Submitted:
06 February 2024
Posted:
07 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Conducting a systematic review of the effectiveness and side effects of COVID-19 vaccines.
- Identifying gaps in current scientific literature related to COVID-19 vaccination issues in Trinidad and Tobago.
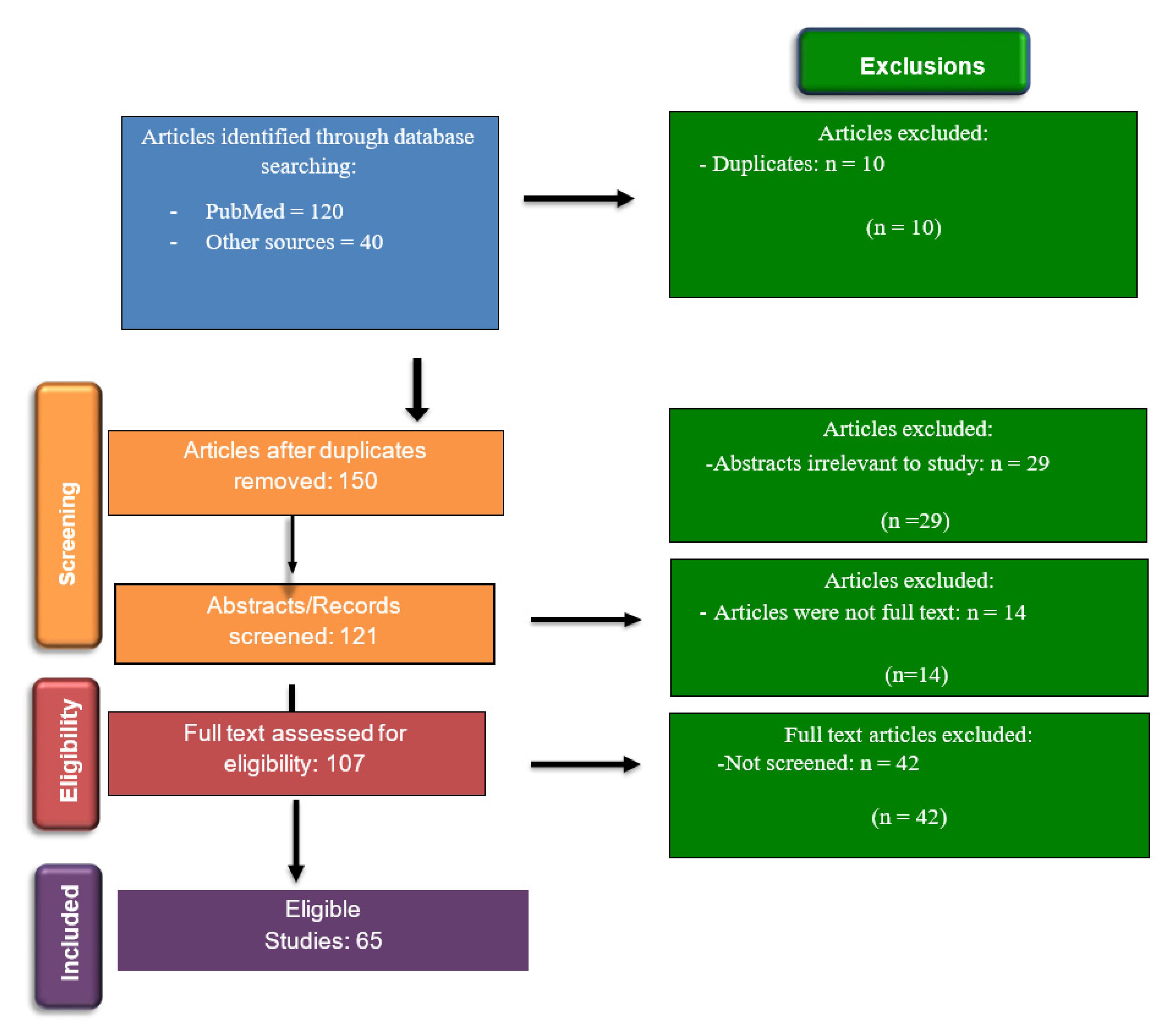
2. Materials and Methods
- Children under the aged 4 or below.
- Research that only provided abstracts and did not have full text available.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Effectiveness of Covid-19 Vaccines
3.1.1. Pfizer-BioNTech
3.1.2. Moderna
3.1.3. Oxford-AstraZeneca
3.1.4. Janssen
3.1.5. Sinopharm
3.1.6. Novavax
3.2. Side Effects of COVID-19 vaccines
3.2.1. Local and systemic side effects
3.2.2. Neurological side effects
3.2.3. Myocarditis and Pericarditis
3.3. COVID-19 Vaccination in Trinidad and Tobago.
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pormohammad, A.; Zarei, M.; Ghorbani, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Razizadeh, M.H.; Turner, D.L.; Turner, R.J. Efficacy and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Vaccines (Basel) 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forni, G.; Mantovani, A.; COVID-19 Commission of Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei, Rome. COVID-19 Vaccines: Where We Stand and Challenges Ahead. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Shao, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W. Real-World Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 114, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Momani, H.; Aldajah, K.; Alda’ajah, E.; ALjafar, Y.; Abushawer, Z. Effectiveness of Pfizer/BioNTech and Sinopharm COVID-19 Vaccines in Reducing Hospital Admissions in Prince Hamza Hospital, Jordan. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 1008521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadj Hassine, I. Covid-19 Vaccines and Variants of Concern: A Review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, A.I.; Ghany, S.; Gilkes, T.; Umakanthan, S. Review of COVID-19 Vaccine Subtypes, Efficacy and Geographical Distributions. Postgrad. Med. J. 2022, 98, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GRADE: Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine Available online:. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/recs/grade/covid-19-pfizer-biontech-vaccine.html (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Rotshild, V.; Hirsh-Raccah, B.; Miskin, I.; Muszkat, M.; Matok, I. Comparing the Clinical Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saciuk, Y.; Kertes, J.; Mandel, M.; Hemo, B.; Shamir Stein, N.; Ekka Zohar, A. Pfizer-BioNTech Vaccine Effectiveness against Sars-Cov-2 Infection: Findings from a Large Observational Study in Israel. Prev. Med. 2022, 155, 106947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez Bernal, J.; Andrews, N.; Gower, C.; Robertson, C.; Stowe, J.; Tessier, E.; Simmons, R.; Cottrell, S.; Roberts, R.; O’Doherty, M.; et al. Effectiveness of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Oxford-AstraZeneca Vaccines on Covid-19 Related Symptoms, Hospital Admissions, and Mortality in Older Adults in England: Test Negative Case-Control Study. BMJ 2021, 373, n1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soiza, R.L.; Scicluna, C.; Thomson, E.C. Efficacy and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines in Older People. Age Ageing 2021, 50, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechotta, V.; Siemens, W.; Thielemann, I.; Toews, M.; Koch, J.; Vygen-Bonnet, S.; Kothari, K.; Grummich, K.; Braun, C.; Kapp, P.; et al. Safety and Effectiveness of Vaccines against COVID-19 in Children Aged 5-11 Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Child Adolesc Health 2023, 7, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenforde, M.W.; Self, W.H.; Naioti, E.A.; Ginde, A.A.; Douin, D.J.; Olson, S.M.; Talbot, H.K.; Casey, J.D.; Mohr, N.M.; Zepeski, A.; et al. Sustained Effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines Against COVID-19 Associated Hospitalizations Among Adults - United States, March-July 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, M.Y.; Maslamani, Y.A.; Muaddi, M.A.; Alameer, A.A.; Alqassim, A.Y.; Doweri, A.A.; Zaylaee, M.M.; Rayani, H.Y.; Darraj, A.Y.; Hejri, Y.M.; et al. Real-World Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Vaccinated Individuals in Jazan, Saudi Arabia. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, E.D., Jr; Kitchin, N.; Xu, X.; Dychter, S.S.; Lockhart, S.; Gurtman, A.; Perez, J.L.; Zerbini, C.; Dever, M.E.; Jennings, T.W.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of a Third Dose of BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1910–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-On, Y.M.; Goldberg, Y.; Mandel, M.; Bodenheimer, O.; Freedman, L.; Kalkstein, N.; Mizrahi, B.; Alroy-Preis, S.; Ash, N.; Milo, R.; et al. Protection of BNT162b2 Vaccine Booster against Covid-19 in Israel. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, F.; Teixeira da Silva, J.A.; Tsigaris, P.; Sharun, K. Safety & Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Narrative Review. Indian J. Med. Res. 2022, 155, 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, I.; Nauman, A.; Paul, P.; Ganesan, S.; Chen, K.-H.; Jalil, S.M.S.; Jaouni, S.H.; Kawas, H.; Khan, W.A.; Vattoth, A.L.; et al. The Efficacy and Effectiveness of the COVID-19 Vaccines in Reducing Infection, Severity, Hospitalization, and Mortality: A Systematic Review. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2022, 18, 2027160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, N.; Stowe, J.; Kirsebom, F.; Toffa, S.; Rickeard, T.; Gallagher, E.; Gower, C.; Kall, M.; Groves, N.; O’Connell, A.-M.; et al. Covid-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against the Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1532–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Gao, L.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, K.; Sun, F. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRADE: Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine Available online:. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/recs/grade/covid-19-moderna-vaccine.html (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Rahmani, K.; Shavaleh, R.; Forouhi, M.; Disfani, H.F.; Kamandi, M.; Oskooi, R.K.; Foogerdi, M.; Soltani, M.; Rahchamani, M.; Mohaddespour, M.; et al. The Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines in Reducing the Incidence, Hospitalization, and Mortality from COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 873596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soheili, M.; Khateri, S.; Moradpour, F.; Mohammadzedeh, P.; Zareie, M.; Mortazavi, S.M.M.; Manifar, S.; Kohan, H.G.; Moradi, Y. The Efficacy and Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines around the World: A Mini-Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Self, W.H.; Tenforde, M.W.; Rhoads, J.P.; Gaglani, M.; Ginde, A.A.; Douin, D.J.; Olson, S.M.; Talbot, H.K.; Casey, J.D.; Mohr, N.M.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) Vaccines in Preventing COVID-19 Hospitalizations Among Adults Without Immunocompromising Conditions - United States, March-August 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, D.A.; Hayes, K.N.; Zullo, A.R.; Mor, V.; Chachlani, P.; Deng, Y.; McCarthy, E.P.; Djibo, D.A.; McMahill-Walraven, C.N.; Gravenstein, S. Comparative Risks of Potential Adverse Events Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination Among Older US Adults. JAMA Netw Open 2023, 6, e2326852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerman, B.A.; Gerlovin, H.; Madenci, A.L.; Kurgansky, K.E.; Ferolito, B.R.; Figueroa Muñiz, M.J.; Gagnon, D.R.; Gaziano, J.M.; Cho, K.; Casas, J.P.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 Vaccines in U.S. Veterans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria-Rose, N.A.; Shen, X.; Schmidt, S.D.; O’Dell, S.; McDanal, C.; Feng, W.; Tong, J.; Eaton, A.; Maglinao, M.; Tang, H.; et al. Booster of mRNA-1273 Strengthens SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Neutralization. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Biologics Evaluation; Research Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine Available online:. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/coronavirus-covid-19-cber-regulated-biologics/moderna-covid-19-vaccine (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Nanduri, S.; Pilishvili, T.; Derado, G.; Soe, M.M.; Dollard, P.; Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Bagchi, S.; Dubendris, H.; Link-Gelles, R.; et al. Effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines in Preventing SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Nursing Home Residents Before and During Widespread Circulation of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant - National Healthcare Safety Network, March 1-August 1, 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazagatos, C.; Monge, S.; Olmedo, C.; Vega, L.; Gallego, P.; Martín-Merino, E.; Sierra, M.J.; Limia, A.; Larrauri, A.; Working Group for the surveillance and control of COVID-19 in Spain; et al. Effectiveness of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines in Preventing SARS-CoV-2 Infections and COVID-19 Hospitalisations and Deaths in Elderly Long-Term Care Facility Residents, Spain, Weeks 53 2020 to 13 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiolet, T.; Kherabi, Y.; MacDonald, C.-J.; Ghosn, J.; Peiffer-Smadja, N. Comparing COVID-19 Vaccines for Their Characteristics, Efficacy and Effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and Variants of Concern: A Narrative Review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaura, A.; Trickey, A.; Shah, A.S.V.; Benedetto, U.; Glampson, B.; Mulla, A.; Mercuri, L.; Gautama, S.; Costelloe, C.E.; Goodman, I.; et al. Comparing the Longer-Term Effectiveness of a Single Dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccines across the Age Spectrum. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 46, 101344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, M.; Okada, H.; Itoh, Y.; Hirata, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Yoshida, E.; Matsui, A.; Kelly, E.J.; Shoemaker, K.; Olsson, U.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) against SARS-CoV-2 in Japan: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Phase 1/2 Trial. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 114, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.A.; Rassen, J.A.; Kabelac, C.A.; Turenne, W.; Leonard, S.; Klesh, R.; Meyer, W.A., 3rd; Kaufman, H.W.; Anderson, S.; Cohen, O.; et al. Association of SARS-CoV-2 Seropositive Antibody Test With Risk of Future Infection. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letafati, A.; Eyvazzadeh, N.; Gharehkhani, A.; Khorshidian, A.; Chalabiani, S.; Soufiani, E.K.; Khakpoor, N.; Shamsodini, B.; Beheshti, T.; Bavili Olyaei, R.T.; et al. Comparison of AstraZeneca and Sinopharm Vaccines as Boosters in Protection against COVID-19 Infection. Biologicals 2023, 82, 101668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadoff, J.; Gray, G.; Vandebosch, A.; Cárdenas, V.; Shukarev, G.; Grinsztejn, B.; Goepfert, P.A.; Truyers, C.; Fennema, H.; Spiessens, B.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Single-Dose Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine against Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2187–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardt, K.; Vandebosch, A.; Sadoff, J.; Le Gars, M.; Truyers, C.; Lowson, D.; Van Dromme, I.; Vingerhoets, J.; Kamphuis, T.; Scheper, G.; et al. Efficacy, Safety, and Immunogenicity of a Booster Regimen of Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine against COVID-19 (ENSEMBLE2): Results of a Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1703–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Mateus, J.; Coelho, C.H.; Dan, J.M.; Moderbacher, C.R.; Gálvez, R.I.; Cortes, F.H.; Grifoni, A.; Tarke, A.; Chang, J.; et al. Humoral and Cellular Immune Memory to Four COVID-19 Vaccines. Cell 2022, 185, 2434–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, K.E.; Le Gars, M.; Sadoff, J.; de Groot, A.M.; Heerwegh, D.; Truyers, C.; Atyeo, C.; Loos, C.; Chandrashekar, A.; McMahan, K.; et al. Immunogenicity of the Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine for COVID-19. JAMA 2021, 325, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Chu, M. Role of COVID-19 Vaccines in SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 898192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, I.; Ul Munamm, S.A.; Ur Rasool, M.; Fatimah, M.; Abu Bakar, M.; Rana, Z.K.; Khatana, U.F.; Jordon, L.; Saqlain, M.; Mahdi, N.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Sinopharm Vaccine (BBIBP-CorV) in Elderly Population of Faisalabad District of Pakistan. Postgrad. Med. J. 2023, 99, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, L.-Y.; Lu, Q.-B.; Cui, F. Vaccination with the Inactivated Vaccine (Sinopharm BBIBP-CorV) Ensures Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Related Disease. Vaccines (Basel) 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqassieh, R.; Suleiman, A.; Abu-Halaweh, S.; Santarisi, A.; Shatnawi, O.; Shdaifat, L.; Tarifi, A.; Al-Tamimi, M.; Al-Shudifat, A.-E.; Alsmadi, H.; et al. Pfizer-BioNTech and Sinopharm: A Comparative Study on Post-Vaccination Antibody Titers. Vaccines (Basel) 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalidoust, M.; Eilami, O.; Ashkan, Z.; Ziyaeyan, M.; Aliabadi, N.; Habibi, M. The Rates and Symptoms of Natural and Breakthrough Infection Pre- and Post- Covid-19 Non-mRNA Vaccination at Various Peaks amongst Iranian Healthcare Workers. Virol. J. 2023, 20, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Belayachi, J.; Yang, Y.; Fu, Q.; Rodewald, L.; Li, H.; Yan, B.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Q.; et al. Real-World Study of the Effectiveness of BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm) COVID-19 Vaccine in the Kingdom of Morocco. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkle, L.M.; Kotloff, K.L.; Gay, C.L.; Áñez, G.; Adelglass, J.M.; Barrat Hernández, A.Q.; Harper, W.L.; Duncanson, D.M.; McArthur, M.A.; Florescu, D.F.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of NVX-CoV2373 in Adults in the United States and Mexico. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, A.M.; Zhou, X.; Kinol, J.; Underwood, E.; Woo, W.; McGarry, A.; Beyhaghi, H.; Áñez, G.; Toback, S.; Dunkle, L.M. NVX-CoV2373 Vaccine Efficacy against Hospitalization: A Post Hoc Analysis of the PREVENT-19 Phase 3, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Vaccine 2023, 41, 3461–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graña, C.; Ghosn, L.; Evrenoglou, T.; Jarde, A.; Minozzi, S.; Bergman, H.; Buckley, B.S.; Probyn, K.; Villanueva, G.; Henschke, N.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dighriri, I.M.; Alhusayni, K.M.; Mobarki, A.Y.; Aljerary, I.S.; Alqurashi, K.A.; Aljuaid, F.A.; Alamri, K.A.; Mutwalli, A.A.; Maashi, N.A.; Aljohani, A.M.; et al. Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine (BNT162b2) Side Effects: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e23526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finsterer, J.; Scorza, F.A.; Scorza, C.A. Post SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Guillain-Barre Syndrome in 19 Patients. Clinics 2021, 76, e3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedmann, M.; Skattør, T.; Stray-Pedersen, A.; Romundstad, L.; Antal, E.-A.; Marthinsen, P.B.; Sørvoll, I.H.; Leiknes Ernstsen, S.; Lund, C.G.; Holme, P.A.; et al. Vaccine Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia Causing a Severe Form of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis With High Fatality Rate: A Case Series. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 721146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Introna, A.; Caputo, F.; Santoro, C.; Guerra, T.; Ucci, M.; Mezzapesa, D.M.; Trojano, M. Guillain-Barré Syndrome after AstraZeneca COVID-19-Vaccination: A Causal or Casual Association? Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 208, 106887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbel, C.H.; Heinze, A.; Karstedt, S.; Morscheck, M.; Tashiro, L.; Cirkel, A.; Hamid, Q.; Halwani, R.; Temsah, M.-H.; Ziemann, M.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Headache after Vaccination against COVID-19 (coronavirus SARS-CoV-2) with the BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine: A Multicentre Observational Cohort Study. Brain Commun 2021, 3, fcab169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Azorín, D.; Do, T.P.; Gantenbein, A.R.; Hansen, J.M.; Souza, M.N.P.; Obermann, M.; Pohl, H.; Schankin, C.J.; Schytz, H.W.; Sinclair, A.; et al. Delayed Headache after COVID-19 Vaccination: A Red Flag for Vaccine Induced Cerebral Venous Thrombosis. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifian-Dorche, M.; Bahmanyar, M.; Sharifian-Dorche, A.; Mohammadi, P.; Nomovi, M.; Mowla, A. Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia and Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Post COVID-19 Vaccination; a Systematic Review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 428, 117607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, N.; Koorapati, G.; Prasad, S.; Jeelani, H.M.; Sherchan, R.; Shrestha, J.; Shayuk, M. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination-Induced Transverse Myelitis. Cureus 2021, 13, e16624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.-J.; Tseng, H.-P.; Lin, C.-L.; Shiu, J.-S.; Lee, M.-H.; Liu, C.-H. Acute Transverse Myelitis Following COVID-19 Vaccination. Vaccines (Basel) 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notghi, A.A.; Atley, J.; Silva, M. Lessons of the Month 1: Longitudinal Extensive Transverse Myelitis Following AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccination. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, e535–e538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, A.; Bartholomew, T.; Rudd, J.; Walker, D. Sequential Contralateral Facial Nerve Palsies Following COVID-19 Vaccination First and Second Doses. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Kaki, M.; Potluri, V.S.; Kahar, P.; Khanna, D. A Comprehensive Review of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Pfizer, Moderna & Johnson & Johnson. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2022, 18, 2002083. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watad, A.; De Marco, G.; Mahajna, H.; Druyan, A.; Eltity, M.; Hijazi, N.; Haddad, A.; Elias, M.; Zisman, D.; Naffaa, M.E.; et al. Immune-Mediated Disease Flares or New-Onset Disease in 27 Subjects Following mRNA/DNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination. Vaccines (Basel) 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat-Khoei, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Katz, J.; Harrison, D.; Tauhid, S.; Bruso, P.; Houtchens, M.K.; Edwards, K.R.; Bakshi, R. COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination Leading to CNS Inflammation: A Case Series. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 1093–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhorn, F.; Graf, T.; Klingebiel, R.; Schäbitz, W.-R.; Rogalewski, A. Postvaccinal Encephalitis after ChAdOx1 nCov-19. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 90, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, D.G.; Cañete, L.A.Q.; Dos Santos, G.A.C.; de Oliveira, R.V.; Brandão, C.O.; da Cruz, L.C.H., Jr. Neurological Symptoms and Neuroimaging Alterations Related with COVID-19 Vaccine: Cause or Coincidence? Clin. Imaging 2021, 80, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, B.; Kamat, I.; Hotez, P.J. Myocarditis With COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines. Circulation 2021, 144, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, N.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, E.K.; Park, J.-H.; Choi, E.-Y.; Choi, J.-O.; Park, H.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccination-Related Myocarditis: A Korean Nationwide Study. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 2234–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hromić-Jahjefendić, A.; Sezer, A.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Serrano-Aroca, Á.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Uversky, V.N.; Redwan, E.M.; Barh, D.; Lundstrom, K. COVID-19 Vaccines and Myocarditis: An Overview of Current Evidence. Biomedicines 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdeldayem, E.H.; Raief Mosaad, B.M.; Yassin, A.; Abdelrahman, A.S. Cardiac MRI in Patients with COVID-19 Infection. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 3867–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, S.M.S.; Alvi, S.A.; Khan, H.; Majeed, R.; Syed, T.; Anwar, A.; Hashmi, A.A. Common Side Effects of Pfizer COVID-19 Vaccine: An Experience From Pakistan. Cureus 2023, 15, e40878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, R.A.; Garout, R.M.; Wahid, S.; Ayub, F.; Firas ZinAlddin, L.M.; Sultan, I. A Survey on the Side Effects of Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine Among Vaccinated Adults in Saudi Arabia. Cureus 2021, 13, e19222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abukhalil, A.D.; Shatat, S.S.; Abushehadeh, R.R.; Al-Shami, N. ’meh; Naseef, H.A.; Rabba, A. Side Effects of Pfizer/BioNTech (BNT162b2) COVID-19 Vaccine Reported by the Birzeit University Community. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oster, M.E.; Shay, D.K.; Su, J.R.; Gee, J.; Creech, C.B.; Broder, K.R.; Edwards, K.; Soslow, J.H.; Dendy, J.M.; Schlaudecker, E.; et al. Myocarditis Cases Reported After mRNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccination in the US From December 2020 to August 2021. JAMA 2022, 327, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Kakiuchi, S.; Rikitake, J.; Matsuba, H.; Sekinada, D.; Kozuki, Y.; Iwata, N. Immune Thrombocytopenia Associated with Pfizer-BioNTech’s BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. IDCases 2021, 25, e01245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, S.; Al Ketbi, L.M.B.; Al Kaabi, N.; Al Mansoori, M.; Al Maskari, N.N.; Al Shamsi, M.S.; Alderei, A.S.; El Eissaee, H.N.; Al Ketbi, R.M.; Al Shamsi, N.S.; et al. Vaccine Side Effects Following COVID-19 Vaccination Among the Residents of the UAE-An Observational Study. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 876336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Pabani, U.K.; Gul, A.; Muhammad, S.A.; Yousif, Y.; Abumedian, M.; Elmahdi, O.; Gupta, A. COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Myocarditis: A Systemic Review and Literature Search. Cureus 2022, 14, e27408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.-J.; Cines, D.B.; Gernsheimer, T.; Kessler, C.; Michel, M.; Tarantino, M.D.; Semple, J.W.; Arnold, D.M.; Godeau, B.; Lambert, M.P.; et al. Thrombocytopenia Following Pfizer and Moderna SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desalegn, M.; Garoma, G.; Tamrat, H.; Desta, A.; Prakash, A. The Prevalence of AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccine Side Effects among Nigist Eleni Mohammed Memorial Comprehensive Specialized Hospital Health Workers. Cross Sectional Survey. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0265140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, T.; Ali, J.; Ali, S.M.; Iftikhar, A.S.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Khan, A.S.; Qamar, J.A.; Sohail, K.; Anwar, A.; Hashmi, A.A. Prevalence of Side Effects of the AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccine: A Multicenter Experience From Pakistan. Cureus 2023, 15, e46543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson & Johnson Updates, U.S. COVID-19 Vaccine Fact Sheet Available online:. Available online: https://www.jnj.com/johnson-johnson-updates-u-s-covid-19-vaccine-fact-sheet (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Haider, T.; Abidi, S.R.Z.; Fatima, M.; Zafar, A.; Siddiqui, R.Q.U.; Khan, W.; Saeed, T.; Anwar, A.; Hashmi, A.A. The Prevalence of Side Effects of Sinopharm COVID-19 Vaccine: An Experience From Pakistan. Cureus 2023, 15, e38180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadras, O.; Mehraeen, E.; Karimi, A.; Tantuoyir, M.M.; Afzalian, A.; Nazarian, N.; Mojdeganlou, H.; Mirzapour, P.; Shamsabadi, A.; Dashti, M.; et al. Safety and Adverse Events Related to Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccines and Novavax;a Systematic Review. Arch Acad Emerg Med 2022, 10, e54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lindo, P. Health Ministry Begins “One Shot and Done” Initiative with J&J Vaccine - Trinidad and Tobago Newsday. Trinidad and Tobago Newsday 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mar, 31 Trinidad and Tobago Receives the First COVID-19 Vaccines through the COVAX Facility Available online:. Available online: https://www.paho.org/en/news/31-3-2021-trinidad-and-tobago-receives-first-covid-19-vaccines-through-covax-facility (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- George, K. Tobago Parents Contacted for Pfizer Vaccine Approval. Trinidad and Tobago Newsday 2021. [Google Scholar]
- The Oxford/AstraZeneca (ChAdOx1-S [recombinant] Vaccine) COVID-19 Vaccine: What You Need to Know. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/the-oxford-astrazeneca-covid-19-vaccine-what-you-need-to-know/ (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Munavalli, G.G.; Guthridge, R.; Knutsen-Larson, S.; Brodsky, A.; Matthew, E.; Landau, M. COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2 Virus Spike Protein-Related Delayed Inflammatory Reaction to Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers: A Challenging Clinical Conundrum in Diagnosis and Treatment. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2022, 314, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.-A. Trinidad and Tobago. In Politics of Identity in Small Plural Societies; Palgrave Macmillan US: New York, 2012; ISBN 9781349342426. [Google Scholar]
- Meo, S.A.; ElToukhy, R.A.; Meo, A.S.; Klonoff, D.C. Comparison of Biological, Pharmacological Characteristics, Indications, Contraindications, Efficacy, and Adverse Effects of Inactivated Whole-Virus COVID-19 Vaccines Sinopharm, CoronaVac, and Covaxin: An Observational Study. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- What Is COVID-19. Available online: https://health.gov.tt/covid-19 (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Individual; Family Health Pediatric COVID-19 Vaccination. Available online: https://www.health.state.mn.us/diseases/coronavirus/vaccine/peds.html (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Rafeek, R.; Sa, B.; Smith, W. Vaccine Acceptance, Knowledge, Attitude and Practices Regarding the COVID-19 Pandemic: Cross-Sectional Study among Dentists in Trinidad and Tobago. Dent. J. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC COVID-19 Response Team. Food and Drug Administration Allergic Reactions Including Anaphylaxis After Receipt of the First Dose of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine - United States, December 14-23, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motilal, S.; Ward, D.; Mahabir, K.; Lopez, T.; Logan, R.; Maharaj, S.; Maloney, J.; Marson, M.; Marcelle, C. COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy in Trinidad and Tobago: A Qualitative Study. Cureus 2023, 15, e43171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopaul, C.D.; Ventour, D.; Thomas, D. ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine Side Effects among Healthcare Workers in Trinidad and Tobago. Vaccines (Basel) 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Sohan, K.; Mohammed, Z.C.M.; Bachan, V. COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake, Acceptance, and Reasons for Vaccine Hesitancy: A Cross-Sectional Study among Pregnant Women in Trinidad, West Indies [Response To Letter]. Int. J. Womens Health 2023, 15, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simulating COVID-19 Vaccination in Trinidad and Tobago. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/simulating-covid-19-vaccination-in-trinidad-and-tobago (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- COVID-19 Fortnightly Update - Tuesday May 02, 2023. Available online: https://health.gov.tt/covid-19-fortnightly-update-tuesday-may-02-2023 (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Fernandes, J.; Jaggernauth, S.; Ramnarine, V.; Mohammed, S.R.; Khan, C.; Panday, A. Neurological Conditions Following COVID-19 Vaccinations: Chance or Association? Cureus 2022, 14, e21919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Review of the Current Status of COVID-19 Vaccines v1.0.pdf. (accessed on 8 October 2023).
- COVID-19 Vaccines - Addressing Hesitancy 2021050302.pdf. (accessed on 15 September 2023).
| Population | Intervention | Comparison | Outcome | Study Type |
| Aged 5-<80 years | Six COVID-19 vaccines including Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, Novavax, AstraZeneca, Sinopharm, and Janssen | Effectiveness and safety | Decreased morbidity and mortality COVID-19 vaccination in Trinidad and Tobago |
All Study Types |
| Covid-19 Vaccines | Type of Vaccine | Vaccine Effectiveness, VE (%) |
|---|---|---|
|
Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 |
Nucleic acid | 95 |
|
Moderna mRNA-1273 |
Nucleic acid | 94.1 |
|
Novavax NVX-CoV2373 |
Protein based | 89.7 |
|
AstraZeneca AZD1222 |
Viral vector | 70.4 |
|
Sinopharm BBIBP-CorV |
Whole virus (inactivated) | 67 |
|
Janssen Ad26.COV2.S |
Viral vector | 66.9 |
| Vaccines | Side effects | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Pfizer-BioNTech |
Common: Burning, pain and swelling at the injection site, fever, joint pain Rare: thrombocytopenia and myocarditis, |
[69,70] [71,72,73] |
| Moderna | Common: pain at the site of injection, fatigue, drowsiness, headache, joint/muscle pain. Rare: myocarditis |
[74] [75,76] |
| Oxford-AstraZeneca | Pain and swelling at the injection site, fever | [77,78] |
| Janssen | Injection site reactions: pain, redness of the skin, and swelling, fatigue, headache, nausea, muscle aches, and fever. | [79] |
| Sinopharm | Burning and pain at injection site , fever, fatigue | [80] |
| Novavax | Injection site pain and swelling, redness, and pruritus, fatigue, headaches |
[81] |
| Author/Year | Aim/Open questions | Type of Study/ Design | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pormohammad et al, 2021 [1] | The current study systematically reviewed the clinical features of the vaccines in clinical trials to provide a better estimate of their efficacy, side effects and immunogenicity. | Systematic review | The adenovirus-vectored and mRNA-based vaccines showed the highest efficacy after first and second doses, respectively. The mRNA-based vaccines had the highest level of side effects reported. |
| Forni et al, 2021 [2] | Will the new vaccines be able to control the COVID-19 pandemic? |
Literature Review | Due to the novelty of the technologies adopted and short development time, these vaccines deploys several unresolved issues that will permit to clarify only on the passage of time. Technical problems connected with the production of billions of doses are imminent challenges. |
| Zheng et al, 2022 [3] | To estimate COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness (VE) against concerned outcomes. | Systematic review | The COVID-19 vaccines were highly protective. |
| Al-Momani et al, 2022 [4] | To establish the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccines in reducing hopitalization of patients in Jordan. | Prospective, Case-control Study |
The overall VE among the participants was 84% (95% Cl 79–88%). VE was higher for Pfizer vaccine recipients than for those who received the Sinopharm vaccine |
|
Hadj Hassine, 2022 [5] |
VE can be jeopardised by the rapid spread and emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs)? | Literature Review |
Covid-19 vaccines have good neutralising activity against the Alpha strain, and a reduced effect on the Beta strain. |
| Francis et al, 2022 [6] | To discuss the most recent WHO-approved Covid-19 vaccine subtypes, and geographical scheduled updates. | Literature Review | As of 16 May 2021, the number of countries that have approved the use of the following vaccines is Oxford/AstraZeneca in 101, Pfizer in 85, Moderna in 46, and Janssen in 41. |
|
https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/recs/grade/covid-19-pfizer-biontech-vaccine.html 2021 [7] |
Should vaccination with Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (2-doses, IM) be recommended for persons 16 years of age and older? |
Report | The pooled VE estimates from the observational studies (OS) demonstrated that the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine reduced symptomatic COVID-19 when was compared to no vaccination. |
| Rotshild et al, 2021 [8] |
To compare the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines to prevent severe disease in the adults and among the elderly. |
Systematic Review and Meta-analysis | BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccines were ranked with the highest probability of efficacy against symptomatic COVID-19. |
| Saciuk et al, 2022 [9] | To measure VE regarding infection, hospitalization and mortality from COVID-19 after adjusting for both person-specific risk variables and virus exposure. | Retrospective cohort study | Of 1,650,885; 28,042 became PCR positive during the study period, of whom 1047 were hospitalized and 164 died. |
| Lopez Bernal et al, 2021 [10] | To compare and diagnose a patient with XLA that presented with an initial diagnosis of THI and CVID. |
Test negative case-control study | Participants aged 80 years and older vaccinated with BNT162b2 before January 2021 had a higher probability of testing positive in the first nine days post-vaccination indicating a higher underlying risk of infection. |
| Soiza et al, 2021 [11] | To review of the main candidate vaccines focusing on the evidence of safety and efficacy in older adult population. | Review article | Pfizer and Moderna vaccine have announced high degrees of efficacy among the elderly. |
| Piechotta et al, 2023 [12] | To assess effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines approved in the EU for children aged 5-11 years. | Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis | Vaccine effectiveness after two doses against omicron infections was 41,6%. |
| Tenforde et al, 2021 [13] | The duration of mRNA vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna) VE against COVID-19–associated hospitalizations was assessed among adults aged ≥18 years. | Cross- sectional study | VE against COVID-19– associated hospitalization was 86% 2–12 weeks and 84% 13–24 weeks from receipt of the second vaccine dose |
| Elamin et al, 2023 [14] | To assess effectiveness of how two doses of the Pfizer and Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccines were in preventing COVID-19 infection six months after administration. | Retrospectivecohort study | Enrolled 4458 participants in Jazan. The majority of them received the Pfizer vaccine. The results showed that the Pfizer and ASZ vaccine’s protection decreased from 93.2% and 90.2%, respectively, during the first three months, to 68.5% and 68.1% after a second six-month interval. |
| Moreira et al, 2022 [15] | To assess the BNT162b2 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech) safety and efficacy against Covid-19 starting 7 days after the third dose. | Clinical trial |
A total of 5081 participants received a third Pfizer-BioNTech dose and 5044 received placebo. Local and systemic events were generally of low grade. No new cases of pericarditis or myocarditis was reported. |
| Bar-On et al, 2021 [16] | To assess the efficacy of a third dose (booster) of the Pfizer-BioNTech in individuals aged 60 and older in Israel. | Prospective study. |
The rate of confirmed infection was lower in the booster group, which included 10.6 million person-days with 934 confirmed infections and 29 cases of severe illness, as compared the nonbooster group, which included approximately 5.2 million person-days with 4439 confirmed infections and 294 cases of severe illness. |
| Chirico et al, 2022 [17] | To examine the scientific literature on the efficacy, effectiveness and safety of COVID-19 vaccines and new SARS-CoV-2 strains. | Literature Review | For some vaccines including Janssen (Ad26.COV2.S), Covaxin (BBV152), Sinopharm (BBIBP-CorV), and Sinovac (CoronaVac), exist information available on their safety and immunogenicity from phase I and II, but evidence of their effectiveness is not clear. There were four serious issues among BNT162b2 participants in a clinical trial including right axillary lymphadenopathy, shoulder injury from vaccine administration, right leg paresthesia and paroxysmal ventricular arrhythmia. Moderna vaccine showed some mild and moderate side effects. A global concern is the highly transmissible Delta variant, which has become predominant worldwide. |
| Mohammed et al, 2022 [18] | To compare the efficacy and effectiveness of seven COVID-19 vaccines. | Systematic Review | The Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine had the highest effectiveness for the first dose of any vaccine against infection with B.1.1.7 variant, it was 70 (CI 55–85) at ≥21 days after vaccination. |
| Andrews et al, 2022 [19] | To explore concerns about the effectiveness of current vaccines against the omicron (B.1.1.529) variant. | Test-negative case-control design | A Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna vaccine booster after either the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 or Pfizer/BioNTech primary course substantially increased protection, which decreases over time. |
| Zeng et al, 2022 [20] | To provide a comprehensive overview of the effectiveness profile of COVID-19 vaccines against variants of concern (VOC). | Systematic Review and Meta-analysis | Eleven COVID-19 vaccines were included in this analysis. Full vaccination was protective against Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron variants, with VE of 88.0%, 73.0%, 63.0%, 77.8% and 55.9% respectively. Booster vaccinations were more effective against Delta and Omicron variants, with a vaccine efficacy of 95.5% and 80.8%, respectively. |
| https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/recs/grade/covid-19-moderna-vaccine.html; 2020 [21] | “Should vaccination with Moderna COVID-19 vaccine be recommended for persons 18 years of age and older during an Emergency Use Authorization?” | Report on a systematic review | Data were reviewed from two published Phase I studies, one Phase II randomized controlled trial and one Phase III randomized controlled trial using data provided by the sponsor and FDA. The Moderna COVID-19 vaccine has a VE of 94.1%. |
| Rahmani et al, 2022 [22] | “To evaluate the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in reducing the incidence, hospitalization, and mortality from COVID-19”. | Systematic Review and Meta-analysis | The Pooled Vaccine Effectiveness (PVE) against SARS-COV 2 infection was in the first and second doses 71% and 87%, respectively; preventing hospitalization was 73% and 89%, respectively. Regarding the infection-related mortality was 68% and 92%, respectively. |
| Soheili et al, 2023 [23] | “To evaluate the efficacy and effectiveness of several COVID-19 vaccines, including AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Moderna, Bharat, and Johnson & Johnson, to better estimate their immunogenicity, benefits, or side effects”. | Meta-analysis | The total effectiveness of all COVID-19 vaccines after the first and second doses were 71% and 91%, respectively. The total efficacy of vaccines after the first and second doses was 81% and 71% |
| Self et al, 2021 [24] |
To assess VE of three COVID-19 vaccines (mRNA-1273 from Moderna, BNT162b2 from Pfizer-BioNTech and Ad26.COV2 from Janssen) in preventing COVID-19 hospitalization. | Case control study |
Among U.S. adults without immunocompromising conditions, vaccines effectiveness against COVID-19 hospitalization during March 11- August 15, 2021, was higher for the Moderna vaccine (93%) than the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine (88%) and Janssen vaccine (71%). |
| Harris et al, 2023 [25] | “To compare the risk of adverse events between mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 (mRNA-1273 and BNT162b2) overall, by frailty level, and by prior history of the adverse events of interest”. | Cohort study | “In this study of 6 388 196 older US adults, a 4% lower risk of pulmonary embolism, a 2% lower risk of thromboembolic events, and a 14% lower risk of diagnosed COVID-19 were observed among those who received the mRNA-1273 vaccine compared with the BNT162b2 vaccine”. |
| Dickerman et al, 2022 [26] | To investigate he messenger RNA (mRNA)–based vaccines for their comparative effectiveness range of outcomes across diverse populations. | Cross- sectional study | “Recipients of the BNT162b2 vaccine had a 27% higher risk of documented SARS-CoV-2 infection and a 70% higher risk of hospitalization for Covid-19 than recipients of the mRNA-1273 vaccine over 24 weeks of follow-up in a period marked by alpha-variant predominance”. |
| Doria-Rose et al, 2021 [27] | To assess the potential risk of the Omicron variant to existing vaccines. | Prospective study | “Omicron was 49-84-fold less sensitive to neutralization than D614G and 5.3-6.2-fold less sensitive than Beta when assayed with serum samples obtained 4 weeks after 2 standard inoculations with 100 µg mRNA-1273”. |
| https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/coronavirus-covid-19-cber-regulated-biologics/moderna-covid-19-vaccine; 2023 [28] | N/A | Technical Report | Ensuring that the correct volume of the Moderna vaccine is withdrawn from the vial to administered to children up to age 11. |
| Nanduri et al, 2021 [29] | To assess the VE of mRNA vaccines among nursing home residents in the US. |
Prospective study | “Two doses of mRNA vaccines were 74.7% effective against infection among nursing home residents early in the vaccination program (March-May 2021). During June-July 2021, when B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant circulation predominated, effectiveness declined significantly to 53.1%”. |
| Mazagatos et al, 2021 [30] | To estimate mRNA COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness for elderly in long-term care facilities (LTCF) in Spain. | Prospective study | COVID-19 mRNA vaccines including Moderna, were highly effective in preventing not only COVID-19 but also hospitalisations, and deaths in elderly LTCF. |
| Fiolet et al, 2022 [31] |
“To provide an up-to-date comparative analysis of the characteristics, adverse events, efficacy, effectiveness and impact of the variants of concern for 19 COVID-19 vaccines”. | Literature Review | All vaccines appear to be safe and effective tools to prevent severe COVID-19. |
| Kaura et al, 2022 [32] | “To compare compared the effectiveness of a single dose strategy of the Oxford-AstraZeneca or Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection across all age groups and over an extended follow-up period”. | Observational cohort study | “534 infections were documented overall, of which 65 (11.9%) required hospitalization, and 29 (5.6%) resulted in death, during the period from 14 to 84 days”. |
| Asano el al, 2022 [33] | To evaluate the immunogenicity and safety of the AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) vaccine in Japanese adults |
Randomized, double-blind trial |
“The AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) vaccine is a replication-deficient simian adenovirus-vectored vaccine encoding the full-length SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.” “In a pooled analysis of four trials conducted in the UK (phase 1/2 and 2/3), Brazil (phase 3) and South Africa (phase 1/2), AZD1222 exhibited an acceptable safety profile and overall vaccine efficacy of 66.7% [95% confidence interval (CI) 57.4–74.0] against COVID-19 >14 days after the second dose.” |
| Harvey et al, 2021 [34] | “Can observational clinical data from commercial laboratories be used to evaluate the comparative risk of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection for individuals who are antibody positive vs those who are antibody negative?” | Observational descriptive cohort study |
“A total of 3 257 478 unique patients with an index antibody test were identified after excluding 132 patients with discordant antibody tests on the index day. Of these, 2 876 773 (88.3%) had a negative index antibody result (seronegatives), 378 606 (11.6%) had a positive index antibody result (seropositives), and 2099 (0.1%) had an inconclusive index antibody result (sero-uncertain).” Seropositive individuals were more likely to have symptoms or a diagnosis of COVID-19 than seronegative individuals. |
| Letafati et al, 2023 [35] | “To evaluate the role played by the type of the 3rd dose of vaccination by comparing the safety and efficacy of two common vaccination histories differing only in the 3rd received dose.” | Cross-sectional study | “Out of 346 cases with respiratory symptoms, 120 cases tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 and had received two doses of Sinopharm and a different booster dose of either AZD1222 (AstraZeneca) or BIBP (Sinopharm).” |
| Sadoff et al, 2021 [36] | To conduc an ongoing phase 3 trial (ENSEMBLE) to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a single dose of Ad26.COV2.S at 5×1010 viral particles for the prevention of Covid-19 and SARS-CoV-2 infection in adults. | Multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3, pivotal trial. | “A total of 44,325 participants underwent randomization, of whom 43,783 received vaccine or placebo; the per-protocol population included 39,321 SARS-CoV-2–negative participants, of whom 19,630 received Ad26.COV2.S and 19,691 received placebo.” “With regard to severe–critical Covid-19, vaccine efficacy was 76.7% (adjusted 95% CI, 54.6 to 89.1) against disease with onset at least 14 days after administration and 85.4% (adjusted 95% CI, 54.2 to 96.9) against disease with onset at least 28 days after administration.” |
| Hardt et al, 2022 [37] | “To investigate the efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine (Janssen) as primary vaccination plus a booster dose.” | Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial | Vaccine efficacy was 75·2%. The booster vaccine exhibited an acceptable safety profile. “In these studies, both homologous and heterologous Ad26.COV2.S boosters had less effect on neutralising antibody titres than boosters of mRNA vaccines; both Ad26.COV2.S and mRNA boosters generally yielded lower titres against delta and omicron variants relative to the wild-type or reference strains.” |
| Zhang et al, 2022 [38] | To compare the development of immune memory in subjects who had received immunization with mRNA-1273, BNT162b2, Ad26.COV2.S, or NVX-CoV2373 vaccine. | Prospective study | “While neutralizing antibody kinetics were different between mRNA and viral vector vaccines, the CD4+ T cell response kinetics were similar.” |
| Stephenson et al, 2021 [39] | “To evaluate the immunogenicity of the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine in humans.” | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1 clinical trial | By day 8 following immunization, binding antibodies were observed in 65% (13 of 20) of vaccine recipients. Binding and neutralizing antibodies continued to increase on days 29, 57, and 71. |
| Zhou et al, 2022 [40] |
“To provide references for subsequent vaccine development and clinical research.’ | Literature Review | All countries play a great role in vaccine research and development, and there are a variety of vaccines that have been listed through clinical trials. |
| Nadeem et al, 2023 [41] | “To assess the safety and efficacy of BBIBPP-CorV (Sinopharm) vaccine within the Pakistani adult population aged 60 or above.” | Retrospective study | Between 5 May 2021 and 31 July 2021, 3426 symptomatic individuals were PCR tested. The results displayed that BBIBPP-CorV (Sinopharm) vaccine 14 days after the second dose was efficient in reducing the risk of symptomatic infection (94.3%), hospitalisations (60.5%) and mortality by 98.6%, among vaccinated individuals with a significant p value of 0.001. |
| Wang et al, 2022 [42] | To review evidences of the safety, efficacy, and effectiveness of Sinopharm vaccine. | Literature Review | Clinical trials conducted during the first wave of the infection suggested BBIBP-CorV offered a good efficacy in preventing new death and infections related to SARS-CoV-2. The protective efficacy was 78.89 %. Vaccine efficacy was 78.07%, calculating the person-years of follow-up. Antibody response declined three months following BBIBP-CorV vaccination, while the T cell response persisted. |
| Alqassieh et al, 2021 [43] | To compare the specific antibody titers in subjects vaccinated with either the Sinopharm vaccine or the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. | Prospective observational cohort | The study showed that 99.3% recipients of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine had a positive IgG titers, while 85.7% recipients of Sinopharm had positive IgG (p < 0.001). |
| Jamalidoust et al, 2023 [44] | “To determine the rate of natural and breakthrough infection and related symptoms of Covid-19 amongst Iranian healthcare workers (HCWs) who were vaccinated by different non-mRNA-based vaccines at peak points.” | Cross-sectional study | “In total, 53% of the HCWs were exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection between 1 and 5 times within two years after the current pandemic, while 20.7% and 32.3% experienced natural and breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection, respectively.” “This study compared the clinical differences between the two peaks of Omicron and Delta.” |
| Zhang et al, 2022 [45] | “To determine real-world BBIBP-CorV vaccine effectiveness (VE) against serious or critical hospitalization of individuals RT-PCR-positive for SARS-CoV-2 during the first five months of BBIBP-CorV use in Morocco.” | Retrospective cohort study | “Among hospitalized subjects, 52.1% were male and 61.1% were less than 60 years old.” “Unadjusted, unboosted full-series BBIBP-CorV vaccine effectiveness against serious or critical hospitalization was 90.2% (95%CI: 87.8—92.0%).” |
| Dunkle et al, 2022 [46] | To investigate the efficacy of NVX-CoV2373 (adjuvanted, recombinant spike protein nanoparticle vaccine) in the U.S. and Mexico. | Phase 3, randomized, observer-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. | In this study, the efficacy of NVX-CoV2373 vaccine was 90.4% and demonstrated to be efficient against COVID-19 infection as shown in the prevention of the disease in the United Kingdom and South Africa. |
| Marchese et al, 2023 [47] | To assess the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine efficacy against hospitalization. |
Phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial |
The study showed that NVX-CoV2373 vaccine demonstrated a 100% efficacy rate against hospitalization. |
| Graña et al, 2022 [48] | To assess the efficacy and safety of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. | Systematic Review | “The authors included and analyzed 41 RCTs assessing 12 different vaccines, including homologous and heterologous vaccine schedules and the effect of booster doses. Thirty-two RCTs were multicenter and five were multinational. The sample sizes of RCTs were 60 to 44,325 participants.” |
| Dighriri et al, 2022 [49] | To assess the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine side effects. | Systematic Review | “The total number of participants in the 14 studies was 10,632 participants. Average of the most frequent side effects of 14 studies were injection site pain 77.34%, fatigue 43%, and muscle pain 39.67%.” |
| Finsterer et al, 2021 [50] | To summarize and discuss Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) as a side effect of SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations. | Review article | Nine articles reporting 18 patients with side effect of SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations such as GBS, ranging between 20- and 86-year-old, ten patients were female and nine patients were male. In all 19 patients, GBS developed after the first dose of the vaccines: Astra Zeneca vaccine (14 patients), the Pfizer vaccine (4 patients) and the Johnson & Johnson vaccine (one patient). The latency between vaccination and GBS onset ranged from 3h to 39 days. |
| Wiedmann et al, 2021 [51] | To reveal side effects of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (Vaxzevria; COVID-19 vaccine AstraZeneca) in Norway at the beginning of the vaccination programme. | Case reports | In Norway, a total of 132 488 first doses of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine were administered mainly to health care workers until halted by the health authorities on March 11th, 2021. It was due to five cases of severe cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), associated with thrombocytopenia and intra-cerebral hemorrhage. They have developed the problem within 2 weeks post-vaccination. One case with splanchnic vein thrombosis and thrombocytopenia were encountered in previously healthy health care worker after having received ChAdOx1 CoV-19 vaccine. |
| Introna et al, 2021 [52] | To report side effects of a COVID-19 vaccine. | Case reports | It was described a case of GBS following the first dose of Oxford/AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine with papilledema as atypical onset. |
| Göbel et al, 2021 [53] | “To examine in detail the clinical characteristics of headaches occurring after vaccination against COVID-19 with the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.” | Prospective observational cohort | “In 66.6% of the participants, headache occurs as a single episode. A bilateral location is indicated by 73.1% of the participants. This is most often found on the forehead (38.0%) and temples (32.1%). A pressing pain character is indicated by 49.2% and 40.7% report a dull pain character. The pain intensity is most often moderate (46.2%), severe (32.1%) or very severe (8.2%). The most common accompanying symptoms are fatigue (38.8%), exhaustion (25.7%) and muscle pain (23.4%).” |
| García-Azorín et al, 2021 [54] | To assess whether the existance of headache with higher probability of intracranial hemorrhage was linked. | Observational study with case-control design | The CVT-related clinical symptoms started earlier in patients with headache than in patients without headache. |
| Sharifian-Dorche et al, 2021 [55] | To systemically review the reported cases of cases of vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) and cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) following the COVID-19 vaccination. | Systematic Review | Two articles were found, which present 13 patients with VITT and CVST after Ad26.COV2 vaccine. Moreover, 12 articles, which present clinical features of 36 patients with VITT and CVST after the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine were examined. |
| Tahir et al, 2021 [56] |
To report a case of Bell's palsy and transverse myelitis secondary to the Johnson and Johnson COVID-19 vaccine. | Case reports | The MRI showed a long segment of increased signal throughout the spinal cord extending at least from C2 up to the thoracic spine, suggestive of transverse myelitis after rule out other causes, with a history of 10 days Johnson and Johnson COVID-19 post-vaccination. |
| Gao et al, 2021 [57] |
To report an exceedingly rare case of longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis (LETM) that occurred shortly after vaccination with the Moderna COVID-19 (mRNA-1273) vaccine. | Case reports | “C-spine MRI revealed extensive intramedullary hyperintensity in the cervical cord at the C2–C5 levels on T2-weighted images, and at the C3 level with T1 ring enhancement of the cervical cord.” |
| Hromić-Jahjefendić et al, 2023 [67] | The objectives of this systematic review and meta-analysis are to find out how often myocarditis occurs after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine, as well as the risk factors and clinical repercussions of this condition. | Systematic Review and Meta-analysis | Myocarditis is one of the potential complications of the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines in adolescents and young adults. “The causal relationship between vaccination and myocarditis has been difficult to establish, and further research is required.” |
| Lindo P, 2021 [82] |
To report on the national vaccine deployment programme assisted by The Health Ministry of Trinidad and Tobago expanded through the implementation of a One Shot and Done initiative for the rollout of the Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) covid19 vaccine. | News report | “The vaccine will be made available to prisoners and staff, healthcare workers, and frontline workers, in addition to residents in coastal and rural communities.” |
| https://www.paho.org/en/news/31-3-2021-trinidad-and-tobago-receives-first-covid-19-vaccines-through-covax-facility; 2021 [83] | To report on the first arrival of COVID-19 vaccines to Trinidad and Tobago. | News report | “(PAHO/WHO)- Today, 30 March, 2021, Trinidad and Tobago received 33,600 doses of COVID-19 vaccines through the COVAX Facility, a global effort between the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance Gavi, UNICEF, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) and the World Health Organization (WHO).” |
| Rafeek et al, 2023 [91] | “To assess Trinidad and Tobago dentists' vaccine acceptance, knowledge, attitude and practices regarding the COVID-19 pandemic.” | Cross-sectional study | 153 dentists completed questionnaires giving a 46.2% response rate with a 5.8% margin of error and a confidence level of 95%. 7.2% of the respondents worked at the university, 86.9% at private practice, and 5.9% at government health centres. |
| Motilal et al, 2023 [93] | “To explore the reasons for COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in Trinidad and Tobago.” | Qualitative study | From 25 participants' responses, the main themes for being vaccine-hesitant were inefficacy, fear, information inadequacy, mistrust, perceived susceptibility, religious hesitations, and herbal alternatives. Additionally, their motivations for receiving the vaccine in the future were surrounded by perceived susceptibility, themes of necessity, health benchmark, and assurance. |
| Gopaul et al, 2022 [94] | “This study examined the safety of this vaccine in terms of the systemic and local adverse events following immunization reported by healthcare worker recipients.” | Cross-sectional study | Among the 687 participants (female = 412; female = 275), prevalence of body pain, fever, chills, myalgia, nausea, headache, fatigue, malaise, and other systemic symptoms decreased significantly 48 h after given the second dose compared to the first dose. |
| Khan et al, 2023 [95] |
To discuss about the effectiveness and safety profile of each COVID-19 vaccine in pregnancy in Trinidad and Tobago. | Letter to the Editor | The Pfizer BioNTech vaccine was the only one approved by the Ministry of Health for use in the second and third trimesters. Lack of confidence in the vaccine attributed to little research of COVID-19 in pregnancy was the reason of vaccine hesitancy in the population of pregnant women in Trinidad and Tobago. |
|
https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/simulating-covid-19-vaccination-in-trinidad-and-tobago 2021 [96] |
To report on a simulation exercise to respond to the COVID-19 pandemy. | WHO news report | “Before the arrival of COVID-19 vaccines, Trinidad and Tobago used simulation exercises to prepare and train the health workforce for the roll-out. Simulation exercises help develop, assess and test the functional capabilities of emergency systems, procedures and mechanisms to respond to public health emergencies.” |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





