organogenesis of Bacopa monnieri using artificial neural networks and regression models. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, U.; Roy, S.; Ahmad, S.; Ali, S.; Elkady, W.M.; Khan, I.; Alsaffar, R.M.; Adnan, M.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I. Pharmacological attributes of Bacopa monnieri extract: Current updates and clinical manifestation. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 972379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.K. Quantitative Estimation of Secondary Metabolite, In-vitro Antioxidant, Anti-Sickling & Anti-Inflammatory Activity by HRBC Membrane Stabilization of Ethanolic Extract of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Pennell. 2024.
- Sharma, H.; Chandra, P. Challenges and Future Prospects: A Benefaction of Phytoconstituents on Molecular Targets Pertaining to Alzheimer's Disease. 2024.
- Singh, S.; Gupta, N.J.C.T.M. Therapeutic Approach of Phytomedicine for Dementia: A Review. 2024, 10, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujarathi, N.A.; Aher, A.A.; Sukhia, A.; Patil, T.S.; Goyal, Y.S.; Keservani, R.K. Nutraceutical interventions in Alzheimer's disease. In Nutraceutical Fruits and Foods for Neurodegenerative Disorders; Elsevier: 2024; pp. 379–404.
- Vinod, A.; Sathianarayanan, S.; Babu, A.E.; Sadanandan, P.; Venu, A.K.; Venkidasamy, B. Bacopa monnieri for Disorders Affecting Brain: Current Perspectives. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 1909–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, R.; Nandi, S.; Pandey, S.; Chatterjee, U.; Mishra, T.; Datta, S.; Prasanth, D.A.; Anand, U.; Mane, A.B.; Kant, N.; et al. Biotechnology for propagation and secondary metabolite production in Bacopa monnieri. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 1837–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Tambekar, O.; Goel, T.; Bodhankar, S.L.; Bansode, D.A.J.T.N.P.J. A Comprehensive Mini Review on the Natural Product Bacopa monnieri for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2024; 14, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mekli, K.; Lophatananon, A.; Maharani, A.; Nazroo, J.Y.; Muir, K.R. Association between an inflammatory biomarker score and future dementia diagnosis in the population-based UK Biobank cohort of 500,000 people. PloS One 2023, 18, e0288045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Lan, T.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, S. Ginsenoside-Rg1 synergized with voluntary running exercise protects against glial activation and dysregulation of neuronal plasticity in depression. Food Funct. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidiropoulou, G.A.; Metaxas, A.; Kourti, M. Natural antioxidants that act against Alzheimer's disease through modulation of the NRF2 pathway: a focus on their molecular mechanisms of action. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1217730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudheer, W.N.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Nagella, P. A comprehensive review on tissue culture studies and secondary metabolite production in Bacopa monnieri L. Pennell: a nootropic plant. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2023, 43, 956–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantait, S.; Subrahmanyeswari, T.; Kamble, S.N.; Singh, S. Strategies for the ameliorated production of pharmaceutically important glycosides via plant cell culture. In Peptide and Protein Drug Delivery Using Polysaccharides; Elsevier: 2024; pp. 51–74.
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.J.A.I.M. Liberat i A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. 2009, 151, 264–269.
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J.J.T.C.d.o.s.r. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. 2019, 2019.
- Keegan, A.P.; Stough, C.; Paris, D.; Luis, C.A.; Abdullah, L.; Ait-Ghezala, G.; Crawford, F.; Mullan, M. Bacopa monnieri supplementation has no effect on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels but beneficially modulates nuclear factor kappa B and cyclic AMP response element-binding protein levels in healthy elderly subjects. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2023, 9, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.F.D.; Souza, M.M.Q.; Amaral, E.C.; Albuquerque, E.R.; Bortoloti, D.S.; Gasparotto Junior, A.; Lourenço, E.L.B.; Lovato, E.C.W.; Lívero, F. Bacopa monnieri in Patients with Parkinson's Disease: A Pilot Study. J. Med. Food 2023, 26, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kean, J.D.; Downey, L.A.; Sarris, J.; Kaufman, J.; Zangara, A.; Stough, C. Effects of Bacopa monnieri (CDRI 08®) in a population of males exhibiting inattention and hyperactivity aged 6 to 14 years: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phytother. Res. PTR 2022, 36, 996–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minale, G.; Saesong, T.; Temkitthawon, P.; Waranuch, N.; Nuengchamnong, N.; Chootip, K.; Kamkaew, N.; Kongbangkerd, T.; Engsuwan, J.; Ingkaninan, K. Characterization of Metabolites in Plasma, Urine and Feces of Healthy Participants after Taking Brahmi Essence for Twelve Weeks Using LC-ESI-QTOF-MS Metabolomic Approach. Mol. (Basel Switz. ) 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheli, L.; Spitoni, S.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Bilia, A.R.; Ghelardini, C.; Pallanti, S. Bacopa monnieri as augmentation therapy in the treatment of anhedonia, preclinical and clinical evaluation. Phytother. Res. PTR 2020, 34, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, S.; Vishnu, V.Y.; Modi, M.; Mohanty, M.; Sharma, A.; Medhi, B.; Mittal, B.R.; Khandelwal, N.; Goyal, M.K.; Lal, V.; et al. Efficacy of Bacopa Monnieri (Brahmi) and Donepezil in Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Double-Blind Parallel Phase 2b Study. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2020, 23, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, F.; Stefani, A.; Melani, F.; Fabrizzi, P.; Nizzardo, A.; Grassi, D.; Bocale, R.; Necozione, S.; Lombardi, F.; Castelli, V.; et al. Improvement of Executive Function after Short-Term Administration of an Antioxidants Mix Containing Bacopa, Lycopene, Astaxanthin and Vitamin B12: The BLAtwelve Study. Nutrients 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Mishra, A.K.; Mishra, U. Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri Linn) in the treatment of dementias - a pilot study. Future Healthc. J. 2019, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.; Bove, M.; Colletti, A.; Rizzo, M.; Fogacci, F.; Giovannini, M.; Borghi, C. Short-Term Impact of a Combined Nutraceutical on Cognitive Function, Perceived Stress and Depression in Young Elderly with Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot, Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Prev. Alzheimer's Dis. 2017, 4, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Abichandani, L.G.; Thawani, V.; Gharpure, K.J.; Naidu, M.U.; Venkat Ramana, G. Efficacy of Standardized Extract of Bacopa monnieri (Bacognize®) on Cognitive Functions of Medical Students: A Six-Week, Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2016, 2016, 4103423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadhu, A.; Upadhyay, P.; Agrawal, A.; Ilango, K.; Karmakar, D.; Singh, G.P.; Dubey, G.P. Management of cognitive determinants in senile dementia of Alzheimer's type: therapeutic potential of a novel polyherbal drug product. Clin. Drug Investig. 2014, 34, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, U.P.; Dingankar, S.R.; Saxena, V.S.; Joseph, J.A.; Bethapudi, B.; Agarwal, A.; Kudiganti, V. An open-label study to elucidate the effects of standardized Bacopa monnieri extract in the management of symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children. Adv. Mind-Body Med. 2014, 28, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benson, S.; Downey, L.A.; Stough, C.; Wetherell, M.; Zangara, A.; Scholey, A. An acute, double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over study of 320 mg and 640 mg doses of Bacopa monnieri (CDRI 08) on multitasking stress reactivity and mood. Phytother. Res. PTR 2014, 28, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, L.A.; Kean, J.; Nemeh, F.; Lau, A.; Poll, A.; Gregory, R.; Murray, M.; Rourke, J.; Patak, B.; Pase, M.P.; et al. An acute, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study of 320 mg and 640 mg doses of a special extract of Bacopa monnieri (CDRI 08) on sustained cognitive performance. Phytother. Res. PTR 2013, 27, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peth-Nui, T.; Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S.; Tong-Un, T.; Piyavhatkul, N.; Rangseekajee, P.; Ingkaninan, K.; Vittaya-Areekul, S. Effects of 12-Week Bacopa monnieri Consumption on Attention, Cognitive Processing, Working Memory, and Functions of Both Cholinergic and Monoaminergic Systems in Healthy Elderly Volunteers. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2012, 2012, 606424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.; Stevens, J. Does Bacopa monnieri improve memory performance in older persons? Results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. (New York N.Y.) 2010, 16, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, C.; Gregory, W.L.; Leo, M.; Kraemer, D.; Bone, K.; Oken, B. Effects of a standardized Bacopa monnieri extract on cognitive performance, anxiety, and depression in the elderly: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. (New York N.Y.) 2008, 14, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhaiya, H.C.; Desai, R.P.; Saxena, V.S.; Pravina, K.; Wasim, P.; Geetharani, P.; Allan, J.J.; Venkateshwarlu, K.; Amit, A.J.J.P.T. Efficacy and tolerability of BacoMind on memory improvement in elderly participants—a double blind placebo controlled study. 2008, 3, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stough, C.; Downey, L.A.; Lloyd, J.; Silber, B.; Redman, S.; Hutchison, C.; Wesnes, K.; Nathan, P.J. Examining the nootropic effects of a special extract of Bacopa monniera on human cognitive functioning: 90 day double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Phytother. Res. PTR 2008, 22, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghav, S.; Singh, H.; Dalal, P.K.; Srivastava, J.S.; Asthana, O.P. Randomized controlled trial of standardized Bacopa monniera extract in age-associated memory impairment. Indian J. Psychiatry 2006, 48, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roodenrys, S.; Booth, D.; Bulzomi, S.; Phipps, A.; Micallef, C.; Smoker, J. Chronic effects of Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri) on human memory. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2002, 27, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stough, C.; Lloyd, J.; Clarke, J.; Downey, L.A.; Hutchison, C.W.; Rodgers, T.; Nathan, P.J. The chronic effects of an extract of Bacopa monniera (Brahmi) on cognitive function in healthy human subjects. Psychopharmacology 2001, 156, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, D.; Barik, J.R.; Barik, J.; Behera, P.K.; Dash, D. Suitability of Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri L.) cultivation on fly ash-amended soil for better growth and oil content. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2021, 23, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhiari, B.M.; Ray, A.; Jena, S.; Champati, B.B.; Sahoo, A.; Halder, T.; Ghosh, B.; Panda, P.C.; Nayak, S. Effect of different drying treatments on the physicochemical, functional, and antioxidant properties of Bacopa monnieri. Biotechnologia 2021, 102, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyasri, R.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Suba, V.; Ramesh, M.; Chen, J.T. Bacopa monnieri and Their Bioactive Compounds Inferred Multi-Target Treatment Strategy for Neurological Diseases: A Cheminformatics and System Pharmacology Approach. Biomolecules 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basheer, A.; Agarwal, A.; Mishra, B.; Gupta, A.; Padma Srivastava, M.V.; Kirubakaran, R.; Vishnu, V. Use of Bacopa monnieri in the Treatment of Dementia Due to Alzheimer Disease: Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Interact. J. Med. Res. 2022, 11, e38542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xin, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, W.; Lv, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, Z.; Ding, Q.; Zhao, H.; et al. Bacopaside I alleviates depressive-like behaviors by modulating the gut microbiome and host metabolism in CUMS-induced mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 170, 115679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Mohammad, T.; Azhar, M.K.; Fatima, H.; Alam, A.; Hasan, G.M.; Islam, A.; Kaur, P.; Hassan, M.I. Investigating MARK4 inhibitory potential of Bacopaside II: Targeting Alzheimer's disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 245, 125364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Anand, U.; Ghosh, S.; Ray, D.; Ray, P.; Nandy, S.; Deshmukh, G.D.; Tripathi, V.; Dey, A. Bacosides from Bacopa monnieri extract: An overview of the effects on neurological disorders. Phytother. Res. PTR 2021, 35, 5668–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepak, M.; Amit, A.J.F. ‘Bacoside B’—the need remains for establishing identity. 2013, 87, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Kulshreshtha, D.K.J.P. Bacoside A1, a minor saponin from Bacopa monniera. 1993, 33, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sycz, Z.; Tichaczek-Goska, D.; Wojnicz, D. Anti-Planktonic and Anti-Biofilm Properties of Pentacyclic Triterpenes-Asiatic Acid and Ursolic Acid as Promising Antibacterial Future Pharmaceuticals. Biomolecules 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, J. Neuroprotective mechanisms of Asiatic acid. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Das, T.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Sahoo, P. Differential detection of aspartic acid in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2023, 21, 7018–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Cai, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Zhou, X.; Ren, L. Poly(aspartic acid)-based self-healing hydrogel with precise antibacterial ability for rapid infected-wound repairing. Colloids Surf.. B Biointerfaces 2023, 221, 112982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. β-Sitosterol protects against food allergic response in BALB/c mice by regulating the intestinal barrier function and reconstructing the gut microbiota structure. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 4456–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swargiary, G.; Mani, S. Molecular docking and simulation studies of phytocompounds derived from Centella asiatica and Andrographis paniculata against hexokinase II as mitocan agents. Mitochondrion 2021, 61, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V, C.S.; Gulia, K.K.; Deepti, A.; Chakrapani, P.S.B.; Baby, S.; Viswanathan, G. Protection by Nano-Encapsulated Bacoside A and Bacopaside I in Seizure Alleviation and Improvement in Sleep- In Vitro and In Vivo Evidences. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.K.; Zhao, Z.G. Isolation and neuronal apoptosis inhibitory property of bacoside-A3 via downregulation of β-amyloid induced inflammatory response. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeggoni, D.P.; Rachamallu, A.; Subramanyam, R. Comparative binding studies of bacosine with human serum albumin and α-1-acid glycoprotein biophysical evaluation and computational approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 209, 114478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.; Maity, T.K.; Singh, J. Antihyperglycemic activity of bacosine, a triterpene from Bacopa monnieri, in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Planta Medica 2011, 77, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Lu, H.; Chen, Q. A Review on Preparation of Betulinic Acid and Its Biological Activities. Mol. (Basel Switz. ) 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, M.; Ye, C.; Qin, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Jin, X. Betulinic acid inhibits the proliferation of human laryngeal carcinoma cells through reactive oxygen species-mediate mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Toxicology in vitro an international journal published in association with BIBRA 2023, 95, 105756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Ma, C.; Fu, K.; Liu, Y.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Cucurbitacin B: A review of its pharmacology, toxicity, and pharmacokinetics. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 187, 106587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Wu, R.; Fu, K.; Li, Y.; Yao, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y. Exploring the effect and mechanism of cucurbitacin B on cholestatic liver injury based on network pharmacology and experimental verification. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 322, 117584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.R.; Jeon, C.W.; Cho, G.; Thomashow, L.S.; Weller, D.M.; Paik, M.J.; Lee, Y.B.; Kwak, Y.S. Glutamic acid reshapes the plant microbiota to protect plants against pathogens. Microbiome 2021, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, W. Poly(Glutamic Acid)-Engineered Nanoplatforms for Enhanced Cancer Phototherapy. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.J.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, A.; Je, J.G.; Seo, M.J.; Jee, Y.H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Ahn, G. (-)-Loliolide Isolated from Sargassum horneri Suppressed Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in IFN-γ/TNF-α-Stimulated HaCaT Keratinocytes. Antioxid. (Basel Switz. ) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.H.; Yun, J.H.; Heo, J.; Lee, I.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Bae, S.; Yun, B.S.; Kim, H.S. Identification of Loliolide with Anti-Aging Properties from Scenedesmus deserticola JD052. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, K.; Bora, K.; Mallik, S.; Zhao, Z. Potential Therapeutic Agents on Alzheimer's Disease through Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Plant-Based Compounds. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202200684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Arif, Y.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. The role of quercetin in plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2021, 166, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika; Maurya, P.K. Health Benefits of Quercetin in Age-Related Diseases. Mol. (Basel Switz. ) 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayanan, B.U.R.; Sagum, R.S. Microwave and Ultrasound Pretreatment of Moringa oleifera Lam. Seeds: Effects on Oil Expression, Oil Quality, and Bioactive Component. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tang, G.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Bi, Y. The characterization of soybean germ oil and the antioxidative activity of its phytosterols. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 40109–40117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakrim, S.; Benkhaira, N.; Bourais, I.; Benali, T.; Lee, L.H.; El Omari, N.; Sheikh, R.A.; Goh, K.W.; Ming, L.C.; Bouyahya, A. Health Benefits and Pharmacological Properties of Stigmasterol. Antioxid. (Basel Switz. ) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, C.; Maugeri, A.; Musumeci, L.; De Sarro, G.; Cirmi, S.; Navarra, M. Inflammation and Obesity: The Pharmacological Role of Flavonoids in the Zebrafish Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, M.M.; Garbarino, V.R.; Pollet, E.; Palavicini, J.P.; Kellogg, D.L., Jr.; Kraig, E.; Orr, M.E. Biological aging processes underlying cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S.; Koh, S.-H. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: the roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandpal, M.; Baral, B.; Varshney, N.; Jain, A.K.; Chatterji, D.; Meena, A.K.; Pandey, R.K.; Jha, H.C. Gut-Brain Axis Interplay via STAT3 pathway: Implications of Helicobacter pylori derived secretome on inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Virulence 2024, 2303853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueck, P.J.; Morris, J.K.; Stanford, J.A. Current Perspectives: Obesity and Neurodegeneration - Links and Risks. Degener. Neurol. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2023, 13, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajares, M.; A, I.R.; Manda, G.; Boscá, L.; Cuadrado, A. Inflammation in Parkinson's Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakis, S.; Thompson, J.R.; Feczko, E.; Miranda-Dominguez, O.; Dunn, G.A.; Selby, M.; Mitchell, A.J.; Sullivan, E.L.; Fair, D.A. Perinatal Western-style Diet Exposure associated with Decreased Microglial Counts throughout the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus in Japanese Macaques. J. Neurophysiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahata, I.; Fukunaga, K. Protein Kinases and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimian, R.; Guruswamy, R.; Boutej, H.; Cordeau, P., Jr.; Weng, Y.C.; Kriz, J. Targeting SRSF3 restores immune mRNA translation in microglia/macrophages following cerebral ischemia. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.H.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhou, Z.P.; Liu, X.C.; Fang, H.; Wang, C.W.; Liu, J.; Liu, R.Y.; Liu, H.K.; et al. Increased cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase drives neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchikawa, H.; Uekawa, K.; Hasegawa, Y. Perivascular macrophages in cerebrovascular diseases. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 114680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, K.A.; Heneka, M.T. Inflammasomes in neurological disorders - mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev.. Neurol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.A.; Pellegrini, M.V. Bacopa monnieri. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Mark Pellegrini declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies., 2023.
- Fatima, U.; Roy, S.; Ahmad, S.; Al-Keridis, L.A.; Alshammari, N.; Adnan, M.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I. Investigating neuroprotective roles of Bacopa monnieri extracts: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic implications. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, R.; Cheng, Y.; Piket, E.; M, Z.A.; Zeitelhofer, M.; Olsson, T.; Ortlieb Guerreiro-Cacais, A.; Jagodic, M. The aging mouse CNS is protected by an autophagy-dependent microglia population promoted by IL-34. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozlu, H.; Cakir Gundogdu, A.; Elmazoglu, Z.; Take Kaplanoglu, G.; Oktar, L.; Karasu, C. Bacopa Monnieri Protects the Directly Affected Organ as Well as Distant Organs Against I/R Injury by Modulating Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Nitrosative Pathways in A Rat Model for Infra-Renal Aortic Occlusion. J. Investig. Surg. Off. J. Acad. Surg. Res. 2021, 34, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaazaa, A.M.; Daoud, N.N.; El-Gendy, O.A.; Al-Shafei, A.I. Neuroprotective role of Bacopa monnieri extract in modulating depression in an experimental rat model. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 308, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-García, M.; Garduño-Solórzano, G.; Lopes, G.; Sanchez, B.A.; Urbatzka, R.; Hentschke, G.S.; Campos, J.E.; Vasconcelos, V.M.O. Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Obesity Potential of Extracts Containing Phenols, Chlorophyll and Carotenoids from Mexican Wild Populations of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wettst. Biology 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ding, K.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, L.; Pan, T.; Zhang, L. Flavonoids Regulate Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Cancer. Mol. (Basel Switz. ) 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khayri, J.M.; Sahana, G.R.; Nagella, P.; Joseph, B.V.; Alessa, F.M.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q. Flavonoids as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Molecules: A Review. Mol. (Basel Switz. ) 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, S.; Urmann, C.; Herzog, R.; Glaser, J.; Bieringer, S.; Geisberger, T.; Eisenreich, W.; Riepl, H. Where Is Bacosine in Commercially Available Bacopa monnieri? Planta Medica 2020, 86, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyasri, R.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Adarshan, S.; Shin, H.; Ramesh, M. Assessing the Anti-inflammatory Effects of Bacopa-Derived Bioactive Compounds Using Network Pharmacology and In Vitro Studies. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 40344–40354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, E.; Jarlapoodi, S.; Serra, F.; Aielli, L.; Khan, H.; Belwal, T.; Falasca, K.; Reale, M. Neuroprotective Potential of Bacopa monnieri: Modulation of Inflammatory Signals. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2023, 22, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.; Mehta, R.; Goswami, S.K.; Hammock, B.D.; Morisseau, C.; Hwang, S.H.; Mallappa, O.; Azeemuddin, M.M.; Rafiq, M.; S, N.M. Neuroprotective effect of herbal extracts inhibiting soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) and cyclooxygenase (COX) against chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 667, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, K.; Bali, A.; Bhatia, P.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. Exploring the ameliorative potential of Bacopa monnieri in acetic acid induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhishek, M.; Rubal, S.; Rohit, K.; Rupa, J.; Phulen, S.; Gurjeet, K.; Raj, S.A.; Manisha, P.; Alka, B.; Ramprasad, P.; Bikash, M. Neuroprotective effect of the standardised extract of Bacopa monnieri (BacoMind) in valproic acid model of autism spectrum disorder in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 293, 115199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemetchek, M.D.; Stierle, A.A.; Stierle, D.B.; Lurie, D.I. The Ayurvedic plant Bacopa monnieri inhibits inflammatory pathways in the brain. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 197, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, N.; Singh, D.; Sandhir, R. Bacopa monnieri prevents colchicine-induced dementia by anti-inflammatory action. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, A.H. Bio-Computational Evaluation of Compounds of Bacopa Monnieri as a Potential Treatment for Schizophrenia. Mol. (Basel Switz. ) 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeet, S.; Khan, A.; Mahanta, S.; Roy, N.; Das, S.K.; Mohanta, Y.K.; Saravanan, M.; Tag, H.; Hui, P.K. Computational Analysis of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wettst. Compounds for Drug Development against Neurodegenerative Disorders. Curr. Comput. -Aided Drug Des. 2023, 19, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deolankar, S.C.; Najar, M.A.; Ramesh, P.; Kanichery, A.; Kudva, A.K.; Raghu, S.V.; Prasad, T.S.K. Discovery of Molecular Networks of Neuroprotection Conferred by Brahmi Extract in Aβ(42)-Induced Toxicity Model of Drosophila melanogaster Using a Quantitative Proteomic Approach. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, F.; Acosta-Hernández, M.E.; Beltrán-Parrazal, L.; Rodríguez-Alba, J.C. The Role of Neuroglobin in the Sleep-Wake Cycle. Sleep Sci. (Sao Paulo Braz. ) 2023, 16, e362–e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, T.L.; Wright, D.K.; Uboldi, A.D.; Tonkin, C.J.; Vo, A.; Wilson, T.; McDonald, S.J.; Mychasiuk, R.; Semple, B.D.; Sun, M.; Shultz, S.R. A pre-existing Toxoplasma gondii infection exacerbates the pathophysiological response and extent of brain damage after traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Neuroinflammation 2024, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Zanuso, B.; de Oliveira Dos Santos, A.R.; Miola, V.F.B.; Guissoni Campos, L.M.; Spilla, C.S.G.; Barbalho, S.M. Panax ginseng and aging related disorders: A systematic review. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 161, 111731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Niculescu, A.G.; Lungu, II; Radu, C.I.; Vladâcenco, O.; Roza, E.; Costăchescu, B.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, R.I. An Overview of Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajam, Y.A.; Rani, R.; Ganie, S.Y.; Sheikh, T.A.; Javaid, D.; Qadri, S.S.; Pramodh, S.; Alsulimani, A.; Alkhanani, M.F.; Harakeh, S.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Human Pathology and Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Perspectives. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu-Tucker, A.; Cotman, C.W. Emerging roles of oxidative stress in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 107, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumien, N.; Cunningham, J.T.; Davis, D.L.; Engelland, R.; Fadeyibi, O.; Farmer, G.E.; Mabry, S.; Mensah-Kane, P.; Trinh, O.T.P.; Vann, P.H.; et al. Neurodegenerative Disease: Roles for Sex, Hormones, and Oxidative Stress. Endocrinology 2021, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.L.; Jia, W.J.; Guo, L.; Jing, R.; Zhao, X.H.; Hu, J.Y.; Li, X.H.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Dou, X.K. Brain microvascular endothelial cell-derived exosomes transmitting circ_0000495 promote microglial M1-polarization and endothelial cell injury under hypoxia condition. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2024, 38, e23387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdari, M.R.; Shakeri, F.; Mohammadi, A.; Bibak, B.; Alesheikh, P.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. Role of Herbal Medicines in the Management of Brain Injury. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1328, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, A.K.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Aquilanti, B.; Velluti, V.; Matera, G.; Gagliardi, L.; Bertelli, M. Food supplements based on palmitoylethanolamide plus hydroxytyrosol from olive tree or Bacopa monnieri extracts for neurological diseases. Acta Bio-Medica Atenei Parm. 2020, 91, e2020007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, T.; Tran, N.; Schurgers, L.; Stenvinkel, P.; Shiels, P.G. Ageing - Oxidative stress, PTMs and disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2022, 86, 101099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, B.R. Fruits and foods to improve kids brain health. In Nutraceutical Fruits and Foods for Neurodegenerative Disorders; Elsevier: 2024; pp. 63–75.
- Shinomol, G.K.; Bharath, M.M.; Muralidhara. Pretreatment with Bacopa monnieri extract offsets 3-nitropropionic acid induced mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunctions in the striatum of prepubertal mouse brain. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 90, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, G.; Hosamani, R.; Muralidhara. Bacopa monnieri Supplements Offset Paraquat-Induced Behavioral Phenotype and Brain Oxidative Pathways in Mice. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mondal, A.C. Neuroprotective, Neurotrophic and Anti-oxidative Role of Bacopa monnieri on CUS Induced Model of Depression in Rat. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 3083–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinomol, G.K.; Muralidhara. Bacopa monnieri modulates endogenous cytoplasmic and mitochondrial oxidative markers in prepubertal mice brain. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2011, 18, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.P.; Singh, H.K.; Prasad, S. Alterations in Hippocampal Oxidative Stress, Expression of AMPA Receptor GluR2 Subunit and Associated Spatial Memory Loss by Bacopa monnieri Extract (CDRI-08) in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Mice. PloS One 2015, 10, e0131862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosamani, R.; Krishna, G.; Muralidhara. Standardized Bacopa monnieri extract ameliorates acute paraquat-induced oxidative stress, and neurotoxicity in prepubertal mice brain. Nutr. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, T.; Kushwaha, P.; Thulasiram, H.V.; Chandrashekar, M.; Chinnathambi, S. Bacopa monnieri reduces Tau aggregation and Tau-mediated toxicity in cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.; Mercado-Ayon, E.; Mercado-Ayon, Y.; Dong, Y.N.; Halawani, S.; Ngaba, L.; Lynch, D.R. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 702, 108698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, S.; Kashyap, S.; Chini, E.; von Zglinicki, T. Mitochondrial dysfunction in cell senescence and aging. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brimson, J.M.; Prasanth, M.I.; Plaingam, W.; Tencomnao, T. Bacopa monnieri (L.) wettst. Extract protects against glutamate toxicity and increases the longevity of Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2020, 10, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosamani, R.; Muralidhara. Prophylactic treatment with Bacopa monnieri leaf powder mitigates paraquat-induced oxidative perturbations and lethality in Drosophila melanogaster. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 47, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Phulara, S.C.; Shukla, V.; Tiwari, S.; Pandey, R. Bacopa monnieri promotes longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans under stress conditions. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Srivastava, S.; Kakkar, P. Bacopa monnieri modulates antioxidant responses in brain and kidney of diabetic rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 27, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.; Nagarajan, R.; Hanif, K.; Siddiqui, H.H.; Nath, C.; Shukla, R. Standardized Extract of Bacopa monniera Attenuates Okadaic Acid Induced Memory Dysfunction in Rats: Effect on Nrf2 Pathway. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2013, 2013, 294501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellore, J.; Pauline, C.; Amarnath, K. Bacopa monnieri Phytochemicals Mediated Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles and Its Neurorescue Effect on 1-Methyl 4-Phenyl 1,2,3,6 Tetrahydropyridine-Induced Experimental Parkinsonism in Zebrafish. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 2013, 972391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morana, O.; Wood, W.; Gregory, C.D. The Apoptosis Paradox in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng, E. Apoptosis (programmed cell death) and its signals - A review. Braz. J. Biol. = Rev. Brasleira De Biol. 2021, 81, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Gu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H. Mitochondrial Mechanisms of Apoptosis and Necroptosis in Liver Diseases. Anal. Cell. Pathol. (Amst. ) 2021, 2021, 8900122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Kim, B.M.; Lee, T.H. Death-associated protein kinase 1 as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shu, F. LMTK2 inhibits Aβ25-35-elicited ferroptosis, oxidative stress and apoptotic damage in PC12 cells through activating Nrf2/ARE signalling pathway. Folia Neuropathol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Mahapatra, K.K.; Mishra, S.R.; Mallick, S.; Negi, V.D.; Sarangi, I.; Patil, S.; Patra, S.K.; Bhutia, S.K. Bacopa monnieri inhibits apoptosis and senescence through mitophagy in human astrocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2020, 141, 111367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Gupta, P.; Garabadu, D. Bacopa monnieri attenuates glutamate-induced nociception and brain mitochondrial toxicity in Zebrafish. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022, 37, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, P.; Trigun, S.K. Bacopa monnieri Extract (CDRI-08) Modulates the NMDA Receptor Subunits and nNOS-Apoptosis Axis in Cerebellum of Hepatic Encephalopathy Rats. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2015, 2015, 535013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Tomita, Y.; Pei, J.V.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Young, J.P.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. The Purified Extract from the Medicinal Plant Bacopa monnieri, Bacopaside II, Inhibits Growth of Colon Cancer Cells In Vitro by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Cells 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, S.; Fatima, M.; Mondal, A.C. Bacopa monnieri alleviates paraquat induced toxicity in Drosophila by inhibiting jnk mediated apoptosis through improved mitochondrial function and redox stabilization. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 121, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Pandey, S.; Yadav, S.K.; Verma, R.; Singh, S.P.; Mahdi, A.A. Role of ethanolic extract of Bacopa monnieri against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) induced mice model via inhibition of apoptotic pathways of dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 135, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.M., 3rd; Cookson, M.R.; Van Den Bosch, L.; Zetterberg, H.; Holtzman, D.M.; Dewachter, I. Hallmarks of neurodegenerative diseases. Cell 2023, 186, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnello, L.; Ciaccio, M. Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Molecular Basis to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, N.; Nahrgang, S.; Petershagen, W.; Dembek, T.A.; Pedrosa, D.; Timmermann, L.; Weber, I.; Oehrn, C.R. Theta frequency deep brain stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus improves working memory in Parkinson's disease. Brain A J. Neurol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turana, Y.; Shen, R.; Nathaniel, M.; Chia, Y.C.; Li, Y.; Kario, K. Neurodegenerative diseases and blood pressure variability: A comprehensive review from HOPE Asia. J. Clin. Hypertens. (Greenwich Conn.) 2022, 24, 1204–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, X.; Wechter, N.; Gray, S.; Mohanty, J.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Olfactory dysfunction in aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 70, 101416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Liu, K.; Pouliopoulos, A.N.; Ji, R.; Jiménez-Gambín, S.; Yousefian, O.; Kline-Schoder, A.R.; Batts, A.; Kokossis, D.; Mintz, A. Blood-Brain Barrier Opening in Alzheimer's Disease Patients Using Portable Focused Ultrasound System. Medrxiv Prepr. Serv. Health Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemitsu, N.; Kanazawa, Y.; Haga, A.; Hayashi, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Harada, M. Determination of Alzheimer's disease based on morphology and atrophy using machine learning combined with automated segmentation. Acta radiologica (Stockholm, Sweden 1987), 2024; 2841851231218384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, A.D.; Amstutz, D.; Petermann, K.; Debove, I.; Sousa, M.; Maradan-Gachet, M.E.; Lachenmayer, M.L.; Waskönig, J.; Murcia-Carretero, S.; Diamantaras, A.A.; et al. Subthalamic stimulation has acute psychotropic effects and improves neuropsychiatric fluctuations in Parkinson's disease. BMJ Neurol. Open 2024, 6, e000524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer's disease. Lancet (Lond. Engl. ) 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwińska, S.; Jeziorek, M. The role of nutrition in Alzheimer's disease. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2021, 72, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer's Disease: Causes and Treatment. Mol. (Basel Switz. ) 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Gopika, S.; Kumar, A.; Garabadu, D. A Comprehensive Review on Preclinical Evidence-based Neuroprotective Potential of Bacopa monnieri against Parkinson's Disease. Curr. Drug Targets 2022, 23, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrino, R.; Schapira, A.H.V. Parkinson disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.K.; Tanner, C.M.; Brundin, P. Parkinson Disease Epidemiology, Pathology, Genetics, and Pathophysiology. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2020, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijms, B.M.; Vromen, E.M.; Mjaavatten, O.; Holstege, H.; Reus, L.M.; van der Lee, S.; Wesenhagen, K.E.J.; Lorenzini, L.; Vermunt, L.; Venkatraghavan, V.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics in patients with Alzheimer's disease reveals five molecular subtypes with distinct genetic risk profiles. Nat. Aging 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, R.; Roy, A. Role of Medicinal Plants against Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2022, 23, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinvillier, D.; Barrast, M.; Couderc-Murillo, P.; Bono-Yagüe, J.; Rousteau, A.; Gómez Escribano, A.P.; Palmeira-Mello, M.V.; Doménech-Carbó, A.; Passe-Coutrin, N.; Sylvestre, M.; et al. Spectroscopic, Electrochemical, and Biological Assays of Copper-Binding Molecules for Screening of Different Drugs and Plant Extracts against Neurodegenerative Disorders. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 16260–16269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandia, R.; Viswanathan, N.; Singhal, S.; Alqahtani, T.; Almikhlafi, M.A.; Simonov, A.N.; Ashraf, G.M. Ameliorative Effects of Phytomedicines on Alzheimer's Patients. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2022, 19, 420–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjaneyulu, J.; R, V.; Godbole, A. Differential effect of Ayurvedic nootropics on C. elegans models of Parkinson's disease. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2020, 11, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasangari, K.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Chaiyasut, C.; Rajan, K.E. Maternal stress-induced changes in adolescent and adult offspring: Neurobehavioural improvement and telomere maintenance. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgonetti, V.; Galeotti, N. Novel Combination of Choline with Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal, and Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wetts Reduced Oxidative Stress in Microglia Cells, Promoting Neuroprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.P.A.; Thuy, L.T.; Thuy My, N.T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Tram, L.H.; Nguyen, T.A.; Toan, D.H.; Tran, T.H.; Tran, T.H.; Bui Van, T.; Van Bach, N. Phenyl glycosides from Bacopa monnieri with their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukat, S.; Zia, M.A.; Uzair, M.; Alsubki, R.A.; Sajid, K.; Shoukat, S.; Attia, K.A.; Fiaz, S.; Ali, S.; Kimiko, I.; Ali, G.M. Synergistic neuroprotection by phytocompounds of Bacopa monnieri in scopolamine-induced Alzheimer's disease mice model. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 7967–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Pandey, S.; Rumman, M.; Mahdi, A.A. Neuroprotective effects of Bacopa monnieri in Parkinson's disease model. Metab. Brain Dis. 2020, 35, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, M.; Ojha, R.P.; Prabu, P.C.; Devi, B.P.; Agrawal, A.; Dubey, G.P. Prevention of age-associated neurodegeneration and promotion of healthy brain ageing in female Wistar rats by long term use of bacosides. Biogerontology 2012, 13, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, H.P.; Bala, P.; Ankisettipalle, S.; ThyagaRajan, S. Bacopa monnieri and L-deprenyl differentially enhance the activities of antioxidant enzymes and the expression of tyrosine hydroxylase and nerve growth factor via ERK 1/2 and NF-κB pathways in the spleen of female wistar rats. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyanka, H.P.; Singh, R.V.; Mishra, M.; ThyagaRajan, S. Diverse age-related effects of Bacopa monnieri and donepezil in vitro on cytokine production, antioxidant enzyme activities, and intracellular targets in splenocytes of F344 male rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 15, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Mishra, B.; Gupta, A.; Srivastava, M.V.P.; Basheer, A.; Sharma, J.; Vishnu, V.Y. Importance of high-quality evidence regarding the use of Bacopa monnieri in dementia. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1134775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, J.D.; Kaufman, J.; Lomas, J.; Goh, A.; White, D.; Simpson, D.; Scholey, A.; Singh, H.; Sarris, J.; Zangara, A.; Stough, C. A Randomized Controlled Trial Investigating the Effects of a Special Extract of Bacopa monnieri (CDRI 08) on Hyperactivity and Inattention in Male Children and Adolescents: BACHI Study Protocol (ANZCTRN12612000827831). Nutrients 2015, 7, 9931–9945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sireeratawong, S.; Jaijoy, K.; Khonsung, P.; Lertprasertsuk, N.; Ingkaninan, K. Acute and chronic toxicities of Bacopa monnieri extract in Sprague-Dawley rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, Y.B.; Chaurasia, S.; Tripathi, E.; Upadhyay, A.; Dubey, G.P. Bacopa monniera Linn. as an antioxidant: mechanism of action. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 34, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, S.; Borowski, T. Neuropharmacological review of the nootropic herb Bacopa monnieri. Rejuvenation Res. 2013, 16, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, A.E.; Chang, D.H.; Münch, G.W.; Steiner-Lim, G.Z. A systematic review of the safety and efficacy on cognitive function of herbal and nutritional medicines in older adults with and without subjective cognitive impairment. Syst. Rev. 2023, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ref | Model/Country | Population | Intervention/Comparison | Outcomes | Side Effects |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [52] | Open-labeled study. USA | 35 health subjects (75% female), 60–78y, with an education corrected score of 25 or above on the MoCA and a score of 9 or below on GDS. | Participants receive BM (CDRI 08) 320 mg/2x/d/3 m. | After 3m, GDS and MoCA did not significantly change; the delayed recall subscale showed a significant improve; mBDNF and proBDNF levels did not exhibit significant changes. There was a significant increase in CREB phosphorylation and a significant reduction of NF-κB phosphorylation. | Nausea, stomach pain, and diarrhea. | ||||
| [53] | The study was a primary, interventional, controlled, parallel, double-blind clinical study. Brazil | 20 volunteers with Parkinson's disease, 13 men and 7 women, 69-85 y | Patients received BME (225 or 450 mg/day) or placebo for 90 d. Motor activity was evaluated before treatment and 30, 60, and 90 d after, and PDQL questionnaire was applied. | The delta percent (Δ%) showed that there were time-dependent improvements in emotional function. | NR | ||||
| [54] | The study was a 14-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, clinical trial (plus a placebo run-in and run-out phases). Australia | 112 boys, 6-14 y, exhibiting inattention and hyperactivity against placebo, with 93 datasets available for analysis | Patients received BM (CDRI 08®) for 14 w: 160 mg of BM or placebo (body weight 20-35 kg) or 320mg/d (if over 35 kg)/ 14 weeks. | No significant differences in behavioral between groups. BM reduced error-making in children and augmented the speed of reaction time. There was significant amelioration in cognitive flexibility, executive functioning, interpersonal problems, and sleep routine. | NR | ||||
| [55] | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Thailand | 48 health patients, 55-80 y, and with Thai ethnicity, read or write in Thai. | Subjects received one bottle of placebo/d/2w (placebo run-in period). Participants were then divided into the treatment (1 bottle of BM essence/d/12 w) and placebo group. | BM essence improved memory speed (assessment by computerized tests). BM active compounds and metabolites were not detected in the plasma and urine samples but were detected in the feces sample. | NR | ||||
| [56] | Randomized study Italy |
42 patients (64% women; >47y) with a significant degree of anhedonia (SHAPS score ≥ 3) and with major depression (DSM 5.0) with no satisfactory response after 4w treatment with citalopram. | Patients received citalopram or citalopram associated with BM (300 mg)/4w. | There was a significant improvement in the Hamilton depression rating scale, SHAPS, strength, and difficulties questionnaire. | NR | ||||
| [57] | Randomized Double-Blind Parallel Phase 2b Study. India | 48 AD and MCI-AD patients, including cognitive and quality of life outcomes. | Patients received either BM (300 mg) or donepezil (10 mg) for 1y. | No difference in the rate of change in memory scale was observed at 3, 6, and 9 m. In the last follow-up, significant difference in the change in PGIMS score between BM and donepezil. | No significant difference in AD in both groups: nausea, diarrhea, asthenia, arthralgia, headache, dizziness, anxiety, and insomnia. | ||||
| [58] | Randomized, double-blind, controlled, parallel arm study. Italy | 80 health subjects, 60 y or more; 25 men and 55 women). | After a 1 w run-in period, subjects received a mix of antioxidants (BM, astaxanthin lycopene, and vitamin B12) or placebo daily/ 8 w. | The consumption of the mix can be effective for counteracting cognitive modifications related to brain aging, such as improvement in trial-making test (TMT) scores, and augment in letter fluency evaluated by the verbal fluency test. | Exacerbation of sinusitis | ||||
| [59] | Pilot study. | 12 participants with dementia > 18y | Participants with dementia (all grades) received 250 mg of BM/3m | All patients showed a positive response: GDS was: 4.42 before BM treatment and 1.92 after 3m. | NR | ||||
| [60] | Double bind, cross-over trial with a placebo comparison Setting: outpatient clinical practice. Italy | 30 elderly subjects, 61-69 y, with basal MMES 20-27 and self-perceived cognitive decline. | Participants received a mix of nutraceuticals based on BM (320mg), L-theanine 100 mg, Crocus sativus 30 mg, biotine 450 μg, vitamin B6 (9,5 mg), folic acid 400 μg, vitamin B12 (33 μg), vitamin D (25 μg) and cupper (2 mg). | There was a significant improvement in the SRDS scores, in both groups. MMSE and PSQ Index significantly improved in the active treatment arm. | NR | ||||
| [61] | Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial non-crossover, parallel trial conducted on outdoor basis. India | 60 health medical students, 19-22y. | Participants received BM (Bacognize®) (150 mg) or placebo 2x/d/6w/ | The use of BM significantly ameliorated cognitive function, and a significant rise in serum calcium was also observed. | NR | ||||
| [62] | Randomized, double-blind placebo and active-controlled clinical trial. India | 109 health subjects, and 123 SDAT patients. being over 60 y, | Participants were divided into Group A: health elderly subjects who received placebo; Group B: health elderly subjects who received the test formulation (BM, Hippophae rhamnoides, and Dioscorea bulbifera; total dose of 500 mg); Group C: SDAT patients treated with donepezil; and Group D: SDAT patients treated with the test formulation. BM (500 mg); donepezil 10 mg, 2x/d/12m | The administration of BM resulted in significant improvement of cognitive functions and reduction in oxidative stress and inflammation related to neurodegeneration in healthy elderly subjects, comparison to placebo, and in SDAT patients, comparison to donepezil. |
NR | ||||
| [63] | Clinical trial conducted as an open-label study. India | 31 children, 3 women and 28 men, 6-12 y, with an age of onset of ADHD before 7 y, as defined by the DSM-IV criteria for ADHD. | Patients received BM extract (BacoMind®) 225 mg/d / 6 months. | There was a significantly reduced in scores of ADHD symptoms (except for social problems), attention-deficit, learning problems, impulsivity, and psychiatric problems. | NR | ||||
| [64] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over study. Australia | 17 health patients, 13 women and 4 men, 18-44 y. | Patients received 320 mg of BM, and 640 mg of BM 1 h, and 2 h after consuming a placebo. A 7-day washout separated the treatments. | There were positive cognitive effects and mood effects; cortisol levels were reduced. | NR | ||||
| [65] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled. Australia | 24 health patients, 20 women and 4 men, aged 18-56 y, who completed a cognitively demanding series of tests. | Patients received BME (KeenMind®-CDRI 08), 320 mg or 640 mg in a cross-over design. | There was no effect in attenuating task-induced ratings of stress and fatigue or cardiovascular activity. | NR | ||||
| [66] | Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled design. Thailand | 60 healthy adults; mean age 62.62y, 23 men and 37 women. | Participants received BM (300 and 600 mg) or placebo/1xd/12w | BM improved working memory, and There was improvement in cognitive processing, attention, and working memory. | NR | ||||
| [67] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Australia | 98 health volunteers, 52 women and 46 men, over 55 y. | Patients received BM (BacoMin), 300 mg/day, or an identical placebo for 12 weeks. | There was an improvement in memory retention and acquisition. | Nausea, increased stool frequency, and abdominal cramps | ||||
| [68] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (with a placebo run-in of 6 weeks). Australia | 54 patients, 60% women and 30% men, without clinical signs of dementia, 65 y or older. | Patients received BM extract, 300 mg/day or a similar placebo for 12 weeks. | There was an amelioration of AVLT delayed word recall memory scores compared to placebo. Depression, anxiety, and heart rate decreased. | Stomach upset | ||||
| [69] | Randomized double-blind placebo controlled. India. | 65 individuals, 50-75 y with self-reported memory impairment (MMSE>24) for at least 1 y. Neuropsychological evaluation was performed at 0, 12, and 24w. Outcomes were analyzed for attention, memory, and speed of information processing. | Patients received BacoMind® 450 mg /d/ 12w or placebo and more 12 w of placebo (24w study). | BM ameliorated performance in the investigated tests associated with attention and verbal memory. Significant interaction was observed between group and time in the digit span backward evaluation (p = 0.008), paired associates dissimilar delayed recall investigation (p = 0.047), list learning delayed recall test (p = 0.014), and in the visual retention-I test (p = 0.035). | NR | ||||
| [70] | Double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Australia (?) | 107 healthy adults (62 completed the study; 21 males and 41 females), 18-60 y | Participants received 2 x 150 mg of BM (KeenMind®) or placebo. Neuropsychological testing was performed at 0 and after 90 d. | BM significantly ameliorated performance on the 'working memory' factor (specifically spatial working memory accuracy). | NR | ||||
| [71] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized study. India | 40 patients > 55 y with complaint of memory loss in daily activities (Wechsler Memory Scale: logical subset score <6) | Patients received 125 mg BM extract or a placebo/ 2x/d/ 12w, followed by the placebo for both groups for another 4 w. Outcomes: MMSE and Wechsler Memory Scale (visual reproduction, logical memory, and learning). | BM led to significant amelioration of logical memory, mental control, and paired associated learning. | NR | ||||
| [72] | Double-blind randomized, placebo control study. Australia | 76 health adults, 48 women and 28 men, 40-65 y. | First session: 3m supply of capsules 450 mg for patients > 90 kg and 300 mg for < 90 kg). Second session: 3m later patients were instructed to take not the capsules. Third session was 6w after the end of trial session. | There was a significant effect on the retention of new information. Rate of learning attention, verbal, visual short-term memory retrieval of pre-experimental knowledge, everyday memory function and anxiety levels were unaffected. |
NR | ||||
| [73] | Double-blind placebo-controlled independent-group design. Australia | 46 healthy volunteers, 18-60y; 11 males and 35 females. | Participants received Keenmind® (standardized: > 55% of combined bacosides A and B), 2×150 mg or placebo/ 12w | There was a significant improvement in learning rate, the speed of visual information processing, and memory consolidation. | Dry mouth, increased appetite, headache, palpitations | ||||
| Study | Question Focus |
Allocation Blinding |
Double- Blind |
Losses (>20%) | Prognostic or Demographic Characteristics | Outcomes | Intention to Treat |
Sample Calculation |
Adequate Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [52] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [53] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [54] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [55] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [56] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [57] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [58] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [59] | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| [60] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| [61] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [62] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [63] | yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [64] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [65] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [66] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [67] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [68] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| [69] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| [70] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [71] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| [72] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [52] | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [53] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| [54] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [55] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Ref | Bioactive Compounds | Molecular Structures | Health Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| [83,84] | Asiatic acid | 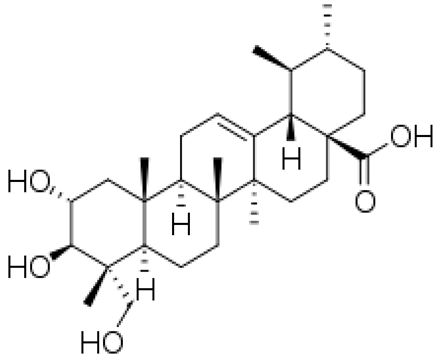 |
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-infective, and antitumor, antimicrobial, neuroprotective diuretic and immunostimulatory |
| [85,86] | Aspartic acid | 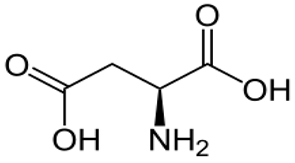 |
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, antibacterial, and fundamental role in memory |
| [87] | β-sitosterol | 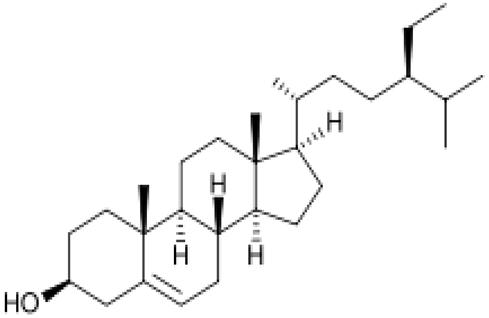 |
Anti-inflammatory, anticancer, hepatoprotective, antioxidant, cardioprotective, antidiabetic, anti-apoptotic and antihistamine |
| [36,88] | Bacogenin | 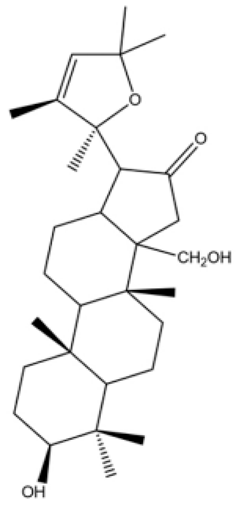 |
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant |
| [41] | Bacopasaponin C | 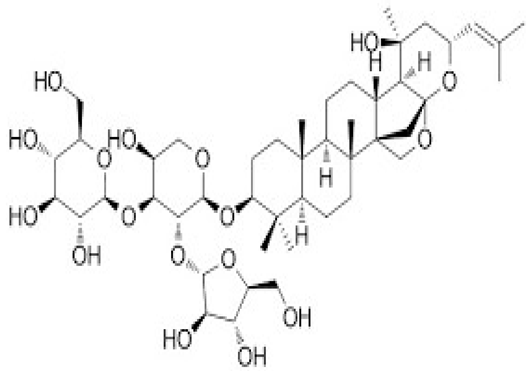 |
Improvement of neurogenesis and cerebral blood flow, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory |
| [78,89] | Bacopaside I | 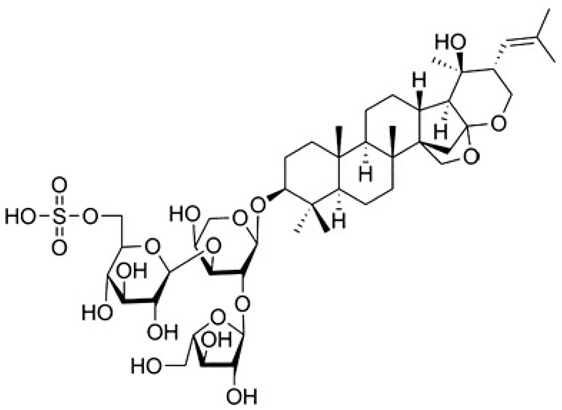 |
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, antidepressant, anticancer, and antiseizure |
| [79,89] | Bacopaside II | 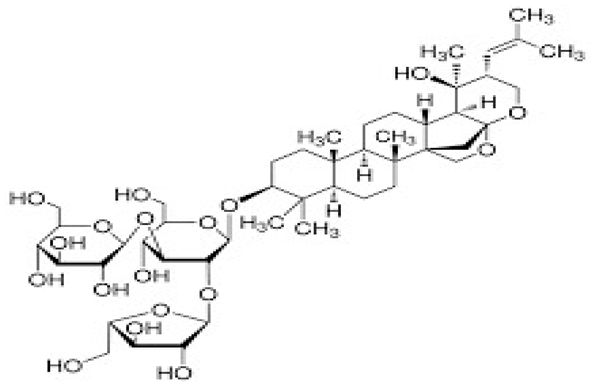 |
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, anti-apoptotic, and neuroprotective |
| [41,89,90] | Bacoside A | 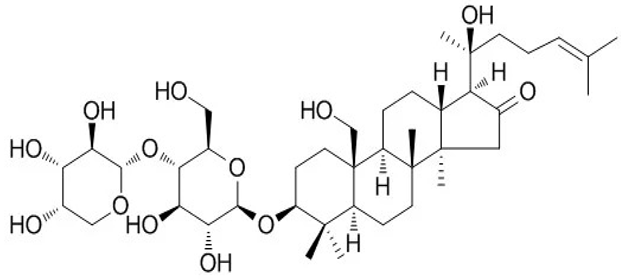 |
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiseizure, anti-apoptotic, neuroprotector, and anti-epileptic |
| [41,90] | Bacoside B | 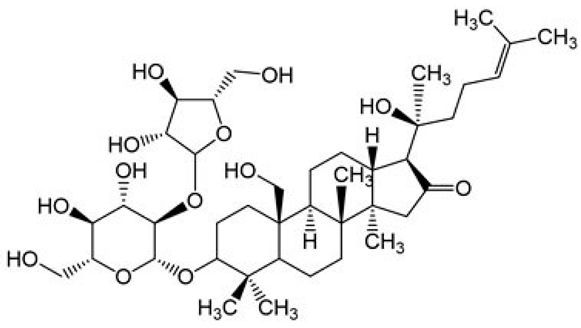 |
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant, |
| [91,92] | Bacosine | 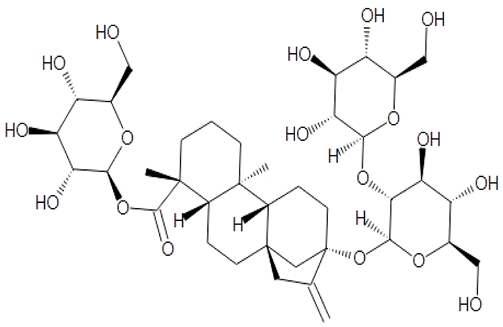 |
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, antitumor, antihyperglycemic and hepatoprotective |
| [41] [93] [94] | Betulinic acid | 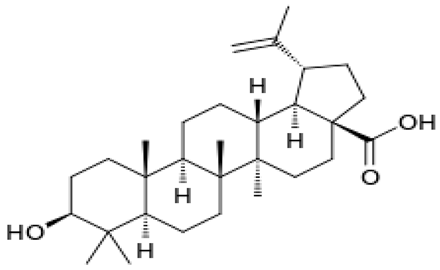 |
Anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antibacterial, antiviral, antidiabetic, antimalarial, anti-HIV, and antitumor |
| [95] | Cucurbitacin B | 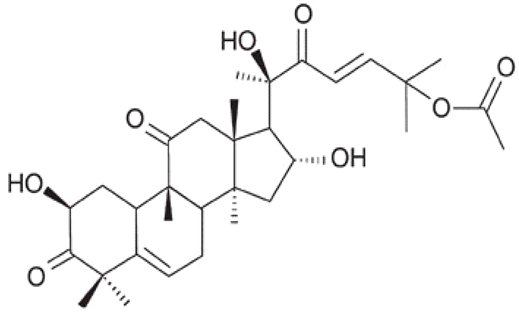 |
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, hypoglycemic, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective, and anticancer |
| [96] | D-mannitol | 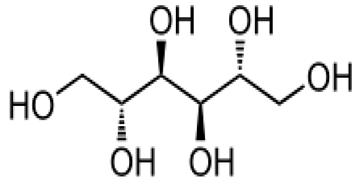 |
Antitumor and immune stimulants |
| [97,98] | Glutamic acid | 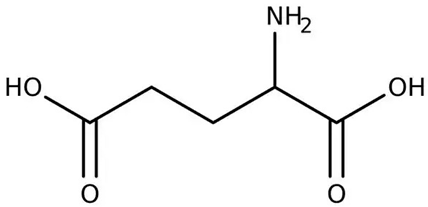 |
Anticancer, antimicrobial, nephroprotection, and antidiabetic |
| [33,41] | Jujubogenin | 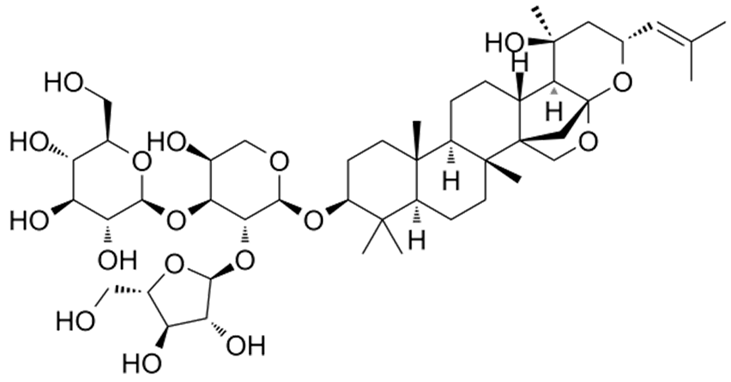 |
Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant |
| [99,100] | Loliolide | 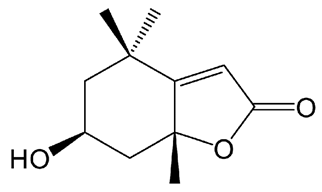 |
Anti-aging, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotector, anti-Parkinson, anti-cholinesterase and antidepressant |
| [33,101] | Pseudojujubogenin glycoside | 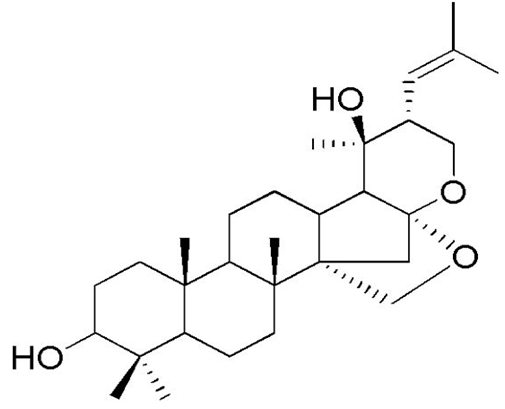 |
Anti-ageing, anticancer, anticonvulsant, antidepressant, anti-emetic, anti-inflammatory. and antibacterial |
| [102,103] | Quercetin |  |
Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, anti-carcinogenic, antidiabetic, and antiviral |
| [104,105] | Stigmastanol | 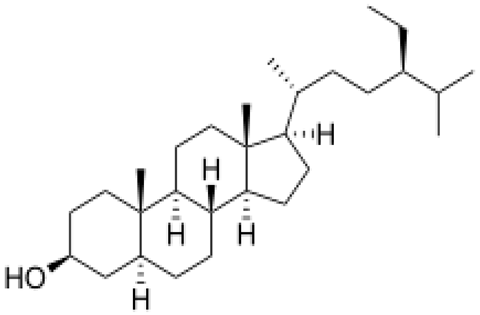 |
Acaricidal effects and antioxidant |
| [106] | Stigmasterol | 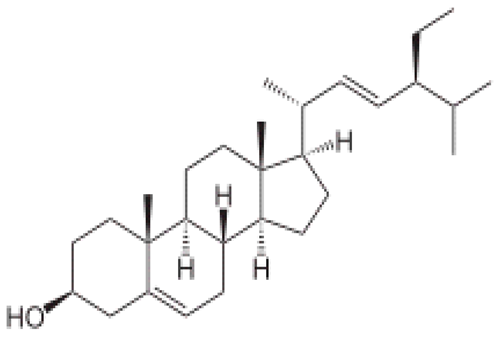 |
Anticancer, anti-osteoarthritis, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, immunomodulatory, antiparasitic, antifungal, antibacterial, antioxidant, and neuroprotective |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).