Submitted:
21 February 2024
Posted:
21 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction:
| Serial No | Name | LD50 (mg/Kg rat) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Malachite Green | 275 |
| 2 | Acid Orange 165 | 60 |
| 3 | Basic Blue 7 | 100 |
| 4 | Basic Blue 81 | 205 |
| 5 | Basic Violet 16 | 90 |
| 6 | Basic Yellow 21 | 171 |
| 7 | Direct orange 62 | 150 |
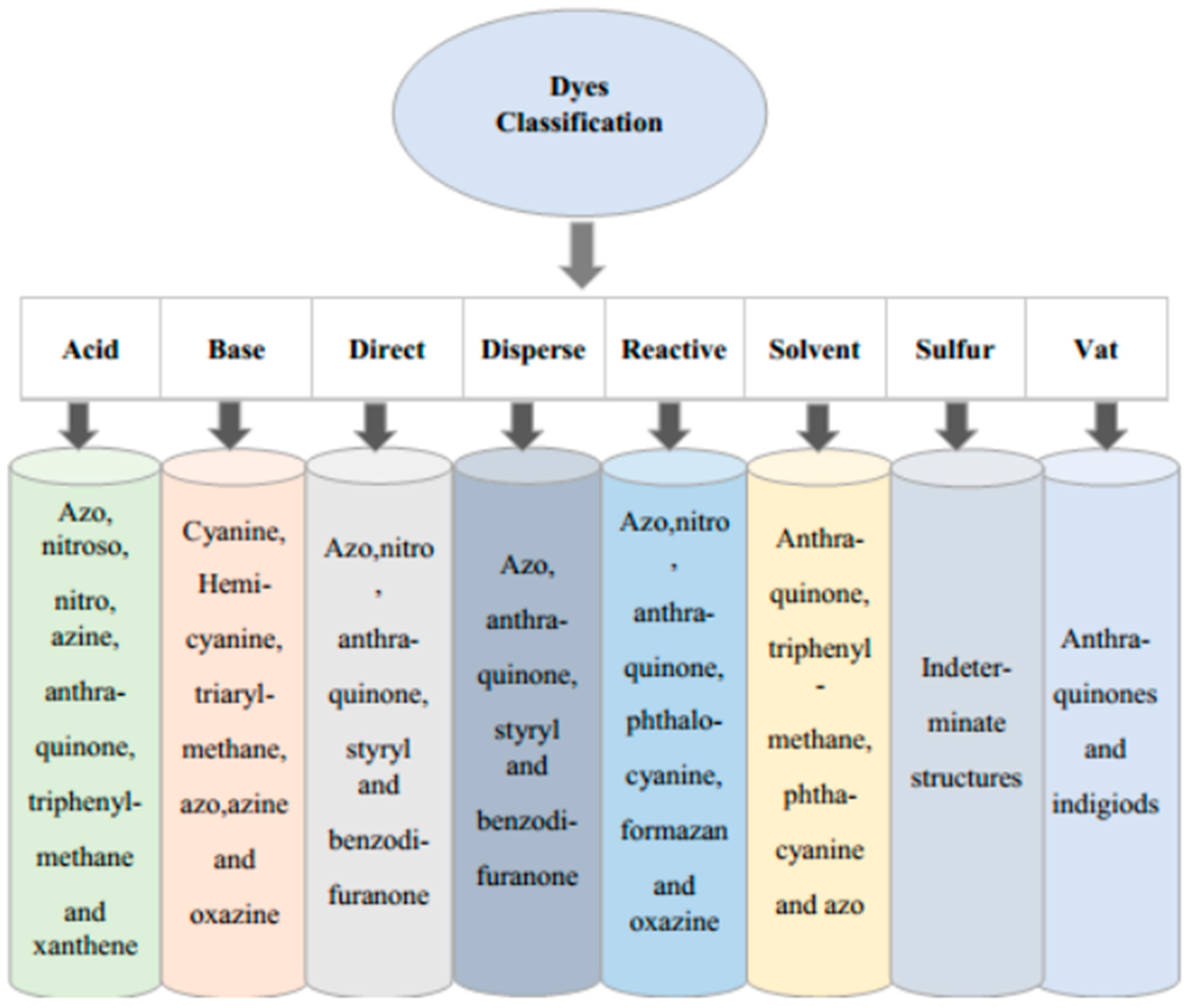
| Class | Application | Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Acid dyes |
Nylon, wool, silk, modified acrylics, paper, leather, food, inkjet printing and cosmetics. |
Acid red 88, Acid red 18 |
|
Cationic (Basic) Dyes |
Poly acrylonitrile, paper, modified polyesters, modified nylons, cationic dye able polyethylene terephthalate, wool, silk, tannin mordant cotton and medicine. |
Crystal Violet, Methylene Blue, Safranin, Basic fuschin |
|
Disperse Dyes |
Nylon, polyester, cellulose, acrylic fibers and cellulose acetate. | Disperse Red 1, Disperse Orange 37 |
| Direct Dyes | Rayon and cotton, Leather, paper and nylon. |
Congo Red, Brilliant Blue, Copper blue 2R |
| Reactive Dyes | Wool, nylon, cotton and other cellulosic. | Reactive Black 5, Reactive Orange 16 |
| Solvent Dyes | Gasoline, plastics, oils, lubricants and waxes. | Solvent Red 1, Solvent Red 49, Solvent Red 24, Solvent Red 111 |
| Sulfur Dyes | Cotton and rayon, paper, leather, silk and wood. | Sulfur Brilliant Green, Sulfur black 1 |
| Vat Dyes | Cotton, rayon and wool. | Vat red 10, Vat violet 13 and Vat orange 1 |
| Azoic dyes | These dyes are utilised in pigments and printing inks. | Methyl Orange, Methyl Red, Rhodamine B |
|
Leather dyes |
By applying high temperatures to the leather, the fat-soluble components of these colours have an attraction to migrate upward into the layers, giving the leather surface a smooth finish. |
Fiebing’s Leather Dye |
Properties:
- Brightness or Dullness
- Dyeing Properties
- Environmental Issues
- Ease of Application
- Low-economy cost
| Dye Name | Type | Color | Molecular formula | Molecular weight (g/mol) | Absorption maxima (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
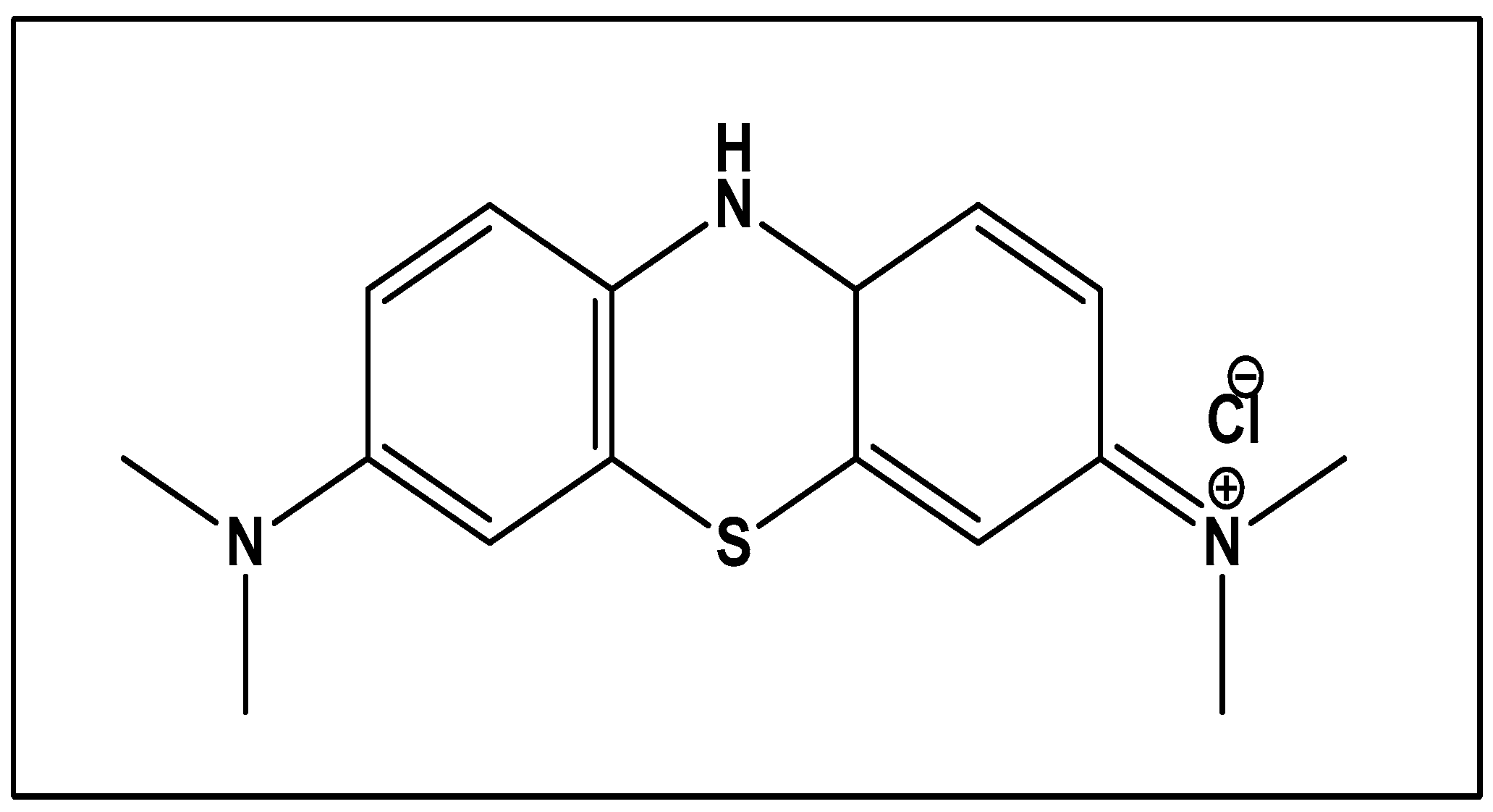
| Methylene Blue | Aniline | Dark green | C16H18N3SCl | 319.85 | 664 |
| Methyl Orange | Azo | Orange-yellow | C14H14N3NaO3S |
327.33 | 460 |
| Methyl Red | Azo | Dark Red | C15H15N3O2 |
269.30 | 540 |
| Rhodamine B | Azo | Reddish-violet | C28H31ClN2O3 |
479.02 | 554 |
| Gentian Violet | Triaryl-methane | Violet | C25N3H30Cl |
407.98 | 536 |
| Indigo Carmine | Indigotine | Indigo to dark blue | C16H8N2Na2O8S2 |
466.35 | 610 |
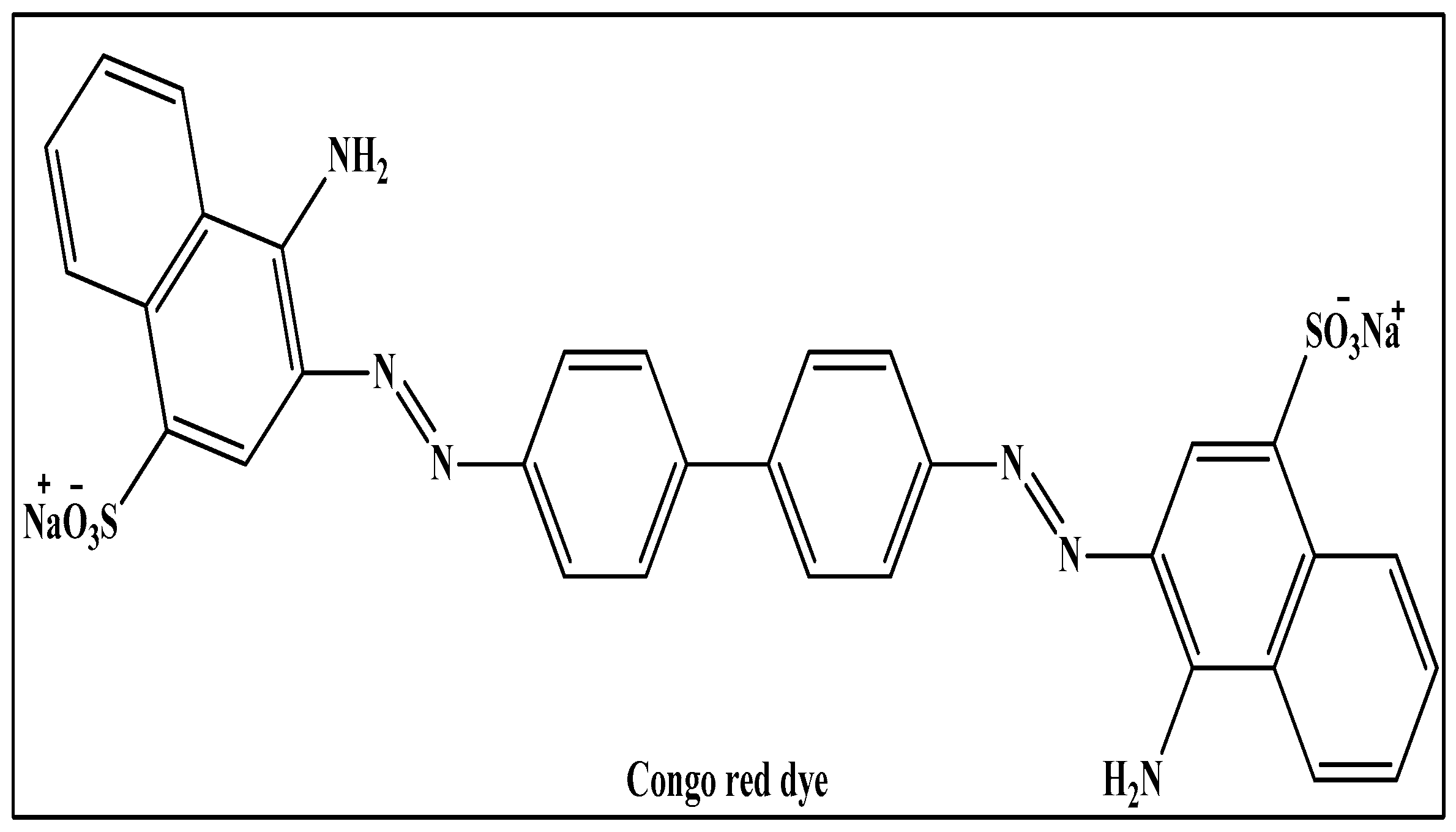
| Congo Red | Azo | Red | C32H22N6Na2O6S2 |
696.66 | 510 |
| Reactive Blue 4 | Anthraquinone | Dark blue | C23H12Cl2N6Na2O8S2 |
681.39 | 596 |
| Basic Violet 3 | Triaryl-methane | Bright blue purple | C25H30ClN3 |
407.98 | 590 |
| Acid Red 114 | Azo | Dark red powder | C37H28N4Na2O10S3 |
830.81 | 514 |
| Class | Chromophores | Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Azo dyes |
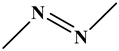
|
Reactive Black 5 |
|
Anthraquinone dyes |
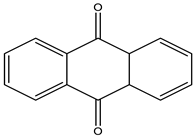
|
Reactive Black 4 |
|
Nitroso dyes |
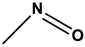
|
Acid Green 1 |
|
Nitro dyes |
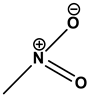
|
Acid Yellow 24 |
|
Indigoid dyes |
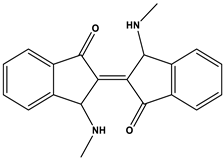
|
Acid Blue 71 |
|
Triarylmethane dyes |
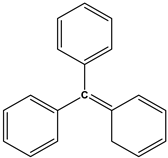
|
Malachite Green |
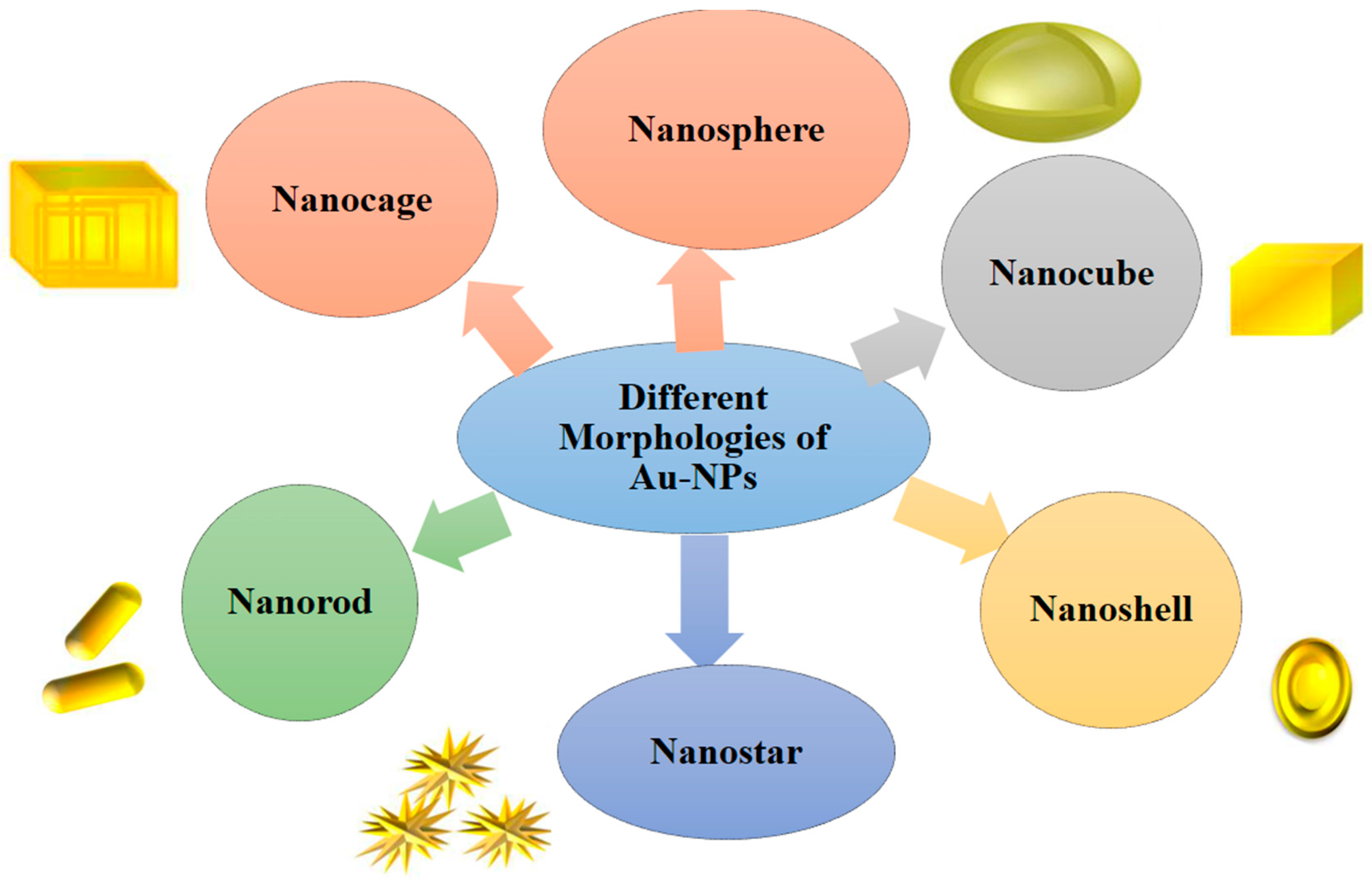
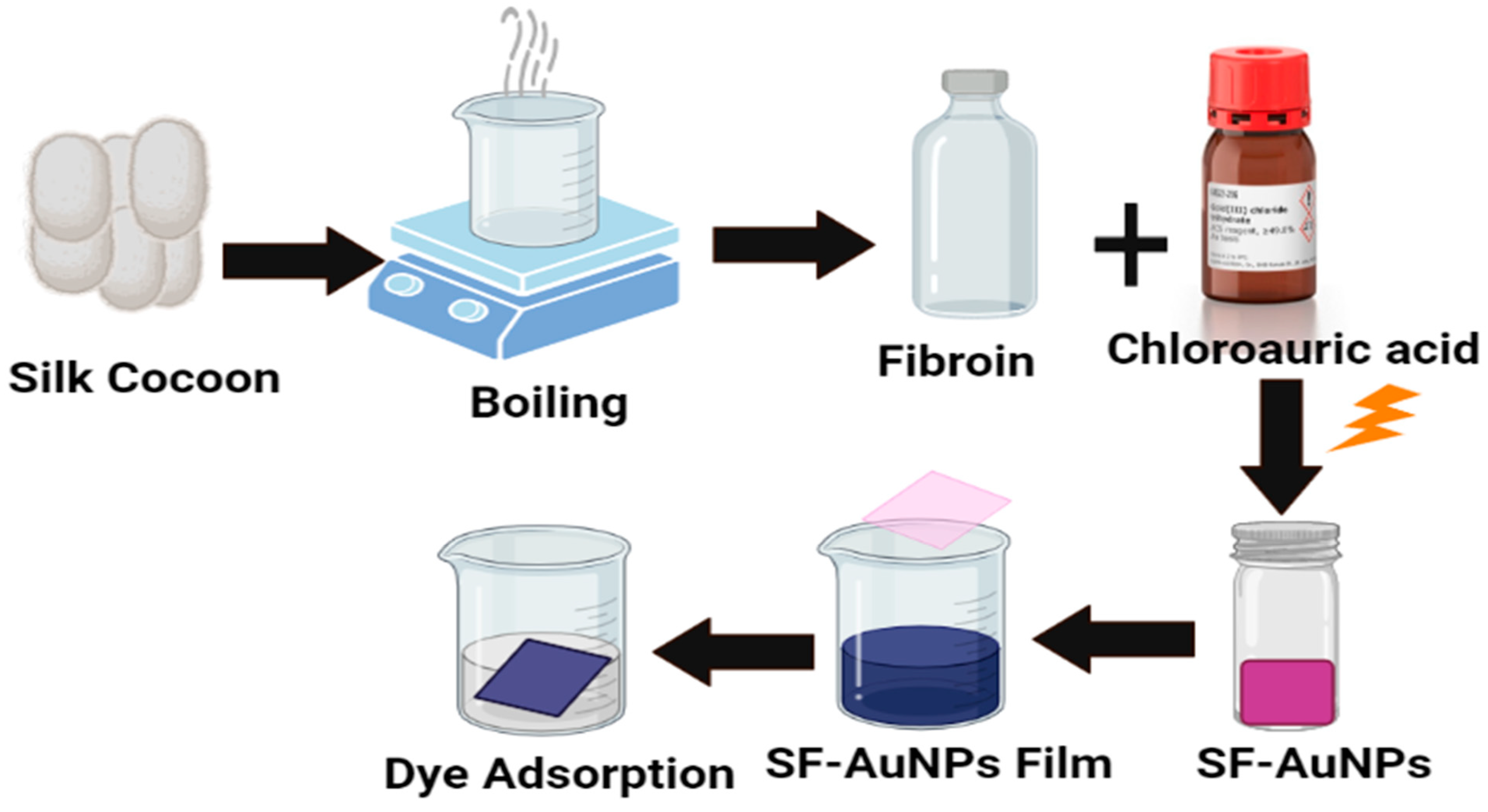
| Sources of (AuNPs) | Dyes removed | Morphology | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| silk fibroin (SF) and silk fibroin-gold nanoparticles (SF-AuNPs | Methylene blue | Spherical | [23] |
| Wedelia urticifolia(plant extracts ) | Rhodamine-B | Spherical | [24] |
| Sargassum horneri(marine algae extract) SH-AuNPs | Methylene blue rhodamine B, and methyl orange. | Spherical | [23] |
| (AuNPs-HNT) with halloysite nanotube | phenothiazine dyes (azure B (AZB) and toluidine blue O (TBO), 4-(4-nitrophenyl)morpholine | Free nit cell structure | [25] |
| Dimrit raisin | Methylene blue (MB) and methyl orange (MO) | Triangular and hexagonal | [26] |
| Rosa canina fruit extract | Methylene blue (MB), Rhodamine B (RhB) and 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) | Spherical | [27] |
| (Graphene/Au-NPs) nanozymes | Methylene blue (MB), rhodamine (RB), methyl orange | Spherical,quasi spherical | [28] |
| Pseudoalteromonas lipolytica (bacteria extract) | methylene blue and Congo red dyes | Spherical | [29] |
| Enoki mushroom (Flammulina velutipes) | Methylene Blue (MB) | Colloidal (oval, spherical, drum-like, hexagonal, and triangular) and crystalline form | [30] |
| Portobello mushroom (Agaricus Bosporus) | Methylene Blue | Oval, spherical, drum-like, hexagonal, and triangular | [31] |
Properties of gold nanoparticles:
Sources of Nanoparticles:
Formation of gold nanoparticles and their use for dyes removal:
Properties of dyes:
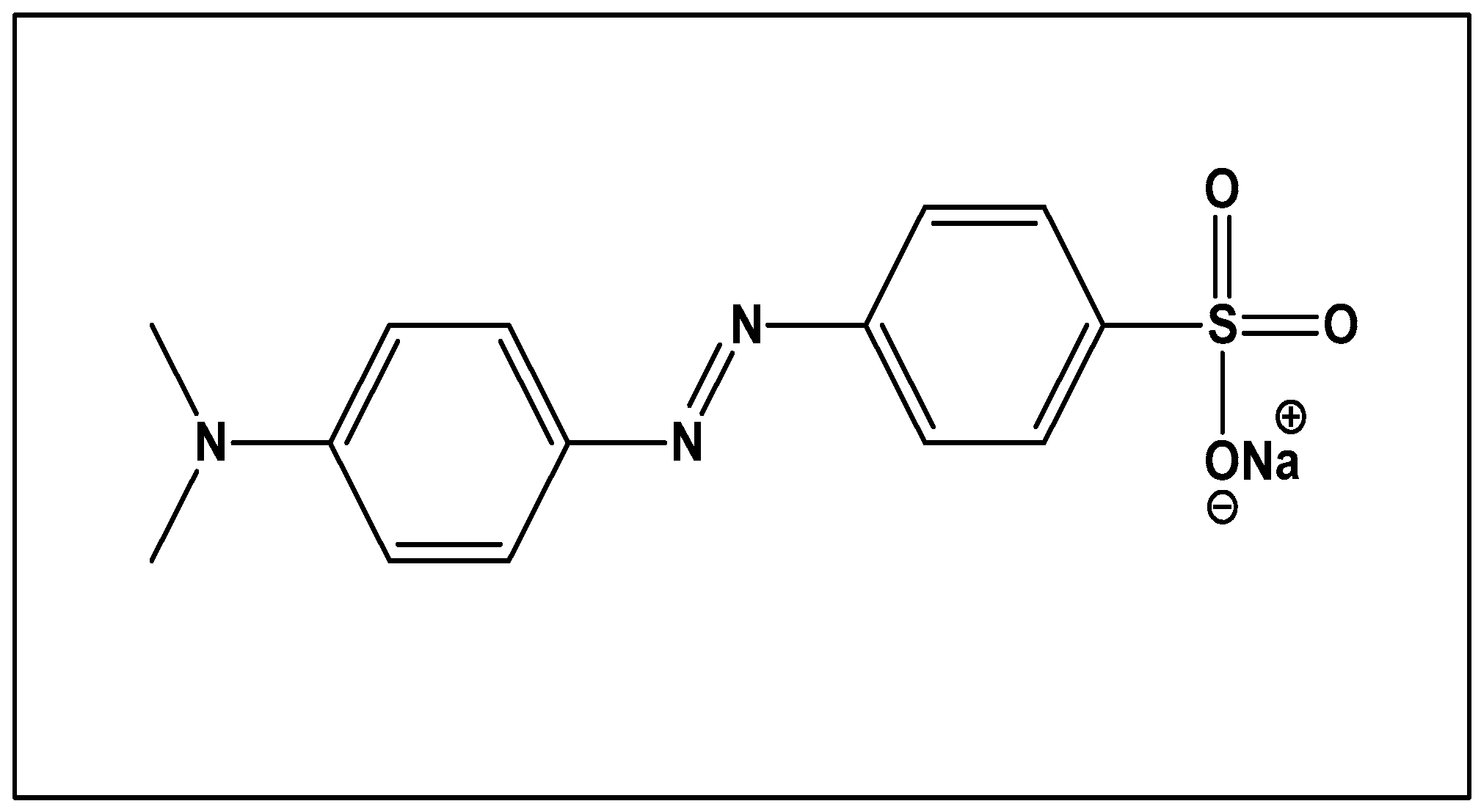
Methyl orange:
Malachite green:
Rhodamine dye:
4-. nitrophenol:
Congo red:
Methylene blue:
Degradation of organic dyes using fabricated Gold Nanoparticles
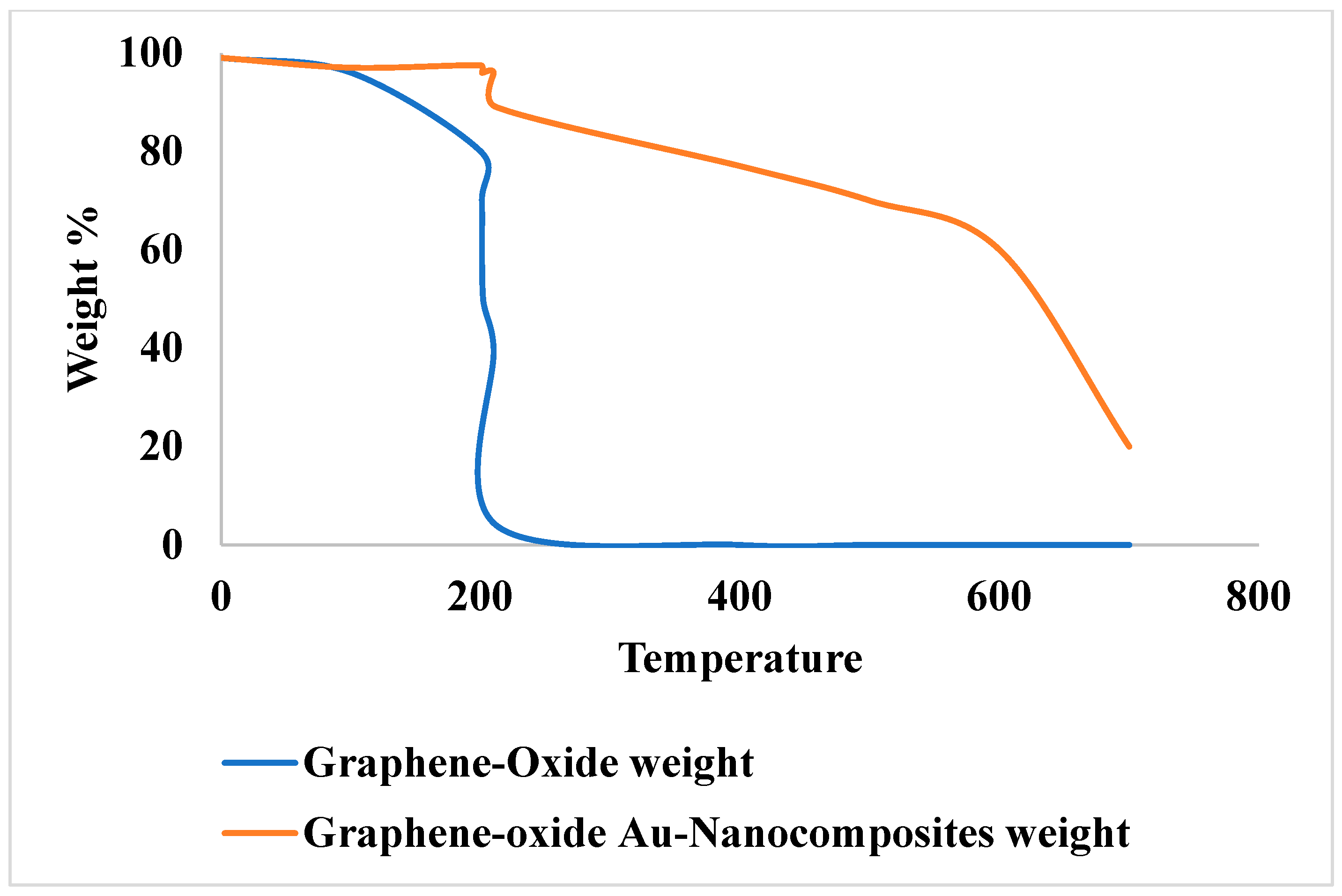
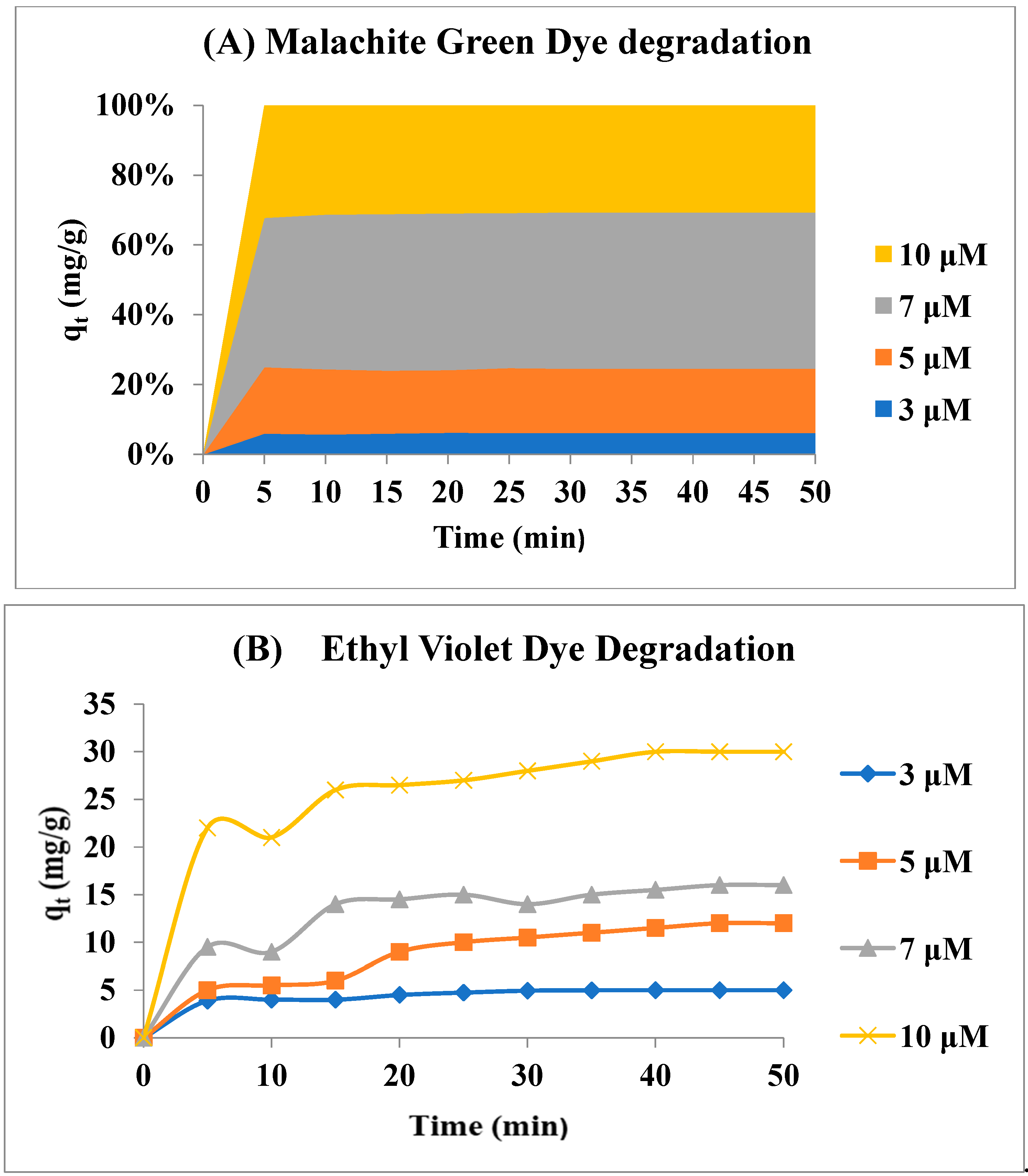
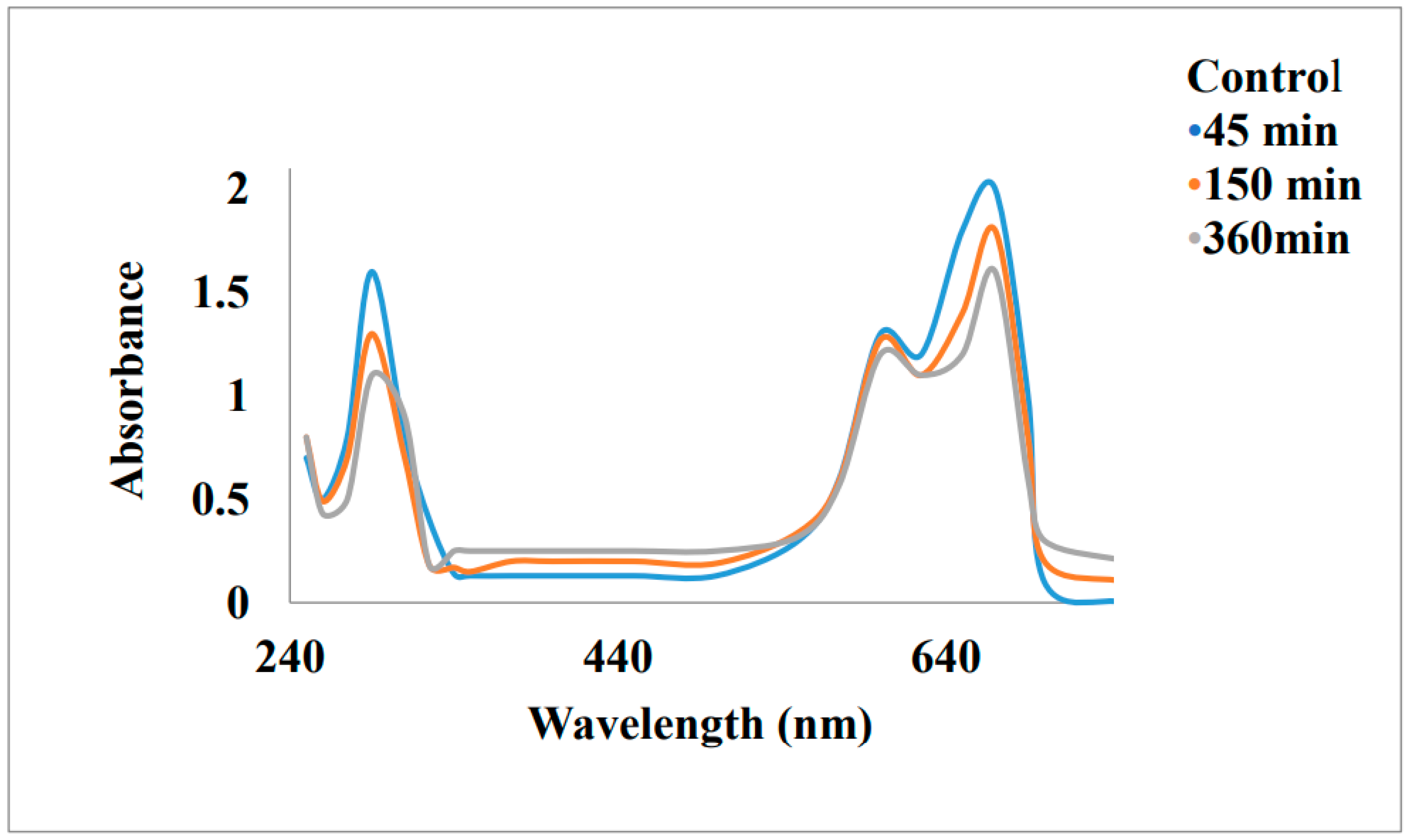
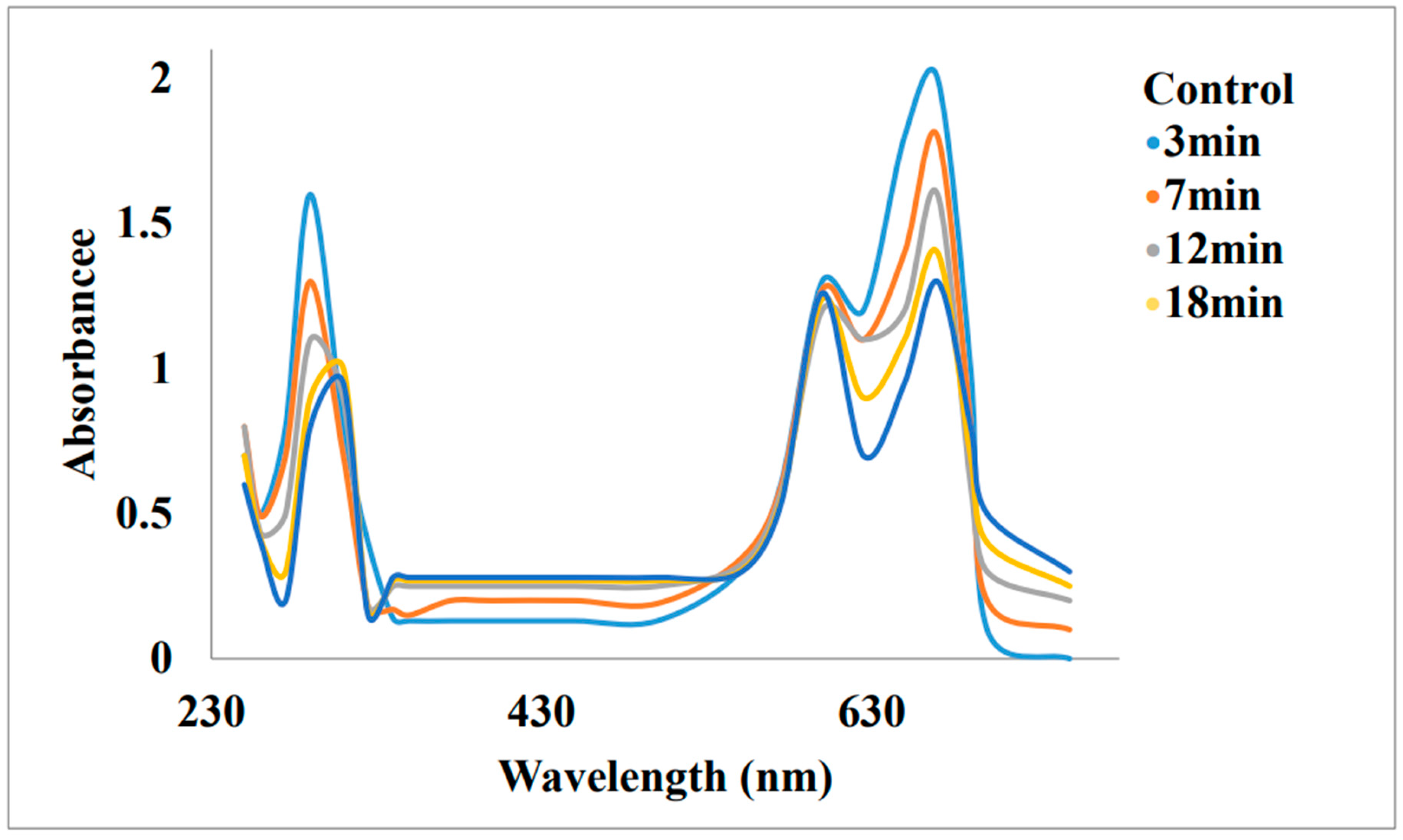
Removal of Malachite Green and Ethyl violet using Graphene oxide Gold Nanoparticles (GeONPs):
Removal of Methylene Blue using AuNPs from Sesbenia grandiflora
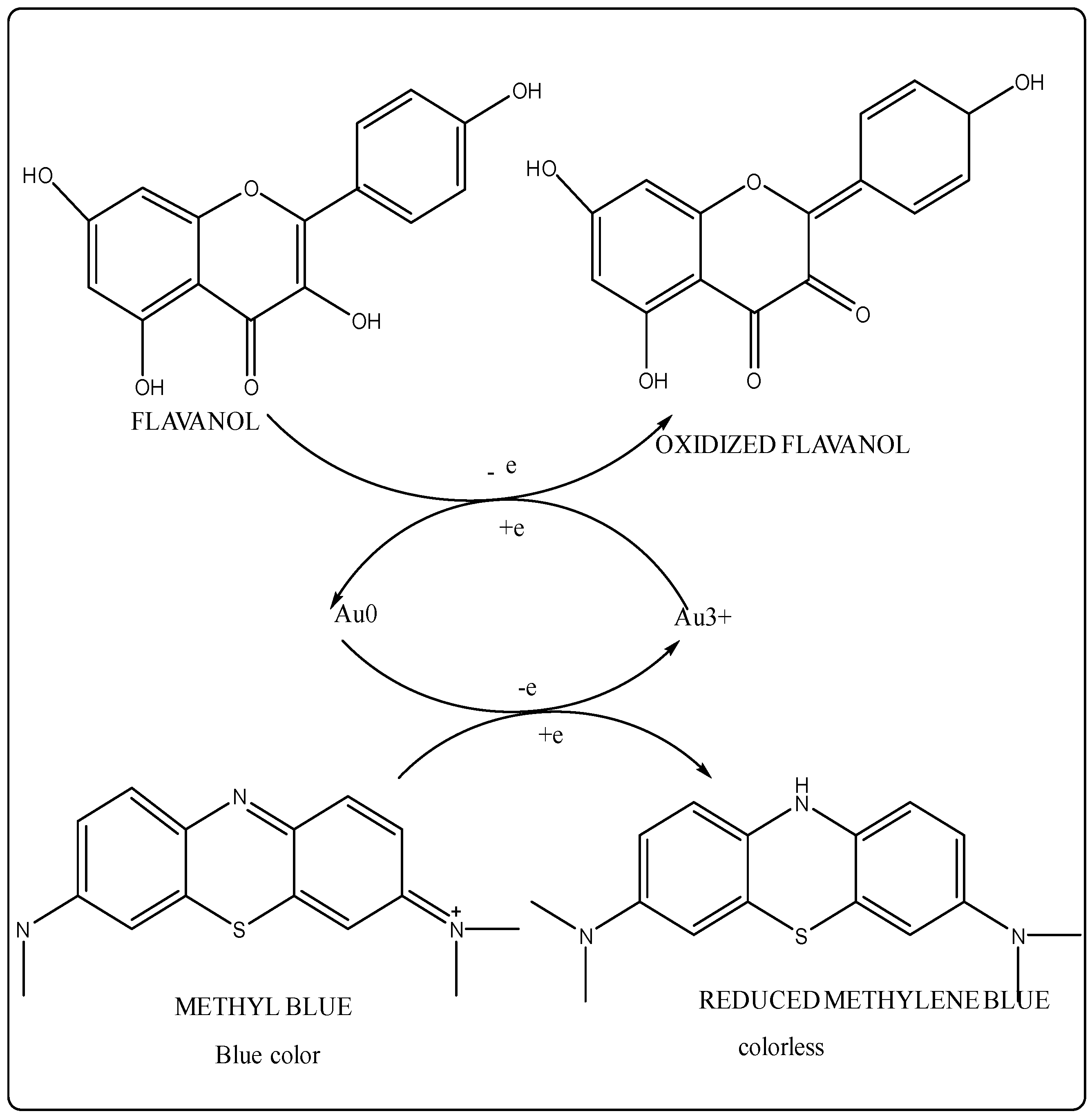
Removal of Methylene Blue using AuNPs from Cassytha Filiforms plant extract:
pH effect:
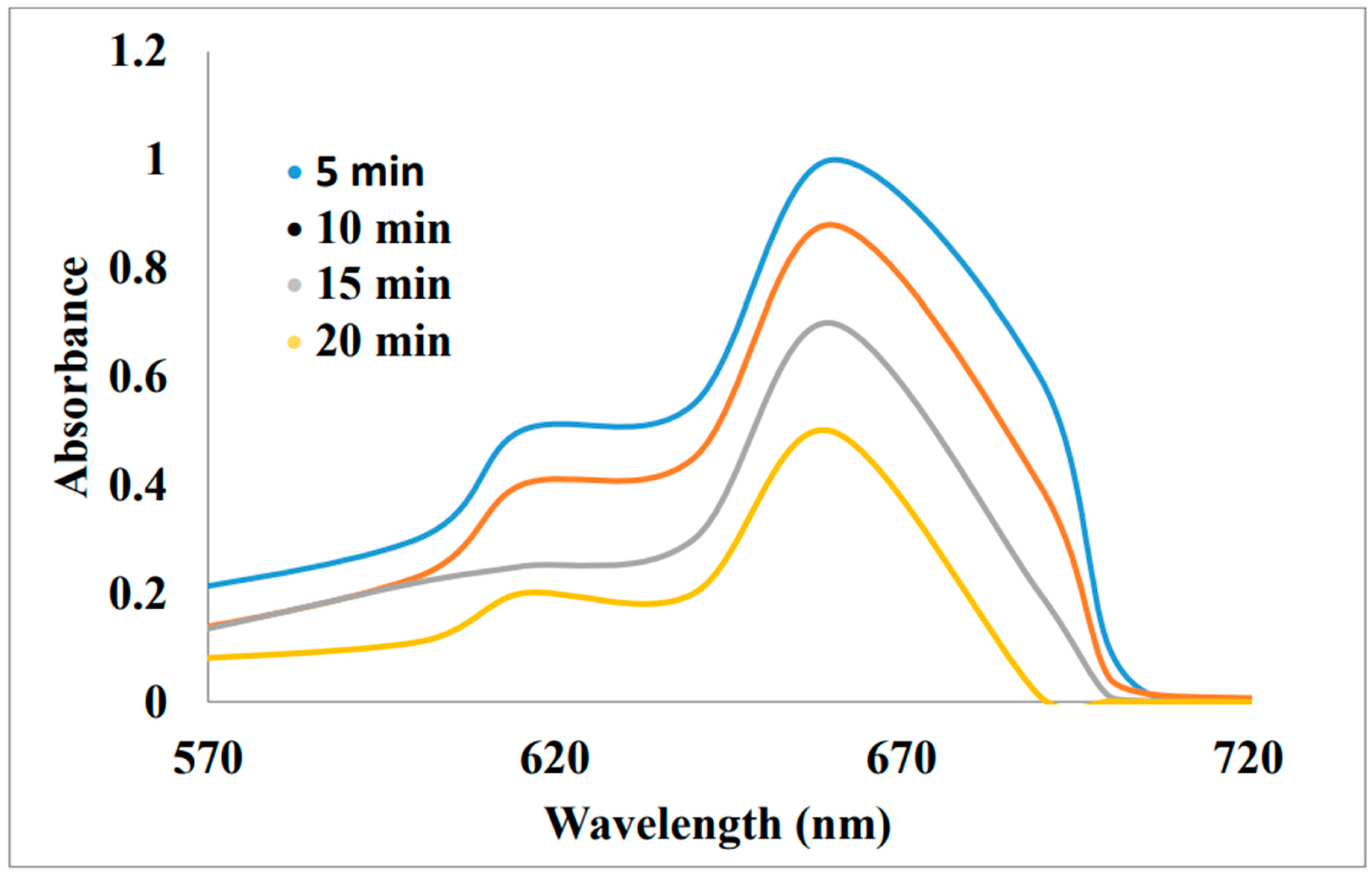
Reduction of Methyl orange and Congo red from Dalbergia coromandeliana Au-NP:
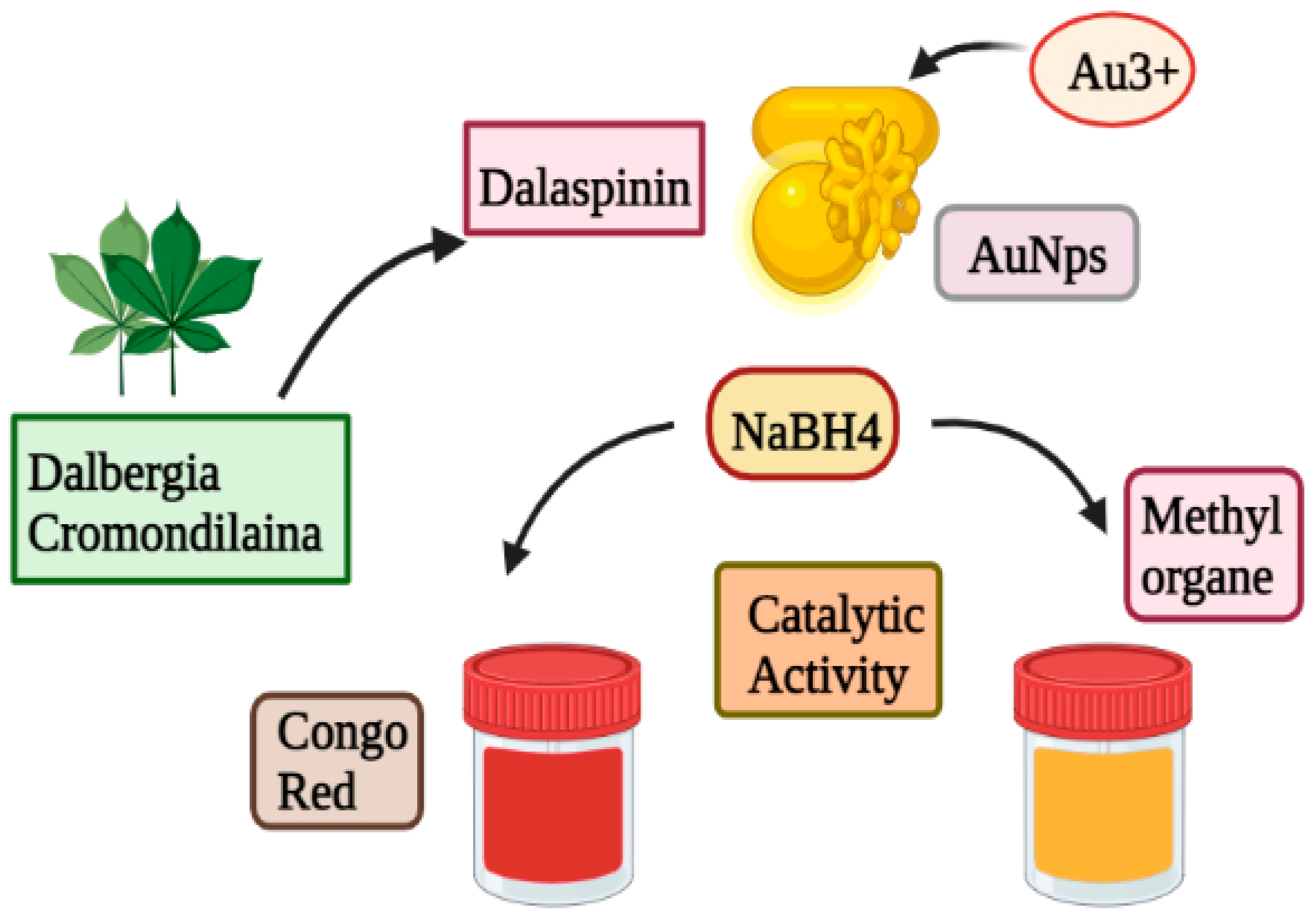
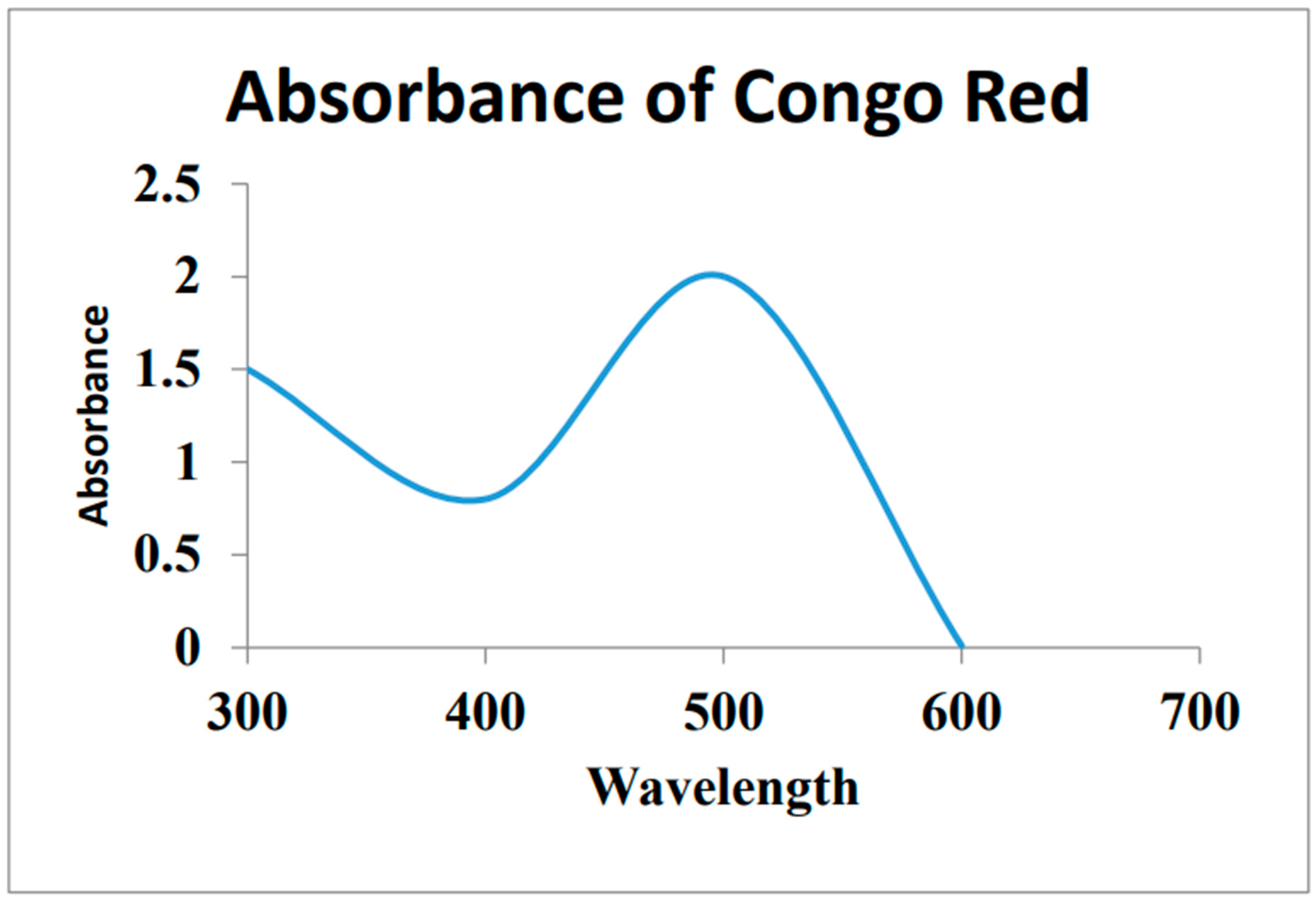
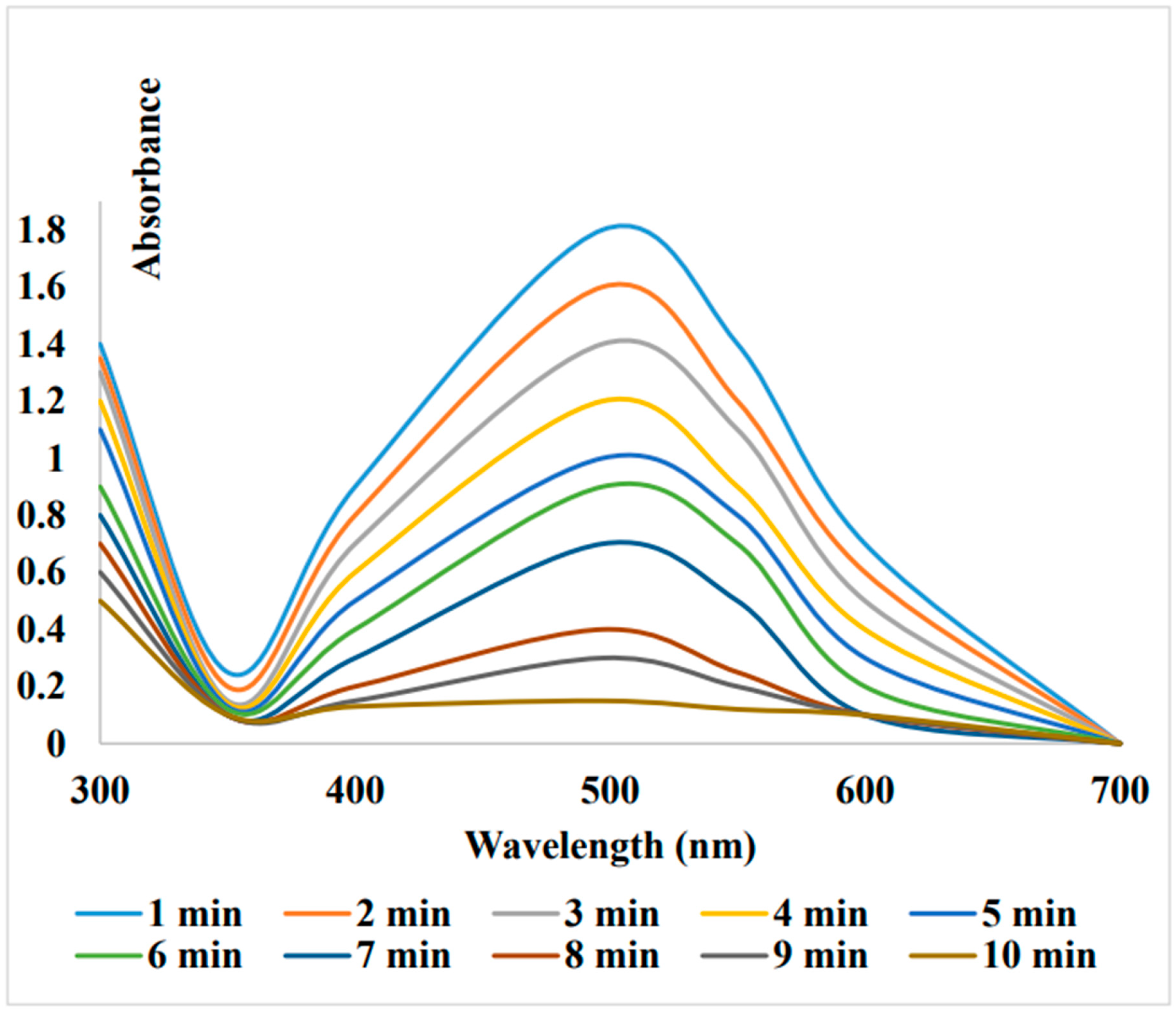
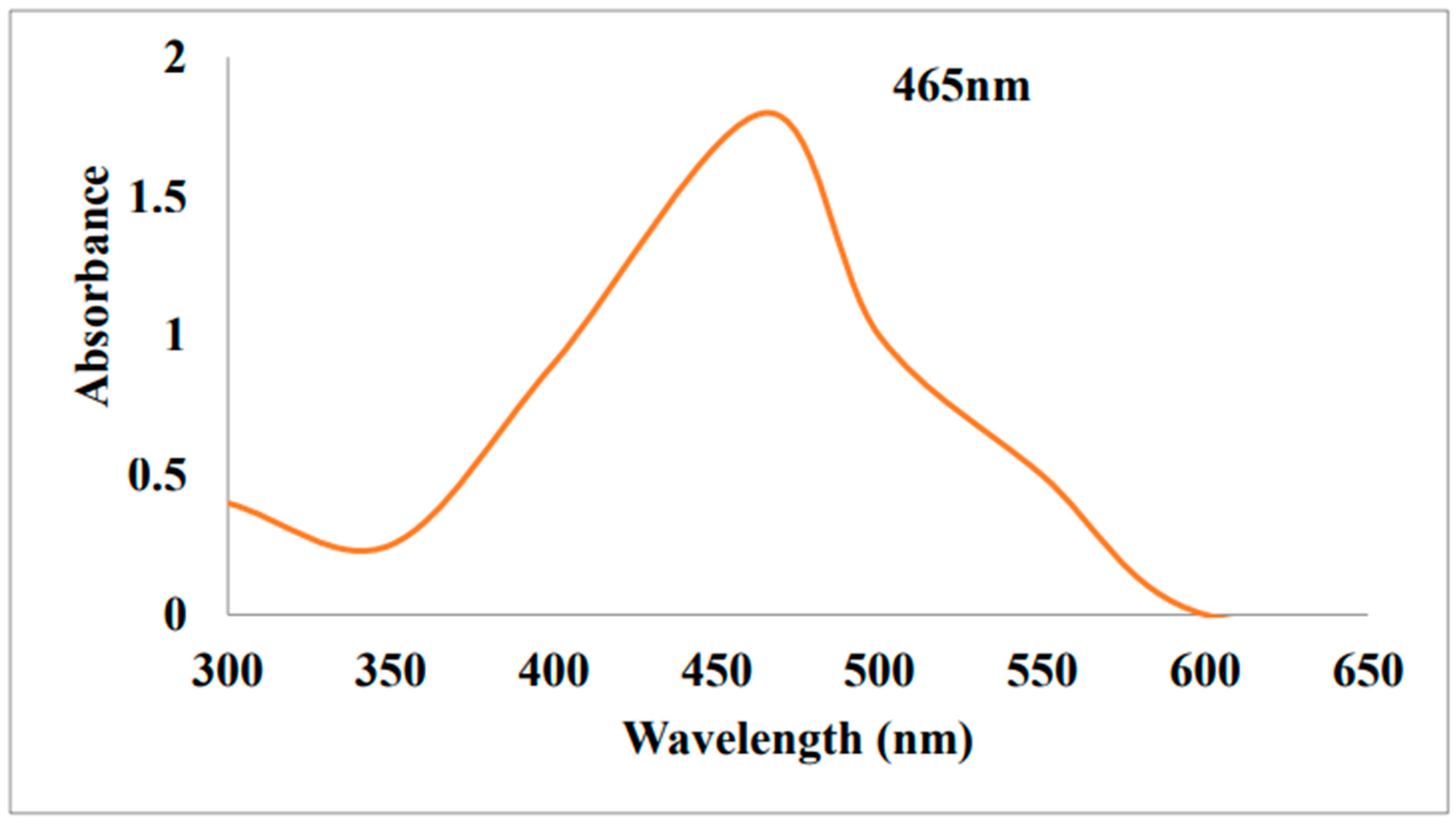
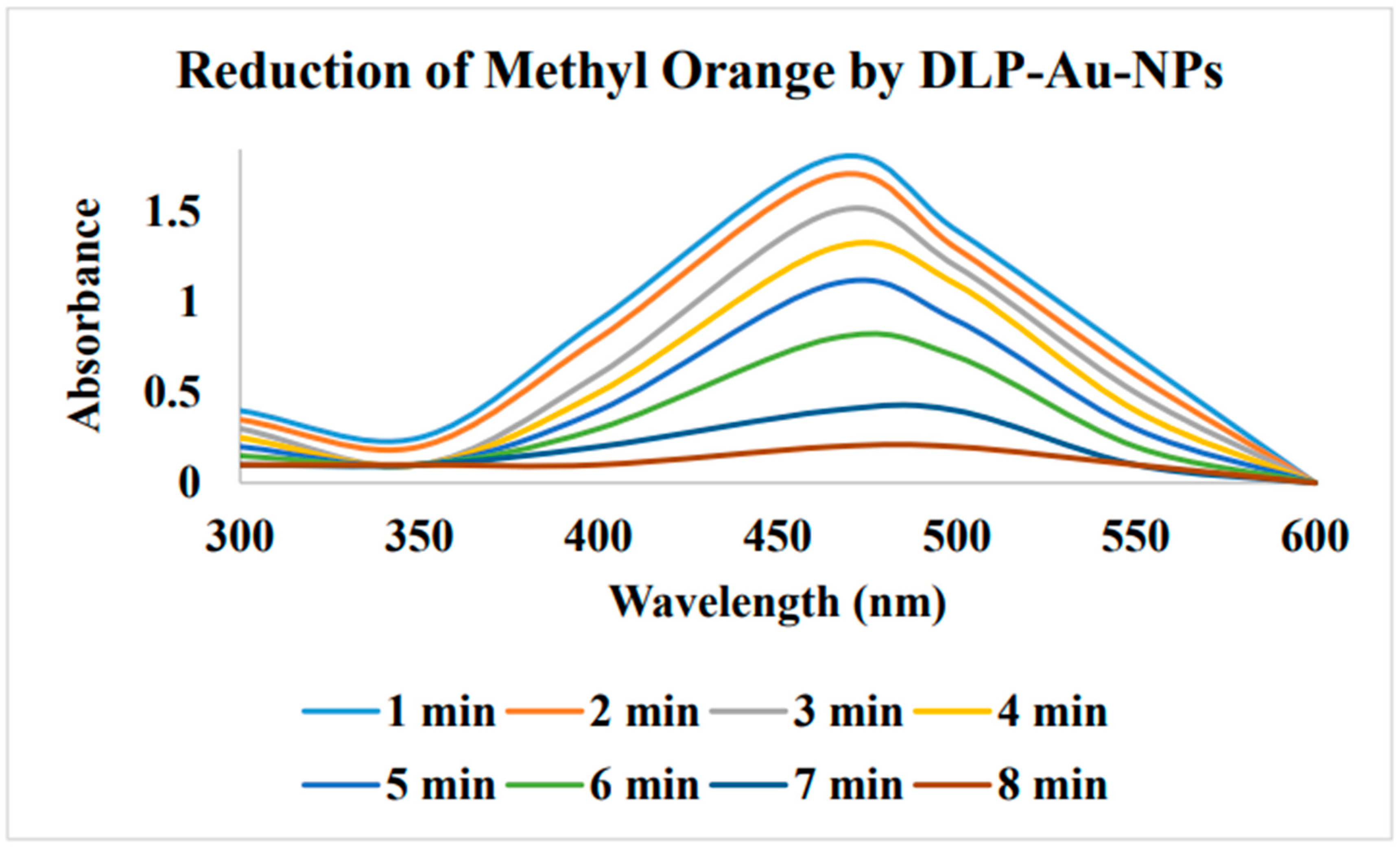
Biogenic Au-NPs on glass beads:
Removal of Malachite green using Activated Carbon Gold Nanopartices (Au-NP-AC):
Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles:
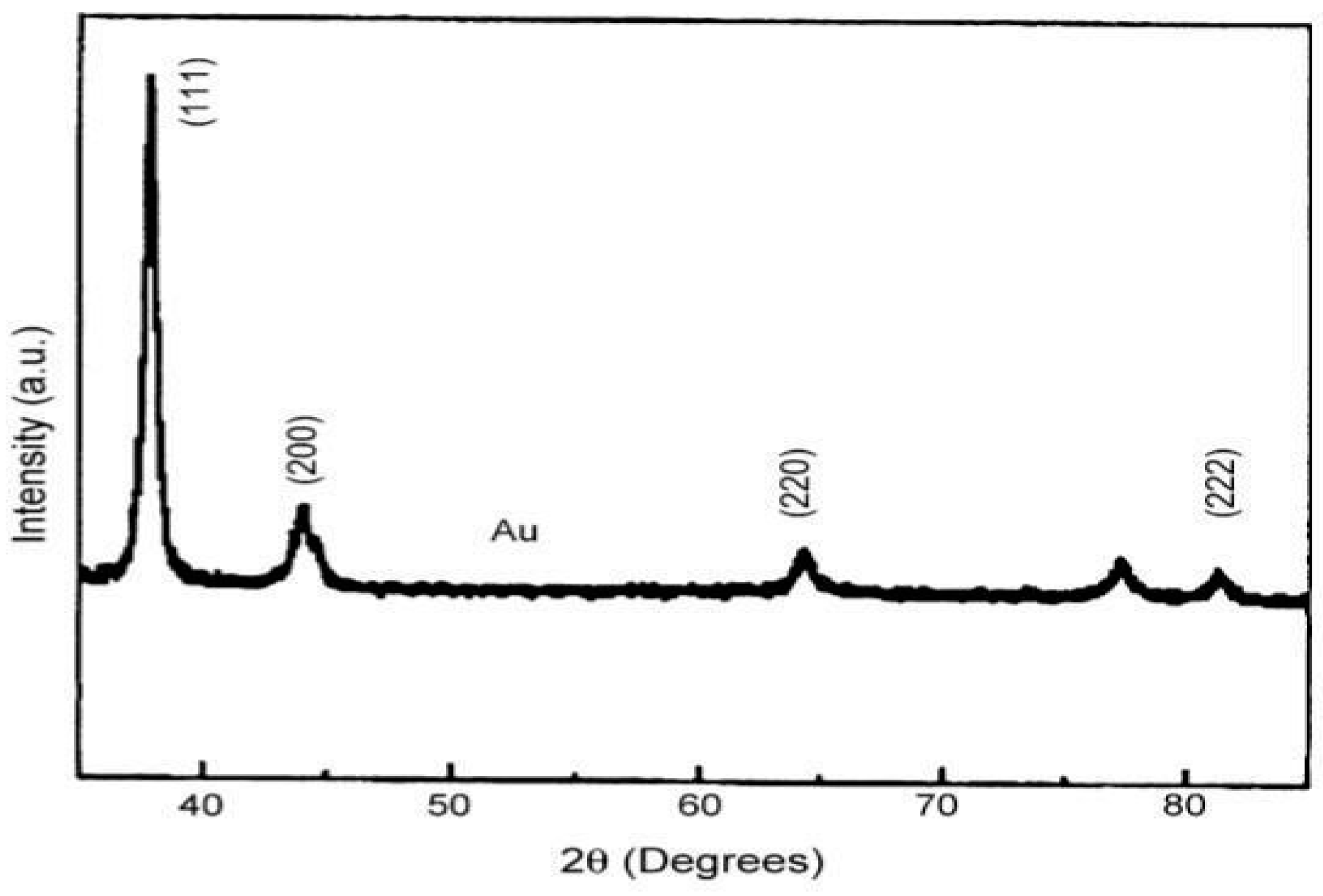
1. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles by using marine alga (Sargassum wightii):
Characterization Techniques:
TEM micrograph
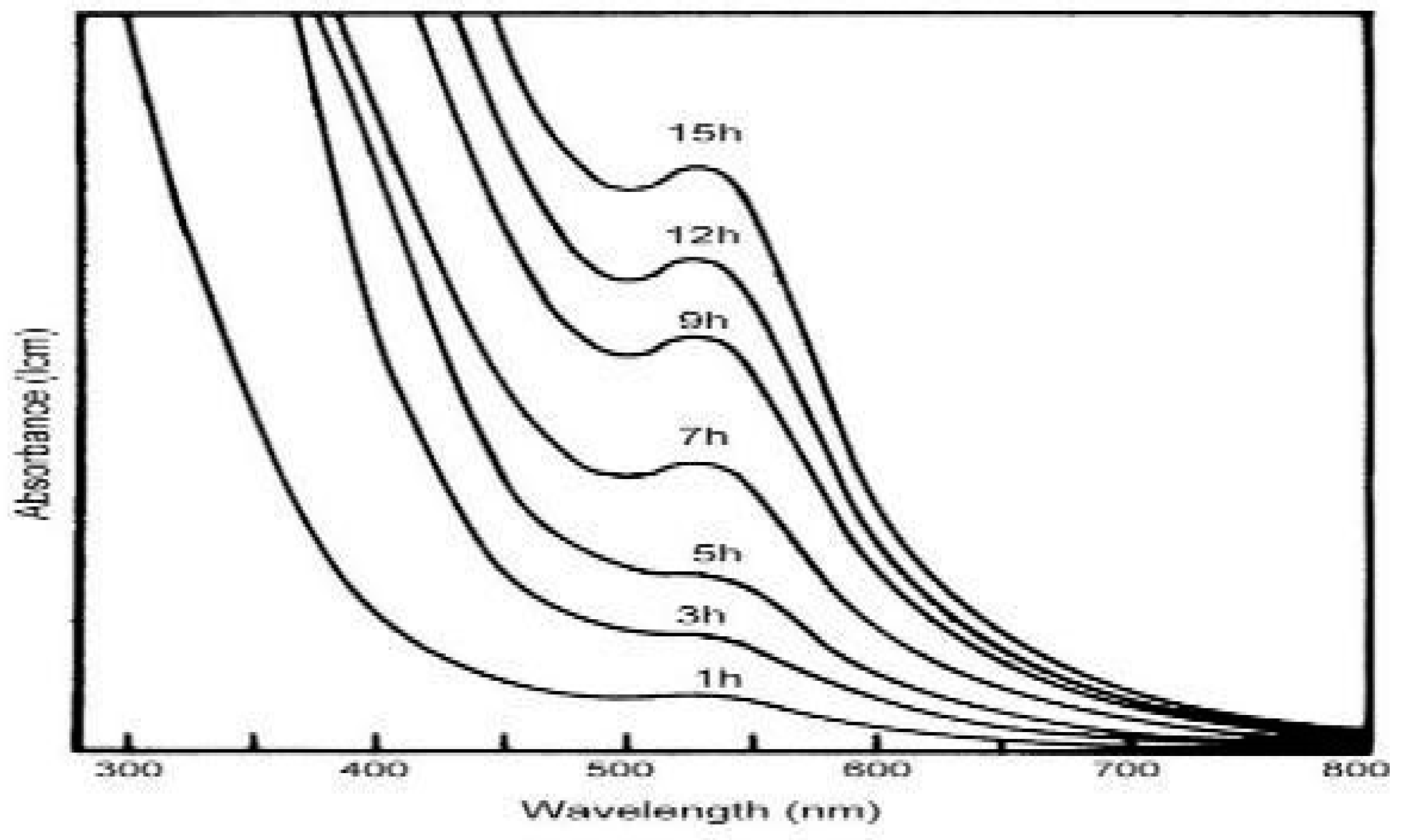
2. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles by using Scutellarin barbata:
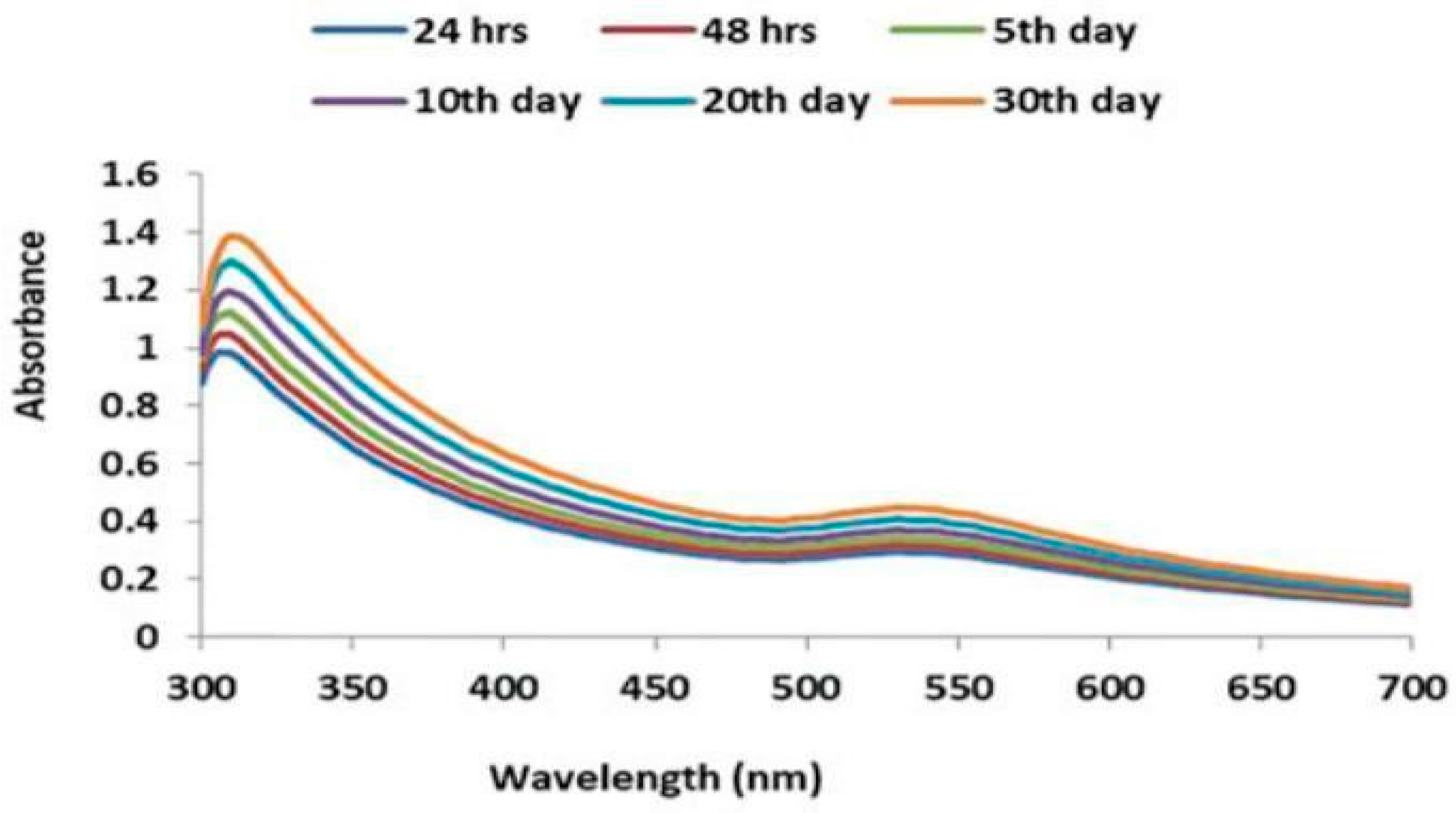
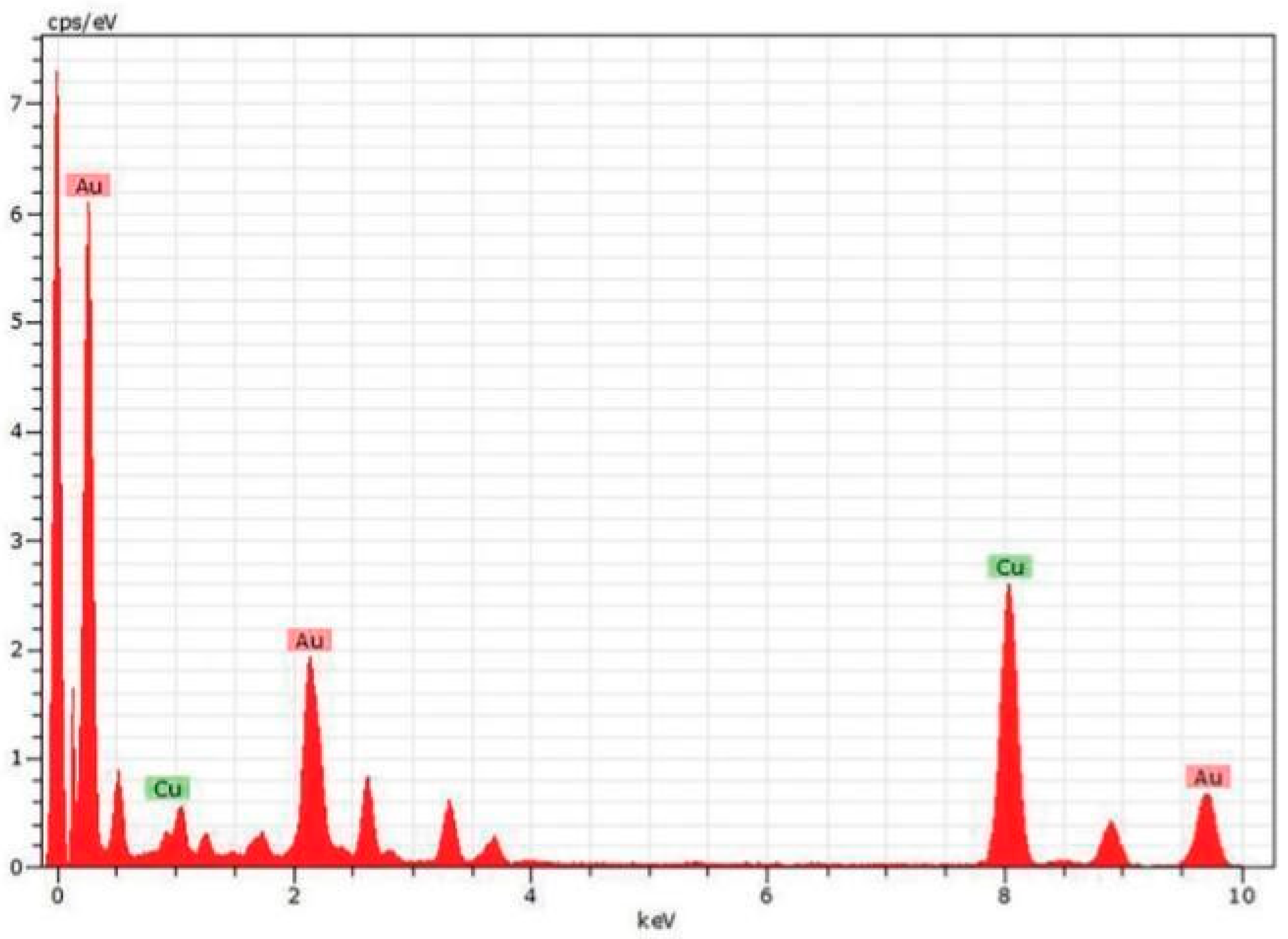
3. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles by Alpinia nigra:
Removal of Rhodamine B and Methyl Orange dyes by using ANL-AnNPs:
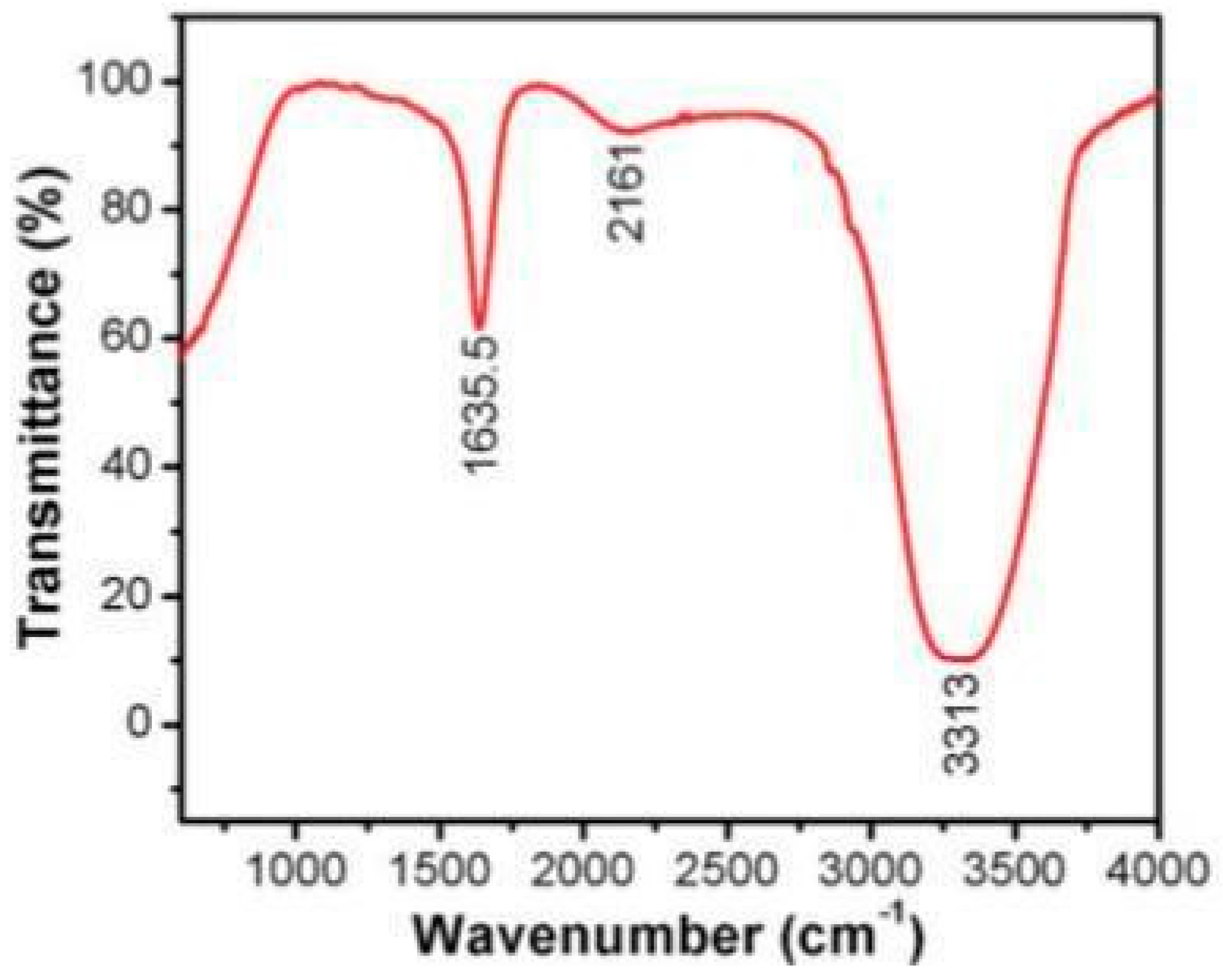
4. Synthesis of graphene/Au-NPs:
5. Adsorption of MB dye using Polyaniline coated gold aryl particles:
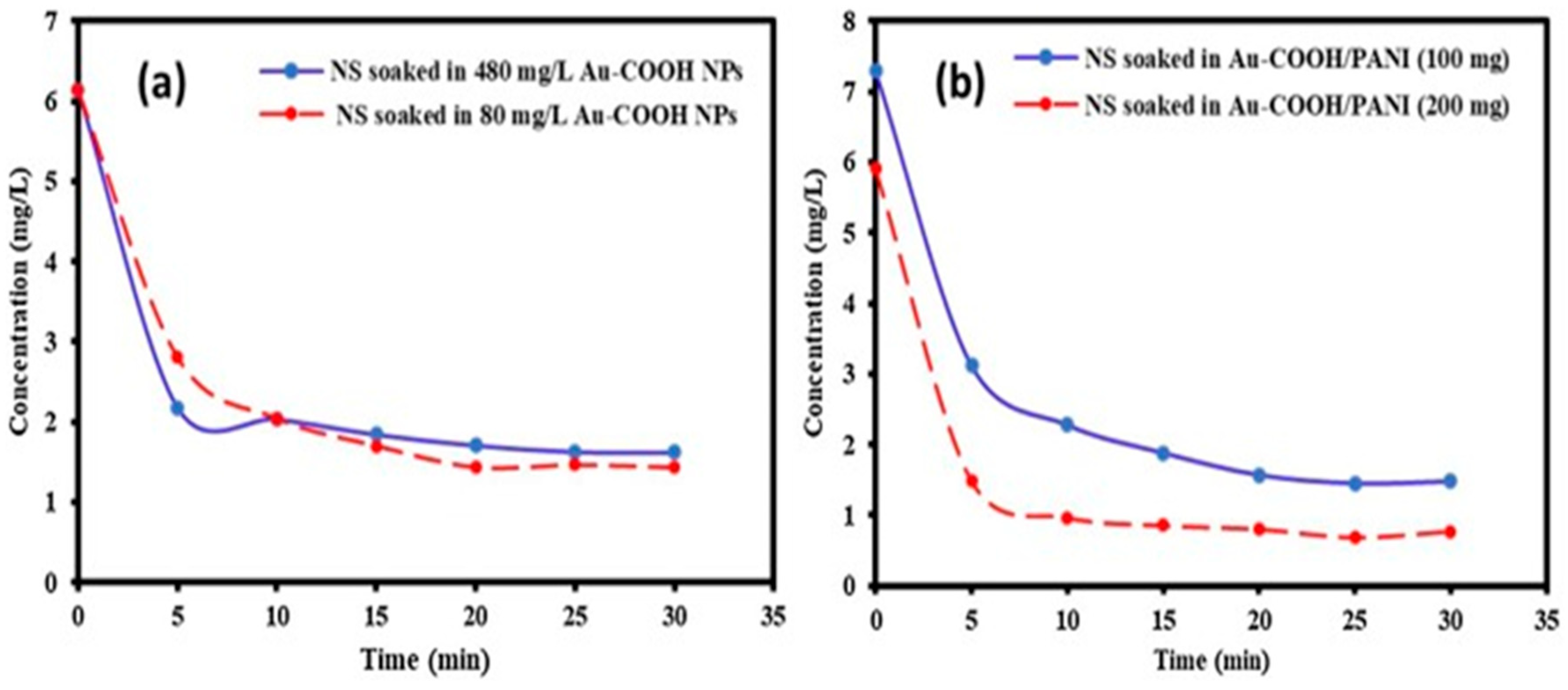
| Sample | Removal (%) |
|---|---|
| Nano sand(5mg) | 65.5 |
|
Au-COOH NPs Au-COOH NPs(80mgl-1) Au-COOH NPs (480mgL-1) |
76.6 73.6 |
|
Au-COOH NPs/ PANI nanocomposites Au-PANI (42mg PANI) Au-PANI (20mg PANI) |
80.0 85.0 |
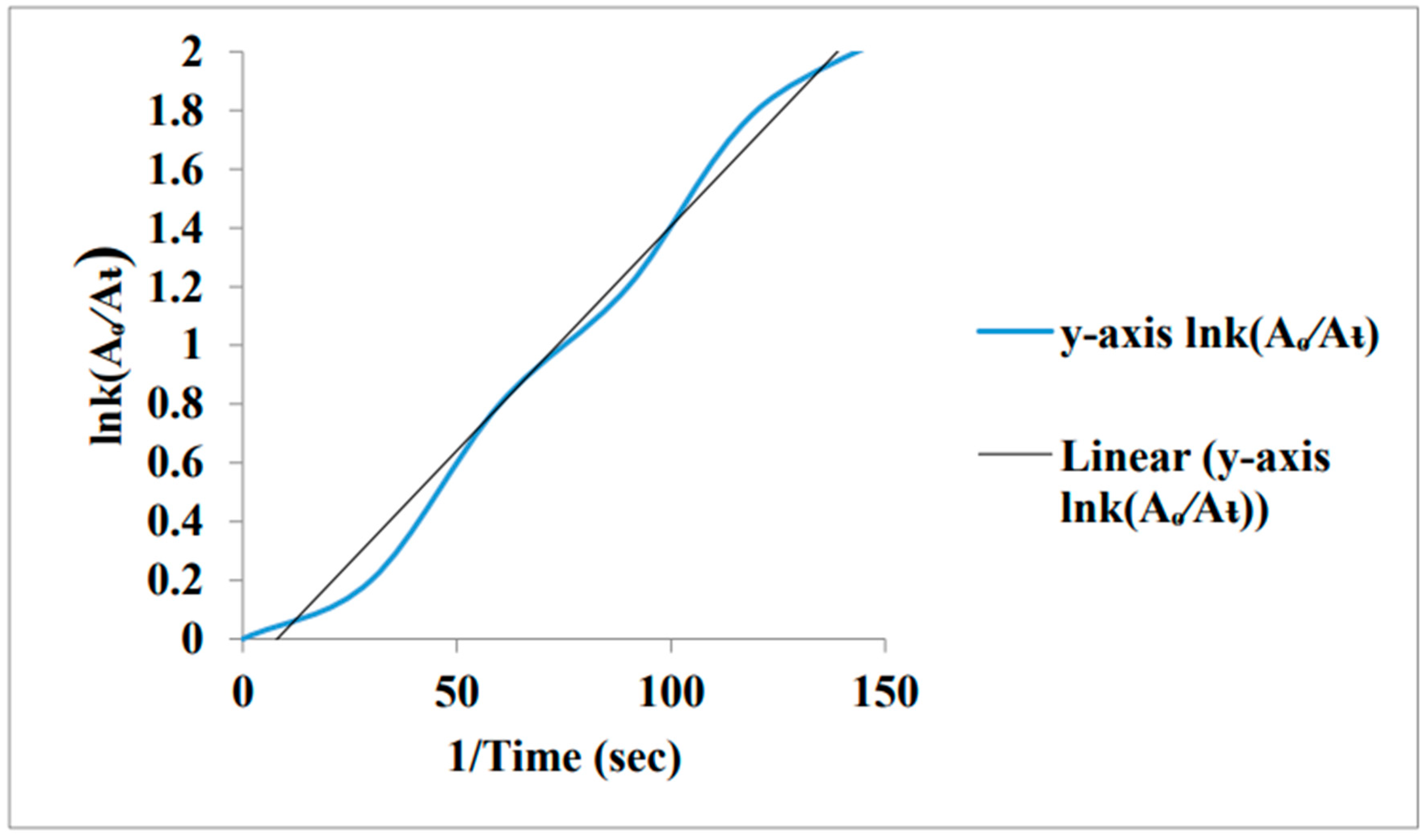
Comparison of Reaction kinetics for both Au-COOH NPs and Au-COOH NPs/PANI
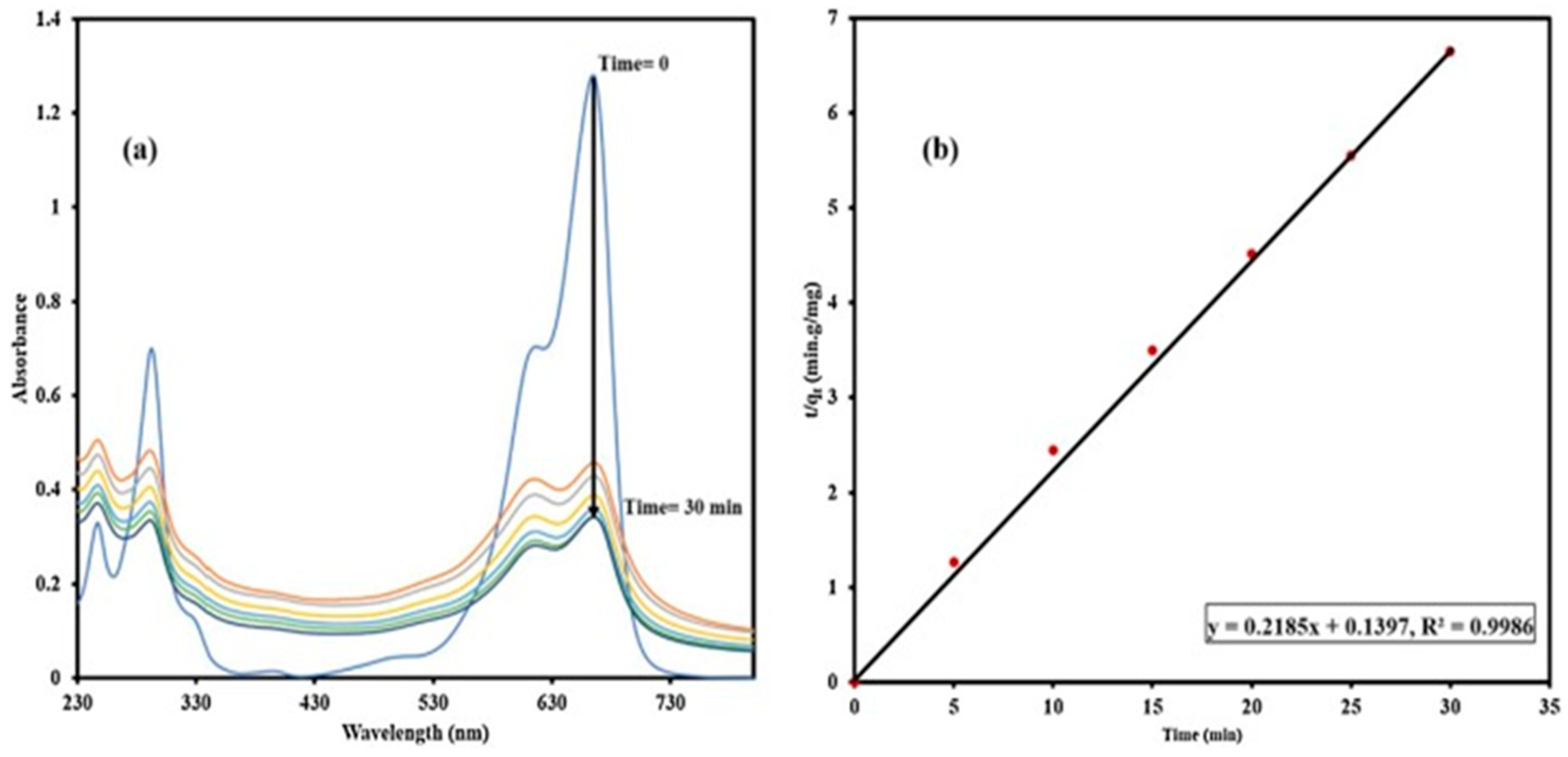
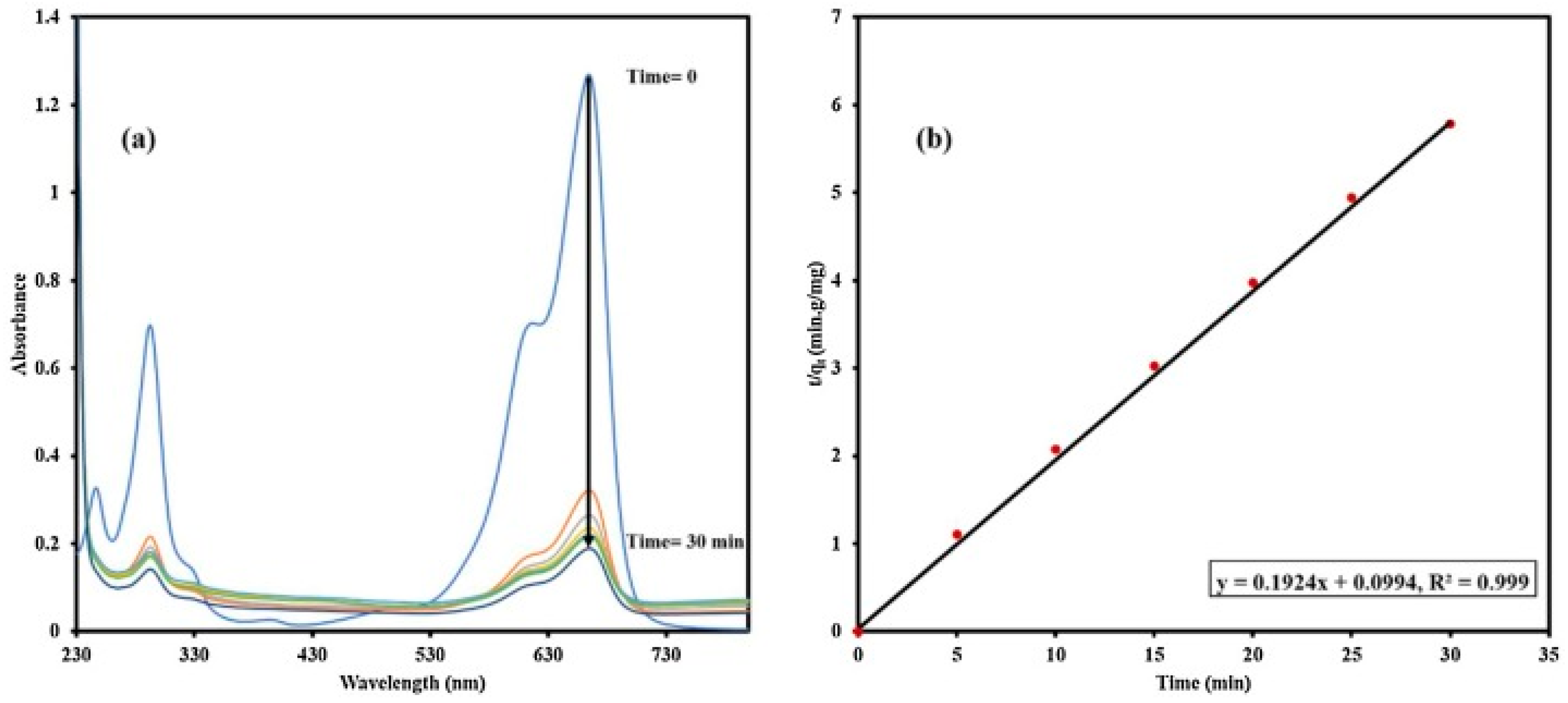
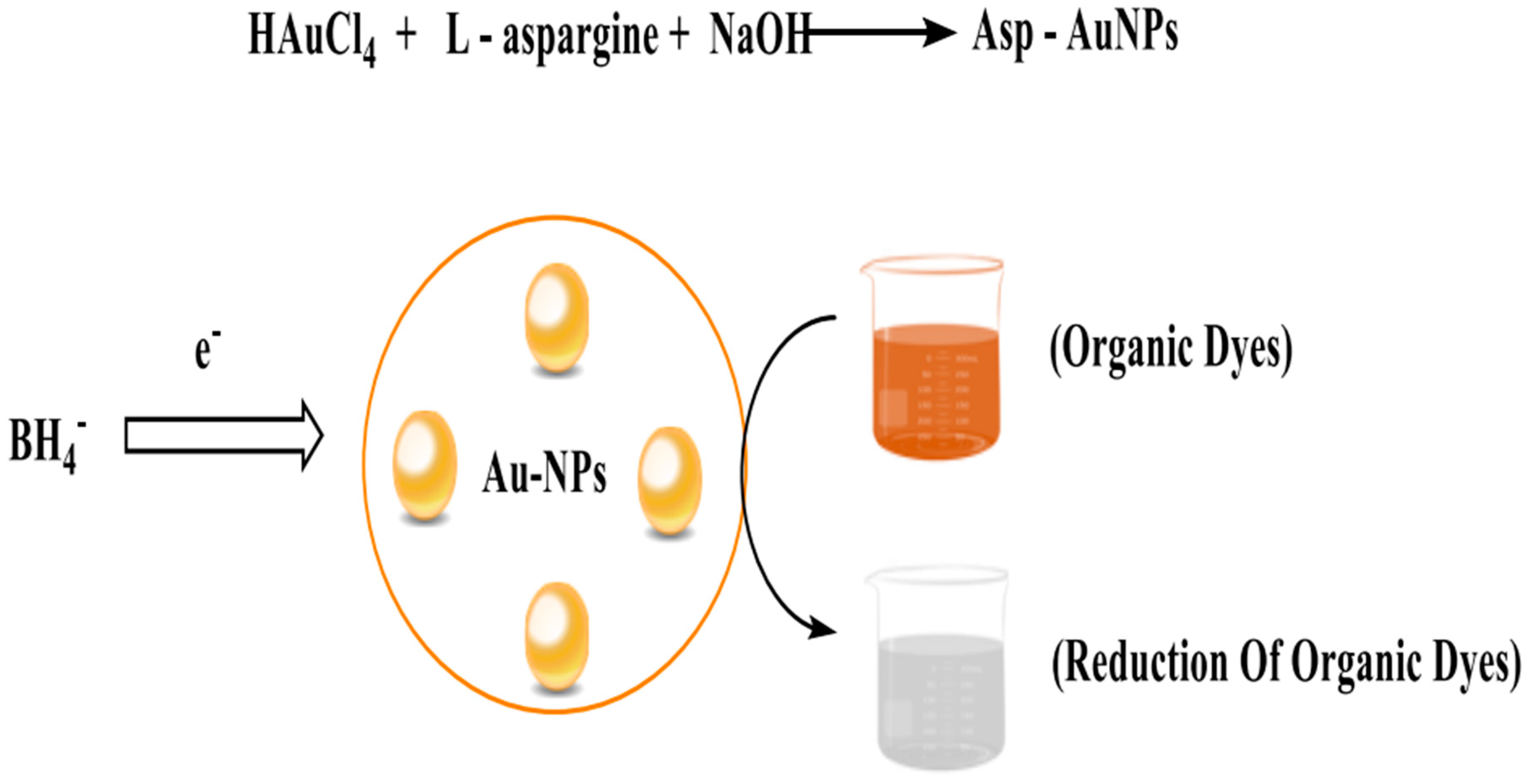
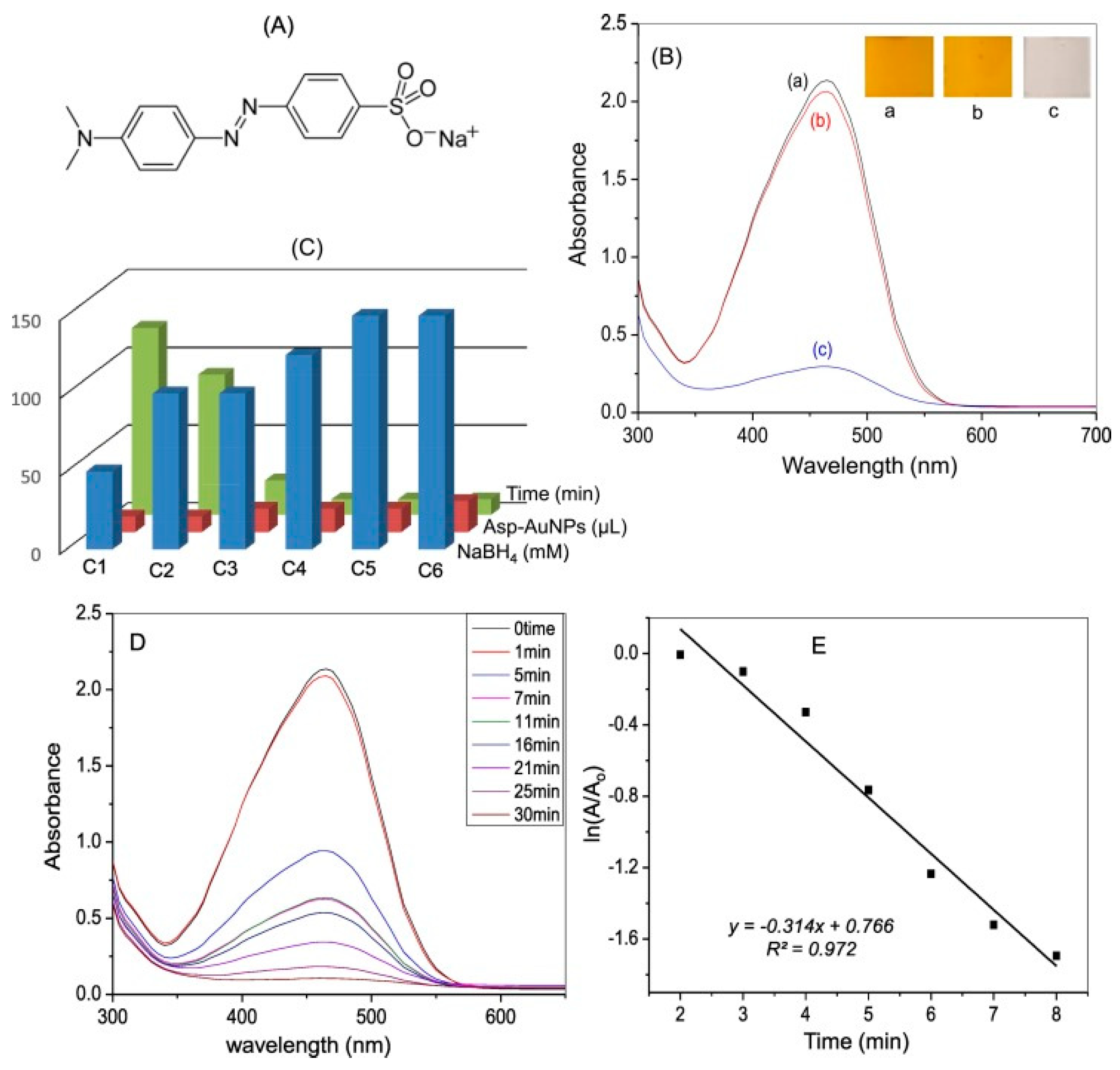
6. Synthesis of Asp-AuNPs:
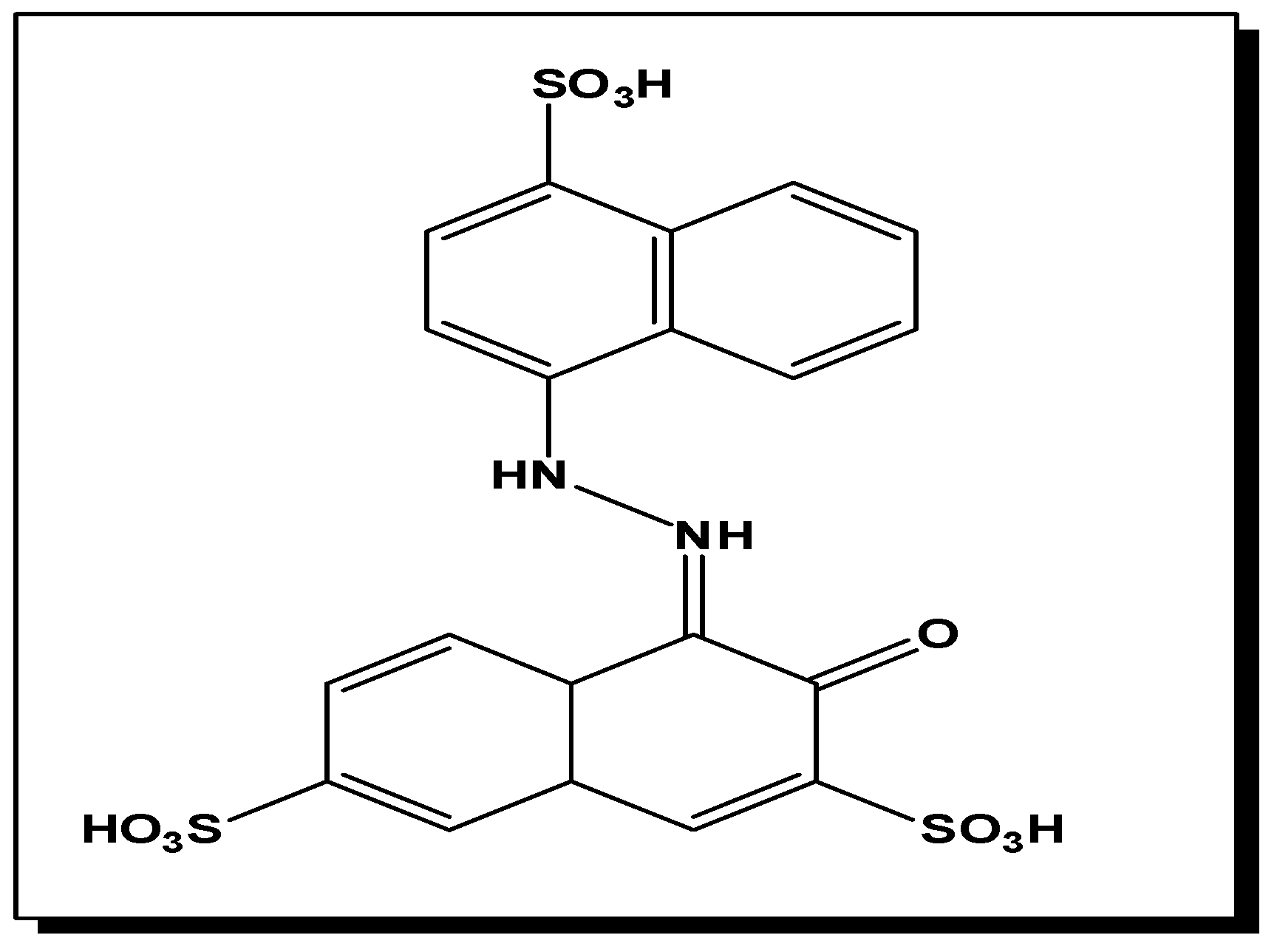
6.(. a) Degradation of Acid Red using Asp-AuNPs
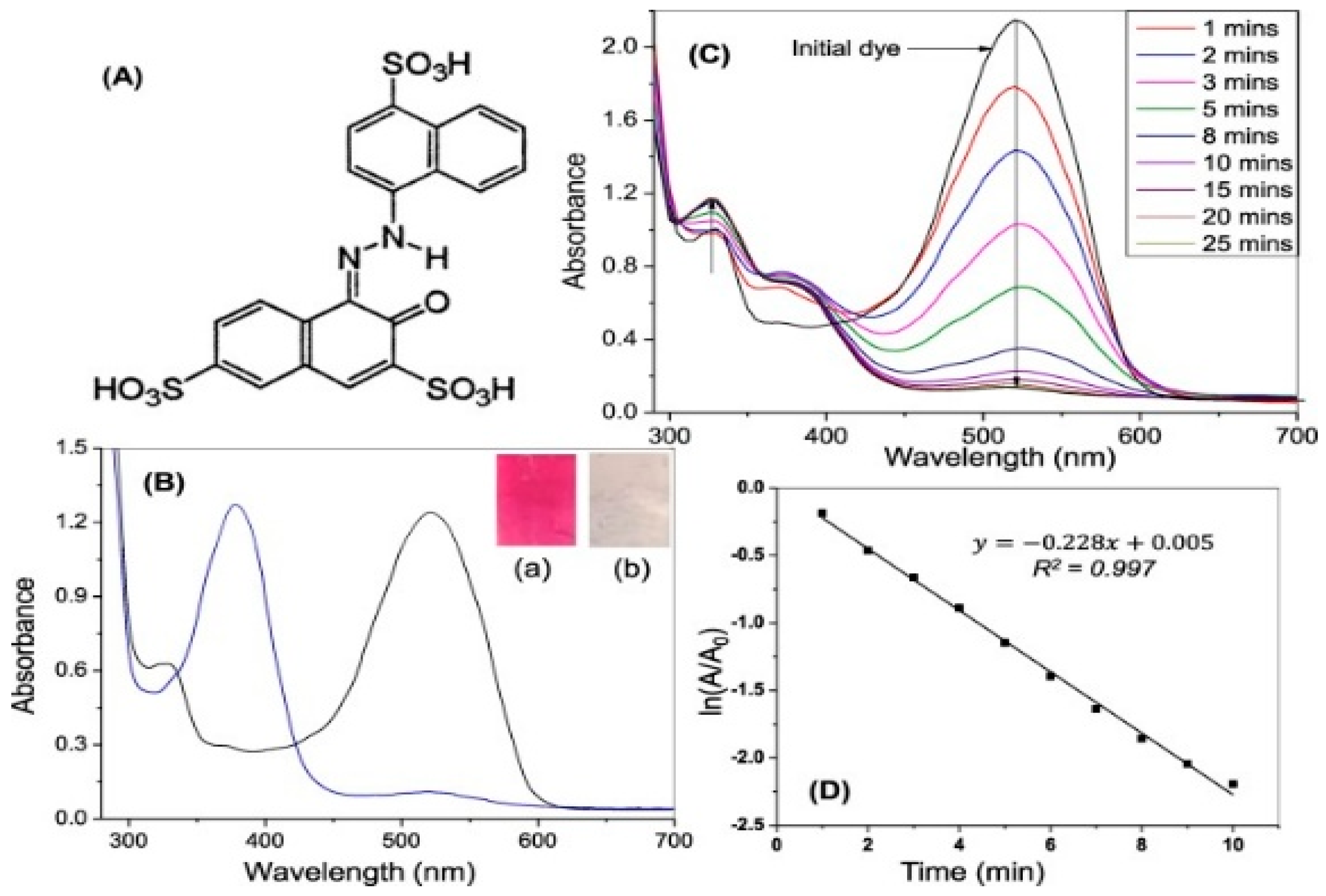
7. Annona squamosa Au-NPs and its degradation activity:
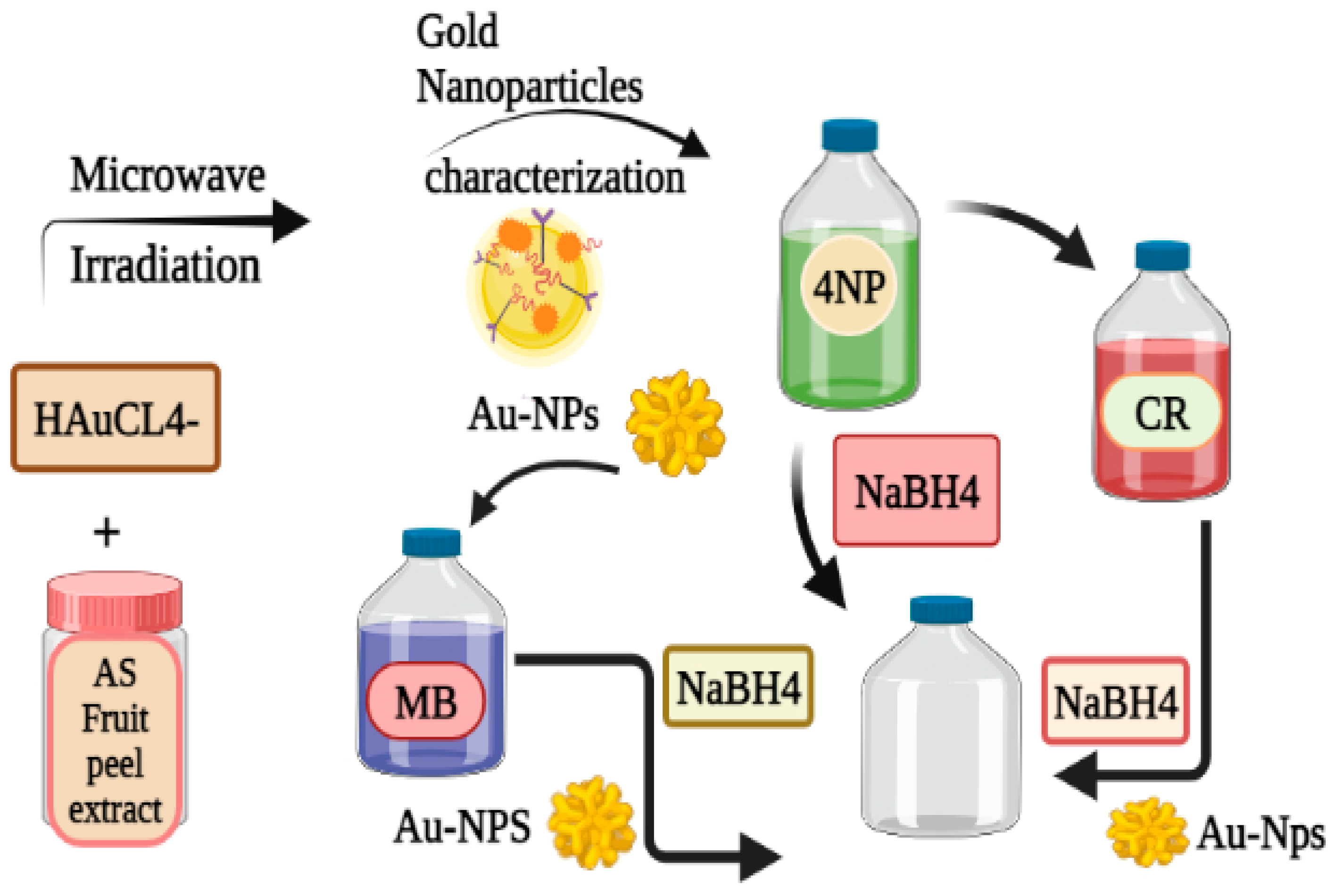
8. Amylopectin-TiO2- Au Nanocomposite and its degradation activity:
Synthesis of Nano-composite:
10. Gold nanoparticles synthesize on activated carbon:
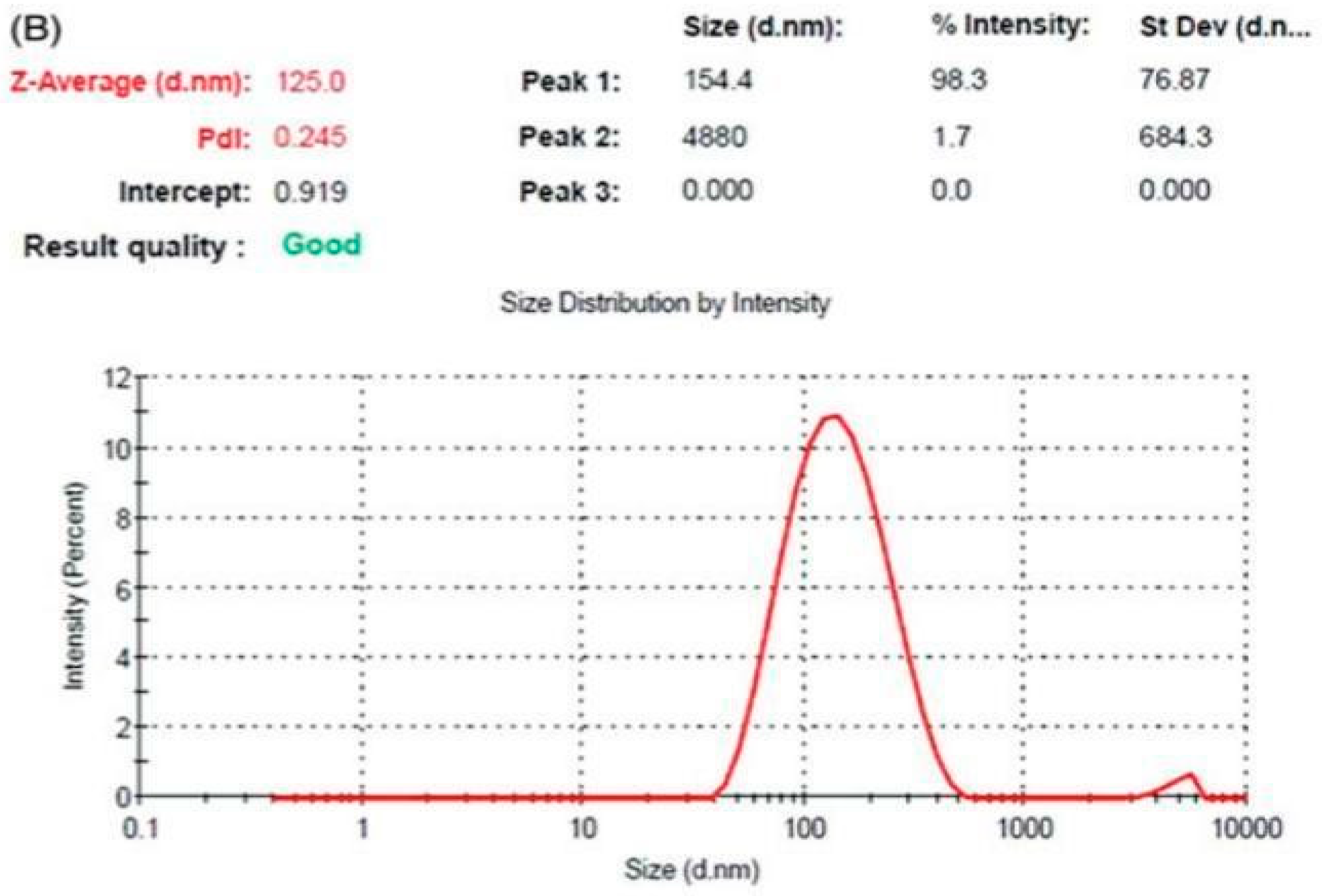
11. IPEI coated GNPs:
Synthesis of lPEI coated GNPs:
Method-I
Method-II
|
Sample Name |
PEI Mw(kDa) |
lPEI: Au (weight ratio) |
Sizeα[nm] |
PDIb |
Zeta potential [mV] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle formation Method I | |||||
| Control-I | 25 | 1:21 | 31.53 | 0.33 | +44 |
| lPEI2.5-Au | 2.5 | 1:21 | 24.12 | 0.22 | +51 |
| Method II | |||||
| Control-II | 25 | 1:21 | 25.55 | 0.23 | +52 |
| pH 3.5 | 25 | 1:21 | 52.42 | 0.43 | +53 |
| pH 5 | 25 | 1:21 | 24.32 | 0.45 | +47 |
| lPEI2.5-Au | 2.5 | 1:21 | 51.42 | 0.25 | +50 |
| Post-synthetic particle properties Method I | |||||
| pH 3 | 25 | 1:21 | 51.55 | 0.44 | +34 |
| pH 5 | 25 | 1:21 | 46.10 | 0.47 | +31 |
| pH 7 | 25 | 1:21 | 49.27 | 0.47 | +16 |
| Method II | |||||
| pH 3 | 25 | 1:21 | 50.50 | 0.46 | +24 |
| pH 5 | 25 | 1:21 | 41.62 | 0.41 | +38 |
| pH 7 | 25 | 1:21 | 50.97 | 0.52 | +14 |
12. Biosynthesis gold nanoparticles using Bacillus marisflavi:
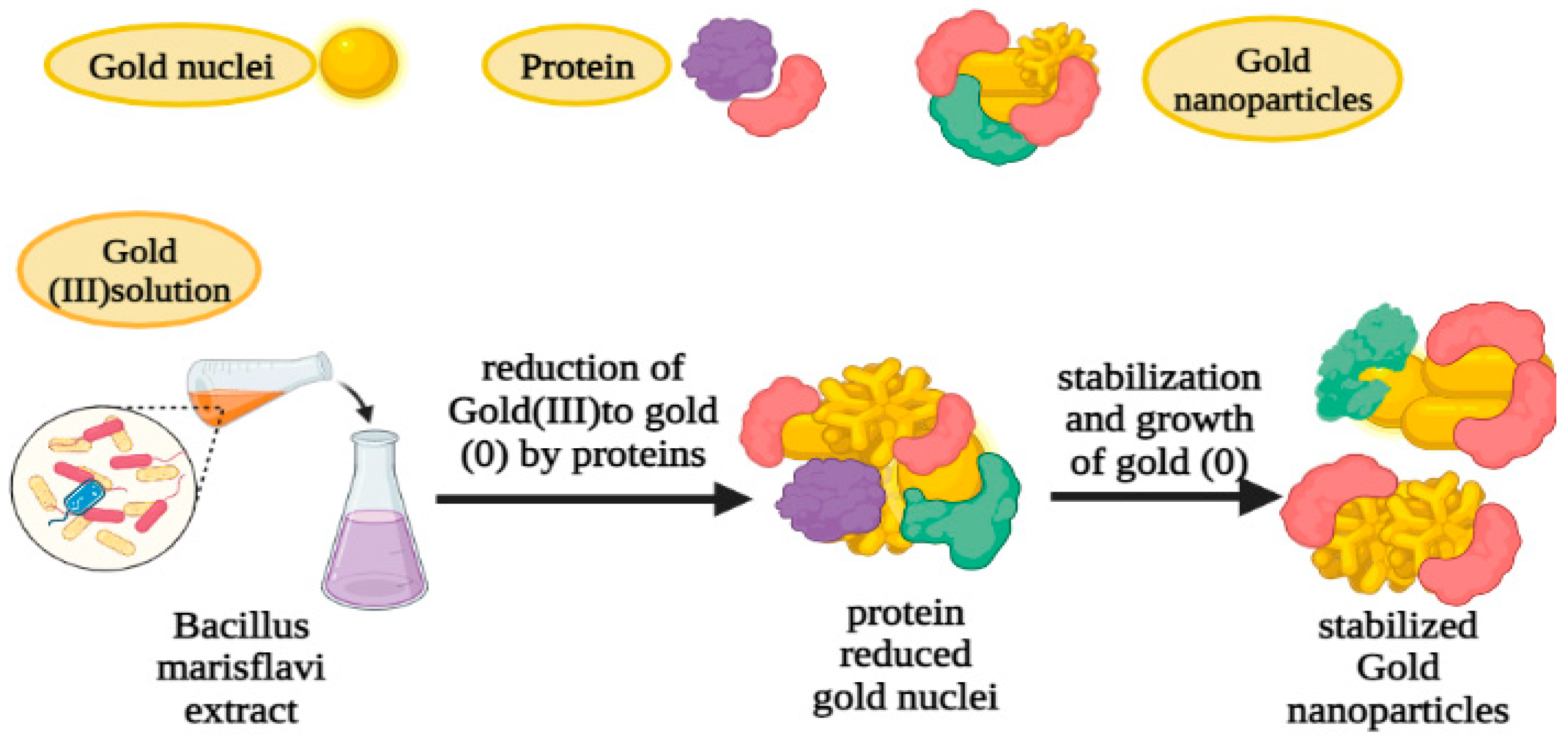
3). Catalytic activities of Asp-AuNPs in degradation of organic dyes:
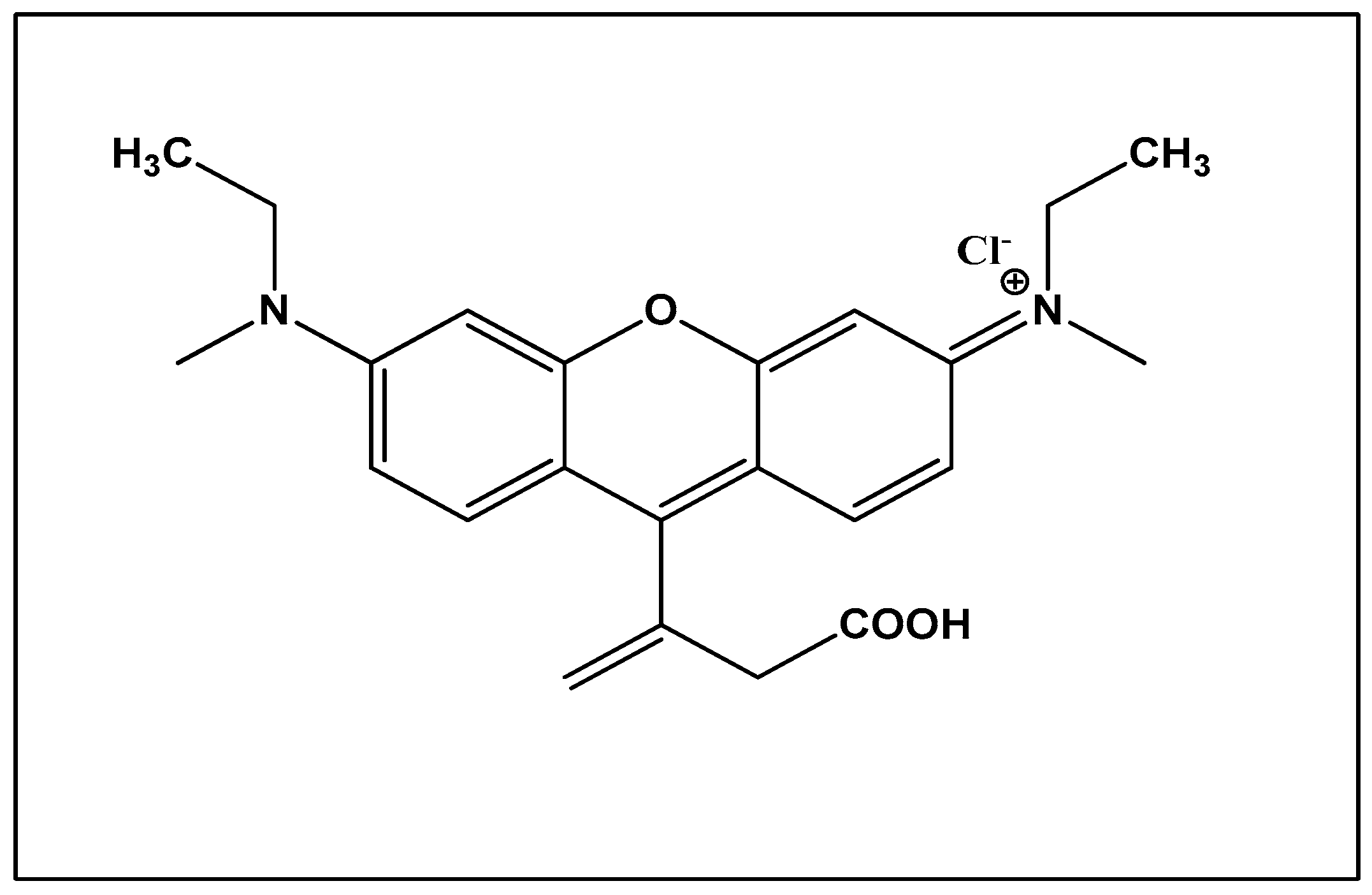
A) Rhodamine B (RB) Degradation
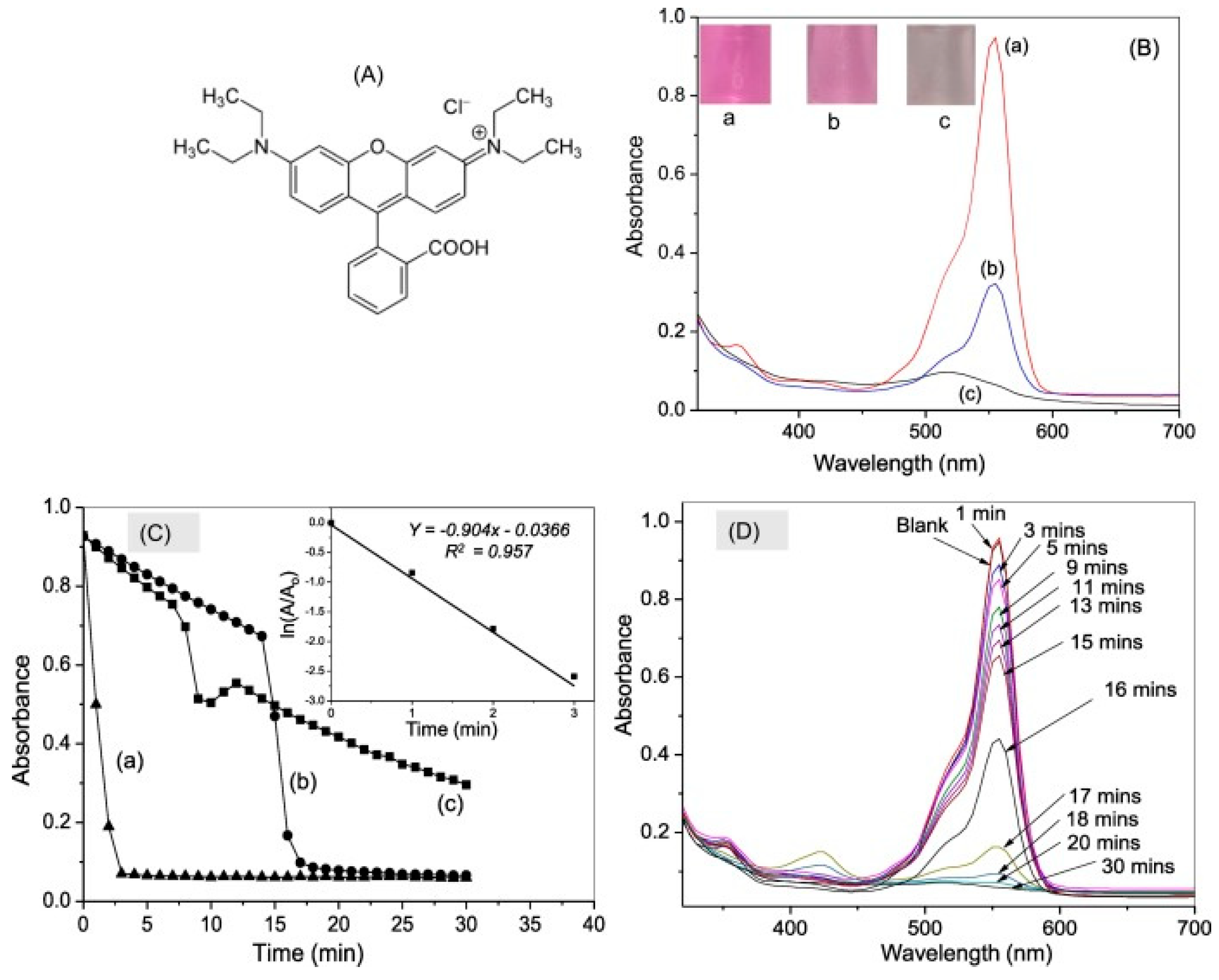
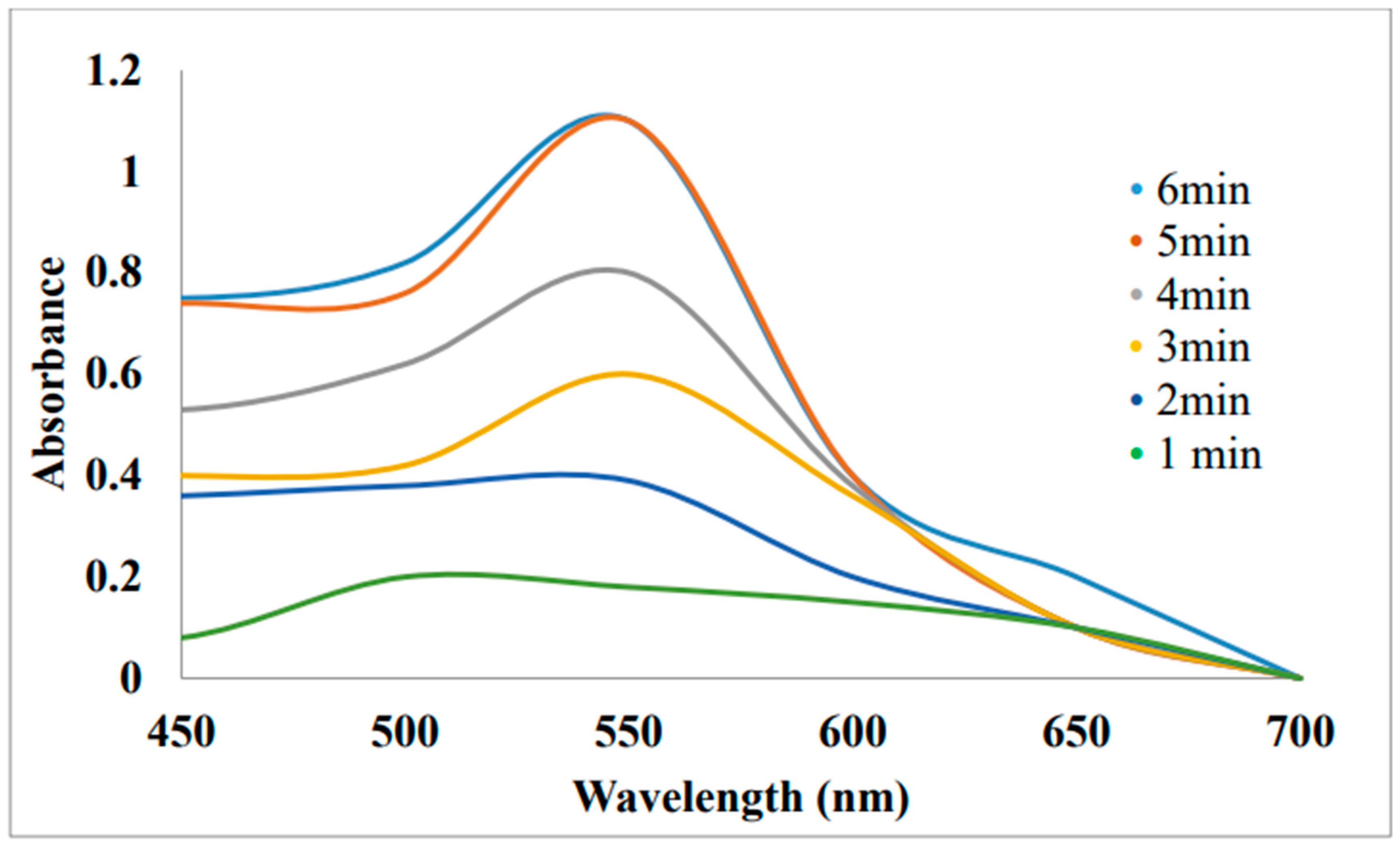
4. Degradation of 4-NP by Annona Squamosa Au-NPs:
Degradation of MB and CR:
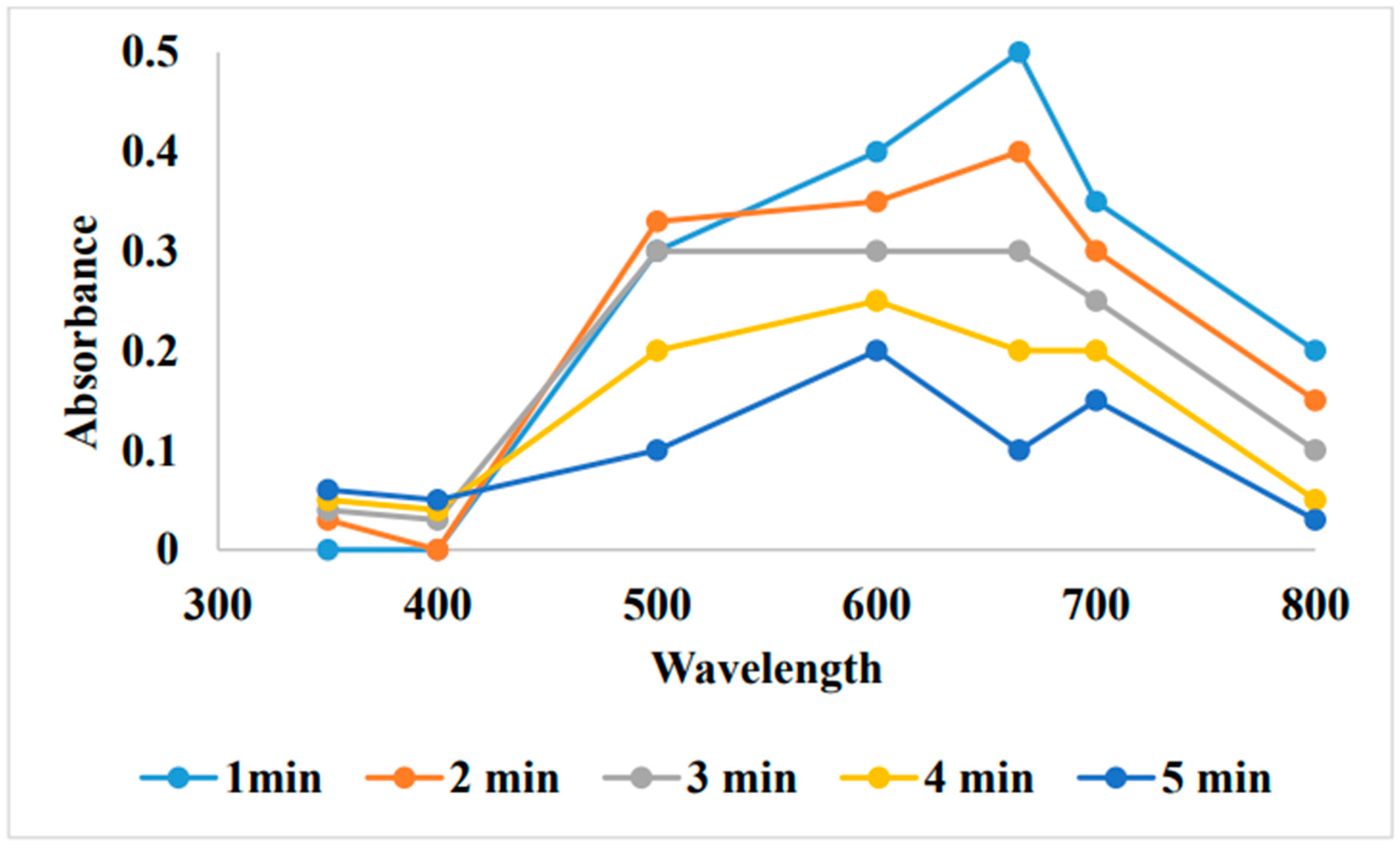
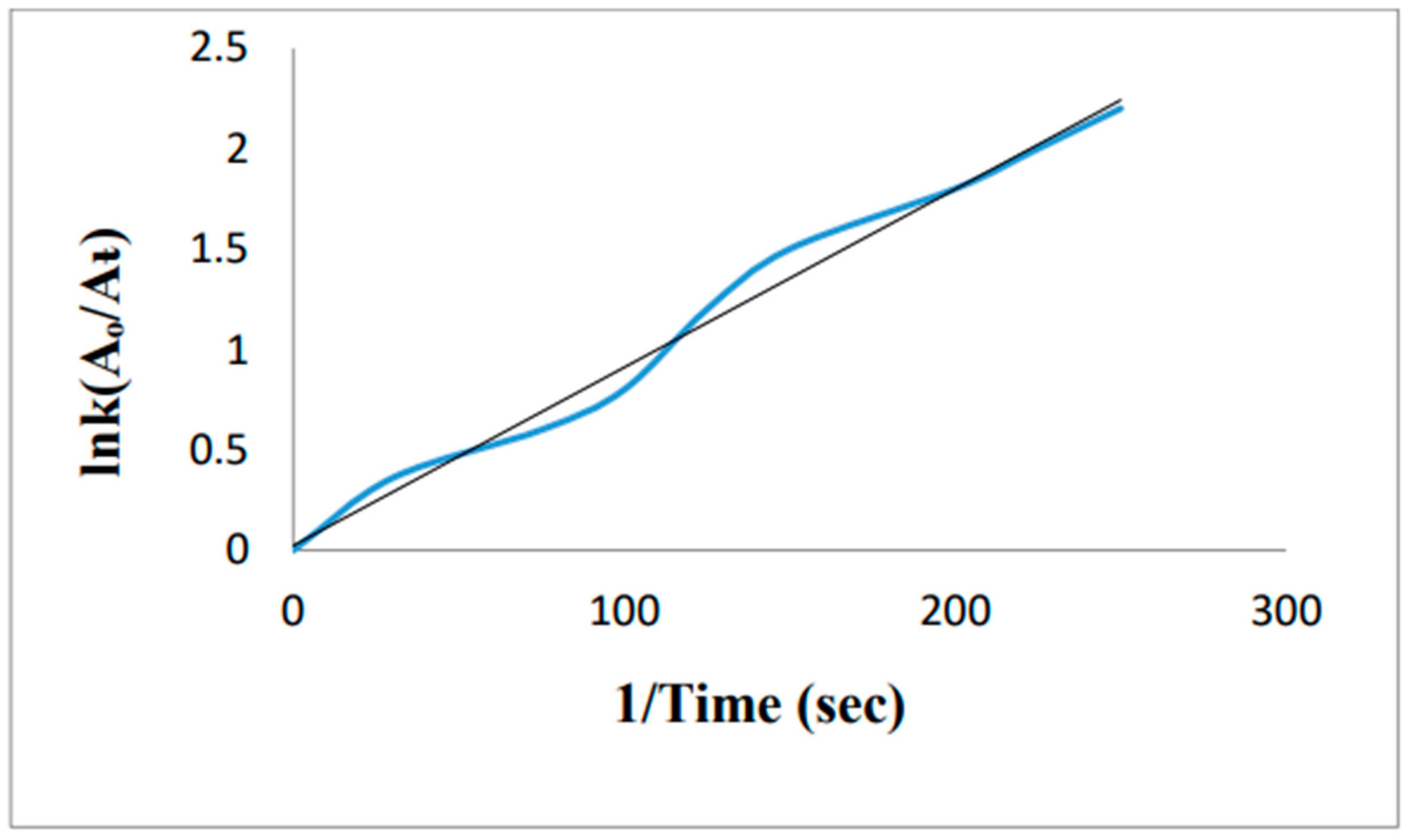
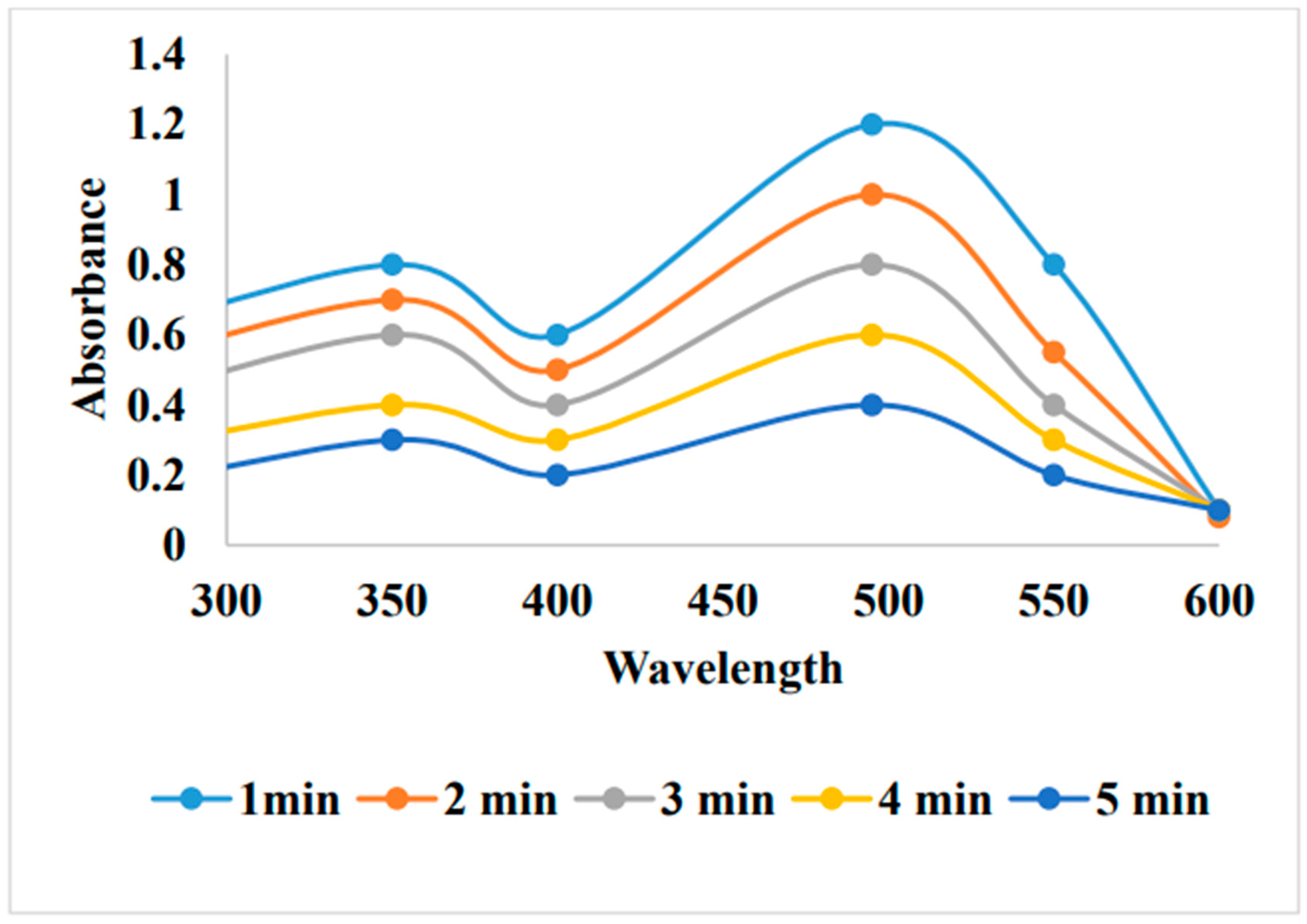
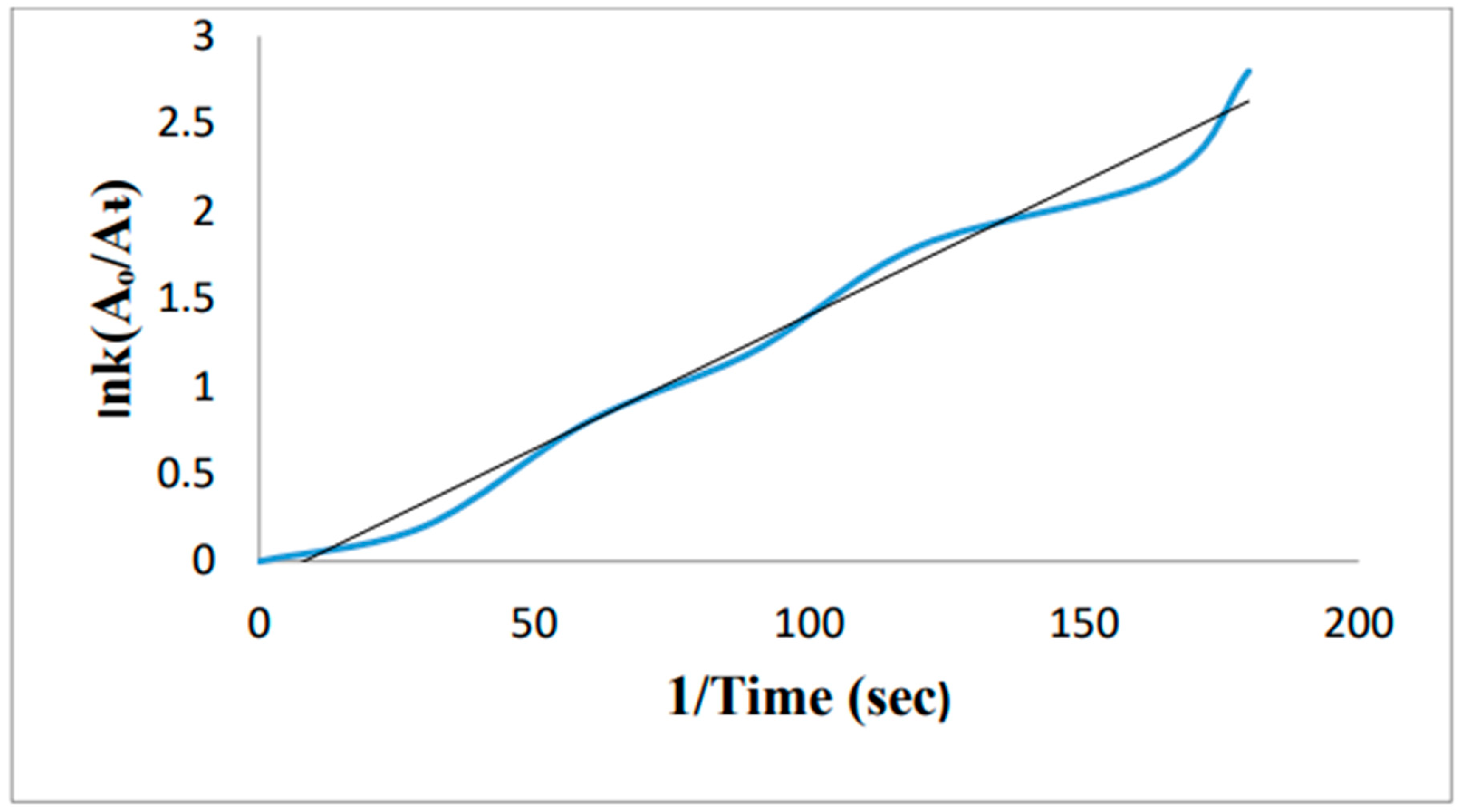
5. Removal of methylene blue by using Au-NPs formed from activated carbon:
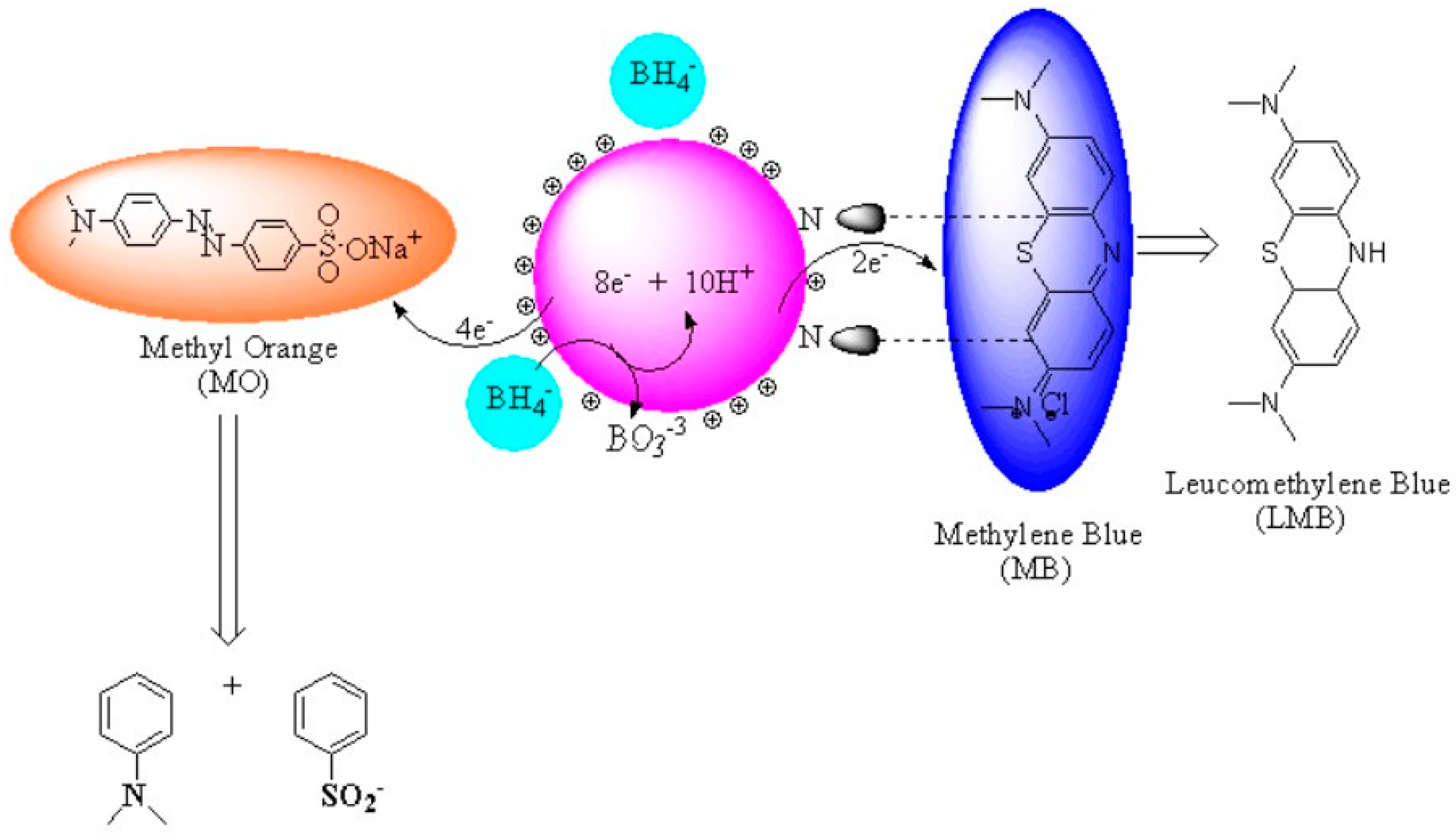
Conclusion:
References
- Kaykhaii, M., Sasani, M., & Marghzari, S. (2018). Removal of dyes from the environment by adsorption process. Chem. Mater. Eng, 6(2), 31-35. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S., & Kaur, A. (2018). Various methods for removal of dyes from industrial effluents-a review. Indian J. Sci. Technol, 11(1). [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S., Bajaj, H. C., & Tayade, R. J. (2018). Recent advances based on the synergetic effect of adsorption for removal of dyes from waste water using photocatalytic process. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 65, 201-222. [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W., Hu, J., Qi, J., Hou, Y., Zhou, C., & Wei, X. (2019). Removal of dyes from wastewater by nanomaterials: a review. Advanced Materials Letters, 10(1), 9-20. [CrossRef]
- Hunger, K. (Ed.). (2007). Industrial dyes: chemistry, properties, applications. John Wiley & Sons.
- Mojsov, K. D., Andronikov, D., Janevski, A., Kuzelov, A., & Gaber, S. (2016). The application of enzymes for the removal of dyes from textile effluents. Advanced technologies, 5(1), 81-86. [CrossRef]
- Naeem, H., Ajmal, M., Muntha, S., Ambreen, J., & Siddiq, M. (2018). Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide sheets integrated with gold nanoparticles and their applications to adsorptive removal and catalytic reduction of water contaminants. RSC advances, 8(7), 3599-3610. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. K., Behera, S. S., Singh, K. R., Mishra, S., Panigrahi, B., Sahoo, T. R., ... & Mandal, D. (2020). Biosynthesized gold nanoparticles as photocatalysts for selective degradation of cationic dye and their antimicrobial activity. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 400, 112704. [CrossRef]
- Sztandera, K., Gorzkiewicz, M., & Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. (2018). Gold nanoparticles in cancer treatment. Molecular pharmaceutics, 16(1), 1-23. [CrossRef]
- Garg, N., Bera, S., Rastogi, L., Ballal, A., & Balaramakrishna, M. V. (2020). Synthesis and characterization of L-asparagine stabilised gold nanoparticles: Catalyst for degradation of organic dyes. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 232, 118126. [CrossRef]
- Song, W. C., Kim, B., Park, S. Y., Park, G., & Oh, J. W. (2022). Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Sargassum horneri extract as catalyst for industrial dye degradation. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 15(9), 104056. [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Henríquez, L., Alfaro-Aguilar, K., Ugalde-Álvarez, J., Vega-Fernández, L., Montes de Oca-Vásquez, G., & Vega-Baudrit, J. R. (2020). Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles from plant extracts and their possible applications as antimicrobial agents in the agricultural area. Nanomaterials, 10(9), 1763. [CrossRef]
- Alle, M., Lee, S. H., & Kim, J. C. (2020). Ultrafast synthesis of gold nanoparticles on cellulose nanocrystals via microwave irradiation and their dyes-degradation catalytic activity. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 41, 168-177. [CrossRef]
- Najahi-Missaoui, W., Arnold, R. D., & Cummings, B. S. (2020). Safe nanoparticles: Are we there yet?. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 385. [CrossRef]
- Martínez, G., Merinero, M., Pérez-Aranda, M., Pérez-Soriano, E. M., Ortiz, T., Villamor, E., ... & Alcudia, A. (2020). Environmental impact of nanoparticles’ application as an emerging technology: A review. Materials, 14(1), 166. [CrossRef]
- Yetisgin, A. A., Cetinel, S., Zuvin, M., Kosar, A., & Kutlu, O. (2020). Therapeutic nanoparticles and their targeted delivery applications. Molecules, 25(9), 2193. [CrossRef]
- Hosny, M., Fawzy, M., El-Borady, O. M., & Mahmoud, A. E. D. (2021). Comparative study between Phragmites australis root and rhizome extracts for mediating gold nanoparticles synthesis and their medical and environmental applications. Advanced Powder Technology, 32(7), 2268-2279. [CrossRef]
- Jamkhande, P. G., Ghule, N. W., Bamer, A. H., & Kalaskar, M. G. (2019). Metal nanoparticles synthesis: An overview on methods of preparation, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. Journal of drug delivery science and technology, 53, 101174. [CrossRef]
- Biao, L., Tan, S., Meng, Q., Gao, J., Zhang, X., Liu, Z., & Fu, Y. (2018). Green synthesis, characterization and application of proanthocyanidins-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 8(1), 53. [CrossRef]
- Dabhane, H., Chatur, S., Jadhav, G., Tambade, P., & Medhane, V. (2021). Phytogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles and applications for removal of methylene blue dye: A review. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, 3, 160-171. [CrossRef]
- Lu, H., Tang, S. Y., Yun, G., Li, H., Zhang, Y., Qiao, R., & Li, W. (2020). Modular and integrated systems for nanoparticle and microparticle synthesis—a review. Biosensors, 10(11), 165. [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, S. B., Adnan, R., Rameez Khan, R. M., & Rashid, M. (2020). Gold, silver, and palladium nanoparticles: a chemical tool for biomedical applications. Frontiers in chemistry, 8, 376. [CrossRef]
- Nadaf, N. Y., & Kanase, S. S. (2019). Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by Bacillus marisflavi and its potential in catalytic dye degradation. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 12(8), 4806-4814. [CrossRef]
- Parushuram, N., Ranjana, R., Harisha, K. S., Shilpa, M., Narayana, B., Neelakandan, R., & Sangappa, Y. (2022). Silk fibroin and silk fibroin-gold nanoparticles nanocomposite films: sustainable adsorbents for methylene blue dye. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 43(8), 1161-1176. [CrossRef]
- Rather, M. Y., Shincy, M., & Sundarapandian, S. M. (2022). Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine-B by phytosynthesized gold nanoparticles. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Shanmugaraj, K., Campos, C. H., Mangalaraja, R. V., Nandhini, K., Aepuru, R., Torres, C. C., ... & Vo, D. V. N. (2022). Gold nanoparticle–decorated earth-abundant clay nanotubes as catalyst for the degradation of phenothiazine dyes and reduction of 4-(4-nitrophenyl) morpholine. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Diğdem, T. R. A. K., & ARSLAN, Y. Biosynthesis of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) with Dimrit Raisin Extract and Their Degradation Activity for Water Contaminants. Düzce Üniversitesi Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi, 10(1), 117-127. [CrossRef]
- Trak, D. & Arslan, Y. (2022). Biosynthesis of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) with Dimrit Raisin Extract and Their Degradation Activity for Water Contaminants . Düzce Üniversitesi Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi, 10 (1), 117-127.
- Alikhani, N., Hekmati, M., Karmakar, B., & Veisi, H. (2022). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) using Rosa canina fruit extractand evaluation of its catalytic activity in the degradation of organic dye pollutants of water. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 139, 109351. [CrossRef]
- Singh, V. K., M. Yadav, S., Mishra, H., Kumar, R., Tiwari, R. S., Pandey, A., & Srivastava, A. (2019). WS2 quantum dot graphene nanocomposite film for UV photodetection. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2(6), 3934-3942. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R., Harip, S., Kumar, A. R., Deobagkar, D., & Zinjarde, S. (2018). Peptide stabilized gold and silver nanoparticles derived from the mangrove isolate Pseudoalteromonas lipolytica mediate dye decolorization. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 555, 180-190. [CrossRef]
- Rabeea, M. A., Owaid, M. N., Aziz, A. A., Jameel, M. S., & Dheyab, M. A. (2020). Mycosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using the extract of Flammulina velutipes, Physalacriaceae, and their efficacy for decolorization of methylene blue. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(3), 103841. [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M. A., Owaid, M. N., Rabeea, M. A., Aziz, A. A., & Jameel, M. S. (2020). Mycosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by the Portabello mushroom extract, Agaricaceae, and their efficacy for decolorization of Azo dye. Environmental nanotechnology, monitoring & management, 14, 100312. [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, A. M., Oraby, A. H., & Asnag, G. M. (2019). Structural, thermal and electrical studies of polyethylene oxide/starch blend containing green synthesized gold nanoparticles. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1180, 15-25. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X., Jain, P. K., El-Sayed, I. H., & El-Sayed, M. A. (2006). Determination of the minimum temperature required for selective photothermal destruction of cancer cells with the use of immunotargeted gold nanoparticles. Photochemistry and photobiology, 82(2), 412-417. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X., & El-Sayed, M. A. (2010). Gold nanoparticles: Optical properties and implementations in cancer diagnosis and photothermal therapy. Journal of advanced research, 1(1), 13-28. [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, A. R., & Kim, B. S. (2021). Bio-functionalized few-layer graphene for in situ growth of gold nanoparticles, improvement of polymer properties, and dye removal. Journal of Cleaner Production, 310, 127515. [CrossRef]
- Verma, N., Jagota, V., Alguno, A. C., Rakhra, M., Kumar, P., & Dugbakie, B. N. (2022). Characterization of fabricated gold-doped ZnO nanospheres and their use as a photocatalyst in the degradation of DR-31 dye. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2022, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, M., Ramazani, S., & Roosta, M. (2011). Gold nanoparticle loaded activated carbon as novel adsorbent for the removal of Congo red. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 4(10), 1208-1217. [CrossRef]
- Cui, W., Lu, W., Zhang, Y., Lin, G., Wei, T., & Jiang, L. (2010). Gold nanoparticle ink suitable for electric-conductive pattern fabrication using in ink-jet printing technology. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 358(1-3), 35-41. [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, T., Kundu, M. K., & Barman, S. (2015). Ultra small gold nanoparticles–graphitic carbon nitride composite: an efficient catalyst for ultrafast reduction of 4-nitrophenol and removal of organic dyes from water. RSC Advances, 5(48), 38760-38773. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K. G., & Kamat, P. V. (2003). Chromophore-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Accounts of chemical research, 36(12), 888-898. [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z., & Bischof, J. C. (2012). Thermophysical and biological responses of gold nanoparticle laser heating. Chemical Society Reviews, 41(3), 1191-1217. [CrossRef]
- Wu, G., Liu, X., Zhou, P., Wang, L., Hegazy, M., Huang, X., & Huang, Y. (2019). A facile approach for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and degradation of congo red using gold nanoparticles or laccase decorated hybrid inorganic nanoparticles/polymer-biomacromolecules vesicles. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 94, 524-533. [CrossRef]
- Katas, H., Moden, N. Z., Lim, C. S., Celesistinus, T., Chan, J. Y., Ganasan, P., & Suleman Ismail Abdalla, S. (2018). Biosynthesis and potential applications of silver and gold nanoparticles and their chitosan-based nanocomposites in nanomedicine. Journal of Nanotechnology, 2018, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Roy, A., Murthy, H. A., Ahmed, H. M., Islam, M. N., & Prasad, R. (2022). Phytogenic synthesis of metal/metal oxide nanoparticles for degradation of dyes. Journal of Renewable Materials, 10(7), 1911. [CrossRef]
- Aljabali, A. A., Akkam, Y., Al Zoubi, M. S., Al-Batayneh, K. M., Al-Trad, B., Abo Alrob, O., ... & Evans, D. J. (2018). Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using leaf extract of Ziziphus zizyphus and their antimicrobial activity. Nanomaterials, 8(3), 174. [CrossRef]
- Nadaf, N. Y., & Kanase, S. S. (2019). Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by Bacillus marisflavi and its potential in catalytic dye degradation. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 12(8), 4806-4814. [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M. K., Kataria, J., & Sharma, S. (2017). A biomimetic synthesis of stable gold nanoparticles derived from aqueous extract of Foeniculum vulgare seeds and evaluation of their catalytic activity. Applied Nanoscience, 7, 439-447. [CrossRef]
- López-Miranda, J. L., Molina, G. A., Esparza, R., González-Reyna, M. A., Silva, R., & Estévez, M. (2021). Green Synthesis of Homogeneous Gold Nanoparticles Using Sargassum spp. Extracts and Their Enhanced Catalytic Activity for Organic Dyes. Toxics, 9(11), 280. [CrossRef]
- Baruah, D., Goswami, M., Yadav, R. N. S., Yadav, A., & Das, A. M. (2018). Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their application in photocatalytic degradation of toxic dyes. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 186, 51-58. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M. T., Dominguez, N., Ahsan, M. A., Dominguez-Cisneros, H., Zuniga, P., Alvarez, P. J., & Noveron, J. C. (2017). Sodium rhodizonate induced formation of gold nanoparticles supported on cellulose fibers for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and organic dyes. Journal of environmental chemical engineering, 5(5), 4185-4193. [CrossRef]
- Guo, M., Li, W., Yang, F., & Liu, H. (2015). Controllable biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles from a Eucommia ulmoides bark aqueous extract. Spectrochimica acta part A: molecular and biomolecular spectroscopy, 142, 73-79. [CrossRef]
- Note, C., Kosmella, S., & Koetz, J. (2006). Poly (ethyleneimine) as reducing and stabilizing agent for the formation of gold nanoparticles in w/o microemulsions. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 290(1-3), 150-156. [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, N., & Khan, I. (2021). Plasmonic gold nanoparticles (AuNPs): properties, synthesis and their advanced energy, environmental and biomedical applications. Chemistry–An Asian Journal, 16(7), 720-742. [CrossRef]
- Narayana, C., Upadhyay, R. K., Chaturvedi, R., & Sagar, R. (2017). A versatile carbohydrate based gelator for oil water separation, nanoparticle synthesis and dye removal. New Journal of Chemistry, 41(6), 2261-2267. [CrossRef]
- Carolin, C. F., Kumar, P. S., & Joshiba, G. J. (2021). Sustainable approach to decolourize methyl orange dye from aqueous solution using novel bacterial strain and its metabolites characterization. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 23, 173-181. [CrossRef]
- Hanafi, M. F., & Sapawe, N. (2020). A review on the water problem associate with organic pollutants derived from phenol, methyl orange, and remazol brilliant blue dyes. Materials Today: Proceedings, 31, A141-A150. [CrossRef]
- Singh, A., Ahmed, A., Sharma, A., Sharma, C., Paul, S., Khosla, A., ... & Arya, S. (2021). Promising photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye via sol-gel synthesized Ag–CdS@ Pr-TiO2 core/shell nanoparticles. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 616, 413121. [CrossRef]
- Astuti, W., Sulistyaningsih, T., & Maksiola, M. (2017). Equilibrium and Kinetics of Adsorption of Methyl Violet from Aqueous Solutions Using Modified Ceiba pentandra Sawdust. Asian journal of chemistry, 29(1). [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S., Sinha, R., & Roy, D. (2004). Toxicological effects of malachite green. Aquatic toxicology, 66(3), 319-329. [CrossRef]
- Raval, N. P., Shah, P. U., & Shah, N. K. (2017). Malachite green “a cationic dye” and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption. Applied Water Science, 7, 3407-3445. [CrossRef]
- Al-Gheethi, A. A., Azhar, Q. M., Kumar, P. S., Yusuf, A. A., Al-Buriahi, A. K., Mohamed, R. M. S. R., & Al-Shaibani, M. M. (2022). Sustainable approaches for removing Rhodamine B dye using agricultural waste adsorbents: A review. Chemosphere, 287, 132080. [CrossRef]
- Bujdák, J., Martínez Martínez, V., López Arbeloa, F., & Iyi, N. (2007). Spectral properties of rhodamine 3B adsorbed on the surface of montmorillonites with variable layer charge. Langmuir, 23(4), 1851-1859. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z., Tian, B., & Zhang, J. (2013). Synthesis and characterization of new rhodamine dyes with large Stokes shift. Dyes and Pigments, 99(3), 1132-1136. [CrossRef]
- Sulistina, D. R., & Martini, S. (2020). The effect of Rhodamine B on the cerebellum and brainstem tissue of Rattus norvegicus. Journal of Public Health Research, 9(2), jphr-2020. [CrossRef]
- Shen, K., & Gondal, M. A. (2017). Removal of hazardous Rhodamine dye from water by adsorption onto exhausted coffee ground. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 21, S120-S127. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, U., Bhanjana, G., Kaur, N., Sharma, R., Kaur, G., Kaushik, A., & Chaudhary, G. R. (2021). Microwave-assisted assembly of Ag2O-ZnO composite nanocones for electrochemical detection of 4-Nitrophenol and assessment of their photocatalytic activity towards degradation of 4-Nitrophenol and Methylene blue dye. Journal of hazardous materials, 416, 125771. [CrossRef]
- El-Aal, M. A., Ali, H. M., & Ibrahim, S. M. (2022). Cu-Doped 1D Hydroxyapatite as a Highly Active Catalyst for the Removal of 4-Nitrophenol and Dyes from Water. ACS omega, 7(30), 26777-26787. [CrossRef]
- Barreca, S., Colmenares, J. J. V., Pace, A., Orecchio, S., & Pulgarin, C. (2014). Neutral solar photo-Fenton degradation of 4-nitrophenol on iron-enriched hybrid montmorillonite-alginate beads (Fe-MABs). Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 282, 33-40. [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, T., Kundu, M. K., & Barman, S. (2015). Ultra small gold nanoparticles–graphitic carbon nitride composite: an efficient catalyst for ultrafast reduction of 4-nitrophenol and removal of organic dyes from water. RSC Advances, 5(48), 38760-38773. [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M. A., Deemer, E., Fernandez-Delgado, O., Wang, H., Curry, M. L., El-Gendy, A. A., & Noveron, J. C. (2019). Fe nanoparticles encapsulated in MOF-derived carbon for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and methyl orange in water. Catalysis Communications, 130, 105753. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J., Wang, N., Zhang, H., & Baeyens, J. (2019). Adsorption of Congo red dye on FexCo3-xO4 nanoparticles. Journal of environmental management, 238, 473-483. [CrossRef]
- Oguzie, E. E. (2004). Influence of halide ions on the inhibitive effect of congo red dye on the corrosion of mild steel in sulphuric acid solution. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 87(1), 212-217. [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A., Mittal, J., Malviya, A., & Gupta, V. K. (2009). Adsorptive removal of hazardous anionic dye “Congo red” from wastewater using waste materials and recovery by desorption. Journal of colloid and interface science, 340(1), 16-26. [CrossRef]
- Khan, I., Saeed, K., Zekker, I., Zhang, B., Hendi, A. H., Ahmad, A., ... & Khan, I. (2022). Review on methylene blue: its properties, uses, toxicity and photodegradation. Water, 14(2), 242. [CrossRef]
- Kallel, F., Chaari, F., Bouaziz, F., Bettaieb, F., Ghorbel, R., & Chaabouni, S. E. (2016). Sorption and desorption characteristics for the removal of a toxic dye, methylene blue from aqueous solution by a low cost agricultural by-product. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 219, 279-288. [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, M., Nazir, N., Iftikhar, M., Naz, S., Zekker, I., Burlakovs, J., ... & Ali Khan, F. (2021). A review on silver nanoparticles: Classification, various methods of synthesis, and their potential roles in biomedical applications and water treatment. Water, 13(16), 2216. [CrossRef]
- Nadaf, N. Y., & Kanase, S. S. (2019). Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by Bacillus marisflavi and its potential in catalytic dye degradation. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 12(8), 4806-4814. [CrossRef]
- AlMashrea, B. A., Abla, F., Chehimi, M. M., Workie, B., Han, C., & Mohamed, A. A. (2020). Polyaniline coated gold-aryl nanoparticles: Electrochemical synthesis and efficiency in methylene blue dye removal. Synthetic Metals, 269, 116528. [CrossRef]
- Roosta, M., Ghaedi, M., Shokri, N., Daneshfar, A., Sahraei, R., & Asghari, A. (2014). Optimization of the combined ultrasonic assisted/adsorption method for the removal of malachite green by gold nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon: experimental design. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 118, 55-65. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A. K., Saha, A., Tarafder, A., Panda, A. B., & Pal, S. (2016). Efficient removal of toxic dyes via simultaneous adsorption and solar light driven photodegradation using recyclable functionalized amylopectin–TiO2–Au nanocomposite. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 4(3), 1679-1688. [CrossRef]
- Singaravelu, G., Arockiamary, J. S., Kumar, V. G., & Govindaraju, K. (2007). A novel extracellular synthesis of monodisperse gold nanoparticles using marine alga, Sargassum wightii Greville. Colloids and surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 57(1), 97-101. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., Xu, J., Yan, Y., Liu, H., Karunakaran, T., & Li, F. (2019). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Scutellaria barbata and its anticancer activity in pancreatic cancer cell (PANC-1). Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology, 47(1), 1617-1627. [CrossRef]
- Baruah, D., Goswami, M., Yadav, R. N. S., Yadav, A., & Das, A. M. (2018). Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their application in photocatalytic degradation of toxic dyes. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 186, 51-58. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q., Yu, D., Fan, C., Huang, Q., Tang, Y., Guo, R., ... & Lin, Y. (2021). Gold nanoparticles adsorbed on graphene as nanozymes for the efficient elimination of dye pollutants. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 5(1), 94-100. [CrossRef]
- Parushuram, N., Ranjana, R., Harisha, K. S., Shilpa, M., Narayana, B., Neelakandan, R., & Sangappa, Y. (2022). Silk fibroin and silk fibroin-gold nanoparticles nanocomposite films: sustainable adsorbents for methylene blue dye. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 43(8), 1161-1176. [CrossRef]
- Das, J., & Velusamy, P. (2014). Catalytic reduction of methylene blue using biogenic gold nanoparticles from Sesbania grandiflora L. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 45(5), 2280-2285. [CrossRef]
- Umamaheswari, C., Lakshmanan, A., & Nagarajan, N. S. (2018). Green synthesis, characterization and catalytic degradation studies of gold nanoparticles against congo red and methyl orange. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 178, 33-39. [CrossRef]
- Cavuslar, O., Nakay, E., Kazakoglu, U., Abkenar, S. K., Ow-Yang, C. W., & Acar, H. Y. (2020). Synthesis of stable gold nanoparticles using linear polyethyleneimines and catalysis of both anionic and cationic azo dye degradation. Materials Advances, 1(7), 2407-2417. [CrossRef]
- Roosta, M., Ghaedi, M., Daneshfar, A., Sahraei, R., & Asghari, A. (2014). Optimization of the ultrasonic assisted removal of methylene blue by gold nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon using experimental design methodology. Ultrasonics sonochemistry, 21(1), 242-252. [CrossRef]
- Gangapuram, B. R., Bandi, R., Alle, M., Dadigala, R., Kotu, G. M., & Guttena, V. (2018). Microwave assisted rapid green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Annona squamosa L peel extract for the efficient catalytic reduction of organic pollutants. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1167, 305-315. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M., Ahmad, F., Koivisto, J. T., & Kellomäki, M. (2020). Green synthesis of controlled size gold and silver nanoparticles using antioxidant as capping and reducing agent. Colloid and Interface Science Communications, 39, 100322. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





