Submitted:
09 March 2024
Posted:
11 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
2. Safety of Fish and Fishery Products
2.1. Autolysis of Fish Components
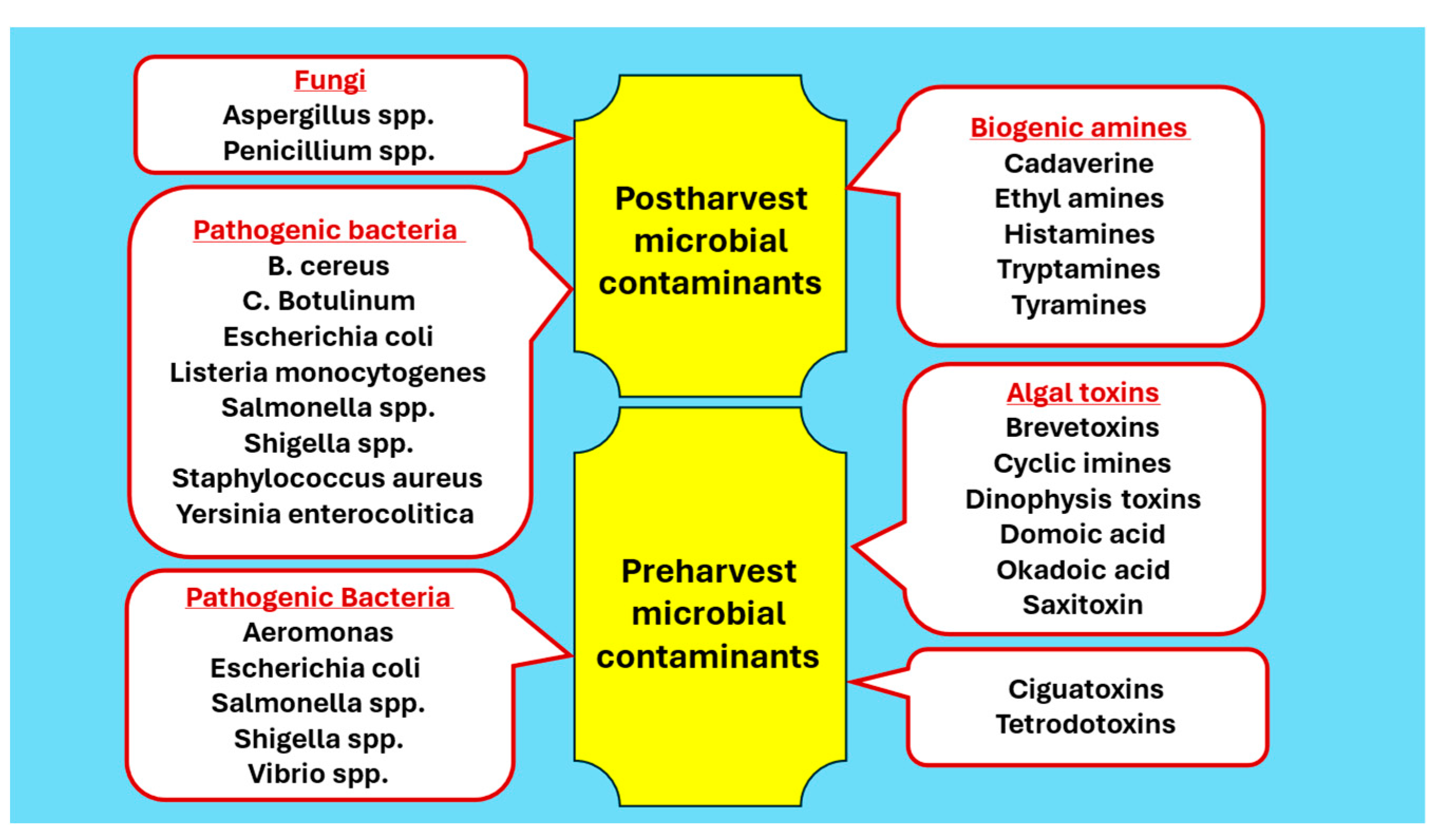
2.2. Microbial Food Safety Hazards
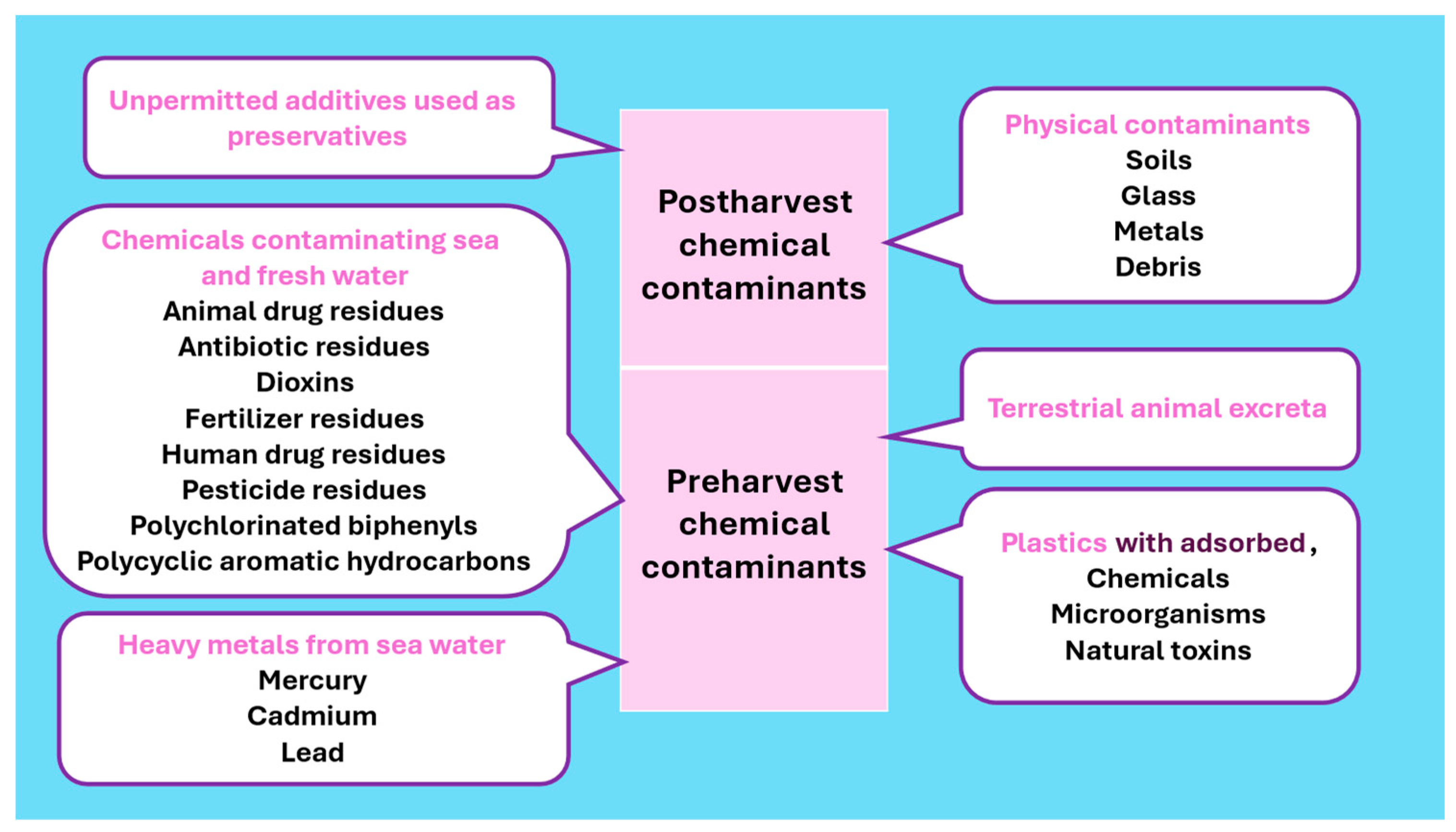
2.4. Chemical Food Safety Hazards
3. Processing and Preservation of Fish and Fish Products
3.1. Conventional Fish Processing and Preservation
3.2. Emerging Food Processing and Preservation Technologies
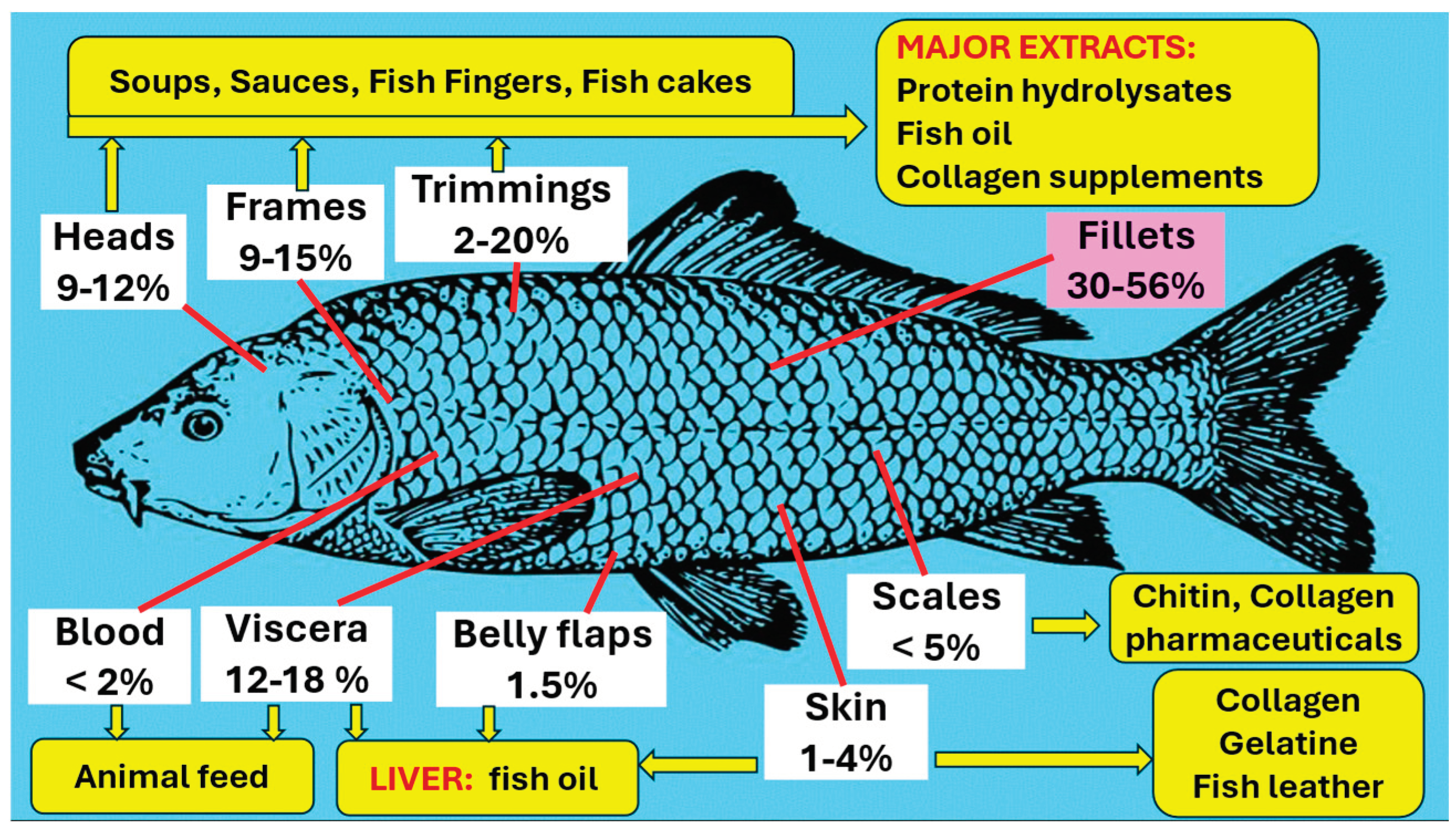
4. Fish Waste Utilization
4.1. Collagen
4.2. Gelatin
4.3. Other Fish Proteins and Derivatives
4.4. Enzymes from Fish
4.5. Chitin and Chitosan
4.6. Fish Oil and Associated Products
4.7. Conventional Uses from Fish Waste
5. Discussion
6. Conclusion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jayasekara, C.; Mendis, E. ; Kim, S-K. Seafood in the human diet for better nutrition and health. In Encycl. Mar. Biotechnol. First Edition. Se-Kwon Kim (Ed.). John Wiley & Sons Ltd. 2020. pp. 2939–2956. [CrossRef]
- Siscovick, D.S.; Barringer, T.A.; Fretts, A.M.; Wu, J.H.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Costello, R.B.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Jacobson, T.A.; M. B. Engler, M.B.; H. M. Alge, H.M.; Appel, L.J.; Mozaffarian, D. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (fish oil) supplementation and the prevention of clinical cardiovascular disease: A science advisory from the American heart association. Circulation, 2017, 135, e867–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture. Towards Blue Transformation. Rome, FAO. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Welch, A.W.; Knapp, A.N.; Tourky, S.E.; Daughtery, Z.; Hitchcock, G.; Benetti, D. The nutrient footprint of a submerged-cage offshore aquaculture facility located in the tropical. Caribbean. J World Aquaculture Soc. 2019, 50, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, N.; Datar, I.; Stachura, D.; Kaplan, D.; Krueger, K. Cell-Based Fish: A novel approach to seafood production and an opportunity for cellular agriculture. Front Sustainable Food Systems 2019, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthana, P.S.; Gopan, S.; Rajabudeen, R.; Fathima, R. Postharvest losses in fisheries sector – facts, figures, challenges and strategies. Int. J. Fisheries Aquatic Studies 2022, 10, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Wang, L. The microbial safety of fish and fish products: Recent advances in understanding its significance, contamination sources, and control strategies. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety 2020, 20, 738–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Yin, T.; You, J.; Liu, R.; Huang, Q.; Sh,i L. ; Wang, L.; Liao, T.; Wang, W.; Ma, H. Recent understanding of stress response on muscle quality of fish: From the perspective of industrial chain. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 140, 104145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabimashhadi, Z.; Gallo, N.; Salvatore, L.; Lionetto, F. Collagen derived from fish industry waste: Progresses and challenges. Polymers 2023, 15, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, J.; Martins, A.; Fidalgo, L.G.; Lima, V.; Amaral, R.A.; Pinto, C.A.; Silva, A.M.; Saraiva, J.A. Fresh fish degradation and advances in preservation using physical emerging technologies. Foods 2021, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Tan, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Mechanisms of fish protein degradation caused by grass carp spoilage bacteria: A bottom-up exploration from the molecular level, muscle microstructure level, to related quality changes. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, A.M.; Silva, F.; Pinto, F.R.; Barroso, S.; Gil, M.M. Quality assessment of chilled and frozen fish-mini review. Foods 2020, 9, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, X.; Li, T.; Deng, S.; Brennan, C.; Benjaku, S.I.; Liu, H.; Wang, F. , Xie, X.; Liu, D., Li, J.; Xiao, G.; Lukai Ma, L.. Advancements in nonthermal physical field technologies for prefabricated aquatic food: A comprehensive review. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety. 2024, 23, e13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dolah, F.M. Marine algal toxins: Origins, health effects, and their increased occurrence. Environ. Health Perspectives, Supplement 1 2002, 8, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G. M. Ocean climate change, phytoplankton community responses, and harmful algal blooms: a formidable predictive challenge. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Hernández-Camacho, C.J.; Álvarez-Santamaría, L.; Paniagua-Mendoza, A.; Robles-Hernández, R.; Rebolledo-Villa, F.; Rosales-Nanduca, H.; Ramos-Rodriguez, A; Acevedo-Whitehouse, K. Largest mortality event to date of California sea lions in Mexico might be linked to a harmful algal bloom. Aquatic Mammals 2022, 48, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinder, S.L.; Hays, G.C.; Brooks, C.J.; Davies, A.P.; Edwards, M.; Walne, A.W.; Gravenor, M.B. Toxic marine microalgae and shellfish poisoning in the British Isles: History, review of epidemiology, and future implications. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.A.; Fernandez, M.; Backer, L.C.; Dickey, R.; Bernstein, J.; Schrank, K.; Kibler, S.; Stephan, W.; Gribble, M.O.; Bienfang, P.; Bowen, R.E.; Degrasse, S.; Quintana, H.A.F.; Loeffer, C.R.; Weismann, R.; Blythe, D.; (23 authors). An updated review of ciguatera fish poisoning: Clinical, epidemiological, environmental, and public health management. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibler, S.R.; Tester, P.A.; Kunkel, K.E.; Moore, S.K.; Litaker, R.W. Effects of ocean warming on growth and distribution of dinoflagellates associated with ciguatera fish poisoning in the Caribbean. Ecological Modelling 2015, 316, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.I.; Ung, A.; Cruchet, P.; Revel, T.; Viallon, J.; Sibat, M.; Varney, P.; Laurent, V.; Hess, P.; Darius, H.T. Evidence for the range expansion of ciguatera in French Polynesia: A revisit of the 2009 mass-poisoning outbreak in Rapa Island (Australes Archipelago). Toxins 2020, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Bottein, M-Y. D.; Faizuddin, M. Ciguatera in the Indian Ocean with special insights on the Arabian Sea and adjacent Gulf and Seas: A Review. Toxins 2021, 13, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randell, J.E. Review of clupeotoxism, an often-fatal illness from the consumption of clupeoid fishes. Pacific Sci. 2005, 59, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Z.; Dickman, M.D. Mid-ocean exchange of container vessel ballast water. 1: seasonal factors affecting the transport of harmful diatoms and dinoflagellates. Marine Ecology - Progress Series 1999, 176, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffredini, E.; Mioni, R.; Mazzette, R.; Bordin, P.; Serratore, P.; Fois, F.; Piano, A.; Cozzi, L.; Croci, L. Detection and quantification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish from Italian production areas. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 184, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, C.D.; Hedderley, D.; Fletcher, G.C. Long-term study of Vibrio parahaemolyticus prevalence and distribution in New Zealand shellfish. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2320–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letchumanan, V.; Yin, W-F. ; Lee, L-H.; Chan, K-G. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from retail shrimps in Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Cheng, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xie, T. Prevalence, characterization, and antibiotic susceptibility of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from retail aquatic products in North China. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, L.E.; Ryan, S.J.; Stewart-Ibarra, A.M.; Finkelsteing, J.L.; Christine, A; King, C. K., Qiao, H.; Polhemas, M.E. A global map of suitability for coastal Vibrio cholerae under current and future climate conditions. Acta Tropica 2015, 149, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, M.; Nelapati, K.; Kiranmayi, B. Vibrio cholerae – A review. Vet. World 2011, 4, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R.R. Infectious disease and environment: cholera as a paradigm for waterborne. Int. J. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Deepa, J.; Sunil, B.; Latha, C.; Vrinda, K.M.; Mini, M.; Aravindakshan, T.V. Prevalence of Campylobacter spp. in marine fishes, crustaceans and molluscs in Kozhikode district, Kerala. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2022, 53, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberoum, A.; Jooyandeh, H. A Review on occurrence and characterization of the Aeromonas species from marine fishes. World J. Fish Marine Sci. 2010, 2, 519–523. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration. Fish and fishery products hazards and controls guidance. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition 2022, 393. https://www.fda.gov/food/seafood-guidance-documents-regulatory-information/fish-and-fishery-products-hazards-and-controls (accessed on 15 January 2024). /.
- Ali, A.; Parisi, A.; Conversano, M.C.; Lannacci, A.; D’Emilio, F.; Mercurio, V.; Normanno, G. Food-borne bacteria associated with seafoods: a brief review. J. Food Quality Hazards Control 2020, 7, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasko, D.A.; Rosovitz, M.J.; Myers, G.S.A.; Mongodin, E.F.; Fricke, W.F.; Gajer, P.; Crabtree, J.; Sebaihia, M.; Thomson, N.R.; Chaudhuri, R.; Henderson, I.R.; Sperandio, V.; Ravel, J. The pangenome structure of Escherichia coli: Comparative genomic analysis of E. coli commensal and pathogenic isolates. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 6881–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, J.L.; Rabinowitz, P.; Weissman, S.J.; Roberts, M.C. Diversity of Escherichia coli found in the Salish Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 967435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakasan, S.; Prabhakar, P.; Lekshmi, M.; Kumar, S.; Nayak, B.B. Isolation of Shiga- toxin producing Escherichia coli harboring variant Shiga-toxin genes from seafood. Vet. World 2018, 11, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagliani, G.G.; Brandi, G.F.; Schiavano, G.F. Incidence and role of Salmonella in seafood safety. Food Res. Inter. 2012, 45, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalinuovo, F.; Gazzotti, T.; Rippa, P.; Ciambrone, L.; Musarella, R.; Pratticò, E. Microbiological stability of canned tuna produced in Italy and in non-European countries. Italian J. Food Safety 2015, 4, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osek, J.; Lachtara, B.; Wieczorek, K. Listeria monocytogenes – How this pathogen survives in food-production environments? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 866462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymczak, B.; Szymczak, M.; Trafiałek, J. Prevalence of Listeria species and L. monocytogenes in ready-to-eat foods in the West Pomeranian region of Poland: Correlations between the contamination level, serogroups, ingredients, and producers. Food Microbiol. 2020, 91, 103532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaraman, G.K.; Gupta, S.S.; Visnuvinayagam, S.; Muthulakshmi, T.; Elangovan, R.; Perumal, V.; Balasubramanium, G.; Lodha, T. , Yadav, A. Prevalence of S. aureus and/or MRSA from seafood products from Indian seafood products. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marijani, E. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of bacteria isolated from marine and freshwater fish in Tanzania. Int. J. Microbiol. 2022, 4652326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Stegeman, J.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Alleman, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; (39 more authors). Human health and ocean pollution. Annals of Global Health 2020, 86, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, A.C.; Solo-Gabriele, H.M.; Galletti, A.; Benzecry, B.; Malone, H.; Boguzewski, V.; Jason, B. Possible impacts of sea level rise on disease transmission and potential adaptation strategies, a review. J. Environ. Management 2018, 217, 951–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donets, M.M.; Tsygankov, V.Y.; Gumovskiy, A.N.; Gumovskaya, Y.P.; Boyarova, M.D.; Busarova, O.Y.; Livinenko, A.V.; Khristoforova, N.K. Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in Pacific salmon from the Kamchatka Peninsula and Sakhalin Island, Northwest Pacific. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2021, 169, 112498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasher, E.; Heng, L.Y.; Zakaria, Z.; Surif, S. Concentrations and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the seawater around Langkawi Island. Malaysian J. Chem. 2013, 975781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongo, I.; Etor, E.E.; Ezemonye, L. Human health risk assessment of PAHs in fish and shellfish from Amariaria community, Bonny River, Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Management 2018, 22, 731– 736. [CrossRef]
- Edward, H.S.; Rugebregt, M.J.; Opier, R.D.A. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) compound in seawater of Cimandiri river estuary, Pelabuhan Ratu. IOP Conference Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 925, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, J.; Cai, W.; Xu, X.; Sun, M. The pollution status of heavy metals in the surface seawater and sediments of the Tianjin coastal area, North China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Bi, L.; Jin, L.; Peng, R. Toxic effects of cadmium on fish. Toxins 2022, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neff, J.M. Ecotoxicology of arsenic in the marine environment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem, 2009; 16, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Véron, A.; Bernier, I.; Hamelin, B. Lead abundances in bony fish from the world oceans: significance for contaminated marine habitats and environmental policies. Comptes Rendus Géoscience — Sciences de la Planète 2021, 353, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamas, A.; Moon, H.; Zheng, J.; Yang Qiu, Y.; Tabassum, T.; Jang, J.H.; Abu-Omar, M.; Scott, S.L.; Suh, S. Degradation rates of plastics in the environment. ACS Sustainable Chem. Engin, 2020, 8, 3494–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, A.B.; Eggert, H. Marine plastic pollution: sources, impacts, and policy issues. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy. 2019, 13, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewwandi, M.; Premarathne, K.S.D.; Wijesekara, H.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Soysa, S.; Vithanage, M. Vector transport of microplastics bound potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in water systems. J. Natl. Sci. Foundation Sri Lanka 2022, 50, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Pan, B.; Sakkiah, S.; Yavas, G.; Ge, W.; Zou, W.; Tong, W.; Hong, H. Persistent organic pollutants in food: Contamination sources, health effects and detection methods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junaid, M.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Sadaf, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, J. Enrichment and dissemination of bacterial pathogens by microplastics in the aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussien, N.H.; Mohammadein, A.; Tantawy, E.M.; Khattab, Y.; Al Malki, J.S. Investigating microplastics and potentially toxic elements contamination in canned tuna, salmon, and sardine fishes from Taif markets, KSA. Open Life Sci. 2021, 16, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandralekha, A.P.L.; Baranage, C.; Samarajeewa, U. Formaldehyde levels in fish from Kandy market. J. Natl. Sci. Coun. Sri Lanka. 1992, 20, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinadasa, B.K.K.K.; Elliott, C.; Jayasinghe, G.D.T.M. , A review of the presence of formaldehyde in fish and seafood. Food Control 2022, 136, 108882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
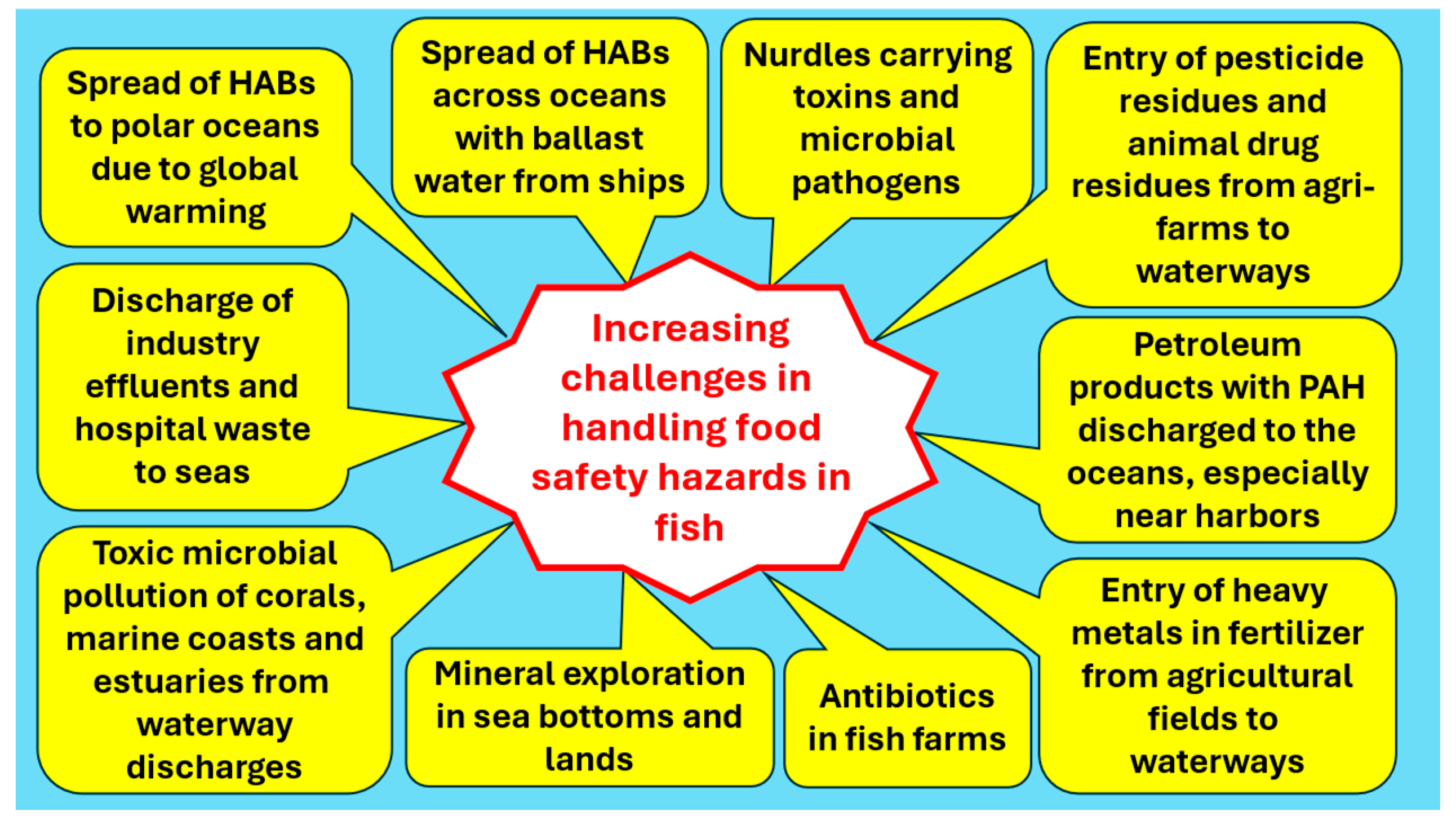
- Samarajeewa, U. Emerging challenges in maintaining marine food-fish availability and food safety. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety, 2023; 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Floris, R.; Serangeli, C.; Di Paola, L. Fishery wastes as a yet undiscovered treasure from the sea: Biomolecules sources, extraction methods and valorization. Mar. Drugs. 2020, 18, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Cipriani, P.; Giulietti, L.; Roiha, I.S.; Paoletti, M.; Palomba, M.; Levsen, A. Air-dried stockfish of Northeast Arctic cod do not carry viable anisakid nematodes. Food Control 2020, 116, 107322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.; Ranjitha, G. Qualities of commercially and experimentally sundried fin fish Scomberoides tol. African J. Food Sci. 2009, 3, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Bantle, M; Hanssler, J. Ultrasonic convective drying kinetics of clip fish during the initial drying period. Drying Technol. 2013, 31, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rubai, H.H.; Hassan, K.A.; Eskandder, M.Z. Drying and salting fish using different methods and their effect on the sensory, chemical and microbial indices. Multidisciplinary Rev. 2020, 3, e2020003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinkova, Z.; Wenzl, T. The occurrence of 16 EPA PAHs in food – A review. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds 2015, 35, 248–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narzary, Y.; Das, S.; Goyal, A.K.; Lam, S.S.; Sarma, H.; Sharma, D. Fermented fish products in South and Southeast Asian cuisine: indigenous technology processes, nutrient composition, and cultural significance. J. Ethn. Food 2021, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, D.; Mayrhofer, S.; Schmidt, J-M. ; Zitz, U.; Domig, K.J. Biogenic amine contents and microbial characteristics of Cambodian fermented foods. Foods 2020, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atapattu, R.; Samarajeewa, U. Fungi associated with dried fish in Sri Lanka. Mycopathologia 1990, 111, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patir, B.; İnanlı, A.G.; Öksüztepe, G.; Ilhak, O.I. Microbiological and chemical qualities of salted grey mullet (Chalcalburnus tarichii PALLAS, 1811). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 1, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Deng,Y. ; Wang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Sun, L.; Wang, R.; Ye, L.; Tao, S.; Liao, J.; Gooneratne, R. Fungal diversity and mycotoxin contamination in dried fish products in Zhanjiang market, China. Food Control, 2021, 121, 107614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Canada. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/food-nutrition/food-safety/food-addtives/lists-permitted/11-preservatives.html (accessed 11 February 2024).
- Ahmad, I.; Traynor, M.P. Impact of high-pressure processing and sous vide cooking on the physicochemical, sensorial, and textural properties of Fresh Whiteleg Shrimp (Litopenaeus setiferus), J. Aquatic Food Product Technol. 2022, 31, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiao, D.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, D. Effects of water distribution and protein degradation on the texture of high pressure-treated shrimp (Penaeus monodon) during chilled storage. Food Control 2022, 132, 108555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roobab, U.; Fidalgo, L.G.; Arshad, R.N.; Khan, A.W.; Zeng, X.; Bhat, Z.F.; Bekhit, A.E.A.; Batool, Z.; Aadil, R.M. High-pressure processing of fish and shellfish products: Safety, quality, and research prospects. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety 2022, 21, 3297–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Meng, L.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Mao, X. Inactivation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and retardation of quality loss in oyster (Crassostrea gigas) by ultrasound processing during storage. Food Res. Inter. 2023, 168, 112722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sireesha, T.; Gowda, N.A.N.; Kambhampati, V. Ultrasonication in seafood processing and preservation: A comprehensive review. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, N.; Rotabakk, B.T.; Lerfall, J. Mild processing of seafood—A review. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety 2022, 21, 340–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiekh, K.A.; Benjakul, S.; Qi, H.; Zhang, B.; Deng, S. Combined hurdle effects of pulsed electric field and vacuum impregnation of Chamuang leaf extract on quality and shelf-life of Pacific white shrimp subjected to high voltage cold atmospheric plasma. Food Packaging and Shelf Life 2021, 28, 100660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouryieh, H.A. Novel and emerging technologies used by the U.S. food processing industry. Innovative Food Sci. Emerging Technol. 2021, 67, 102559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Luan, A.; Yi, S.; Wu, J. , Wang, F. ; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Moderate protein degradation and lipid oxidation induced by cold plasma and its effect on the quality of dried fish products, J. Food Composition Anal. 2023, 123, 105636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Yi, C.; Lv, Y.; Luo, H.; Yang, T. The antibacterial mechanism of compound preservatives combined with low voltage electric fields on the preservation of steamed mussels (Mytilus edulis) stored at ice-temperature. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1126456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Mohammadi, X.; Wiktor, A.; Singh, A.; Pratap Singh, A. Applications of pulsed light decontamination technology in food processing: An overview. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, G.; Ji, S.; Zou, L.; Liang, J.; Walayat, N.; Chen, J.; Lyu, F.; Ding, Y. Effect of pulse light on the quality of refrigerated (4◦C) large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). LWT 2022, 167, 113855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Liu, X.; Dong, X.; Dong, S.; Xiang, Q.; Bai, Y. Effects of UVC light-emitting diodes on microbial safety and quality attributes of raw tuna fillets. LWT 2021, 139, 110553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.A.; Li, X.R.; Wang, L.X. Photodynamic inactivation in food systems: A review of its application, mechanisms, and future perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Prado-Silva, L.; Brancini, G.T.P.; Braga, G.U.L.; Liao, X. Y. , Ding, T., Sant'Ana, A. S. Antimicrobial photodynamic treatment (aPDT) as an innovative technology to control spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms in agri-food products: An updated review. Food Control 2022, 132, 108527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-S.; Zeng, W.-H.; Hwang, C.-C.; Chiu, K.; Ou, T.-Y.; Chang, T.-H.; Tsai, Y.-H. Effect of a novel microwave assisted induction heating (MAIH) technology on the quality of prepackaged Asian hard clam (Meretrix lusoria). Foods 2021, 10, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Hwang, C.-C.; Kao, J.-C.; Ou, T.-Y.; Chang, T.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-C. Cooking and pasteurizing evaluation of barramundi (Lates calcarifer) meats subjected to an emerging microwave-assisted induction heating (MAIH) technology. Innovative Food Sci. Emerging Technol. 2022, 80, 103089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankyamma, V.; Madhusudana Rao, B.; Debbarma, J.; Naga, P.P.V. Physicochemical, microstructural, and microbial qualities of dehydrated tuna chunks: Effects of microwave power and drying methods. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valø, T.; Jakobsen, A.N.; Lerfall, J. The use of atomized purified condensed smoke (PCS) in cold-smoke processing of Atlantic salmon—Effects on quality and microbiological stability of a lightly salted product. Food Control 2020, 112, 107155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldenstrøm, L.; Gaarder, M. Ø.; Lerfall, J. Sensory methodology in product optimization of cold smoked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) processed with atomized purified condensed smoke. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 4650–4667. [CrossRef]
- Blogoslawski, W.; Stewart, M.E. Some ozone applications in seafood, Ozone: Sci. Engineering 2011, 33, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, A.A. Ozone as a safe and environmentally friendly tool for seafood industry. J Aquatic Food Product Technol. 2016, 25, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, N.; Rotabakk, B.T. , Lerfall, J. Mild processing of seafood—A review. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety 2022, 21, 340–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosansu, S.; Mol, S.; Haskaraca, G. Sous-vide cooking: Effects on seafood quality and combination with other hurdles. Int. J. Gastronomy Food Sci. 2022, 29, 100586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamae, S.; Temdee, W.; Buatong, J.; Zhang, B.; Hong, H.; Benjakul, S. Enhancement of safety and quality of ready to-cook Asian green mussel using acidic electrolyzed water depuration in combination with sous vide cooking. Innov. Food Sci. Emerging Technol. 2023, 87, 103391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaraw, P.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Verma, A K. ; Barba, F.J.; Singh, V.P.; Kumar, P.; Lorenzo, J.M. Edible films/coating with tailored properties for active packaging of meat, fish and derived products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, B.N.; Silva, G.N.S.; Araújo, F.F.; Néri-Numa, I.A.; Pastore, G.M.; Bicas, J.L.; Molina, G. Beyond natural aromas: The bioactive and technological potential of monoterpenes. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2022, 128, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.L.; Langellotti, A.L.; Torrieri, E.; Masi, P. Emerging technologies in seafood processing: An overview of innovations reshaping the aquatic food industry. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety 2024, 23, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelti, A.L.; Teka, T.A.; Forsido, S.F.; Tamiru, M.; Bultosa, G.; Alkhtib, A.; Burton, E. ; Bio-based smart materials for fish product packaging: a review. Int. J. Food Properties 2022, 2022 25, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Wei, A.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, L.; Xia, N.; Wang, J. Protein-based active films: Raw materials, functions, and food applications. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety 2024, 23, e13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Fahmy, H.; Salah, S. Application of interactive and intelligent packaging for fresh fish shelf-life monitoring. Front Nutr. 2021, 21, 677884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, S.; Ammini, P.; Nayak, B.B.; Kumar, S.H. Survival behaviour of Salmonella enterica in fish and shrimp at different conditions of storage, LWT. 2020, 132, 109795. [CrossRef]
- Podolska, M.; Pawlikowski, B.; Nadolna-Ałtyn, K.; Pawlak, J.; Szymczak, K.; Szostakowska, B. How effective is freezing at killing Anisakis simplex, Pseudoterranova krabbei, and P. decipiens larvae? An experimental evaluation of time-temperature conditions. Parasitology Res. 2019, 118, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H. Effects of high-pressure processing on aquatic products with an emphasis on sensory evaluation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 6980–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nema, P.K.; Sehrawat, R.; Ravichandran, C.; Kaur, B.P.; Kumar, A.; Tarafdar, A. Inactivating food microbes by high-pressure processing and combined nonthermal and thermal treatment: A review. J. Food Quality 2022, 5797843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekonomou, S.I.; Bulut, S.; Karatzas, K.A.G.; Boziaris, I.S. Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes in raw and hot smoked trout fillets by high hydrostatic pressure processing combined with liquid smoke and freezing. Innov. Food Sci. Emerging Technol. 2020, 64, 102427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell-Perez, M.E.; Moreira, R.G. Irradiation and consumers acceptance. Innov. Food Process. Technol. 2021, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alvarez, O.; Chamorro, S.; Brenes, A. Protein hydrolysates from animal processing by-products as a source of bioactive molecules with interest in animal feeding: A review, Food Res. Inter. 2015, 73, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S-W. ; Mendis, E. Bioactive compounds from marine processing byproducts – A review. Food Res. Inter. 2006, 39, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, A.; Di Lena, G.; Gabrielli, P.; Santini, A.; Lombardi-Boccia, G.; Lucarini, M. Nutrients and bioactive compounds in seafood: Quantitative literature research analysis. Fishes 2022, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Lista, A.; Siekapen, M.M.; Ghaffari-Bohlouli, P.; Nie, L.; Alimoradi, H.; Shavandi, A. Fish collagen: Extraction, characterization, and applications for biomaterials engineering. Polymers (Basel) 2020, 12, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh N.E; Wassef, E.A.; Abdel-Mohson, H.H. Sustainable fish and seafood production and processing. C.M. Galankis (Ed.), 2022, Academic Press, London. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355081677.
- Subhan, F.; Hussain, Z.; Tauseef, I.; Shehzad, A.; Wahid, F. A review on recent advances and applications of fish collagen. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotphruethipong, L.; Hutamekalin, P.; Nilsuwan, K.; Sukketsiri, W.; Aluko, R.E.; Abdul, N.R.; Benjakul, S. Combined effects of defatted hydrolyzed collagen from salmon skin and vitamin C on proliferation and migration of human fibroblast cell. Fishes 2022, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsuwan, K.; Patil, U.; Tu, C.; Zhang, B.; Benjakul, S. Salmon skin acid-soluble collagen produced by a simplified recovery process: Yield, compositions, and molecular characteristics. Fishes 2022, 7, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsuwan, K.; Fusang, K.; Pripatnanont, P.; Benjakul, S. Properties and characteristics of acid-soluble collagen from salmon skin defatted with the aid of ultrasonication. Fishes 2022, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, J.Z.; Akhter, N.; Ashraf, Q.S.; Mir, S.A.; Makroo, H.A.; Majid, D.; Francisco, J.; Barba, F.J. Khaneghah, A.M.; Dar, B.N. A comprehensive review on gelatin: Understanding impact of the sources, extraction methods, and modifications on potential packaging applications. Food Packaging and Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.Y.; Dumont, M-J. ; Simpson, B.K. Preparation and physicochemical characterization of films prepared with salmon skin gelatin extracted by a trypsin-aided process. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2020, 3, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Kang, H. Effect of chitosan-gelatin coating containing nano-encapsulated tarragon essential oil on the preservation of pork slices. Meat Sci. 2020, 166, 2020–108137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditi, M.; Varsha, L. Fish processing: Product and by-product, processing and marketing. Int. J. Fisheries Aquatic Studies 2020, 8, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.; Pan, C.; Chen, W.; Ruan, Q.; Luo, X.; Lv, M.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Ma, H. Gelatin from specific freshwater and saltwater fish extracted using six different methods: Component interactions, structural characteristics, and functional properties. LWT 2024, 191, 115656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza-Espinoza, D.M.; del Carmen Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Aubourg, S.P.; Salazar-Leyva, J.A.; Rodríguez-Felix, F.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Chemical-structural identification of crude gelatin from jellyfish (Stomolophus meleagris) and evaluation of its potential biological activity. Fishes 2023, 8, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.S.; Sarbon, N.M. Physical and mechanical characteristics of gelatin-based films as a potential food packaging material: A review. Membranes (Basel) 2022, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurdiani, R.; Ma'rifah, R.D.A.; Busyro, I.K.; Jaziri, A.A.; Prihanto, A.A.; Firdaus, M.; Talib, R.A.; Huda, N. Physical and functional properties of fish gelatin-based film incorporated with mangrove extracts. PeerJ. 2022, 10, e13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbew Gedif, H.; Tkaczewska, J.; Jamróz, E.; Zaj ˛ac, M.; Kasprzak, M.; Pajak, P.; Grzebieniarz, W.; Nowak, N. Developing technology for the production of innovative coatings with antioxidant properties for packaging fish products. Foods 2023, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nimry, S.; Abu Dayah, A.; Hasan, I.; Daghmash, R. Cosmetic, biomedical and pharmaceutical applications of fish gelatin/hydrolysates. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Cruz, G.; León-López, A.; Cruz-Gómez, V.; Jiménez-Alvarado, R.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Collagen hydrolysates for skin protection: Oral administration and topical formulation. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Ye, X.; Hou, Z.; Shiguo Chen, S. Sustainable utilization of proteins from fish processing by-products: Extraction, biological activities and applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 104276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtel, P.J.; Morey, A.; Oliveira, A.C.M.; Wu, T.H.; Plante, S.; Bower, C.K. Chemical and nutritional properties of Pacific Ocean perch (Sebastes alutus) whole fish and by-products. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2010, 34, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Vázquez, A. Bioactive peptides: A review. Food Quality and Safety 2017, 1, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, Y. Review and perspective on bioactive peptides: A roadmap for research, development, and future opportunities. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 9, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinakarkumar, Y.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Margavelu, G.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Chandran, M. Production and characterization of fish protein hydrolysate: Effective utilization of trawl by-catch. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou,W-J. ; Wang, F-X.; Yu, J.; Li, X-H.; Liu, Y-L. Cryoprotective effects of protein hydrolysates prepared from by-products of silver carp (Hypophthalmuchthys molitrix) on freeze thawed surimi. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanapala, P.; Pola, S. Chapter 17 - Bioactive peptides as a potential antioxidants from marine byproducts, Kim, S-K.; Shin, K-H.; Venkatesan, J. (Eds), In Marine Antioxidants, Academic Press, 2023, 241-247. [CrossRef]
- Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.-K. Bioactive peptide of marine origin for the prevention and treatment of non-communicable diseases. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangkheirakpam, M.R.; Mahanand, S.S.; Majumdar, R.K.; Sharma, S.; Hidangmayum, D.D.; Netam, S. Fish waste utilization with reference to fish protein hydrolysate – A Review. Fishery Technol. 2019, 56, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Nikoo, M.; Benjakul, S.; Xu, X. Antioxidant and cryoprotective effects of Amur sturgeon skin gelatin hydrolysate in unwashed fish mince. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaklader, M.R.; Howieson, J.; Foysal, M.J.; Hanif, M.A.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Fotedar, R. Fish waste to sustainable additives: Fish protein hydrolysates alleviate intestinal dysbiosis and muscle atrophy induced by poultry by-product meal in Lates calcarifer juvenile. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1145068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, S.; Odila, J.; Voss, G.; Martins, R.; Rosa, A.; Couto, J.A.; Almeida, A.; Pintado, M. Fish by-products: A source of enzymes to generate circular bioactive hydrolysates. Molecules 2023, 28, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomklao, S.; Kuepethkaew, S.; Benjakul, S.; Zhang, Y.; Simpson, B.K. Enzymes from fish processing waste materials and their commercial applications. In Fish Waste to Valuable Products. Sustainable Materials and Technology. Maqsood, S.; Naseer, M.N.; Benjakul, S; Zaidi, A.A. (Eds) Springer, Singapore. 2024. pp. 147–194. [CrossRef]
- Hisham, F.; Akmal, M.H.M.; Ahmad, F.; Ahmad, K.; Samat, N. Biopolymer chitosan: Potential sources, extraction methods, and emerging applications. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhu, H.; Huang, J.; Zhao, J.; Yan, B.; Ma, S.; Zhang, H.; Fan, D. The physicochemical properties of chitosan prepared by microwave heating. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, M.; Goswami, P.; Paritosh, K.; Kumar, M.; Pareek, N.; Vivekanand, V. Seafood waste: a source for preparation of commercially employable chitin/chitosan materials. Bioresour. Bioprocess 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploydee, E.; Chaiyanan, S. Production of high viscosity chitosan from biologically purified chitin isolated by microbial fermentation and deproteinization. Int. J. Polymer Sci. 2014, 162173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahing, F.A.; Wid, N. Extraction and characterization of chitosan from shrimp shell waste in Sabah. Trans. Sci. Technol. 2016, 3, 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Torri, G.; Crini, G. Fundamentals and applications of chitosan. Sustainable Agriculture Reviews. 2019, 338. Springer International Publishing AG, 978-3-030-16538-3; 978-3-030-16537-6.ff10.1007/978-3-030-16538-3_2ff.ffhal-02152878.
- Oliver, L.; Dietrich, T.; Marañón, I.; Villarán, M.C.; Barrio, R.J. Producing omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: A review of sustainable sources and future trends for the EPA and DHA market. Resources 2020, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateiro, M.; Domínguez, R.; Varzakas, T.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Movilla Fierro, E.; Lorenzo, J.M. Omega-3-rich oils from marine side streams and their potential application in food. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewska, K.; Oszajca, K.; Zep, W.; Piekarska, A.; Sidorkiewicz, M. The impact of short-term shark liver oil supplementation on the fatty acid composition of erythrocyte membranes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Karadeniz, F. Biological importance and applications of squalene and squalane. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 65, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalfoh, E.; Ahmad, M.I.; Binhweel, F. , Shaah, M.A.; Senusi, W.; Hossain, M.S.; Alsaadi, S. Fish waste oil extraction using supercritical CO2 extraction for biodiesel production: Mathematical, and kinetic modeling. Renewable Energy 2024, 220, 119659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Kleter, G.A. , Bouzembrak, Y.; Dupouy, E., Frewer, L.F.; Natour, F.N.R.A., Marvin, H.J.P. Making food systems more resilient to food safety risks by including artificial intelligence, big data and internet things into food safety, early warning and risk identification tools. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Safety 2024, 23, e13296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fish component | Degrading enzyme / catalyst | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Glycogen | Glycolytic enzymes | Lactic acid and reduced pH |
| Proteins and peptides | Chymotrypsin, trypsin, calpains cathepsins, carboxypeptidases | Amino acids and softening of tissues, belly burst |
| Collagen and connective tissues | Collagenases | Proteins, glycopeptides and softening of tissues |
| Nucleotides | Nucleases | Purines, pyrimidines, hypoxanthine |
| Trimethylamine oxide | TMAO demethylase | Amines, formaldehyde |
| Lipids | Triacyl Lipases, phospholipases, lipoxygenases, peroxidases |
Free fatty acids, glycerol, oxides, peroxides |
| Lipids | Light UV, copper, iron catalyzed | Hydroperoxides, aldehydes, ketones, alcohols |
| Method | Action (Effect on quality and safety) [Reference] |
|---|---|
| Air drying (Wind drying) |
Open air drying at 0-2 oC for 3 months. 75% moisture is lost. (Shelf life 12 months. Low temperature minimizes microbial growth; Anisakid parasites devitalized in 7.5 months ) [64]. |
| Salt drying (Osmotic dehydration) |
Eviscerated fish is dipped in salt water, or sprinkled with salt and dried under sun, or with hot air drafts (Increased free fatty acids and partial loss of nutritional quality; amenable to mold attacks at low salt concentrations) [65]. |
| Salt & ultrasound drying | Hybrid of ultrasound with ambient drying applied to salted cod fish (Ultrasound reduces drying time at low temperatures retaining quality) [66]. |
| Sun & oven drying | Sun drying, solar drying and oven drying (The methods leave room for partial microbial spoilage affecting quality and safety; products are characterized by hard textures, protein leaching and degradation, and lipid oxidation as inherent enzymes continue to be active till the water activity becomes limiting [67]. |
| Smoke curing | The preservatives carried with the smoke deposit low molecular acids, aldehydes, phenolics etc. Bring about surface preservation of fish and slow moisture removal retaining the texture. Partial cooking by low heat and burning of dripping fats occur. (The carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons deposited on surface; change organoleptic properties for consumer preference) [62,68]. |
| Fermenting | Mostly use undersized and low value fish. Autolysis and diverse microbial actions metabolize proteins and carbohydrates producing alkaline conditions, restricting spoilage organisms, and delivering soft solid texture, fish pastes, or fish sauces. Sodium chloride, nitrates/ nitrites and herbs when used protect against spoilage generating desirable organoleptic characteristics. (Biogenic amine formation impairs food safety) [69,70]. |
| Method | Action (Food quality and safety outcome) [Reference] |
|---|---|
| High Pressure Processing (HPP) | Operate at pressure of 100 -1000 MPa on fish as a non-thermal process (Retains sensory and nutritional quality; inactivate microorganisms and spoilage enzymes) [75,76,77]. |
| Ultrasound Technology | Use high frequency sound waves at 20 – 1000 kHz (Retains sensory and nutritional quality; inactivate microorganism and enzymes) [78,79]. |
| Pulsed Electric Field (PEF) | Apply short bursts of electricity at high voltage at 20-80 kV/cm. Combine effectively with gas modifications and refrigeration. (Affects cell permeability inactivating microorganisms; lipid oxidation and high cost are limitations) [80,81,82]. |
| Cold Plasma (CP) | Generate ions, charged particles, radicals and electrons in the gaseous environment around the fish muscles using an intense electric field (Oxidize cell membranes of microorganisms; oxidation of lipids and proteins in fish muscles limits the application even at atmospheric temperature) [82,83]. |
| Low Voltage variable frequency electrostatic field & chemical preservatives | LVVFEF carries the benefit of combining the action of two methods, the voltage and chemical preservatives or low temperature treatment (LVVFEF interferes with biochemical reactions involving charged particles and formation of mini-ice crystals when combined with freezing. It inactivates spoilage bacteria Pseudomonas and Bacillus subtilis) [84] |
| Pulsed Light | Application of UV light pulses at high energy inactivating microorganisms on surface. (Prevents replication of DNA due to formation of dimers resulting in cell death; surface sterilization of fillet occurs with 300Jj/pulse; pigments lose color; low penetration; less effective on non-smooth skin surfaces) [85,86]. UV light emitting diodes with wavelength limitation of 365 nm are considered a safer technique in place of mercury lamps emanating UV light but carries more heat production than light (Causes lipid oxidation) [87]. |
| Photodynamic inactivation | Activates internal cellular or external photosensitizers, light, and molecular oxygen generating Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). ROS attacks proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids in microorganisms inactivating them (Microorganisms differ in their response to treatment; some microorganisms may generate tolerance; photosensitizers may continue to be active in foods entering human body; requires examining fish after treatment for safety) [88,89]. |
| Microwave Heating | Electromagnetic waves of frequency 2.45 GHz -S band- having capacity to penetrate fish muscles is used to generate heat internally. More efficient combined effect from microwave assisted induction heating is gaining recognition (Possess advantage of pasteurization and cooking to preferred temperatures for varying consumer needs; heat would change the sensory characters of fresh fish) [90,91]. |
| Microwave drying | Rapid fish drying compared with solar drying to prepare dry fish (Better microbiological safety, smooth texture; increase lipid oxidation and protein denaturation compared to air drying) [92]. |
| Smoke technology | Smoke purified to eliminate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is sprayed on fish in atomized gaseous form. (Inhibit bacteria, add smoky flavor and texture of consumer preference; products were darker than smoked fish; need to lower water activity and pH to make the treatment safe from microorganisms; sensorily atomized smoke treated fish is similar to traditionally smoked salmon) [93,94]. |
| Ozone treatment | Sanitizing benefit from ozone is used by exposing fish to the gas, ozonized water, or ozonized ice slurries. (It inactivates microorganisms and suppress lipid oxidation) [95,96]. |
| Vacuum cooking | Vacuum cooking in sealed plastic pouches retain sensory properties of fish. Acidic electrolyzed water retains the quality to a higher extent. (Carries the advantage of post-process contamination control, and longer storage life of omega-3-fatty acids; Carry the risk of proliferating anaerobic Clostridium spores) [97,98,99]. |
| Edible coatings/ films | They are biopolymers applied as thin films on fish muscles to protect from contaminants (May incorporate antioxidants, antimicrobials, monoterpenes, flavors, and vitamins; may contain constituents that cause microbial cell death; varying film forming abilities is a limitation; consumer awareness and safety are low) [100,101,102]. |
| Active packaging | Active packages may carry oxygen scavengers, carbon dioxide absorbents or emitters, moisture regulators, antimicrobials, antioxidants (tea polyphenols), and flavor releasers for product safety and consumer preferences (Selective depending on the fish type and consumer demand; packaging mostly biodegradable) [103,104]. |
| Intelligent packaging | These third-generation packaging screen the quality of fish and signal the changes. Packaging may response to moisture, light, pH, oxygen, heat and bacterial growth indicating loss of freshness and quality [105]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





