Submitted:
08 March 2024
Posted:
11 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
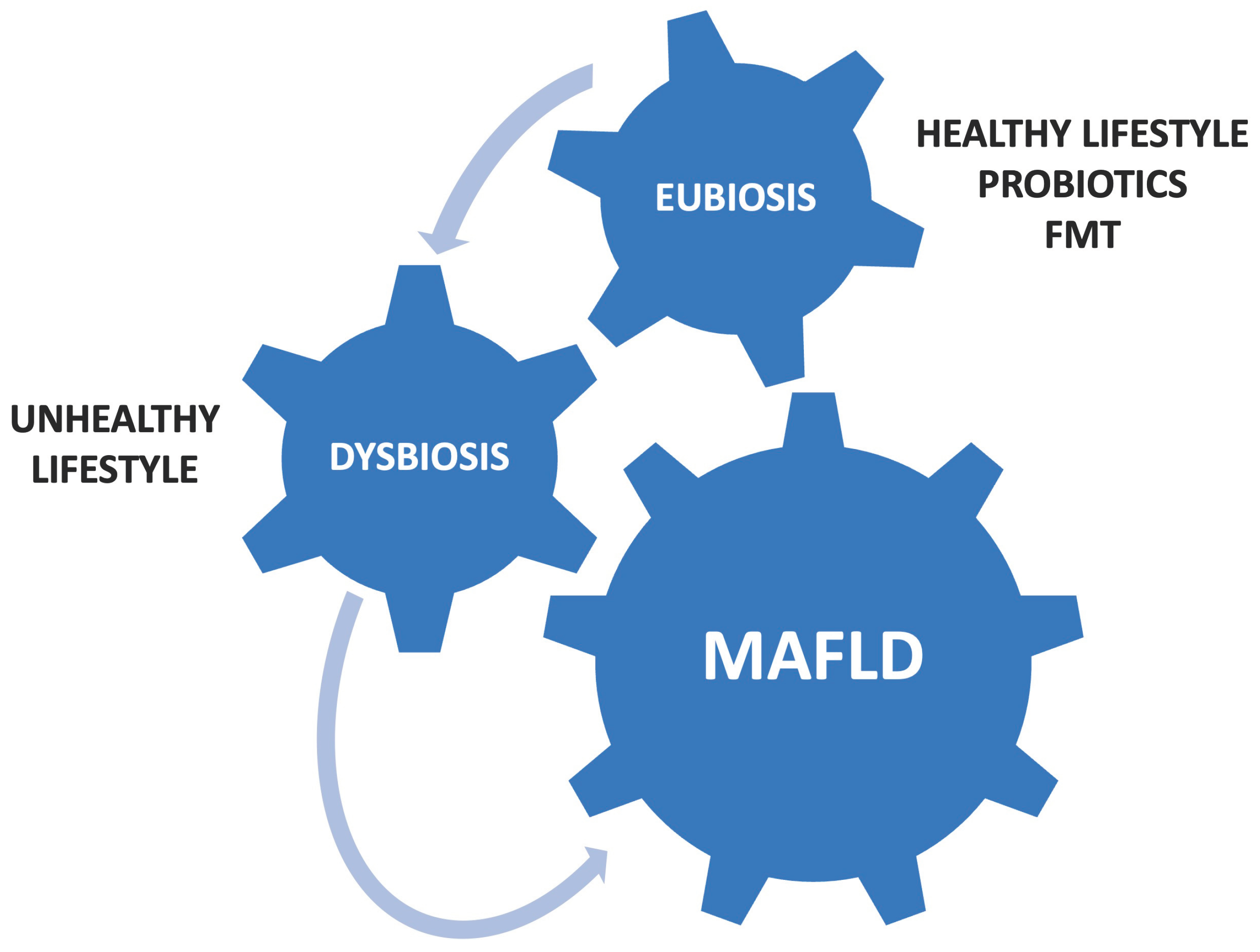
2. Gut Dysbiosis and MAFLD
3. Dietary Regimens in MAFLD
4. Use of Probiotics in MAFLD
5. FMT in MAFLD Patients
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perazzo, H.; Pacheco, A.G.; Griep, R.H.; Gracindo, R.; Goulart, A.C.; da Fonseca, M.D. Changing from NAFLD through MAFLD to MASLD: Similar prevalence and risk factors in a large Brazilian cohort. J Hepatol 2023, 80, e72–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.L.; Ng, C.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Chan, K.E.; Tan, D.J.; Lim, W.H.; Yang, J.D.; Tan, E.; Muthiah, M.D. Global incidence and prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol 2023, 29, S32–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): a systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.; Ekstedt, M.; Wong, G.L.; Hagström, H. Changing epidemiology, global trends and implications for outcomes of NAFLD. J Hepatol 2023, 79, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Spagnuolo, R.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Scarpellini, E.; Boccuto, L.; Luzza, F. Ultrasound Prevalence and Clinical Features of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Real-Life Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina 2023, 59, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Scarpellini, E.; Pellicano, R.; Fagoonee, S.; Larussa, T.; Luzza, F. Mediterranean diet and probiotics supplementation to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Minerva Med 2020, 111, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Scarpellini, E.; Colica, C.; Boccuto, L.; Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Aiello, V.; Romano, B.; De Lorenzo, A.; Izzo, A.A.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Obesity: A Role for Probiotics. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J Hepatol 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carding, S.; Verbeke, K.; Vipond, D.T.; Corfe, B.M.; Owen, L.J. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota in disease. Microb Ecol Health Dis 2015, 26, 26191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Vigliotti, C.; Witjes, J.; Le, P.; Holleboom, A.G.; Verheij, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020, 17, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasirwan, C.O.M.; Muradi, A.; Hasan, I.; Simadibrata, M.; Rinaldi, I. Correlation of gut Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio with fibrosis and steatosis stratified by body mass index in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biosci Microbiota Food Health 2021, 40, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasirwan, C.O.M.; Lesmana, C.R.A.; Hasan, I.; Sulaiman, A.S.; Gani, R.A. The role of gut microbiota in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: pathways of mechanisms. Biosci Microbiota Food Health, 2019, 38, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.; Rivera, L.; Furness, J.B.; Angus, P.W. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in NAFLD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016, 13, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Scarpellini, E.; Boccuto, L.; Spagnuolo, R.; Tilocca, B.; Roncada, P.; Luzza, F. Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Gut Microbiota: From Fatty Liver to Dysmetabolic Syndrome. Medicina 2023, 59, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Milic, N.; Di Renzo, L.; Preveden, T.; Medić-Stojanoska, M.; De Lorenzo, A. Metabolic aspects of adult patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2016, 22, 7006–7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Luzza, F. Mediterranean diet and NAFLD: where are we now? Minerva Endocrinol (Torino) 2021, 46, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Procopio, A.C.; Paravati, M.R.; Costa, G.; Milić, N.; Alcaro, S.; Luzza, F. Mediterranean Diet: The Beneficial Effects of Lycopene in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Greco, M.; Milic, N.; Accattato, F.; Foti, D.; Gulletta, E.; Luzza, F. Effect of Mediterranean Diet and Antioxidant Formulation in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelli, C.; Tarocchi, M.; Abenavoli, L.; Di Renzo, L.; Galli, A.; De Lorenzo, A. Effect of a counseling-supported treatment with the Mediterranean diet and physical activity on the severity of the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017, 23, 3150–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamah, S.; Amin, A.; Al-Kassir, A.L.; Chuang, J.; Covasa, M. Dietary Fat Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Impact on Regulatory Pathways Controlling Food Intake. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Milic, N.; Luzza, F.; Boccuto, L.; De Lorenzo, A. Polyphenols Treatment in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J Transl Int Med 2017, 30, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Ge, X.; Lu, J.; Xu, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q.; Song, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, C. Diet and Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Cirrhosis, and Liver Cancer: A Large Prospective Cohort Study in UK Biobank. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelusi, S.; Valenti, L. Building Mass to Prevent non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease? Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 2019, 8, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Boccuto, L.; Federico, A.; Dallio, M.; Loguercio, C.; Di Renzo, L.; De Lorenzo, A. Diet and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Mediterranean Way. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2019, 16, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Heimbach, J.T.; Pot, B.; Tancredi, D.J.; Lenoir-Wijnkoop, I.; Lähteenmäki-Uutela, A.; Gueimonde, M.; Bañares, S. Health claims substantiation for probiotic and prebiotic products. Gut Microbes 2011, 2, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Guevarra, R.B.; Kim, Y.T.; Kwon, J.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, J.H. Role of Probiotics in Human Gut Microbiome-Associated Diseases. J Microbiol Biotechnol 2019, 29, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Shi, M.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Zeng, R. Effects of probiotics on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a review of human clinical trials. Front Nutr 2023, 2023 10, 1155306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobyliak, N.; Abenavoli, L.; Mykhalchyshyn, G.; Kononenko, L.; Boccuto, L.; Kyriienko, D.; Dynnyk, O. A multi-strain probiotic reduces the fatty liver index, cytokines and aminotransferase levels in NAFLD patients: evidence from a randomized clinical trial. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 2018, 27, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.B.; Jun, D.W.; Kang, B.K.; Lim, J.H.; Lim, S.; Chung, M.J. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of a multispecies probiotic mixture in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep 2019, 5, 9–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aller, R.; De Luis, D.A.; Izaola, O.; Conde, R.; Gonzalez Sagrado, M.; Primo, D.; De La Fuente, B.; Gonzalez, J. Effect of a probiotic on liver aminotransferases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients: a double blind randomized clinical trial. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2011, 15, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamad Nor, M.H.; Ayob, N.; Mokhtar, N.M.; Raja Ali, R.A.; Tan, G.C.; Wong, Z.; Shafiee, N.H.; Wong, Y.P.; Mustangin, M.; Nawawi, K.N.M. The Effect of Probiotics (MCP® BCMC® Strains) on Hepatic Steatosis, Small Intestinal Mucosal Immune Function, and Intestinal Barrier in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Lin, H.; Huang, J.; Watkins, P.A.; Moser, A.B.; Desimone, C.; Song, X.Y.; Diehl, A.M. Probiotics and antibodies to TNF inhibit inflammatory activity and improve nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2003, 37, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzhalii, E.; Virchenko, O.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Beregova, T.; Stremmel, W. Treatment efficacy of a probiotic preparation for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A pilot trial. J Dig Dis 2017, 18, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindigni, S.M.; Surawicz, C.M. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2017, 46, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.W.; Kuo, C.H.; Kuo, F.C.; Wang, Y.K.; Hsu, W.H.; Yu, F.J.; Hu, H.M.; Hsu, P.I.; Wang, J.Y.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation: Review and update. J Formos Med Assoc 2019, 118, S23–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegretti, J.R.; Mullish, B.H.; Kelly, C.; Fischer, M. The evolution of the use of faecal microbiota transplantation and emerging therapeutic indications. Lancet 2019, 394, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Barrio, M.; Lavín, L.; Santos-Laso, Á.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Odriozola, A.; Rodriguez-Duque, J.C.; Rivas, C.; Iruzubieta, P.; Crespo, J. Faecal Microbiota Transplantation, Paving the Way to Treat Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakotonirina, A.; Galperine, T.; Allémann, E. Fecal microbiota transplantation: a review on current formulations in Clostridioides difficile infection and future outlooks. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2022, 22, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weingarden, A.R.; Vaughn, B.P. Intestinal microbiota, fecal microbiota transplantation, and inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basson, A.R.; Zhou, Y.; Seo, B.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A.; Cominelli, F. Autologous fecal microbiota transplantation for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Transl Res 2020, 226, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinott, E.; Youngster, I.; Meir, A.Y.; Tsaban, G.; Kaplan, A.; Zelicha, H.; Rubin, E.; Koren, O.; Shai, I. Autologous fecal microbiota transplantation can retain the metabolic achievements of dietary interventions. Eur J Intern Med 2021, 92, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Deng, Z.; Luo, W.; He, X.; Chen, Y. Effect of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022, 12, 759306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, L.; Rahman, A.; Nair Parvathy, S.; Beaton, M.; Silverman, J.; Qumosani, K.; Hramiak, I.; Hegele, R.; Joy, T.; Meddings, J.; et al. Allogenic Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Improves Abnormal Small Intestinal Permeability: A Randomized Control Trial. Am J Gastroenterol 2020, 115, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.J.; Smits, L.P.; Pekmez, C.T.; Prodan, A.; Meijnikman, A.S.; Troelstra, M.A.; Bouter, K.E.C.; Herrema, H.; Levin, E.; Holleboom, A.G.; et al. Donor fecal microbiota transplantation alters gut microbiota and metabolites in obese individuals with steatohepatitis. Hepatol Commun 2020, 4, 1578–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Maurizi, V.; Rinninella, E.; Tack, J.; Di Berardino, A.; Santori, P.; Rasetti, C.; Procopio, A.C.; Boccuto, L.; Scarpellini, E. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in NAFLD Treatment. Medicina 2022, 58, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, A.; Ismaiel, A.; Procopio, A.C.; Luzza, F.; Abenavoli, L.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Noninvasive biochemical markers and surrogate scores in evaluating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Minerva Med 2022, 113, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Scarlata, G.G.; Scarpellini, E.; Procopio, A.C.; Ponziani, F.R.; Boccuto, L.; Cetkovic, N.; Luzza, F. Therapeutic success in primary biliary cholangitis and gut microbiota: a safe highway? Minerva Gastroenterol (Torino) 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.J.; Gou, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Song, X.J.; Zhang, L. Role of intestinal flora in primary sclerosing cholangitis and its potential therapeutic value. World J Gastroenterol 2022, 28, 6213–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Giubilei, L.; Procopio, A.C.; Spagnuolo, R.; Luzza, F.; Boccuto, L.; Scarpellini, E. Gut Microbiota in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Complex Interplay. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study design | Study groups | Intervention | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Randomized controlled trial [19] | Overweight-MAFLD group (n=50) | Moderately hypocaloric MD or MD diet and antioxidant supplementation or no treatment for six months | Significant improvement of anthropometric parameters, lipid profile, liver steatosis, and liver stiffness in group treated with MD diet and antioxidant supplementation |
| Uncontrolled trial [20] | MAFLD group (n=46) | MD and moderate physical activity for 6 months | Significant improvement of BMI, waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, AST, ALT, GGT, HDL, LDL, TG, serum glucose, total-cholesterol/HDL ratio, LDL/HDL ratio, TG/HDL ratio, HOMA-IR, FLI, Kotronen index, and fatty liver score |
| Prospective cohort study [23] | MAFLD group (n=3527) vs. liver cirrhosis group (n=1643) vs. liver cancer group (n=669) | WD or Prudent diet | WD was significantly associated with increased risk of chronic liver diseases; Prudent diet was significantly associated with a lower risk of liver cirrhosis |
| Study design | Study groups | Intervention | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Randomized controlled trial [29] | MAFLD group (n=59) | Administration of Symbiter or placebo for 8 weeks | FLI significantly decreased in probiotic group Probiotics significantly reduced the level of serum AST and GGT No significant difference in liver stiffness among groups |
| Randomized controlled trial [30] | Obese-MAFLD group (n=69) | Administration of probiotics or placebo for 12 weeks | Significant decrease of the intrahepatic fat fraction and in TG levels in the probiotics group |
| Randomized controlled trial [31] | MAFLD group (n=28) | One tablet per day with 500 millions of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus or with one placebo tablet (120 mg of starch) for 3 months | ALT, AST and GGT levels significant decreased in group treated with probiotics No significant changes in anthropometric parameters |
| Randomized controlled trial [32] | MAFLD group (n=46) | Administration of probiotics or placebo for 6 months | Significant improvement of intestinal permeability with a reduction in fat absorption after probiotics treatment |
| Study design | Study groups | Intervention | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Randomized controlled trial [43] | FMT group (n=47) vs. non-FMT group (n=28) vs. healthy controls (n=10) | Administration of probiotics in non-FMT group Administration of 200 ml of bacterial cocktail from healthy donors for 3 days in FMT-group |
Promotion of gut eubiosis after FMT Better efficacy of FMT among lean-MAFLD patients than obese-MAFLD patients |
| Randomized controlled trial [44] | Allogenic FMT group (n=15) vs. autologous FMT group (n=6) | Allogenic or autologous FMT | Allogenic FMT significantly improved intestinal permeability better than autologous FMT No significant statistical differences in insulin resistance and hepatic proton density fat fraction between autologous and allogeneic FMT |
| Randomized controlled trial [45] | Autologous FMT (n=11) vs. allogenic FMT (n=10) | Allogenic or autologous FMT | Allogeneic FMT significantly improved necro-inflammatory histology and bio-humoral liver profile |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





