Submitted:
08 March 2024
Posted:
11 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
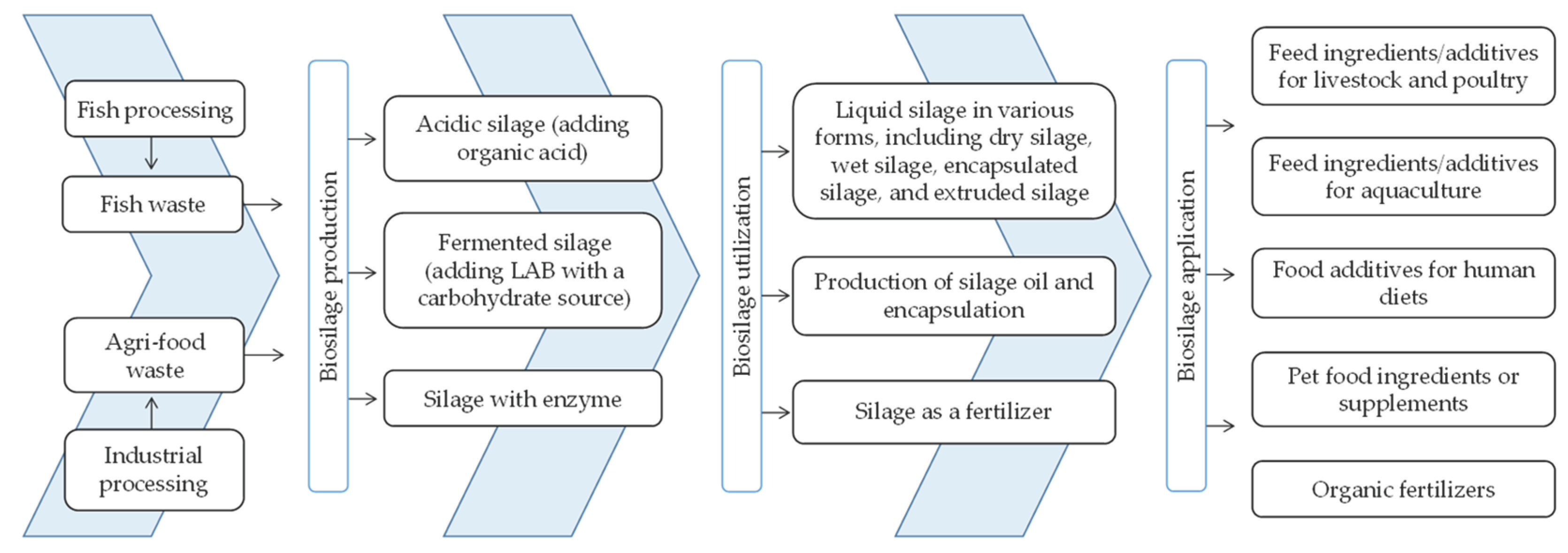
2. Ensiling Technology: A Brief Overview
2.1. Acidic Fish Silage Production
2.2. Fermented Fish Silage Production
2.3. Fish Silage Oil Production
2.4. Enhancing the Utility of Fish Silage through Encapsulation Technologies
3. Utilization of Fish Silage in Animal Nutrition: A Valuable Feed Ingredient
3.1. Utilization of Fish Silage in Aquafeeds
4. Pros and Cons of Fish Silage Production
5. Utilization of Fish Silage as a Fertilizer
6. Innovative Approaches to Sustainable Protein Alternatives through Food Waste Valorization
7. Conclusions and Future Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Metian, M. Fish Matters: Importance of Aquatic Foods in Human Nutrition and Global Food Supply. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2013, 21, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dossou, S.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; El Basuini, M.F.; El-Hais, A.M.; Olivier, A. Effect of partial replacement of fish meal by fermented rapeseed meal on growth, immune response and oxidative condition of red sea bream juvenile Pagrus major. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossou, S.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; El Basuini, M.F.; Olivier, A.; Zaineldin, A.I. Growth performance, blood health, antioxidant status and immune response in red sea bream (Pagrus major) fed Aspergillus oryzae fermented rapeseed meal (RM-Koji). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 75, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, M.K.; Kari, Z.A.; Van Doan, H.; Kabir, M.A.; Che Harun, H.; Mohamad Sukri, S.A.; Goh, K.W.; Wee, W.; Khoo, M.I.; Wei, L.S. Fermented Soybean Meal (FSBM) in African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) Diets: Effects on Growth Performance, Fish Gut Microbiota Analysis, Blood Haematology, and Liver Morphology. Life 2022, 12, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Kim, I.H. Fish meal – nutritive value. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2011, 95, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.L.; Toppe, J. Fish silage hydrolysates: Not only a feed nutrient, but also a useful feed additive. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 66, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampathkumar, K.; Yu, H.; Loo, S.C.J. Valorisation of industrial food waste into sustainable aquaculture feeds. Future Foods 2023, 7, 100240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.; Cobcroft, J.M.; Cole, A.; Condon, K.; Jerry, D.R.; Mangott, A.; Praeger, C.; Vucko, M.J.; Zeng, C.; Zenger, K.; Strugnell, J.M. The Future of Aquatic Protein: Implications for Protein Sources in Aquaculture Diets. One Earth 2019, 1, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, S.M.; Roy, K.; Mraz, J.; Wan, A.H.L.; Davies, S.J.; Tibbetts, S.M.; Øverland, M.; Francis, D.S.; Rocker, M.M.; Gasco, L.; Spencer, E.; Metian, M.; Trushenski, J.T.; Turchini, G.M. Towards achieving circularity and sustainability in feeds for farmed blue foods. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S. Application of fermentation strategy in aquafeed for sustainable aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 987–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howieson, J.; Chaklader, M.R.; Chung, W.H. Market-driven assessment of alternate aquafeed ingredients: seafood waste transformation as a case study. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2023, 63, 1933–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, S.M.; Turchini, G.M. ‘Aquafeed 3.0’: creating a more resilient aquaculture industry with a circular bioeconomy framework. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1156–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumbos, C.I.; Mente, E.; Karapanagiotidis, I.T.; Vlontzos, G.; Athanassiou, C.G. Insect-Based Feed Ingredients for Aquaculture: A Case Study for Their Acceptance in Greece. Insects 2021, 12, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogari, G.; Amato, M.; Biasato, I.; Chiesa, S.; Gasco, L. The Potential Role of Insects as Feed: A Multi-Perspective Review. Animals (Basel) 2019, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Tran, G.; Heuzé, V.; Ankers, P. State-of-the-art on use of insects as animal feed. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 197, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, Z.; Toth, J.D.; Westendorf, M.L. Food waste for livestock feeding: feasibility, safety, and sustainability implications. Glob. Food Sec. 2018, 17, 154–161. [Google Scholar]
- Garcı́a, A.J.; Esteban, M.B.; Márquez, M.C.; Ramos, P. Biodegradable municipal solid waste: Characterization and potential use as animal feedstuffs. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, W.Y.; Man, Y.B.; Wong, M.H. Use of food waste, fish waste and food processing waste for China's aquaculture industry: Needs and challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.Y.K.; Lo, I.M.C. Investigation of the available technologies and their feasibility for the conversion of food waste into fish feed in Hong Kong. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7169–7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Luo, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Shao, J. Effects of poultry by-product meal replacing fish meal on growth performance, feed utilization, intestinal morphology and microbiota communities in juvenile large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquac. Rep. 2023, 30, 101547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irm, M.; Taj, S.; Jin, M.; Luo, J.; Andriamialinirina, H.J.T.; Zhou, Q. Effects of replacement of fish meal by poultry by-product meal on growth performance and gene expression involved in protein metabolism for juvenile black sea bream (Acanthoparus schlegelii). Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaklader, M.R.; Siddik, M.A.B.; Fotedar, R. Total replacement of fishmeal with poultry by-product meal affected the growth, muscle quality, histological structure, antioxidant capacity and immune response of juvenile barramundi, Lates calcarifer. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0242079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Magouz, F.I.; Mansour, M.; Saleh, A.A.; Asely, A.M.E.; Fadl, S.E.; Ahmed, H.A.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Mahboob, S.; Al-Misned, F. Evaluation of Yeast Fermented Poultry By-Product Meal in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Feed: Effects on Growth Performance, Digestive Enzymes Activity, Innate Immunity, and Antioxidant Capacity. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 6, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapkevicius, M.L.N.E.; Nout, M.J.R.; Rombouts, F.M.; Houben, J.H.; Wymenga, W. Biogenic amine formation and degradation by potential fish silage starter microorganisms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 57, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toppe, J.; Olsen, R.L.; Peñarubia, O.R.; James, D.G. Production and utilization of fish silage. A manual on how to turn fish waste into profit and a valuable feed ingredient or fertilizer. FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018, 1–28.
- Sajib, M.; Langeland, M.; Undeland, I. Effect of antioxidants on lipid oxidation in herring (Clupea harengus) co-product silage during its production, heat-treatment and storage. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, R.L.; Toppe, J.; Karunasagar, I. Challenges and realistic opportunities in the use of by-products from processing of fish and shellfish. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 36, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, H.G.; Rasco, B.A. Fish protein hydrolysates: production, biochemical, and functional properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 43–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyurt, G.; Özkütük, A.S.; Boğa, M.; Durmuş, M.; Kuley Boğa, E. Biotransformation of Seafood Processing Wastes Fermented with Natural Lactic Acid Bacteria; The Quality of Fermented Products and Their Use in Animal Feeding. Turkish J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 17, 543–555. [Google Scholar]
- Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Palma Esposito, F.; Riccio, G.; Rizzo, C.; de Pascale, D. Fish Waste: From Problem to Valuable Resource. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Alvarez, O.; Chamorro, S.; Brenes, A. Protein hydrolysates from animal processing by-products as a source of bioactive molecules with interest in animal feeding: A review. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuley, E.; Özyurt, G.; Özogul, I.; Boğa, M.; Akyol, I.; Rocha, J.M.; Özogul, F. The Role of Selected Lactic Acid Bacteria on Organic Acid Accumulation during Wet and Spray-Dried Fish-Based Silages. Contributions to the Winning Combination of Microbial Food Safety and Environmental Sustainability. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nørgaard, J.V.; Petersen, J.K.; Tørring, D.B.; Jørgensen, H.; Lærke, H.N. Chemical composition and standardized ileal digestibility of protein and amino acids from blue mussel, starfish, and fish silage in pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 205, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, T.M.; Dantas, F.d.M.; Monteiro Dos Santos, D.K.; Kojima, J.T.; Pastrana, Y.M.; De Jesus, R.S.; Gonçalves, L.U. Fish Viscera Silage: Production, Characterization, and Digestibility of Nutrients and Energy for Tambaqui Juveniles. Fishes 2023, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyurt, G.; Gökdoğan, S.; Şimşek, A.; Yuvka, I.; Ergüven, M.; Kuley Boğa, E. Fatty acid composition and biogenic amines in acidified and fermented fish silage: a comparison study. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 70, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raa, J.; Gildberg, A. Fish silage: a review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1982, 16, 383–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, Y.; Oikawa, H.; Satomi, M. Reduction of lipids in fishmeal prepared from fish waste by a yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 121, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz de Arruda, L.; Borghesi, R.; Oetterer, M. Use of Fish Waste as Silage - A Review. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2007, 50, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatterson, I.N. Fish silage - Preparation, properties and uses. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1982, 7, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espe, M.; Holen, E.; He, J.; Provan, F.; Chen, L.; Øysæd, K.B.; Seliussen, J. Hydrolyzed fish proteins reduced activation of caspase-3 in H2 O2 induced oxidative stressed liver cells isolated from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Springerplus 2015, 4, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropea, A.; Potortì, A.G.; Lo Turco, V.; Russo, E.; Vadalà, R.; Rando, R.; Di Bella, G. Aquafeed Production from Fermented Fish Waste and Lemon Peel. Fermentation 2021, 7, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, J.C.R.; Ibarra, J.I.; Romero, F.A.; Ulloa, P.R.; Ulloa, J.A.; Matsumoto, K.S.; Cordoba, B.V.; Manzano, M.Á.M. Preparation of Biological Fish Silage and its Effect on the Performance and Meat Quality Characteristics of Quails (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2013, 56, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbenro, O.A.; Jauncey, K. Water stability, nutrient leaching and nutritional properties of moist fermented fish silage diets. Aquac. Eng. 1995, 14, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.K.; Swapna, H.C.; Bhaskar, N.; Halami, P.M.; Sachindra, N.M. Effect of fermentation ensilaging on recovery of oil from fresh water fish viscera. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2010, 46, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Boldaji, F.; Dastar, B.; Ghoorchi, T.; Zerehdaran, S.; Ashayerizadeh, A. Evaluation of increasing concentrations of fish waste silage in diets on growth performance, gastrointestinal microbial population, and intestinal morphology of broiler chickens. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 275, 114874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, D.T.N.; Nortvedt, R. Chemical and nutritional quality of silage made from raw or cooked lizard fish (Saurida undosquamis) and blue crab (Portunus pelagicus). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 2519–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyurt, G.; Özogul, Y.; Kuley Boğa, E.; Özkütük, A.S.; Durmuş, M.; Uçar, Y.; Özogul, F. The Effects of Fermentation Process with Acid and Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains on the Biogenic Amine Formation of Wet and Spray-Dried Fish Silages of Discards. J. Aquat. Food Prod. 2019, 28, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Suzuki-Utsunomiya, K.; Komori, Y.; Kamijo, A.; Yumura, I.; Tanabe, K.; Miyawaki, A.; Koga, K. Fermentation of non-sterilized fish biomass with a mixed culture of film-forming yeasts and lactobacilli and its effect on innate and adaptive immunity in mice. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidotti, R.M.; Carneiro, D.J.; Viegas, E.M. Acid and fermented silage characterization and determination of apparent digestibility coefficient of crude protein for Piaractus mesopotamicus. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2002, 33, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, P.Z.; Lee, C.M.; Park, E. Characterization of Squid-Processing Byproduct Hydrolysate and Its Potential as Aquaculture Feed Ingredient. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5587–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özogul, Y.; Durmuş, M.; Kuley Boğa, E.; Uçar, Y.; Özogul, F. The Function of Emulsions on the Biogenic Amine Formation and their Indices of Sea Bass Fillets (Dicentrarchus Labrax) Stored in Vacuum Packaging. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Brink, B.; Damink, C.; Joosten, H.M.L.J.; Huis in 't Veld, J.H.J. Occurrence and formation of biologically active amines in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1990, 11, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, H. Concentrations of biogenic amines in fish, squid and octopus and their changes during storage. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2604–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, H.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Xia, G.; Cen, J.; Huang, H.; Hao, S. Biogenic amines in commercial fish and fish products sold in southern China. Food Control 2012, 25, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Mah, J.H.; Hwang, H.J. Biogenic amine formation and bacterial contribution in fish, squid and shellfish. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özogul, F.; Gökbulut, C.; Özogul, Y.; Özyurt, G. Biogenic amine production and nucleotide ratios in gutted wild sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) stored in ice, wrapped in aluminium foil and wrapped in cling film at 4 °C. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, J.H.; Han, H.K.; Oh, Y.J.; Kim, M.G.; Hwang, H.J. Biogenic amines in Jeotkals, Korean salted and fermented fish products. Food Chem. 2002, 79, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeesi, R.; Shabanpour, B.; Pourashouri, P. Quality Evaluation of Produced Silage and Extracted Oil from Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Wastes Using Acidic and Fermentation Methods. Waste Biomass Valor. 2021, 12, 4931–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goosen, N.J.; de Wet, L.F.; Görgens, J.F.; Jacobs, K.; de Bruyn, A. Fish silage oil from rainbow trout processing waste as alternative to conventional fish oil in formulated diets for Mozambique tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 188, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goosen, N.J.; de Wet, L.F.; Görgens, J.F. Rainbow trout silage oil as immunity enhancing feed ingredient in formulated diets for South African abalone Haliotis midae. Aquaculture 2014, 430, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camaño Echavarria, J.A.; Rivera Torres, A.M.; Zapata Montoya, J.E. Sorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties of the dry silage of red tilapia viscera (Oreochromis spp.) obtained in a direct solar dryer. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyurt, G.; Uslu, L.; Durmuş, M.; Sakarya, Y.; Uzlaşir, T.; Küley, E. Chemical and physical characterization of microencapsulated Spirulina fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum. Algal Res. 2023, 73, 103149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuley, E.; Uslu, L.; Durmus, M.; Sakarya, Y.; Özyurt, G. Enhancement of Spirulina platensis bioactivity by probiotic fermentation and encapsulation by spray-drying. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 6015–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmus, M.; Özogul, Y.; Ozyurt, G.; Ucar, Y.; Kosker, A.R.; Yazgan, H.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Özogul, F. Effects of citrus essential oils on the oxidative stability of microencapsulated fish oil by spray-drying. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 978130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyurt, G.; Sakarya, Y.; Durmuş, M. Chemical and physical characterization of spray dried fish oil with different combination ratios of wall component. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e17223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Boldaji, F.; Dastar, B.; Ghoorchi, T.; Zerehdaran, S. Preparation of fish waste silage and its effect on the growth performance and meat quality of broiler chickens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4097–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabani, A.; Jazi, V.; Ashayerizadeh, A.; Barekatain, R. Inclusion of fish waste silage in broiler diets affects gut microflora, cecal short-chain fatty acids, digestive enzyme activity, nutrient digestibility, and excreta gas emission. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 4909–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammoumi, A.; Faid, M.; El yachioui, M.; Amarouch, H. Characterization of fermented fish waste used in feeding trials with broilers. Process Biochem. 1998, 33, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, W.A.; Fontenot, J.P.; Allen, V.G.; Abazinge, M.D. Seafood processing wastes ensiled with straw: Utilization and intake by sheep. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 4983–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Babu, L.K.; Panda, A.K.S.T.; Mohanty, A.; Panigrahy, K.K.; Samal, P. Effect of dietary supplementation of fermented fish silage on serum biochemical parameters of broiler Japanese quails (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Vet. World 2017, 10, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejeda-Arroyo, E.; Cipriano-Salazar, M.; Camacho-Diaz, L.M.; Salem, A.Z.; Kholif, A.E.; Elghandour, M.M.; Dilorenzo, N.; Cruz-Lagunas, B. Diet inclusion of devil fish (Plecostomus spp.) silage and its impacts on ruminal fermentation and growth performance of growing lambs in hot regions of Mexico. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2015, 47, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, K.H.; Mroz, Z. Organic acids for performance enhancement in pig diets. Nutr. Res. Rev. 1999, 12, 117–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.K.; Koh, C.B. The utilization and mode of action of organic acids in the feeds of cultured aquatic animals. Rev. Aquac. 2017, 9, 342–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, M.; Kocabagli, N.; Kahraman, R.; Bostan, K. Effects of dietary supplementation with organic acids and zinc bacitracin on ileal microflora, pH and performance in broilers. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 1999, 23, 451–455. [Google Scholar]
- Goosen, N.J.; de Wet, L.F.; Görgens, J.F. Rainbow trout silage as immune stimulant and feed ingredient in diets for Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goosen, N.J.; de Wet, L.F.; Görgens, J.F. The effects of protein hydrolysates on the immunity and growth of the abalone Haliotis midae. Aquaculture 2014, 428, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitroglou, A.; Merrifield, D.L.; Carnevali, O.; Picchietti, S.; Avella, M.; Daniels, C.; Güroy, D.; Davies, S.J. Microbial manipulations to improve fish health and production – a Mediterranean perspective. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitroglou, A.; Merrifield, D.L.; Moate, R.; Davies, S.J.; Spring, P.; Sweetman, J.; Bradley, G. Dietary mannan oligosaccharide supplementation modulates intestinal microbial ecology and improves gut morphology of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, 3226–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, M.A.B.; Chungu, P.; Fotedar, R.; Howieson, J. Bioprocessed poultry by-product meals on growth, gut health and fatty acid synthesis of juvenile barramundi, Lates calcarifer (Bloch). PLoS One 2019, 14, e0215025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; He, R.; Xu, W.; Mai, K.; He, G. Effects of soybean meal fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum P8 on growth, immune responses, and intestinal morphology in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 2016, 464, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.J.; Guroy, D.; Hassaan, M.S.; El-Ajnaf, S.M.; El-Haroun, E.R. Evaluation of co-fermented apple-pomace, molasses and formic acid generated sardine based fish silages as fishmeal substitutes in diets for juvenile European sea bass (Dicentrachus labrax) production. Aquaculture 2020, 521, 735087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wang, L.; Shao, X.; Liu, M. Dietary Different Replacement Levels of Fishmeal by Fish Silage Could Influence Growth of Litopenaeus vannamei by Regulating mTOR at Transcriptional Level. Front Physiol. 2020, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Arruda, L.F.; Borghesi, R.; Portz, L.; Cyrino, J.E.P.; Oetterer, M. Fish silage in black bass (Micropterus Salmoides) feed as an alternative to fish meal. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2009, 52, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Wang, J.; Chang, Q.; Mai, K. Effects of different levels of fish protein hydrolysate in the diet on the nonspecific immunity of Japanese sea bass, Lateolabrax japonicus (Cuvieret Valenciennes, 1828). Aquac. Res. 2006, 37, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espe, M.; Sveier, H.; Høgøy, I.; Lied, E. Nutrient absorption and growth of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fed fish protein concentrate. Aquaculture 1999, 174, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espe, M.; Ruohonen, K.; El-Mowafi, A. Hydrolysed fish protein concentrate (FPC) reduces viscera mass in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fed plant-protein-based diets. Aquac. Nutr. 2012, 18, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Olvera-Novoa, M.A.; Arredondo-Figueroa, J.L.; Hall, G.M.; Shirai, K. Feasibility of fishmeal replacement by shrimp head silage protein hydrolysate in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L) diets. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridwanudin, A.; Sheen, S.S. Evaluation of Dietary Fish Silage Combined with Poultry by Product Meal or Soybean Meal to Replace Fish Meal for Orange-Spotted Grouper Epinephelus coioides. J. Fish. Soc. Taiwan 2014, 41, 287–297. [Google Scholar]
- Fagbenro, O.; Jauncey, K. Growth and protein utilization by juvenile catfish (Clarias gariepinus) fed dry diets containing co-dried lactic-acid-fermented fish-silage and protein feedstuffs. Bioresour. Technol. 1995, 51, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbenro, O.; Jauncey, K. Growth and protein utilization by juvenile catfish (Clarias gariepinus) fed moist diets containing autolysed protein from stored lactic-acid-fermented fish-silage. Bioresour. Technol. 1994, 48, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbenro, O.; Jauncey, K.; Haylor, G. Nutritive value of diet containing dried lactic acid fermented fish silage and soybean meal for juvenile Oreochromis niloticus and Clarias gariepinus. Aquat. Living Resour. 1994, 7, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbenro, O.A.; Bello-Olusoji, O.A. Preparation, nutrient composition and digestibility of fermented shrimp head silage. Food Chem. 1997, 60, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbenro, O.A.; Jauncey, K. Physical and nutritional properties of moist fermented fish silage pellets as a protein supplement for tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 1998, 71, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbenro, O.; Jauncey, K. Chemical and nutritional quality of dried fermented fish silages and their nutritive value for tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1994, 45, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltan, M.A.; El-Laithy, S.M. Evaluation of fermented silage made from fish, tomato and potato by-products as a feed ingredient for Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish 2008, 12, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltan, M.A.; Tharwat, A.A. Use of fish silage for partial or complete replacement of fish meal in diets of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Egypt. J. Nutr. Feeds 2006, 9, 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Soltan, M.A.; Fouad, I.M.; El-Zyat, A.M.; Abou Zead, M.Y. Possibility of Using Fermented Fish Silage as Feed Ingredient in the Diets of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Glob. Vet. 2017, 18, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Soltan, M.A.; Hanafy, M.A.; Wafa, M.I.A. An evaluation of fermented silage made from fish by-products as a feed ingredient for African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Glob. Vet. 2008, 2, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Kim, Y.C.; Okorie, O.E.; Devnath, S.; Yoo, G.; Lee, S. Use of Fermented Fisheries By-products and Soybean Curd Residues Mixture as a Fish Meal Replacer in Diets of Juvenile Olive Flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. J. World Aquac Soc. 2007, 38, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, K.; Kaviraj, A.; Mukhopadhyay, P.K. Evaluation of fermented fish-offal in the formulated diet of the freshwater catfish Heteropneustes fossilis. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, K.; Kaviraj, A.; Mukhopadhyay, P.K.; Datta, M.; Sengupta, C. Evaluation of fermented fish-offal in formulated diet of the Indian major carp, rohu, Labeo rohita (Hamilton). Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2007, 37, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachindra, N.M.; Bhaskar, N. In vitro antioxidant activity of liquor from fermented shrimp biowaste. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 9013–9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwanna, L.C. Nutritional Value and Digestibility of Fermented Shrimp Head Waste Meal by African Catfish Clariasgariepinus. Pak. J. Nutr. 2003, 2, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, D.; Kalinowski, T.; Obach, A.; Robaina, L.; Tort, L.; Caballero, M.J.; Izquierdo, M.S. Vegetable lipid sources for gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata): effects on fish health. Aquaculture 2003, 225, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, M.A.B.; Howieson, J.; Ilham, I.; Fotedar, R. Growth, biochemical response and liver health of juvenile barramundi (Lates calcarifer) fed fermented and non-fermented tuna hydrolysate as fishmeal protein replacement ingredients. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Jung, W.G.; Myung, S.H.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, D.S. Substitution effects of fishmeal with tuna byproduct meal in the diet on growth, body composition, plasma chemistry and amino acid profiles of juvenile olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2014, 431, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, I.; Dauksas, E.; Remme, J.F.; Richardsen, R.; Løes, A.K. Fish and fish waste-based fertilizers in organic farming – With status in Norway: A review. Waste Manag. 2020, 115, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayan, S. A review of fish meal replacement with fermented biodegradable organic wastes in aquaculture. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2018, 6, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Hadj Saadoun, J.; Bertani, G.; Levante, A.; Vezzosi, F.; Ricci, A.; Bernini, V.; Lazzi, C. Fermentation of Agri-Food Waste: A Promising Route for the Production of Aroma Compounds. Foods 2021, 10, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Feng, K.; Liu, J. Oriented Fermentation of Food Waste towards High-Value Products: A Review. Energies 2020, 13, 5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; de Souza, T.S.P.; Holland, B.; Dunshea, F.; Barrow, C.; Suleria, H.A.R. Valorization of Food Waste to Produce Value-Added Products Based on Its Bioactive Compounds. Processes 2023, 11, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Luiz, S.F.; Azeredo, D.R.P.; Cruz, A.G.; Ajlouni, S.; Ranadheera, C.S. Apple Pomace as a Functional and Healthy Ingredient in Food Products: A Review. Processes 2020, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekata, P.E.S.; Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Nawaz, A.; Hano, C.; Walayat, N.; Lorenzo, J.M. Strategies to Increase the Value of Pomaces with Fermentation. Fermentation 2021, 7, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyawoot, N.; So, S.; Cherdthong, A.; Chanjula, P. Effect of Feeding Discarded Durian Peel Ensiled with Lactobacillus casei TH14 and Additives in Total Mixed Rations on Digestibility, Ruminal Fermentation, Methane Mitigation, and Nitrogen Balance of Thai Native–Anglo-Nubian Goats. Fermentation 2022, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Aquatic animal | Feeding trial | Ensiling conditions | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black Bass (Micropterus Salmoides) | 66 days | Acid fish silage | Up to 15% acid fish silage as a partial substitute for fish meal can be used in the formulation of carnivorous fish feed | [84] |
| Japanese sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) | 14 days | Fish protein hydrolysate produced from acid ensiling | Enhanced growth performance of Japanese sea bass was observed when 15% of the fishmeal was replaced with fish silage | [85] |
| Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) | 91 days | Fish protein hydrolysate produced from acid ensiling | The best growth performance of Atlantic salmon was observed when silage protein hydrolysate was included in the diet at levels below 15% | [86] |
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L) | 56 days | Shrimp head silage protein hydrolysate | Shrimp head hydrolysate is a promising alternative protein source for feeding tilapia, and it can improve the growth ratio even at dietary inclusion levels as high as 15% | [88] |
| Orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) | 42 days | Fish protein hydrolysate produced from acid ensiling | The combination of 10% or 20% fish silage with poultry by-product meal could replace 50% of fish meal protein in the diets without any adverse effects on the growth performance | [89] |
| African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) | 70 days | Fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum using carbohydrate substrates such as molasses. Fish silage was co-dried with soybean meal, poultry by-product meal, hydrolysed feather meal, and meat and bone meal | Fermented fish silage co-dried with protein feedstuffs is a suitable protein supplement, capable of providing up to 50% of dietary protein without adversely affecting feed efficiency, fish growth, or health | [90,91] |
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) | 70 days | Dried fermented fish silage and soybean meal blend | Co-dried fermented fish silage and soybean meal can be used as partial replacements for fish meal protein in dry aquaculture diets | [92] |
| Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) | 14 days | Raw heads of the river prawn were fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum using molasses or cassava starch as the carbohydrate source. Hydrolysed feather meal, poultry by-product meal or soybean meal, used as alternative filler, was blended with the liquid silage and solar-dried | Dried shrimp head silage meal is a suitable and promising protein feedstuff for fish diets. The digestibility coefficients of dry matter, crude protein, gross energy, and essential amino acids in the silage fed to catfish fingerlings exceeded 70% | [93] |
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | 15 days | Fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum using carbohydrate substrates such as molasses. The wet silage was combined with poultry by-product meal, a blend of soybean-hydrolyzed feather meal, or menhaden fish meal for pellet production | Moist fish silage pellets were both physically stable and highly digestible by Oreochromis niloticus, making them suitable as farm-made fish feeds | [94] |
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | 30 days | Fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum using carbohydrate substrates such as molasses, corn flour, or tapioca flour | Co-dried fermented fish silage is a suitable protein feedstuff in fish diets. The pellets produced from fermented silage demonstrated higher digestibility and excellent water stability | [95] |
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | 90 days | Dried fermented fish silage was combined with tomato by-product meal and potato by-product meal in a proportion of 30:40:30 w/w | Replacing 30% of dietary protein with dried fish silage in tilapia diets did not have adverse effects on growth or feed utilization parameters | [96] |
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) | 90 days | Fish silage was prepared by fermenting fish waste (60%), yogurt (5%) as a source of Lactobacillus plantarum, molasses (5%), and rice bran (30%) as a filler for 30 days | Replacing 25% of fish meal with dried fermented fish silage in tilapia diets and 50% of fish meal in catfish diets did not significantly adversely affect the growth or feed utilization parameters of the fish | [97] |
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | 84 days | Fermented fish silage was prepared by mixing fish waste (60%), rice bran (30%), dried molasses (5%), and yogurt (5%) as a source of Lactobacillus spp. for the lactic acid anaerobic fermentation process over 30 days | Replacing up to 50% of fishmeal with dried fermented fish silage did not have any negative effects on the growth and feed utilization of tilapia. Additionally, it resulted in a 15.59% reduction in feeding costs | [98] |
| African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) | 90 days | Fermented silage was prepared by mixing fish waste (60%), orange peel (30%) as a filler, molasses (5%), and yogurt (5%) as a source of Lactobacillus spp. for the lactic acid anaerobic fermentation process | Replacing 50% of fish meal with dried fermented fish silage in diets did not significantly adversely affect the growth or feed utilization parameters of catfish, and this replacement reduced feed costs | [99] |
| Olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) | 70 days | A mixture of fermented fisheries by-products and soybean curd residues | Up to 30% of fish meal can be replaced by this mixture without affecting the growth performance of juvenile olive flounder | [100] |
| Catfish (Heteropneustes fossilis), Indian major carp (Labeo rohita) | 60 days | Fish offal wastes were fermented, along with mustard oil cake and rice bran, using a mixture of a commercial suspension of microorganisms, molasses, and water | Fermented fish viscera could be included up to a 30% level as a partial replacement for fishmeal in the formulation of the fish diet | [101,102] |
| European sea bass (Dicentrachus labrax) | 63 days | Apple pomace fermented fish silage, molasses fish silage, and formic acid silages | Fish silage produced from organic acids or through fermentation with carbohydrate sources and lactic acid bacteria is an effective partial replacement for fish meal in aquaculture feeds | [82] |
| Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) | 52 days | Fish viscera silage produced from acid ensiling | Fish viscera silage can serve as a source of dietary protein and essential amino acids in tilapia diets. The viscera silage can stimulate the cellular non-specific immunity of Oreochromis mossambicus, and protein hydrolysis products are responsible for this stimulation | [76] |
| Tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) | 21 days | Acid silage and fermented silage with 5% yogurt and 15% of different carbohydrate sources (molasses, wheat bran, and cassava waste) were produced with 0.25% antifungal agent | Acidic and fermented fish viscera silages function as energy-rich components in aquafeed due to their high fat content in dry matter, and they are efficiently digested in the diets of juvenile tambaqui. Further assessment is required to determine the optimal inclusion level of viscera silages in aquafeeds | [35] |
| White shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) | 56 days | Acid fish silage | Replacing fishmeal with fish silage at a 25% inclusion level resulted in superior growth performance in white shrimp | [83] |
| African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) | 14 days | Fermented shrimp head waste meal by fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum using carbohydrate substrates such as cane molasses | Replacing fish meal with 30% fermented shrimp head waste meal can be a cost-effective and sustainable option in the diet of African catfish | [104] |
| Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) | 52 days | Silage oil recovered from fish processing waste | Silage oil effectively substituted the control oil without any negative effects on production performance, while improving cellular non-specific immunity and simultaneously decreasing total mortalities. Additionally, silage oil is a cost-effective alternative dietary oil for tilapia diets | [60] |
| South African abalone (Haliotis midae) | 153 days | Silage oil recovered from fish processing waste | Incorporating silage oil can enhance cellular immune function in H. midae, but it's important to optimize the inclusion level to counteract any negative effects on production efficiency | [61] |
| Barramundi (Lates calcarifer) | 56 days | Fish hydrolysate was prepared through the fermentation of tuna fish waste using baker’s yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (instant dried yeast) and Lactobacillus casei | Replacing fish meal with tuna hydrolysate at 50% and 75% inclusion levels negatively impacted the growth, feed utilization, and digestibility of juvenile barramundi | [107] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





