Submitted:
12 March 2024
Posted:
12 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodological Framework
2.1. Data Compilation
2.2. Selection of Research Database
2.3. Choice of Science Mapping Tool: Navigating the Scientific Landscape
3. Findings and Discussions
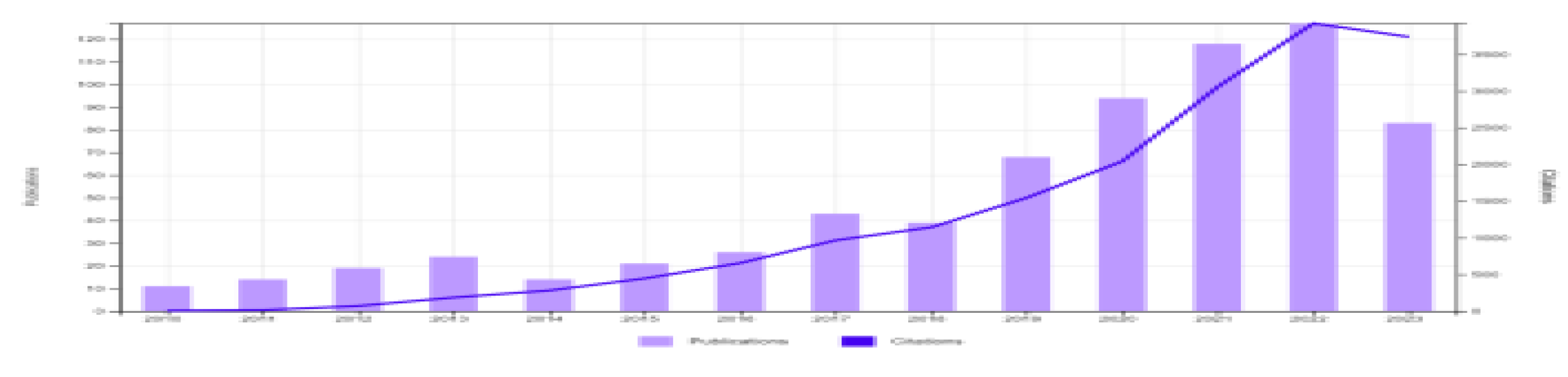
3.1. Output Analysis and Growth Trends
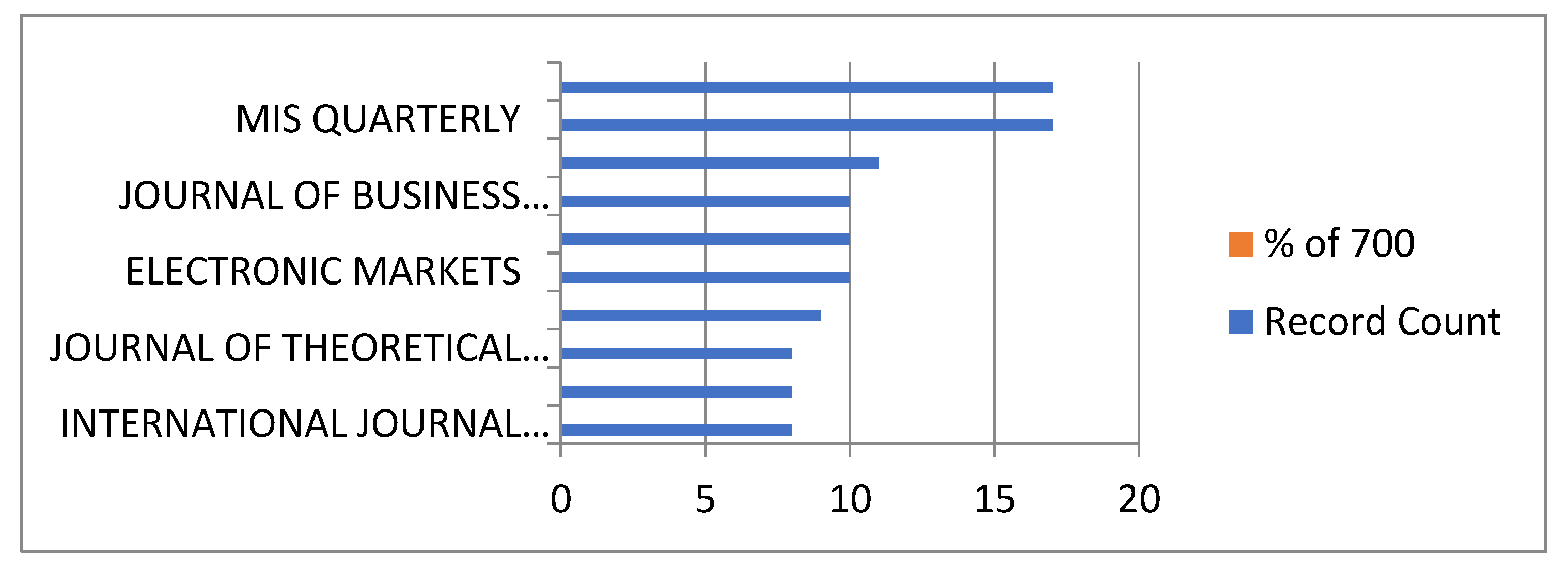
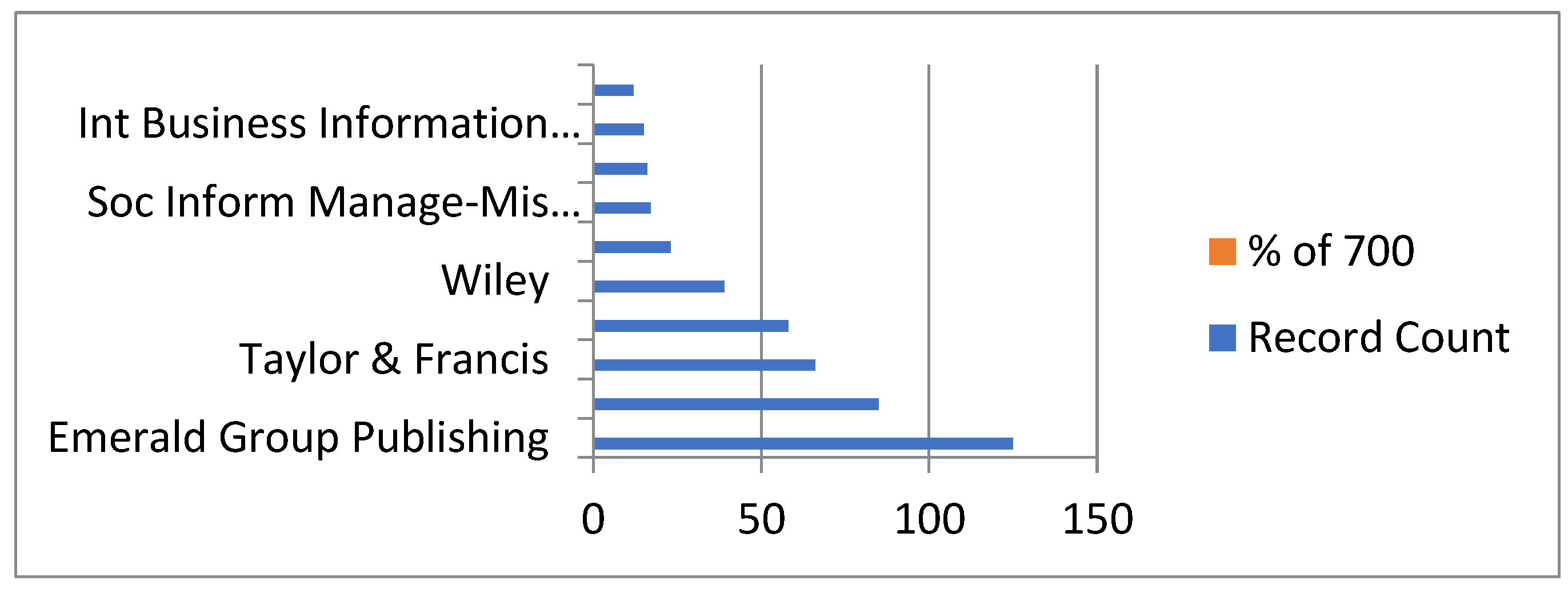
3.2. Key Contributions from Top Publications, Journals, and Publishers
3.3. Bibliometric Mapping: Unveiling Patterns and Trends
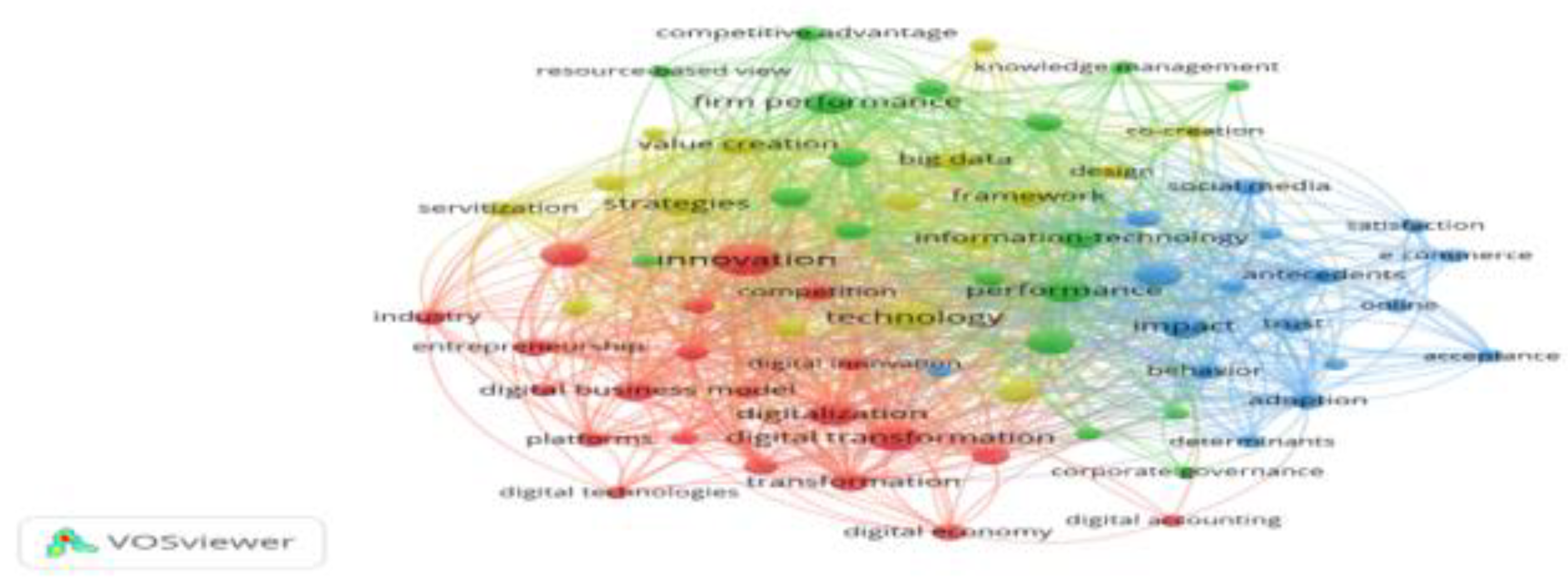
3.3.1. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
3.3.2. Investigating Trends in Auditing and Digital Accounting Research within the Digital Business Environment
| Keywords | Links | Total Links Strength | Occurrences | Cluster Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Innovation | 66 | 524 | 122 | Red |
| Technology | 64 | 372 | 78 | Yellow |
| Digital Transformation | 60 | 263 | 69 | Red |
| Firm Performance | 58 | 259 | 61 | Green |
| Digitalization | 63 | 225 | 59 | Red |
| Strategies | 60 | 277 | 58 | Yellow |
| Management | 62 | 240 | 57 | Green |
| Model | 60 | 226 | 57 | Blue |
| Information-Technology | 45 | 180 | 42 | Green |
| Digital Business | 47 | 132 | 41 | Yellow |
3.3.3. Bibliographic Coupling of Authors
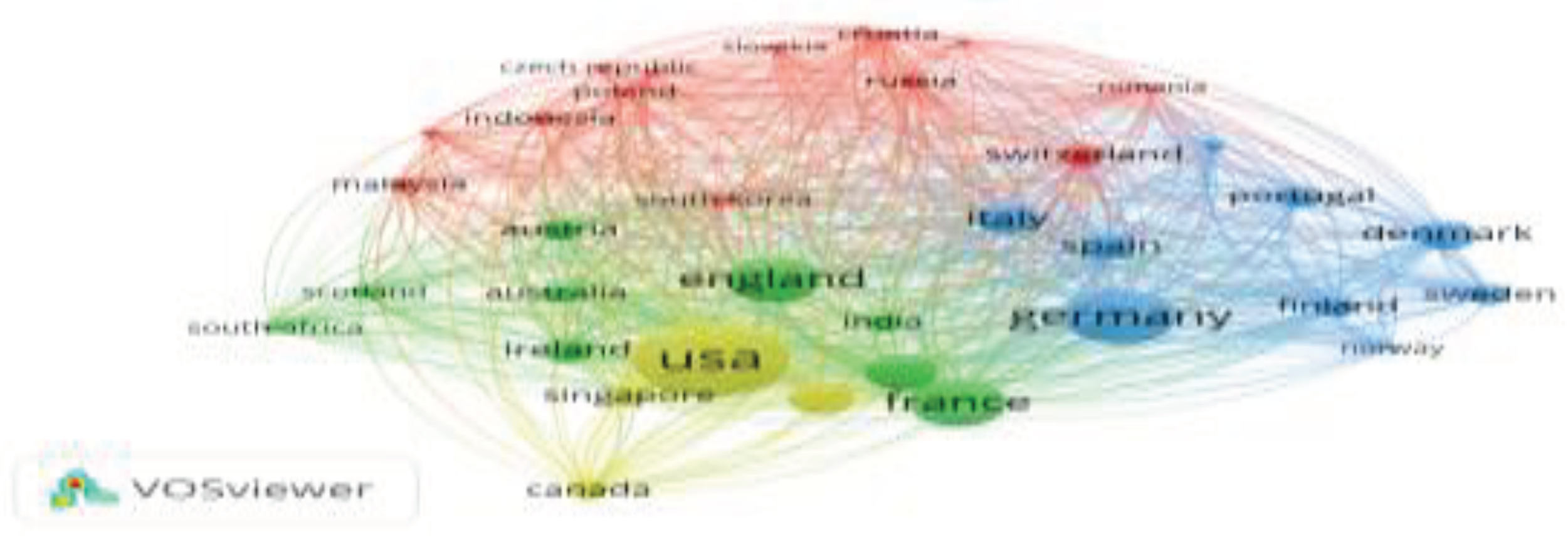
3.3.4. Bibliographic Coupling of Nations
4. Conclusion
4.1. Theoretical Consequences
4.2. Practical Implications
4.3. Future Directions
References
- 1. Aboelmaged, M., Alhashmi, S. M., Hashem, G., Battour, M., Ahmad, I., & Ali, I. (2023). Unveiling the path to sustainability: two decades of knowledge management in sustainable supply chain – a scientometric analysis and visualization journey. Benchmarking: Int. J. 2023. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Abu Huson, Y.; Sierra-García, L.; Garcia-Benau, M.A. A bibliometric review of information technology, artificial intelligence, and blockchain on auditing. Total. Qual. Manag. Bus. Excel. 2023, 35, 91–113,. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Haroon, H.; Ornos, E.D.B.; Malibary, H.; Hussain, A.; Baig, M.; Santali, E.Y.; Alestad, J.H.; Muzaheed, M.; Rabaan, A.A.; et al. Bibliometric analysis and network visualization mapping of global research in Q fever vaccine. F1000Research 2022, 11, 364,. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.A.; Albaz, M.M.; Metwaly, A.Z. The Role of Artificial Intelligence Technologies in Improving the Performance of the Management Accountant considering the Egyptian State’s Trend Toward Digital Transformation. World Res. Bus. Adm. J. 2022, 2, 167–182. [CrossRef]
- al Hbabi, K.N.; Alomari, Z.S. The Impact of Knowledge Management Processes on Organizational Innovation. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2020, 10, 949–967,. [CrossRef]
- Allioui, H.; Mourdi, Y. Exploring the Full Potentials of IoT for Better Financial Growth and Stability: A Comprehensive Survey. Sensors 2023, 23, 8015,. [CrossRef]
- Al-Qudah, L.A.; Qudah, H.A.; Abu Hamour, A.M.; Abu Huson, Y.; Al Qudah, M.Z. The effects of COVID-19 on conditional accounting conservatism in developing countries: evidence from Jordan. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2022, 9, 2152156. [CrossRef]
- Amankwah-Amoah, J.; Khan, Z.; Wood, G.; Knight, G. COVID-19 and digitalization: The great acceleration. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 136, 602–611,. [CrossRef]
- Awan, U.; Shamim, S.; Khan, Z.; Zia, N.U.; Shariq, S.M.; Khan, M.N. Big data analytics capability and decision-making: The role of data-driven insight on circular economy performance. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 168, 120766,. [CrossRef]
- Bhimani, A.; Willcocks, L. 10. Bhimani, A.; Willcocks, L. Digitisation,‘Big Data’and the transformation of accounting information. Accounting and business research 2014, 44, 469–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkle, C.; Pendlebury, D.A.; Schnell, J.; Adams, J. Web of Science as a data source for research on scientific and scholarly activity. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2020, 1, 363–376,. [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, F.; Matt, D.T.; Bonfanti, A.; De Longhi, A.; Pedrini, G.; Orzes, G. Digital transformation challenges: strategies emerging from a multi-stakeholder approach. TQM J. 2020, 32, 697–724,. [CrossRef]
- Brynjolfsson, E.; Hitt, L.M. Beyond Computation: Information Technology, Organizational Transformation and Business Performance. J. Econ. Perspect. 2000, 14, 23–48,. [CrossRef]
- Busulwa, R.; Evans, N. Digital transformation in accounting; Routledge.
- Chawla, R.N.; Goyal, P. Emerging trends in digital transformation: a bibliometric analysis. Benchmarking: Int. J. 2021, 29, 1069–1112,. [CrossRef]
- De Bellis, N. Bibliometrics and citation analysis: from the science citation index to cybermetrics; scarecrow press.
- Dewett, T.; Jones, G.R. The role of information technology in the organization: a review, model, and assessment. Journal of management 2001, 27, 313–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Ismagilova, E.; Hughes, D.L.; Carlson, J.; Filieri, R.; Jacobson, J.; Jain, V.; Karjaluoto, H.; Kefi, H.; Krishen, A.S.; et al. Setting the future of digital and social media marketing research: Perspectives and research propositions. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 59, 102168,. [CrossRef]
- Gahegan, M. Four barriers to the development of effective exploratory visualisation tools for the geosciences. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1999, 13, 289–309,. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.J.A.; da Silva, A.C.F.; Ferreira, C.G. The Future of Accounting: How Will Digital Transformation Impact the Sector? Informatics 2022, 9, 19,. [CrossRef]
- Goyal, K.; Kumar, S. Financial literacy: A systematic review and bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2021, 45, 80–105,. [CrossRef]
- Grover, V.; Chiang, R.H.; Liang, T.P.; Zhang, D. Creating Strategic Business Value from Big Data Analytics: A Research Framework. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2018, 35, 388–423,. [CrossRef]
- Gusenbauer, M. Search where you will find most: Comparing the disciplinary coverage of 56 bibliographic databases. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 2683–2745,. [CrossRef]
- Hanelt, A.; Bohnsack, R.; Marz, D.; Marante, C.A. A Systematic review of the literature on digital transformation: insights and implications for strategy and organizational change. J. Manag. Stud. 2021, 58, 1159–1197,. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.R.; Loebbecke, C. Engaging scientometrics in information systems. J. Inf. Technol. 2017, 32, 85–109,. [CrossRef]
- Kastrin, A.; Hristovski, D. Scientometric analysis and knowledge mapping of literature-based discovery (1986–2020). Scientometrics 2021, 126, 1415–1451,. [CrossRef]
- Huson, Y.A.; Almousa, M.; Alqudah, M. Exploring Corporate Tax Avoidance: Effects on Comprehensive Budget Income–a Practical Analys. Effects on Comprehensive Budget Income–a Practical Analysis: Alqudah, M., 2024. Exploring Corporate Tax Avoidance, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, V. Neurostrategy: A scientometric analysis of marriage between neuroscience and strategic management. J. Bus. Res. 2024, 170,. [CrossRef]
- Kehinde, T.; Chan, F.T.; Chung, S. Scientometric review and analysis of recent approaches to stock market forecasting: Two decades survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213,. [CrossRef]
- Kokina, J.; Blanchette, S. Early evidence of digital labor in accounting: Innovation with Robotic Process Automation. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2019, 35, 100431,. [CrossRef]
- Lang, V.; Lang, V. Lang, V.; Lang, V. Digitalization and digital transformation. Digital Fluency: Understanding the Basics of Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain Technology, Quantum Computing, and Their Applications for Digital Transformation. 2021, 1-50.
- Liu, L.; Jones, B.F.; Uzzi, B.; Wang, D. Data, measurement and empirical methods in the science of science. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2023, 7, 1046–1058,. [CrossRef]
- Lynn, T.; Rosati, P.; Lejeune, A.; Emeakaroha, V. Lynn, T.; Rosati, P.; Lejeune, A.; Emeakaroha, V. (2017, December). A preliminary review of enterprise serverless cloud computing (function-as-a-service) platforms. In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing Technology and Science (CloudCom) (pp. 162-169). IEEE.
- Manita, R.; Elommal, N.; Baudier, P.; Hikkerova, L. The digital transformation of external audit and its impact on corporate governance. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 150, 119751,. [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, K.C.; Rozario, A.M.; Vasarhelyi, M.A. Moffitt, K.C.; Rozario, A.M.; Vasarhelyi, M.A. Robotic process automation for auditing. Journal of emerging technologies in accounting 2018, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, V. Big data and analytics. Strategic and organisational impacts. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mosteanu, N.R.; Faccia, A. Digital systems and new challenges of financial management–FinTech, XBRL, blockchain and cryptocurrencies. Quality–Access to Success 2020, 21, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Mosweu, O. A framework to authenticate records in a government accounting system in Botswana to support the auditing process; Pretoria: University of South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, D.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Goyal, K. Mapping five decades of international business and management research on India: A bibliometric analysis and future directions. Journal of Business Research 2022, 145, 864–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, A.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, F. How would the COVID-19 pandemic reshape retail real estate and high streets through acceleration of E-commerce and digitalization? J. Urban Manag. 2021, 10, 110–124,. [CrossRef]
- Ogbuke, N.J.; Yusuf, Y.Y.; Dharma, K.; Mercangoz, B.A. Big data supply chain analytics: ethical, privacy and security challenges posed to business, industries and society. Prod. Plan. Control. 2022, 33, 123–137,. [CrossRef]
- Otia, J.E; The SAI's perspective: Bracci, E. Digital transformation and the public sector auditing.
- Pizzi, S.; Venturelli, A.; Variale, M.; Macario, G.P. Assessing the impacts of digital transformation on internal auditing: A bibliometric analysis. Technol. Soc. 2021, 67, 101738,. [CrossRef]
- Rauschnabel, P.A.; Babin, B.J.; Dieck, M.C.T.; Krey, N.; Jung, T. What is augmented reality marketing? Its definition, complexity, and future. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 142, 1140–1150,. [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Lamorena,.J.; Del Barrio-García, S.; Alcántara-Pilar, J.M. A review of three decades of academic research on brand equity: A bibliometric approach using co-word analysis and bibliographic coupling. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 139, 1067–1083,. [CrossRef]
- Roszkowska, P. Fintech in financial reporting and audit for fraud prevention and safeguarding equity investments. J. Account. Organ. Chang. 2021, 17, 164–196,. [CrossRef]
- Saarikko, T.; Westergren, U.H.; Blomquist, T. Digital transformation: Five recommendations for the digitally conscious firm. Bus. Horizons 2020, 63, 825–839,. [CrossRef]
- Saggi, M.K.; Jain, S. A survey towards an integration of big data analytics to big insights for value-creation. Inf. Process. Manag. 2018, 54, 758–790,. [CrossRef]
- Sahut, J.-M.; Iandoli, L.; Teulon, F. The age of digital entrepreneurship. Small Bus. Econ. 2021, 56, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestino, A.; Prete, M.I.; Piper, L.; Guido, G. Internet of Things and Big Data as enablers for business digitalization strategies. Technovation 2020, 98, 102173–102173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, W.; Ndiweni, E.; Boulkeroua, M.; Echchabi, A.; Ndlovu, T. Digital technology disruption on bank business models. International Journal of Business Performance Management 2020, 21, 184–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Lai, K.; Vejvar, M.; Cheng, T.C.E. Data-driven auditing: A predictive modeling approach to fraud detection and classification. J. Corp. Account. Finance 2019, 30, 64–82,. [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, C.R.; Larivière, V. Measuring research: What everyone needs to know. Oxford University Press. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sustacha, I.; Baños-Pino, J.F.; del Valle, E. Research trends in technology in the context of smart destinations: a bibliometric analysis and network visualization. Cuadernos de Gestión 2022, 22, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.-L.; Bui, T.-D.; Lim, M.K.; Fujii, M.; Mishra, U. Assessing data-driven sustainable supply chain management indicators for the textile industry under industrial disruption and ambidexterity. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2022, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turban, E.; Pollard, C.; Wood, G. Information Technology for Management: Driving Digital Transformation to Increase Local and Global Performance, Growth and Sustainability; John Wiley & Sons, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538,. [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1053–1070,. [CrossRef]
- Varadarajan, R.; Welden, R.B.; Arunachalam, S.; Haenlein, M.; Gupta, S. Digital product innovations for the greater good and digital marketing innovations in communications and channels: Evolution, emerging issues, and future research directions. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2022, 39, 482–501,. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wu, X.; Shi, S.; Leung, W.K. The dualistic view of challenge-hindrance technostress in accounting information systems: Technological antecedents and coping responses. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2023, 73,. [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Yue, W.L.; Le Vu, H. Visualization and analysis of mapping knowledge domain of road safety studies. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 118, 131–145,. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Orabi, T.; Al-Hyari, H.S.A.M.; Almomani, H.M.; Ababne, A.; Abu Huson, Y.; Ahmed, E.; Albanna, H. A bibliometric review of job satisfaction and organizational commitment in businesses area literatures. Hum. Syst. Manag. 2023, Preprint, 1–23,. [CrossRef]
- Huson YA, A.; Sierra-García, L.; Garcia-Benau, M.A.; Aljawarneh, N.M. EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION INTO THE INTEGRATION OF CLOUD-BASED ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN AUDITING. PressAcademia Procedia 2024, 18, 113–114. [Google Scholar]
- Albalawee, N.; Huson, Y.; Budair, Q.; Alqmool, T.; Arasheedi, N. Connecting legal compliance and financial integrity: A bibliometric survey of accounting practices in the corporate supply chain. Uncertain Supply Chain Manag. 2024, 12, 893–906,. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





