Submitted:
04 March 2024
Posted:
04 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of DVS Cross-Linked Polymers
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Sorption Studies
2.5. Modeling of the Sorption Experiments
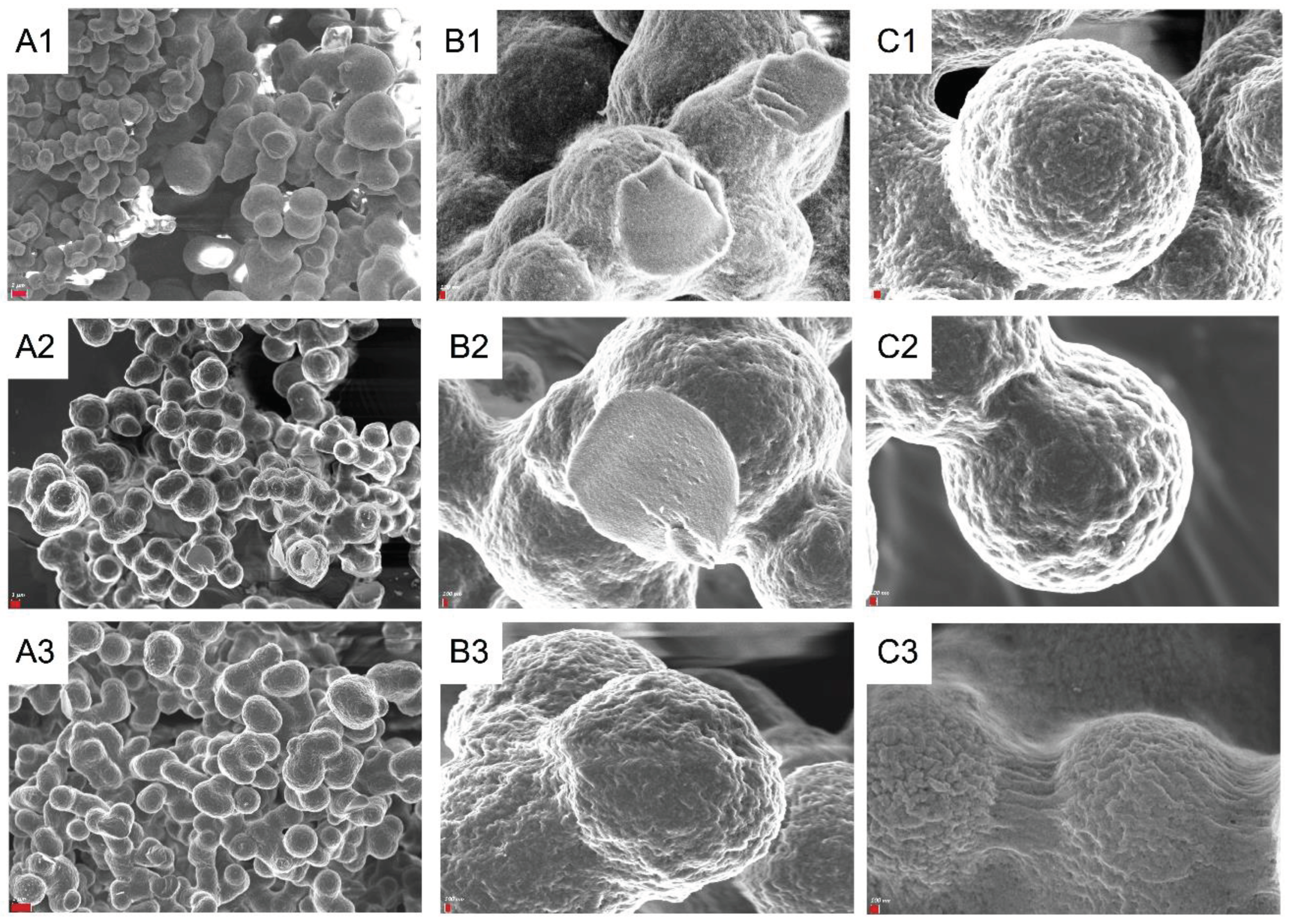
3. Results
- DVS and, in particular, that the eco-friendly material resulting from the cross-linking of starch shows a high affinity for CIP and makes it suitable for inland water and seawater remediation[14,15,16]. Nevertheless, this approach failed to obtain sorbent materials with the ability to trap IBU despite both CIP and IBU show some degree of structural similarity (Figure S1). It was concluded that the cavities formed during the cross-linking were not suitable to host the IBU molecule. On this basis we hypothesized that the pre-incubation of the carbohydrate with IBU prior to the addition of the cross-linker DVS may pre-organize the systems in a manner that resembles the molecular imprinting technology. Being aware that it is unlikely that the cross-linking of polysaccharides generates cavities complementary in size and charge to small molecules such as IBU, we were encouraged by the fact that the cross-linking of cyclodextrin in the presence or absence of toluene yields different polymers, being mainly linear in the former case and globular in the latter [19].
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Evaluation of the Polymers as Sorbents of IBU
3.3. Evaluation of Polymers as Sorbents of a Cocktail of Drugs
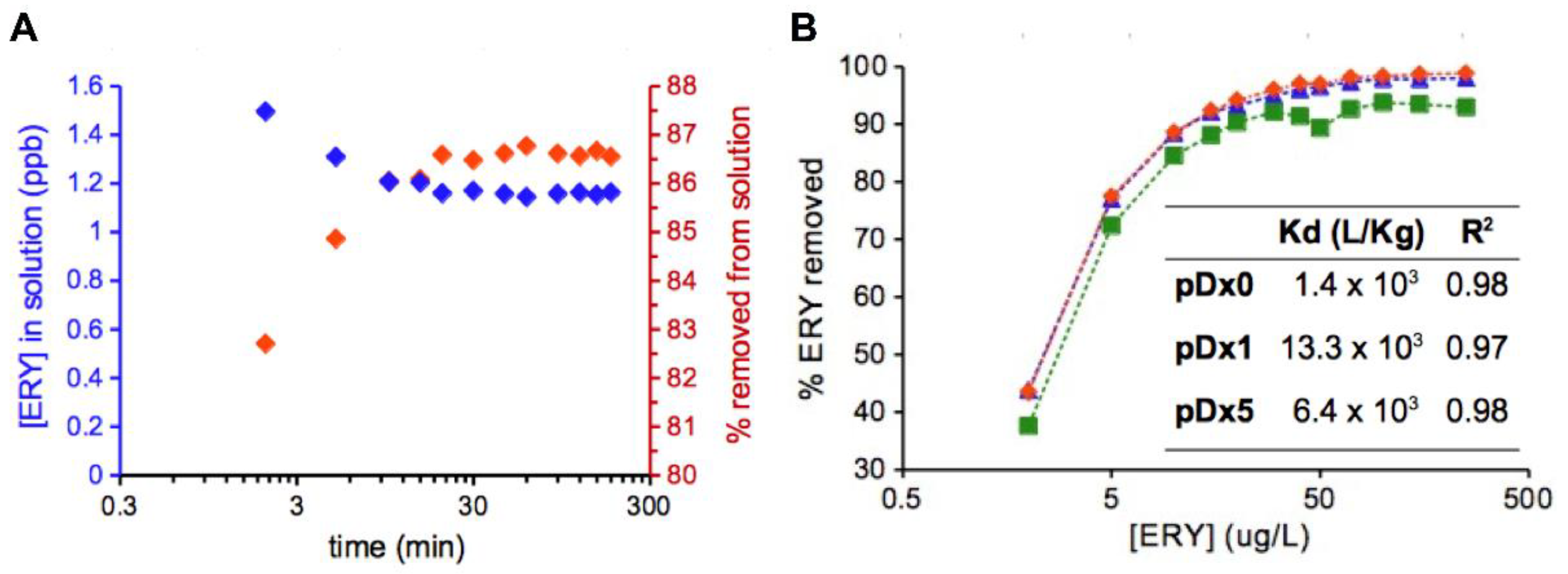
3.4. Evaluation of the Polymers as Sorbents of ERY
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN World Water Development Report; UN, 2020. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/publications/un-world-water-development-report-2020.
- FAO Coping with Water Scarcity. An Action Framework for Agriculture and Food Security; Rome, 2013. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i3015e.pdf.
- Liu, B.; Zhang, S.; Chang, C. Emerging pollutants—Part II: Treatment. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1603–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of Emerging Concern in Aquatic Systems: Chemistry, Occurrence, Effects, and Removal Methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019; US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, GA, 2019.
- Ahmad, M.; Khan, A.U. Global Economic Impact of Antibiotic Resistance: A Review. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 19, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamanmalek, S.; Brooks, B.W.; Rice-Boayue, J. Spatial Hazards of Antibiotic Resistance in Wastewater-Impacted Streams during Low Instream Flow Conditions. ACS EST Water 2022, 2, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafhauser, B.H.; Kristofco, L.A.; de Oliveira, C.M.R.; Brooks, B.W. Global Review and Analysis of Erythromycin in the Environment: Occurrence, Bioaccumulation and Antibiotic Resistance Hazards. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Tadi, D.A.; Fu, J.; Azizian, K.; Kouhsari, E. Global Status of Azithromycin and Erythromycin Resistance Rates in Neisseria Gonorrhoeae: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2022, 95, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Chiu, C.-H.; Heininger, U.; Hozbor, D.F.; Tan, T.Q.; von König, C.-H.W. Emerging Macrolide Resistance in Bordetella Pertussis in Mainland China: Findings and Warning from the Global Pertussis Initiative. Lancet Reg. Health - West. Pac. 2021, 8, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, C.; Patrone, V.; Lopez, C.M.; Morelli, L.; Rebecchi, A. Incidence of Tetracycline and Erythromycin Resistance in Meat-Associated Bacteria: Impact of Different Livestock Management Strategies. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mammery, A.; Ramírez de Arellano, E.; Cañada-García, J.E.; Cercenado, E.; Villar-Gómara, L.; Casquero-García, V.; García-Cobos, S.; Lepe, J.A.; Ruiz de Gopegui Bordes, E.; Calvo-Montes, J.; et al. An Increase in Erythromycin Resistance in Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus from Blood Correlates with the Use of Macrolide/Lincosamide/Streptogramin Antibiotics. EARS-Net Spain (2004–2020). Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ilurdoz, M.S.; Sadhwani, J.J.; Reboso, J.V. Antibiotic Removal Processes from Water & Wastewater for the Protection of the Aquatic Environment - a Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Jaramillo, F.; Giron-Gonzalez, M.; Salto-Gonzalez, R.; Hernandez-Mateo, F.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Novel Cross-Linked Saccharide Based Polymers as Bile Acid Sequestrants. Molecules 2015, 20, 3716–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Sanfrutos, J.; Lopez-Jaramillo, F.; Elremaily, M.; Hernández-Mateo, F.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. Divinyl Sulfone Cross-Linked Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis and Applications as Sorbents and Encapsulating Agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 3565–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado, S.; Megia-Fernandez, A.; Ortega-Muñoz, M.; Hernandez-Mateo, F.; Lopez-Jaramillo, F.J.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. Removal of the Water Pollutant Ciprofloxacin Using Biodegradable Sorbent Polymers Obtained from Polysaccharides. Polymers 2023, 15, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahab, N.S.; Abdelrahman, M.M. Simultaneous Determination of Methocarbamol and Ibuprofen by First Derivative Synchronous Fluorescence Spectroscopic Method in Their Binary Mixture and Spiked Human Plasma. J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrán, J.L.; Pignatello, J.J.; Teixidó, M. ISOT_Calc: A Versatile Tool for Parameter Estimation in Sorption Isotherms. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 94, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, C.; Ritter, H. Formation of Physical Hydrogels via Host−Guest Interactions of β-Cyclodextrin Polymers and Copolymers Bearing Adamantyl Groups. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 7418–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yang, H. Construction of Natural Polymeric Imprinted Materials and Their Applications in Water Treatment: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, K.C. Infrared Spectra of Sulfones and Related Compounds. Anal. Chem. 1949, 21, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Herrmann, N.; Bonerz, M.; Knacker, T.; Siegrist, H.; Joss, A. A Rapid Method to Measure the Solid–water Distribution Coefficient (Kd) for Pharmaceuticals and Musk Fragrances in Sewage Sludge. Water Res. 2004, 38, 4075–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORMAN List of Emerging Substances. Available online: http://www.normandata.eu/?q=node/81.
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. iLOGP: A Simple, Robust, and Efficient Description of N -Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient for Drug Design Using the GB/SA Approach. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 3284–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.H. Revisiting the Temkin Isotherm: Dimensional Inconsistency and Approximate Forms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 13140–13147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Drug | pDx0 | pDx1 | pDx5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atenolol | 413.7 (0.983) | 264.7 (0.990) | 415.7 (0.890) |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | 28.4 (0.865) | 33.3 (0.815) | 35.0 (0.870) |
| Ofloxacin | No linear fitting | 677.9 (0,915) | 631.8 (0.951) |
| Ciprofloxacin | 65.6 (0.589) | 926.9 (0.832) | 654.0 (0.940) |
| Carbamazepine | 18.0 (0.989) | 20.1 (0.968) | 22.5 (0.990) |
| Erythromycin | 61.0 (0.975) | 4285.0 (0.988) | 4657.7 (0.954) |
| K1 | K2 | MWSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pDx0 | 5.951 (1.828) | 39.34 (1.944) | 0.05 |
| pDx1 | 18.690 (0.908) | 128.80 (0.874) | 0.01 |
| pDx5 | 13.040 (0.906) | 89.180 (0.820) | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





