1. Introduction
1.1. Background
Marine sustainability refers to the responsible and balanced use of marine resources and ecosystems to ensure their long-term health and resilience [
1]. Marine sustainability and the well-being of dolphins are interconnected because dolphins are marine mammals that depend on healthy and sustainable marine ecosystems for their survival. Ensuring the sustainability of marine environments is crucial for protecting dolphins and other marine species [
2]. Dolphins have always been a subject of fascination for biologists and ecologists because of their highly intelligent nature and complex social behavior [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. In Taiwan, these marine mammals are essential for the natural world, serving as vital indicators of the health of marine and coastal ecosystems [
8,
9]. However, understanding dolphin behavior and ecology is a challenging task.
Dolphin behavior is quite intricate, and it can be categorized into psychological and physiological aspects. We can typically observe dolphin behavior through their social activities [
3], play [
6,
7], and resting times [
5]. Nonetheless, dolphins also exhibit a behavior known as "vomiting fish," which they often use as a method to catch prey [
10]. However, excessive vomiting fish behavior may indicate an underlying issue, such as illness, malnutrition, environmental stress, or other health or behavioral problems.
1.2. Motivation
Manually observing the daily behaviors of dolphins takes a lot of time and effort. Prolonged human observation can lead to visual fatigue, exhaustion, and inconsistent interpretation standards caused by various factors, including subjective opinions, varying levels of experience, and decreases in concentration. As a result, caretakers invest substantial human resources and time in searching for potential abnormal dolphin behaviors in image analysis, but still face the risk of interpretation errors due to human factors.
To address these challenges, a research project has been undertaken at Farglory Ocean Park. The project involves deploying cameras above dolphin pools to capture long-term footage, which is then analyzed using artificial intelligence to detect any abnormal behaviors in dolphins. By doing so, this system effectively lowers the chances of missing unusual behaviors and making incorrect judgments. It plays a vital role in the early assessment and treatment of dolphin care, and the analysis results serve as a reference for diagnosis. Additionally, it helps reduce costs related to dolphin care operations, such as manpower and time, within the ocean park.
1.3. Objectives
In this study, several important modules were proposed:
Image Preprocessing Module: To reduce the impact of oblique sunlight causing water surface reflections, this module employs image enhancement techniques in two steps: contrast and brightness adjustment [
11], and sharpening processing [
12]. These steps enhance the contours of dolphins in the images, ensuring the accuracy and effectiveness of subsequent analysis.
Pose Estimation Module: The DeepLabCut [
13,
14] deep learning model was used to identify the dolphin skeletons in the images. This model was trained based on a pre-trained ResNet50 [
15] architecture and defined 11 keypoints of the dolphin skeleton. It was capable of recognizing the skeletons of multiple dolphins, ensuring that the root-mean-square error (RMSE) of each skeleton fell below 10.
Behavior Analysis Module: Developed a custom behavior analysis module named AquaAI Dolphin Decoder with Long Short-Term Memory (ADD-LSTM). This module initially uses a pose estimation model to perform a preliminary analysis of the processed dolphin keypoints, categorizing dolphin behaviors into six types based on set thresholds, including vomit fish, side swimming, swimming together, playing with the toys, resting by the shore, and hook the swimming ring. Finally, a double-layer bidirectional LSTM recurrent neural network [
16,
17] is used to further classify dolphin behaviors, achieving a behavior recognition accuracy of 94.3%.
2. Related works
2.1. Papers Survey of Dolphin Behavior
Dolphin behavior is varied and intricate, and it can be classified into psychological and physiological aspects. Dolphins exhibit their behavior through social activities [
3], play [
6,
7], and resting times [
5]. However, they also display "vomiting fish" behavior, which they use to catch prey [
10]. But if a dolphin exhibits excessive vomiting fish behavior, it could be a sign of underlying issues such as illness, malnutrition, environmental stress, or other health or behavioral problems.
Observing the daily behavior of dolphins is crucial to assess their physiological and psychological well-being. Effective identification and recording methods are required to monitor their behavior accurately. We have compiled the characteristics and descriptions of dolphin behavior mentioned by Jensen, Ann-Louise M., et al. [
4] and other academic papers, and presented this information in
Table 1.
2.2. Papers Survey of Dolphin Detection
In
Section 2.2.1, we discussed various existing methods and technologies for dolphin detection, while
Section 2.2.2 highlighted the limitations and challenges associated with these methods.
2.2.1. Existing Approaches for Dolphin Detection
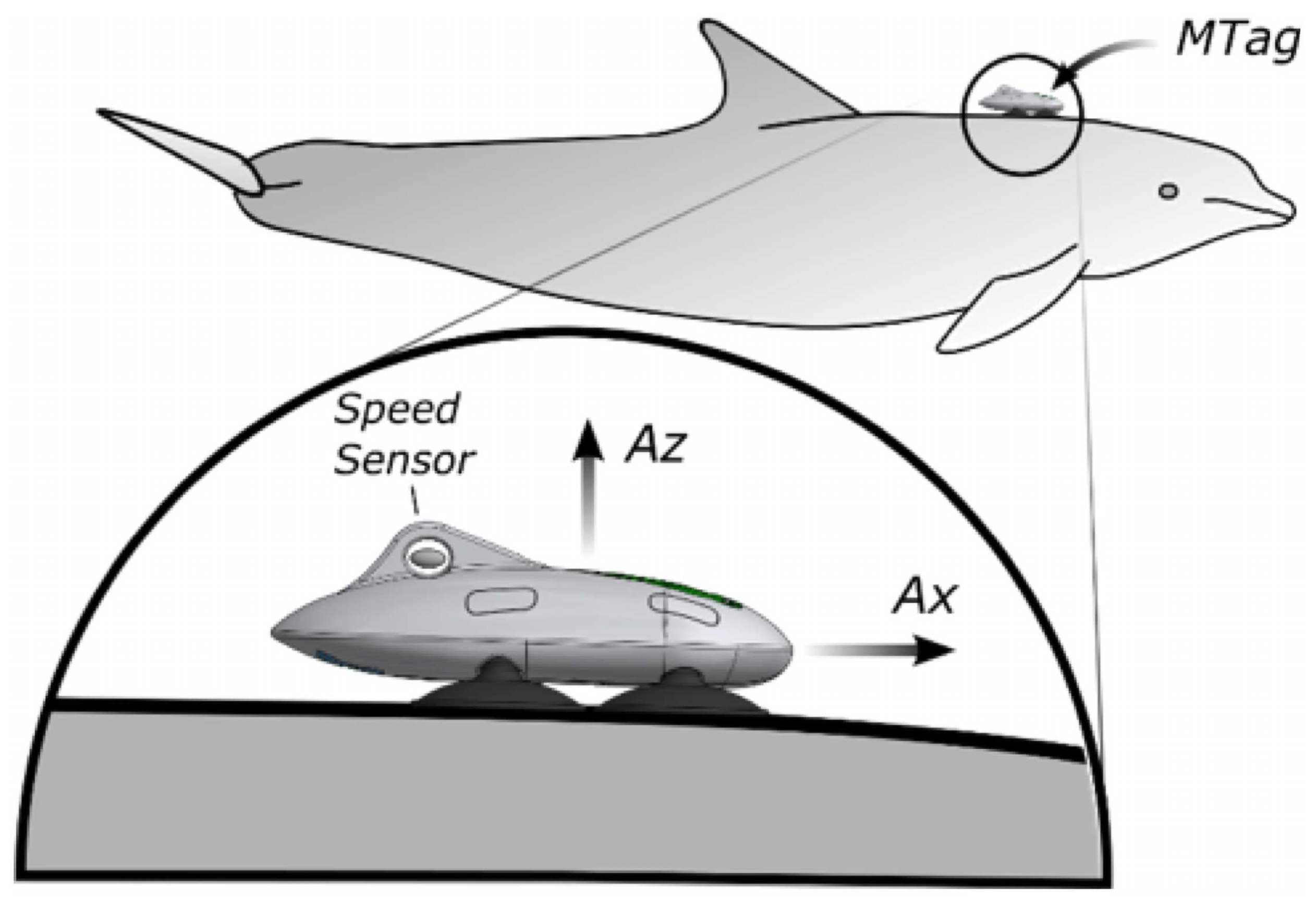
Sensor-based methods: Sensor-based methods for dolphin identification involve utilizing their physiological characteristics. These methods typically require attaching sensors to the back of dolphins (
Figure 1) to detect and analyze physiological signals related to the dolphins, such as their position, acceleration, heart rate [
18,
19,
20,
21].
Vision-based tracking methods: Karnowski, J., Hutchins et al. [
22] proposed an algorithm that can detect and track dolphins automatically. The algorithm compared the performance of two methods for dolphin detection: Robust Principal Component Analysis (RPCA) and Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM). Additionally, they created the first dataset for dolphin detection that includes ground truth data. By utilizing the detection results, they were able to initialize a real-time compressed tracking algorithm, which enabled automated dolphin tracking.
Gabaldon, Joaquin, et al. [
23] proposed a framework based on deep learning to monitor and analyze dolphin behavior in artificial captive environments. They used Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and the Faster R-CNN algorithm to detect dolphins in video footage. The study utilized Kalman filtering for post-processing to obtain short-term trajectories and kinematic information about the dolphins (
Figure 2). The framework also employed heatmaps based on position and velocity to analyze the spatial utilization patterns of dolphins. They also calculated a motion diversity index, joint entropy, to reveal daily patterns in dolphin activity levels. The results demonstrated that this framework can enable long-term automated monitoring and analysis of dolphin behaviors such as resting, clockwise, and counterclockwise swimming.
Pose estimation-based methods: Pose estimation-based methods are used to identify and interpret the posture or joint positions of dolphins from images. These methods utilize tools such as OpenPose [
24] or DeepLabCut [
13,
14] to recognize keypoints on dolphins. This involves analyzing the body structure and movements of dolphins in captured images or videos, which allows for detailed behavioral studies.
Mathis, Alexander, et al. [
13] proposed an animal skeleton detection tool. They used the transfer learning principle to achieve high-precision animal body part pose estimation based on a small amount of annotated data. The core of this method is to use a pre-trained deep neural network (ResNet-50) to extract features, and then fine-tune it on a small amount of user-defined annotation data. Later, Lauer, Jessy, et al. [
14] extended the functionality of the DeepLabCut tool to enable multi-animal pose estimation, recognition, and tracking. The research addresses complex challenges in multi-animal scenarios such as occlusion, similar appearance between animals, and frequent interactions.
2.2.2. Limitations of Current Approaches
Sensor-based methods: It has been found that using sensors to detect dolphins is an effective and accurate method. However, it can have adverse effects on the health of the dolphins. In their research, Julie M., et al. [
25] studied the potential risks of attaching sensors to dolphins, particularly regarding their well-being and behavior. They discovered that installing biotelemetry or recording devices on dolphins could increase the hydrodynamic resistance of their streamlined bodies, affecting their posture, swimming patterns, and energy balance.
Vision-based tracking methods: Significant progress has been made in dolphin identification through vision-based tracking methods. These techniques use RPCA for background subtraction and compressed tracking algorithms for automated dolphin tracking, which deliver a precision rate of 78.8% in dolphin identification [
22]. Another approach is to use neural networks like Faster R-CNN and Kalman filters for dolphin recognition and trajectory generation, which achieve an accuracy rate of 81% in dolphin identification [
23].
However, it’s worth noting that these methods may only provide insight into dolphin location and trajectories, and may not capture more complex behaviors such as social interactions or distinct swimming patterns. Additionally, the processing of data is complex and requires significant computational resources and time. Therefore, image tracking has limitations in terms of accuracy, individual recognition, and behavior monitoring.
Pose estimation-based methods: It is common to use pose estimation methods to recognize different animal behaviors. For instance, DeepLabCut and Support Vector Machine (SVM) models have been adopted to identify cattle behavior [
26] and analyze the movements of primates and pigs [
27,
28]. However, there has been a scarcity of research on using pose estimation techniques to recognize dolphin skeletons. The only study conducted in this area was by Qi, Hong, et al. [
29], who used OpenPose technology for dolphin skeleton detection. Nevertheless, there has been no research utilizing DeepLabCut for similar dolphin skeleton detection.
It is essential to note that OpenPose is mainly designed for human joint point recognition, and its keypoint recognition rate for animals is not very high. Washabaugh, Edward P., et al. [
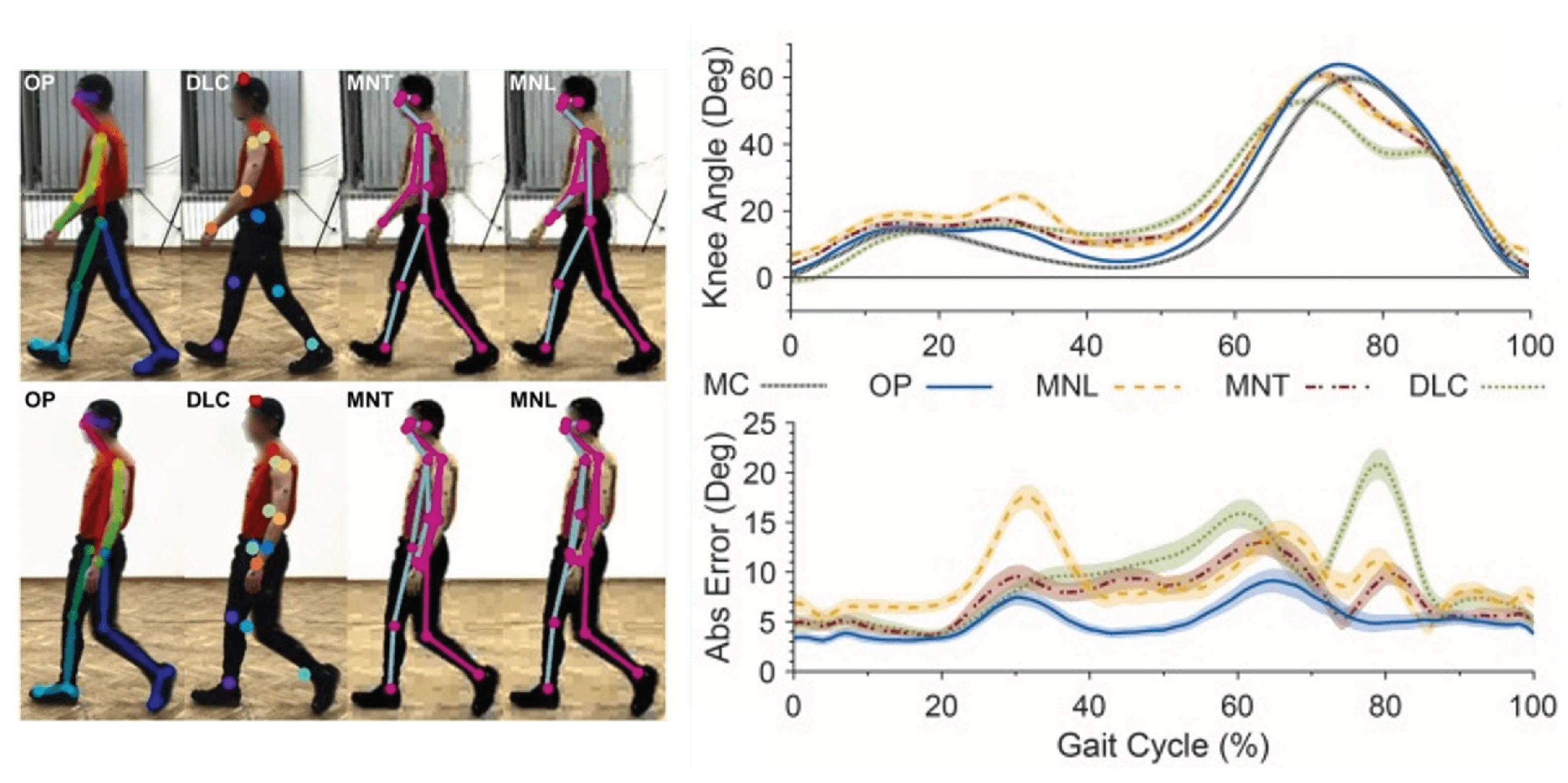
30] compared four open-source pose estimation methods (OpenPose, TensorFlow MoveNet Lightning, TensorFlow MoveNet Thunder, and DeepLabCut) for human posture analysis. The experimental results showed that OpenPose performed the best for human gait analysis (
Figure 3). However, the authors also noted in the paper that although OpenPose may outperform other pose estimation methods during human gait, DeepLabCut might perform better in animal model pose estimation. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to explore the use of DeepLabCut for dolphin skeleton detection and compare the accuracy of different methods.
3. Papers Survey of Behavior Classification
Pose estimation-based techniques have enabled more accurate methods of analyzing animal behavior. Various classification models, such as Support Vector Machines (SVMs), Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTMs), Convolutional LSTMs, and others, are used for this purpose. For instance, Khin, May Phyu, et al. [
26] employed DeepLabCut and an SVM model to study the behavior and skeleton of cattle. They divided the body of the cattle into eight key parts and utilized the SVM model to classify behaviors such as standing, drinking water, eating, sitting down, and tail raised. The average accuracy achieved for each behavior was 88.75%.
Liu, Ruiqing, Juncai Zhu, and Xiaoping Rao [
17] conducted a study on identifying mouse behavior using an improved DeepLabCut network for keypoint detection and behavior recognition through Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory (ConvLSTM) networks. The authors utilized an enhanced DeepLabCut keypoint detection algorithm to identify specific points on the mouse’s body, such as the nose, ears, and tail base. Then, they used ConvLSTM networks to analyze the data from these keypoints and classify behaviors like walking, resting, grooming, and others.
After reviewing the studies mentioned above, it has become evident that pose estimation holds great importance in analyzing animal behavior. However, this technique is not used extensively in the study of dolphin behavior. Therefore, this research aims to implement pose estimation methods to analyze dolphin behavior. The study will also compare the effectiveness of various classification models and propose an optimal method for analyzing dolphin behavior.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. System Overview
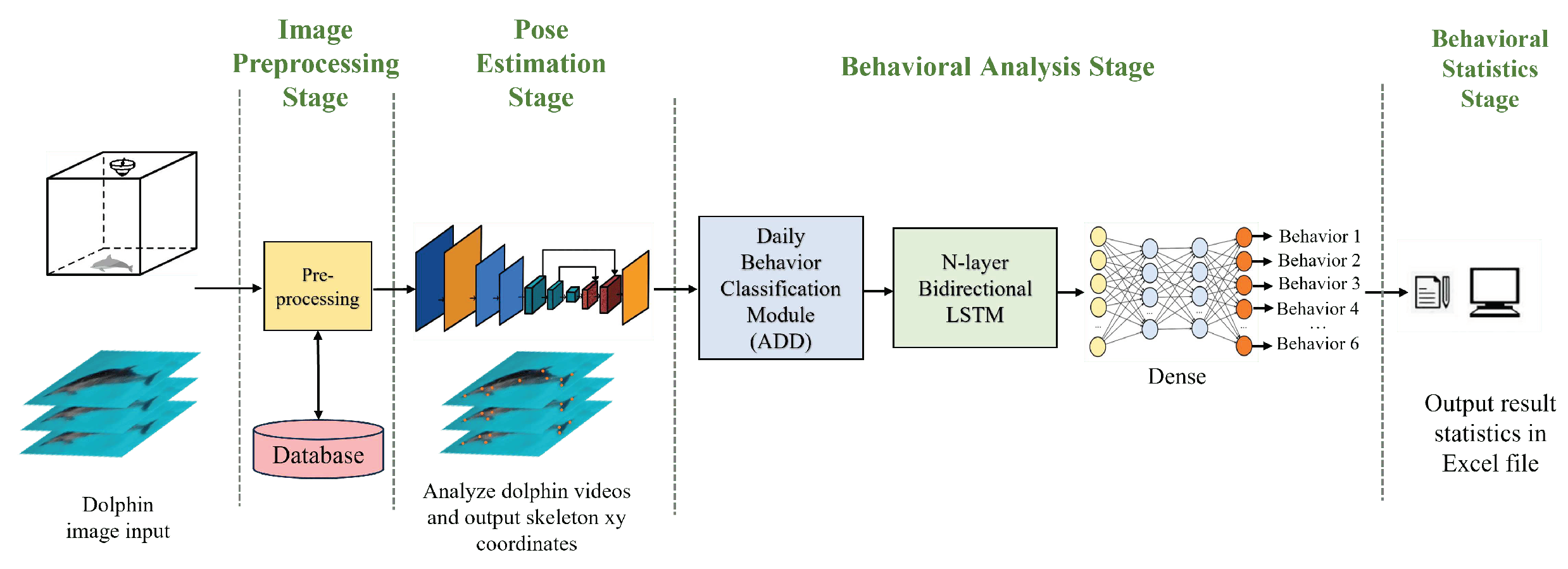
The architecture of the system used in this thesis is shown in
Figure 4. At Farglory Ocean Park, three network cameras have been installed above the pools to capture images of dolphins. The images are then transmitted to a PC and undergo four stages of processing. In the first stage, an
Image Preprocessing module prepares the images for further analysis by other modules. The second stage involves a
Pose Estimation Module which locates various keypoints on the dolphins. In the third stage, the keypoints data is sent to a
Behavior Analysis Module for the classification of six different types of behavior. Finally, in the fourth stage, the behavior data is consolidated into an Excel file for future analysis by the user.
4.2. Data Preparation and Image Preprocessing
4.2.1. Data Preparation
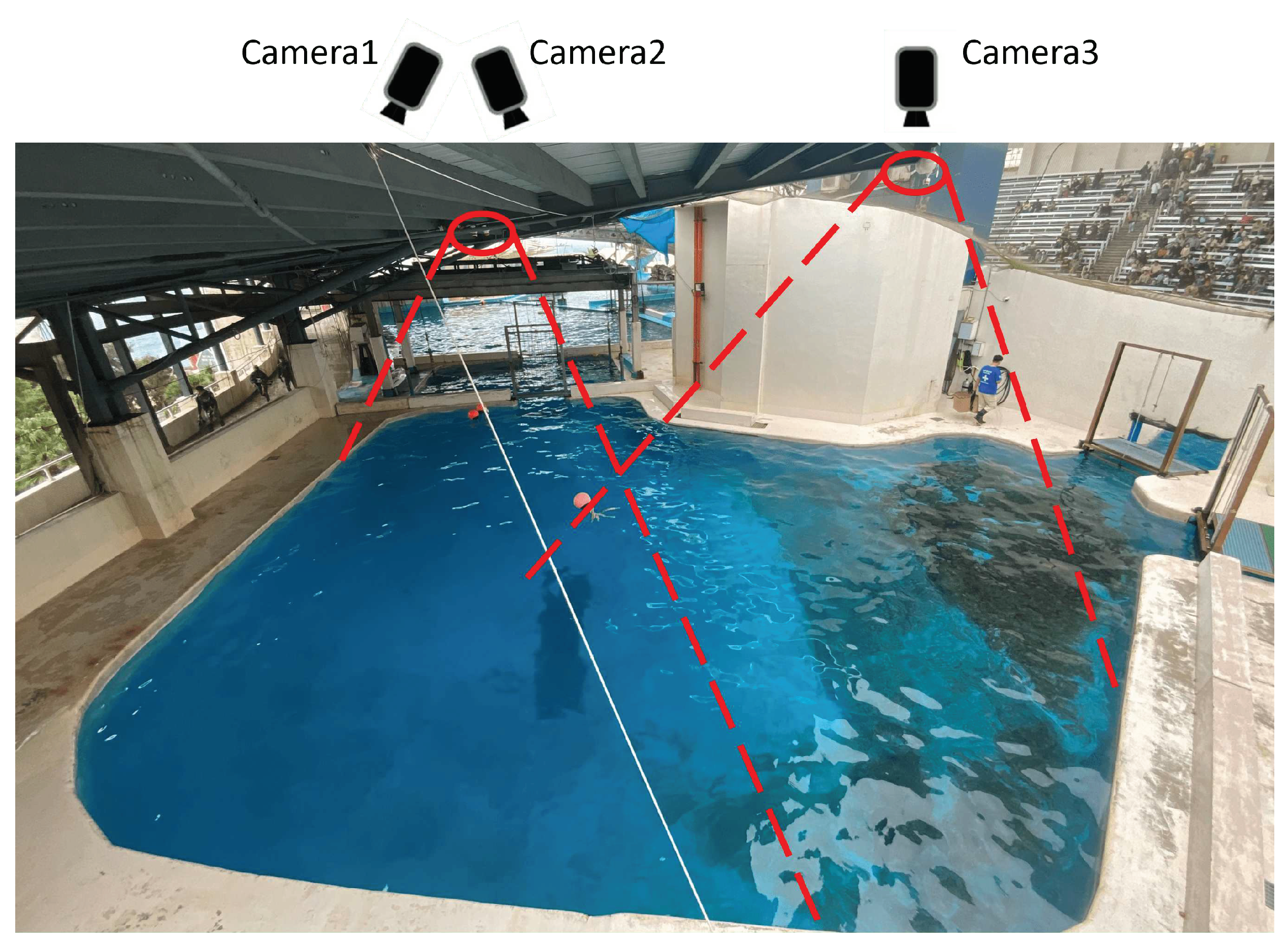
At Farglory Ocean Park, six dolphins are living in several interconnected pools with gates that allow them to move between them. For our research, we selected one pool that was about 150 square meters in size to observe the daily behavior of the dolphins. To capture the entire pool, we installed three network cameras at a height of approximately 5 meters above the water. You can see how the cameras were placed in
Figure 5.
The videos we recorded have a resolution of 1280x720 pixels and a frame rate of 5 fps. We captured over 200 hours of dolphin video footage, which is equivalent to about one month of daytime pool footage. This footage was used as a dataset for our subsequent training and validation phases. However, filming the pools during the daytime can be challenging due to sunlight reflecting on the water. In the next section, we will introduce the method of image preprocessing that we used to address this issue.
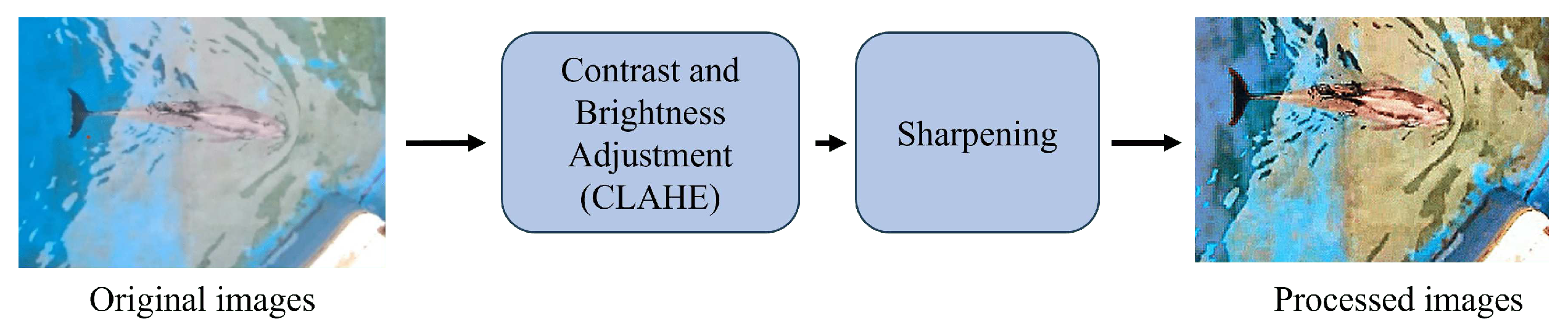
4.2.2. Image Preprocessing
When taking photos from an elevated position above a swimming pool, several potential issues can affect the quality of the images. These include blurred images caused by the refraction of light by water waves, as well as obstructions due to the reflection of sunlight. To ensure that the data we use for analysis is of high quality, we will perform image enhancement during the preprocessing stage. This will help to improve the visibility of the dolphin contours within the images.
Image enhancement refers to the process of enhancing the overall quality, contrast, detail, and resolution of digital images. The primary objective of this process is to make images more visible and interpretable. Image enhancement plays a crucial role in the preprocessing stage, as it helps in improving the quality and features of the original image, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of model training and testing. We have proposed an image processing workflow that combines contrast color adjustment [
11] and sharpening [
12] techniques to improve the recognition of dolphins in images, as demonstrated in
Figure 6. The results indicate that this method is highly effective in enhancing the visual clarity of dolphins while preserving the natural color of the image. The image preprocessing is divided into two parts as follows:
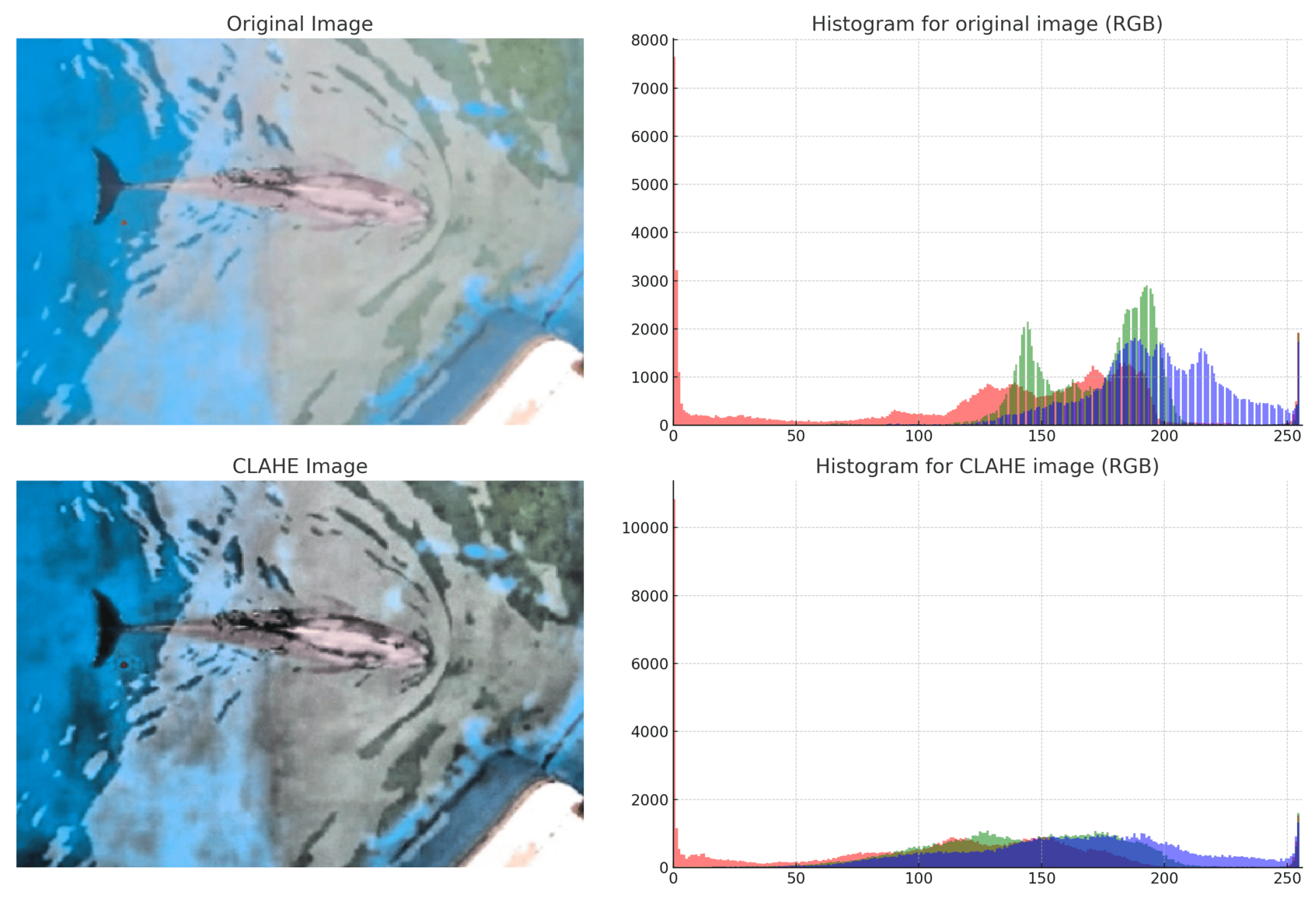
Contrast and Brightness Adjustment: It is common for images captured in pool environments to have low contrast and uneven brightness due to unstable lighting conditions. To address this issue, a study was conducted that employed the CLAHE (Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization) [
11] technique for image enhancement. CLAHE enhances local contrast by dividing the image into small blocks and performing histogram equalization on each. This improves the contrast without affecting the overall brightness balance. The RGB channels were processed separately and a comparison of histograms before and after processing demonstrated a significant improvement in contrast, as shown in
Figure 7. This step is crucial for enhancing the clarity of edges and contours in dolphins photographed under varying lighting conditions.
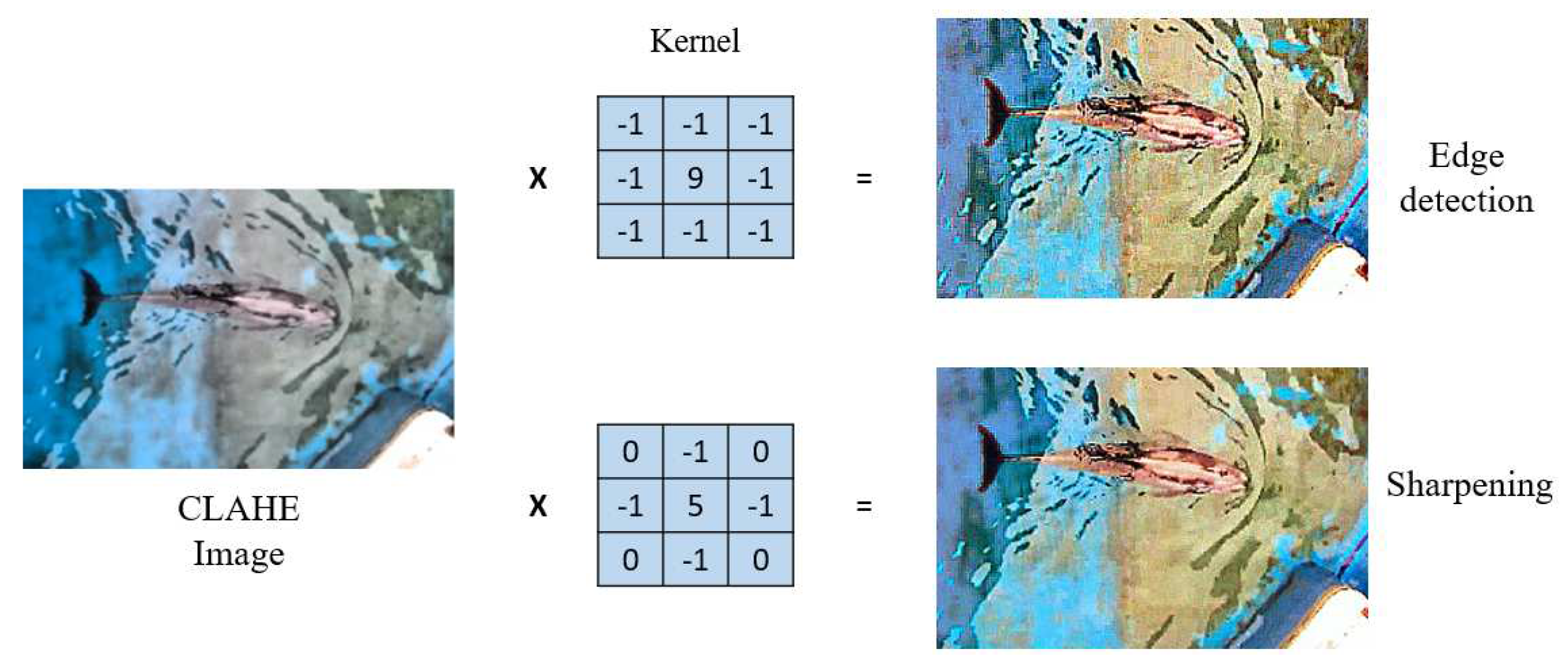
Sharpening Process: The clarity of details in pool images of dolphins is often reduced due to the effects of water ripples and other environmental factors. To improve the clarity of the edges and contours of dolphins, a study was conducted that involved a sharpening process [
12]. This sharpening step intensified the edge information in the images, resulting in a significant increase in the clarity of details, making the morphology and features of dolphins more pronounced. An adaptive sharpening technique was employed in this process, which involved comparing two different types of convolution kernels to achieve the optimal sharpening effect while avoiding the introduction of excessive visual noise. The sharpening effects and comparisons can be seen in
Figure 8.
After applying the image enhancement techniques mentioned above, we effectively improved the dolphin’s contour and reduced sunlight reflection. This helped to enhance the recognition accuracy for subsequent pose estimation, resulting in a 3% improvement.
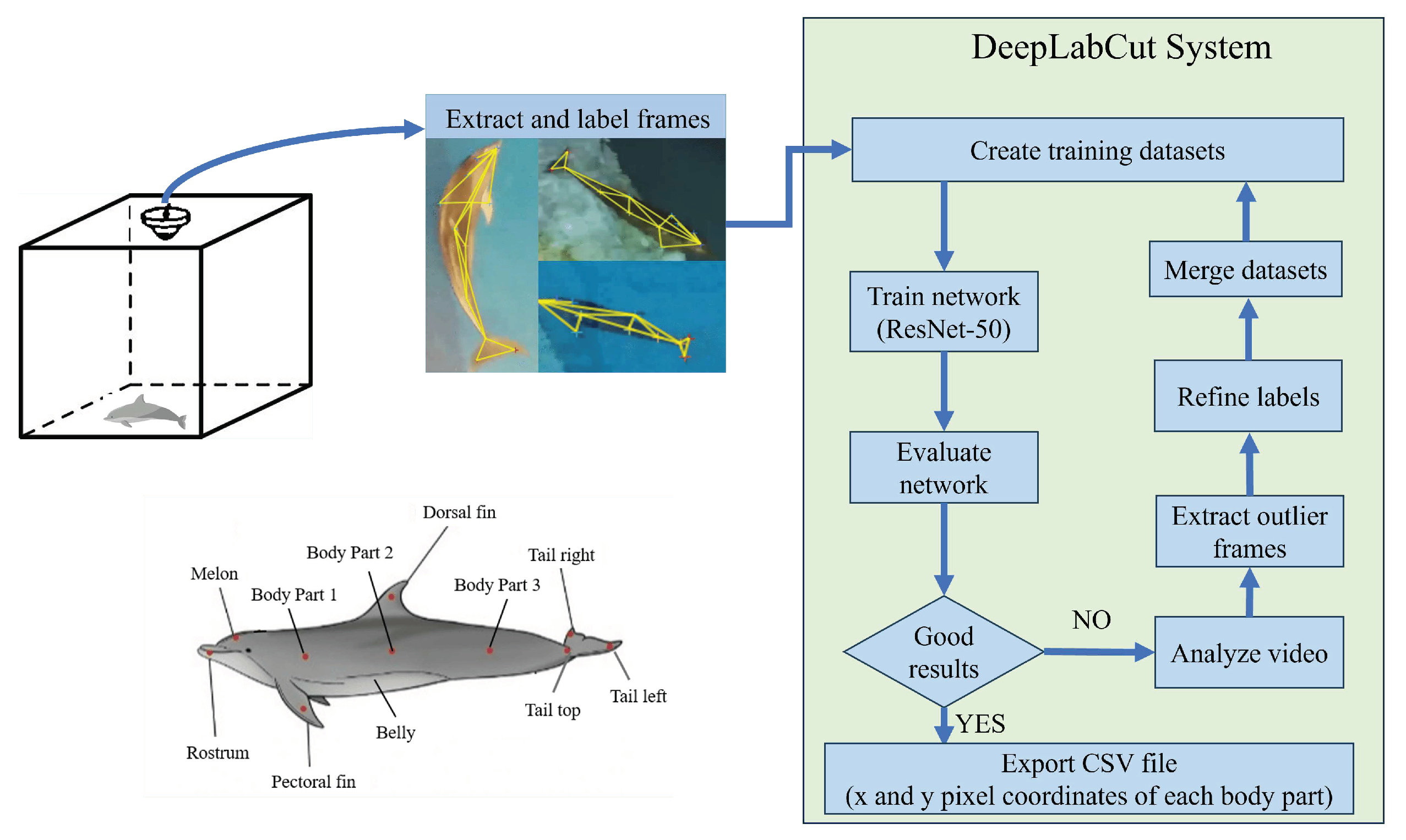
4.3. Pose Estimation Model: DeepLabCut
DeepLabCut [
13,
14] is an open-source tool that uses deep learning techniques to analyze and understand animal movements and positions in video data. It is specifically designed for pose estimation in animal behavior studies. In this study, we used DeepLabCut to analyze the dolphin skeleton.
To label the dolphin skeleton, we extracted one image per second from the filmed video and categorized the dolphins into 11 keypoints such as rostrum, melon, dorsal fin, pectoral fin, belly, tail fin, and other parts of the body. DeepLabCut’s transfer learning-based approach enabled us to accurately identify these keypoints without requiring extensive training data.
Around 1200 dolphin skeleton images were labeled, and we trained them utilizing the pre-trained ResNet50 network [
15]. The network architecture is described in the following section. We evaluated the accuracy of skeleton recognition using RMSE (Root Mean Square Error) and PAF (Partial Affinity Fields) [
24]. If the results were not satisfactory, we fine-tuned the marking points and repeated the training until the desired performance was achieved.
Eventually, we obtained data on the location of each keypoint at different times, which will be used for deep analysis of the dolphin’s behavioral patterns and characteristics.
Figure 9 shows the system flowchart we used for this study.
4.3.1. ResNet50
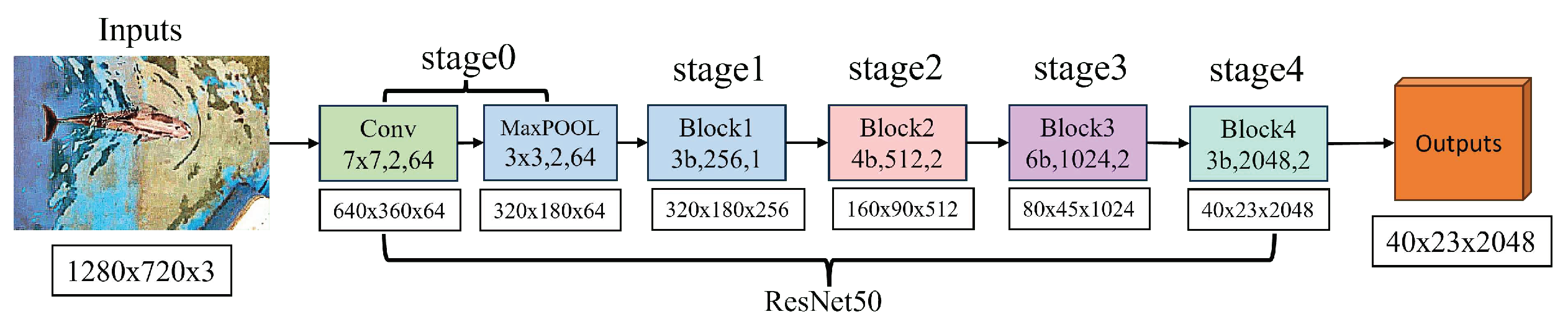
The technology behind DeepLabCut is based on transfer learning principles. Its backbone network is ResNet50, a Residual Neural Network that has been pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset for large-scale image recognition. This training enables it to identify various features, from simple shapes to intricate textures. The structure of ResNet50 is pivotal in this process, illustrated in
Figure 10. When processing images of 1280x720 resolution, the image first undergoes a 7x7 convolutional layer with a stride of 2, followed by a 3x3 max pooling layer with the same stride. This marks the entrance of the image into the core architecture of ResNet50. Each stage in ResNet50 is made up of numerous residual blocks, as shown in
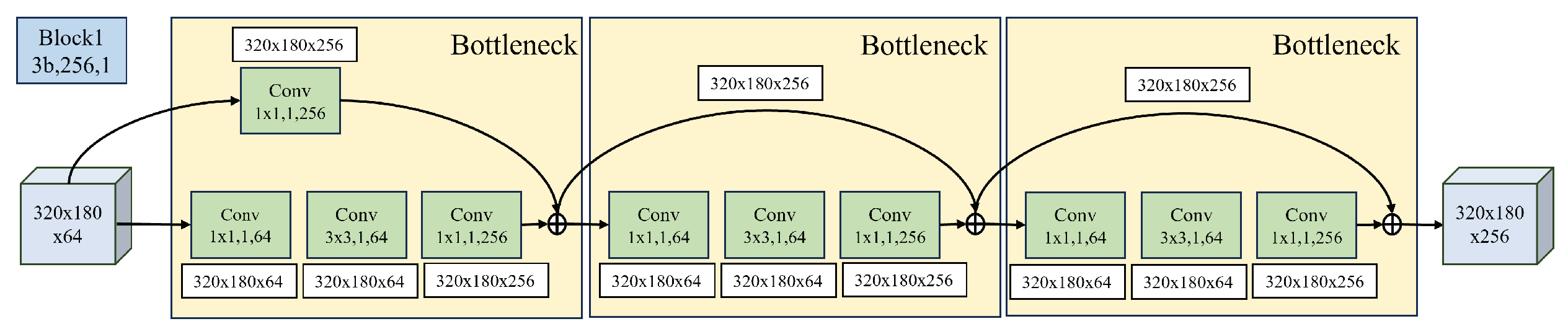
Figure 11. These residual blocks are crucial components of ResNet50, featuring skip connections that enhance feature learning, prevent information loss during training, and address gradient vanishing.
The ResNet50 network has four stages, with each stage performing a specific operation on the feature map. In Stage 1, the network extracts the initial feature map while maintaining its spatial size but increasing its depth. In the subsequent stages (from Stage 2 to Stage 4), the network deepens the depth and complexity gradually while reducing the spatial size of the feature map. These operations work together to obtain increasingly abstract features from the original image. This process is essential in providing visual information needed in the final stage of detecting dolphin keypoints.
In DeepLabCut, the input image undergoes five stages of processing using ResNet50. Each stage encodes the features of the image into deeper feature maps. The feature map output of each stage is a transformation of the previous stage, capturing features at different levels by increasing the depth and reducing the spatial size of the feature maps. These feature maps are used to accurately detect dolphin keypoints, which allows for high-precision analysis of dolphin postures.
4.3.2. The Network Architecture of DeepLabCut
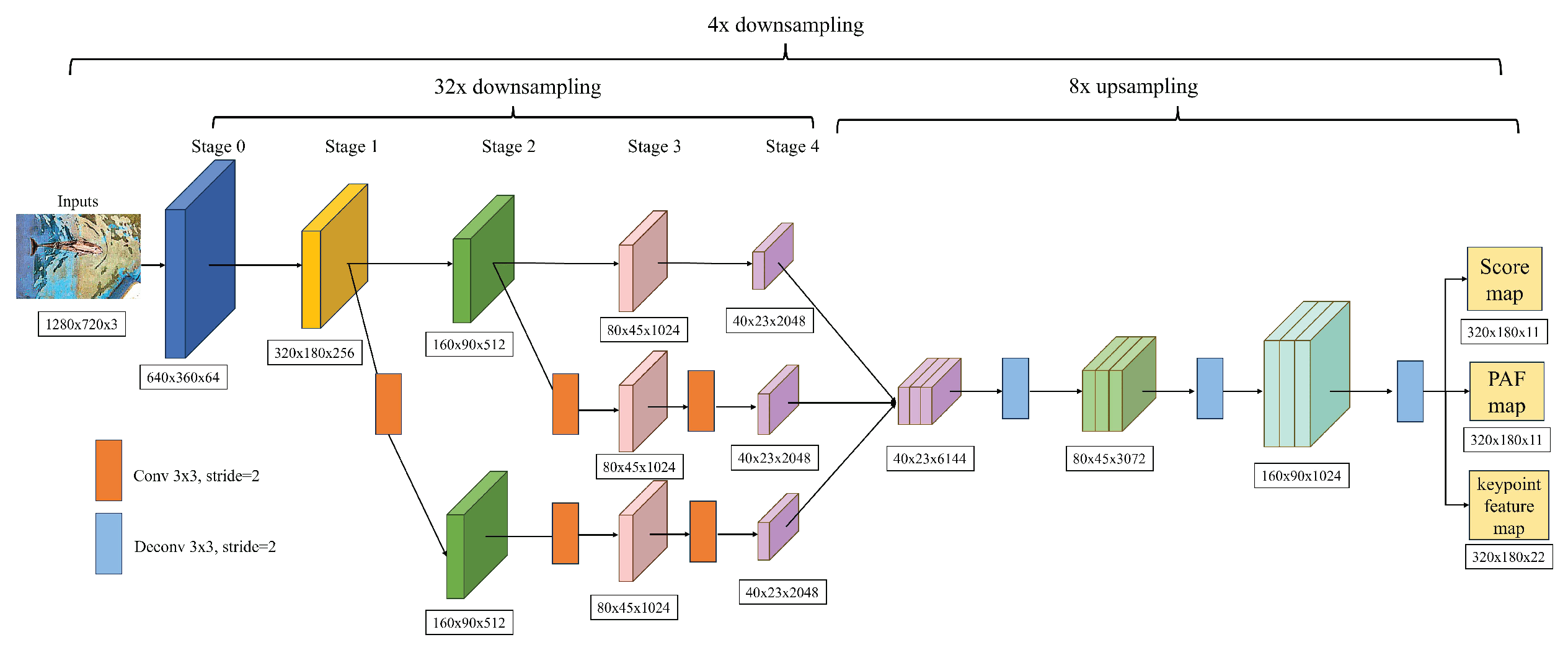
DeepLabCut uses a technique called multiscale feature fusion to detect features of different scales effectively. This technique is illustrated in
Figure 12. When processing input images with a resolution of 1280x720, the system first goes through a series of downsampling operations using the residual blocks of ResNet50, which achieve a downsampling ratio of 32 times. To enhance the model’s ability to capture spatial information and fuse multiscale features, additional downsampling steps are implemented in Stage 1 and Stage 2. This involves using a 3x3 convolutional layer with a stride of 2 to generate feature maps of different resolutions, which are then combined through a specific fusion strategy to create a comprehensive feature map of size 40x23.
The size of the receptive field of feature maps is crucial in detecting keypoints. This study reveals that the Stage 1 branch’s feature maps have a smaller receptive field, making it ideal for capturing details and low-level features like edges and textures. The Stage 2 branch provides feature maps with a medium-sized receptive field, which is suitable for recognizing medium-scale structures. On the other hand, the original ResNet50’s feature maps have the largest receptive field, making them capable of capturing higher-level features such as the overall shape and motion patterns of the dolphin.
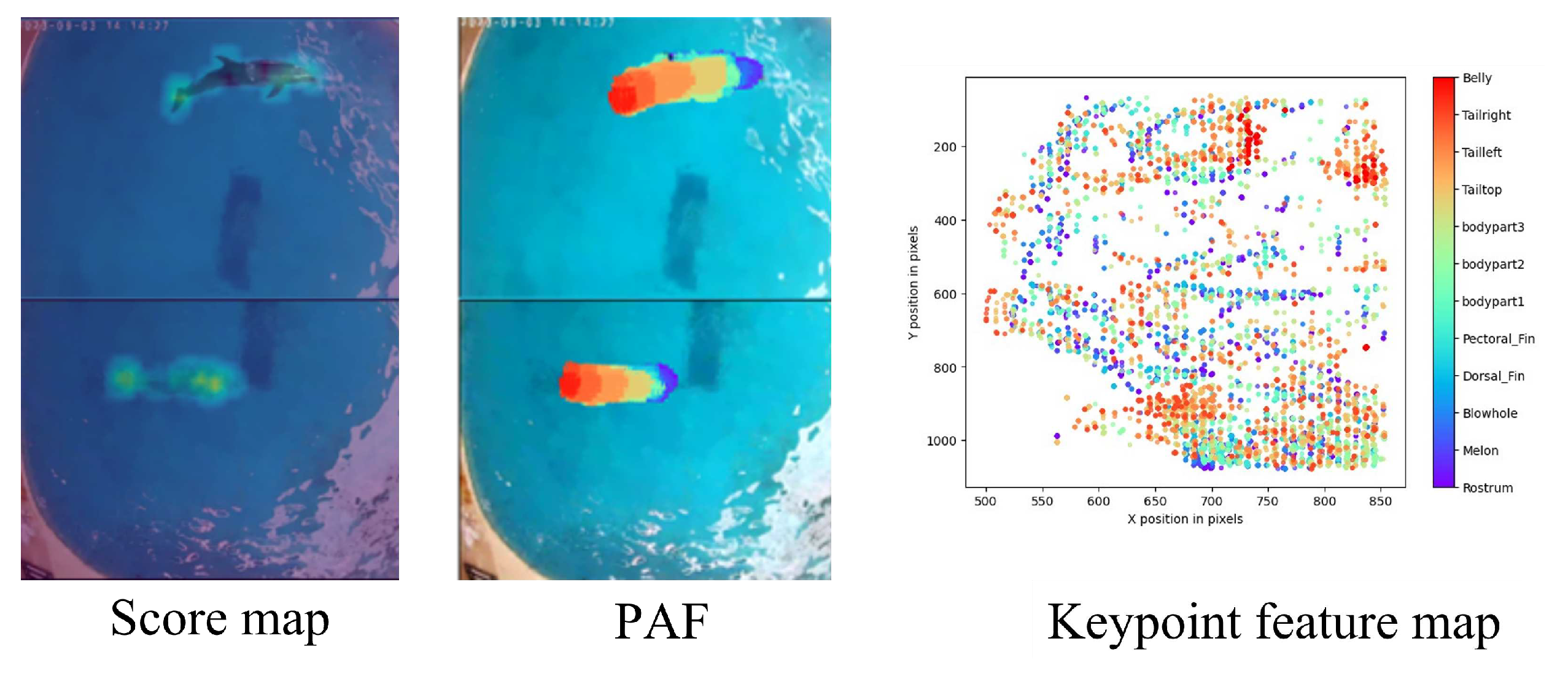
To improve the accuracy of detecting dolphin keypoints, the feature maps are subjected to a process of multiscale fusion. This process involves upsampling the feature maps by a factor of 8 and applying three 3x3 transposed convolution operations. The final output is three feature maps, namely the score map, Part Affinity Field (PAF), and keypoint feature map, each with a size of 320x180. You can see the detailed representation of these feature maps in
Figure 13.
DeepLabCut uses a combination of score map and PAF to locate individual keypoints and understand their spatial and anatomical context relative to each other. This dual consideration leads to accurate and reliable pose estimation. While the score map indicates the location of keypoints, PAF reveals how these keypoints are interconnected.
4.4. Behavior Analysis Model
We were able to obtain the coordinates of various keypoints on dolphins after conducting Pose Estimation Analysis. In this paper, we introduce a system for analyzing six different dolphin behaviors called "AquaAI Dolphin Decoder" (ADD). The six behaviors that ADD can detect are vomiting fish, resting, side swimming, swimming together, playing with balls, and hooking the swimming ring. A detailed description of ADD will be provided in the next section (
Section 4.4.1). Once we have recognized these six behaviors, which have time sequences, we input the results into a double-layer bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model [
31] to improve its accuracy. We will explain the LSTM model in the following sections (
Section 4.4.2). Additionally, we also tried other classification models such as unidirectional LSTM, Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) [
32], and Support Vector Machine (SVM) for comparison. We found that the double-layer bidirectional LSTM model achieved the highest accuracy after comparing the results.
4.4.1. AquaAI Dolphin Decoder (ADD)
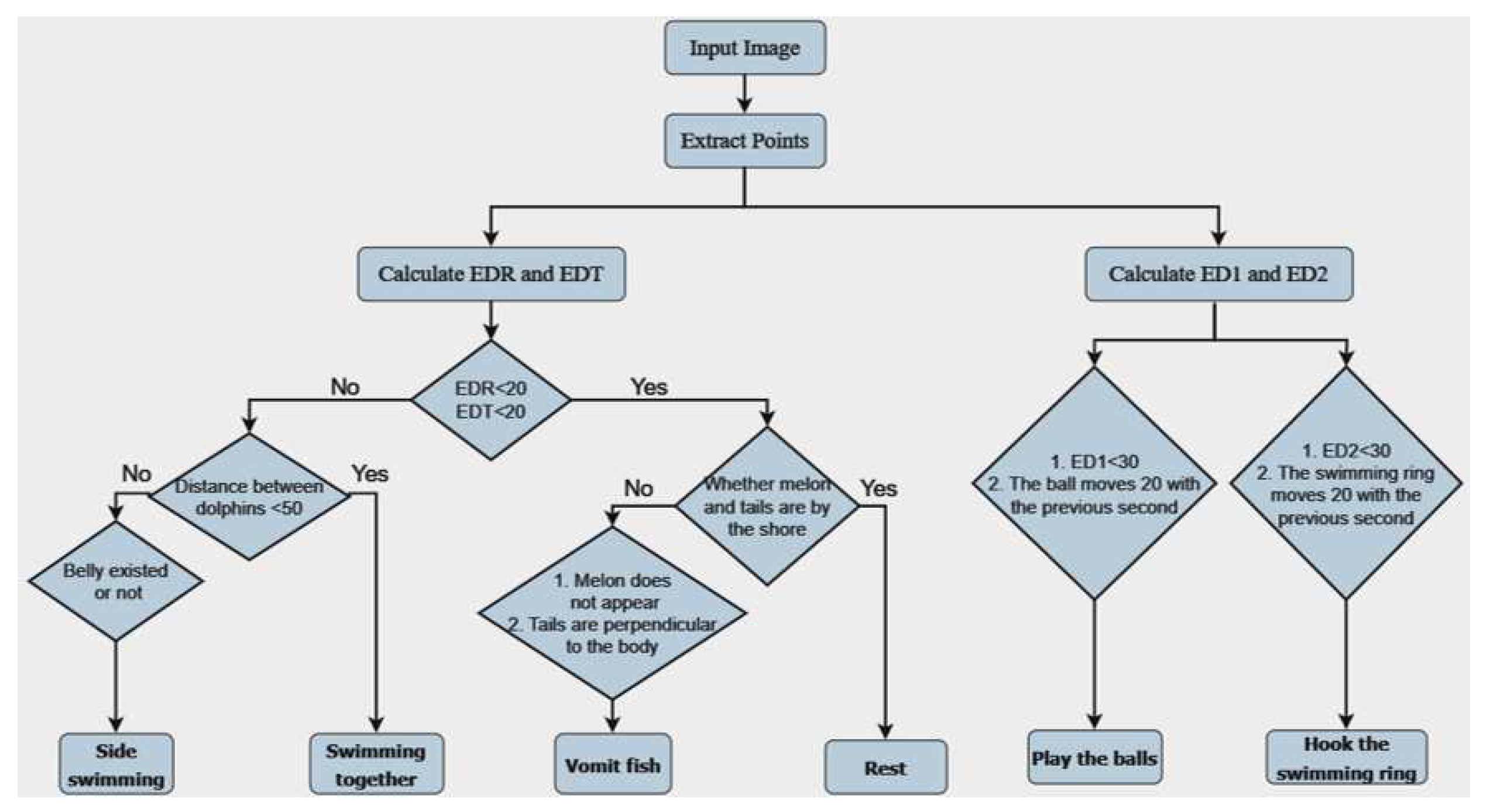
Our Dolphin Behavior Analysis System process is detailed in
Figure 14. This process consists of two main steps:
- (1)
In the first step of our analysis, we focus on the motion of dolphins. We start by calculating the Euclidean distances (EDR and EDT) between the rostrum and tail of the dolphin in each frame. This method measures the straight-line distance between two points. If EDR and EDT exceed the pre-defined threshold of 20, we classify the dolphin as swimming. Additionally, if the distance between two dolphins is less than 50, we categorize it as swimming together. If we observe a specific posture of the dolphin’s belly, we classify it as side swimming. On the other hand, if EDR and EDT are below 20, we consider the dolphin might be resting or vomiting fish. Specifically, if the rostrum and tail of the dolphin are close to the shore, we classify it as resting. If we can’t see the dolphin’s head (possibly submerged in water) and the tail is vertical to the body, we categorize it as vomiting fish.
- (2)
In the second step, we interact with objects present in the scene. We measure the Euclidean distance (ED1) between the dolphin’s rostrum and the ball, and the Euclidean distance (ED2) between the dolphin’s dorsal fin and the swimming ring. If the value of ED1 is less than 30, and the ball has moved more than 20 pixels in the past second, we classify the dolphin as playing with the ball. Similarly, if the value of ED2 is less than 30, and the swimming ring has moved more than 20 pixels in the past second, we categorize the dolphin as hooking the swimming ring.
We have set these thresholds based on our observations of dolphin behavior and previous data analysis. This approach enables us to initially differentiate between various behavior patterns exhibited by dolphins.
4.4.2. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
The study utilized a tool called AquaAI Dolphin Decoder (ADD) to analyze dolphin behavior. To improve the accuracy of behavior prediction, the study used a type of recurrent neural network (RNN) called Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network [
31]. LSTM is a specialized RNN that captures temporal dependencies within behavior patterns. It is useful for handling sequential data. Unlike traditional RNNs, LSTM overcomes the issues of vanishing or exploding gradients that arise when dealing with long sequences. This is due to its unique network structure that includes several key components: the Forget Gate, the Input Gate, the Cell State, and the Output Gate.
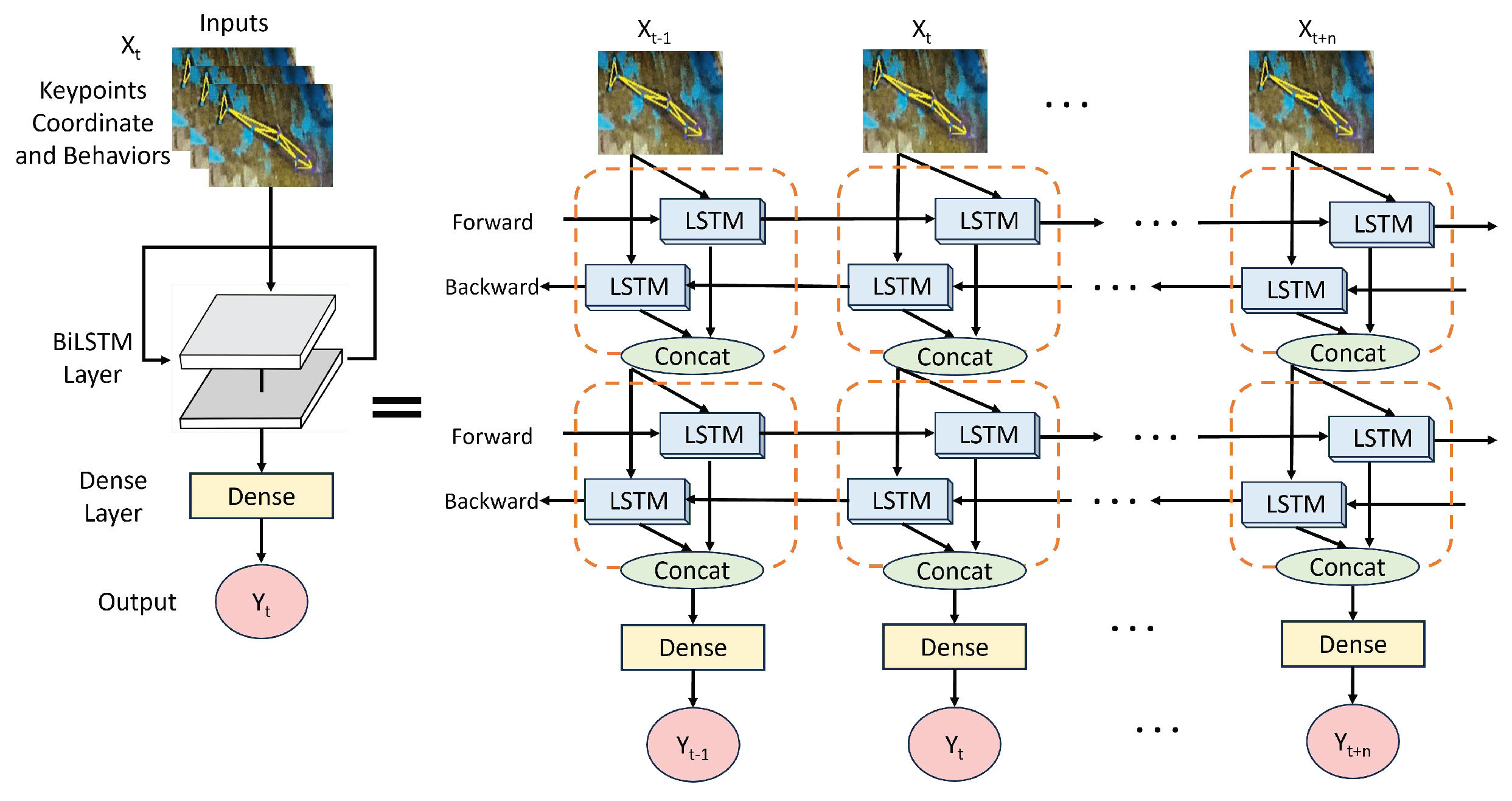
In our research, we utilized a double-layer bidirectional LSTM (BiLSTM) architecture, as depicted in
Figure 15. Unlike the standard LSTM, the BiLSTM has bidirectional inputs, which enables it to take into account both the forward and backward contexts of the time series data simultaneously. The first layer of the BiLSTM was designed with 128 units (64x2), while the second layer had 64 units (32x2). This design enables the model to capture a wide range of features in the first layer and then perform more detailed processing and optimization of these features in the second layer, effectively handling complex time-series data.
We used the AquaAI Dolphin Decoder (ADD) to obtain behavioral temporal data and combined it with the coordinates of the dolphin’s keypoints. This allowed us to create an integrated data input method that captures subtle variations in dolphin body movements through keypoint coordinates. Through time-series analysis, this approach provides a comprehensive understanding of dolphin behavior patterns and enables accurate predictions.
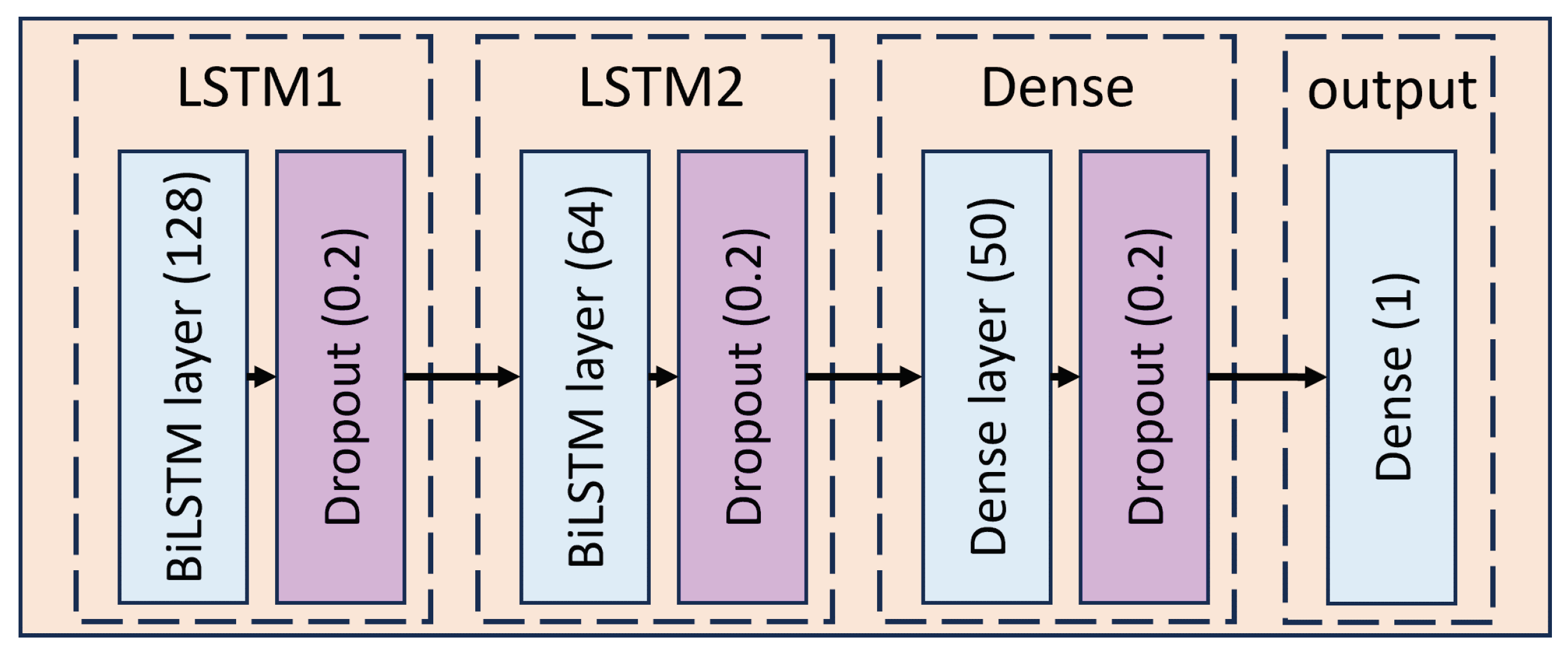
To prevent overfitting during the training process, we added a Dropout layer after each BiLSTM layer, as illustrated in
Figure 16. The Dropout layer randomly drops some neural network connections during training, which helps to improve the model’s ability to generalize. For our model, we set the Dropout rate to 0.2, which means that approximately 20% of the neurons are randomly ignored during training to reduce the risk of overfitting. In the final part of the model, the BiLSTM network’s output passes through a Dense layer (fully connected layer). This Dense layer’s task is to transform the complicated features extracted by the BiLSTM layers into specific outputs that correspond to the six specific behavioral categories of dolphins, as shown in
Figure 17.
5. Results
5.1. Experimental Environment
Table 2 provides a detailed list of the hardware specifications and software versions used for training the neural network and developing dolphin skeleton detection and behavior analysis in this study. The computer setup was located at the Farglory Ocean Park. The model proposed in this research is built using TensorFlow, DeepLabCut, and other open-source neural network frameworks. The training process primarily took place on the Windows system and the Google Colab platform, utilizing Nvidia RTX 3060 GPU for accelerated computations to improve training efficiency and processing capability.
5.2. Experiment of DeepLabCut
As part of our study, we used nearly 200 hours of dolphin footage gathered at Farglory Ocean Park to create our dataset. We annotated a total of 1200 images, identifying both the dolphin skeletons and environmental features within them. The dataset was then split into two parts: a training set (80%) and a test set (20%). Our annotations for the dolphin skeletons included 11 keypoints, such as the rostrum, melon, dorsal fin, pectoral fin, belly, and tail fin. For the training process, we utilized the ResNet50-based configuration from DeepLabCut, with specific parameter settings applied.
Batch size: 8
Learning rate remained at 0.0001 for the first 7,500 iterations.
Subsequently, it was adjusted to 5e-05 between 7,500 and 12,000 iterations.
Further fine-tuning was performed with a learning rate of 1e-05 between 12,000 and 100,000 iterations.
Finally, the learning rate was finely tuned to 1e-06 between 100,000 and 220,000 iterations.
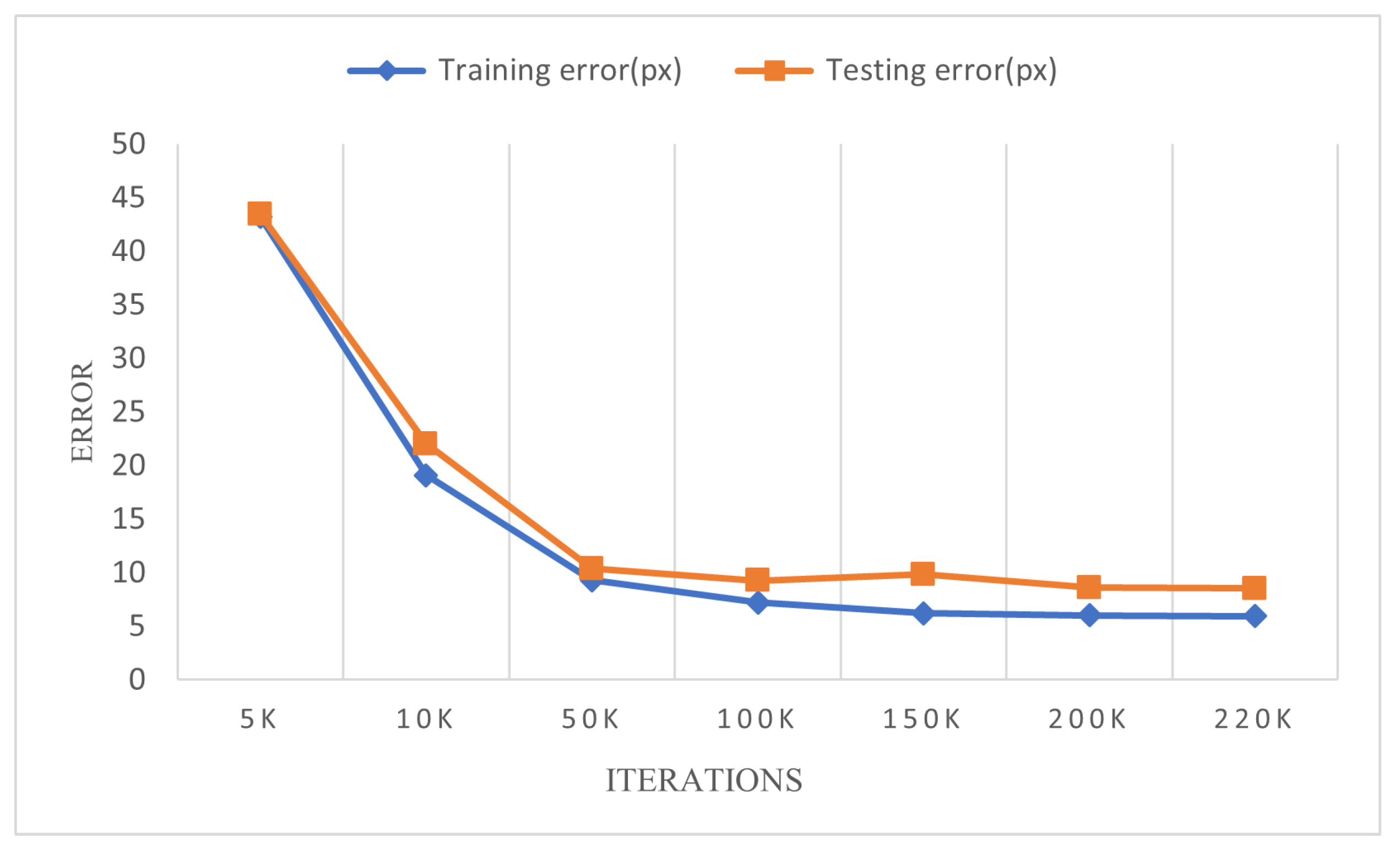
We utilized a technique of gradually adjusting the learning rate to optimize the training process and improve the model’s performance. Furthermore, we plotted the changes in training error (train error) and testing error (test error) during each iteration, as illustrated in
Figure 18. The graph highlights that the model achieved a stable state after 150k iterations, with the final training error reduced to 5.95 pixels and the testing error reduced to 8.55 pixels. Additionally, we conducted a comparative analysis of the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) values and confidence scores of the model for different body parts. The RMSE formula is presented in Equation
1. A comprehensive performance evaluation and analysis of these results are provided and summarized in
Table 3.
Here, "yp" represents the predicted value, and "yl" represents the labeled value, providing a quantitative measure of labeling accuracy.
5.3. Experiment of Behavior Analysis Model
For the task of classifying dolphin behavior, we used various metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of our model. These metrics included accuracy, recall, precision, F-score, and area under the ROC curve (AUC). Since the task requires detecting six distinct behaviors, achieving high accuracy and good recall is crucial in order to minimize the number of false negatives. Here are the formulas for Accuracy, Recall, Precision, and F-score:
Accuracy represents the ratio of correctly classified samples to the total number of samples.
The recall represents the ratio of correctly predicted positive samples to the actual number of positive samples. It is also known as sensitivity or true positive rate.
Precision represents the ratio of correctly predicted positive samples to the total number of samples predicted as positive.
The F-score is a measure of classifier performance that considers both precision and recall. It’s the harmonic mean of these two metrics.
The AUC (Area Under the Curve) is a critical evaluation metric for classification models. It provides a comprehensive assessment of the classifier’s performance. By analyzing the AUC score, we can gain insights into the model’s ability to distinguish between various categories of dolphin behavior.
AUC=1 : This represents a perfect classifier, where there is at least one threshold that can yield perfect predictions. In most practical cases, perfect classifiers are rare.
0.5 < AUC < 1 : A classifier with AUC in this range is better than random guessing. When appropriate thresholds are set, it provides predictive value.
AUC < 0.5 : A classifier with an AUC below 0.5 performs worse than random guessing. However, if you always invert the predictions, it would be better than random guessing.
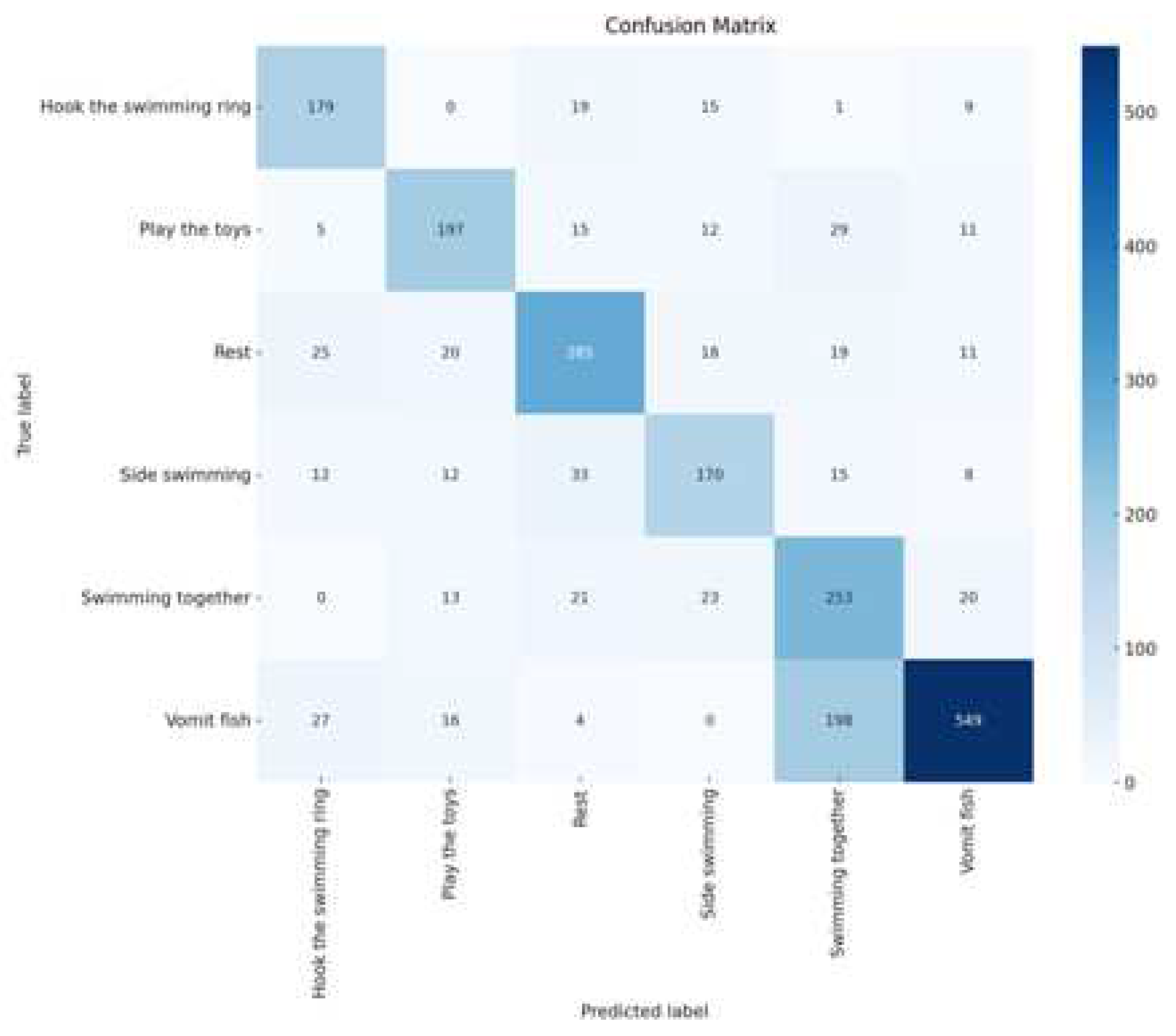
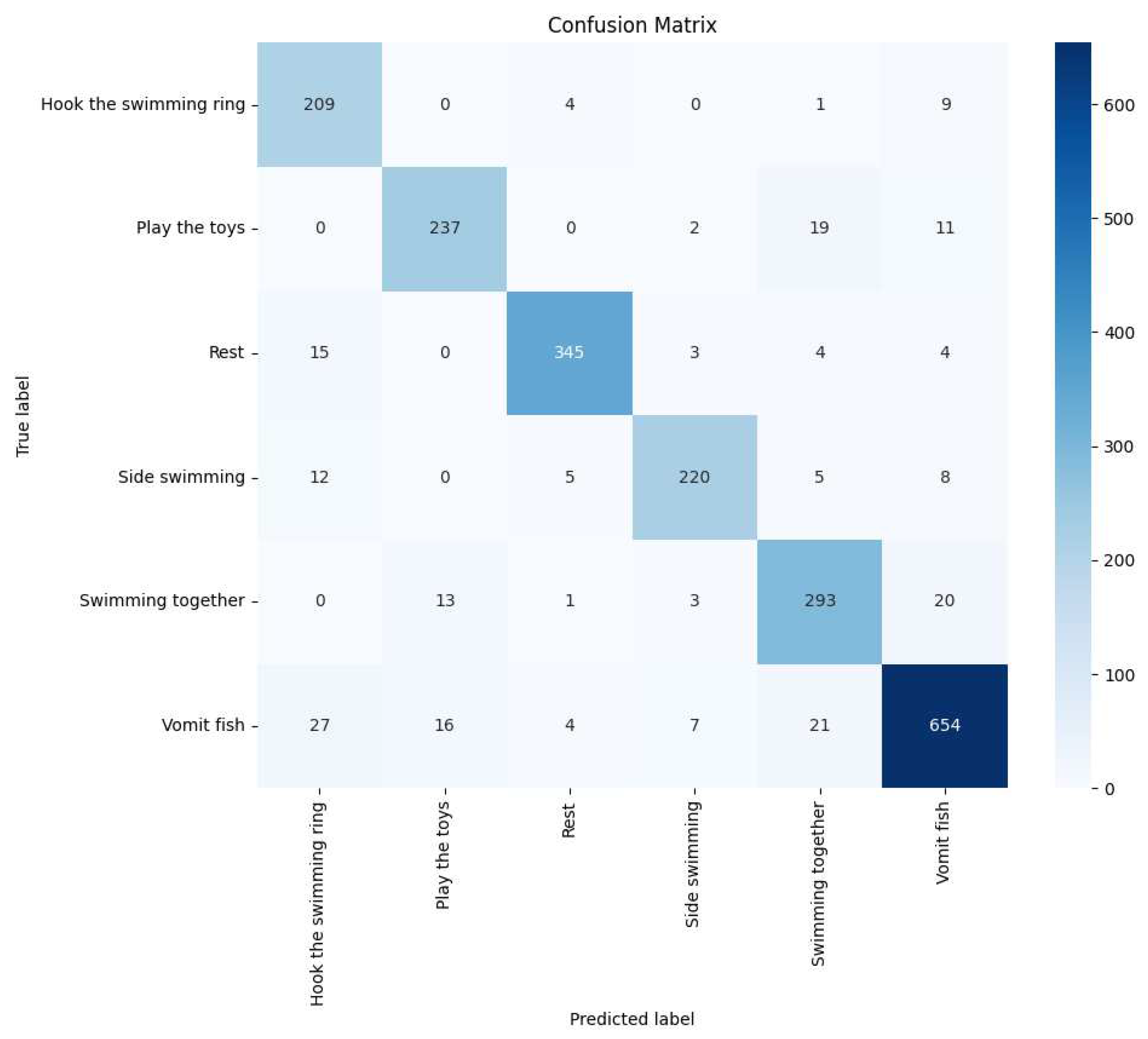
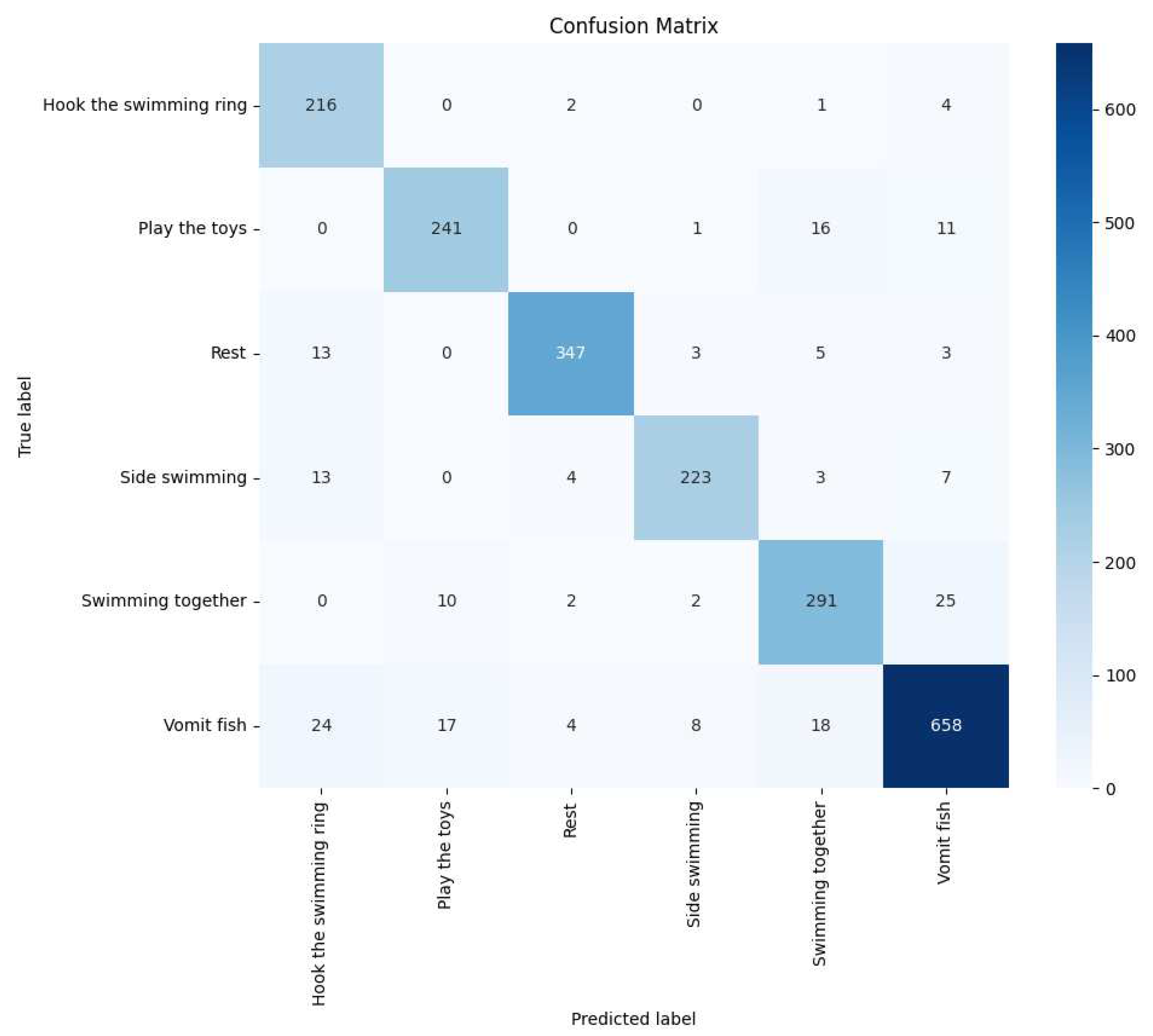
We also used the Confusion Matrix as an evaluation tool to provide a more comprehensive assessment of the model’s performance in classifying dolphin behavior tasks. In the confusion matrix, each row represents the predicted class by the model, while each column represents the actual class. This approach allows us to see how accurately the model identified each dolphin’s behavior and how often it misclassified. For instance, a cell in the matrix shows how many times the model predicted the "playing with toys" behavior when it was actually "resting."
5.3.1. AquaAI Dolphin Decoder(ADD)
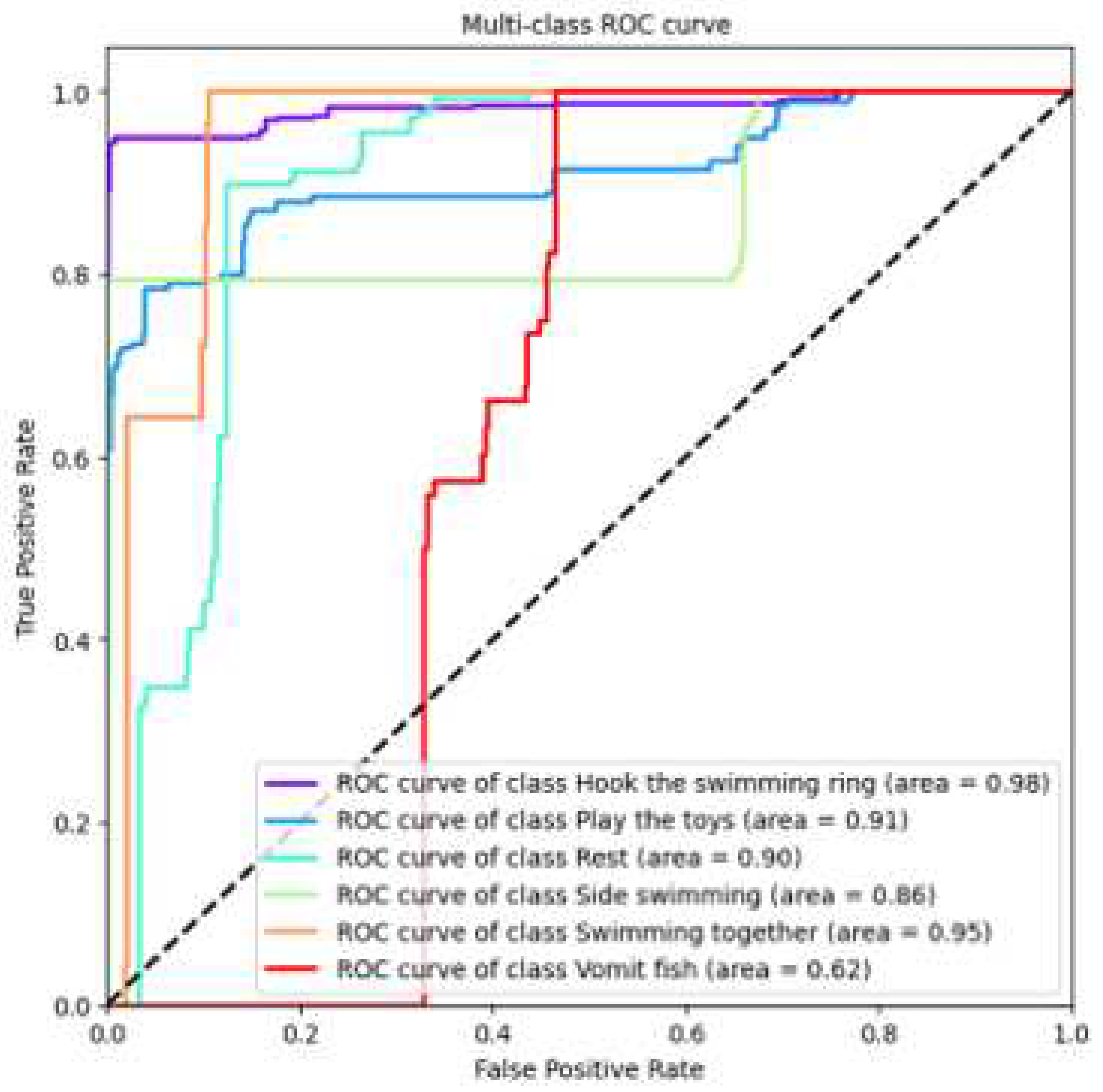
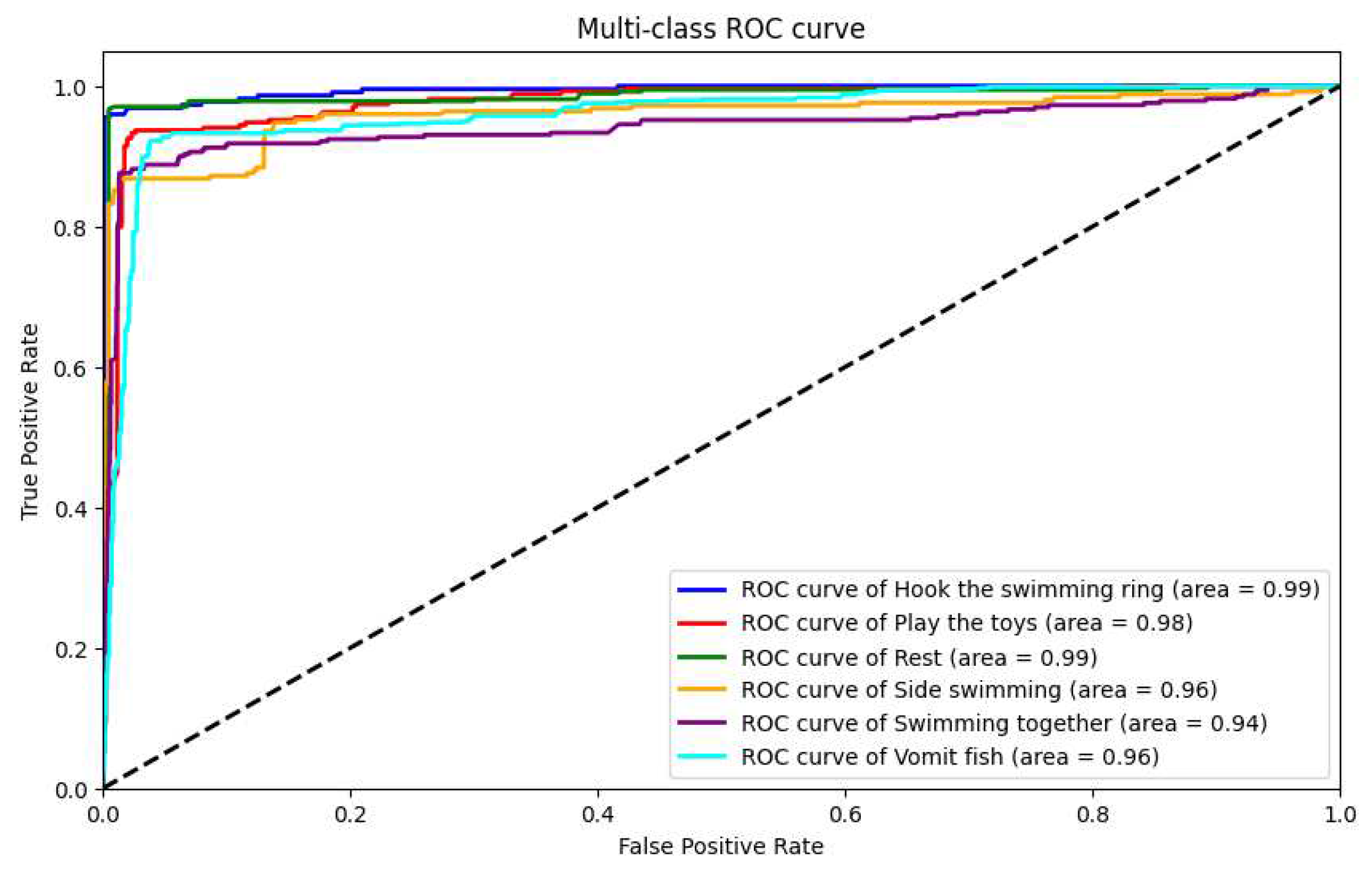
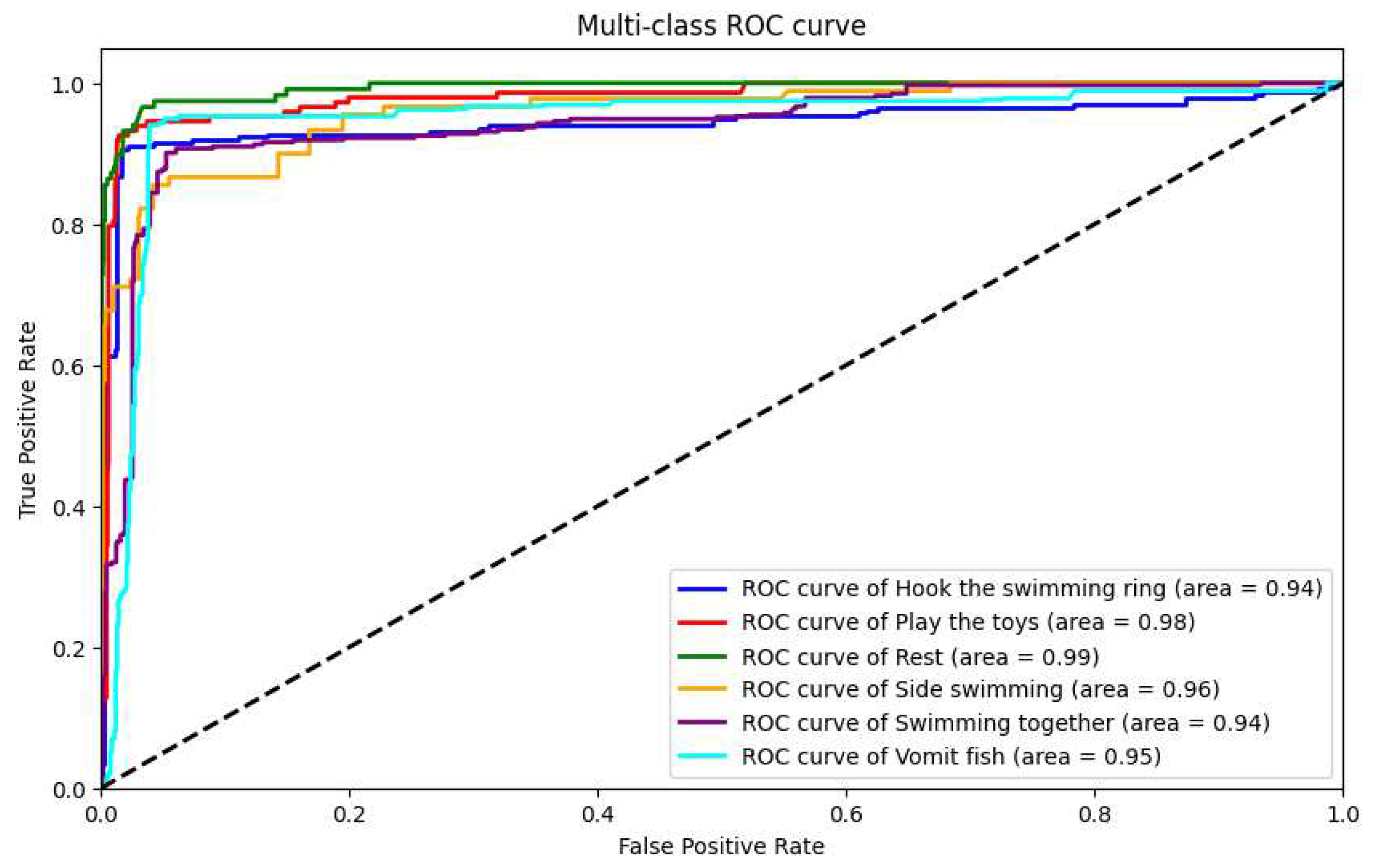
In our research, we utilized our custom-developed AquaAI Dolphin Decoder (ADD) to classify dolphin behaviors. Initially, the model achieved an accuracy of 85.5%, a recall rate of 84.6%, a precision of 85.1%, and an F1 score of 84.8%. In addition, to showcase the model’s performance, we plotted ROC curves for the six behaviors separately, as shown in
Figure 19. We also generated and visualized confusion matrices, as shown in
Figure 20. Upon observation, we found that the accuracy of identifying behaviors such as vomiting fish, resting, and side swimming was relatively low.
5.3.2. Long Short-Term Memory(LSTM)
To improve the classification accuracy of the six behaviors, we initially employed a double-layer unidirectional LSTM model. During the model training process, we set the number of training epochs to 200 and used 20% of the dataset as validation data. We utilized the Adam optimizer [
33] to compile and train the model. After training, the model achieved an accuracy of 90.1%, a recall rate of 90.2%, a precision of 89.4%, and an F1 score of 89.7%. Furthermore, we also plotted ROC curves for these six behaviors separately to visually demonstrate the model’s performance, as shown in
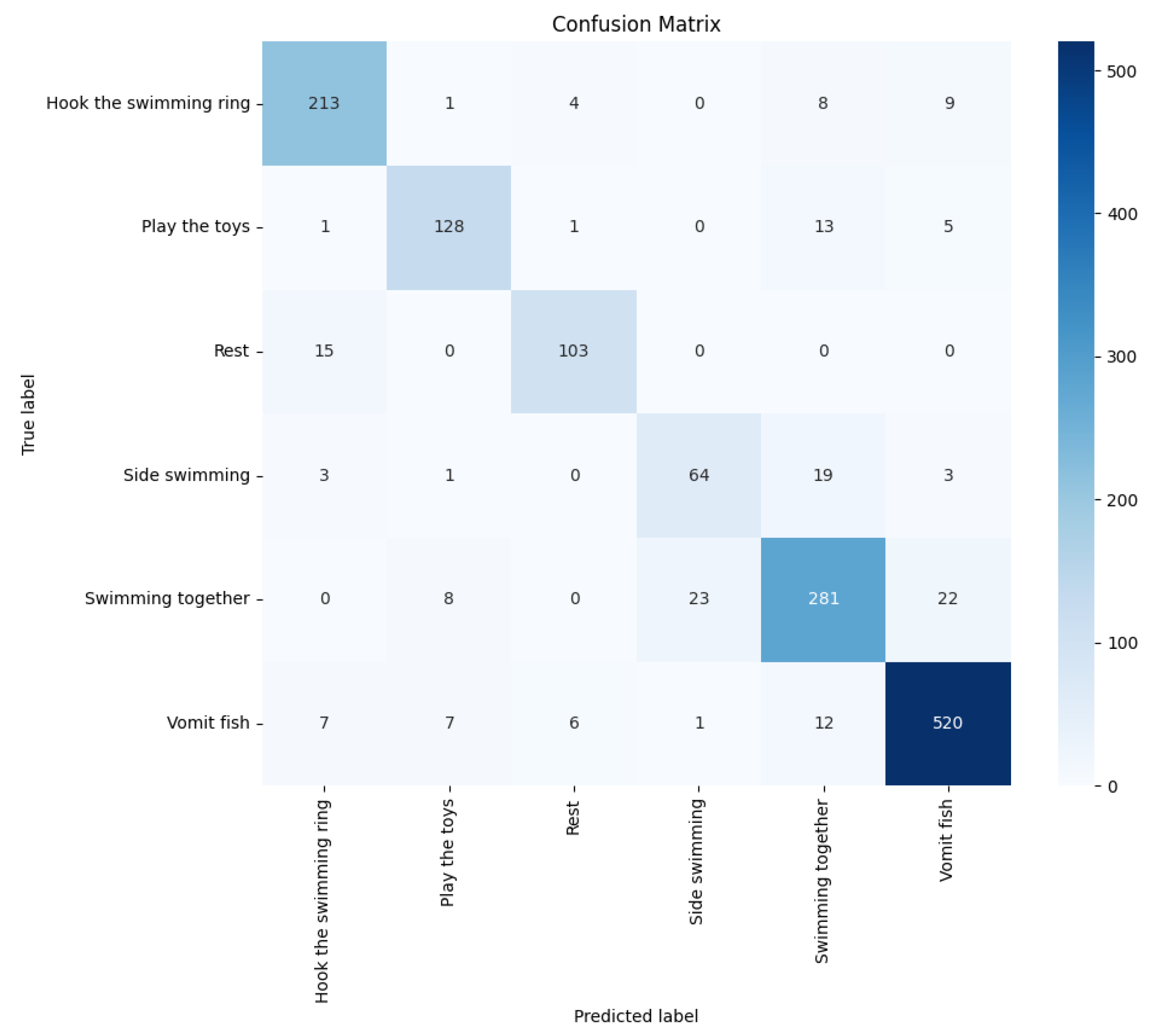
Figure 21. Additionally, confusion matrices were generated and visualized, as seen in
Figure 22.
5.3.3. Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory(BiLSTM)
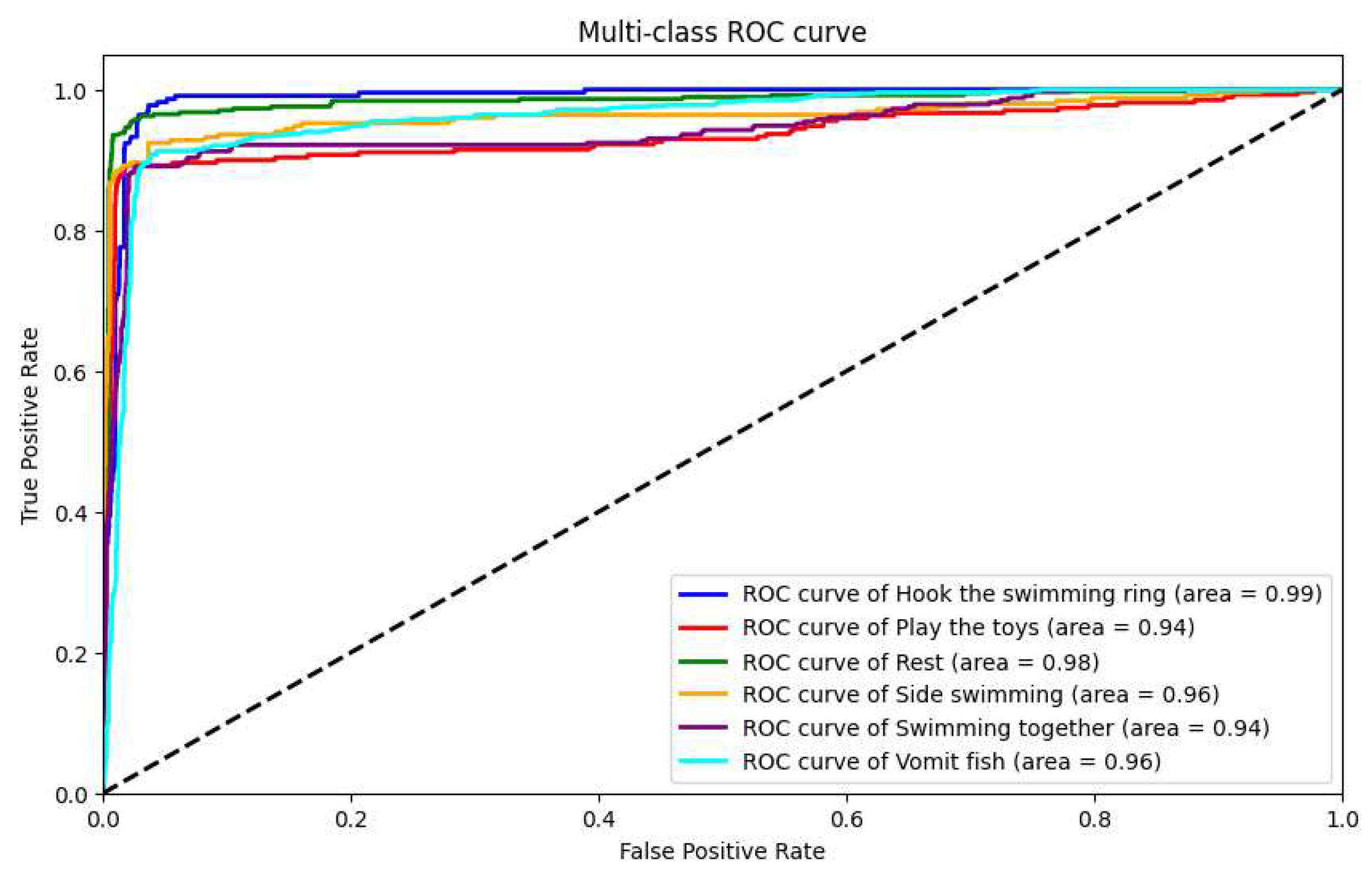
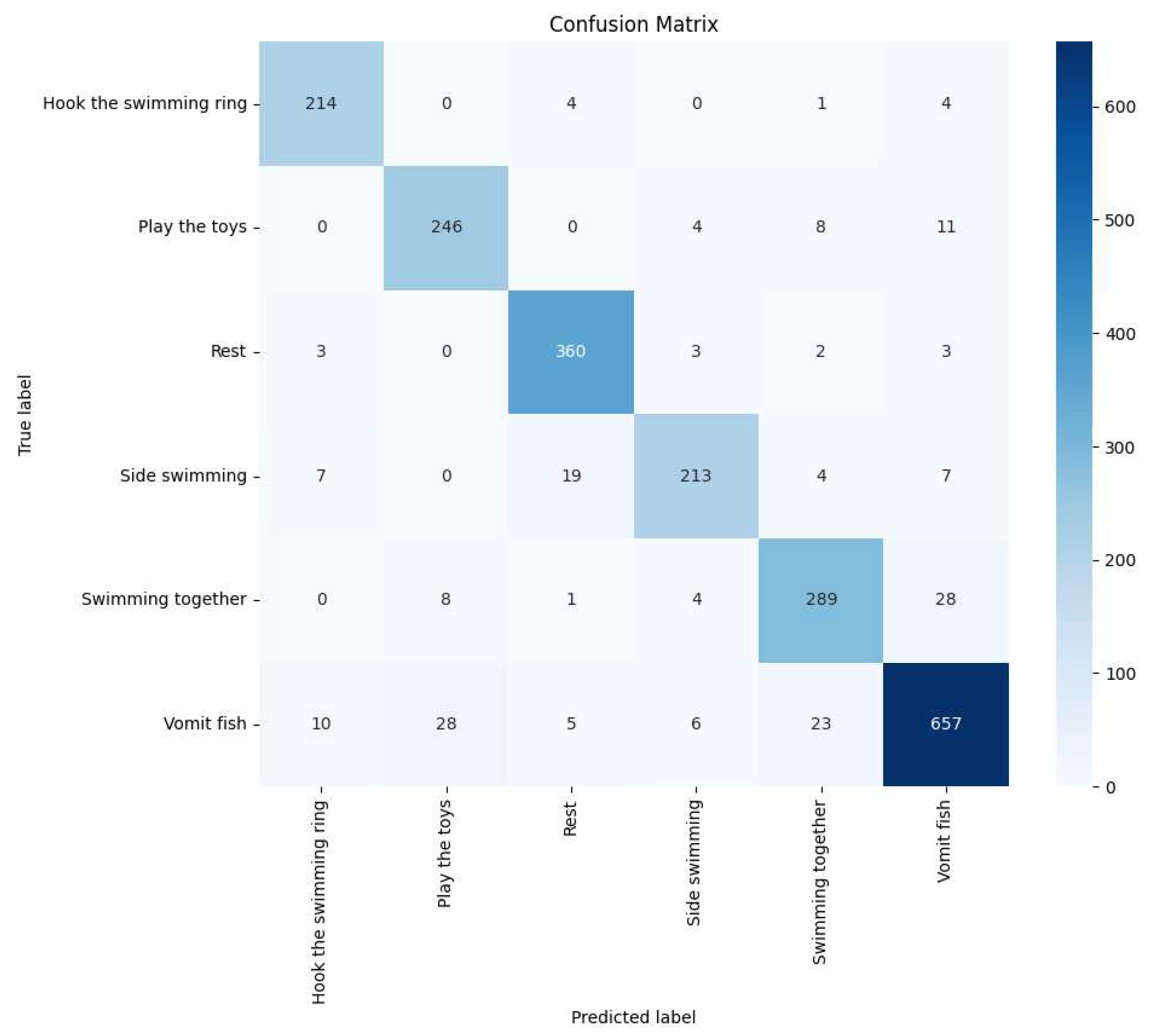
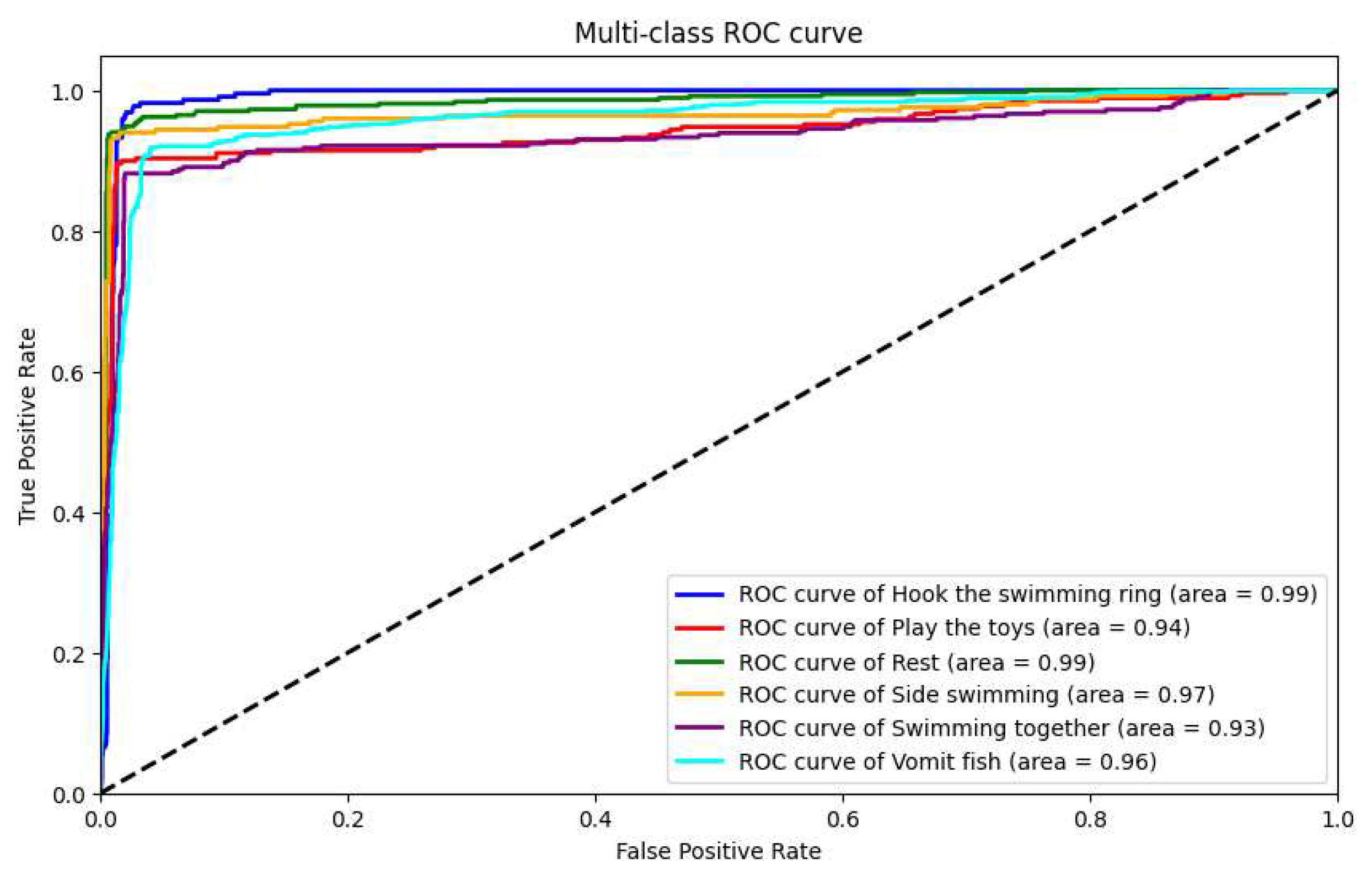
Subsequently, we introduced a double-layer bidirectional LSTM model for testing, with training parameters identical to the aforementioned unidirectional LSTM model. This model achieved an accuracy of 94.3%, a recall rate of 92.9%, a precision of 93.6%, and an F1 score of 93.2%, demonstrating superior performance compared to the double-layer unidirectional LSTM. For this model, we also plotted ROC curves and confusion matrices, as shown in
Figure 23 and
Figure 24, respectively.
5.3.4. Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)
This study also incorporated a Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) model for analysis. Similar to the LSTM models, the GRU model was evaluated with the same training parameters and dataset. The results showed that the GRU model achieved an accuracy of 90.9%, a recall rate of 91.3%, a precision of 90.3%, and an F1 score of 90.7%. These results were further visualized using ROC curves and confusion matrices, as depicted in
Figure 25 and
Figure 26, respectively.
5.3.5. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
This study also explored the application of Support Vector Machine (SVM) in dolphin behavior analysis. We chose an SVM model with a Gaussian Radial Basis Function (RBF) kernel, which performs exceptionally well in handling nonlinear data. However, in the context of dolphin behavior classification, the SVM model exhibited slightly lower performance compared to the LSTM and GRU models.
The SVM model achieved an accuracy of 88.6%, a recall rate of 85.6%, a precision rate of 86.3%, and an F1 score of 85.9%. These results are visually presented through ROC curves and confusion matrices, as shown in
Figure 27 and
Figure 28, providing an intuitive representation of the SVM model’s performance.
This comparison highlights that SVM slightly underperformed compared to the LSTM and GRU models in terms of accuracy and other metrics. It underscores the advantage of using recurrent neural networks like LSTM and GRU in sequence-based behavioral analysis tasks, as time dependency plays a crucial role in these tasks.
6. Discussion
6.1. Experiment Result Comparison
To further validate the performance of our model, we conducted a comparative analysis with several popular classification models, including ADD combined with LSTM, GRU, and SVM. In
Table 4, we showcase the performance comparison of these methods. Through this comparison, we found that the double-layer bidirectional LSTM combined with ADD demonstrated the best performance in dolphin behavior classification tasks. This comparison considered various models’ performance on key performance metrics such as accuracy, recall, F-score, and AUC. The results show that the double-layer bidirectional LSTM structure provides superior capability in handling time-series data, especially when dealing with complex dolphin behavior patterns. It can more accurately identify and classify different behaviors compared to other models. This finding underscores the advantages of the double-layer bidirectional LSTM structure in complex behavior classification tasks, demonstrating the effectiveness and sophistication of our model in dolphin behavior analysis.
Additionally, we conducted a comparative analysis of the experimental results obtained in this study with the findings of other relevant research, as shown in
Table 5. By making these comparisons, it can be observed that the solution proposed in this paper, which is based on DeepLabCut and classification model technology, has advantages in handling dolphin behavior classification tasks.
We have compared the findings of our study with other related research methods, which are listed in
Table 5. Each paper has different applications for detecting dolphins, but our proposed method addresses a gap in analyzing dolphin behavior. Our solution, which utilizes DeepLabCut and classification model techniques, has several advantages in classifying dolphin behavior and provides accurate observations of their daily activities.
6.2. Ablation Study
In this paper, an ablation study was conducted to evaluate the effect of each module on the system performance. The study aimed to analyze the functionality and performance of each module and determine its contribution to the overall system. The results of the study are presented in
Table 6. The experimental design used in the study is described below:
Baseline Experiment: We initially employed the basic model, which utilizes only DeepLabCut and the ADD algorithm for dolphin behavior analysis. The performance metrics obtained for this baseline model are as follows: accuracy of 82.4%, recall of 81.4%, precision of 81.8%, and an F-score of 81.6%.
Addition of Preprocessing Module: Next, we introduced the preprocessing module and observed its impact on system performance. The results showed that the preprocessing module effectively improved system performance, achieving an accuracy of 85.5%, a recall of 84.6%, a precision of 84.6%, and an F-score of 84.8%.
Addition of Double-Layer BiLSTM Module: Finally, we introduced the double-layer BiLSTM module, further enhancing the system’s performance. The results demonstrate that the inclusion of this module significantly improved the system’s performance, with an accuracy of 94.3%, a recall of 92.9%, a precision of 93.6%, and an F-score of 93.2%.
7. Conclusions
7.1. Summary
In the past, there hasn’t been much research on how to detect dolphin behavior, and the existing methods have some limitations. But in our recent collaboration with the Farglory Ocean Park, we came up with a new way to observe captive dolphins. We used image preprocessing techniques to reduce sunlight reflection and enhance dolphin contours, which made it easier to analyze the images. Then we labeled the skeletons of the dolphins using a tool called DeepLabCut and used that to train a model. The results showed that we could control the root-mean-square error (RMSE) of each skeleton to be below 10.
We also developed a custom analysis module called AquaAI Dolphin Decoder with Long Short-Term Memory (ADD-LSTM). This module analyzes the dolphins’ keypoints information obtained through the pose estimation model and classifies their daily behaviors into six categories: vomiting fish, resting, side swimming, swimming together, playing with balls, and hooking the swimming ring. We used predefined thresholds for each behavior to make the classification. To provide an even more detailed classification of dolphin behavior, we used a double-layer bidirectional LSTM recurrent neural network. This approach resulted in an accuracy rate of 94.3%, a recall rate of 92.9%, a precision rate of 93.6%, and an F1 score of 93.2%.
7.2. Contributions
The primary focus of this paper is to introduce an innovative method for observing and analyzing dolphin behavior. In the beginning, we have used image preprocessing techniques to enhance the dolphin’s contours, which has led to an improvement in the accuracy and efficiency of the subsequent analyses. Later, we have successfully integrated the DeepLabCut pose estimation tool and a custom classification module (ADD-LSTM), which has enabled us to effectively analyze long-duration videos with an impressive accuracy rate of 94.3%. The application of this method has significantly reduced the workload of dolphin caregivers and decreased labor costs. This study shows the strong potential of combining pose estimation tools with advanced machine learning techniques in dolphin behavior analysis. It also provides new perspectives and methods for future research in this field.
7.3. Future Works
We have developed a method to identify dolphins at Farglory Ocean Park, which we plan to apply to whale and dolphin rescue centers, like the Sicao Rescue Center. This will enable long-term observations of dolphins and whales without relying heavily on human resources. Our model currently identifies six different dolphin behaviors, and we plan to expand its capabilities in two ways. First, we aim to enhance the model’s application scope and accuracy by increasing the recognition of other behaviors. Second, we plan to introduce sound recognition technology to identify and observe dolphin daily breathing sounds, which will provide richer research data for marine biology and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of dolphin conservation and medical rescue efforts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Shih-Pang Tseng and Jhing-Fa Wang; methodology, Shih-Pang Tseng and Shao-En Hsu; software, Shao-En Hsu; validation, Jhing-Fa Wang and I-Fan Jen; resources, I-Fan Jen; data curation, I-Fan Jen; writing—original draft preparation, Shao-En Hsu; writing—review and editing, Shih-Pang Tseng; visualization, Shao-En Hsu; supervision, Jhing-Fa Wang; project administration, I-Fan Jen. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was partial supported by Farglory Ocean Park, Hualien, Taiwan. This work was also partial supported by the Changzhou College of Information Technology under the contract "2019KYQD03". And this work was also partial supported by Sanda University under the contract "20121ZD05".
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, V.Y.; Lu, D.J.; Han, Y.S. Hybrid Intelligence for Marine Biodiversity: Integrating Citizen Science with AI for Enhanced Intertidal Conservation Efforts at Cape Santiago, Taiwan. Sustainability 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnhoff, L.; Glotin, H.; Bernard, S.; Dabin, W.; Le Gall, Y.; Menut, E.; Meheust, E.; Peltier, H.; Pochat, A.; Pochat, K.; Rimaud, T.; Sourget, Q.; Spitz, J.; Van Canneyt, O.; Mérigot, B. Behavioural Responses of Common Dolphins Delphinus delphis to a Bio-Inspired Acoustic Device for Limiting Fishery By-Catch. Sustainability 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, S.H.; Wells, R.S.; Würsig, B. ECOLOGY, BEHAVIOR AND SOCIAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BOTTLENOSE DOLPHIN: A REVIEW. Marine Mammal Science 1986, 2, 34–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.; Delfour, F.; Carter, T.J. Anticipatory behavior in captive bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus): a preliminary study. Zoo biology 2013, 32 4, 436–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Kohshima, S. Resting behaviors of captive bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Physiology & Behavior 2003, 79, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczaj, S.A.; Makecha, R.N.; Trone, M.C.; Paulos, R.D.; Ramos, J.A.A. Role of Peers in Cultural Innovation and Cultural Transmission: Evidence from the Play of Dolphin Calves. International Journal of Comparative Psychology 2006, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczaj, S.A.; Eskelinen, H.C. Why do Dolphins Play. Animal Behavior and Cognition 2014, 1, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, F.C.; We, N.Y.; Chou, L.S. Bioaccumulation of persistent organic pollutants in stranded cetaceans from Taiwan coastal waters. Journal of hazardous materials 2014, 277, 127–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczmarski, L.; Huang, S.; Wong, W.; Chang, W.L.; Chan, C.; Keith, M. Distribution of a Coastal Delphinid Under the Impact of Long-Term Habitat Loss: Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphins off Taiwan’s West Coast. Estuaries and Coasts 2017, 40, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.; Pandolfo, L.; Sazima, I. Vomiting Behavior of the Spinner Dolphin (Stenella longirostris) and Squid Meals. Aquatic Mammals 2004, 30, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, A.M. Realization of the Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) for Real-Time Image Enhancement. Journal of VLSI signal processing systems for signal, image and video technology 2004, 38, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.N.; Schott, J.R. Application of Spectral Mixture Analysis and Image Fusion Techniques for Image Sharpening. Remote Sensing of Environment 1998, 63, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, A.; Mamidanna, P.; Cury, K.M.; Abe, T.; Murthy, V.N.; Mathis, M.W.; Bethge, M. DeepLabCut: markerless pose estimation of user-defined body parts with deep learning. Nature Neuroscience 2018, 21, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, J.; Zhou, M.; Ye, S.; Menegas, W.; Schneider, S.; Nath, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Santo, V.D.; Soberanes, D.; Feng, G.; Murthy, V.N.; Lauder, G.V.; Dulac, C.; Mathis, M.W.; Mathis, A. Multi-animal pose estimation, identification and tracking with DeepLabCut. Nature Methods 2022, 19, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2015; 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hayashibe, M.; Owaki, D. Prediction of Whole-Body Velocity and Direction From Local Leg Joint Movements in Insect Walking via LSTM Neural Networks. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2022, 7, 9389–9396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhu, J.; Rao, X. Murine Motion Behavior Recognition Based on DeepLabCut and Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Network. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Shorter, K.A.; Rocho-Levine, J.; van der Hoop, J.M.; Moore, M.J.; Barton, K. Behavior Inference From Bio-Logging Sensors: A Systematic Approach for Feature Generation, Selection and State Classification. Volume 2: Control and Optimization of Connected and Automated Ground Vehicles; Dynamic Systems and Control Education; Dynamics and Control of Renewable Energy Systems; Energy Harvesting; Energy Systems; Estimation and Identification; Intelligent Transportation and Vehicles; Manufacturing; Mechatroni 2018. [CrossRef]
- Lauderdale, L.K.; Shorter, K.A.; Zhang, D.; Gabaldon, J.; Mellen, J.D.; Walsh, M.T.; Granger, D.A.; Miller, L.J. Bottlenose dolphin habitat and management factors related to activity and distance traveled in zoos and aquariums. PLoS ONE 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorter, K.A.; Shao, Y.; Ojeda, L.V.; Barton, K.; Rocho-Levine, J.; van der Hoop, J.; Moore, M.J. A day in the life of a dolphin: Using bio-logging tags for improved animal health and well-being. Marine Mammal Science 2017, 33, 785–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Inamori, D.; Funasaka, N.; Sakamoto, K.Q. Towards non-invasive heart rate monitoring in free-ranging cetaceans: a unipolar suction cup tag measured the heart rate of trained Risso’s dolphins. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B 2021, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnowski, J.; Hutchins, E.L.; Johnson, C.M. Dolphin Detection and Tracking. 2015 IEEE Winter Applications and Computer Vision Workshops, 2015; 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaldon, J.; Zhang, D.; Lauderdale, L.K.; Miller, L.J.; Johnson-Roberson, M.; Barton, K.; Shorter, K.A. Computer-vision object tracking for monitoring bottlenose dolphin habitat use and kinematics. PLoS ONE 2022, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Hidalgo, G.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. OpenPose: Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation Using Part Affinity Fields. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2018, 43, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hoop, J.M.; Fahlman, A.; Hurst, T.; Rocho-Levine, J.; Shorter, K.A.; Petrov, V.; Moore, M.J. Bottlenose dolphins modify behavior to reduce metabolic effect of tag attachment. Journal of Experimental Biology 2014, 217, 4229–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khin, M.P.; Zin, T.T.; Mar, C.C.; Tin, P.; Horii, Y. Cattle Pose Classification System Using DeepLabCut and SVM Model. 2022 IEEE 11th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), 2022; 494–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuguen, R.T.; Bardeloza, D.K.; Negrete, S.B.; Matsumoto, J.; ichi Inoue, K.; Shibata, T. Primate Markerless Pose Estimation and Movement Analysis Using DeepLabCut. 2019 Joint 8th International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV) and 2019 3rd International Conference on Imaging, Vision & Pattern Recognition (icIVPR), 2019; 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahnakian, F.; Heikkonen, J.; Björkman, S. Multi-pig Pose Estimation Using DeepLabCut. 2021 11th International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), 2021; 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Xue, M.; Peng, X.R.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y. Dolphin movement direction recognition using contour-skeleton information. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2020, 82, 21907–21923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washabaugh, E.P.; Shanmugam, T.A.; Ranganathan, R.; Krishnan, C. Comparing the accuracy of open-source pose estimation methods for measuring gait kinematics. Gait & posture 2022, 97, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Computation 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J. ; Çaglar Gülçehre.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. ArXiv, 2014; abs/1412.3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. International Conference on Learning Representations, 2014; abs/1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
Figure 1.
The Sensor attached to the back of the dolphin. [
19]
Figure 1.
The Sensor attached to the back of the dolphin. [
19]
Figure 2.
Example of vision-based tracking [
23] (A) The dolphins’ recognition results. (B) The heatmap of dolphin swimming directions.
Figure 2.
Example of vision-based tracking [
23] (A) The dolphins’ recognition results. (B) The heatmap of dolphin swimming directions.
Figure 3.
Comparing the Error of Various Pose Estimation Models for Different Knee Joint Angles. [
30]. Abbreviations:Deg (degrees), MC (motion capture), OP (OpenPose), MNL (MoveNet Lightning), MNT (MoveNet Thunder), DLC (DeepLabCut)
Figure 3.
Comparing the Error of Various Pose Estimation Models for Different Knee Joint Angles. [
30]. Abbreviations:Deg (degrees), MC (motion capture), OP (OpenPose), MNL (MoveNet Lightning), MNT (MoveNet Thunder), DLC (DeepLabCut)
Figure 4.
The system overview
Figure 4.
The system overview
Figure 5.
Experimental setup diagram
Figure 5.
Experimental setup diagram
Figure 6.
The block diagram of preprocessing
Figure 6.
The block diagram of preprocessing
Figure 7.
RGB color histogram after CLAHE enhancement
Figure 7.
RGB color histogram after CLAHE enhancement
Figure 8.
Comparative analysis of image processing techniques
Figure 8.
Comparative analysis of image processing techniques
Figure 9.
The block diagram of DeepLabCut
Figure 9.
The block diagram of DeepLabCut
Figure 10.
The architecture diagram of ResNet50
Figure 10.
The architecture diagram of ResNet50
Figure 11.
ResNet50 network residual block diagram
Figure 11.
ResNet50 network residual block diagram
Figure 12.
DeepLabCut’s network architecture diagram
Figure 12.
DeepLabCut’s network architecture diagram
Figure 13.
The maps of the dolphins
Figure 13.
The maps of the dolphins
Figure 14.
Dolphin behavior classification tree
Figure 14.
Dolphin behavior classification tree
Figure 15.
The architecture of double-layer BiLSTM
Figure 15.
The architecture of double-layer BiLSTM
Figure 16.
The BiLSTM layer with dropout model
Figure 16.
The BiLSTM layer with dropout model
Figure 17.
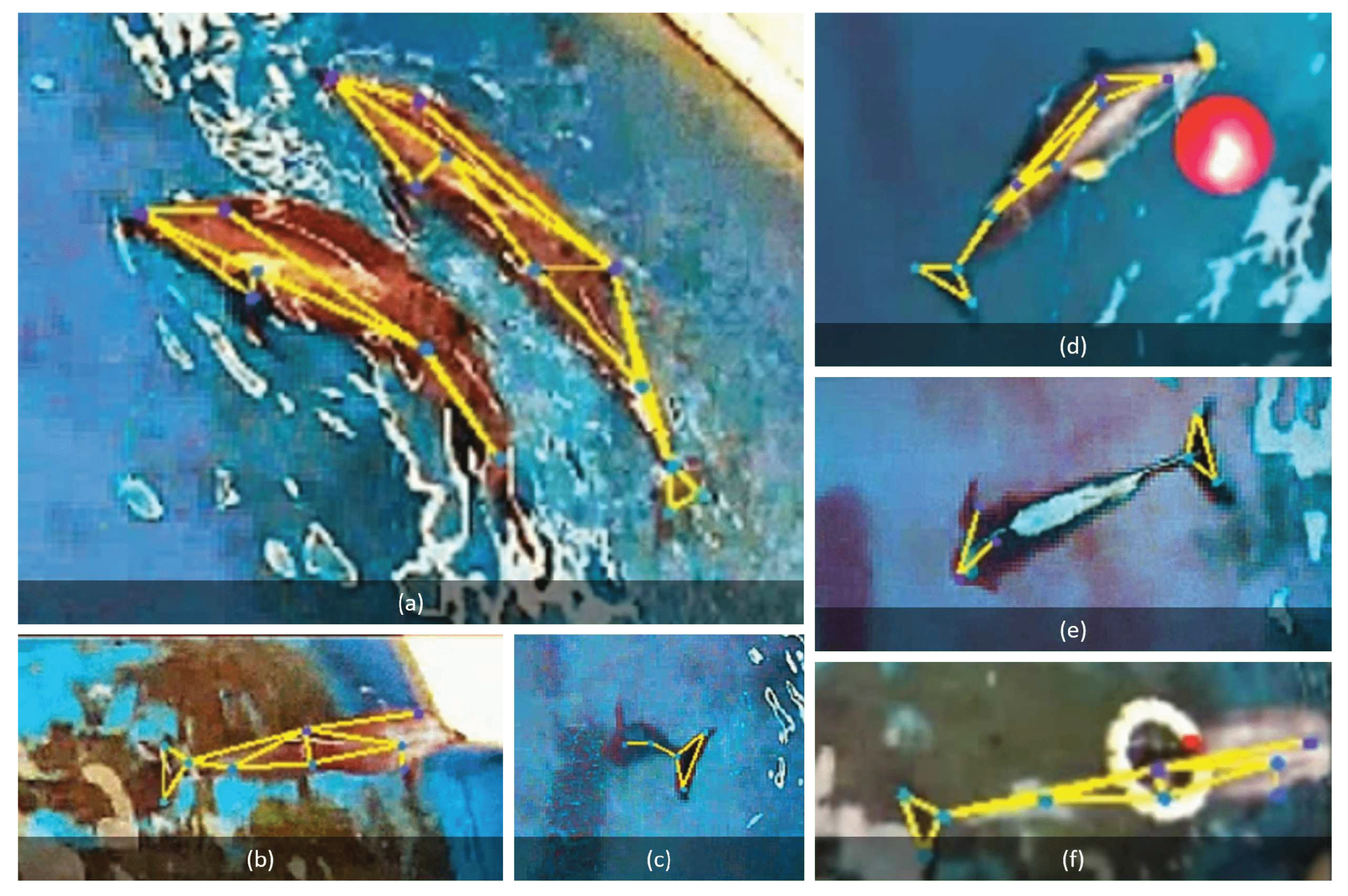
The six behaviors of dolphins. (a) Swimming together (b) Rest (c) Vomit fish (d) Play the toys (e) Side swimming (f) Hook the swimming ring
Figure 17.
The six behaviors of dolphins. (a) Swimming together (b) Rest (c) Vomit fish (d) Play the toys (e) Side swimming (f) Hook the swimming ring
Figure 18.
Training error and testing error for each iteration
Figure 18.
Training error and testing error for each iteration
Figure 19.
The ROC curve of ADD
Figure 19.
The ROC curve of ADD
Figure 20.
The confusion matrix of ADD
Figure 20.
The confusion matrix of ADD
Figure 21.
The ROC curve of LSTM
Figure 21.
The ROC curve of LSTM
Figure 22.
The confusion matrix of LSTM
Figure 22.
The confusion matrix of LSTM
Figure 23.
The ROC curve of BiLSTM
Figure 23.
The ROC curve of BiLSTM
Figure 24.
The confusion matrix of BiLSTM
Figure 24.
The confusion matrix of BiLSTM
Figure 25.
The ROC curve of GRU
Figure 25.
The ROC curve of GRU
Figure 26.
The confusion matrix of GRU
Figure 26.
The confusion matrix of GRU
Figure 27.
The ROC curve of SVM
Figure 27.
The ROC curve of SVM
Figure 28.
The confusion matrix of SVM
Figure 28.
The confusion matrix of SVM
Table 1.
Descriptions of the behaviors [
4].
Table 1.
Descriptions of the behaviors [
4].
| |
Behavior |
Description |
| 1 |
Spyhopping [4] |
Vertical in the water with its head above the surface. |
| 2 |
Swim together [3] |
Multiple dolphins swimming together. |
| 3 |
Side swimming [4] |
Exposing their belly while swimming. |
| 4 |
Jump [4] |
Temporarily leaping out of the water and then returning
to the surface. |
| 5 |
Play the toys [7] |
Playing with toys using their fins or heads. |
| 6 |
Vomit fish [10] |
Submerging in a head-down position at the bottom
of the water while extending their tail fins vertically
out of the water surface. |
| 7 |
Rest by the shore [4] |
Remaining motionless with the dorsal fin and head
above the water surface. |
| 8 |
Looking [4] |
Floating on their side at the surface of the water, with
one eye above the water level for observation. |
Table 2.
Experimental environment
Table 2.
Experimental environment
| Experimental Environment |
|---|
| Hardware Specification |
Operating System |
Windows |
| |
CPU |
Intel i7-12700K |
| |
GPU |
Nvidia RTX3060 |
| |
RAM |
32GB |
| Software Version |
Python3.8+TensorFlow2.10.0+Deeplabcut2.2.2 |
Table 3.
RMSE values and confidence scores for each keypoint
Table 3.
RMSE values and confidence scores for each keypoint
| Keypoints |
RMSE |
Confidence Score |
| Rostrum |
8.29 |
95.9% |
| Melon |
5.76 |
97.8% |
| Dorsal fin |
5.06 |
97.3% |
| Pectoral fin |
3.8 |
98.3% |
| Bodypart1 |
6.77 |
96.5% |
| Bodypart2 |
4.53 |
97.9% |
| Bodypart3 |
5.81 |
97.1% |
| Tail top |
6.49 |
96.7% |
| Tail left |
3.58 |
98.5% |
| Tail right |
3.24 |
98.7% |
| Belly |
3.98 |
98.1% |
Table 4.
Comparison of different classification models
Table 4.
Comparison of different classification models
| Methods |
Accuracy |
Recall |
Precision |
F-score |
| ADD |
85.5% |
84.6% |
85.1% |
84.8% |
| ADD+SVM |
88.6% |
85.6% |
86.3% |
85.9% |
| ADD+LSTM |
90.1% |
90.2% |
89.4% |
89.7% |
| ADD+GRU |
90.9% |
91.3% |
90.3% |
90.7% |
| ADD+BiLSTM |
94.3% |
92.9% |
93.6% |
93.2% |
Table 5.
Compare different approaches with our proposed system
Table 5.
Compare different approaches with our proposed system
| Methods |
Purpose |
Accuracy |
Recall |
Precision |
F-score |
| Compressive Tracking [22] |
Detect and track dolphins |
- |
75.7% |
78.8% |
77.2% |
| OpenPose [29] |
The angles of dolphin swimming |
86% |
85% |
81% |
82.9% |
| Faster R-CNN [23] |
Track the trajectories of dolphins |
81% |
80.4% |
82.3% |
81.3% |
| Ours |
Identify the daily behaviors of dolphins |
94.3% |
92.9% |
93.6% |
93.2% |
Table 6.
An ablation study of the proposed method with various models
Table 6.
An ablation study of the proposed method with various models
| Settings |
Accuracy |
Recall |
Precision |
F-score |
| Baseline |
82.4% |
81.4% |
81.8% |
81.6% |
| +Preprocessing |
85.5% |
84.6% |
85.1% |
84.8% |
| +Double-Layer BiLSTM |
94.3% |
92.9% |
93.6% |
93.2% |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).