Submitted:
28 February 2024
Posted:
29 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Eligibility Criteria
Information Sources
Search Strategy
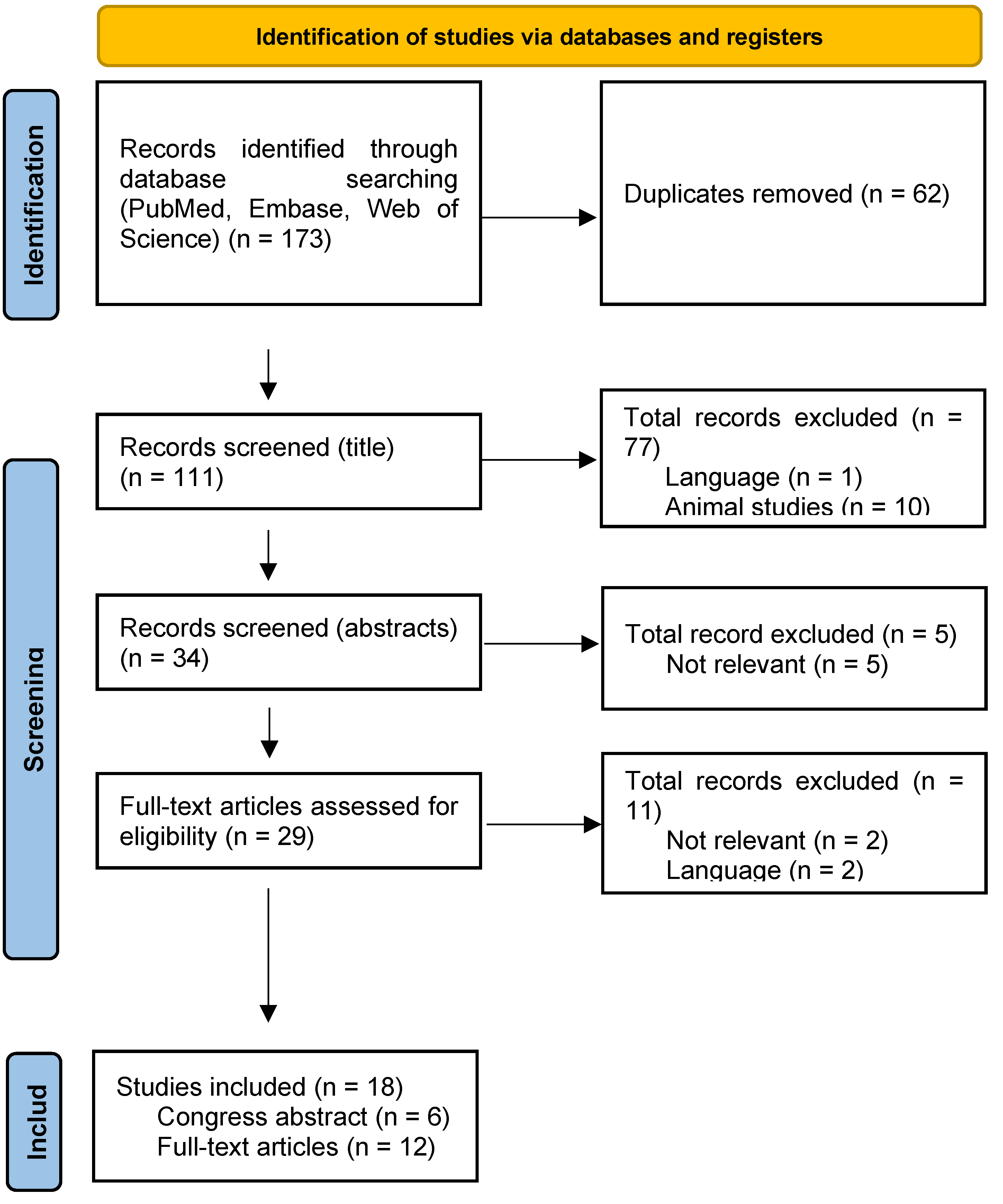
Selection Process
Data Collection Process
Description of Cases
Results
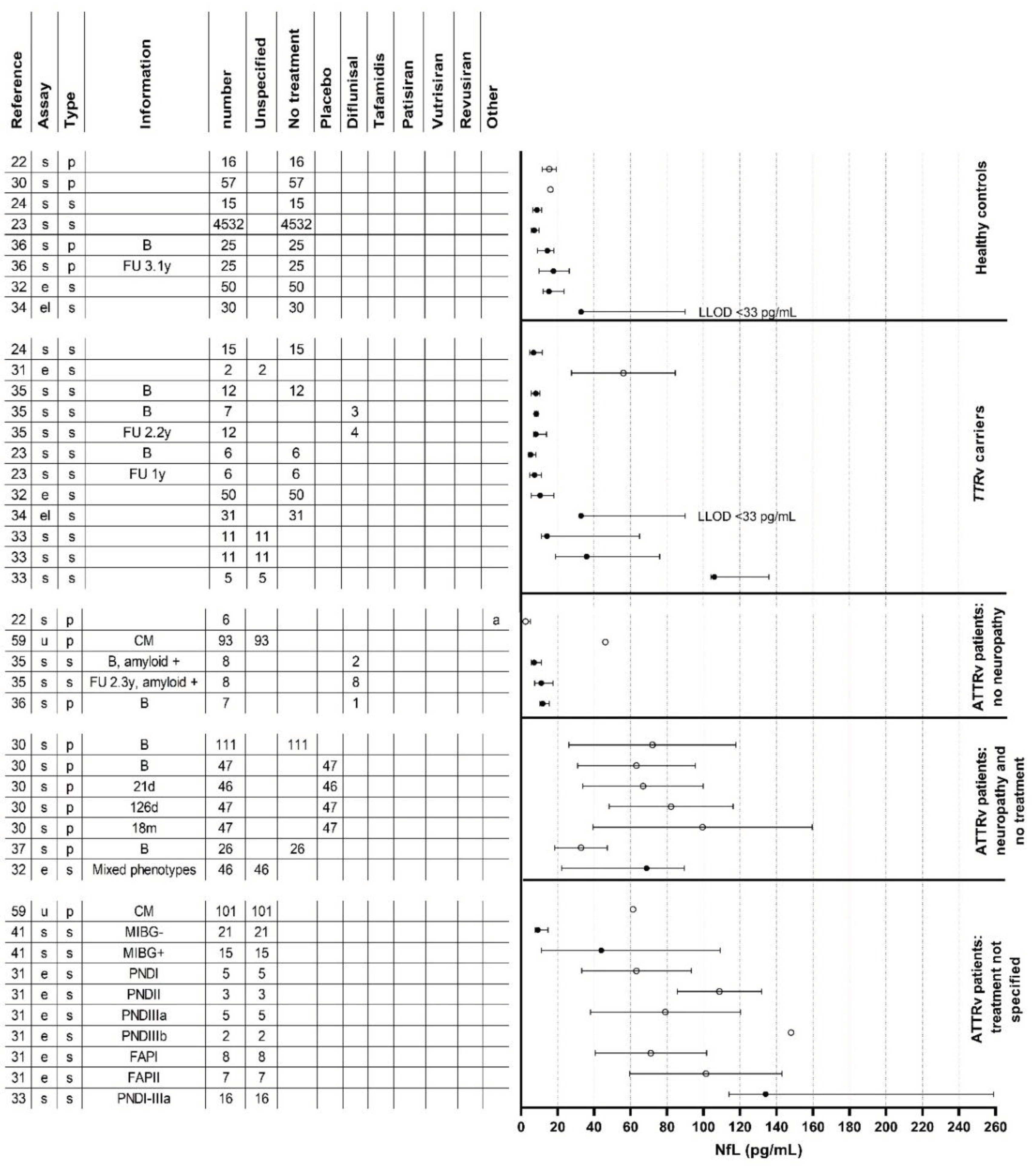
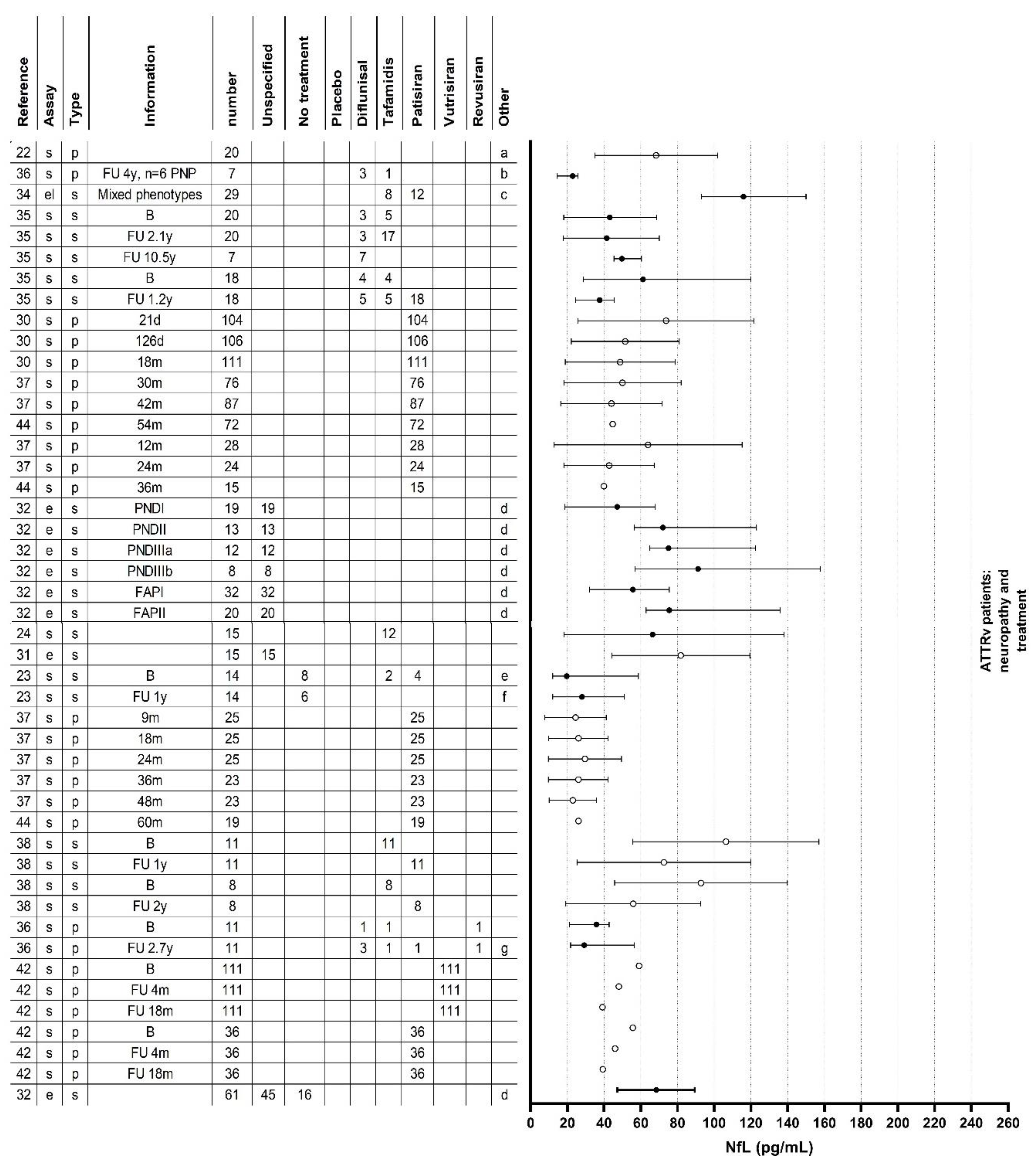
Results of Individual Studies
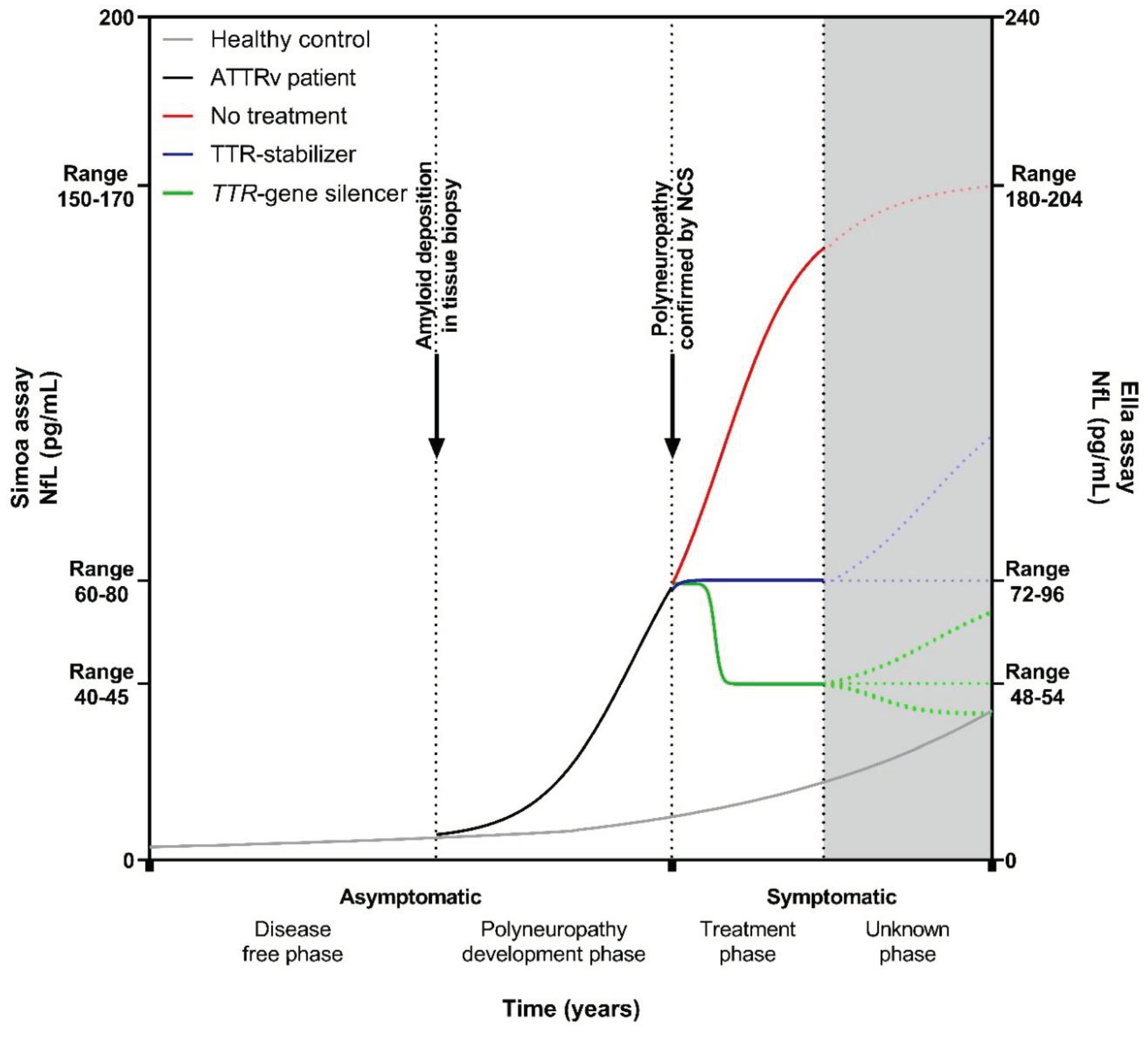
Neurofilament Light Chain in Relation to Polyneuropathy and Disease Severity
Neurofilament Light Chain in an Asymptomatic Disease Stage
Neurofilament Light Chain in Relation to Small Fiber and Autonomic Neuropathy
Neurofilament Light Chain in Relation to Treatment
Neurofilament Light Chain and Cerebral Manifestations in Hereditary ATTR Amyloidosis
Confounders Affecting Neurofilament Light Chain Levels
Discussion
Clinical Implications
Considerations for Future Research
Limitations
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATTRv | hereditary transthyretin amyloid |
| ATTRwt | wildtype transthyretin amyloid |
| AL | immunoglobulin light chain amyloid |
| APOLLO | phase 3 study of Patisiran for treatment of hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy |
| CADT | compound autonomic dysfunction test |
| CM | cardiomyopathy |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| EMG | electromyography |
| ESC | electrochemical skin conductance |
| FAP | familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy |
| HELIOS | phase 3 open-label study of Vutrisiran in patients with hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy |
| IENFD | intra-epidermal nerve fiber density |
| mNIS+7 | modified neuropathy impairment score +7 |
| MRC | medical research council |
| NCS | nerve conduction studies |
| NfL | neurofilament light chain |
| NIS | neuropathy impairment score |
| NIS-LL | neuropathy impairment score lower limb |
| NIS-UL | neuropathy impairment score upper limb |
| Norfolk QOL-DN | Norfolk quality of life diabetic neuropathy |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro-brain-type natriuretic peptide |
| OLE | open label extension |
| PND | polyneuropathy disability |
| PNP | polyneuropathy |
| QST | quantitative sensory testing |
| R-ODS | Rasch-built overall disability score |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristics |
| SFN-SIQ | small fiber neuropathy- symptom inventory questionnaire |
| Simoa | single-molecule array |
| TTR | transthyretin |
| TTRv | transthyretin gene variant |
References
- Buxbaum, J.N.; Dispenzieri, A.; Eisenberg, D.S.; Fändrich, M.; Merlini, G.; Saraiva, M.J.M.; Sekijima, Y.; Westermark, P. Amyloid Nomenclature 2022: Update, Novel Proteins, and Recommendations by the International Society of Amyloidosis (ISA) Nomenclature Committee. Amyloid. 2022, 29, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazenberg, B.P.C. Amyloidosis. A Clinical Overview. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2013, 39, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.C.; Robinson-Papp, J. Amyloid Neuropathies. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2012, 79, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, L.F.; Magalhães, R.; Freitas, J.; Taipa, R.; Pires, M.M.; Osório, H.; Dias, D.; Pessegueiro, H.; Correia, M.; Coelho, T. CNS Involvement in V30M Transthyretin Amyloidosis: Clinical, Neuropathological and Biochemical Findings. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2015, 86, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnolo, M.; Cacciavillani, M.; Cipriani, A.; Salvalaggio, A.; Castellani, F.; Pilichou, K.; Briani, C. Peripheral Nerve Involvement in Wild-Type Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 44, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.; Suhr, O.B.; Hund, E.; Obici, L.; Tournev, I.; Campistol, J.M.; Slama, M.S.; Hazenberg, B.P.; Coelho, T. First European Consensus for Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment of Transthyretin Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 29 Suppl 1, S14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.A.; Comenzo, R.; Falk, R.H.; Fermand, J.P.; Hazenberg, B.P.; Hawkins, P.N.; Merlini, G.; Moreau, P.; Ronco, P.; Sanchorawala, V.; et al. Definition of Organ Involvement and Treatment Response in Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis (AL): A Consensus Opinion from the 10th International Symposium on Amyloid and Amyloidosis. Am. J. Hematol. 2005, 79, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyck, P.J.; Davies, J.L.; Litchy, W.J.; O’Brien, P.C. Longitudinal Assessment of Diabetic Polyneuropathy Using a Composite Score in the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study Cohort. Neurology 1997, 49, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, P.J.; Dyck, P.J.; Kennedy, W.R.; Kesserwani, H.; Melanson, M.; Ochoa, J.; Shy, M.; Stevens, J.C.; Suarez, G.A.; O’Brien, P.C. Limitations of Quantitative Sensory Testing When Patients Are Biased toward a Bad Outcome. Neurology. 1998, 50, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casellini, C.M.; Parson, H.K.; Richardson, M.S.; Nevoret, M.L.; Vinik, A.I. Sudoscan, a Noninvasive Tool for Detecting Diabetic Small Fiber Neuropathy and Autonomic Dysfunction. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2013, 15, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigetti, M.; Romozzi, M.; Bisogni, G.; Cardellini, D.; Cavallaro, T.; Di Paolantonio, A.; Fabrizi, G.M.; Fenu, S.; Gentile, L.; Grandis, M.; et al. HATTR Pathology: Nerve Biopsy Results from Italian Referral Centers. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Coelho, T.; Rodrigues, A.; Felgueiras, H.; Oliveira, P.; Guimarães, A.; Melo-Pires, M.; Taipa, R. Clinicopathological Correlations of Sural Nerve Biopsies in TTR Val30Met Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy. Brain Commun. 2019, 1, fcz032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenezer, G.J.; Liu, Y.; Judge, D.P.; Cunningham, K.; Truelove, S.; Carter, N.D.; Sebastian, B.; Byrnes, K.; Polydefkis, M. Cutaneous Nerve Biomarkers in Transthyretin Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Ueda, M.; Misumi, Y.; Nomura, T.; Inoue, Y.; Isoguchi, A.; Kanenawa, K.; Tasaki, M.; Yamashita, T.; Sonoda, Y.; et al. Reduced Intraepidermal Nerve Fibre Density in Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2019, 26 (sup1), 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, L.; Galosi, E.; Vanoli, F.; Fasolino, A.; Di Pietro, G.; Luigetti, M.; Sabatelli, M.; Fionda, L.; Garibaldi, M.; Alfieri, G.; et al. Skin Biopsy and Quantitative Sensory Assessment in an Italian Cohort of ATTRv Patients with Polyneuropathy and Asymptomatic Carriers: Possible Evidence of Early Non-Length Dependent Denervation. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, L.; Adam, C.; Beaudonnet, G.; Beauvais, D.; Cauquil, C.; Not, A.; Morassi, O.; Benmalek, A.; Trassard, O.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; et al. Skin Amyloid Deposits and Nerve Fiber Loss as Markers of Neuropathy Onset and Progression in Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauvais, D.; Labeyrie, C.; Cauquil, C.; Francou, B.; Eliahou, L.; Not, A.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Adam, C.; Slama, M.S.; Benmalek, A.; et al. Detailed Clinical, Physiological and Pathological Phenotyping Can Impact Access to Disease-Modifying Treatments in ATTR Carriers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2023. [online ahead of print]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, P.J.B.; González-Duarte, A.; Obici, L.; Polydefkis, M.; Wiesman, J.F.; Antonino, I.; Litchy, W.J.; Dyck, P.J. Development of Measures of Polyneuropathy Impairment in HATTR Amyloidosis: From NIS to MNIS + 7. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 405, 116424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, V.; Ferraro, P.M.; Guglielmino, V.; Luigetti, M. Kidney Involvement in Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis: Is There a Role for Cystatin C? Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 16, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as Biomarkers in Neurological Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandelius, Å.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Adiutori, R.; Malaspina, A.; Laura, M.; Reilly, M.M.; Rossor, A.M. Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain Concentration in the Inherited Peripheral Neuropathies. Neurology. 2018, 90, e518–e524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, M.; Foiani, M.; Heslegrave, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Lunn, M.P.; Malaspina, A.; Gillmore, J.D.; Rossor, A.M.; Reilly, M.M. Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain Concentration Is Increased and Correlates with the Severity of Neuropathy in Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2019, 24, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loser, V.; Benkert, P.; Vicino, A.; Lim Dubois Ferriere, P.; Kuntzer, T.; Pasquier, J.; Maceski, A.; Kuhle, J.; Theaudin, M. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Reliable Biomarker of Hereditary Transthyretin-Related Amyloidosis-A Swiss Reference Center Experience. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2023, 28, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louwsma, J.; Brunger, A.F.; Bijzet, J.; Kroesen, B.J.; Roeloffzen, W.W.H.; Bischof, A.; Kuhle, J.; Drost, G.; Lange, F.; Kuks, J.B.M.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain, a Biomarker for Polyneuropathy in Systemic Amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2021, 28, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.D.; Martirosian, R.A.; Mun, K.T.; Chong, D.S.; Llorente, I.L.; Uphaus, T.; Gröschel, K.; Wölfer, T.A.; Tiedt, S.; Hinman, J.D. Temporal Patterning of Neurofilament Light as a Blood-Based Biomarker for Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 841898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, A.; Manigold, T.; Barro, C.; Heijnen, I.; Berger, C.T.; Derfuss, T.; Kuhle, J.; Daikeler, T. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain: A Biomarker of Neuronal Injury in Vasculitic Neuropathy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1093–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, H.; Hietala, M.A.; Jonsson, M.; Andreasen, N.; Styrud, E.; Karlsson, I.; Edman, A.; Popa, C.; Rasulzada, A.; Wahlund, L.-O.; et al. Neurochemical Aftermath of Amateur Boxing. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 1277–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokotis, P.; Manios, E.; Schmelz, M.; Fotiou, D.; Dialoupi, I.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Roussou, M.; Lykka, A.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Kastritis, E. Involvement of Small Nerve Fibres and Autonomic Nervous System in AL Amyloidosis: Comprehensive Characteristics and Clinical Implications. Amyloid. 2020, 27, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, L.F.; Maceski, A.; Conceição, I.; Obici, L.; Magalhães, R.; Cortese, A.; Leppert, D.; Merlini, G.; Kuhle, J.; Saraiva, M.J. Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain: An Early Biomarker for Hereditary ATTR Amyloid Polyneuropathy. Amyloid. 2020, 27, 79–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ticau, S.; Sridharan, G. V; Tsour, S.; Cantley, W.L.; Chan, A.; Gilbert, J.A.; Erbe, D.; Aldinc, E.; Reilly, M.M.; Adams, D.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker of Hereditary Transthyretin-Mediated Amyloidosis. Neurology 2021, 96, e412–e422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luigetti, M.; Di Paolantonio, A.; Guglielmino, V.; Romano, A.; Rossi, S.; Sabino, A.; Servidei, S.; Sabatelli, M.; Primiano, G. Neurofilament Light Chain as a Disease Severity Biomarker in ATTRv: Data from a Single-Centre Experience. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 2845–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Primiano, G.; Antonini, G.; Ceccanti, M.; Fenu, S.; Forcina, F.; Gentile, L.; Inghilleri, M.; Leonardi, L.; Manganelli, F.; et al. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain: A Promising Early Diagnostic Biomarker for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis? Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.S.; Razvi, Y.; O’Donnell, L.; Veleva, E.; Heslegrave, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Vucic, S.; Kiernan, M.C.; Rossor, A.M.; Gillmore, J.D.; et al. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain in Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis: Validation in Real-Life Practice. Amyloid 2024. [online ahead of print]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moreno, J.; Gragera-Martínez, Á.; Rodríguez, A.; Borrachero-Garro, C.; García-Garrido, S.; Barceló, C.; Manovel-Sánchez, A.; Ribot-Sansó, M.A.; Ibargüen-González, L.; Gomila, R.; et al. Biomarkers of Axonal Damage to Favor Early Diagnosis in Variant Transthyretin Amyloidosis (A-ATTRv). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunger, A.F.; Berends, M.; Bijzet, J.; Van Der Zwaag, P.; Kroesen, B.J.; Teunissen, C.; In ’T Veld, S.; Drost, G.; Lange, F.; Gans, R.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain, an Early Biomarker for Polyneuropathy in Hereditary ATTR Amyloidosis. In Ann. Rheum. Dis., Proceedings of the European Congress of Rheumatology, Copenhagen, Denmark, 01-06-2022 to 04-06-2022; p. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.H.V.; Prokaeva, T.; Zheng, L.; Doros, G.; Kaku, M.C.; Spencer, B.; Berk, J.; Sanchorawala, V. Neurofilament Light Chain Kinetics as a Biomarker for Polyneuropathy in V122I Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Amyloid 2023. [online ahead of print]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticau, S.; Aldinc, E.; Polydefkis, M.; Adams, D.; Coelho, T.; Ueda, M.; Hale, C.; Vest, J.; Nioi, P. Treatment Response and Neurofilament Light Chain Levels with Long-Term Patisiran in Hereditary Transthyretin-Mediated Amyloidosis with Polyneuropathy: 24-Month Results of an Open-Label Extension Study. Amyloid 2023. [online ahead of print]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Mochizuki, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Takasone, K.; Aldinc, E.; Ticau, S.; Jia, G.; Sekijima, Y. Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker for Monitoring Response to Change in Treatment in Hereditary ATTR Amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2023, 30, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Araki, S. Transthyretin-Related Familial Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 2005, 62, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, M.D.; Kincaid, J.C. The Molecular Biology and Clinical Features of Amyloid Neuropathy. Muscle & nerve. 2007, 36, 411–423. [Google Scholar]
- Berends, M.; Nienhuis, H.L.A.; Brunger, A.; Bijzet, J.; Van Der Zwaag, P.A.; Hazenberg, B.P.C.; Noordzij, W.; Slart, R.H.J. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain (SNfL) in Relation to Myocardial Sympathetic Neuronal Damage Based on 123I-Meta-Iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) Scintigraphy in Hereditary Transthyretin (ATTRv) Amyloidosis. In Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging, Proceedings of the 35th Annual Congress of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine, Barcelona, Spain, 15-10-2022 to 19-10-2022; Springer: New York, United States, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigetti, M.; Aldinc, E.; Ticau, S.; Polydefkis, M.; Nienhuis, H.; Karam, C.; Ajroud-Driss, S.; Sekijima, Y.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Barnes, J.; et al. NfL Levels Significantly Decrease in Response to Treatment with Patisiran or Vutrisiran in hATTR Amyloidosis with Polyneuropathy. In J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst., Proceedings of the 13th Annual Meeting of the Italian Association for the Study of the Peripheral Nervous System, Naples, Italy, 25-05-2023 to 27-05-2023; Wiley: New Jersey, United States, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceicao, I.; Polydefkis, M.; Obici, L.; Adams, D.; Gillmore, J.; Masri, A.; Brannagan, T.; Coelho, T.; Jung, S.; Wessman, P.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain as a Potential Biomarker in Patients with Hereditary ATTR-Polyneuropathy in NEURO-TTRansform. In Eur. J. Neurol., Proceedings of the 9th Congress of the European Academy Neurology, Budapest, Hungary, 01-07-2023 to 04-07-2023; Wiley: New Jersey, United States, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gilling, K.; Aldinc, E.; Ticau, S.; Polydefkis, M.; Adams, D.; Reilly, M.; Nioi, P. P-48 Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker in Hereditary Transthyretin-Mediated Amyloidosis: 36-Month Data from the Patisiran Global Open-Label Extension. In Clin. Neurophysiol., Proceedings of the Congress for Clinical Neuroscience with Advanced Training Academy of the German Society for Clinical Neurophysiology and Functional Neuroimaging, Hamburg, Germany, 02-03-203 to 04-03-2023; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gao, F.; Ye, X.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Fu, J.; Shen, Y.; Al-Shahi Salman, R.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain Predicts Risk of Recurrence in Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Aging (Albany. NY). 2020, 12, 23727–23738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekijima, Y.; Yazaki, M.; Oguchi, K.; Ezawa, N.; Yoshinaga, T.; Yamada, M.; Yahikozawa, H.; Watanabe, M.; Kametani, F.; Ikeda, S.I. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy in Posttransplant Patients with Hereditary ATTR Amyloidosis. Neurology. 2016, 87, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taipa, R.; Sousa, L.; Pinto, M.; Reis, I.; Rodrigues, A.; Oliveira, P.; Melo-Pires, M.; Coelho, T. Neuropathology of Central Nervous System Involvement in TTR Amyloidosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2023, 145, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermunt, L.; Otte, M.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Killestein, J.; Lemstra, A.W.; van der Flier, W.M.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.L.; Vijverberg, E.G.B.; Bouwman, F.H.; Gravesteijn, G.; et al. Age- and Disease-Specific Reference Values for Neurofilament Light Presented in an Online Interactive Support Interface. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2022, 9, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.C.; Sotirchos, E.S.; Smith, M.D.; Lord, H.-N.; DuVal, A.; Mowry, E.M.; Calabresi, P.A. Contributors to Serum NfL Levels in People without Neurologic Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 92, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhak, A.; Kuhle, J.; Green, A.J. Challenges and Opportunities for the Promising Biomarker Blood Neurofilament Light Chain. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 542–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baka, P.; Steenken, L.; Escolano-Lozano, F.; Steffen, F.; Papagianni, A.; Sommer, C.; Pogatzki-Zahn, E.; Hirsch, S.; Protopapa, M.; Bittner, S.; et al. Studying Serum Neurofilament Light Chain Levels as a Potential New Biomarker for Small Fiber Neuropathy. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024. [online ahead of print]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigetti, M.; Primiano, G.; Basile, V.; Vitali, F.; Pignalosa, S.; Romano, A.; Sabino, A.; Marino, M.; Di Santo, R.; Ciasca, G.; et al. Serum Neurofilament and Free Light Chain Levels in Patients Undergoing Treatment for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lieverloo, G.G.A.; Wieske, L.; Verhamme, C.; Vrancken, A.F.J.; van Doorn, P.A.; Michalak, Z.; Barro, C.; van Schaik, I.N.; Kuhle, J.; Eftimov, F. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2019, 24, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Coelho, T.; Berk, J.L.; Cruz, M.W.; Ericzon, B.G.; Ikeda, S.I.; Lewis, W.D.; Obici, L.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Rapezzi, C.; et al. Guideline of Transthyretin-Related Hereditary Amyloidosis for Clinicians. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.T.; Medress, Z.A.; Barres, B.A. Axon Degeneration: Molecular Mechanisms of a Self-Destruction Pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.; Koike, H.; Slama, M.; Coelho, T. Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis: A Model of Medical Progress for a Fatal Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.S.; Chan, A.; Costelha, S.; Fishman, S.; Willoughby, J.L.S.; Borland, T.D.; Milstein, S.; Foster, D.J.; Gonçalves, P.; Chen, Q.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of RNAi as a Treatment for Transthyretin-Mediated Amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2016, 23, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticau, S.; Sridharan, G.; Tsour, S.; Cantley, W.; Chan, A.; Gilbert, J.A.; Erbe, D.; Vest, J.; Fitzgerald, K.; Vaishnaw, A.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain May Serve As a Biomarker of Neuropathy in hATTR Amyloidosis with Cardiomyopathy. In J. Card. Fail. Proceedings of the Heart Failure Society of America's Annual Scientific Meeting 2020, Online Meeting, 13-12-2020 to 07-12-2020; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhle, J.; Barro, C.; Andreasson, U.; Derfuss, T.; Lindberg, R.; Sandelius, Å.; Liman, V.; Norgren, N.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Comparison of Three Analytical Platforms for Quantification of the Neurofilament Light Chain in Blood Samples: ELISA, Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay and Simoa. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasson, U.; Gobom, J.; Delatour, V.; Auclair, G.; Noam, Y.; Lee, S.; Wen, J.; Jeromin, A.; Arslan, B.; Maceski, A.; et al. Assessing the Commutability of Candidate Reference Materials for the Harmonization of Neurofilament Light Measurements in Blood. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2023, 61, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, A.; Viel, S.; Perret, M.; Brocard, G.; Casey, R.; Lombard, C.; Laurent-Chabalier, S.; Debouverie, M.; Edan, G.; Vukusic, S.; et al. Comparison of Simoa(TM) and Ella(TM) to Assess Serum Neurofilament-Light Chain in Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2021, 8, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, H.; Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, E.-H.; Hwang, M.; Park, H.; Koh, S.-H. Comparing Neurofilament Light Chain Levels in Serum and Plasma. Dement. Neurocogni. disord. 2023, 22, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, P.; Ponleitner, M.; Rommer, P.S.; Haslacher, H.; Mucher, P.; Leutmezer, F.; Petzold, A.; Wotawa, C.; Lanzenberger, R.; Berger, T.; et al. Seven Day Pre-Analytical Stability of Serum and Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rübsamen, N.; Willemse, E.A.J.; Leppert, D.; Wiendl, H.; Nauck, M.; Karch, A.; Kuhle, J.; Berger, K. A Method to Combine Neurofilament Light Measurements From Blood Serum and Plasma in Clinical and Population-Based Studies. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 894119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, C.R.; Paulsen, A.J.; Pinto, A.A.; Merten, N.; Cruickshanks, K.J. Effect of Long-Term Storage on the Reliability of Blood Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease and Neurodegeneration. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2022, 85, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkert, P.; Meier, S.; Schaedelin, S.; Manouchehrinia, A.; Yaldizli, Ö.; Maceski, A.; Oechtering, J.; Achtnichts, L.; Conen, D.; Derfuss, T.; et al. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain for Individual Prognostication of Disease Activity in People with Multiple Sclerosis: A Retrospective Modelling and Validation Study. Lancet. Neurol. 2022, 21, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, J.L.; Suhr, O.B.; Obici, L.; Sekijima, Y.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Yamashita, T.; Heneghan, M.A.; Gorevic, P.D.; Litchy, W.J.; Wiesman, J.F.; et al. Repurposing Diflunisal for Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2013, 310, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppens, S.; Lehmann, S.; Hopley, C.; Hirtz, C. Neurofilament-Light, a Promising Biomarker: Analytical, Metrological and Clinical Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauvais, D.; Labeyrie, C.; Cauquil, C.; Francou, B.; Eliahou, L.; Not, A.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Adam, C.; Slama, M.S.; Benmalek, A.; et al. Detailed Clinical, Physiological and Pathological Phenotyping Can Impact Access to Disease-Modifying Treatments in ATTR Carriers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2023, 0, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study (ref) | Comparisons between groups | Number of subjects | Fold increase in median NfL | NfL and correlation with disease characteristics | NfL and no correlation with disease characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-text articles | |||||
| Kapoor et al. 2019 [22] | Healthy controls vs ATTRv no neuropathy |
16 6 |
0.2 (15.5 vs 2.5)* | NIS scale, CMTES-R | |
| Healthy controls vs ATTRv-PNP |
16 20 |
4.4 (15.5 vs 68.4) | |||
| ATTRv no neuropathy vs ATTRv-PNP |
6 20 |
27.4 (2.5 vs 68.4)* | |||
| Maia et al. 2020 [29] | Healthy controls vs TTRv carriers |
16 16 |
- | PND score | |
|
TTRv carriers vs ATTRv-PNP |
16 16 |
- | |||
| Healthy controls vs ATTRv-PNP PND I |
16 13 |
4.8 | |||
| Healthy controls vs ATTRv-PNP PND ≥II |
16 13 |
15.4 | |||
| Louwsma et al. 2021 [24] | Healthy controls vs TTRv carriers |
15 15 |
0.8 (8.8 vs 6.9) | PND score, sural nerve amplitude in ATTRv patients, troponin T in ATTRv patients with PNP | Sural nerve amplitude in TTRv carriers, digit 5 ulnar nerve amplitude, NT-proBNP, creatinine |
| Healthy controls vs ATTRv-PNP |
15 15 |
7.5 (8.8 vs 66.4) | |||
|
TTRv carriers vs ATTRv-PNP |
15 15 |
9.6 (6.9 vs 66.4) | |||
| ATTRv-PNP PND I vs ATTRv-PNP PND ≥I |
15 15 |
5.6 (21 vs 116) | |||
| Healthy controls vs AL no neuropathy |
10 10 |
1.7 (13.6 vs 22.7) | Troponin T in AL patients with and without PNP | NT-proBNP, creatinine | |
| Healthy controls vs AL-PNP |
10 10 |
11 (13.6 vs 149) | |||
| AL no neuropathy vs AL-PNP |
10 10 |
6.6 (22.7 vs 149) | |||
| Ticau et al. 2021 [30] | Healthy controls vs ATTRv-PNP (all) baseline |
57 189 |
4.3 (16.3 vs 69.4)* | Change in mNIS+7 after 18 months of treatment with patisiran | mNIS+7 at baseline and PND score at baseline |
| ATTRv-PNP patisiran 18 months vs ATTRv-PNP placebo 18 months |
111 47 |
2.0 (48.8 vs 99.5)* | |||
| Healthy controls vs ATTRv-PNP patisiran 18 months |
57 111 |
3.0 (16.3 vs 48.8)* | |||
| Healthy controls vs ATTRv-PNP placebo 18 months |
57 47 |
6.1 (16.3 vs 99.5)* | |||
| Luigetti et al. 2022 [31] | Healthy controls vs TTRv carriers and ATTRv-PNP |
26 17 |
4.5 (18 vs 81.8)* | NIS scale, Sudoscan values from feet, interventricular septum thickness, Norfolk QOL-DN | FAP stage, PND score, CADT |
| Loser at el. 2022 [23] |
TTRv carriers vs ATTRv-PNP |
6 14 |
B: 3.6 (5.4 vs 19.7) FU 1 year: 3.7 (7.5 vs 28.0) |
B and t1: PND score, FAP stage, R-ODS, SFN-SIQ, Norfolk-QOL-DN, NIS, NIS-UL, NIS-LL, ESC feet, ESC hands, NCS motor sum score, NCS sensory sum score. | CADT, handgrip right, handgrip left, |
| Sato et al. 2023 [38] | ATTRv-PNP tafamidis vs ATTR-PNP patisiran one year | 11 11 |
0.7 (106.4 vs 72.6)* | NIS score one and two years after treatment switch | |
| ATTRv-PNP tafamidis vs ATTR-PNP patisiran two years | 8 8 |
0.6 (92.8 vs 55.9)* | |||
| Lau et al. 2023 [36] | Healthy controls vs ATTRv no neuropathy |
25 7 |
0.8 (14.5 vs 11.9) | Creatinine | NIS-LL subscore, NT-proBNP, troponin I |
| Healthy controls vs ATTRv-PNP |
25 11 |
2.5 (14.5 vs 35.9) | |||
| ATTRv no neuropathy vs ATTRv-PNP |
7 11 |
3.0 (11.9 vs 35.9) | |||
| ATTRv no neuropathy vs ATTRv-PNP |
7 6 |
FU 4 years: 1.5 | |||
| Ticau et al. 2023 [37] | ATTRv-PNP baseline vs ATTRv-PNP patisiran 52 months |
111 87 |
0.6 (72.0 vs 44.1)* | Change in mNIS+7 and Norfolk QOL-DN sustained after 24 months additional patisiran treatment | |
| ATTRv-PNP patisiran Global OLE baseline vs ATTRv-PNP patisiran 24 months Global OLE |
111 87 |
0.9 (48.8 vs 44.1)* | |||
| ATTRv-PNP patisiran 30 months vs ATTRv-PNP placebo 18 months → 12 months patisiran Global OLE |
76 28 |
1.3 (50.1 vs 64.0)* | |||
| ATTRv-PNP patisiran 42 months vs ATTRv-PNP placebo 18 months → 24 months patisiran Global OLE |
87 24 |
1.0 (44.1 vs 42.8)* | |||
| ATTRv-PNP baseline vs ATTRv-PNP patisiran 18 months Phase II OLE |
26 25 |
0.8 (32.9 vs 26.1)* | |||
| ATTRv-PNP baseline vs ATTRv-PNP patisiran 48 months Global OLE |
26 23 |
0.7 (32.9 vs 23.0)* | |||
| Romano et al. 2024 [32] | Healthy controls vs TTRv carriers |
5 50 |
0.7 (17.7 vs 13.1) | PND score, NIS score, FAP stage |
|
| Healthy controls vs ATTRv-PNP |
5 61 |
4.2 (17.7 vs 74.0) | |||
|
TTRv carriers vs ATTRv-PNP |
50 61 |
5.6 (13.1 vs 74.0) | |||
| González-Moreno et al. 2024 [34] | Healthy controls vs TTRv V30M carriers |
30 31 |
Incalculable (<33 vs <33) |
NIS score | FAP stage |
| Healthy controls vs symptomatic ATTRv V30M |
30 29 |
Incalculable (<33 vs 116) |
|||
|
TTRv V30M carriers vs symptomatic ATTRv V30M |
31 29 |
Incalculable (<33 vs 116) |
|||
| Carroll et al. 2024 [33] | Asymptomatic (PND 0) vs symptomatic (PND ≥ I) |
11 16 |
9.4 (14.3 vs 134) | Baseline: PND score, FAP stage, NIS, NIS-LL, CMTSS, CMTES, CMTNS, MRC scores | eGFR, creatinine, Baseline: Norfolk-QOL-DN |
| Abstracts | |||||
| Ticau et al. 2020 [58] | Healthy controls vs ATTRv-CM no neuropathy |
53 93 |
3.3 (16.3 vs 54.1)* | PND score |
Cardiomyopathy |
| Healthy controls vs ATTRv-CM PND >0 |
53 101 |
3.8 (16.3 vs 61.4)* | |||
| Healthy controls vs ATTRv-PNP APOLLO |
53 193 |
4.3 (16.3 vs 69.4)* | |||
| ATTRv-CM no neuropathy vs ATTRv-CM PND >0 |
93 101 |
1.3 (46.2 vs 61.4)* | |||
| ATTRv-CM no neuropathy vs ATTRv-PNP APOLLO |
93 193 |
1.5 (46.2 vs 69.4)* | |||
| ATTRv-CM PND >0 vs ATTRv-PNP APOLLO |
101 193 |
1.1 (61.4 vs 69.4)* | |||
| Brunger et al. 2022 [35] |
TTRv carriers vs ATTRv no neuropathy |
12 8 |
0.9 (8.2 vs 7.1) | PND score |
|
|
TTRv carriers vs ATTRv-PNP TTR-stabilizer |
12 20 |
5.3 (8.2 vs 43.2) | |||
|
TTRv carriers vs ATTRv-PNP patisiran |
12 18 |
7.5 (8.2 vs 61.2) | |||
|
TTRv carriers and ATTRv no neuropathy vs TTRv carrier who developed PNP baseline |
20 7 |
1.1 (7.6 vs 8.40) | |||
| ATTRv-PNP TTR-stabilizer Vs ATTRv-PNP patisiran |
20 18 |
1.4 (43.2 vs 61.2) | |||
| ATTRv-PNP TTR-stabilizer vs TTRv carrier who developed PNP PND ≥I |
20 7 |
1.2 (43.2 vs 49.8) | |||
| ATTRv-PNP patisiran vs TTRv carrier who developed PNP PND ≥I |
18 7 |
0.8 (61.2 vs 49.8) | |||
| Berends et al. 2022 [41] | [123I]mIBG-scintigraphy negative TTRv carriers and ATTRv patients vs [123I]mIBG-scintigraphy positive TTRv carriers and ATTRv patients |
22 16 |
4.8 (9.2 vs 44.0) | NCS, PND score, NT-proBNP, troponin T, late heart-to-mediastinum ratio, wash-out rate, Ewing battery tests, [123I]mIBG-scintigraphy | |
| Conçeicao et al. 2023 [43] | ATTRv-PNP eplontersen vs ATTRv-PNP inotersen until week 35 followed by eplontersen |
144 24 |
|||
| Luigetti et al. 2023 [42] | ATTRv-PNP patisiran baseline vs ATTRv-PNP patisiran 4 months |
36 36 |
0.8 (55.7 vs 46.0)* | ||
| ATTRv-PNP patisiran baseline vs ATTRv-PNP patisiran 18 months |
36 36 |
0.7 (55.7 vs 39.3)* | |||
| ATTRv-PNP vutrisiran baseline vs ATTRv-PNP vutrisiran 4 months |
111 111 |
0.8 (59.1 vs 48.1)* | |||
| ATTRv-PNP vutrisiran baseline vs ATTRv-PNP vutrisiran 18 months |
111 111 |
0.7 (59.1 vs 39.2)* | |||
| ATTRv-PNP patisiran baseline vs ATTRv-PNP vutrisiran baseline |
36 111 |
1.1 (55.7 vs 59.1)* | |||
| ATTRv-PNP patisiran 18 months vs ATTRv-PNP vutrisiran 18 months |
36 111 |
1.0 (39.3 vs 39.2)* | |||
| Gilling et al. 2023 [44] | ATTRv-PNP placebo baseline vs ATTRv-PNP placebo → patisiran 36 months |
47 15 |
(63.2 vs 40.0)* | ||
| ATTRv-PNP patisiran baseline vs ATTRv-PNP patisiran 18months + Global OLE patisiran 36 months |
111 72 |
(72.0 vs 44.8)* | |||
| ATTRv-PNP Phase II OLE patisiran 24 months + Global OLE 36 months | 19 | 26.1* | |||
| Study (ref) |
Source type |
Assay | NfL cutoff level (pg/mL) |
Disease stage | Sensitivity (%) |
Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maia et al. 2020 [29] | Plasma | Simoa | 10.6 | PND 0 and PND ≥ I |
96.2 | 93.8 |
| 10.6 | PND 0 and PND I |
92.3 | 93.8 | |||
| 66.9 | PND I and PND ≥ II (Cohort #1) |
61.5 | 92.3 | |||
| 75.7 | PND I and PND ≥ II (Cohort #2) |
84.6 | 80.0 | |||
| Ticau et al. 2021 [30] | Plasma | Simoa | 37 | Healthy controls and ATTRv-PNP |
84.9 | 94.4 |
| Loser et al. 2022 [23] | Serum | Simoa | 11.7 | Asymptomatic and symptomatic |
85.7 | 100 |
| Romano et al. 2024 [32] | Serum | Ella | 37.0 | Healthy controls and ATTRv-PNP |
81.4 | 98.0 |
| 37.0 | Healthy controls and PND I |
63.2 | 98.0 | |||
| 37.1 | Asymptomatic carriers and symptomatic ATTRv patients |
81.4 | 100 | |||
| 37.1 | Asymptomatic carriers and PND I | 63.2 | 100 | |||
| 57.70 | PND I and PND ≥ II |
82.4 | 73.7 | |||
| González-Moreno et al. 2024 [34] | Serum | ELISA | 93.55 | Asymptomatic V30M TTRv carriers and ATTRv V30M patients |
79 | 87 |
| 92.6 | Healthy controls and ATTRv V30M patients |
79 | 80 | |||
| Carroll et al. 2024 [33] | Serum | Simoa | 52.2 | PND ≤ I and PND > II |
100 | 55.5 |
| 64.5 | Asymptomatic patients and symptomatic patients or sensorimotor converters |
92.0 | 88.5 | |||
| 88.9 | Asymptomatic patients and symptomatic patients and all converters |
62.9 | 96.2 |
| Study (ref) | Effect of no treatment on NfL levels | Effect of treatment on NfL levels |
|---|---|---|
| Ticau et al. 2021 [30] | Patisiran: ↓ | |
| Loser et al. 2022 [23] | No treatment: ↑ |
Tafamidis or patisiran: ↑ Initiation of patisiran: ↓ |
| Sato et al. 2023 [38] | After one- and two- years with patisiran: ↓ Tafamidis: ↑ |
|
| Ticau et al. 2023 [30] | Placebo: ↑ | Patisiran: ↓ |
| Brunger et al. 2022 [35] | No treatment and no neuropathy: ↑ | Diflunisal/tafamidis: = Patisiran: ↓ |
| Conçeicao et al. 2023 [43] | Eplontersen week 85: trend ↓ | |
| Luigetti et al. 2023 [42] | No treatment: ↑ | Patisiran or vutrisiran: ↓ |
| Gilling et al. 2023 [44] | Patisiran: ↓ Placobo → 36 months patisiran: ↓ to similar levels as patients continuously on patisiran. |
|
| Carroll et al. 2024 [33] | TTR-gene silencer: ↓ (n = 8) and ↑ (n = 4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





