Submitted:
15 March 2024
Posted:
18 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Merkel Cell Carcinoma
1.1.1. Polyomavirus-Related Merkel Cell Carcinoma
1.1.2. Ultraviolet-Related Merkel Cell Carcinoma
1.1.3. Merkel Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis and Treatment
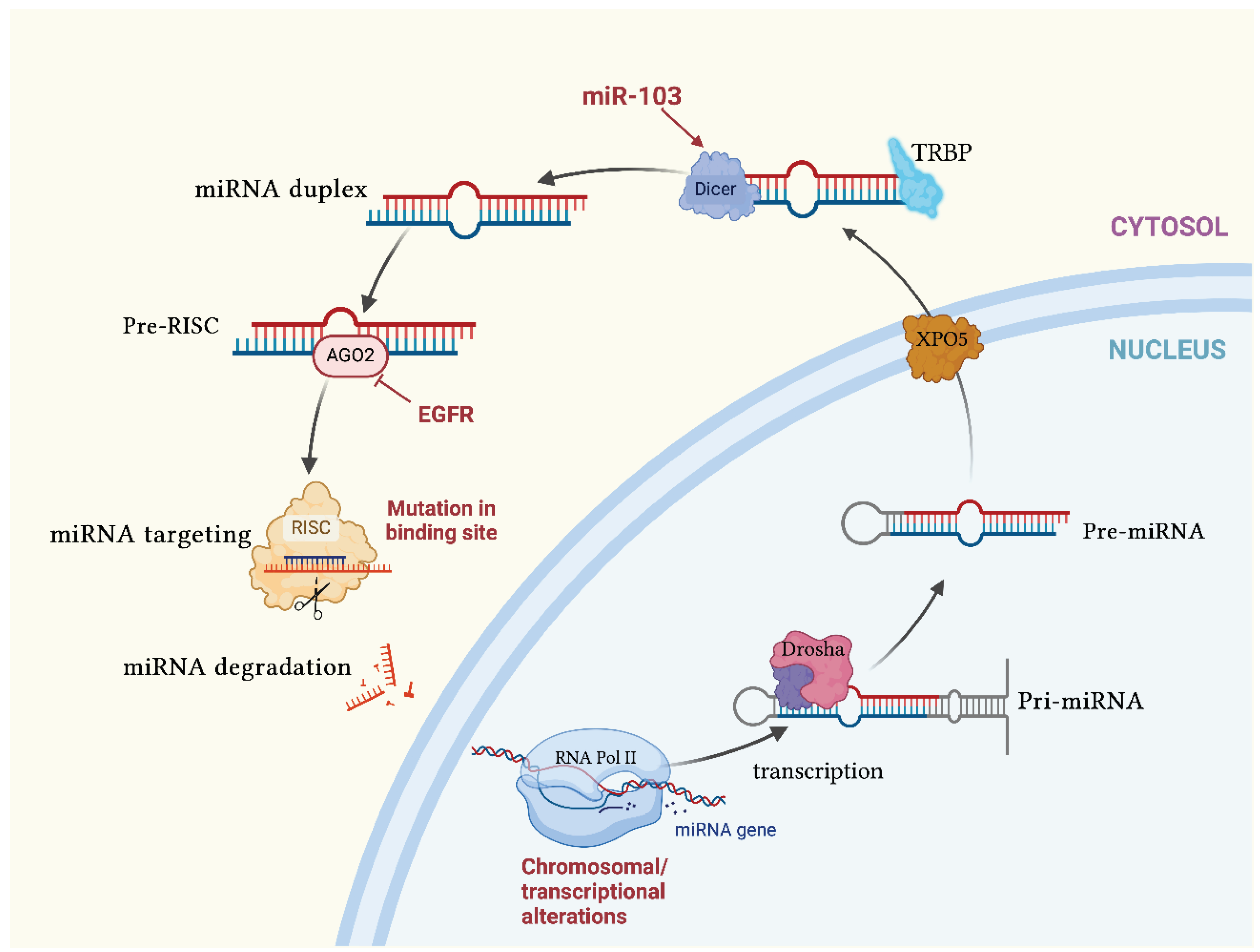
1.2. MicroRNAs
1.2.2. Functions of microRNAs in Cancers
2. Role of miRNAs in Merkel Cell Carcinoma
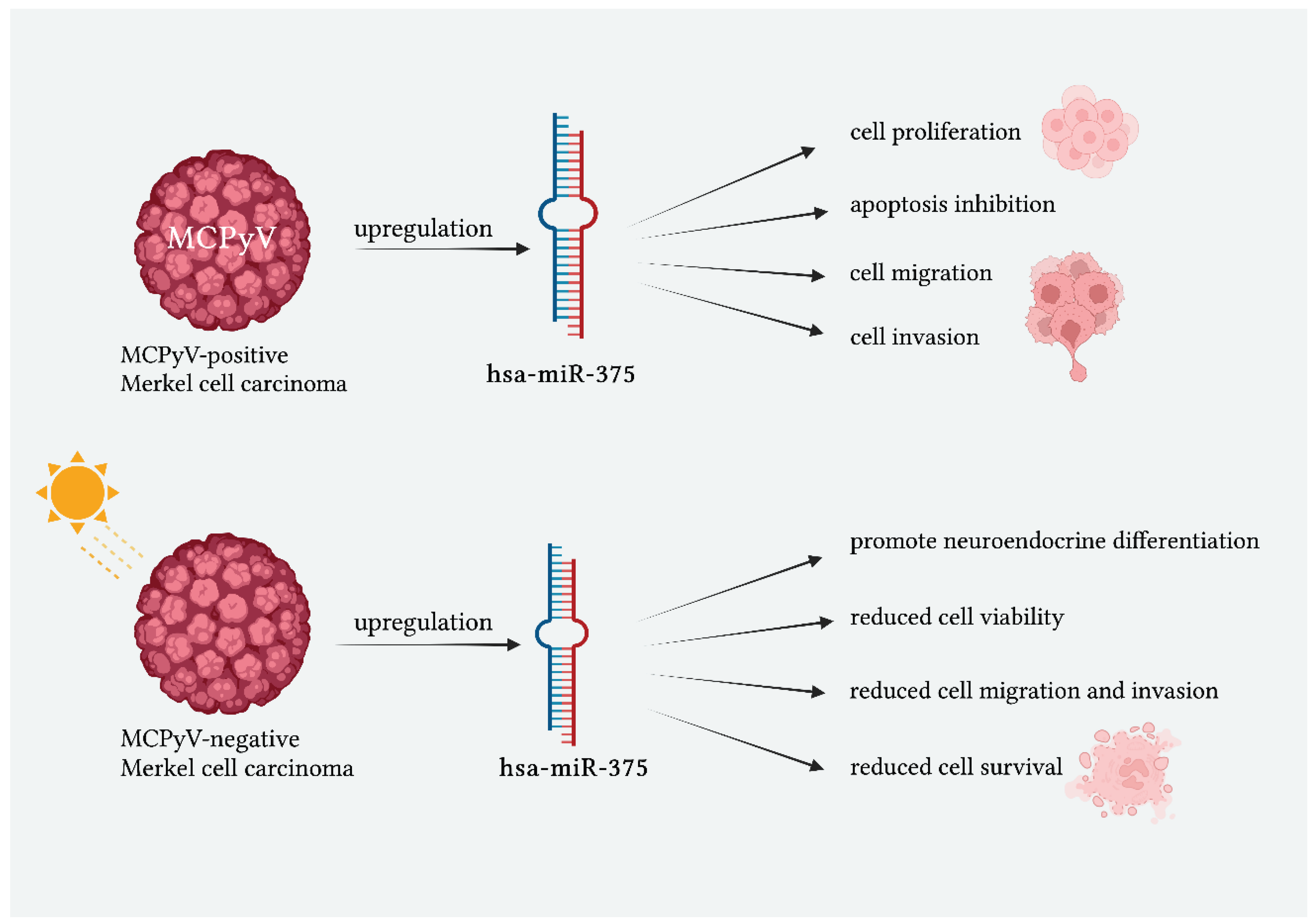
2.1. miR-375 and Merkel Cell Carcinoma
2.1.1. miR-375 Related to the Viral State
2.2. Other miRNAs Dysregulated in Merkel Cell Carcinoma
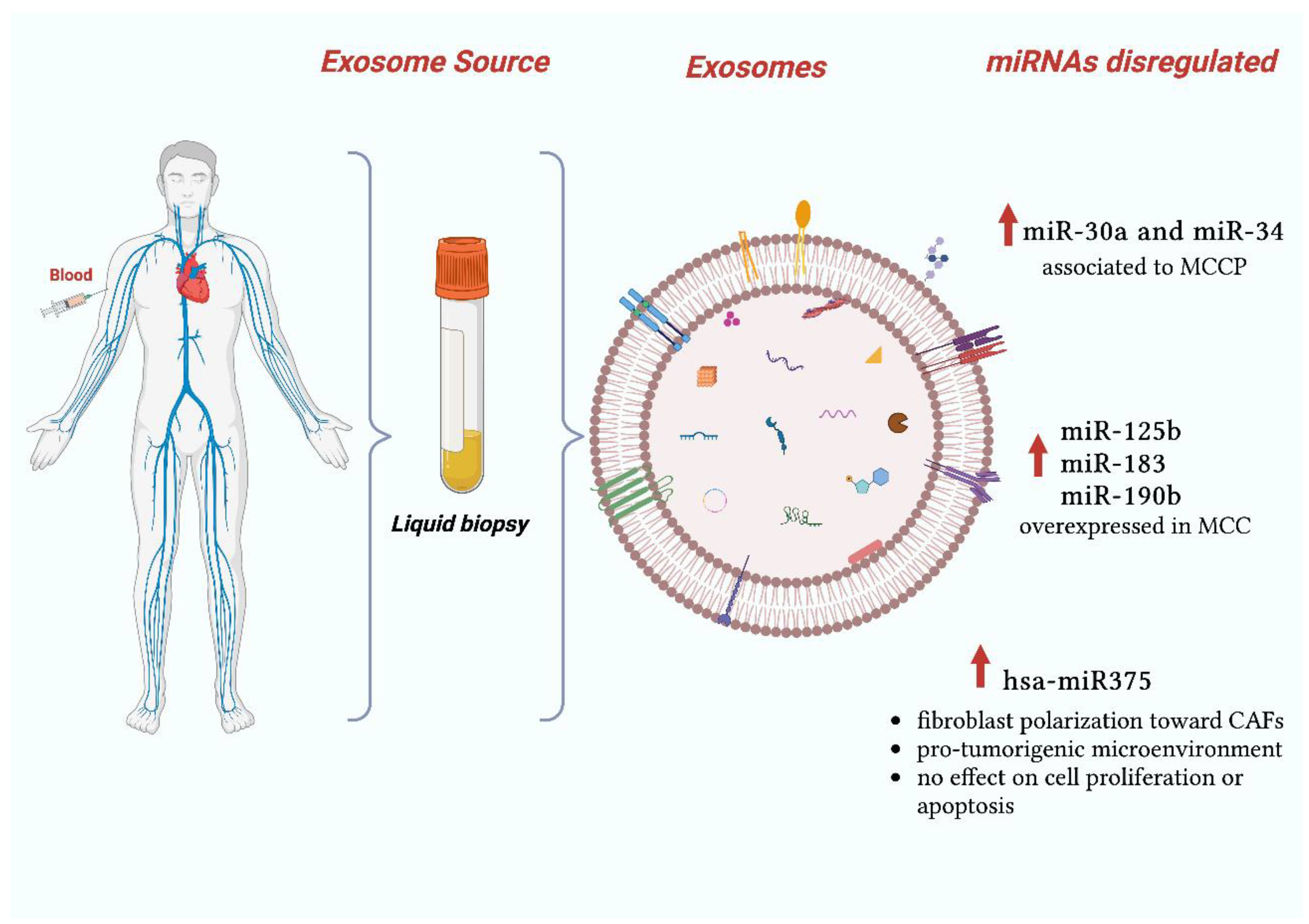
2.3. Exosomal miRNAs in Merkel Cell Carcinoma
2.4. CircRNAs in Merkel Cell Carcinoma
3. Possible Uses and Limitations of miRNAs in Merkel Cell Carcinoma
3.1. miRNAs possible Clinical Applications
3.2. miRNAs Limitations
4. Application of Artificial Intelligence in MCC
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gauci, M.-L.; Aristei, C.; Becker, J.C.; Blom, A.; Bataille, V.; Dreno, B.; Del Marmol, V.; Forsea, A.M.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Grob, J.-J.; et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Merkel Cell Carcinoma: European Consensus-Based Interdisciplinary Guideline – Update 2022. Eur J Cancer 2022, 171, 203–231. [CrossRef]
- Samimi, M.; Kervarrec, T.; Touze, A. Immunobiology of Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Curr Opin Oncol 2020, 32, 114–121. [CrossRef]
- Papa, V.; Li Pomi, F.; Borgia, F.; Vaccaro, M.; Pioggia, G.; Gangemi, S. Immunosenescence and Skin: A State of Art of Its Etiopathogenetic Role and Crucial Watershed for Systemic Implications. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 7956. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; MacDonald, M.; You, J. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection and Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Curr Opin Virol 2016, 20, 20–27. [CrossRef]
- Zaggana, E.; Konstantinou, M.P.; Krasagakis, G.H.; de Bree, E.; Kalpakis, K.; Mavroudis, D.; Krasagakis, K. Merkel Cell Carcinoma—Update on Diagnosis, Management and Future Perspectives. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 15, 103. [CrossRef]
- Schowalter, R.M.; Pastrana, D. V.; Pumphrey, K.A.; Moyer, A.L.; Buck, C.B. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus and Two Previously Unknown Polyomaviruses Are Chronically Shed from Human Skin. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 509–515. [CrossRef]
- Stakaitytė, G.; Wood, J.; Knight, L.; Abdul-Sada, H.; Adzahar, N.; Nwogu, N.; Macdonald, A.; Whitehouse, A. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus: Molecular Insights into the Most Recently Discovered Human Tumour Virus. Cancers (Basel) 2014, 6, 1267–1297. [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. MCV and Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Molecular Success Story. Curr Opin Virol 2012, 2, 489–498. [CrossRef]
- DeCaprio, J.A. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus and Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2017, 372, 20160276. [CrossRef]
- Verhaegen, M.E.; Mangelberger, D.; Harms, P.W.; Vozheiko, T.D.; Weick, J.W.; Wilbert, D.M.; Saunders, T.L.; Ermilov, A.N.; Bichakjian, C.K.; Johnson, T.M.; et al. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Is Oncogenic in Transgenic Mice. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2015, 135, 1415–1424. [CrossRef]
- Pietropaolo, V.; Prezioso, C.; Moens, U. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus and Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 1774. [CrossRef]
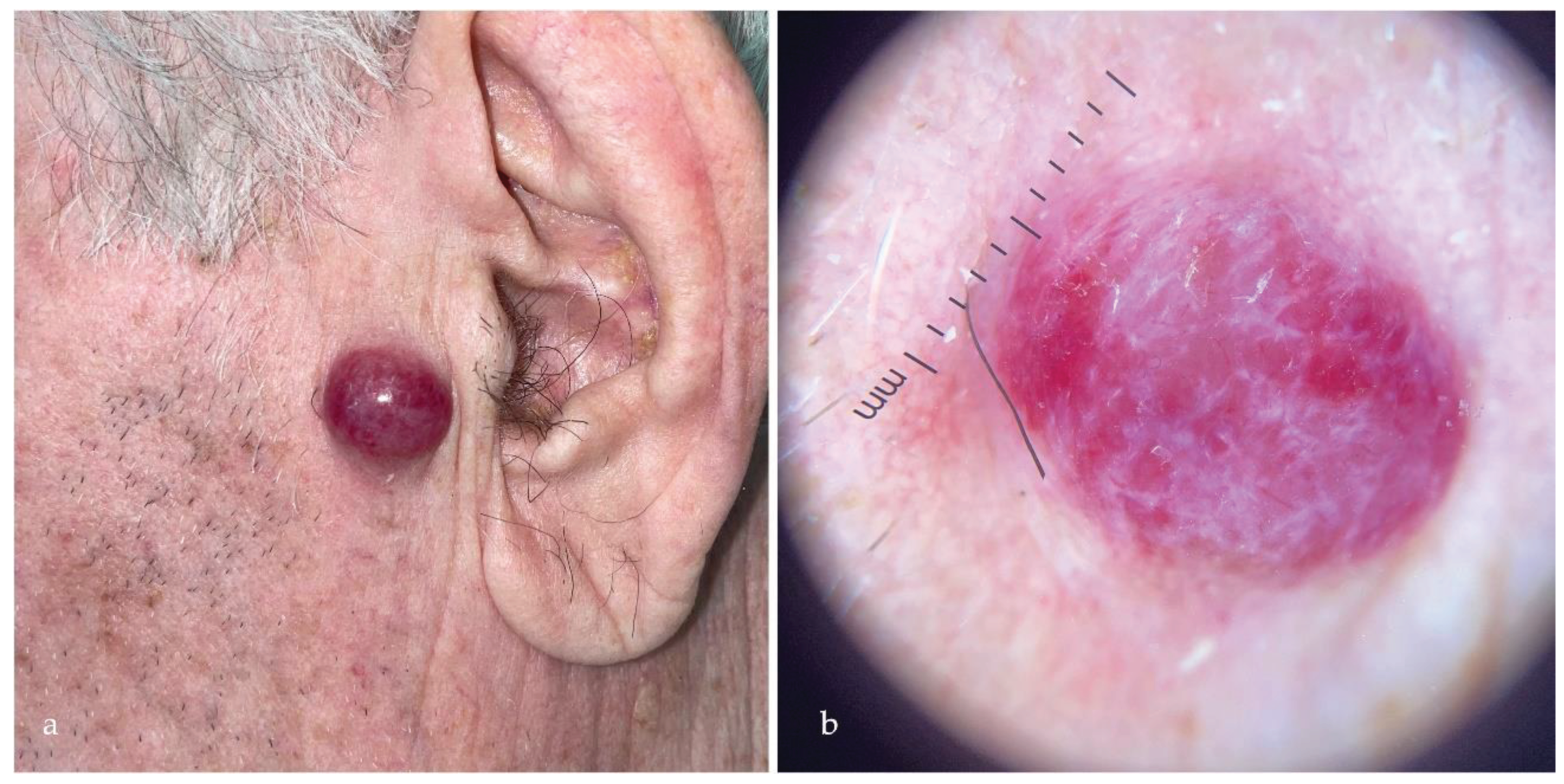
- Dalle, S.; Parmentier, L.; Moscarella, E.; Phan, A.; Argenziano, G.; Thomas, L. Dermoscopy of Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Dermatology 2012, 224, 140–144. [CrossRef]
- Lallas, A.; Moscarella, E.; Argenziano, G.; Longo, C.; Apalla, Z.; Ferrara, G.; Piana, S.; Rosato, S.; Zalaudek, I. Dermoscopy of Uncommon Skin Tumours. Australasian Journal of Dermatology 2014, 55, 53–62. [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, C.; Chamberlain, A.J.; Haskett, M.; Rosendahl, C.; Goh, M.; Beck, H.; Keir, J.; Varghese, P.; Mar, A.; Hosking, S.; et al. Clinical and Dermoscopic Characteristics of Merkel Cell Carcinoma. British Journal of Dermatology 2013, 169, 294–297. [CrossRef]
- Kachare, S.D.; Wong, J.H.; Vohra, N.A.; Zervos, E.E.; Fitzgerald, T.L. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Is Associated with Improved Survival in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2014, 21, 1624–1630. [CrossRef]
- Oliveto, S.; Mancino, M.; Manfrini, N.; Biffo, S. Role of MicroRNAs in Translation Regulation and Cancer. World J Biol Chem 2017, 8, 45. [CrossRef]
- Rani, V.; Sengar, R.S. Biogenesis and Mechanisms of MicroRNA-mediated Gene Regulation. Biotechnol Bioeng 2022, 119, 685–692. [CrossRef]
- Dexheimer, P.J.; Cochella, L. MicroRNAs: From Mechanism to Organism. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, T.-H.; Huang, Y.-M.; Wei, P.-L.; Lin, J.-C. Involvement of MicroRNA in Solid Cancer: Role and Regulatory Mechanisms. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 343. [CrossRef]
- Rizk, N.I.; Midan, H.M.; Helal, G.K.; Abulsoud, A.I.; Elshaer, S.S.; El-Husseiny, A.A.; Fathi, D.; Abdelmaksoud, N.M.; Abdel Mageed, S.S.; Elballal, M.S.; et al. The Emerging Role of MiRNAs in Merkel Cell Carcinoma Pathogenesis: Signaling Pathway Crosstalk. Pathol Res Pract 2023, 249, 154771. [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, K.; Miyoshi, T.; Siomi, H. Many Ways to Generate MicroRNA-like Small RNAs: Non-Canonical Pathways for MicroRNA Production. Molecular Genetics and Genomics 2010, 284, 95–103. [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, C.; Cervellera, C.F.; Lanzillotti, C.; Touzé, A.; Gaboriaud, P.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Rotondo, J.C. MicroRNA Dysregulations in Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. J Med Virol 2023, 95. [CrossRef]
- Konstantinell, A.; Coucheron, D.; Sveinbjørnsson, B.; Moens, U. MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19, 1873. [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, J.C.; Mazziotta, C.; Lanzillotti, C.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F. Epigenetic Dysregulations in Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Driven Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 11464. [CrossRef]
- Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Zurac, S. MiRNAs in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Skin Cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8. [CrossRef]
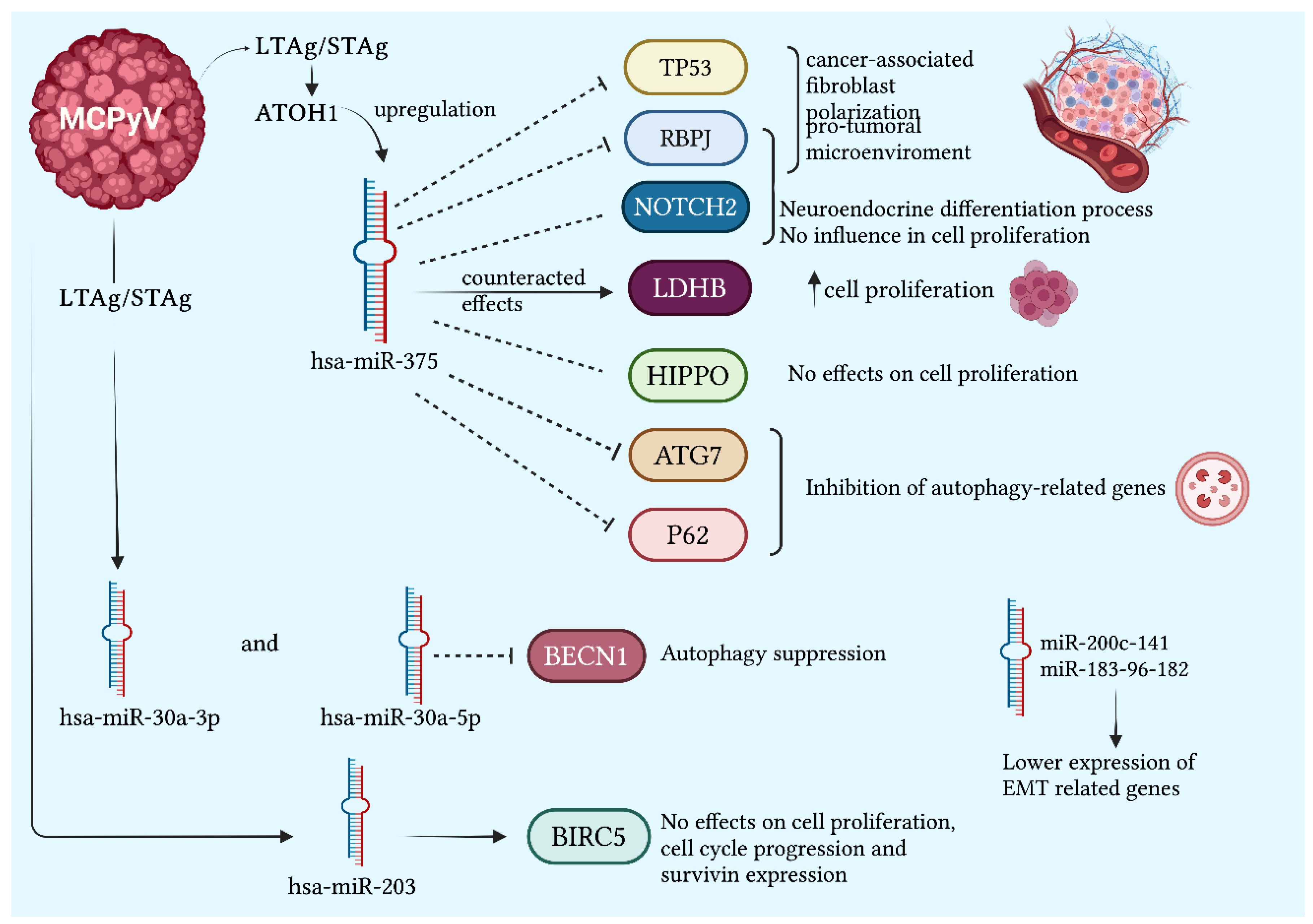
- Fan, K.; Gravemeyer, J.; Ritter, C.; Rasheed, K.; Gambichler, T.; Moens, U.; Shuda, M.; Schrama, D.; Becker, J.C. MCPyV Large T Antigen-Induced Atonal Homolog 1 Is a Lineage-Dependency Oncogene in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2020, 140, 56-65.e3. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Xie, H.; Shi, H.; Gao, J.; Juhlin, C.C.; Björnhagen, V.; Höög, A.; Lee, L.; Larsson, C.; Lui, W. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Oncoproteins Induce MicroRNAs That Suppress Multiple Autophagy Genes. Int J Cancer 2020, 146, 1652–1666. [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Ritter, C.; Nghiem, P.; Blom, A.; Verhaegen, M.E.; Dlugosz, A.; Ødum, N.; Woetmann, A.; Tothill, R.W.; Hicks, R.J.; et al. Circulating Cell-Free MiR-375 as Surrogate Marker of Tumor Burden in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research 2018, 24, 5873–5882. [CrossRef]
- Renwick, N.; Cekan, P.; Masry, P.A.; McGeary, S.E.; Miller, J.B.; Hafner, M.; Li, Z.; Mihailovic, A.; Morozov, P.; Brown, M.; et al. Multicolor MicroRNA FISH Effectively Differentiates Tumor Types. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2013, 123, 2694–2702. [CrossRef]
- Abraham, K.J.; Zhang, X.; Vidal, R.; Paré, G.C.; Feilotter, H.E.; Tron, V.A. Roles for MiR-375 in Neuroendocrine Differentiation and Tumor Suppression via Notch Pathway Suppression in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Am J Pathol 2016, 186, 1025–1035. [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Lee, L.; Caramuta, S.; Höög, A.; Browaldh, N.; Björnhagen, V.; Larsson, C.; Lui, W.-O. MicroRNA Expression Patterns Related to Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection in Human Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2014, 134, 507–517. [CrossRef]
- Costa-Pinheiro, P.; Ramalho-Carvalho, J.; Vieira, F.Q.; Torres-Ferreira, J.; Oliveira, J.; Gonçalves, C.S.; Costa, B.M.; Henrique, R.; Jerónimo, C. MicroRNA-375 Plays a Dual Role in Prostate Carcinogenesis. Clin Epigenetics 2015, 7, 42. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Chu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, J.; Lu, C.; Lü, R.; Ding, M.; Mao, N. MicroRNA-375 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in Osteosarcoma by Targeting PIK3CA. Tumor Biology 2015, 36, 8579–8584. [CrossRef]
- CUI, F.; WANG, S.; LAO, I.; ZHOU, C.; KONG, H.; BAYAXI, N.; LI, J.; CHEN, Q.; ZHU, T.; ZHU, H. MiR-375 Inhibits the Invasion and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer via Targeting SP1 and Regulating EMT-Associated Genes. Oncol Rep 2016, 36, 487–493. [CrossRef]
- Osako, Y.; Seki, N.; Kita, Y.; Yonemori, K.; Koshizuka, K.; Kurozumi, A.; Omoto, I.; Sasaki, K.; Uchikado, Y.; Kurahara, H.; et al. Regulation of MMP13 by Antitumor MicroRNA-375 Markedly Inhibits Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int J Oncol 2016, 49, 2255–2264. [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Lin, J.; Tsung, A. Manipulation of Autophagy by MIR375 Generates Antitumor Effects in Liver Cancer. Autophagy 2012, 8, 1833–1834. [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Zebisch, A.; Horny, K.; Schrama, D.; Becker, J.C. Highly Expressed MiR-375 Is Not an Intracellular Oncogene in Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Associated Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 529. [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Spassova, I.; Gravemeyer, J.; Ritter, C.; Horny, K.; Lange, A.; Gambichler, T.; Ødum, N.; Schrama, D.; Schadendorf, D.; et al. Merkel Cell Carcinoma-Derived Exosome-Shuttle MiR-375 Induces Fibroblast Polarization by Inhibition of RBPJ and P53. Oncogene 2021, 40, 980–996. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Xie, H.; Scicluna, P.; Lee, L.; Björnhagen, V.; Höög, A.; Larsson, C.; Lui, W.-O. MiR-375 Regulation of LDHB Plays Distinct Roles in Polyomavirus-Positive and -Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10, 443. [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Gravemeyer, J.; Ritter, C.; Rasheed, K.; Gambichler, T.; Moens, U.; Shuda, M.; Schrama, D.; Becker, J.C. MCPyV Large T Antigen-Induced Atonal Homolog 1 Is a Lineage-Dependency Oncogene in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2020, 140, 56-65.e3. [CrossRef]
- Gambichler, T.; Mohtezebsade, S.; Wieland, U.; Silling, S.; Höh, A.-K.; Dreißigacker, M.; Schaller, J.; Schulze, H.-J.; Oellig, F.; Kreuter, A.; et al. Prognostic Relevance of High Atonal Homolog-1 Expression in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2017, 143, 43–49. [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, S.M.; Wright, M.C.; Bolock, A.M.; Geng, X.; Maricich, S.M. Ectopic Atoh1 Expression Drives Merkel Cell Production in Embryonic, Postnatal and Adult Epidermis. Development 2015. [CrossRef]
- Ning, M.S.; Kim, A.S.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.E.; Zhang, H.; Andl, T. Characterization of the Merkel Cell Carcinoma MiRNome. J Skin Cancer 2014, 2014, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Veija, T.; Sahi, H.; Koljonen, V.; Bohling, T.; Knuutila, S.; Mosakhani, N. MiRNA-34a Underexpressed in Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Virchows Archiv 2015, 466, 289–295. [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Park, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Yin, J.; Liu, Q.; Wei, M. Progress on the Relationship between MiR-125 Family and Tumorigenesis. Exp Cell Res 2015, 339, 252–260. [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhao, P.; Xiao, Z.; Han, X.; Fu, F.; Fu, L. Γδ T Cells in Cancer Immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 8900–8909. [CrossRef]
- Stark, M.S.; Tyagi, S.; Nancarrow, D.J.; Boyle, G.M.; Cook, A.L.; Whiteman, D.C.; Parsons, P.G.; Schmidt, C.; Sturm, R.A.; Hayward, N.K. Characterization of the Melanoma MiRNAome by Deep Sequencing. PLoS One 2010, 5, e9685. [CrossRef]
- Persson, H.; Kvist, A.; Rego, N.; Staaf, J.; Vallon-Christersson, J.; Luts, L.; Loman, N.; Jonsson, G.; Naya, H.; Hoglund, M.; et al. Identification of New MicroRNAs in Paired Normal and Tumor Breast Tissue Suggests a Dual Role for the ERBB2/Her2 Gene. Cancer Res 2011, 71, 78–86. [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Shuda, M.; Guastafierro, A.; Feng, H.; Toptan, T.; Tolstov, Y.; Normolle, D.; Vollmer, L.L.; Vogt, A.; Dömling, A.; et al. Survivin Is a Therapeutic Target in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Sci Transl Med 2012, 4. [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wu, X.; Xiang, S.; Qiao, M.; Cen, X.; Pan, X.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Z. Regulatory Mechanism of MiR-20a-5p Expression in Cancer. Cell Death Discov 2022, 8, 262. [CrossRef]
- Orouji, E.; Peitsch, W.K.; Orouji, A.; Houben, R.; Utikal, J. Unique Role of Histone Methyltransferase PRDM8 in the Tumorigenesis of Virus-Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 1057. [CrossRef]
- Gravemeyer, J.; Lange, A.; Ritter, C.; Spassova, I.; Song, L.; Picard, D.; Remke, M.; Horny, K.; Sriram, A.; Gambichler, T.; et al. Classical and Variant Merkel Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines Display Different Degrees of Neuroendocrine Differentiation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2021, 141, 1675-1686.e4. [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular Vesicles: Exosomes, Microvesicles, and Friends. Journal of Cell Biology 2013, 200, 373–383. [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Chen, H.; Guo, Z.; Shen, J.; Luo, W.; Xie, F.; Wan, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; He, J. Circular RNAs and Their Role in Exosomes. Front Oncol 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Mashouri, L.; Yousefi, H.; Aref, A.R.; Ahadi, A. mohammad; Molaei, F.; Alahari, S.K. Exosomes: Composition, Biogenesis, and Mechanisms in Cancer Metastasis and Drug Resistance. Mol Cancer 2019, 18, 75. [CrossRef]
- HUANG, K.; TANG, Y.; HE, L.; DAI, Y. MicroRNA-340 Inhibits Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis by Targeting the MDM2-P53 Pathway. Oncol Rep 2016, 35, 887–895. [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, S.; Grossmann, K.; Cassidy, P.; Yang, C.; Fan, M.; Kopelovich, L.; Leachman, S.; Pfeffer, L. Detection of Exosomal MiRNAs in the Plasma of Melanoma Patients. J Clin Med 2015, 4, 2012–2027. [CrossRef]
- Imamura, T.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Miyamae, M.; Okajima, W.; Ohashi, T.; Kiuchi, J.; Nishibeppu, K.; Kosuga, T.; Konishi, H.; et al. Low Plasma Levels of MiR-101 Are Associated with Tumor Progression in Gastric Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 106538–106550. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Deng, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, C.; Meng, L.; Qiao, S.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lü, J.; Li, W.; et al. A Direct Quantification Method for Measuring Plasma MicroRNAs Identified Potential Biomarkers for Detecting Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 21865–21874. [CrossRef]
- Foj, L.; Ferrer, F.; Serra, M.; Arévalo, A.; Gavagnach, M.; Giménez, N.; Filella, X. Exosomal and Non-Exosomal Urinary MiRNAs in Prostate Cancer Detection and Prognosis. Prostate 2017, 77, 573–583. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, F.; Zhao, Q.; Zhan, F.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X. Circulating Exosomal MiR-125a-3p as a Novel Biomarker for Early-Stage Colon Cancer. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 4150. [CrossRef]
- Butz, H.; Nofech-Mozes, R.; Ding, Q.; Khella, H.W.Z.; Szabó, P.M.; Jewett, M.; Finelli, A.; Lee, J.; Ordon, M.; Stewart, R.; et al. Exosomal MicroRNAs Are Diagnostic Biomarkers and Can Mediate Cell–Cell Communication in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur Urol Focus 2016, 2, 210–218. [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.; Peruzzi, P.P.; Lawler, S. MicroRNAs in Cancer: Biomarkers, Functions and Therapy. Trends Mol Med 2014, 20, 460–469. [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Jin, H. MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Cancer: Opportunities and Challenges. Biomed Res Int 2015, 2015, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peng, R.; Wang, J.; Qin, Z.; Xue, L. Circulating MicroRNAs as Potential Cancer Biomarkers: The Advantage and Disadvantage. Clin Epigenetics 2018, 10, 59. [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Kong, S.; Wang, F.; Ju, S. CircRNAs: Biogenesis, Functions, and Role in Drug-Resistant Tumours. Mol Cancer 2020, 19, 119. [CrossRef]
- Holdt, L.M.; Kohlmaier, A.; Teupser, D. Molecular Roles and Function of Circular RNAs in Eukaryotic Cells. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2018, 75, 1071–1098. [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Chen, R.E.; Olsen, M.N.; Wang, P.L.; Brown, P.O. Cell-Type Specific Features of Circular RNA Expression. PLoS Genet 2013, 9, e1003777. [CrossRef]
- Fontemaggi, G.; Turco, C.; Esposito, G.; Di Agostino, S. New Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Impact of CircRNAs in Human Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 3154. [CrossRef]
- Allegra, A.; Cicero, N.; Tonacci, A.; Musolino, C.; Gangemi, S. Circular RNA as a Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis and Prognosis and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 1700. [CrossRef]
- Abere, B.; Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Cao, S.; Toptan, T.; Grundhoff, A.; Fischer, N.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Encodes Circular RNAs (CircRNAs) Enabling a Dynamic CircRNA/MicroRNA/MRNA Regulatory Network. mBio 2020, 11. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, H.; Ji, W.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Duan, G. Virology, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Control of COVID-19. Viruses 2020, 12, 372. [CrossRef]
- Boyer, M.; Cayrefourcq, L.; Dereure, O.; Meunier, L.; Becquart, O.; Alix-Panabières, C. Clinical Relevance of Liquid Biopsy in Melanoma and Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 960. [CrossRef]
- Badalamenti, G.; Incorvaia, L.; Algeri, L.; Carreca, I.U.; Brando, C.; Madonia, G.; Peri, M.; Cucinella, A.; Perez, A.; Barraco, N.; et al. Immunometabolic Predictive Factors in Merkel Cell Carcinoma (MCC) Patients Treated with Avelumab. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2022, 40, e21525–e21525. [CrossRef]
- Mantripragada, K.; Birnbaum, A. Response to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma Metastatic to the Heart and Pancreas. Cureus 2015. [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, P.T.; Bhatia, S.; Lipson, E.J.; Kudchadkar, R.R.; Miller, N.J.; Annamalai, L.; Berry, S.; Chartash, E.K.; Daud, A.; Fling, S.P.; et al. PD-1 Blockade with Pembrolizumab in Advanced Merkel-Cell Carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2016, 374, 2542–2552. [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, H.L.; Russell, J.; Hamid, O.; Bhatia, S.; Terheyden, P.; D’Angelo, S.P.; Shih, K.C.; Lebbé, C.; Linette, G.P.; Milella, M.; et al. Avelumab in Patients with Chemotherapy-Refractory Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Multicentre, Single-Group, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol 2016, 17, 1374–1385. [CrossRef]
- Walocko, F.M.; Scheier, B.Y.; Harms, P.W.; Fecher, L.A.; Lao, C.D. Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma Response to Nivolumab. J Immunother Cancer 2016, 4, 79. [CrossRef]
- Thiem, A.; Kneitz, H.; Schummer, P.; Herz, S.; Schrama, D.; Houben, R.; Goebeler, M.; Schilling, B.; Gesierich, A. Coincident Metastatic Melanoma and Merkel Cell Carcinoma with Complete Remission on Treatment with Pembrolizumab. Acta Dermato Venereologica 2017, 97, 1252–1254. [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, H.L.; Russell, J.S.; Hamid, O.; Bhatia, S.; Terheyden, P.; D’Angelo, S.P.; Shih, K.C.; Lebbé, C.; Milella, M.; Brownell, I.; et al. Updated Efficacy of Avelumab in Patients with Previously Treated Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma after ≥1 Year of Follow-up: JAVELIN Merkel 200, a Phase 2 Clinical Trial. J Immunother Cancer 2018, 6, 7. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Sharma, G.; Doss, C.G.P.; Lee, S.-S. Therapeutic MiRNA and SiRNA: Moving from Bench to Clinic as Next Generation Medicine. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2017, 8, 132–143. [CrossRef]
- Incorvaia, L.; Fanale, D.; Badalamenti, G.; Brando, C.; Bono, M.; De Luca, I.; Algeri, L.; Bonasera, A.; Corsini, L.R.; Scurria, S.; et al. A “Lymphocyte MicroRNA Signature” as Predictive Biomarker of Immunotherapy Response and Plasma PD-1/PD-L1 Expression Levels in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Pointing towards Epigenetic Reprogramming. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 3396. [CrossRef]
- Cabibi, D.; Caruso, S.; Bazan, V.; Castiglia, M.; Bronte, G.; Ingrao, S.; Fanale, D.; Cangemi, A.; Calò, V.; Listì, A.; et al. Analysis of Tissue and Circulating MicroRNA Expression during Metaplastic Transformation of the Esophagus. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 47821–47830. [CrossRef]
- Fanale, D.; Amodeo, V.; Bazan, V.; Insalaco, L.; Incorvaia, L.; Barraco, N.; Castiglia, M.; Rizzo, S.; Santini, D.; Giordano, A.; et al. Can the MicroRNA Expression Profile Help to Identify Novel Targets for Zoledronic Acid in Breast Cancer? Oncotarget 2016, 7, 29321–29332. [CrossRef]
- Schowalter, R.M.; Pastrana, D. V.; Pumphrey, K.A.; Moyer, A.L.; Buck, C.B. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus and Two Previously Unknown Polyomaviruses Are Chronically Shed from Human Skin. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 509–515. [CrossRef]
- Elloumi, F.; Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Parker, J.S.; Gulley, M.L.; Amos, K.D.; Troester, M.A. Systematic Bias in Genomic Classification Due to Contaminating Non-Neoplastic Tissue in Breast Tumor Samples. BMC Med Genomics 2011, 4, 54. [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, K.; Stanislaw, S.; Spain, L.; Gallegos, L.L.; Rowan, A.; Schnidrig, D.; Rosenbaum, H.; Harle, A.; Au, L.; Hill, S.M.; et al. Representative Sequencing: Unbiased Sampling of Solid Tumor Tissue. Cell Rep 2020, 31, 107550. [CrossRef]
- Jutzi, T.B.; Krieghoff-Henning, E.I.; Holland-Letz, T.; Utikal, J.S.; Hauschild, A.; Schadendorf, D.; Sondermann, W.; Fröhling, S.; Hekler, A.; Schmitt, M.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Skin Cancer Diagnostics: The Patients’ Perspective. Front Med (Lausanne) 2020, 7. [CrossRef]
- Steele, L.; Velazquez-Pimentel, D.; Thomas, B.R. Do AI Models Recognise Rare, Aggressive Skin Cancers? An Assessment of a Direct-to-consumer Application in the Diagnosis of Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Amelanotic Melanoma. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2021, 35. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Li, S.; Yang, P.; Wang, R.; Zhou, P.; Li, J. Dissecting the Tumour Immune Microenvironment in Merkel Cell Carcinoma Based on a Machine Learning Framework. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 2023, 51, 397–407. [CrossRef]
- Muthamilselvan, S.; Ramasami Sundhar Baabu, P.; Palaniappan, A. Microfluidics for Profiling MiRNA Biomarker Panels in AI-Assisted Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2023, 22. [CrossRef]
- Korfiati, A.; Grafanaki, K.; Kyriakopoulos, G.C.; Skeparnias, I.; Georgiou, S.; Sakellaropoulos, G.; Stathopoulos, C. Revisiting MiRNA Association with Melanoma Recurrence and Metastasis from a Machine Learning Point of View. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 1299. [CrossRef]
| Authors | miRNAs upregulated in MCC | Sample types | miRNAs’ role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fan et al.[28] | miR-375 | MCCP versus MCCN tissues and cel lines | miR-375 serum level showed high diagnostic accuracy to discriminate tumor-bearing and tumor-free patients with MCC. |
| Ning et al.[43] | miRNA-9 miRNA-502-3p miRNA-7 miRNA-340 miRNA-182 miRNA-190b miRNA-873 miRNA-183 |
MCC tissues versus non-MCC skin tumor and normal skin | Enhancing tumor motility and promoting colony formation. Specifically miR-182 was localized within tumor cells and, as expected from the qRT-PCR data, expression in surrounding tissue and normal skin was low compared to that in MCC cells. |
| Renwick et al.[29] | miRNA-205 miRNA-375 |
MCC versus non-MCC tissue and cell lines | Downregulating the expression of gene targets through interaction with the three prime untranslated region (3′ UTR) of the respective genes. Potential diagnostic role by distinguish BCC from MCC |
| Xie et al.[31] | miR-150 | MCC metastases versus primary tumor | Association with tumor metastasis and disease-specific survival |
| Authors | miRNAs downregulated in MCC | Sample types | miRNAs’ role |
| Ning et al.[43] | miRNA-3170 miRNA-125b miRNA-374c |
MCC tissues versus non-MCC skin tumor and normal skin | Not reported. |
| Authors | miRNAs upregulatd in MCCP | Sample types | miRNAs’ role |
| Veija et al.[44] | miR-34a miR-1539 miR-30a miR-142-3p |
MCCP versus MCCN tissues | Possible role in the oncogenesis of MCCP. Slight underexpression of miR-181d was detectable in MCCP |
| Gravemeyer et al.[52] | miR-200c-141 miR-183-96-1832 miR-30a-5pmiR-375 |
MCCP versus MCCN cell lines | Establishment of a connection between the neuroendocrine features of MCC and the lack of EMT |
| Abraham et al. [30] | miR-375 | MCCP versus MCCN cell lines | Roles of MiR-375 in neuroendocrine differentiation |
| Xie et al.[31] |
miR-30a-3p miR-769-5p miR-34a miR-375 |
MCCP versus MCCN tissues | Specifically upregulated in MCCP compared to MCCN |
| Author | miRNAs disregulated in MCCN | Sample types | miRNAs’ role |
| Veija et al.[44] | miR-34a | MCCP versus MCCN tissues | Statistically significative reduction of miR-34a in MCCN |
| Xie et al.[31] | miR-203 | MCCP versus MCCN tissues | Specific activity only in MCCN |
| Kumar et al.[39] | miR-375 | MCCP versus MCCN tissues and cel lines | Silencing of LDHB reduced cell growth in MCPyV− cell lines, while its silencing in MCPyV+ cell lines rescued the cell growth effect mediated by miR-375 inhibition |
| Orouji et al. [51] | miR-20a-5p | miR-20a-5p downregulation in MCCN led to high levels of PRDM8 protein, which is involved in silencing tumor suppressor gene. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





