Submitted:
12 March 2024
Posted:
13 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.1.1. Measure of Correlation of Qubit-Qutrit System
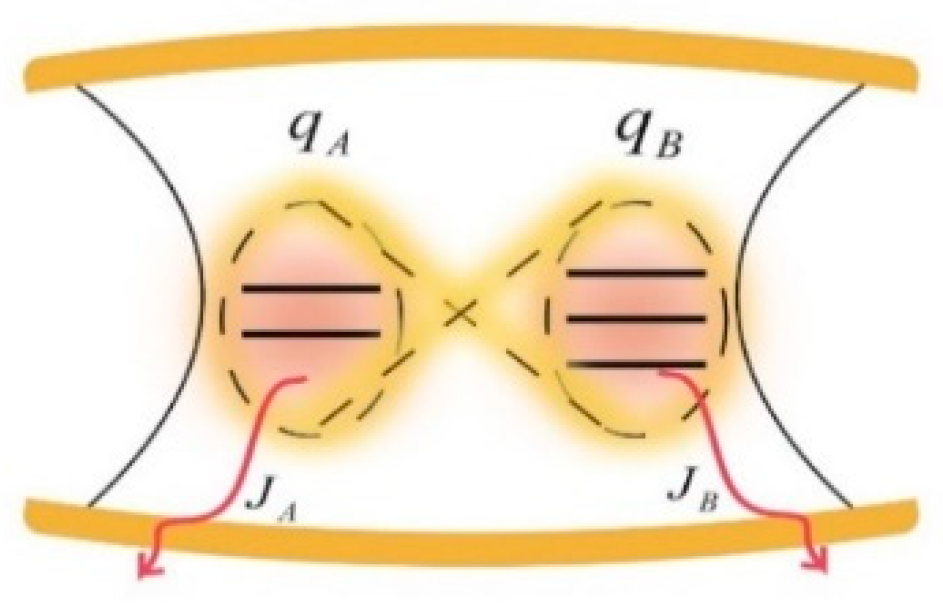
2.2. The Physical Model
3. Noises Used
3.1. Static Noise
3.2. Random Telegraph Noise
3.3. Ornstein-Uhenbeck
4. Numerical Results
4.1. Static Noise
- Density matrix
- Different environment/common environment
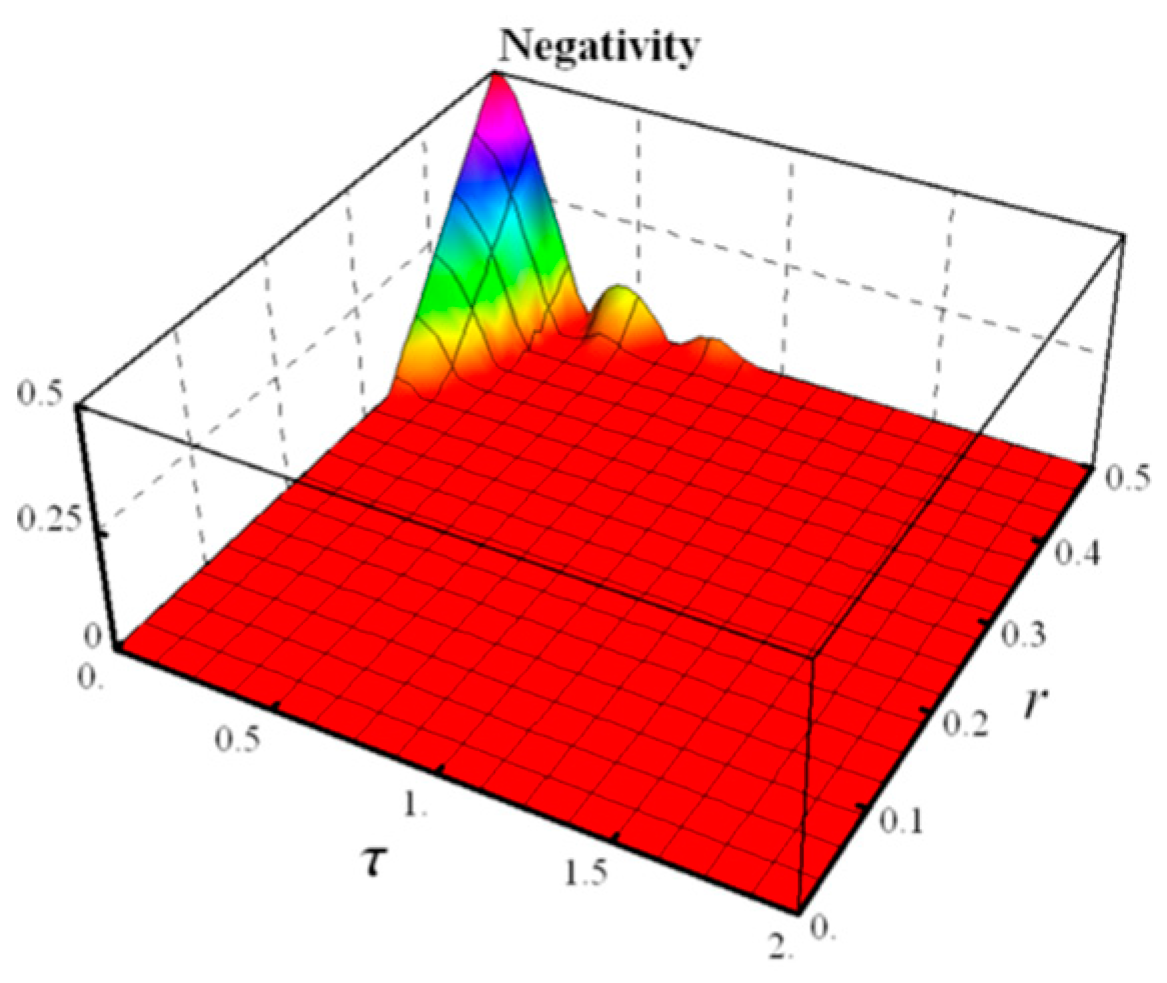
4.2. Random Telegraph Noise
- Density matrix
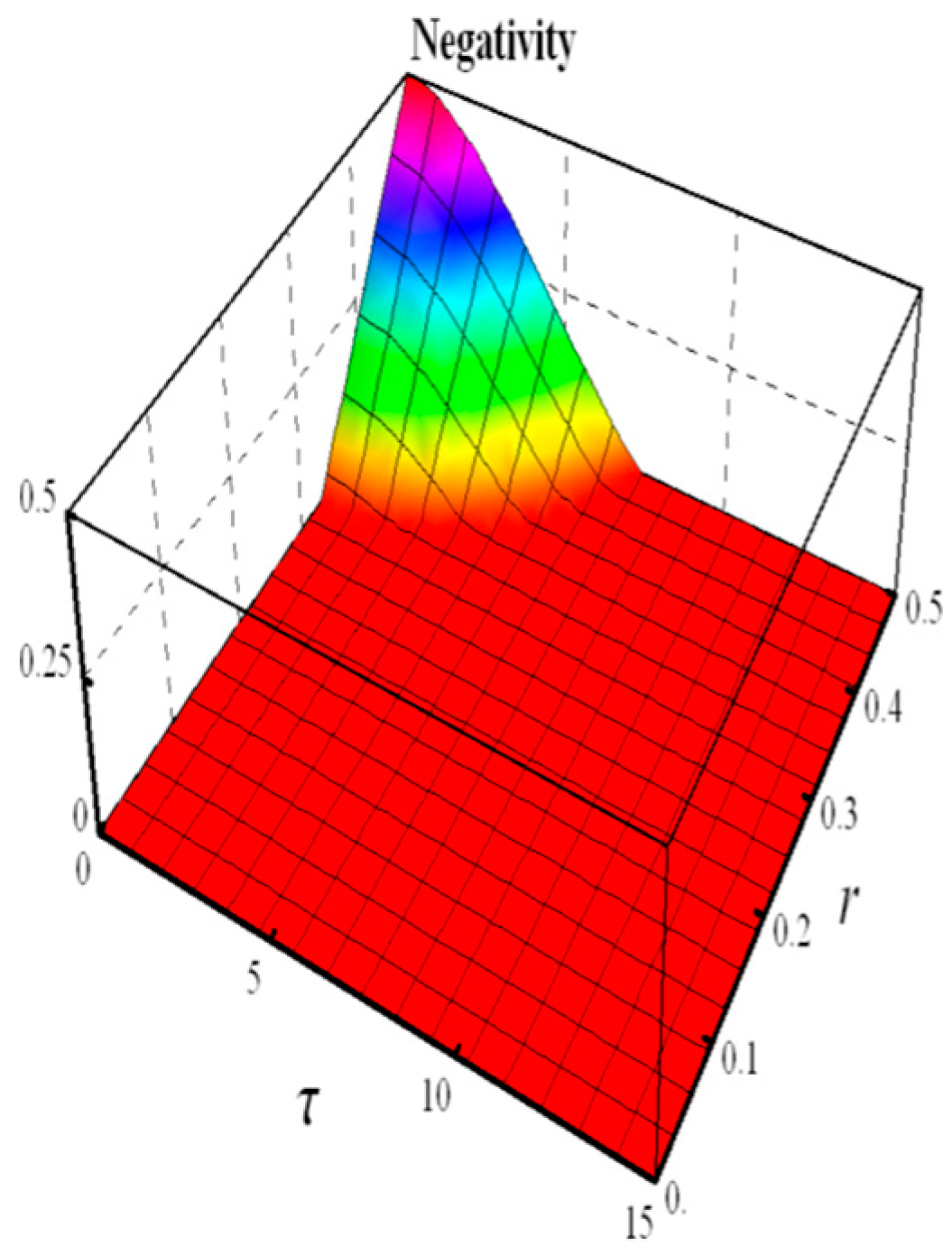
- Negativity
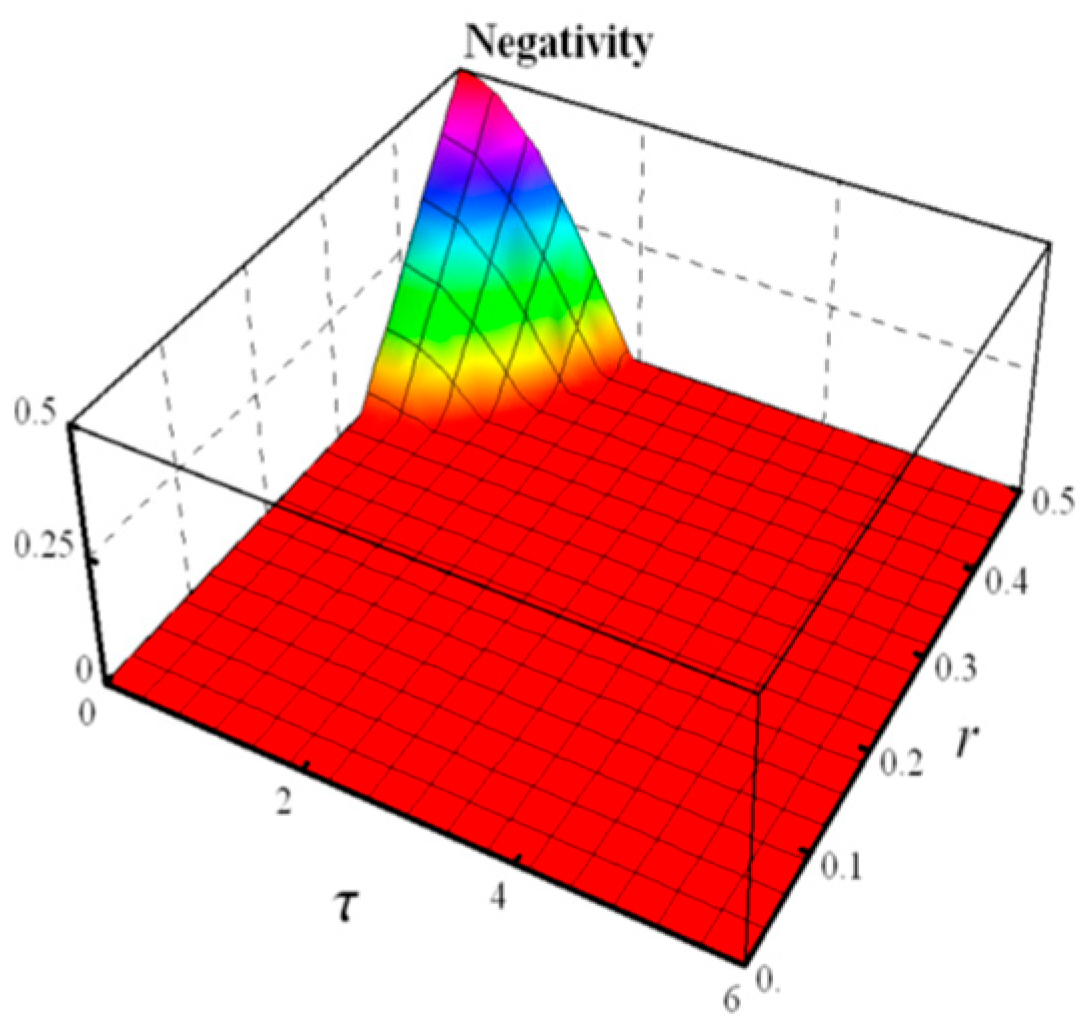
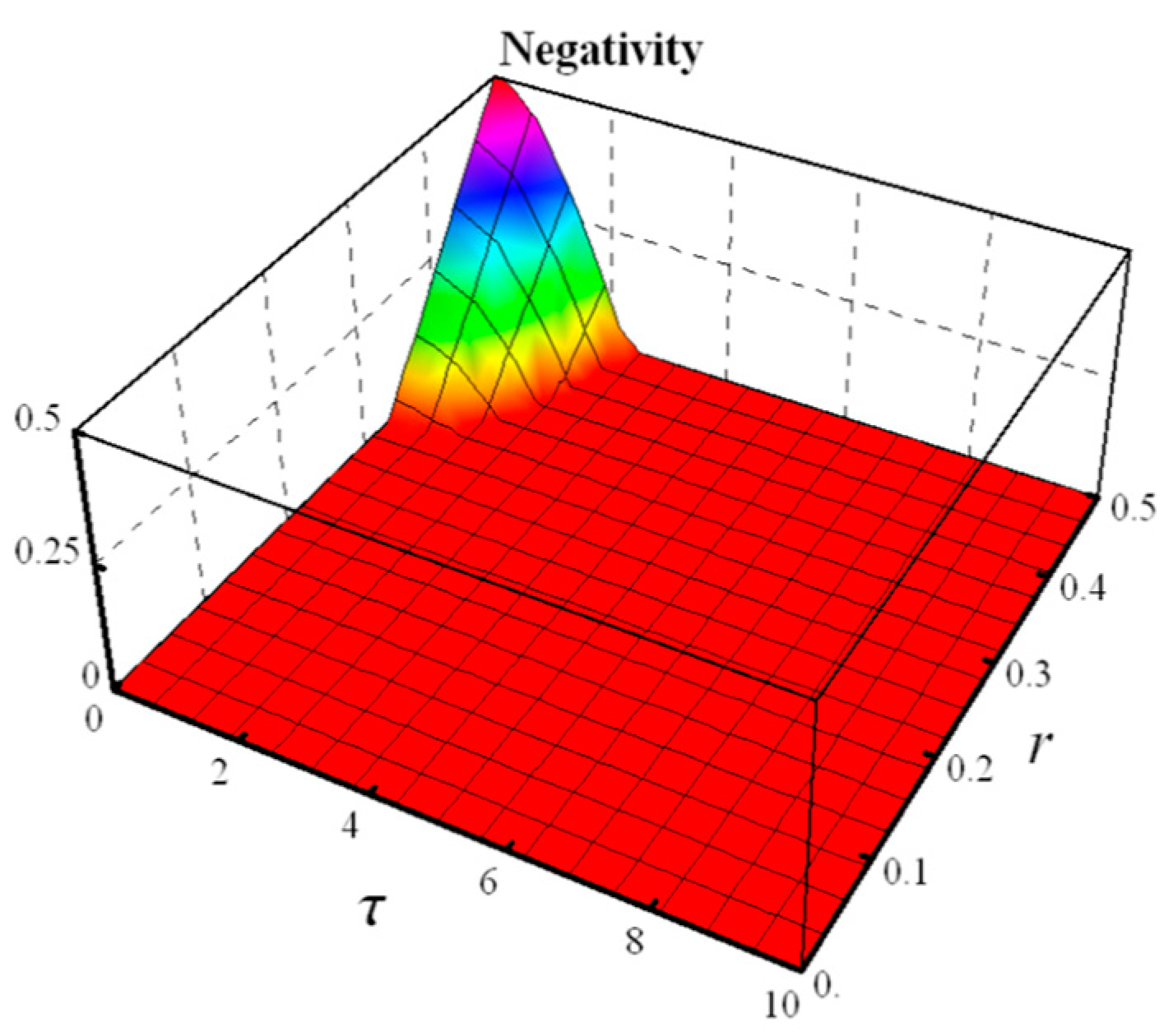
4.3. ORNSTEIN-UHENBECK
- Density matrix
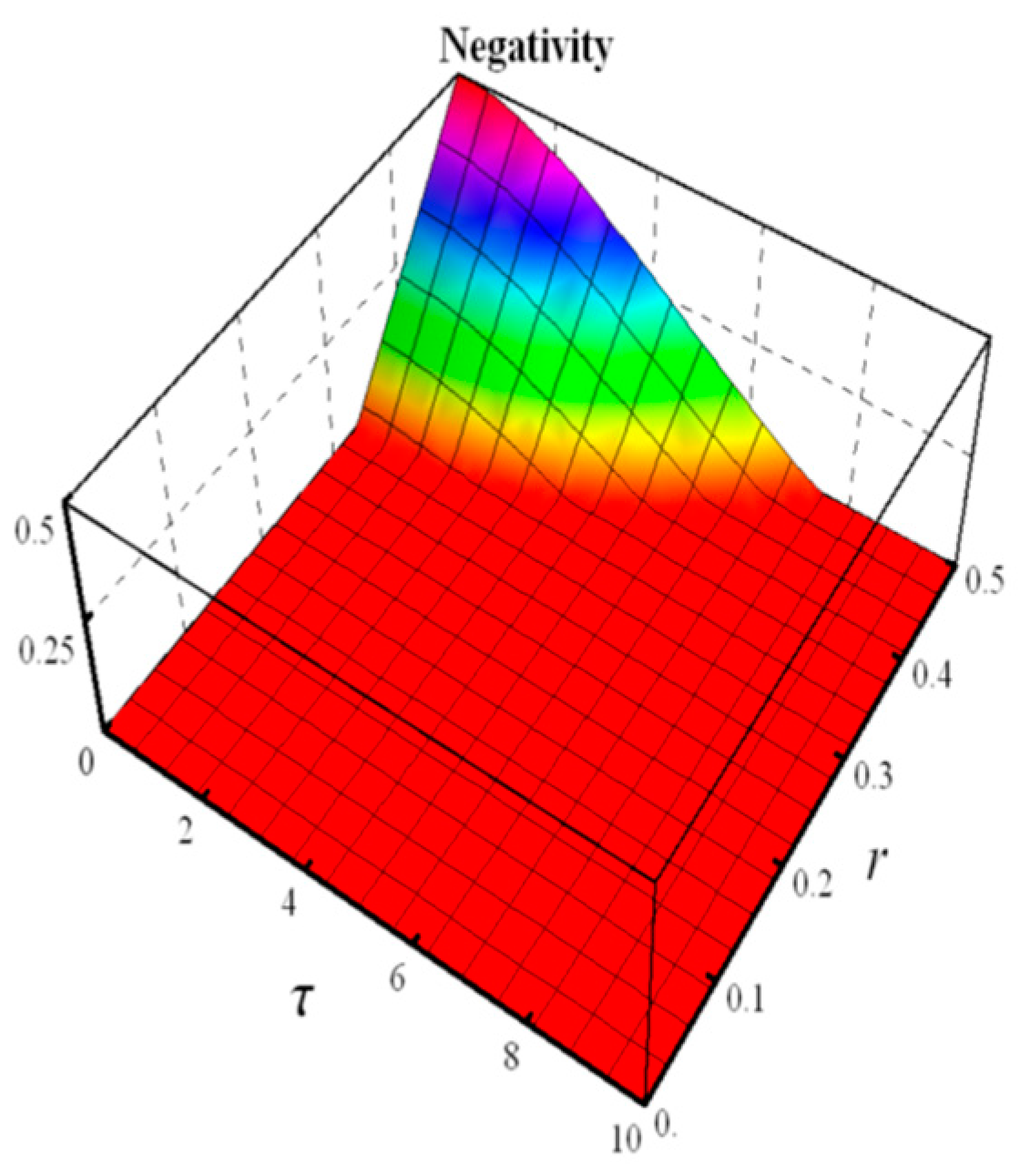
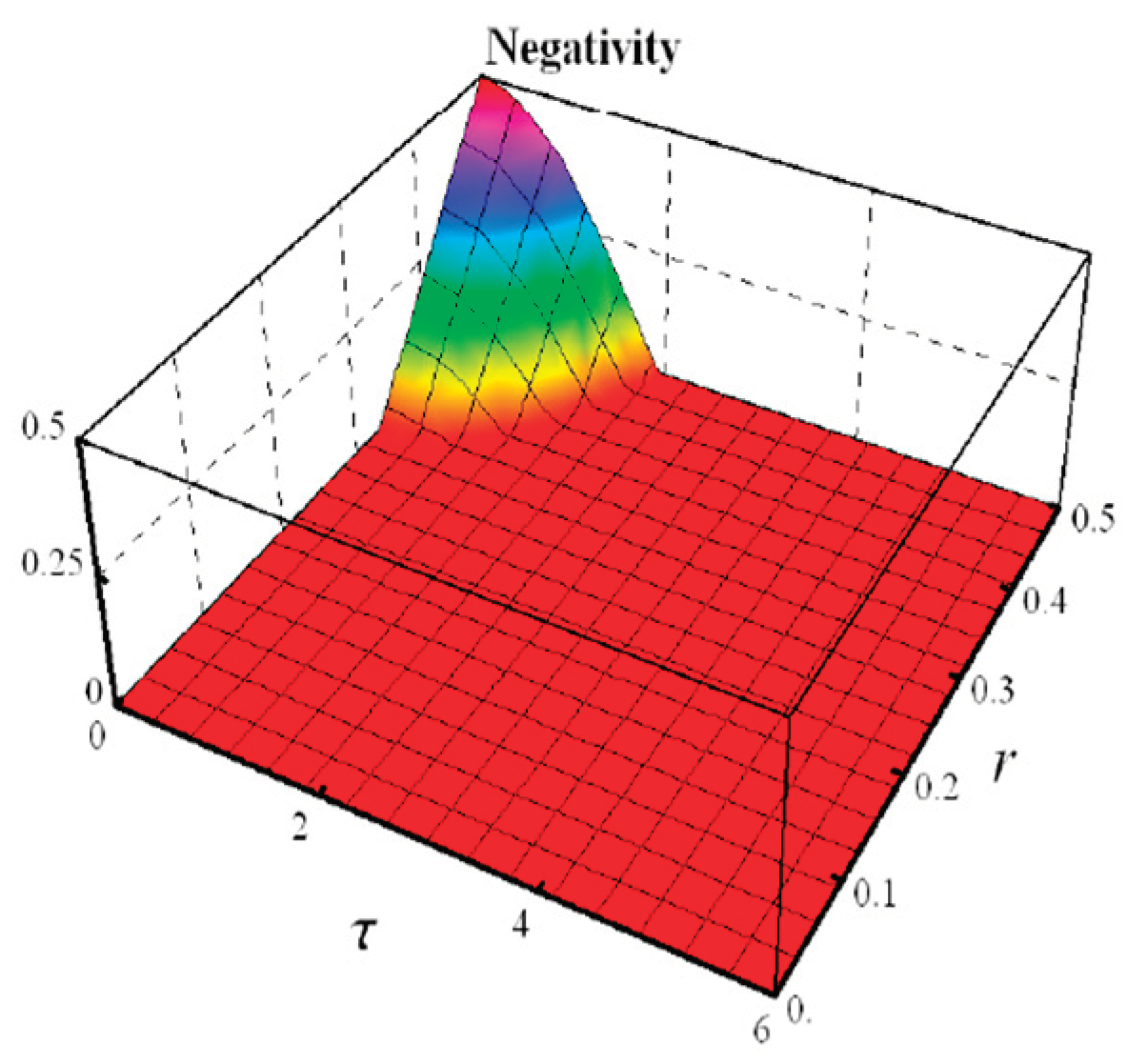
- Negativity
5. Analytical Results
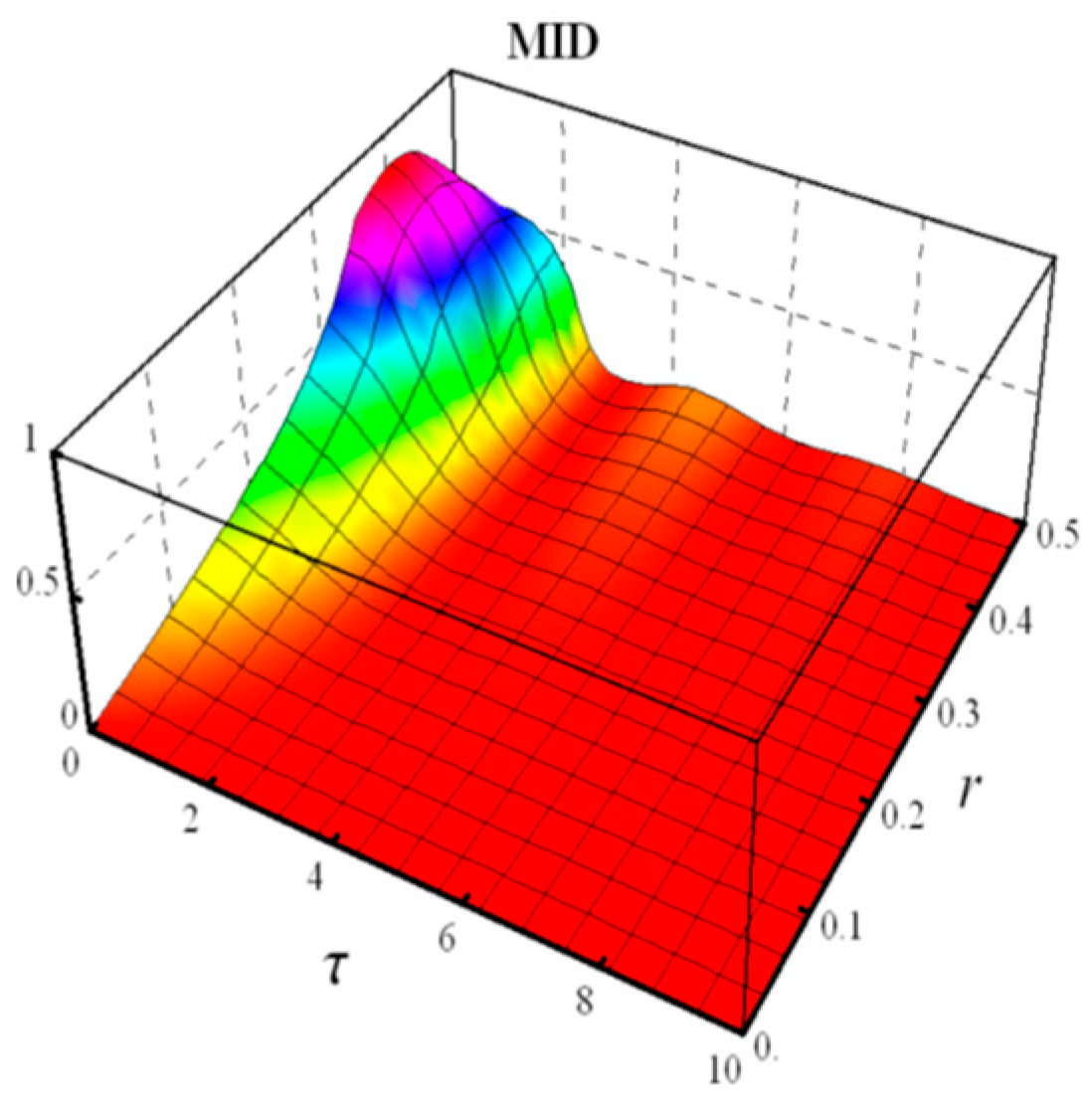
5.1. Static Noise
- Negativity
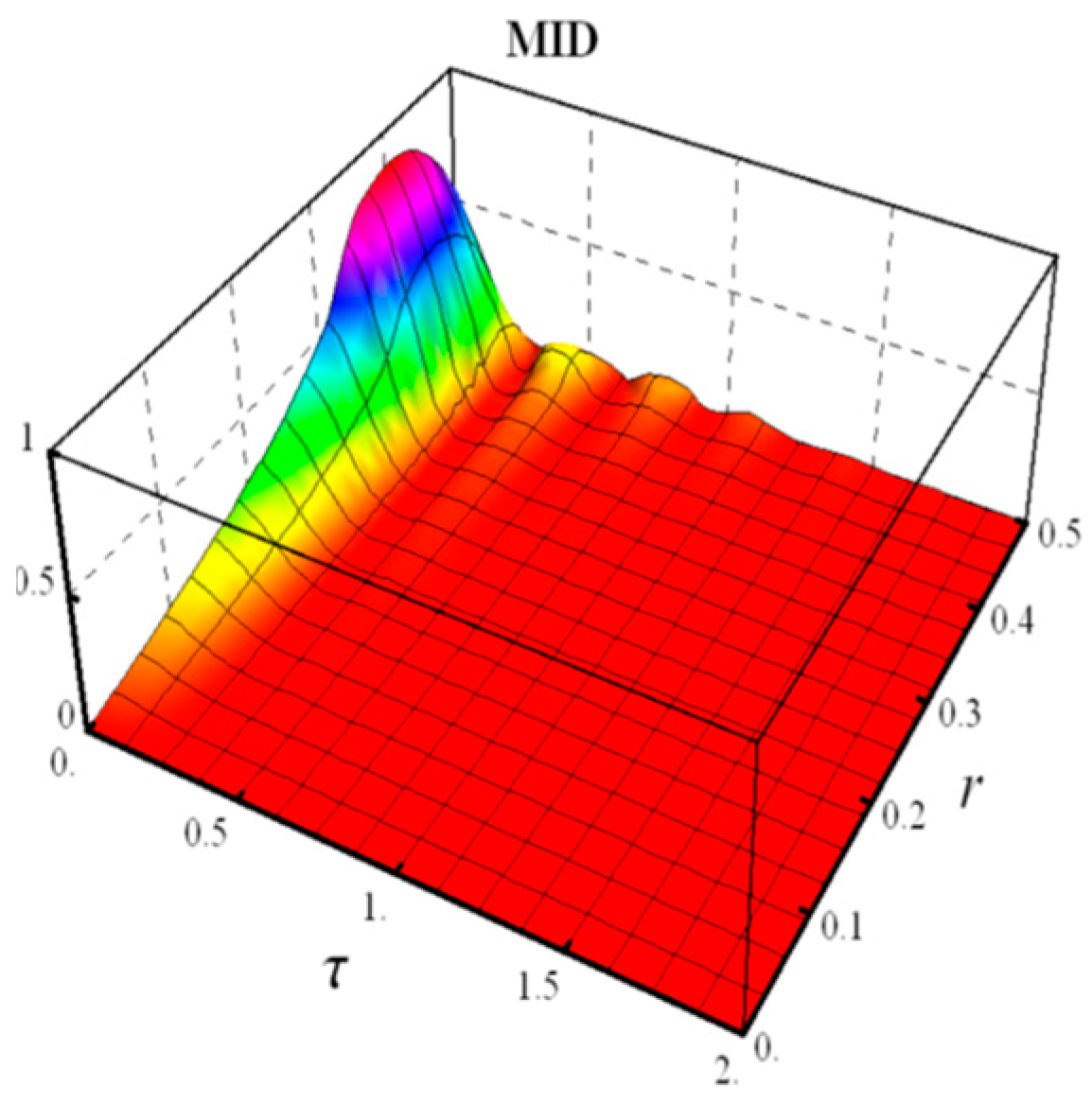
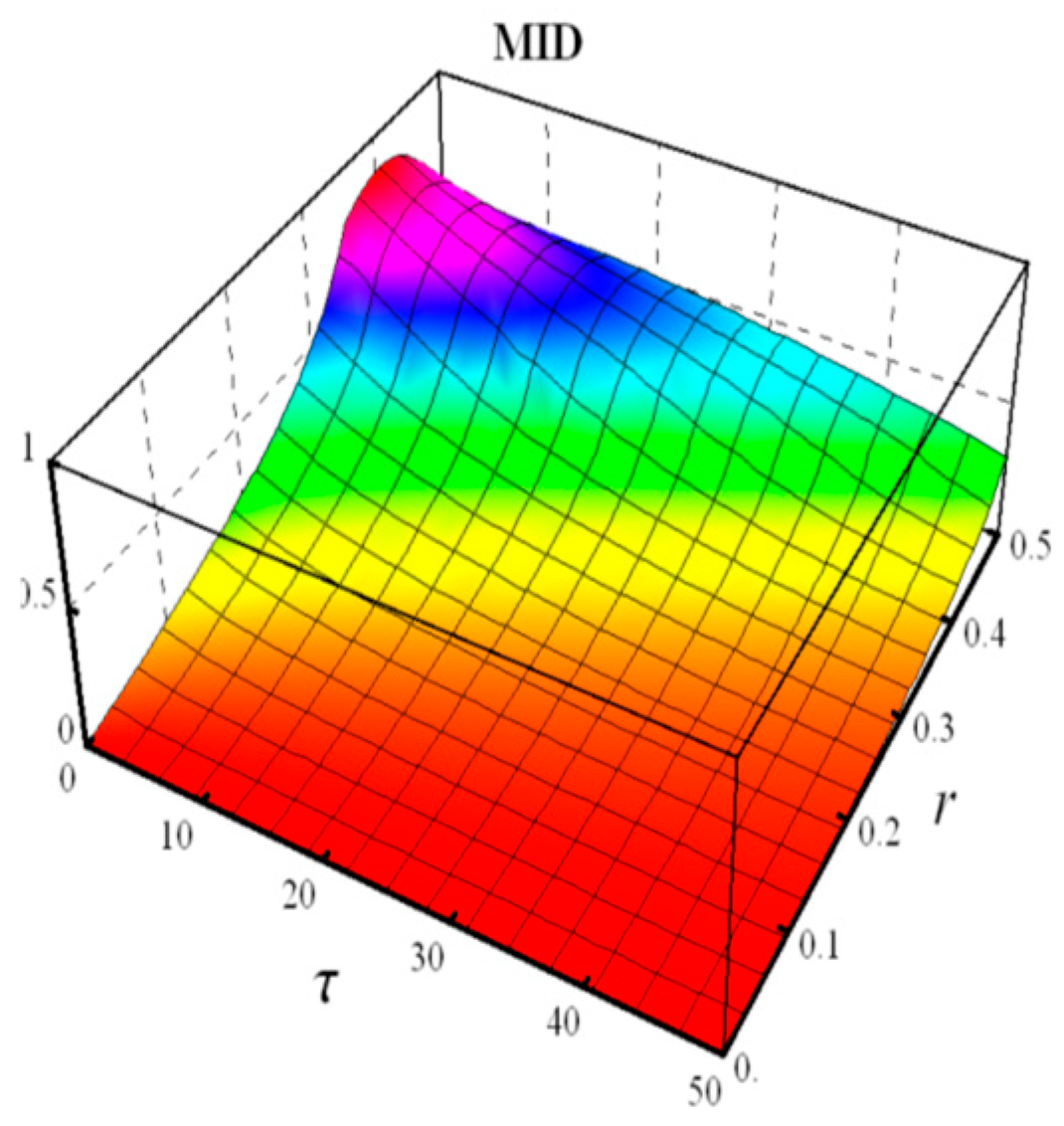
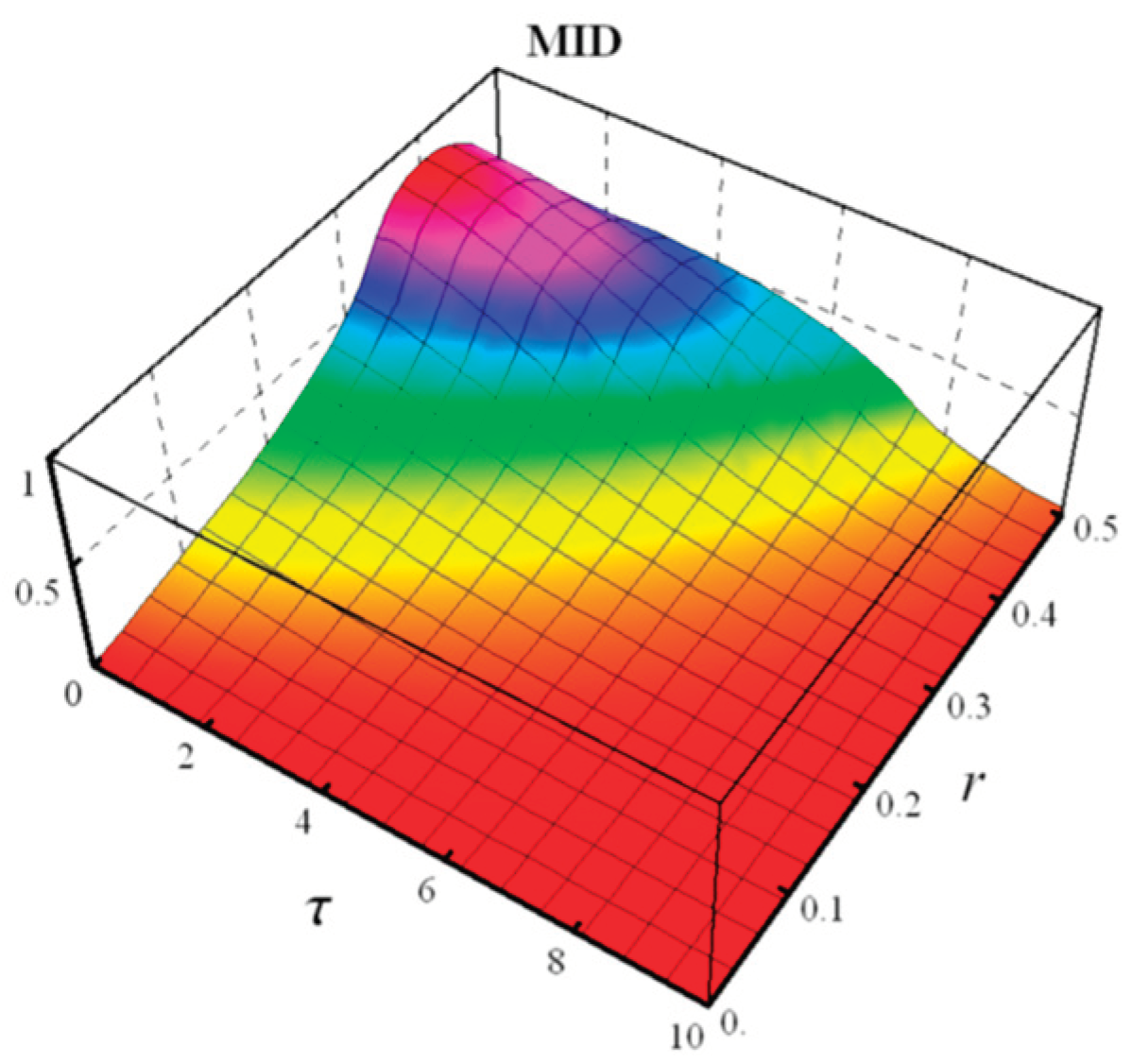
- Measured-Induced Disturbance (MID)
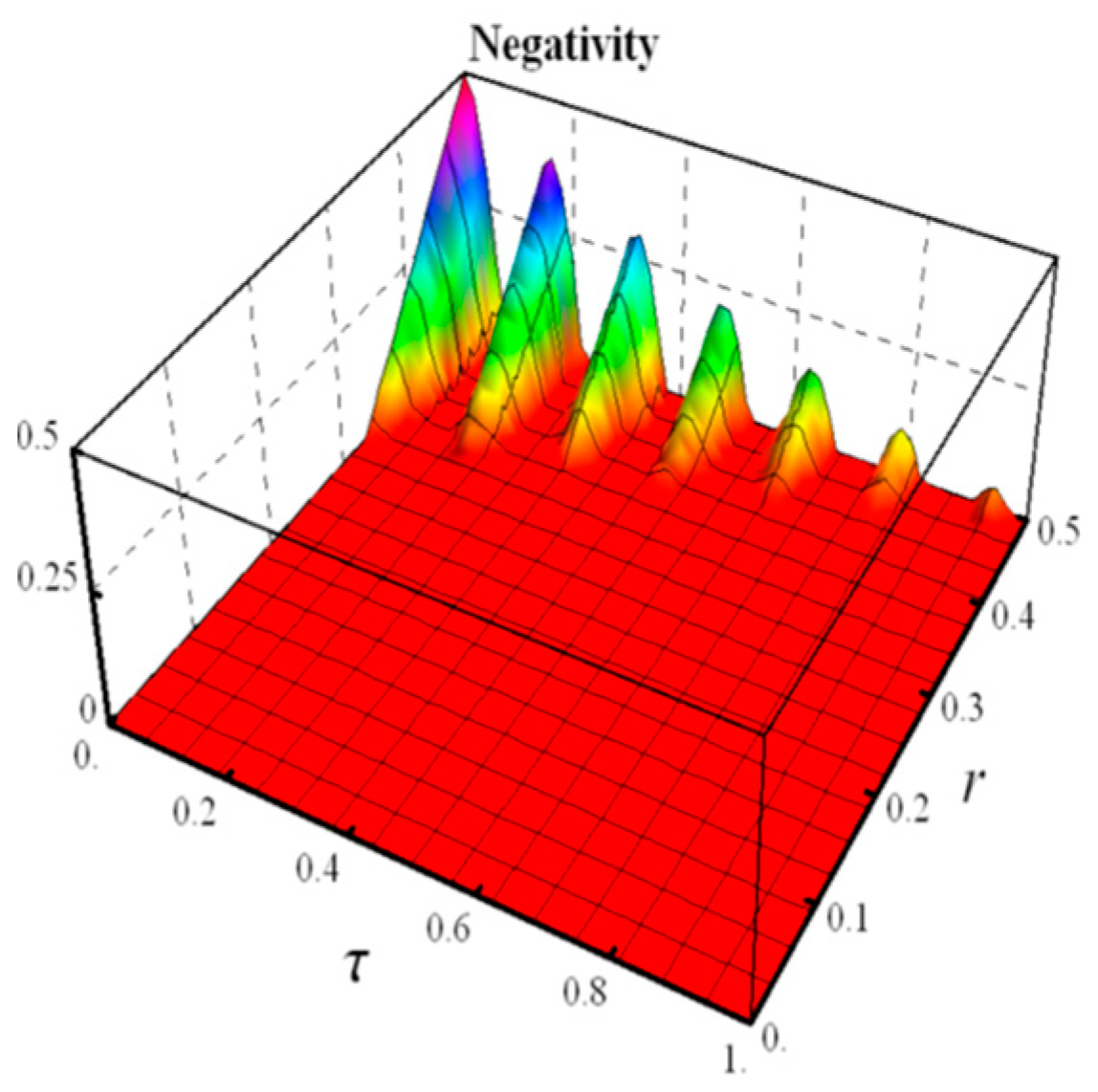
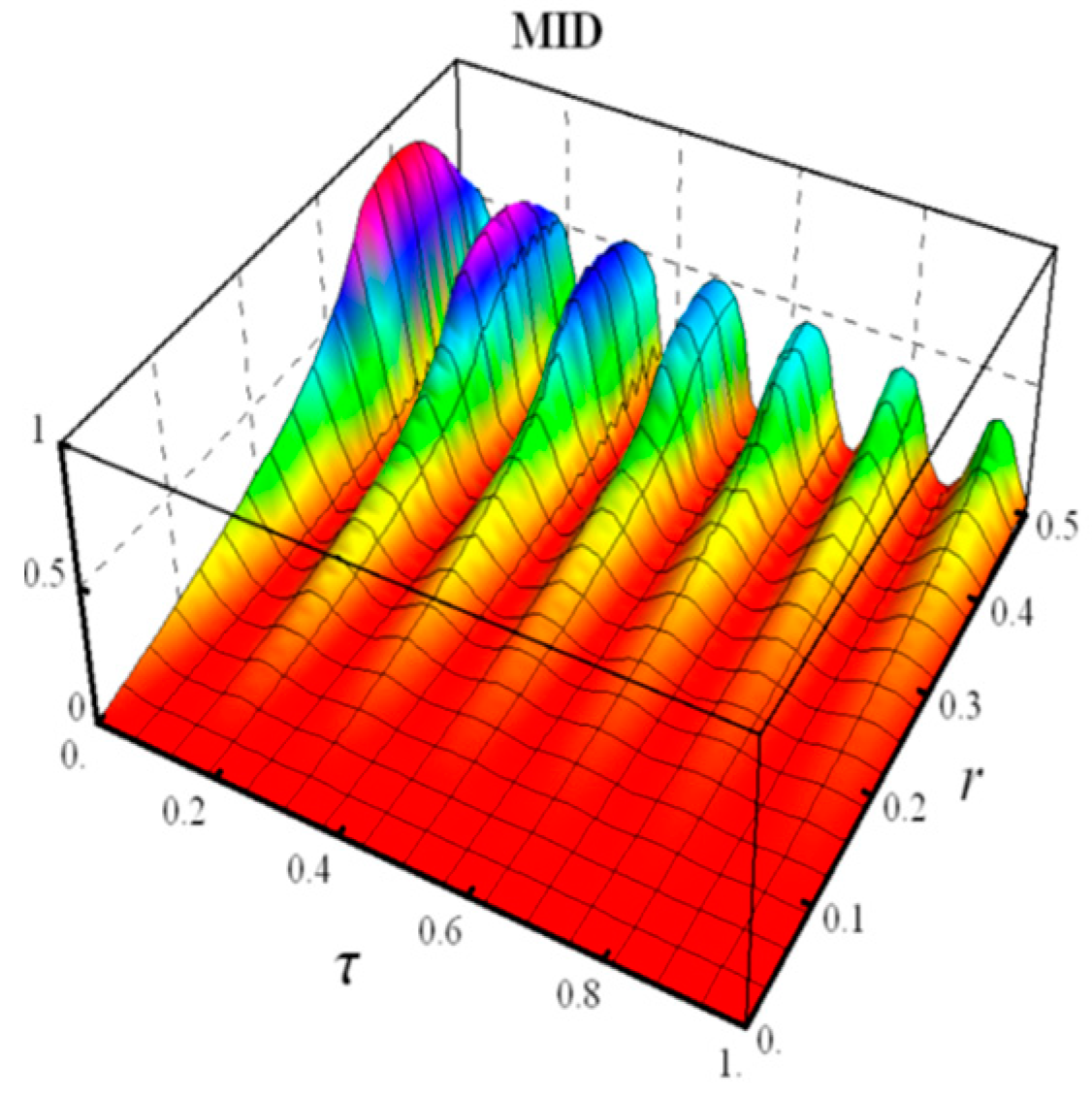
5.2. Random Telegraph Noise
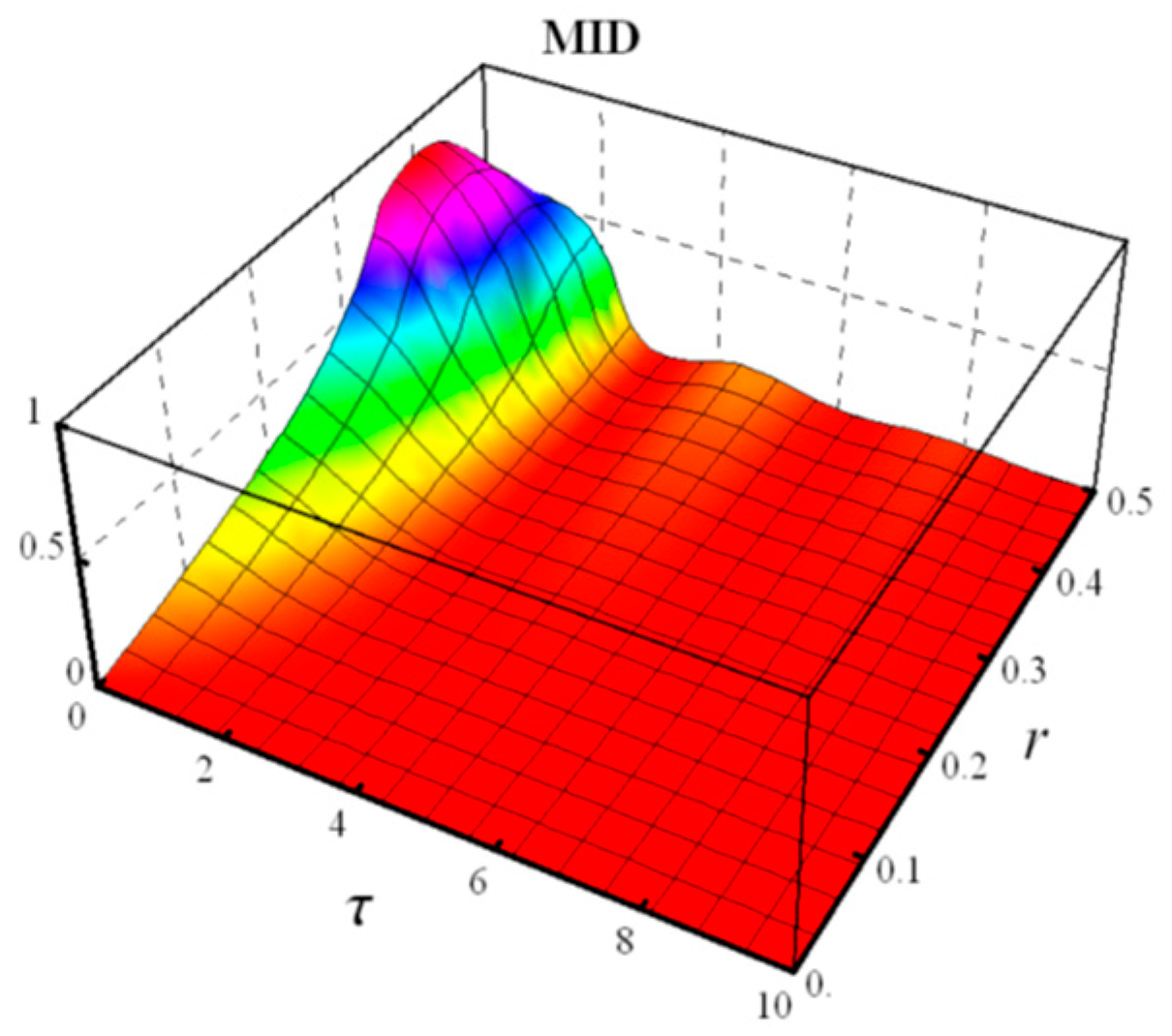
- Negativity and MID
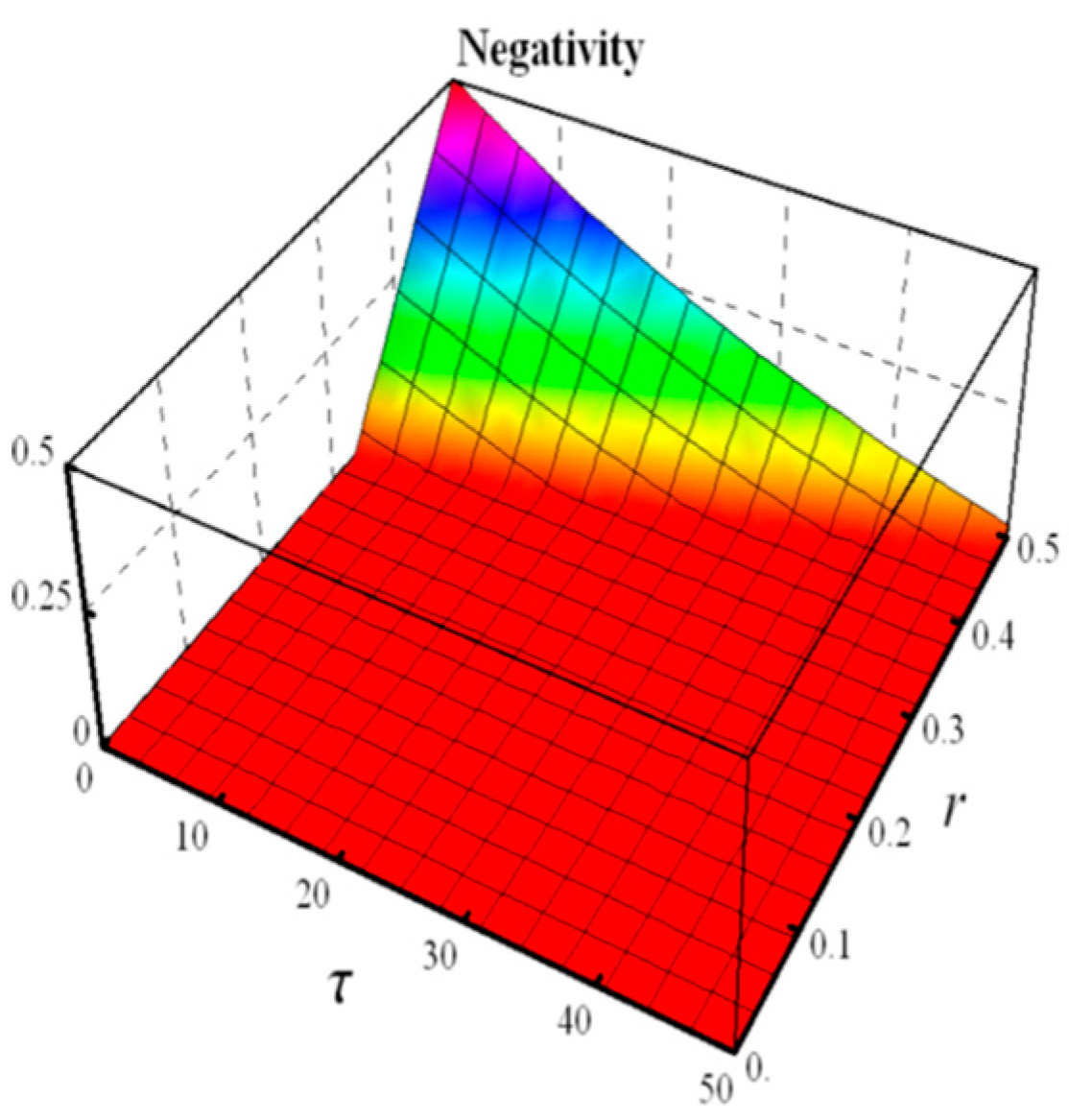
5.3. Ornstein-Uhlenbeck (OU)
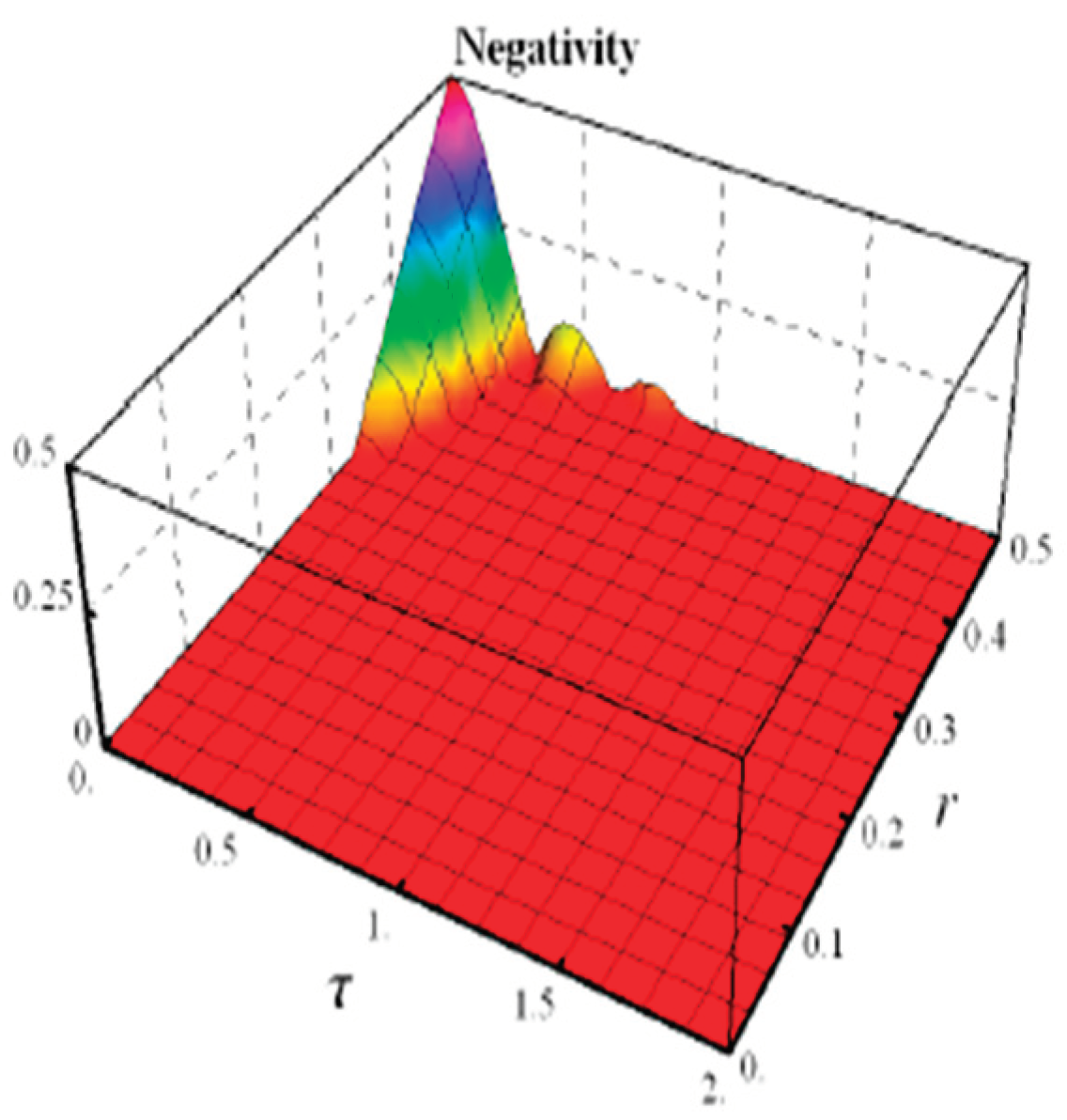
- Negativity
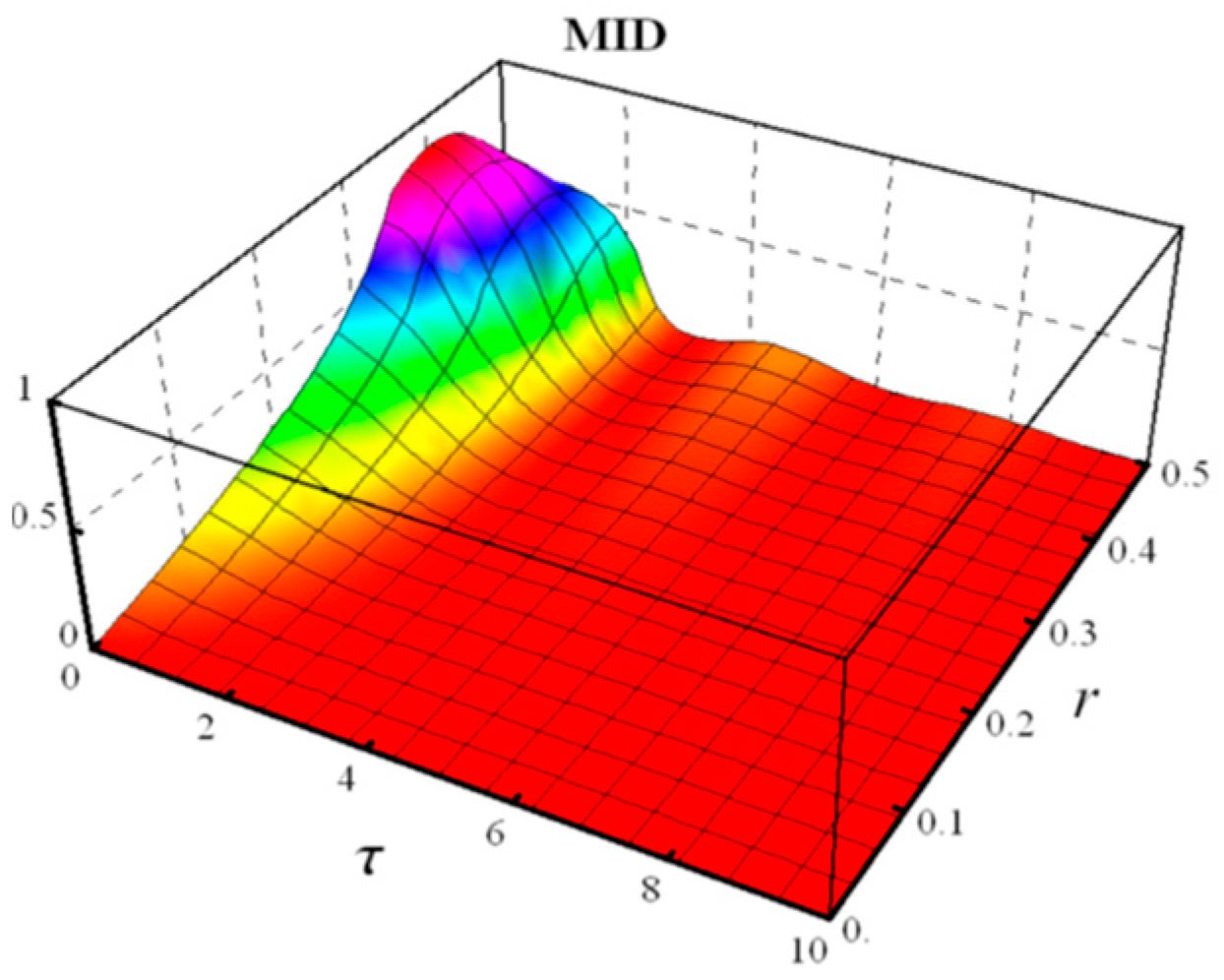
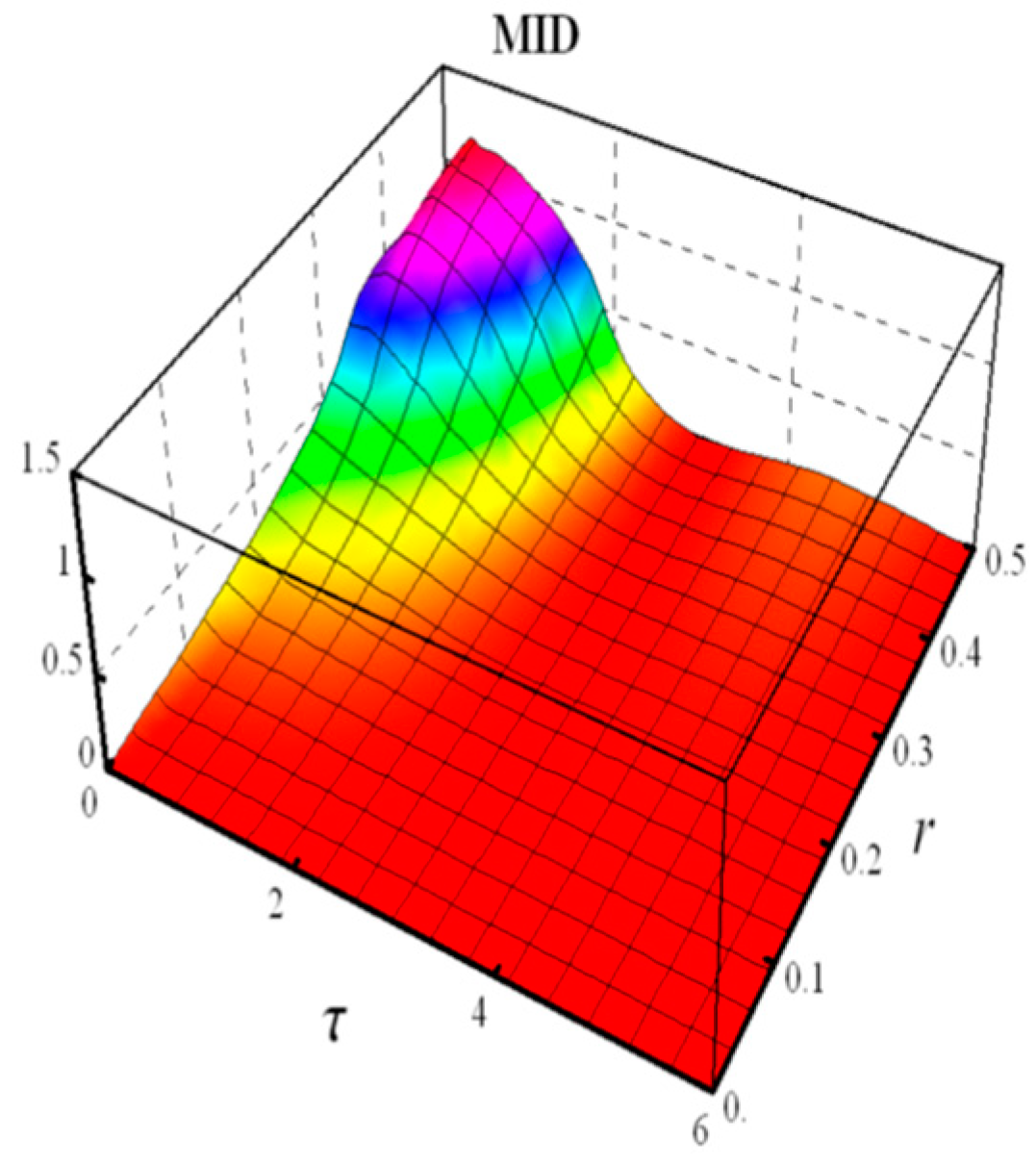
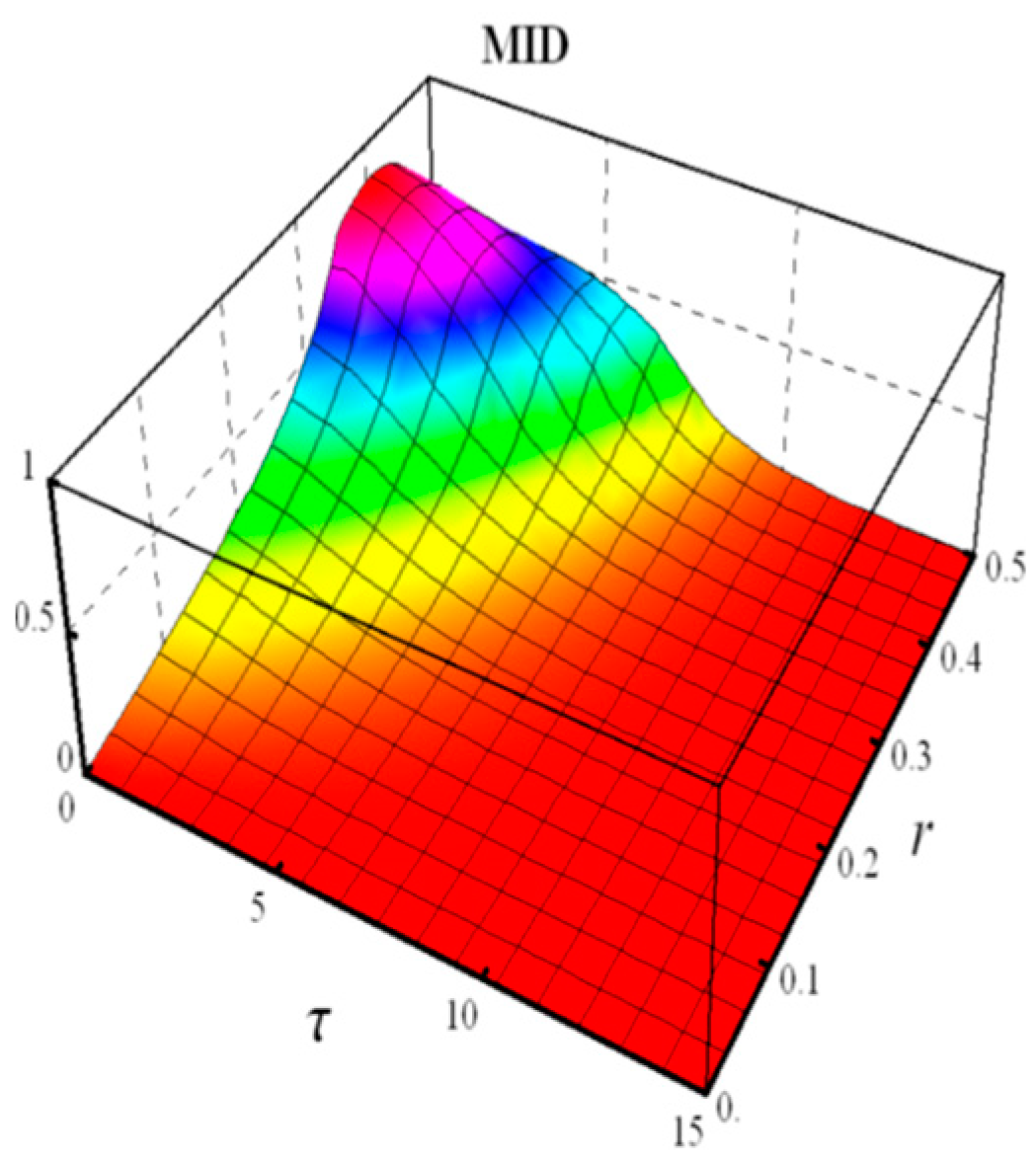
- Measured- Induced Disturbance (MID)
6. Conclusion
References
- C.H. Bennet and S. j. Wiesner, Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 (1992) 2881.
- Shor et al: Algorithms exist on a quantum computer science and appears in the SIAM journal of computing26 pp.1484-1509 (1997).
- M. Piani, P. Horodecki, R. Horodecki, No-local-broadcasting theorem for multipartite quantum correlations, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 (9) (2008) 090502. [CrossRef]
- B.P. Lanyon, M. Barbieri, M.P. Almeida, A.G. White, Experimental quantum computing without entanglement, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 (20) (2008) 200501. [CrossRef]
- Datta, A. Shaji, C.M. Caves, Quantum discord and the power of one qubit, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 (5) (2008) 050502. [CrossRef]
- S. Luo, Using measurement-induced disturbance to characterize correlations as classical or quantum, Phys. Rev. A 77 (2) (2008) 022301. [CrossRef]
- H. Ollivier, W.H. Zurek, Quantum discord: a measure of the quantumness of correlations, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 (1) (2001) 017901. [CrossRef]
- L. Henderson, V. Vedral, Classical, quantum and total correlations, J. Phys. A, Math. Gen. 34 (35) (2001) 6899–6905. [CrossRef]
- W.H. Zurek, Decoherence, einselection, and the quantum origins of the classical, Rev. Mod. Phys. 75 (3) (2003) 715–775. [CrossRef]
- T. Yu, J. Eberly, Sudden death of entanglement: classical noise effects, Opt. Commun. 264 (2) (2006) 393–397. [CrossRef]
- T. Yu, J.H. Eberly, Sudden death of entanglement, Science 323 (5914) (2009) 598–601. [CrossRef]
- Franco, G. Compagno, Experimental recovery of quantum correlations in absence of system environment back-action, Nat. Commun. 4 (2013) 2851. [CrossRef]
- Orieux, A. D’Arrigo, G. Ferranti, R.L. Franco, G. Benenti, E. Paladino, G. Falci, F. Sciarrino, P. Mataloni, Experimental on-demand recovery of entanglement by local operations within non-Markovian dynamics, Sci. Rep. 5 (1) (2015). [CrossRef]
- D’Arrigo, G. Benenti, R.L. Franco, G. Falci, E. Paladino, Hidden entanglement, system-environment information flow and non-Markovianity, Int. J. Quantum Inf. 12 (02) (2014) 1461005. [CrossRef]
- Mortezapour, R.L. Franco, Protecting quantum resources via frequency modulation of qubits in leaky cavities, Sci. Rep. 8 (1) (2018). [CrossRef]
- Z.-X. Man, Y.-J. Xia, R.L. Franco, Cavity-based architecture to preserve quantum coherence and entanglement, Sci. Rep. 5 (1) (2015). [CrossRef]
- D’Arrigo, R.L. Franco, G. Benenti, E. Paladino, G. Falci, Hidden entanglement in the presence of random telegraph dephasing noise, Phys. Scr. T 153 (2013) 014014. [CrossRef]
- F. Benatti, R. Floreanini, M. Piani, Environment induced entanglement in Markovian dissipative dynamics, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 (7) (2003). [CrossRef]
- R.L. Franco, G. Compagno, Overview on the phenomenon of two-qubit entanglement revivals in classical environments, in: Quantum Science and Technology, Springer International Publishing, 2017, pp. 367–391.
- K. Modi, A. Brodutch, H. Cable, T. Paterek, V. Vedral, The classical-quantum boundary for correlations: discord and related measures, Rev. Mod. Phys. 84 (4) (2012) 1655–1707. [CrossRef]
- Leggio, R.L. Franco, D.O. Soares-Pinto, P. Horodecki, G. Compagno, Distributed correlations and information flows within a hybrid multipartite quantum classical system, Phys. Rev. A 92 (3) (2015). [CrossRef]
- F. Altintas, A. Kurt, R. Eryigit, Classical memoryless noise-induced maximally discordant mixed separable steady states, Phys. Lett. A 377 (1–2) (2012) 53–59. [CrossRef]
- J. Trapani, M.G.A. Paris, Nondivisibility versus backflow of information in understanding revivals of quantum correlations for continuous-variable systems interacting with fluctuating environments, Phys. Rev. A 93 (4) (2016). [CrossRef]
- T. Yu, J.H. Eberly, Finite-time disentanglement via spontaneous emission, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 (14) (2004) 140404. [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, R. Lo Franco, G. Compagno, Non-Markovian effects on the dynamics of entanglement, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 (16) (2007) 160502. [CrossRef]
- Tchoffo, M., Tsokeng, A.T., Tiokang, O.M., Nganyo, P.N., Fai, L.C.: Phys. Lett. A 383, 1856 (2019).
- Y.Akbari-Kourbolagh1 ·Z.Pazhotan1 : Dynamics of Entanglement for a qubit-qutrit System Coupled to the Independent Classical Noises in Perpendicular Directions International Journal of Theoretical Physics (2022).
- Kenfack, L.T., Tchoffo, M., Javed, M., Fai, L.C.: Quantum Inf. Process. 19, 107 (2020).
- 30 K. Ann, G. Jaeger, Entanglement sudden death in qubit–qutrit systems, Phys. Lett. A 372 (5) (2008) 579–583. [CrossRef]
- G. Karpat, Z. Gedik, Correlation dynamics of qubit–qutrit systems in a classical dephasing environment, Phys. Lett. A 375 (47) (2011) 4166–4171. [CrossRef]
- W. Hai-Rui, R. Bao-Cang, L. Tao, H. Ming, D. Fu-Guo, Dynamics of entanglement for a two-parameter class of states in a qubit-qutrit system, Commun. Theor. Phys. 57 (6) (2012) 983. [CrossRef]
- M. Ramzan, M.K. Khan, Decoherence and entanglement degradation of a qubit-qutrit system in non-inertial frames, Quantum Inf. Process. 11 (2) (2012) 443–454. [CrossRef]
- G. Karpat, Z. Gedik, Invariant quantum discord in qubit–qutrit systems under local dephasing, Phys. Scr. 2013 (T153) (2013) 014036. [CrossRef]
- H. Yuan, L.-F. Wei, Correlation dynamics of two-parameter qubit—qutrit states under decoherence, Chin. Phys. B 22 (5) (2013) 050303. [CrossRef]
- J.-L. Guo, H. Li, G.-L. Long, Decoherent dynamics of quantum correlations in qubit–qutrit systems, Quantum Inf. Process. 12 (11) (2013) 3421–3435. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yang, A.-M. Wang, Correlation dynamics of a qubit—qutrit system in a spin chain environment with Dzyaloshinsky—Mariya interaction, Chin. Phys. B 23 (2) (2014) 020307. [CrossRef]
- K.O. Yashodamma, P.J. Geetha Sudha, Effectiveness of depolarizing noise in causing sudden death of entanglement, Quantum Inf. Process. 13 (11) (2014) 2551–2565. [CrossRef]
- J.-L. Guo, J.-L. Wei, W. Qin, Enhancement of quantum correlations in qubit–qutrit system under decoherence of finite temperature, Quantum Inf. Process. 14 (4) (2015) 1399–1410. [CrossRef]
- M. Jafarpour, F.K. Hasanvand, D. Afshar, Dynamics of entanglement and measurement-induced disturbance for a hybrid qubit-qutrit system interacting with a spin-chain environment: a mean field approach, Commun. Theor. Phys. 67 (1) (2017) 27. [CrossRef]
- Basit, H. Ali, F. Badshah, G.-Q. Ge, Enhancement of quantum correlations in qubit-qutrit systems under the non-Markovian environment, Commun. Theor. Phys. 68 (1) (2017) 29. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G. Vemuri, G.S. Agarwal, Anderson localization with second quantized fields in a coupled array of waveguides, Phys. Rev. A 82 (5) (2010) 053805. [CrossRef]
- G. De Chiara, G.M. Palma, Berry phase for a spin 1 / 2 particle in a classical fluctuating field, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 (9) (2003) 090404. [CrossRef]
- G. De Chiara, G.M. Palma, Berry phase for a spin 1 / 2 particle in a classical fluctuating field, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 (9) (2003) 090404. [CrossRef]
- Fiasconaro, B. Spagnolo, Stability measures in metastable states with Gaussian colored noise, Phys. Rev. E 80 (4) (2009) 041110. [CrossRef]
- M.A.C. Rossi, M.G.A. Paris, Non-Markovian dynamics of single- and two-qubit systems interacting with Gaussian and non-Gaussian fluctuating transverse environments, J. Chem. Phys. 144 (2) (2016) 024113. [CrossRef]
- G. Vidal, R.F. Werner, Computable measure of entanglement, Phys. Rev. A 65 (3) (2002) 032314. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



