1. Introduction
Nowadays, resilience is acknowledged as an important field of study that covers a wide range of elements and facets (Cvetković, 2023; Goyal, 2019; Jaiye & Benjamine, 2021). This conceptual domain now includes societal and economic factors in addition to human characteristics (Tariq, Pathirage, & Fernando, 2021). Although it has been around over the previous 70–80 years, the resilience hypothesis has seen a resurgence, particularly in the recent two to three decades. Resilience theory’s main concern is with the qualities that people and systems have that allow them to withstand adverse events, such as natural and man-made disasters (Van Breda, 2001). As a result, resilience is now understood to encompass a wide range of ideas related to overcoming obstacles and effectively adjusting to one’s surroundings (McCubbin, 2001). Resilience is seen as a crucial quality in the modern world that aids in overcoming uncertainty and difficult difficulties. This is especially evident in the study of various system dynamics and equilibriums in the field of resource economics (Kennedy & Linnenluecke, 2022). Roughly speaking, resilience turns into an essential skill that permits prosperity despite adversity, in addition to survival. To put it succinctly, resilience has advanced beyond traditional methods and is now a crucial component for people as well as society (Cvetković, 2023). This idea is becoming more and more relevant when thinking about a variety of difficult problems and offers vital guidance for creating a stronger social and economic framework.
The term "resilience" was used originally in 1973, expanding its meaning to include not only the system’s durability but also its extraordinary capacity to adapt to a variety of disturbances and withstand changes (Assarkhaniki, Rajabifard, & Sabri, 2020). Conversely, when talking about the resilience of materials like steel, the focus is on how well they can hold their structure and shape in the face of outside pressures (Ma, Zhou, Deng, & Xu, 2023). With this discovery, a fuller understanding of systems as dynamic entities that actively regulate their dynamics while simultaneously preserving stability will be possible. Systems are known for their remarkable flexibility and resilience to a wide range of obstacles, as well as their capacity to recognize and absorb changes (Holling, 1973).
The multidimensionality of the resilience concept—which ranges from human resourcefulness, endurance, leaps and rebirth to elasticity and material resilience like that of steel—is one of its key features (Kabir, Hossain, & Haque, 2022; Parker, 2020). Diverse viewpoints on resilience are common, and they all add to our understanding of this intricate and all-encompassing idea. According to some authors (Cvetković, 2017), resilience may be defined more broadly as a measure of how well people and society adjust to changing conditions while seizing new possibilities. Furthermore, Foster (2007) provides an additional framework, characterizing regional resilience as the area’s capacity to anticipate, anticipate, and effectively respond to disruptions as well as recover from them. Resilience, for instance, might entail having the capacity to endure and adjust to unforeseen circumstances (Cvetković, Bošković, & Ocal, 2021; Hochrainer-Stigler et al., 2021). This may include people’s capacity to bounce back from hardship or trauma swiftly and take decisive action to get beyond obstacles. Resilience is fundamentally the capacity to adjust, bounce back, and maintain integrity, whether that integrity is material or spiritual (Bronfman et al., 2023).
A deeper understanding of resilience is made possible by this multifunctional approach, which also serves as a basis for investigating how human psychology, social dynamics, and material attributes interact to influence resilience in diverse settings. According to Perrings (1998), resilience is a crucial indicator of a system’s ability to tolerate strain and unforeseen difficulties while maintaining stability in a changing and unpredictable environment. This method offers a deeper knowledge of how various system components interact and adjust to unanticipated occurrences by focusing on the system’s capacity to retain its integrity and basic operations under stress. However, other writers (Mileti, 1999) stress the importance of the local component of disaster resilience, emphasizing that a community must be able to resist major natural occurrences with minimal loss or damage.
Global perspectives are used to characterize resilience at the worldwide level, especially when discussing the international plan for disaster risk reduction. According to UNIDDR (2009), resilience is the capacity of systems, communities, or societies that are subjected to risks to withstand, assimilate, and appropriately respond to such risks. The reconstruction of essential fundamental structures and functions is also implied by the global concept of resilience. On a global scale, resilience is regarded as essential to attaining stability and sustainability in communities (U-NISDR, 2009). The Law on Disaster Risk Reduction and Emergency Management of the Republic of Serbia (Official Gazette of the Republic of Serbia 87/18) defines resilience at the national level. According to this national definition, resilience represents the necessary ability of communities exposed to hazards to adequately respond to the challenges of various disasters.
The focus of community disaster resilience is on social groups’ abilities to recover from disasters and resume their pre-event functioning (Norris, Stevens, Pfefferbaum, Wyche, & Pfefferbaum, 2008). According to Maguire and Hagan (2007), it is distinguished by three main processes or characteristics that emerge in society during a disaster: the ability of social groupings to adapt to new conditions, recover quickly, and be resilient in the face of adversity. The diversity of persons within the community contributes significantly to this component since it fosters the creation of groups with differing degrees of resilience. It is important to stress that a variety of factors can influence how resilient social groupings are, such as sociodemographic traits and the accessibility of resources. Previous studies have shown that dealing with disasters is often more challenging for older persons, which can have a detrimental effect on their resilience (Fuchs & Thaler, 2018). In addition, a social community can be defined as a collection of individuals with varying traits who are bound together by social ties, sharing similar viewpoints, and engaging in group activities in certain settings (Ostadtaghizadeh, Ardalan, Paton, Jabbari, & Khankeh, 2015). To establish a resilient community, this definition places a strong emphasis on the community’s capacity for cooperation and participation in disaster risk reduction efforts.
Starting from an undetermined level of community (societal) resilience to disasters in Serbia, this paper aims to delve into the intricate dynamics of community disaster resilience within the context of Serbia. Also, the study aims to thoroughly investigate and comprehend the various aspects of resilience exhibited by communities in the face of disasters, with a specific focus on assessing how demographic and socioeconomic factors contribute to and shape this resilience. By examining the demographic and socio-economic conditions, the research seeks to uncover patterns, correlations and influences that play a crucial role in determining how communities respond and adapt to disasters in Serbia. Through this investigation, the paper aims to contribute valuable insights into the factors that enhance or hinder community disaster resilience.
1.1. Literature Review
In the global context, the analysis of community resilience to disasters can be divided into two key perspectives: objective and subjective methodologies (Béné et al., 2016). Objective approaches aim to quantify disaster resilience independently of individual perceptions. These approaches focus on measuring characteristics defined outside the community members, such as economic capabilities, assets, and other measurable variables. Most resilience assessment frameworks often use objective methods to analyze specific factors, such as income and property, which can be easily numerically expressed (Jones & Samman, 2016).
Community disaster resilience, as a key dimension, can be measured at different levels, including communities, families, and other social groups. The measure of community resilience depends on various coping capacities, such as planning, human resources, economic resources, and other factors (Buckle, 2006). These capacities play a significant role in preserving the social structure and functionality of society during and after catastrophic events. In the domain of disaster studies, research efforts are directed towards a deeper understanding of resilience through four key areas of interest (Zhou, Wang, Wan, & Jia, 2010): 1) resilience as a biophysical attribute; 2) resilience as a social attribute; 3) resilience of socio-ecological systems; and 4) the attribute of a specific geographical area. Additionally, it is possible to identify three distinct levels of community (social) resilience, each characterized by its specifics: 1) resilience manifested in resisting significant changes; 2) resilience expressed through effectively opposing minor marginal changes; and 3) resilience arising from openness and the ability to adapt to diverse challenges and changes in the environment (Dovers & Handmer, 1992; Walker, Holling, Carpenter, & Kinzig, 2004).
Examining community resilience to disasters represents a challenging process due to the complex interactions between people, communities, societies, and the environment. Currently, there are various conceptual frameworks proposed for measuring this concept (Adger, 2000; Tobin, 1999). Generally, most of these frameworks similarly conceptualize disaster resilience, focusing on similar factors that have the potential to reduce vulnerability and increase community resilience. These factors include economic resources, assets and skills, information and knowledge, support and support networks, access to services, and shared values within the community. However, the limitation of most of these frameworks is that they often focus attention only on a specific dimension of disaster resilience and do not give enough consideration to a broader understanding of this concept (Mayunga, 2007).
From the "DROP" model (Disaster Resilience of Place model), researchers (Cutter, Ash, & Emrich, 2014) constructed the Community Resilience Index (BRIC). The purpose of this index is to develop a standardized measure that consolidates various aspects of resilience. It focuses on creating a metric that can be reproduced, taking into account diverse dimensions of resilience. Alternatively, the BRIC (Community Resilience Index) considers the community as the fundamental unit of analysis, focusing on interpersonal interactions that occur in a specific geographical location (Bronfman et al., 2023; Cutter et al., 2014). This approach aims to comprehensively examine key aspects contributing to community resilience, with each of the mentioned dimensions considered as a crucial factor. Besides that, social resilience is analyzed through the community members’ interpersonal connections and cohesion, community capital explores levels of resources and support within the community, while economic resilience focuses on the ability to survive economic challenges.
The proposed framework of social resilience, known as the "5S," represents a comprehensive approach to assessing social resilience. This innovative approach takes into account key characteristics and indicators relevant to this area, allowing a deeper consideration of the key aspects of social resilience. It provides a solid foundation for analyzing and enhancing social resilience in various situations and circumstances. The proposed framework of social resilience consists of five sub-dimensions of social resilience, namely social structure, social capital, social mechanisms, social equity and diversity, and social beliefs, comprising 16 characteristics and corresponding 46 indicators (Saja, Teo, Goonetilleke, & Ziyath, 2018): a) social structure; b) social capital; c) social mechanisms/competencies/values; d) social equity and diversity; e) social beliefs/culture/faith. The resilience of social communities to disasters has become a crucial societal goal that attracts the attention of researchers and decision-makers in various sectors and scientific disciplines. A literature analysis has indicated several challenges that require attention, suggesting the significance of upcoming research (Cvetković, 2023): insufficient examination of the impact of social identity on building resilience in social communities; lack of consensus on the content and scope of the resilience concept, specific dimensions, and indicators of social community resilience, etc.
1.1.1. Income level
Regarding the impact of income on the level of community resilience to disasters, it has been found that socioeconomically disadvantaged families lack material resources, such as adequate nutritional care and materials that promote cognitive development (such as books and technology), as well as reduced expectations regarding the life chances of their children (Wagnild, 2003). The foundation of community resilience is built upon four key categories of adaptive capabilities: Economic Development, Social Capital, Information and Communication, and Community Competence (Liddell & Ferreira, 2019). In another study, it was found that poor households were less resilient and were more likely to fall back into poverty due to COVID-19, while the opposite was true for wealthier households with high socioeconomic status (Ur Rahman, Jian, Junrong, & Shafi, 2021). Income has already been identified as a significant indicator of adaptive capacity, responsible for reducing community resilience when responding to a natural disaster. It plays a crucial role in shaping how well a community can cope, recover, and adapt to environmental challenges, emphasizing the importance of addressing economic disparities in building effective disaster response strategies (Deria, Ghannad, & Lee, 2020).
When it comes to the impact of income on the community’s resilience to disasters, it has been determined that impoverished families lack material resources, such as adequate nutritional care and materials that stimulate cognitive development (such as books and technology), as well as reduced expectations regarding the life chances of their children (Wagnild, 2003). In another study, it was found that poor households were less resilient and were more likely to fall back into poverty due to COVID-19, while the opposite was true for wealthier households with high socioeconomic status (Ur Rahman et al., 2021). Income has already been identified as a significant indicator of adaptive capacity, responsible for reducing community resilience when responding to a natural disaster. It plays a crucial role in shaping how well a community can cope, recover, and adapt to environmental challenges, emphasizing the importance of addressing economic disparities in building effective disaster response strategies (Deria et al., 2020).
The steady income of families plays a crucial role in shaping the educational outcomes of children (Chevalier, Harmon, O’Sullivan, & Walker, 2013). This impact can be explained on several levels. Firstly, stable income allows families to provide for the basic needs of their children, such as quality nutrition, secure housing, and access to healthcare. These basic elements have a direct connection to the physical and mental development of children, which can impact their ability to learn and succeed in school. Additionally, a steady income enables families to invest in the education of their children. This includes purchasing educational materials, books, technology, and providing additional support, such as private lessons or extracurricular activities. On the other hand, families with low incomes often face financial uncertainties that can hinder a focus on education (Chevalier et al., 2013).
However, the vulnerability of individuals with lower socioeconomic status to the negative impacts of natural disasters is not limited to immediate consequences (Chevalier et al., 2013). In the response phase, the lack of financial resources often results in delayed or insufficient emergency aid, making it difficult for impoverished communities to cope with the immediate consequences of the disaster (Cannoodt, Mock, & Bucagu, 2012). This delayed response can contribute to an increase in casualties since essential services such as medical aid and evacuation may not be immediately available to those in need. In research conducted after Hurricane Katrina (Logan, 2006), researchers found that the lower economic strata of people suffered disproportionately greater consequences of a material nature, as a higher percentage of the community with lower incomes was located in areas that were flooded during the extraordinary event.
1.1.2. Employment status
Research conducted in China in 2018 (Cui, Han, & Wang, 2018) did not reveal a statistically significant correlation between employment status and the perceived societal resilience to earthquake-induced disasters. Based on the results of flood-related research (Cvetković, 2016), it can be concluded that employed citizens demonstrate greater awareness and readiness regarding floods compared to the unemployed. A significantly higher number of employed individuals know about floods compared to the unemployed. Furthermore, it can be observed that employed individuals are more familiar with safety procedures and express greater readiness for evacuation. In a study conducted at Yalova University in Turkey (Inal, Altıntaş, & Doğan, 2019), the relationship between general beliefs about disaster preparedness and various socio-demographic characteristics was examined, with a particular focus on the different impacts of employment. The overall score of general beliefs in disaster preparedness was statistically significantly associated with higher monthly income, higher employment status, previous experience with any disaster, and attendance of any disaster-related training. The results showed that participants with higher monthly income and better employment status have more positive beliefs about general disaster preparedness.
Then, in a subsequent study conducted in Tehran (Najafi, Ardalan, Akbarisari, Noorbala, & Jabbari, 2015), it was found that the level of monthly income, previous experience with disasters, place of residence, and occupation were significant factors significantly influencing the perception of disaster preparedness. On the other hand, no statistically significant correlation was found with gender, level of education, household size, type of house, homeownership, and the head of the household’s position. Additionally, in a study on household preparedness for disasters in Bangladesh (Tohan, Kabir, Hoque, & Roy, 2023), a low level of preparedness was identified, and major predictors of preparedness, such as gender, marital status, income level, previous disaster experience, loss of someone due to a disaster, presence of a member with special needs, homeownership, and the material from which the house is made, were identified.
Furthermore, in a study (Solomon, Bravo, Rubio-Stipec, & Canino, 1993) examining the family’s role in the mental health of victims, the worst outcomes were observed among single parents and parents in marital communities exposed to the impacts of disasters. Then, in one of the studies (Hung, 2017), an investigation covering heterosexual couples living in Florida was implemented. The research aimed to answer how decision-makers in the three-phase decision-making process in households prepare for hurricanes. Households making joint decisions throughout the decision-making process have significantly higher levels of preparedness compared to households where women make decisions independently throughout the process or where no one makes decisions throughout the process.
1.1.3. Gender
In research dedicated to analyzing the relationship between gender and resilience to various natural and man-made disasters, this topic emerges as an exceptionally current, challenging, and highly complex area of study (Combs et al., 2010; Drabek, 1969; Ikeda, 1995; Mano-Negrin & Sheaffer, 2004; Mehta, 2007; Mulilis, 1999; Myers, 1994; Norris, 1992; Rodríguez, Kennedy, Quarantelli, Ressler, & Dynes, 2009; Rüstemli & Karanci, 1999). The mentioned studies point towards a deeper understanding of the threat of natural disasters by women compared to men (Davidson & Freidenburg, 1996; Palm, 1995). Some researchers, within their investigations, highlight the more significant preparedness of the female gender concerning responding to natural disasters, especially in terms of knowledge about them (Mano-Negrin & Sheaffer, 2004; Tomio, Sato, Matsuda, Koga, & Mizumura, 2014).
Regarding men, researchers’ analyses (Able & Nelson, 1990) indicate that, in the context of disasters, they demonstrate a pronounced sense of responsibility regarding the commitment and maintenance of necessary supplies crucial for survival in disaster-induced situations. Additionally, men have shown a greater inclination towards taking preventive technical measures and using household protection means against potential natural disasters (Kabir et al., 2022; Szalay, Inn, Vilov, & Strohl, 1996). On the other hand, it can be emphasized that men often largely ignore warnings from relevant state authorities, particularly disregarding warnings from their spouses about natural disasters (Turner, Nigg, & Young, 1981).
1.1.3. Age
Regarding age, numerous studies from various fields have confirmed that older citizens exhibit significant readiness to respond to different disasters (Huerta & Horton, 1978; Melick & Logue, 1985; Murphy, 1994; Murrell & Norris, 1984). This underscores the considerable advantages and qualities of older individuals in various aspects of life. These longstanding experiences enrich their perspective, enabling them to analyze situations more quickly and make intelligent decisions. Providing accessibility and support in emergencies could significantly enhance their ability to respond effectively, simultaneously considering their physical needs and limitations (Durkin, Aroni, & Coulson, 1983; Johnson, Johnston, & Peters, 1989).
Enhancing resilience among older adults is promoted by prior life experiences, social networks, and spiritual beliefs (Timalsina & Songwathana, 2020). Elderly individuals in the United States exhibit notably lower levels of readiness for natural disasters compared to younger adults, with age, physical limitations, lower educational attainment, and income level being notable contributors (Al-Rousan, Rubenstein, & Wallace, 2014). Active and well-elderly individuals make a positive contribution to the resilience of communities during crises, indicating their potential as valuable assets for their communities (Cohen et al., 2016). Elderly survivors of Typhoon Haiyan exhibit resilience by demonstrating strength, engaging in self-regulating behaviour, and maintaining a positive mindset (Almazan et al., 2019). In post-disaster settings, individual resilience is adversely affected by factors such as age, health, and social conditions, while being female serves as a protective factor (Liddell & Ferreira, 2019).
1.1.4. Education
Engaging in educational initiatives, psychoeducational efforts, and providing parental guidance have the potential to encourage preparedness activities and may impact behaviour in the context of natural disasters (Sakurai & Sato, 2016). In the context of the relationship between education and disaster resilience, the findings of Drzewiecki, Wavering, Milbrath, Freeman, and Lin (2020) study indicated a greater adjusted prevalence odds ratio (POR) of resilience to natural hazard-induced disasters among adults with professional education, in contrast to those with no more than primary education. Feng, Hossain, and Paton (2018) discovered that enhancing disaster resilience within community settings can be achieved by tapping into the informal education derived from everyday activities.
In Thailand, education increases disaster preparedness primarily by influencing social capital and disaster risk perception, whereas this relationship is not observed in the Philippines (Hoffmann & Muttarak, 2017). Education contributes to fostering awareness of disaster safety and resilience from an early age, thereby enhancing community safety and resilience (Nifa, Abbas, Lin, & Othman). Preventive education and community capital are influential factors in disaster resilience, as illustrated in the Cohen-Harris Model of Urban Resilience which integrates efforts from families, organizations, and communities (Hamiel, Wolmer, Spirman, & Laor).
1.1.5. Marital status
Married people experience greater psychological well-being than those who are single, divorced, or widowed, largely because of the social connections and support they receive (Ross, 1995). Also, health status is influenced indirectly and in a non-specific manner by factors related to marriage, and a broad conceptual framework involving stress and social support serves as a basis for understanding these dynamics (Burman & Margolin, 1992). Besides that, Cotten (1999) found that individuals in marital unions exhibit superior mental and physical well-being compared to those who are not married.
Additionally, psychological distress is socially dispersed among and across the four marital status groups. Kim and Lee (2021) found that marital status influences the level of preparedness for bioterrorism, followed by age, education, perceived personal impact, perceived coping efficacy, perceived resilience, and perceived front-line preparedness. On the contrary, Cui et al. (2018) did not find evidence supporting the correlations between marital status and an individual’s perception of community resilience. Moreover, these findings are consistent with several other studies that have explored the level of resilience (Leykin, Lahad, Cohen, Goldberg, & Aharonson-Daniel, 2013; Pfefferbaum et al., 2016).
2. Methods
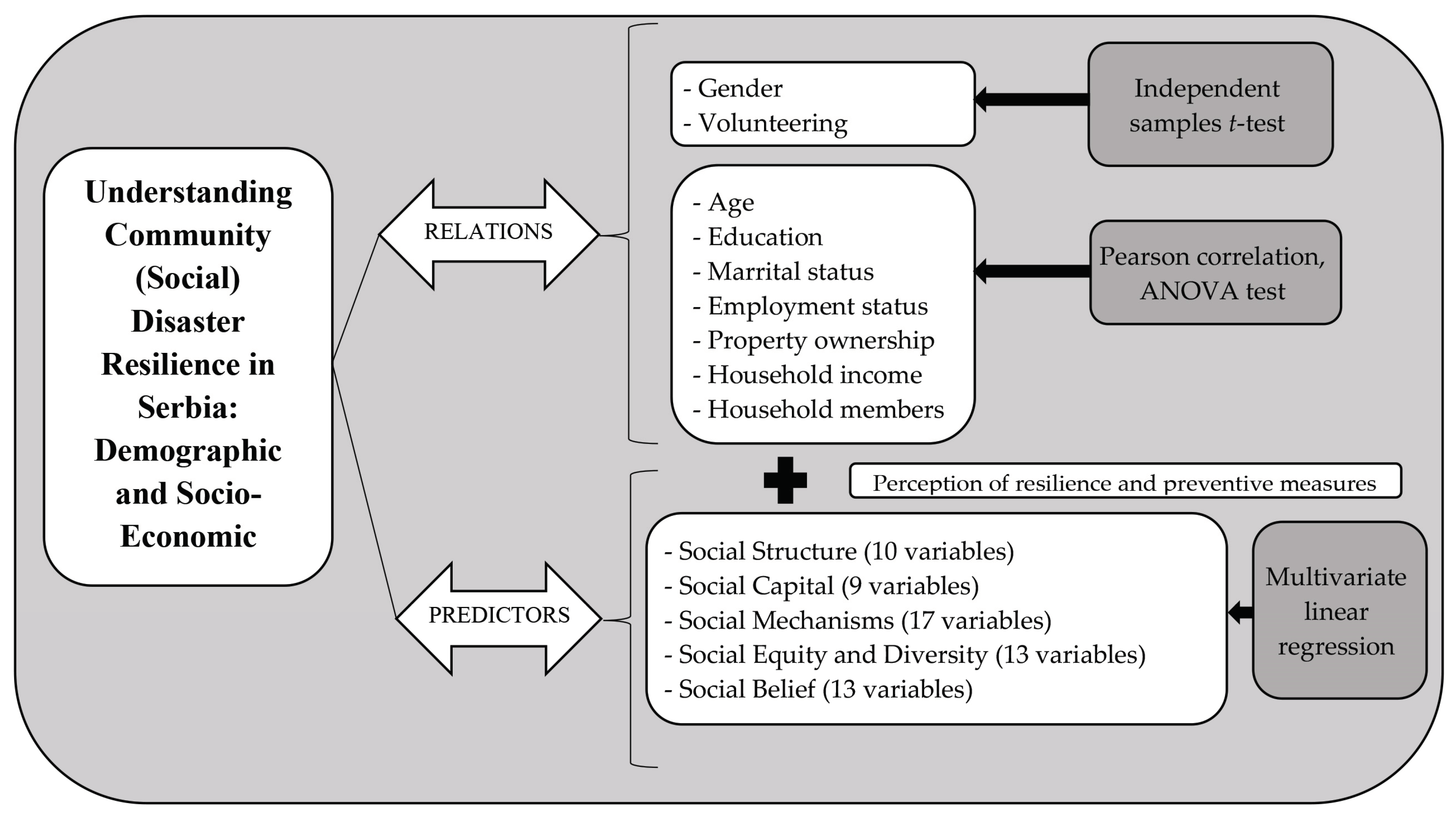
This research employed a comprehensive quantitative methods approach to investigate community (social) disaster resilience in Serbia, with a particular focus on demographic and socio-economic impacts (
Figure 1). The survey was carried out utilising a questionnaire distributed and subsequently collected online from 321 participants during January 2024. The participants were invited to engage with the online questionnaire in their native language through the implementation of the snowball sampling method. This method involved initial participants recruiting others within their network, creating a chain reaction that contributed to the diverse pool of respondents. The central hypothesis focuses on the extent to which age, education and gender may predict the community (social) disaster resilience in the Serbia model (social structure, social capital, social mechanisms, social equity and diversity, and social belief).
2.1. Study Area
The geographical expanse of the Republic of Serbia covers 88,499 square kilometres, positioning it at the intersection of central and south-eastern Europe within the Southern Pannonian Plain and the central Balkans. It shares borders with Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Montenegro to the southwest, and Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west (
Figure 2).
Between the 1970s and 2002, Serbia experienced approximately 5000 disasters and according to data from UNOCHA’s Reliefweb, floods were the most frequent disasters, with fifteen catastrophic floods occurring between 1988 and 2014 (Cvetković et al., 2021). From 2007 to 2016, Serbia witnessed around 20 disasters, resulting in 90 fatalities, 620 injuries, displacement of 1470 individuals, and material damage estimated at 2 million dollars (Cvetković, Öcal, & Ivanov, 2019). Serbia is situated in a region with moderate seismic activity, characterized by varying seismic intensity, frequency, and magnitude of earthquakes. The distribution of epicentres is irregular, posing challenges in identifying seismically active faults (Ocal, Cvetković, Baytiyeh, Tedim, & Zečević, 2020). Historically, stronger earthquakes (with intensities of VIII–IX) were documented in locations including Rudnik, Lazarevac, Juhor, Krupanj, Jagodina, and Vitina from 1900 to 1970. However, since 1970, only three moderate-intensity earthquakes have been recorded in Kopaonik (a mountain), Mionica, and Trstenik (Marovic et al., 2002). Referring to official data sourced from the Emergency Situations Department of Serbia, there was a 50% increase in the number of fires in 2017 compared to the corresponding period in the preceding year. Additionally, as per the records maintained by the Directorate for Fire-Rescue Units of the Sector for Emergency Situations, spanning from 2012 to 2022, Serbia witnessed 38,279 residential fires. Within these incidents, 665 individuals lost their lives, 1747 sustained injuries, and 2134 were successfully rescued (Cvetković et al., 2022a). For a comparative perspective over the years in the mentioned timeframe, the situation unfolded as follows (number of fires/deaths): 2012 (946/7), 2013 (836/6), 2014 (887/8), 2015 (827/5), 2016 (872/10), 2017 (899/18), 2018 (842/14), 2019 (796/10), 2020 (842/23), and 2021 (828/21) (V. M. Cvetković et al., 2022a). According to the National Strategy for Protection and Rescue ("Official Gazette of RS," No. 86/2011 of November 18, 2011), Serbia experienced around 134,686 fires from 2003 to 2011. Notably, in 2020, fires in housing units claimed the lives of 51 individuals across Serbia. The Ministry of Interior reported that fire and rescue services conducted over 4000 interventions, with more than 3000 specifically addressing fire incidents.
Figure 2.
Study area. Location of Serbia.
Figure 2.
Study area. Location of Serbia.
2.2. Socio-economic and demographic characteristics
The initial call to participate in an online survey was disseminated through social media platforms and distributed among the authors’ network and their connections. The respondents in this study, totalling 321 individuals, exhibit a diverse distribution across a range of socio-economic and demographic factors. In terms of gender, the sample comprises 32.7% male and 67.3% female participants. Age-wise, the distribution is as follows: 12.1% are up to 20 years old, 51.4% fall within the 20-30 age range, 12.1% are between 30-40 years old, another 12.1% are aged 40-50, and the remaining 12.1% are over 50. Educationally, the respondents vary widely: 7.1% completed primary school, 39.2% finished secondary school, 9.3% pursued higher education, 28.0% earned a bachelor’s degree, 14.6% achieved a master’s degree, and 1.5% attained a doctorate. Regarding marital status, 26.1% of respondents are single, 34.5% are in a relationship, 5.6% are engaged, 27.1% are married, and 6.5% are divorced. In terms of employment, 52.3% are employed, 39.2% are unemployed, and 8.4% are retired. Regarding ownership of property, 52.9% have personal ownership, 34.2% own property as a family member, and 12.7% rent their residence. Household income distribution is as follows: 17.8% earn less than the average, 50.5% have an average income of 700 EUR, and 29.9% earn above average. The number of household members is varied, with 0.9% having up to 1 member, 17.8% having up to 2 members, 66.4% having up to 5 members, and 15% having over 5 members. Volunteering is prevalent among 53.2% of respondents, while 46.8% do not engage in volunteer activities. This comprehensive overview offers valuable insights into the socio-economic and demographic composition of the sample, providing a nuanced understanding of the surveyed population’s characteristics (
Table 1).
2.3. Questionnaire Design
The study employed an adapted version of the ’5S’ social resilience framework (Saja et al., 2018), encompassing five sub-dimensions – social structure (10 variables), social capital (9 variables), social mechanisms (17 variables), social equity and diversity (13 variables), and social belief (13 variables). This customized framework includes 62 indicators, providing a thorough assessment of community (social) disaster resilience in the research context. The questionnaire examined citizens’ fundamental socio-economic and demographic characteristics, their attitudes towards the mentioned five sub-dimensions, as well as their engagement in preventive measures and their perception of resilience to various disasters.
A meticulously designed survey instrument was crafted, incorporating a combination of closed-ended queries and a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). The initial segment of the questionnaire was dedicated to capturing the socio-demographic profile of the participants, thereby delving into the social context and gender distribution among respondents. Following this, subsequent sections of the questionnaire delved into a myriad of topics, encompassing inquiries about social structure, social capital, social mechanisms, social equity, and social beliefs. This thoughtful approach aimed to comprehensively explore and analyze various facets of the social landscape, providing a nuanced understanding of the factors contributing to community (social) disaster resilience (
Appendix A).
We referred to various published survey methodologies (Alshehri, Rezgui, & Li, 2015; Bronfman et al., 2023; Drzewiecki et al., 2020; Leykin et al., 2013; Ma et al., 2023; Ostadtaghizadeh et al., 2015; Pfefferbaum et al., 2016; Qasim et al., 2016; Renschler et al., 2010; Saja et al., 2018; Tariq et al., 2021) and modified them to suit the context of community (social) disaster resilience in Serbia. A preliminary questionnaire test was carried out in Belgrade (central Serbia) in December 2023, involving 35 individuals, to assess the clarity and effectiveness of the questionnaire through online systems. Our study adhered to the principles outlined in the Helsinki Declaration, which provides guidelines for socio-medical research involving human subjects. Participants gave informed consent before participating in the study. The research protocol received approval from the Scientific-Professional Society for Disaster Risk Management’s scientific research group review board, ID - 01012024.
2.4. Analyses
To explore the relationship between predictors and community (social) disaster resilience in Serbia, with a particular focus on demographic and socio-economic impacts, statistical methods including t-tests, one-way ANOVA, Pearson’s correlation, and multivariate linear regression were employed. As the initial homogeneity test for variance indicated a violation of the assumption of homogenous variance, the results from two tests—Welsh and Brown–Forsythe—that are robust to the violation of this assumption were considered. The preliminary analysis revealed the application of the same test. All tests were two-tailed, with a significance level set at p < 0.05. The statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS statistics (IBM SPSS Statistics, Version 26, New York, NY, USA). The internal consistency of Likert scales for the Social Structure Subscale (10 variables) is good with a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.81, Social Capital Subscale (9 variables) 0.84, Social Mechanisms Subscale (17 variables) 0.85, Social Equity Subsale (13 variables) 0.87, and Social Belief Subscale (13 variables) 0.87.
3. Results
The study’s findings are presented in four dimensions: predictors of the community (social) disaster resilience; perception of preventive measures and disaster resilience; community (social) disaster resilience framework (social structure, capital, mechanisms, equality and belief); and influences of demographic and socioeconomic factors on the community (social) disaster resilience framework.
3.1. The predictors of community (social) disaster resilience (social structure, social capital, social mechanisms, social equity-diversity and social belief)
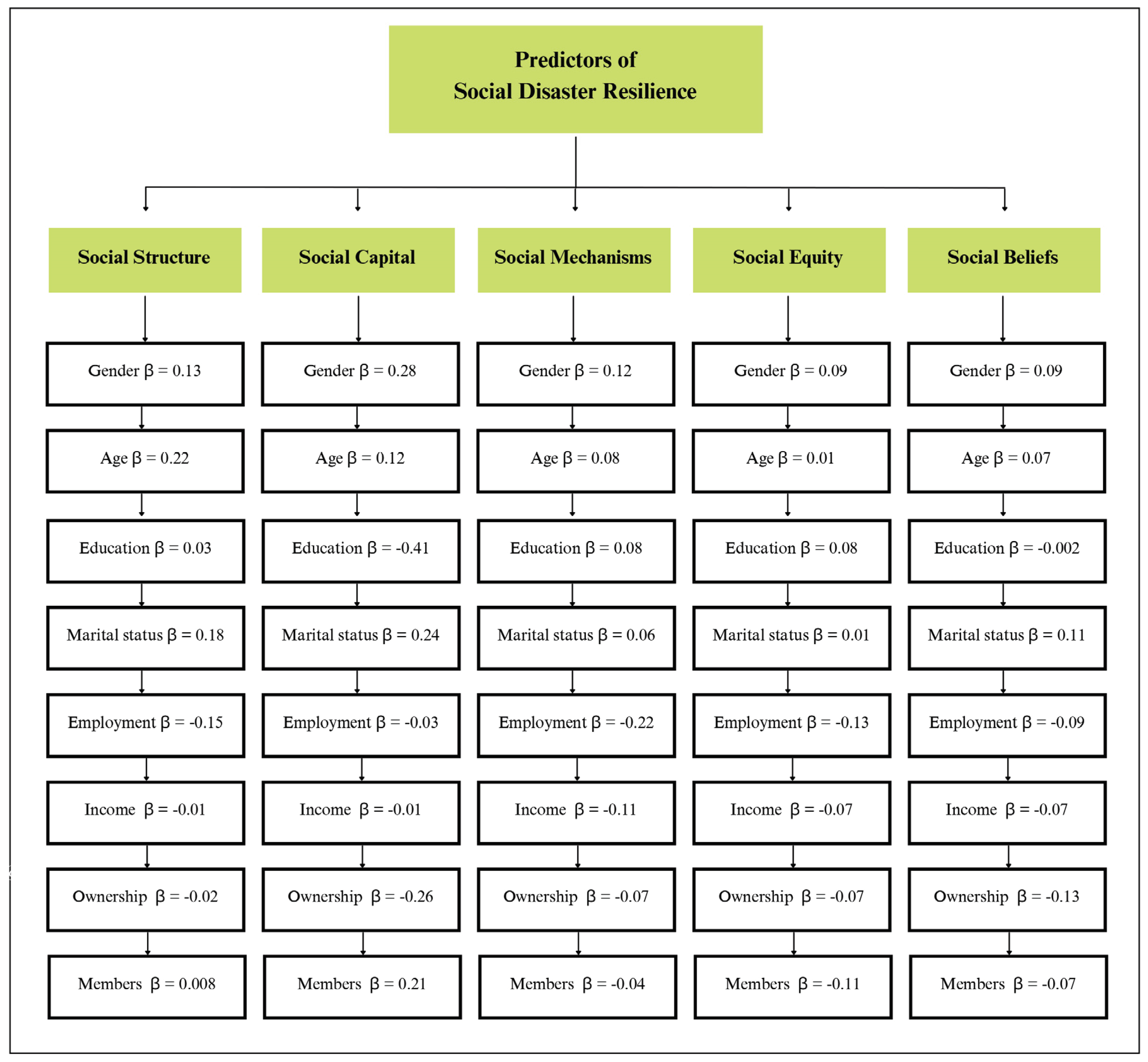
Firstly, the central hypothesis was tested, which aimed to determine whether gender, age, and educational level could predict community (social) disaster resilience (social structure, social capital, social mechanisms, social equity and social belief) in Serbia. Multivariate regression analysis was used to determine the extent to which five scores of the subscales (social structure, social capital, social mechanisms, social equity and social belief) were associated with eight demographic and socio-economic variables: gender, age, education level, marital status, employment status, monthly income, property ownership, household members (
Figure 3). Analyses showed that the assumptions of normality, linearity, multicollinearity and homogeneity of variance had not been violated.
The results of the multivariate regressions for the social structure subscale show that the most significant predictor is age (
β = 0.22), explaining 3.61% of the variance in social structure. This is followed by marital status (
β = 0.18, 2.25%), employment status (
β = 0.15, 1.69%), and gender (
β = 0.13, 1.44%). The remaining variables (e.g., education level, income, property ownership, and household members) were not significantly affected by social structure. This model (
R2 = 0.09, Adj.
R2 = 0.07,
F = 4.22,
t = 21.5,
p < 0.01) with all mentioned independent variables explains the 7% variance of social structure (
Table 2).
Additional analyses revealed that the most significant predictor of social capital subscale was education (
β = −0.41), explaining 15.21% of the variance in social capital. This is followed by gender (
β = 0.28, 6.76%), property ownership (
β = −0.26, 6.25%), marital status (
β = 0.24, 4.41%), and number of household members (
β = 0.21, 4.01%), and age (
β = 0.27, 1.01%). The monthly income was not significantly affected by social capital. This model (
R2 = 0.30, Adj.
R2 = 0.28,
F = 17.13,
t = 28.58,
p < 0.01) with all mentioned independent variables explains the 28% variance of social capital (
Table 2).
Regarding social mechanisms, analyses revealed that the most significant predictor was employment status (
β = 0.41), explaining 4.84% of the variance in social mechanisms. This is followed by gender (
β = 0.12, 1.22%), and income level (
β = −0.11, 1.19%). The remaining variables were not significantly affected by social mechanisms. This model (
R2 = 0.11, Adj.
R2 = 0.08,
F = 4.79,
t = 24.95,
p < 0.01) with all mentioned independent variables explains the 8% variance of social mechanisms (
Table 2).
Further analyses revealed that the most significant predictor of social equity and diversity subscale was employment status (
β = 0.13), explaining 1.21% of the variance in social equity and diversity. This is followed by a number of household members (
β = 0.11, 1.02%). The remaining variables were not significantly affected by social equity and diversity. This model (
R2 = 0.06, Adj.
R2 = 0.04,
F = 2.70,
t = 24.86,
p < 0.01) with all mentioned independent variables explains the 4% variance of social equity and diversity (
Table 2).
Furthermore, analyses revealed that the most significant predictor of the social beliefs subscale was property ownership (
β = −0.13), explaining 1.39% of the variance in social beliefs. The remaining variables were not significantly affected by social beliefs. This model (
R2 = 0.06, Adj.
R2 = 0.03,
F = 2.59,
t = 26.18,
p < 0.01) with all mentioned independent variables explains the 3% variance of social beliefs (
Table 2).
Figure 3.
The predictors of community (social) disaster resilience.
Figure 3.
The predictors of community (social) disaster resilience.
3.2. Perception of preventive measures and disaster resilience
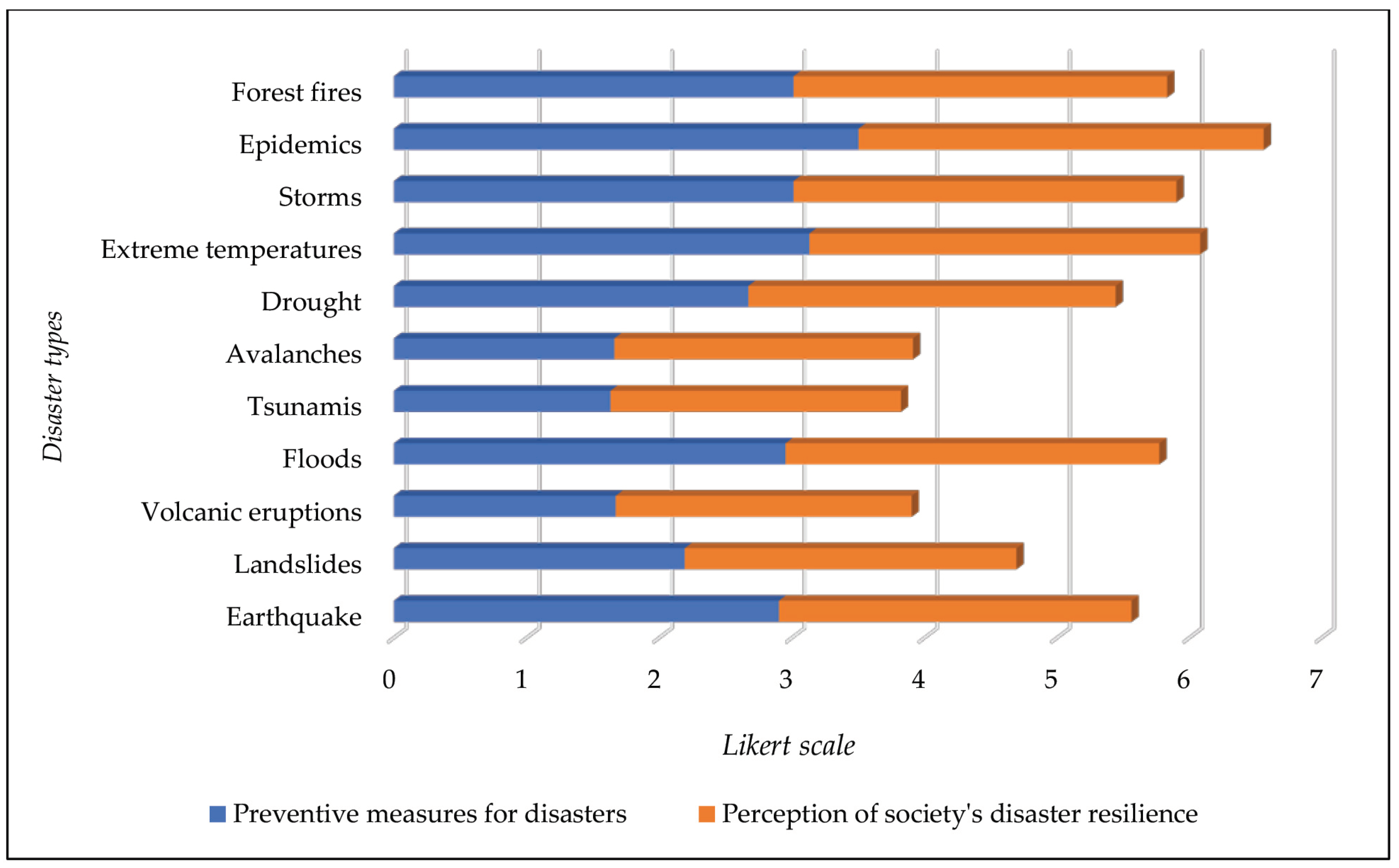
The following results present scale ratings for disaster preventive measures and disaster resilience levels, assessed on a scale ranging from 1 (very low) to 5 (very high), based on responses from a total of 321 participants. Regarding that, participants perceive a relatively high level of preventive measures (M = 3.50), indicating a strong awareness and proactive approach toward epidemic-related disasters. The perception of society’s resilience (M = 3.06) remains positive but slightly lower than preventive measures. On the other side, respondents express a notable emphasis on preventive measures (M = 3.13) for disasters related to extreme temperatures. The perception of society’s resilience (M = 2.95) is also relatively high, suggesting confidence in dealing with temperature-related challenges. For storms, participants show a moderate focus on preventive measures (M = 3.01). The perception of society’s resilience (M = 2.89) is in line with the preventive measures, indicating a balanced perspective on dealing with storm-related disasters.
Similar to storms, respondents demonstrate a moderate emphasis on preventive measures (M = 3.01) for forest fires. The perception of society’s resilience (M = 2.82) is slightly lower but still suggests a reasonable level of confidence. For floods, participants prioritize preventive measures (M = 2.95), and the perception of society’s resilience (M = 2.82) aligns closely. This indicates a proactive stance and confidence in managing flood-related disasters. The focus on preventive measures (M = 2.67) for drought is moderate, and the perception of society’s resilience (M = 2.77) is in a similar range. This suggests a balanced approach to addressing challenges related to drought. For earthquakes, preventive measures (M = 2.90) show a moderate emphasis, and the perception of society’s resilience (M = 2.66) aligns closely. This indicates a cautious but relatively confident approach to earthquake-related disasters.
On the other side, participants express a relatively lower emphasis on preventive measures for tsunamis (M = 1.63) and avalanches (M = 1.66). Also, the perception of society’s resilience for tsunamis (M = 2.19) and avalanches (M = 2.25) is slightly higher but remains relatively lower compared to other disaster types such as floods. For landslides, preventive measures (M = 2.19) are lower, and the perception of society’s resilience (M = 2.50) aligns with this trend. This suggests a less proactive stance toward landslide-related disasters. On the end, participants assign the lowest priority to preventive measures (M = 1.67) for volcanic eruptions, and the perception of society’s resilience (M = 2.23) is also relatively lower. This indicates a lower level of perceived preparedness for volcanic eruption-related disasters.
Further analysis showed that preventive measures are most commonly taken in the face of the hazards of epidemics (M = 3.50), extreme temperatures (M = 3.13), and storms (M = 3.01). This indicates a high level of awareness and a proactive approach to risks associated with epidemics, extreme temperatures, and storms.
The perception of society’s resilience is highest in the face of the hazards of epidemics (M = 3.06), followed by extreme temperatures (M = 2.95), and drought (M = 2.77). Respondents express a relatively high level of confidence in society’s ability to cope with epidemics, extreme temperatures, and drought (
Table 3 and
Figure 4).
On the other hand, the hazards of volcanic eruptions (M = 1.67), landslides (M = 2.19), and tsunamis (M = 1.63) show lower priorities in taking preventive measures, and the perception of society’s resilience is also lower in these cases. This indicates the need for additional efforts in raising awareness and preparedness for these specific types of hazards. This analysis reveals variations in the approach to taking preventive measures and the perception of society’s resilience depending on the type of natural hazard. Identifying these differences can serve as a basis for further planning and implementing interventions to enhance preventive strategies and strengthen overall societal resilience to various hazards (
Table 3 and
Figure 4).
3.3. Community (social) disaster resilience framework (social structure, capital, mechanisms, equality and belief)
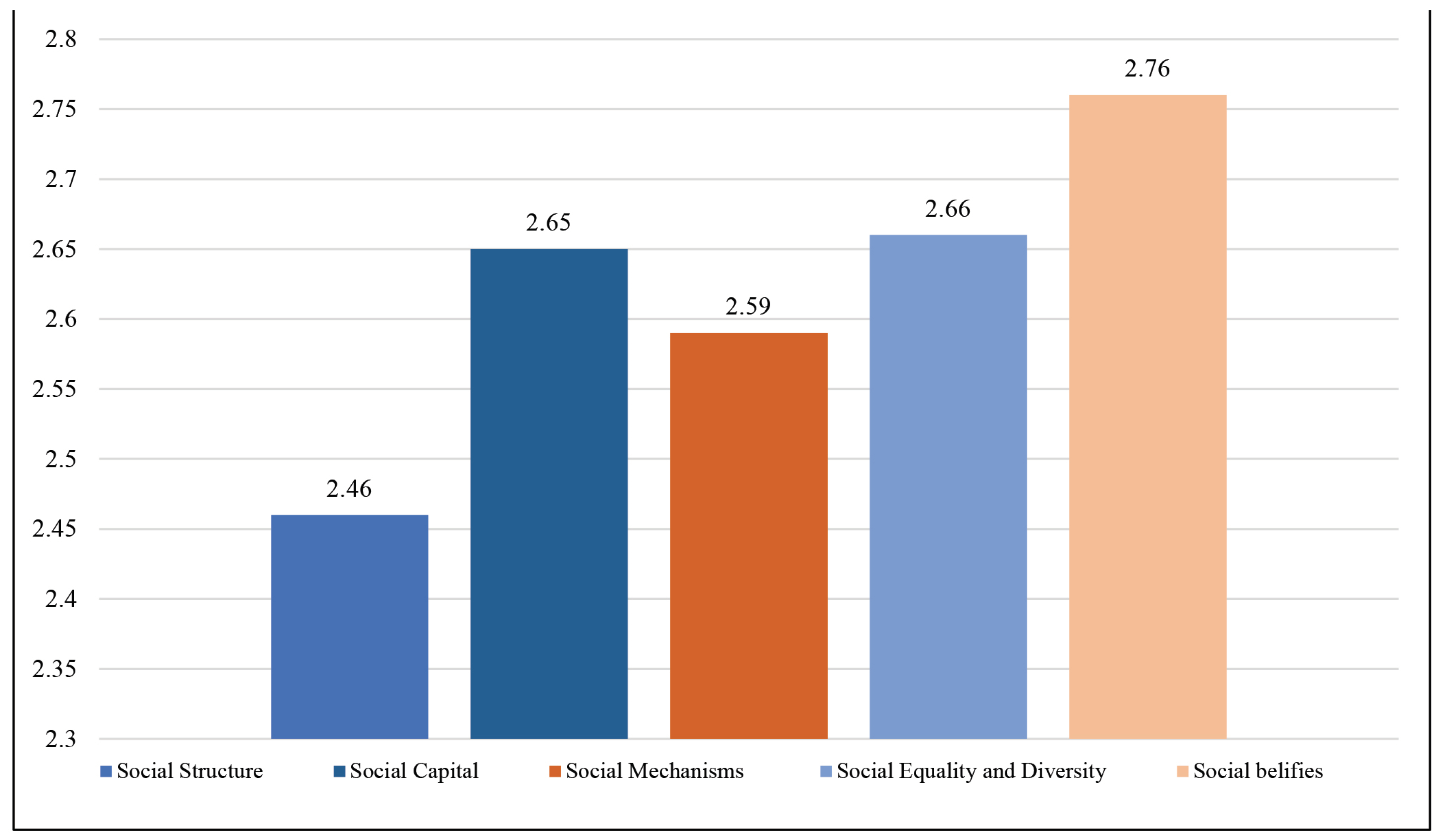
In the continuation of the research on social resilience to disasters, participants were asked to objectively assess various attitudes regarding key dimensions of society, including social structure, capital, mechanisms, equality, and beliefs. The obtained attitude scores reflect their perceptions towards these crucial aspects that significantly influence the preparation and response to disasters, consequently impacting the societal resilience to disasters in Serbia. The obtained results of mean values for subscales indicate that participants gave the highest ratings to beliefs within the social beliefs category (M = 2.76), while the lowest values were recorded in the social structure category (M = 2.46). Following this, the ratings for social equity and diversity (M = 2.66), social capital (M = 2.65), and social mechanisms (M = 2.59) are next (
Figure 5).
About the assessment of social structure (M = 2.46), 10 attitudes were analyzed. According to the obtained results, the development of response services in disasters by different first responders received the highest rating (M = 2.93). Such a rating may indicate a level of trust in the work of such services and their readiness to assist in disasters. The second-rated attitude (M = 2.81) pertains to the level of development of leadership in the community. Participants indicate a positive attitude towards the quality of leadership within the community, which could have an impact on effective management in various disasters. In the third place, the collaboration of local authorities with different entities relevant to preventive measures in disasters was evaluated (M = 2.61) (
Table 4).
On the contrary, the least-rated attitudes were the development of financial resources for disaster management purposes (M = 2.24), the development of technological resources for disaster management purposes (M = 2.34), and the level of development of human resources for disaster management purposes (M = 2.37). Participants believe that there is room for improvement in financial resources for protection and rescue, indicating a lack of such funds and effective financial strategies for disaster management. Additionally, there is a clear emphasis on the need to enhance technological resources in all phases of disaster management. Moreover, although a slightly higher rating was recorded, it also points to the need for improvement in the development of human resources for preparation, mitigation, response, and recovery from disasters. Certainly, this may involve improving human resource management policies regarding additional hiring of skilled personnel, training, and further development (
Table 4).
The analysis of attitudes regarding social structure shows that participants have a positive attitude towards the development of response services and leadership in the community while recognizing the need for improvement in financial, technological, and human resources. Also, the identified mean values indicate an overall neutral stance of the community towards issues of disaster preparedness and response.
Table 4.
Results of the survey on participants’ attitudes towards social structure, capital, mechanisms, equality, and belief.
Table 4.
Results of the survey on participants’ attitudes towards social structure, capital, mechanisms, equality, and belief.
| |
Attitudes |
M (SD) |
Total |
| SOCIAL STRUCTURE |
Organization and structuring of the local community for disaster response |
2.51 (1.08) |
2.46 (0.94) |
| Access to essential services such as health, education, and social assistance during disasters |
2.62 (1.14) |
| Quality of regulatory governance in disaster management |
2.54 (1.11) |
| Quality of risk assessment and developed plans for protection and rescue |
2.50 (1.16) |
| Level of development of human resources in society for protection and rescue |
2.37 (1.05) |
| Level of development of financial resources in society for protection and rescue |
2.24 (1.12) |
| Level of development of technological resources in society for protection and rescue |
2.34 (1.00) |
| Collaboration of local authorities with all relevant entities in designing preventive measures |
2.61 (1.08) |
| Development of response services in disasters - police, firefighting and rescue units, civil protection, etc. |
2.93 (1.13) |
| Developed leadership in the community |
2.81 (1.07) |
| SOCIAL CAPITAL |
Level of mutual trust and support within the community |
2.88 (1.11) |
2.65 (0.93) |
| Existence and strength of social networks and connections |
2.80 (1.11) |
| Participation in volunteer activities and community projects |
2.47 (1.03) |
| Regular dialogue and collaboration between local communities and authorities |
2.48 (1.08) |
| Involvement of different social groups in decision-making and planning during disasters |
2.53 (1.07) |
| The existence of local initiatives for disaster preparedness involving various socioeconomic groups |
2.42 (1.09) |
| Existence and strength of economic cooperation between different socio-economic groups. |
2.58 (1.14) |
| Level of interaction and collaboration with other communities, organizations, or businesses |
3.10 (1.22) |
| Strength of family ties and interactions within the community |
2.43 (1.17) |
| SOCIAL MECHANISMS |
Education and training for emergencies |
2.66 (1.18) |
2.59 (0.95) |
| Understanding and respecting cultural diversity |
2.67 (1.17) |
| Level of personal and collective responsibility towards community resilience and safety in disasters |
2.44 (1.08) |
| Community preparedness for disasters |
2.48 (1.12) |
| Household preparedness for disasters |
2.39 (1.12) |
| Perception of disaster risks |
2.40 (1.14) |
| Implementation of campaigns to enhance disaster preparedness |
2.46 (1.15) |
| Application of special measures to protect critical infrastructure |
2.47 (1.13) |
| Citizen awareness of disaster risks |
2.48 (1.20) |
| Capability for rapid evacuation and the existence of shelters |
2.50 () |
| The ability for prompt decision-making in relevant institutions without bureaucratic complications |
2.63 (1.13) |
| Active community involvement in the implementation of protection and preparedness measures |
2.81 (1.07) |
| Level of faith and optimism in the community’s ability to face disasters |
2.70 (1.03) |
| Level of flexibility and adaptability in dealing with unforeseen situations. |
2.72 (1.18) |
| Collective willingness to learn from previous disasters and improve future responses |
2.59 (1.15) |
| Effectiveness of early warning and people’s notification systems |
2.62 (1.21) |
| Development of disaster insurance |
2.71 (1.16) |
|
SOCIAL EQUALITYANDDIVERSITY
|
Access to resources and services without discrimination |
2.76 (1.11) |
2.66 (0.95) |
| Measures to protect and promote the rights of minority groups |
2.55 (1.05) |
| Community readiness to address social injustices |
2.85 (1.16) |
| Level of availability and access to key resources (water, food, shelter) |
2.92 (1.18) |
| Access to medical services and emergency interventions regardless of socioeconomic status |
2.71 (1.04) |
| The extent of social aid and support available to different groups in the community during disasters |
2.65 (1.04) |
| Presence and active participation of various social groups in planning and implementing measures |
2.72 (1.14) |
| Existence of programs targeting specific needs of vulnerable groups, such as the elderly, etc. |
2.39 (1.16) |
| Availability of personalized emergency plans for individuals with special needs. |
2.63 (1.13) |
| Access to transportation and evacuation that suits different levels of mobility and needs. |
2.59 (1.09) |
| Openness and adaptation of communication strategies for different linguistic and cultural communities |
2.58 (1.09) |
| Involvement of various social groups in planning, decision-making, and implementation measures |
2.54 (1.20) |
| Justice in access and participation in local disaster management bodies |
2.58 (1.09) |
|
SOCIAL BELIEFS
|
Trust in the work of social institutions and services during disasters |
2.45 (1.08) |
2.76 (0.91) |
| Level of development of disaster resilience culture |
3.03 (1.13) |
| Significance of cultural and religious values in the life of the community |
2.81 (1.06) |
| Openness to dialogue and understanding between different cultural and religious groups |
2.92 (1.16) |
| Participation in traditional and religious rituals that strengthen collective identity |
2.92 (1.21) |
| Adherence to traditional social norms and values in the community |
2.83 (1.20) |
| Level of individual involvement in local cultural activities and communal events |
2.93 (1.21) |
| Respect for and preservation of local customs and traditions during and after disasters |
2.94 (1.19) |
| Intensity and regularity of community participation in religious ceremonies and rituals |
2.83 (1.20) |
| Influence of religious leaders and institutions on decision-making in the community |
2.64 (1.07) |
| Intensity and regularity of community participation in religious ceremonies and rituals |
3.03 (1.14) |
| Activities of religious institutions related to disaster preparedness and emergencies |
2.72 (1.23) |
| Local culture and tradition shape the interpretation of disasters |
2.80 (1.21) |
Through further analysis, participants’ attitudes towards social capital (M = 2.65) were examined, encompassing 9 attitudes. The obtained results indicate that the highest-rated attitude pertains to the “Level of mutual trust and support within the community” (M = 2.88). Such a result suggests a high level of mutual trust and support within the community, indicating a prerequisite for strong interpersonal bonds and a positive social environment. In the second place, participants rated the “Existence and strength of social networks and connections” (M = 2.80) highly. This aspect, with a high rating, points to the existence of strong social networks, reflecting a robust interconnectedness among community members. In the third place, the “Level of interaction and collaboration with other communities, organizations, or businesses” (M = 3.10) was rated. The obtained value reflects a high degree of interaction and collaboration with other communities, organizations, or businesses, which is significant for broader social connectivity (
Table 4).
Conversely, the least-rated aspect concerns the “Existence of local initiatives for disaster preparedness involving various socio-economic groups” (M = 2.42). The obtained result indicates that participants hold a more negative attitude towards the existence of local initiatives for disaster preparedness that involve various socio-economic groups. Then, the second-lowest-rated attitude pertains to “Participation in volunteer activities and community projects” (M = 2.47). This value unequivocally suggests that participants perceive a lower level of engagement in volunteer activities and various community projects. Of course, this may indicate the need for further encouragement of greater involvement in various volunteer activities and initiatives. In the third place, the least-rated attitude concerns the “Strength of family ties and interactions within the community” (M = 2.43). Therefore, the strength of family ties and interactions within the community is at a lower level, which could negatively impact society’s resilience to disasters (
Table 4).
Overall, the ratings show that participants perceive a high level of mutual trust and support, strong social networks and connections, and a high degree of interaction and collaboration with other communities. On the other hand, volunteer activities and projects received lower ratings, indicating potential room for improvement in encouraging community involvement. Mean values suggest a generally neutral stance towards dialogue with authorities, involvement of different social groups in decision-making during disasters, and the existence of local initiatives for disaster preparedness involving various socio-economic groups.
Analysis of the survey results on participants’ attitudes towards social mechanisms (M = 2.59) indicates that the highest-rated attitude is “Active community involvement in the implementation of disaster protection and preparedness measures” (M = 2.81). Such a value reflects the active engagement of the community in implementing protective and preparatory measures for disasters. The high rating suggests a positive attitude towards the active role of the community in enhancing resilience and safety. In the second place, the “Level of flexibility and adaptability in dealing with unforeseen situations” (M = 2.72) is rated. Participants highlight the community’s high adaptability to unforeseen situations, which can be crucial for effective responses in disasters. With the highest rating, in the third place, the "Development of disaster insurance" (M = 2.71) is assessed. Recognizing the importance of insurance indicates an awareness of the necessity of financial protection in disasters (
Table 4).
On the other hand, the lowest-rated aspect is "Household preparedness for disasters" (M = 2.39). Such a value suggests and indicates lower perceptions of household readiness to cope with disasters. For these reasons, continuous efforts are needed to strengthen and improve household preparedness measures for disasters. The second-lowest-rated attitude is “Perception of disaster risks” (M = 2.40). The result indicates lower levels of perception of disaster risks, emphasizing the need to increase awareness of potential dangers to enhance overall preparedness. Additionally, a lower level of citizen awareness of disaster risks (M = 2.48) is identified. This rating suggests that citizens may not have a sufficient level of awareness of potential disaster risks (
Table 4).
The obtained high values for active community involvement, flexibility, adaptability, and the development of disaster insurance indicate a positive attitude towards specific social mechanisms. Conversely, low ratings for household preparedness, perception of risks, and citizen awareness suggest the need for a stronger focus on these aspects to improve overall community preparedness. Mean values also suggest a neutral stance towards education, cultural diversity, and citizen awareness of risks, indicating areas for further reflection and improvement.
Further analysis of the survey results regarding participants’ attitudes towards social equity and diversity (M = 2.66) reveals that the highest-rated attitude is related to the “Level of availability and access to key resources (water, food, shelter)” (M = 2.92). The obtained value indicates the recognition of the importance of providing resources such as food and water for all community members during disasters. The second-rated attitude pertains to “Community readiness to address social injustices” (M = 2.85). This rating indicates a high level of community readiness to confront social injustices during disasters, implying an awareness of the need for an adequate response to social challenges before, during, and after disasters. The third-rated attitude is related to "Access to resources and services without discrimination" (M = 2.76). Participants demonstrate an awareness and positive attitude towards access to resources and services without discrimination. All of this unequivocally suggests the importance of equal access for everyone, regardless of specific demographic and socio-economic characteristics (
Table 4).
In contrast, the least-rated attitudes are related to the "Existence of programs targeting specific needs of vulnerable groups, such as the elderly, etc." (M = 2.39). This value indicates significant challenges in recognizing and addressing the specific needs of vulnerable groups, such as the elderly and people with disabilities. Therefore, there is a need to work on improving access to support for such groups during disasters. In the second place, the attitude related to “Measures to protect and promote the rights of minority groups” (M = 2.55) is rated. The score for this attitude indicates challenges in implementing measures to protect and promote the rights of minority groups during disasters. Hence, additional steps need to be considered to ensure adequate protection of the rights of minority groups during disasters. Finally, the third least-rated attitude is related to the “Involvement of various social groups in planning, decision-making, and implementation measures” (M = 2.54). This value suggests a need for improvement in involving different social groups in planning, decision-making, and implementing measures during disasters. It may also indicate the need for greater inclusivity in decision-making processes (
Table 4).
Overall, high scores for the availability of key resources and community readiness to address social injustices suggest a positive attitude towards aspects of equality and diversity. On the other hand, low scores for programs targeting the specific needs of vulnerable groups, protection of minority rights, and the involvement of different social groups in planning indicate the need for improvement in these areas to ensure a fair and inclusive response to disasters.
In the end, attitudes regarding social beliefs were also examined (M = 2.76), and it was found that the highest recorded value pertained to the level of development of disaster resilience culture (M = 3.03). This may indicate a high level of development of a culture resilient to disasters, as well as a positive attitude towards the development of community awareness and practices related to disaster preparedness and response. In second place is the assessment of the attitude regarding participation in traditional and religious rituals that strengthen collective identity (M = 2.92). The obtained result suggests significant participation in traditional and religious rituals that enhance collective identity. Therefore, there is a positive inclination toward preserving and strengthening the collective identity through traditional and religious practices. In the third place is the assessment of the attitude regarding the intensity and regularity of community participation in religious ceremonies and rituals (M = 3.03). Hence, there is a positive attitude toward the community’s engagement in religious ceremonies and rituals.
In contrast, the least rated values are related to the attitude concerning trust in the work of social institutions and services during disasters (M = 2.45). It can be said that there are certain challenges in trusting the work of social institutions and services during disasters. This may suggest the need to enhance trust in social institutions during catastrophes. Following this, there is an assessment of the attitude related to the influence of religious leaders and institutions on decision-making in the community (M = 2.64). This value indicates the limited influence of religious leaders and institutions on decision-making in the community. Certainly, this may suggest a lower level of faith in religious authorities in the decision-making process during disasters. Finally, in the third place, there is an assessment of the attitude concerning the activities of religious institutions related to disaster preparedness and emergencies (M = 2.72). This value indicates challenges in the activities of religious institutions related to disaster preparedness. It suggests the need for a stronger focus by religious institutions on disaster preparedness.
High ratings for attitudes such as the development of a culture resilient to disasters, participation in traditional and religious rituals, and regular involvement in religious ceremonies and rituals indicate a positive orientation toward tradition, faith, and culture. On the other hand, challenges in trust towards social institutions during disasters, limited influence of religious leaders in decision-making, and the need to improve the activities of religious institutions related to disaster preparedness suggest areas that require additional attention and improvement to enhance society’s resilience to disasters.
3.4. Influences of demographic and socioeconomic factors on the community (social) disaster resilience framework
One-way ANOVA results showed the correlation between education status and the following variables: social structure (
p = 0.032); social capital (
p = 0.000); social mechanisms (
p = 0.040); social equity and diversity (
p = 0.039); preventive measures (
p = 0.000); and disaster resilience (
p = 0.000). No statistically significant correlation was found with other variables (
Table 5).
Further analyses revealed that respondents with a secondary school degree provided higher scores for social structure (M = 2.62; SD = 1.06) compared to those with a university degree (M = 2.30; SD = 0.80). Also, respondents with a secondary school degree provided higher scores for social mechanisms (M = 2.77; SD = 1.03) compared to those with a university degree (M = 2.44; SD = 0.85). And, the respondents with a secondary school degree provided higher scores for social equity and diversity (M = 2.80; SD = 1.11) compared to those with a university degree (M = 2.25; SD = 0.59). It can be said that the findings indicate that respondents with a secondary school degree consistently provided higher scores across dimensions, including social structure, social mechanisms, and social equity and diversity, compared to those with a university degree.
On the other side, the findings indicate that respondents with a university degree provided higher scores for social capital (M = 2.96; SD = 0.82) compared to those respondents with a secondary school degree (M = 2.17; SD = 0.79). Moreover, respondents with a university degree provided higher scores for preventive measures (M = 2.77; SD = 0.86) compared to those respondents with a secondary school degree (M = 2.28; SD = 0.86). Similarly, respondents with a university degree provided higher scores for disaster resilience perception (M = 2.94; SD = 0.83) compared to those respondents with a secondary school degree (M = 2.18; SD = 0.78). These results suggest that respondents with a university degree reported higher scores across social capital, preventive measures, and disaster resilience perception, in comparison to those respondents with a secondary school degree.
Further analysis revealed a correlation between employment status and the following variables: social structure (
p = 0.010); social mechanisms (
p = 0.000); social equity and diversity (
p = 0.002); and social beliefs (
p = 0.013). No statistically significant correlation was found with other variables (
Table 4). Additional examinations demonstrate that employed respondents provided lower scores for social structure (M = 2.31; SD = 0.78) compared to those with unemployed respondents (M = 2.65; SD = 0.97). Continued analysis shows that employed respondents provided lower scores for social mechanisms (M = 2.38; SD = 0.71) compared to those with retired respondents (M = 2.85; SD = 0.92). Also, employed respondents provided lower scores for social equity/diversity (M = 2.53; SD = 0.88) compared to those with unemployed respondents (M = 2.90; SD = 0.95). Besides that, the analysis revealed that employed respondents provided lower scores for social beliefs (M = 2.67; SD = 0.90) compared to those with unemployed respondents (M = 2.93; SD = 0.79). Thus, unemployed respondents tend to rate social structure, equality/diversity, and beliefs to a greater extent compared to employed respondents.
Upon further examination, a correlation was identified between ownership of property and the following variables: social capital (
p = 0.003); social beliefs (
p = 0.020); preventive measures (
p = 0.000); and disaster resilience (
p = 0.002). No statistically significant correlation was found with other variables (
Table 5).
Respondents with personal property provided lower scores for social capital (M = 2.27; SD = 0.98) compared to those with family member ownership respondents (M = 2.75; SD = 0.94). Similarly, respondents with personal property provided lower scores for social beliefs (M = 2.45; SD = 1.11) compared to those with family member’s ownership respondents (M = 2.81; SD = 0.85). Moreover, respondents with personal property provided lower scores for preventive measures (M = 2.17; SD = 0.71) compared to those with family member ownership respondents (M = 2.72; SD = 0.90). Besides that, respondents with personal property provided lower scores for predisaster resilience (M = 2.26; SD = 1.03) compared to those with family member’s ownership respondents (M = 2.74; SD = 0.93). Respondents who personally own property consistently yielded lower scores across various dimensions, including social capital, social beliefs, preventive measures, and predisaster resilience, in comparison to respondents who have family member ownership.
Regarding the household income, a correlation was identified with the following variables: social structure (
p = 0.002); social mechanisms (
p = 0.001); social equity and diversity (
p = 0.001); and social beliefs (
p = 0.001). No statistically significant correlation was found with other variables (
Table 5).
Further analysis reveals that respondents with below-average household incomes provided lower scores for social mechanisms (M = 2.37; SD = 0.90) compared to those with average household incomes (M = 2.74; SD = 0.93). Likewise, respondents with below-average household incomes provided lower scores for social equity and diversity (M = 2.52; SD = 0.92) compared to those with average household incomes (M = 2.97; SD = 0.88). Additionally, respondents with below-average household incomes provided lower scores for social beliefs (M = 2.58; SD = 1.01) compared to those with average household incomes (M = 3.03; SD = 0.77). In contrast, respondents with below-average household incomes provided higher scores for social structures (M = 2.67; SD = 1.04) compared to those with average household incomes (M = 2.34; SD = 0.87). A detailed examination reveals that respondents with below-average household incomes consistently assigned lower scores across various dimensions.
Regarding household members number, a correlation was identified with the following variables: social structure (
p = 0.018); social capital (
p = 0.012); preventive measures (
p = 0.002); social equity and diversity (
p = 0.004); social beliefs (
p = 0.000); and disaster resilience (
p = 0.003). No statistically significant correlation was found with other variables (
Table 5). Additional analysis indicates that respondents who are living in a household with 2 members, provided lower scores for social structures (M = 2.20; SD = 0.94) compared to those who are living in a household with over 4 members (M = 2.65; SD = 0.95). On the contrary, respondents who are living in a household with over 4 members provided higher scores for social mechanisms (M = 2.73; SD = 0.93) compared to those who are living in a household with 2 members (M = 2.21; SD = 0.96). Similarly, respondents who are living in a household with over 4 members provided higher scores for social equity and diversity (M = 2.75; SD = 0.91) compared to those who are living in a household with 2 members (M = 2.29; SD = 0.91). Besides that, respondents who are living in a household with over 4 members provided higher scores for social beliefs (M = 2.86; SD = 0.86) compared to those who are living in a household with 2 members (M = 2.25; SD = 0.97). It was found that respondents who were living in a household with 2 to 4 members provided higher scores for disaster resilience (M = 2.80; SD = 0.98) compared to those who were living in a household with over 4 members (M = 2.38; SD = 0.74). The analysis indicates that respondents in households with 2 members, generally, provide lower scores for social structures, while those in households with over 4 members tend to give higher scores for social mechanisms, social equity and diversity, and social beliefs. Additionally, respondents in households with 2 to 4 members demonstrate higher scores for disaster resilience compared to those in households with over 4 members.
Further examination showed the correlation between marital status and the following variables: social structure (
p = 0.000); social capital (
p = 0.000); social mechanisms (
p = 0.000); social equity and diversity (
p = 0.000); social beliefs (
p = 0.000); preventive measures (
p = 0.000); and disaster resilience (
p = 0.000). No statistically significant correlation was found with other variables (
Table 5).
Through further analysis, it has been discovered that respondents who are single provided higher scores for social structure (M = 2.70; SD = 0.77) compared to those who are in a relationship (M = 2.33; SD = 0.92). Then, it was determined that respondents who were single provided higher scores for social capital (M = 3.03; SD = 1.04) compared to those who were in a relationship (M = 2.37; SD = 0.76). Also, it was determined that respondents who are single provided higher scores for social mechanisms (M = 2.97; SD = 0.94) compared to those who are in a relationship (M = 2.41; SD = 0.90). As well, respondents who are single provided higher scores for social equality and diversity (M = 2.98; SD = 0.99) compared to those who are in a relationship (M = 2.62; SD = 0.82). Moreover, respondents who are single provided higher scores for social beliefs (M = 3.00; SD = 0.86) compared to those who are in a relationship (M = 2.62; SD = 0.81). In addition, respondents who are single provided higher scores for preventive measures (M = 2.84; SD = 0.99) compared to those who are who are divorced (M = 2.62; SD = 0.81). Furthermore, respondents who are single provided higher scores for disaster resilience (M = 3.10; SD = 0.99) compared to those who are who are divorced (M = 2.35; SD = 0.79). The analysis reveals that single respondents consistently provided higher scores across various dimensions, including social structure, social capital, social mechanisms, social equality and diversity, social beliefs, preventive measures, and disaster resilience, compared to those in a relationship or divorced.
More analyses found that there was a relationship between age and social structure (r = 0.568), social mechanisms (
r = −0.223), social equity and diversity (
r = −0.213), and social beliefs (
r = −0.229) (
Table 6). Further analysis of the results shows that with the increase in the age of the respondents, the rating of social structure increases. On the other hand, a negative correlation was found, which shows that with the growth of the age of the respondents, the rating of social mechanisms, social equity diversity and social beliefs decreases. Further investigation into the causes of this apparent relationship would be helpful to obtain a more thorough knowledge of the dynamics impacting the respondents’ perceptions.
The results of the
t-test suggest a statistically significant difference between males and females in terms of social capital (
p = 0.00); preventive measures (
p = 0.010) and disaster resilience (
p = 0.032). We did not find a statistically significant difference between males and females in terms of social structure, social mechanisms, social equity and diversity, and social beliefs (
Table 7).
The results of further analyses suggest that males, to a greater extent than females, rate the following variables higher: social capital (males M = 3.01; females M = 2.48); preventive measures (males M = 2.76; females M = 2.48); and disaster resilience (males M = 3.06; females M = 2.46) (
Table 7).
The results of the
t-test suggest a statistically significant difference between volunteers and non-volunteer in terms of perception of disaster resilience (
p = 0.035). No statistically significant differences were observed between volunteer and non-volunteers concerning social structure, social capital, social mechanisms, social equity and diversity, social beliefs, and preventive measures (
Table 8). The results of further analyses found that volunteers, to a greater extent than non-volunteers, rate disaster resilience (volunteer M = 2.76; non-volunteer M = 2.54) (
Table 8).
4. Discussion
In this paper, we present the findings of a quantitative study that explores how demographic and socioeconomic factors impact community (social) disaster resilience. The results of the multivariate regression analyses, across various community disaster resilience subscales, indicate that age emerged as the most significant predictor for the social structure subscale. The results obtained can be explained by the fact that older individuals may contribute to shaping a community’s social structure, based on prior life experiences, social networks, and spiritual beliefs (Cohen et al., 2016; Timalsina & Songwathana, 2020). Their prolonged exposure to community dynamics and disaster-related events might lead to a more nuanced understanding of the social leadership structures, and the effectiveness of response services (Almazan et al., 2019; Liddell & Ferreira, 2019). Besides that, additional examinations revealed a correlation between age and dimensions such as social structure, social mechanisms, social equity and diversity, and social beliefs. Subsequent scrutiny of the outcomes indicates that as the respondents’ age increases, there is a positive association with higher ratings for social structure.
Conversely, a negative correlation was identified, indicating that as the age of the respondents advances, the ratings for social mechanisms, social equity diversity, and social beliefs tend to decrease. This inclination might be attributed to a range of factors such as accumulated life experiences, historical perspectives, and potentially deeper involvement in community affairs (Huerta & Horton, 1978; Melick & Logue, 1985; Murphy, 1994; Murrell & Norris, 1984). Older individuals, having witnessed and participated in various community activities over time, might harbour a more optimistic view of the existing social structures and leadership dynamics (Van Rijsbergen, Jaworska, Rousselet, & Schyns, 2014).
At the same time, education stood out as the primary predictor for the social capital subscale. The findings indicate that respondents with a secondary school degree consistently provided higher scores across dimensions, including social structure, social mechanisms, and social equity and diversity, compared to those with a university degree. This positive association may be attributed to several factors linked to higher education, such as increased social awareness, communication skills, and a broader perspective on community dynamics (Cvetković & Stanišić, 2015; Drzewiecki et al., 2020; Feng et al., 2018; Hoffmann & Muttarak, 2017). Besides that, respondents with a university education reported higher scores across social capital, preventive measures, and disaster resilience perception compared to respondents with a secondary school degree. Moreover, individuals with a university education may perceive higher levels of social connectedness, engagement, and support. They might also be more proactive in taking preventive measures and demonstrate a greater perception of resilience in the face of disasters compared to those with a secondary school degree (Nifa et al. 2017).
Additionally, employment status proved to be the most influential predictor for both social mechanisms and social equity-diversity subscales, with property ownership being the key predictor for the social beliefs sub-scale. Further analysis revealed a correlation between employment status and the following variables: social structure; social mechanisms; social equity and diversity; and social beliefs. Unemployed respondents tend to rate social structure, equality/diversity, and beliefs to a greater extent compared to employed respondents. One possible explanation is that unemployed respondents may have more time to engage in community-related activities and reflection (Lim & Sander, 2013), leading to a heightened awareness and assessment of social structures, equality, diversity, and beliefs. On the other hand, employed individuals may have a more structured daily routine, potentially limiting their direct involvement in community matters (Kroll & Lampert, 2011; Scheid, 1993; Wanberg, 2012).
Upon further examination, respondents who personally own property consistently yielded lower scores across various dimensions, including social capital, social beliefs, preventive measures, and predisaster resilience, in comparison to respondents who have family member ownership. It is possible that owners of personal property experience less support or resources from the community in disasters (Beatley, 1998; Riad, Norris, & Ruback, 1999). Additionally, there may be differences in risk perception and readiness for preventive measures between owners of personal property and those with family member ownership. Regarding the household income, a correlation was identified with the following variables: social structure, mechanisms, equity and diversity; and social beliefs. A detailed examination reveals that respondents with below-average household incomes consistently assigned lower scores across various dimensions. Specifically, in comparison to those with average household incomes, respondents with below-average incomes provided lower scores for social mechanisms, social equity and diversity, and social beliefs. It can be assumed that individuals with below-average household incomes may face economic constraints (Adeagbo, Daramola, Carim-Sanni, Akujobi, & Ukpong, 2016; Li, 2007), affecting their perceptions of social mechanisms, equity and diversity, and social beliefs. Lower income levels might limit access to resources and opportunities (Pereira & Oliveira, 2020), influencing the way individuals assess community aspects related to social structure and beliefs.
Further examination reveals that respondents residing in households with two members tend to assign lower scores for social structures, whereas those in households with more than four members are inclined to give higher ratings for social mechanisms, social equity and diversity, and social beliefs. Furthermore, respondents in households with two to four members exhibit elevated scores for disaster resilience in comparison to those in households with more than four members. A potential explanation for these findings could be that individuals in smaller households may perceive limitations or challenges in the social structures within their community (Contoyannis, Jones, & Rice, 2004). On the other hand, those in larger households might experience a greater sense of interconnectedness (Foster et al., 2017), contributing to more positive evaluations of social mechanisms, social equity and diversity, as well as social beliefs.
Further examination showed the correlation between marital status and the analysis reveals that single respondents consistently provided higher scores across various dimensions, compared to those in a relationship or divorced. The relationship between marital status and these dimensions may imply that being single is associated with specific attitudes or behaviours that contribute to a more positive evaluation of social capital, preventive measures, and disaster resilience. This finding aligns with the research conducted by Kim and Lee (2021), who similarly identified the influence of marital status on the preparedness levels for bioterrorism. The connection between marital status and disaster-related attitudes underscores the need for a nuanced understanding of individual characteristics in shaping community resilience perceptions. Contrary to that, our results are not in line with Cui et al. (2018), who did not find evidence supporting correlations between marital status and an individual’s perception of community resilience. Furthermore, these findings align with several other studies that have investigated the level of resilience (Leykin et al., 2013; Pfefferbaum et al., 2016).
The calculated mean value of the community (social) disaster resilience index, falls within the lower range of possible values on a Likert scale from 1 to 5. This suggests that the overall level of disaster resilience within the community is relatively modest. The value being closer to the lower end of the scale, indicates that there may be room for improvement in enhancing the community’s resilience to disasters. Considering that Khan et al. (2022) found that the resilience index was higher in high-income countries (Switzerland, Germany, France, New Zealand, and Australia) followed by upper-middle, lower-middle, and low-income economies, such as the middle-income economy in Serbia, the results are somewhat expected (Zhang & Huang, 2018).
The examination of specific subscales highlights that participants bestowed the highest ratings on the social beliefs subscale, emphasizing a positive perception in this dimension. On the contrary, the social structure subscale received the lowest ratings, indicating potential vulnerabilities in this aspect of community resilience. Furthermore, the assessment of other subscales showed descending order ratings: social equity and diversity, social capital, and social mechanisms. A potential explanation for the low scores on the social structure subscale could be a lack of resources, organization, or effective mechanisms within the community that support proper disaster risk management (Cvetković et al., 2023; Cvetković et al., 2021).
Further analysis showed that preventive measures are most commonly taken in the face of the hazards of epidemics, extreme temperatures, and storms. The perception of society’s resilience is highest in the face of the hazards of epidemics, followed by extreme temperatures, and drought. Respondents express a relatively high level of confidence in society’s ability to cope with epidemics, extreme temperatures, and drought. These findings could be influenced by the perceived severity (Cvetković, Nikolić, Nenadić, Ocal, & Zečević, 2020; Cvetković, Öcal, et al., 2019; Sattler, Kaiser, & Hittner, 2000; Wirtz & Rohrbeck, 2018) and frequency of these specific hazards (Appleby-Arnold, Brockdorff, Jakovljev, & Zdravković, 2018; Bollettino et al., 2020), as well as existing awareness and preparedness initiatives (Kusumastuti, Arviansyah, Nurmala, & Wibowo, 2021) customized for these types of disasters. Also, this indicates a high level of awareness and a proactive approach to risks associated with epidemics, extreme temperatures, and storms (Cvetković et al., 2022b).
On the other hand, the hazards of volcanic eruptions, landslides, and tsunamis show lower priorities in taking preventive measures, and the perception of society’s resilience is also lower in these cases. The results obtained in this way may indicate a low level of perception of the hazards of such events, considering that, except for landslides, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis, are not typical for the region of Serbia (Cvetković et al., 2019). Also, this indicates the need for additional efforts in raising awareness and preparedness for these specific types of hazards. This analysis reveals variations in the approach to taking preventive measures and the perception of society’s resilience depending on the type of natural hazard. Identifying these differences can serve as a basis for further planning and implementing interventions to enhance preventive strategies and strengthen overall societal resilience to various hazards (Kusumastuti et al., 2021).
The obtained results of mean values for subscales indicate that participants gave the highest ratings to beliefs within the social beliefs category, while the lowest values were recorded in the social structure category. Following this, the ratings for social equity and diversity, social capital, and social mechanisms are next. The examination of perspectives on social structure indicates that participants view the advancement of response services and community leadership positively while acknowledging areas for enhancement in financial, technological, and human resources (Asadzadeh, Pakkhoo, Saeidabad, Khezri, & Ferdousi, 2020; Kusumastuti et al., 2021). Additionally, the calculated mean values suggest a generally neutral community stance regarding disaster preparedness and response matters.
In terms of social capital, the overall evaluations indicate that participants hold a perception of elevated mutual trust and support, robust social networks and connections, and extensive interaction and collaboration with other communities. Conversely, volunteer activities and projects received lower ratings, suggesting a possible need for enhancement in promoting community engagement (Kumar & Kumar, 2020). Mean values indicate a generally neutral stance towards dialogue with authorities, involvement of diverse social groups in decision-making during disasters, and the existence of local initiatives for disaster preparedness involving various socio-economic groups. In the realm of social mechanisms, the elevated values obtained for active community involvement, flexibility, adaptability, and the promotion of disaster insurance underscore a positive attitude towards specific social mechanisms. Conversely, the low ratings for household preparedness, risk perception, and citizen awareness indicate the necessity for a more robust focus on these aspects to enhance overall community preparedness. Besides that, mean values also suggest a neutral stance towards education, cultural diversity, and citizen awareness of risks, signalling areas for further reflection and improvement within the domain of social mechanisms.
Commendably high scores for the availability of key resources and community readiness to address social injustices reflect a positive attitude towards aspects of equity and diversity. Conversely, low scores for programs targeting the specific needs of vulnerable groups (Baker, Baker, & Flagg, 2012), protection of minority rights, and the involvement of different social groups in planning indicate the need for improvement in these areas to ensure a fair and inclusive response to disasters. Elevated assessments concerning aspects such as fostering a disaster-resilient culture (Albanese et al., 2008), active engagement in traditional and religious practices, and consistent participation in religious ceremonies signify a favourable inclination towards tradition, faith, and cultural values. Conversely, issues related to trust in social institutions during disasters, the restricted influence of religious leaders (Cvetković, Romanić, & Beriša, 2023) in decision-making processes, and the necessity for enhancing the efficacy of religious institutions in disaster preparedness (Sheikhi, Seyedin, Qanizadeh, & Jahangiri, 2021) highlight domains necessitating additional scrutiny and improvement to augment community disaster resilience.
The limitations of our study include (1) potential bias may exist in the process of choosing individuals to participate in the survey and complete questionnaires or an uneven representation of certain groups in the study sample, (2) insufficiently representative sample of respondents, (3) researchers lack complete control over the environment in which respondents participate in online surveys, leading to diverse conditions that can influence response consistency, (4) restrict the ability to ask additional questions or seek clarifications from respondents, reducing the depth of understanding individual responses, (5) the absence of physical presence could pose challenges in monitoring alterations in respondent behaviour or recognizing issues throughout the survey.