Submitted:
17 March 2024
Posted:
18 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
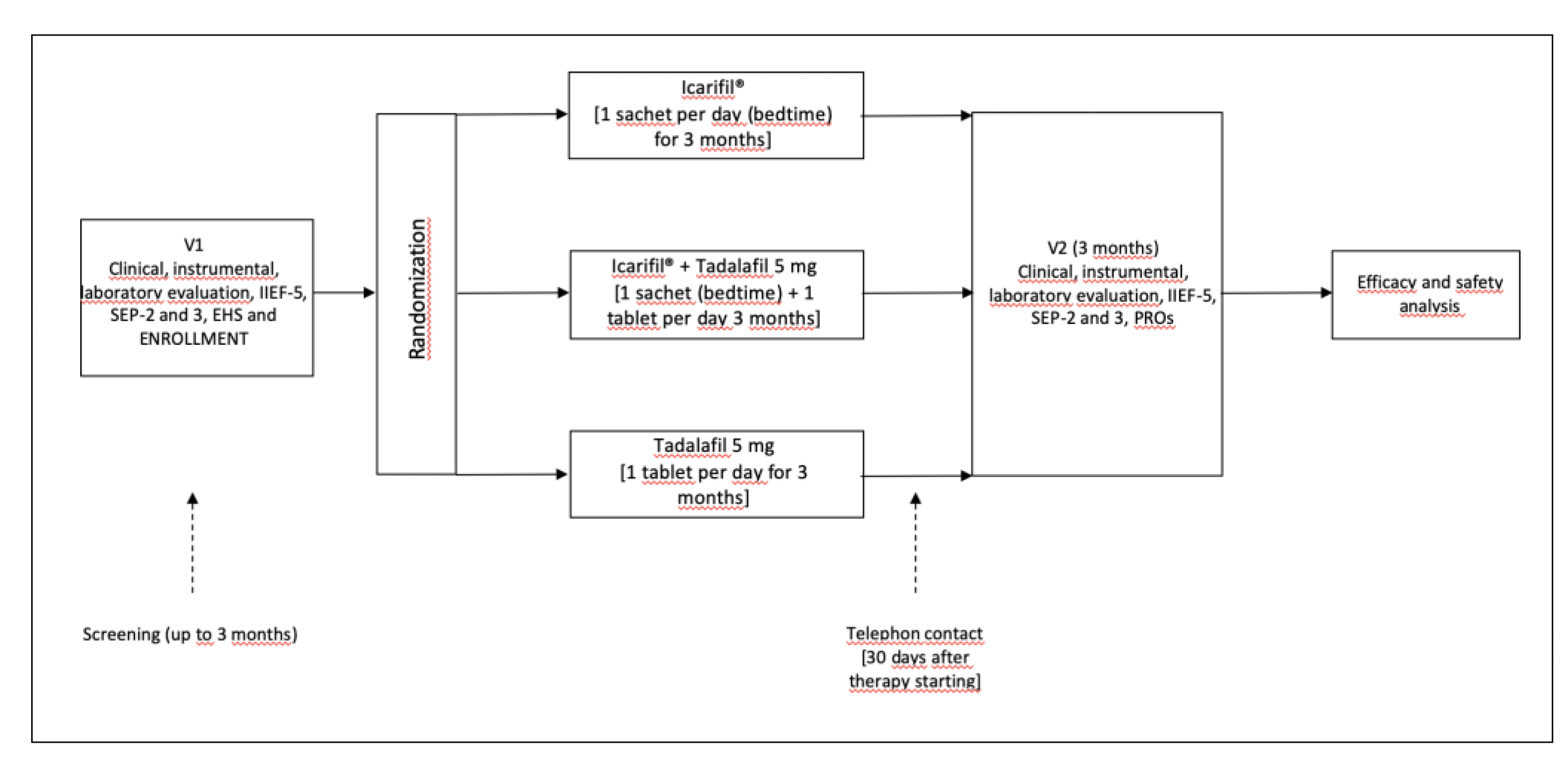
2.1. Study Design and Schedule
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Composition and Characterization of the Extracts Used
2.4. Questionnaires
2.5. Statistical Analysis, Outcome Measures and Ethical Considerations
Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Follow-Up Results
3.3. Patients and Their Partners Reported Outcome (PROs)
3.4. Adverse Effects
Discussion
4.1. Major Finding
4.2. Results in Comparison with Other Studies
4.3. Strengths and Limitations of the Present Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- La Croce, G.; Schifano, N.; Pescatori, E.; Caraceni E.; Colombo, F.; Bettocchi, C.; Carrino, M.; Vitarelli, A.; Pozza, D.; Fiordelise, S.; Varvello, F.; Paradiso, M.; Silvani, M.; Mondaini, N.; Natali, A.; Falcone, M.; Ceruti, C.; Salonia, A.; Antonini, G.; Cai, T.; Palmieri, A.; Dehò, F.; Capogrosso, P. Which patient may benefit the most from penile prosthesis implantation? Andrology 2022, 10(8):1567-1574. [CrossRef]
- Yafi, F.A.; Jenkins, L.; Albersen, M.; Corona, G.; Isidori, A.M.; Goldfarb, S.; Maggi, M.; Nelson, C.J.; Parish, S.; Salonia, A.; Tan, R.; Mulhall, J.P.; Hellstrom, W.J. Erectile dysfunction. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2016, 2:16003. PMID: 27188339; PMCID: PMC5027992. [CrossRef]
- Shamloul, R.; Ghanem, H. Erectile dysfunction. Lancet 2013, 381(9861):153–165. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.W.; Fugl-Meyer, K.S.; Corona, G.; Hayes, R.D.; Laumann, E.O.; Moreira, E.D. Jr.; Rellini, A.H.; Segraves, T. Definitions/epidemiology/risk factors for sexual dysfunction. J Sex Med 2010, 7(4 Pt 2):1598-607. PMID: 20388160. [CrossRef]
- https://www.marketdataforecast.com/market-reports/pde-inhibitors-market-revenue. Access on 3th, Febraury, 2024.
- Salonia, A.; Bettocchi, C.; Boeri, L.; Capogrosso, P.; Carvalho, J.; Cilesiz, N.C.; Cocci, A.; Corona, G.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Gül, M.; Hatzichristodoulou, G.; Jones, T.H.; Kadioglu, A.; Martínez Salamanca, J.I.; Milenkovic, U.; Modgil, V.; Russo, G.I.; Serefoglu, E.C.; Tharakan, T.; Verze, P.; Minhas, S.; EAU Working Group on Male Sexual and Reproductive Health. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Sexual and Reproductive Health-2021 Update: Male Sexual Dysfunction. Eur Urol 2021, 80(3):333-357. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, J.; Song, G.; Feng, Y.; Pan, J.; Yang, X.; Xin, Z.; Hu, P.; Sun, T.; Liu, K.; Xu, W.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Ruan, Y. Acetyl-L-carnitine improves erectile function in bilateral cavernous nerve injury rats via promoting cavernous nerve regeneration. Andrology 2022, 10(5):984-996. Epub 2022 May 1. PMID: 35420721.Gingseng. [CrossRef]
- Nobili, S.; Lucarini, E.; Murzilli, S.; Vanelli, A.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Ghelardini, C. Efficacy Evaluation of Plant Products in the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction Related to Diabetes. Nutrients 2021, 13(12):4520. PMID: 34960072; PMCID: PMC8707335. [CrossRef]
- Ștefănescu, R.; Farczadi, L.; Huțanu, A.; Ősz, B.E.; Mărușteri, M.; Negroiu, A.; Vari, C.E. Tribulus terrestris Efficacy and Safety Concerns in Diabetes and Erectile Dysfunction, Assessed in an Experimental Model. Plants (Basel) 2021, 10(4):744. PMID: 33920217; PMCID: PMC8069229. [CrossRef]
- Amante, C.; De Soricellis, C.; Luccheo, G.; Di Vernieri, A.; Luccheo, L.; Falcone, G.; Del Gaudio, P. Icarifil, a Natural Mixture Based on L-Citrulline and L-Carnitine as a Novel Multicomponent Nutraceutical to Modulate ROS and PDE5. Appl Sci 2023, 13, 12358. [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ 2010, 340:c332. PMID: 20332509; PMCID: PMC2844940. [CrossRef]
- Cappelleri, J.C.; Rosen, R.C.; Smith, M.D.; Mishra, A.; Osterloh, I.H. Diagnostic evaluation of the erectile function domain of the International Index of Erectile Function. Urology 1999, 54:346–351.
- Tang, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Yi, L.; Zhu, X.; Zeng, X.; Tang, Y. Comparison of the simplified International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) in patients of erectile dysfunction with different pathophysiologies. BMC Urol 2014, 14:52. PMID: 24996819; PMCID: PMC4094415. [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.B.; Allen, K.R.; Ni, X.; Rosen, R.C. Minimal clinically import-ant differences in the vaginal insertion and successful intercourse items of the sexual encounter profile. J Sex Med 2012, 9(1):169-179. [CrossRef]
- Rosen, R.C.; Riley, A.; Wagner, G.; Osterloh, I.H.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Mishra, A. The international index of erectile function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology 1997, 49(6):822-30. PMID: 9187685. [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, I.; Lue, T.F.; Padma-Nathan, H.; Rosen, R.C.; Steers, W.D.; Wicker, P.A. Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Sildenafil Study Group. N Engl J Med 1998, 338(20):1397-404. [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Palumbo, F.; Liguori, G.; Mondaini, N.; Scroppo, F.I.; Di Trapani, D.; Cocci, A.; Zucchi, A.; Verze, P.; Salonia, A.; Palmieri, A. The intra-meatal application of alprostadil cream (Vitaros®) improves drug efficacy and patient's satisfaction: results from a randomized, two-administration route, cross-over clinical trial. Int J Impot Res 2019, 31(2):119-125. Epub 2018 Oct 15. PMID: 30323234. [CrossRef]
- Rhim, H.C.; Kim, M.S.; Park, Y.-J.; Choi, W.S.; Park, H.K.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, A.; Paick, S.H. The potential role of arginine supplements on erectile dysfunction: A systemic review and meta-analysis. J Sex Med 2019, 16, 223–234.
- Trinchieri, M.; Perletti, G.; Magri, V.; Stamatiou, K.; Cai, T.; Montanari, E.; Trinchieri, A. Erectile and Ejaculatory Dysfunction Associated with Use of Psychotropic Drugs: A Systematic Review. J Sex Med 2021, 18(8):1354-1363. Epub 2021 Jul 8. PMID: 34247952. [CrossRef]
- Aguayo, E.; Martínez-Sánchez, A.; Fernández-Lobato, B.; Alacid, F. L-Citrulline: A Non-Essential Amino Acid with Important Roles in Human Health. Appl Sci 2021, 11, 3293.
- Cormio, L.; De Siati, M.; Lorusso, F.; Selvaggio, O.; Mirabella, L.; Sanguedolce, F.; Carrieri, G. Oral L-citrulline supplementation improves erection hardness in men with mild erectile dysfunction. Urology 2011, 77, 119–122.
- Choi, Y.D.; Park, C.W.; Jang, J.; Kim, S.H.; Jeon, H.Y.; Kim, W.G.; Lee, S.J.; Chung, W.S. Effects of Korean ginseng berry extract on sexual function in men with erectile dysfunction: A multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical study. Int J Impot Res 2013, 25, 45–50.
- Ciccone, V.; Piragine, E.; Gorica, E.; Citi, V.; Testai, L.; Pagnotta, E.; Matteo, R.; Pecchioni, N.; Montanaro, R.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of the Natural H2S-Donor Erucin in Vascular Endothelium. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 15593.
- Jupiter, R.C.; Yoo, D.; Pankey, E.A.; Reddy, V.V.; Edward, J.A.; Polhemus, D.J.; Peak, T.C.; Katakam, P.; Kadowitz, P.J. Analysis of erectile responses to H2S donors in the anesthetized rat. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2015, 309, H835–H843.
- Gauthaman, K.; Ganesan, A.P.; Prasad, R.N.V. Sexual Effects of Puncturevine (Tribulus terrestris) Extract (Protodioscin): An Evaluation Using a Rat Model. J Altern Complement Med 2003, 9, 257–265.
- Porst, H.; Brock, G.B.; Kula, K.; Moncada, I.; Montorsi, F.; Basson, B.R.; Kinchen, K.; Aversa, A. Effects of once-daily tadalafil on treatment satisfaction, psychosocial outcomes, spontaneous erections, and measures of endothelial function in men with erectile dysfunction but naive to phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors. J Androl 2012, 33(6):1305-22. Epub 2012 Jul 12. PMID: 22790642. [CrossRef]
- Mirone, V.; Napolitano, L.; D'Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Mitidieri, E.; Sorrentino, R.; Vanelli, A.; Vanacore, D.; Turnaturi, C.; La Rocca, R.; Celentano, G.; Arcaniolo, D.; Cirino, G. A new original nutraceutical formulation ameliorates the effect of Tadalafil on clinical score and cGMP accumulation. Arch Ital Urol Androl 2021, 93(2):221-226. PMID: 34286560. [CrossRef]
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | ||
| p | ||||
| Number of enrolled patients | 51 | 50 | 51 | |
| Age (years) | 0.71 | |||
| Median (IQR †) | 51 (42-67) | 53 (43-66) | 53 (42-69) | |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 0.72 | |||
| Median (IQR †) | 28 (26-30) | 27 (25–30) | 27 (26–31) | |
| Charlson Comorbidity index (CCI) | 0.12 | |||
| 0 | 49 (96.1) | 48 (96.0) | 50 (98.1) | |
| 1 | 2 (3.9) | 2 (4.0) | 1 (1.9) | |
| 2 | 0 (-) | 0 (-) | 0 (-) | |
| Number of sexual partners | 0.37 | |||
| 1 | 41 (80.3) | 39 (76.4) | 40 (78.4) | |
| 2 or more | 10 (19.7) | 11 (23.6) | 11 (22.6) | |
| Sexual partners age | 0.84 | |||
| Median (IQR †) | 48 (39-65) | 48 (38-66) | 49 (39-67) | |
| Duration of erectile dysfunction (months) | 0.91 | |||
| Median (IQR †) | 7 (6-9) | 8 (6-9) | 8 (6-9) | |
| Etiology of the disease | 0.09 | |||
| Organic | 5 (9.8) | 4 (8.0) | 5 (9.8) | |
| Psycogenic | 18 (35.3) | 20 (40.0) | 19 (37.2) | |
| Mixed | 28 (54.9) | 26 (52.0) | 27 (53.0) | |
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | |||||
| p | |||||||
| Baseline | Follow-up | Baseline | Follow-up | Baseline | Follow-up | ||
| IIEF-5 |
<0.001* 0.82# |
||||||
| Median (IQR †) | 15 (13-15) | 19 (18-21) | 14 (13-15) | 23 (21-25) | 14 (13-15) | 22 (21-25) | |
| p | <0.003 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| SEP-2 |
<0.001* <0.001# |
||||||
| Positive response (%) | 19 (37.2) | 29 (56.9) | 19 (38.0) | 47 (94.0) | 20 (39.2) | 42 (82.3) | |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| SEP-3 |
<0.001* <0.001# |
||||||
| Positive response (%) | 11 (21.5) | 30 (58.8) | 13 (26.0) | 47 (94.0) | 12 (23.5) | 43 (84.3) | |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| EHS |
<0.001* 0.09# |
||||||
| Median (IQR †) | 2 (1-3) | 3 (3) | 2 (1-3) | 4 (3-4) | 2 (1-3) | 3 (3-4) | |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





