Submitted:
29 March 2024
Posted:
01 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
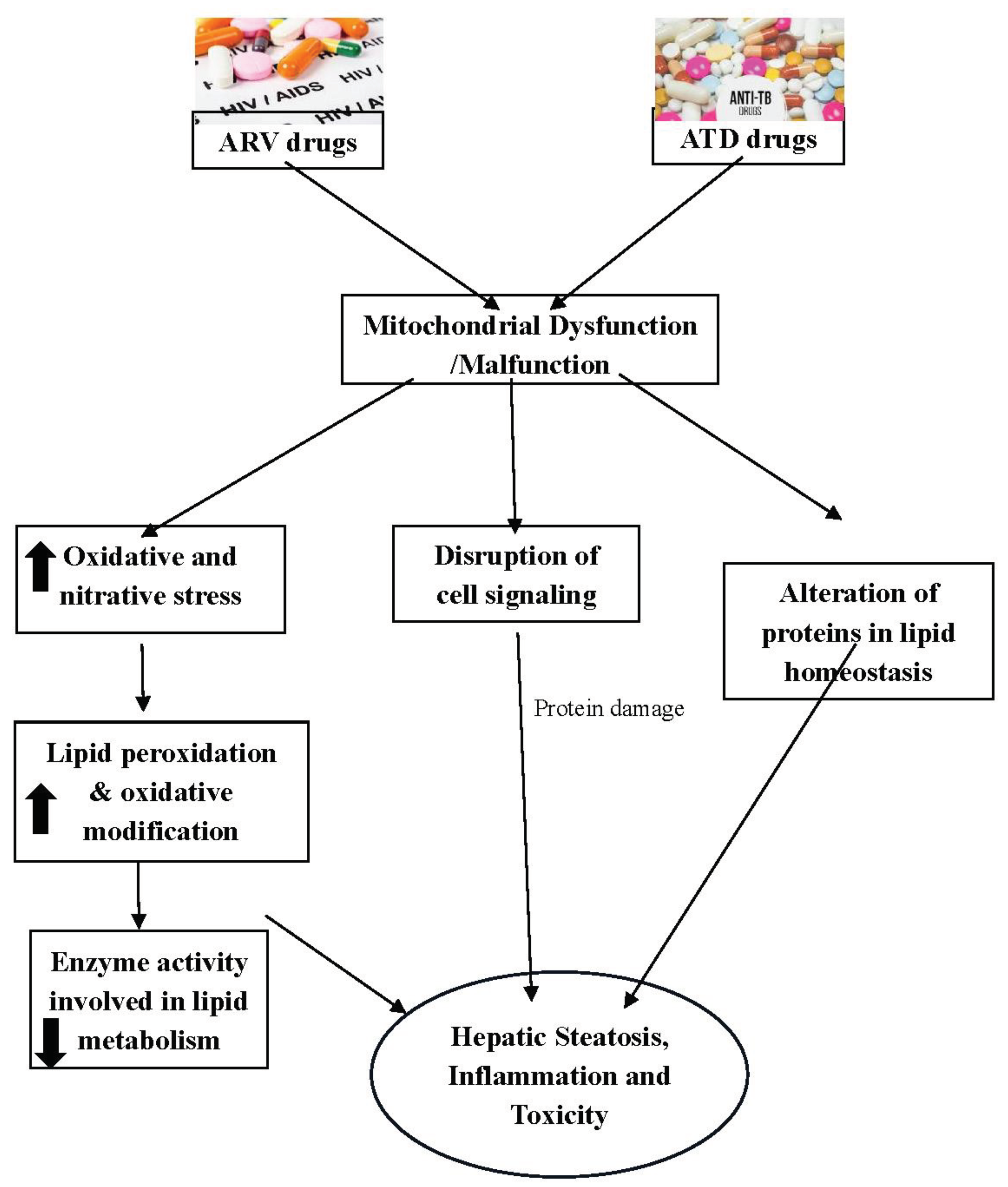
1. Introduction
2. Antiretroviral (ARV) Drugs
2.1. Nucleoside Analogues Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTI)
2.1.1. Zidovudine (AZT)
2.1.2. Lamivudine (3TC)
2.1.3. Stavudine (d4T)
2.2. Non-Nucleoside Analogues Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTI)
2.2.1 Nevirapine (NVP)
2.2.2. Efavirenz (EFV)
2.3. Protease Inhibitors (PIs)
2.3.1. Ritonavir/Lopinavir
3. ARV Induced Hepatotoxicity
4. Antitubercular (ATD) Drugs
4.1. Isoniazid (INH)
4.2. Rifampicin (RIF)
4.3. Pyrazinamide (PYR)
5. ATDs Induced Hepatotoxicity
6. HIV/AIDS Co-Infection with TB in Humans and Use of AZT and INH for Therapy
7. Herbal Medicine as Alternative for Drugs Induced Hepatotoxicity
8. Conclusion
References
- Singh, O.; Garg, T.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.K. Microbicides for the Treatment of Sexually Transmitted HIV Infections. J Pharm (Cairo) 2014, 2014, 352425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplowitz, N. Biochemical and Cellular Mechanisms of Toxic Liver Injury. Semin Liver Dis 2002, 22, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, H.J. Drug-Induced Liver Disease. Clin Liver Dis 2000, 4, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Diaz, M.; Lucena, M.I.; Kaplowitz, N.; Stephens, C.; Medina-Cáliz, I.; González-Jimenez, A.; Ulzurrun, E.; Gonzalez, A.F.; Fernandez, M.C.; Romero-Gómez, M.; et al. Use of Hy’s Law and a New Composite Algorithm to Predict Acute Liver Failure in Patients with Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 109–118.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Fang, J.-J.; Xu, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-X. Evaluation of Prognostic Markers in Severe Drug-Induced Liver Disease. World J Gastroenterol 2007, 13, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, H.J. Hepatotoxicity. Dis Mon 1993, 39, 675–787. [Google Scholar]
- Organization, WH. HIV/AIDS. Geneva. 2020 [Accessed on 2024 Mar 24]. Available from: Https://Www.Who.
- Girardi, E.; Sabin, C.A.; d’Arminio Monforte, A.; Hogg, B.; Phillips, A.N.; Gill, M.J.; Dabis, F.; Reiss, P.; Kirk, O.; Bernasconi, E.; et al. Incidence of Tuberculosis among HIV-Infected Patients Receiving Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy in Europe and North America. Clin Infect Dis 2005, 41, 1772–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 9. World Health Organization. GLOBAL TB REPORT 2016 WITH HIV + TB, 2016.
- Onyebujoh, P. An Evaluation of the Impact of Early Initiation of Highly Active Anti-Retroviral Therapy (HAART) on Tuberculosis (TB) Treatment Outcomes for TB Patients Co-Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) 2014.
- Raghu, R.; Karthikeyan, S. Zidovudine and Isoniazid Induced Liver Toxicity and Oxidative Stress: Evaluation of Mitigating Properties of Silibinin. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2016, 46, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahid, P.; Dorman, S.E.; Alipanah, N.; Barry, P.M.; Brozek, J.L.; Cattamanchi, A.; Chaisson, L.H.; Chaisson, R.E.; Daley, C.L.; Grzemska, M.; et al. Official American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guidelines: Treatment of Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis 2016, 63, e147–e195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, R.; Sivanesan, K. Evaluation of Ameliorative Ability of Silibinin against Zidovudine and Isoniazid-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Hyperlipidaemia in Rats: Role of Silibinin in Phase I and II Drug Metabolism. Chem Biol Interact 2017, 273, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, I. Adverse Effects of Antiretroviral Therapy in HIV-1 Infected Children. J Trop Pediatr 2006, 52, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, R.; Jesudas, B.; Bhavani, G.; Ezhilarasan, D.; Karthikeyan, S. Silibinin Mitigates Zidovudine-Induced Hepatocellular Degenerative Changes, Oxidative Stress and Hyperlipidaemia in Rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 2015, 34, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hest, R.; Baars, H.; Kik, S.; van Gerven, P.; Trompenaars, M.-C.; Kalisvaart, N.; Keizer, S.; Borgdorff, M.; Mensen, M.; Cobelens, F. Hepatotoxicity of Rifampin-Pyrazinamide and Isoniazid Preventive Therapy and Tuberculosis Treatment. Clin Infect Dis 2004, 39, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, D.; Valiquette, C.; Pelletier, M.; Parisien, I.; Rocher, I.; Menzies, D. Incidence of Serious Side Effects from First-Line Antituberculosis Drugs among Patients Treated for Active Tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003, 167, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awodele, O.; Agbaje, E.O.; Adesina, E.A.; Akintonwa, A. Hepatoprotective Role of neutrosecR on Hepatic Damage Induced by Combination of Zidovudine and Combined Anti-Tuberculous Agents in Rats. Tokai J Exp Clin Med 2011, 36, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dean, G.L.; Edwards, S.G.; Ives, N.J.; Matthews, G.; Fox, E.F.; Navaratne, L.; Fisher, M.; Taylor, G.P.; Miller, R.; Taylor, C.B.; et al. Treatment of Tuberculosis in HIV-Infected Persons in the Era of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy. AIDS 2002, 16, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palella, F.J.; Delaney, K.M.; Moorman, A.C.; Loveless, M.O.; Fuhrer, J.; Satten, G.A.; Aschman, D.J.; Holmberg, S.D. Declining Morbidity and Mortality among Patients with Advanced Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 1998, 338, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischl, M.A.; Richman, D.D.; Grieco, M.H.; Gottlieb, M.S.; Volberding, P.A.; Laskin, O.L.; Leedom, J.M.; Groopman, J.E.; Mildvan, D.; Schooley, R.T. The Efficacy of Azidothymidine (AZT) in the Treatment of Patients with AIDS and AIDS-Related Complex. A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. N Engl J Med 1987, 317, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, C.V.; Anderson, P.L.; Kakuda, T.N.; Schacker, T.W.; Henry, K.; Gross, C.R.; Brundage, R.C. Concentration-Controlled Compared with Conventional Antiretroviral Therapy for HIV Infection. AIDS 2002, 16, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasela, C.S.; Hudgens, M.G.; Jamieson, D.J.; Kayira, D.; Hosseinipour, M.C.; Kourtis, A.P.; Martinson, F.; Tegha, G.; Knight, R.J.; Ahmed, Y.I.; et al. Maternal or Infant Antiretroviral Drugs to Reduce HIV-1 Transmission. N Engl J Med 2010, 362, 2271–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.; Day, B.J.; Copeland, W.C. Mitochondrial Toxicity of NRTI Antiviral Drugs: An Integrated Cellular Perspective. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2003, 2, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, S.M.; Walker, D.M.; Carter, M.M.; Cook, D.L.; McCash, C.L.; Cordova, E.M.; Olivero, O.A.; Poirier, M.C.; Walker, V.E. Mutagenicity of Zidovudine, Lamivudine, and Abacavir Following in Vitro Exposure of Human Lymphoblastoid Cells or in Utero Exposure of CD-1 Mice to Single Agents or Drug Combinations. Environ Mol Mutagen 2007, 48, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Leeuwen, R.; Katlama, C.; Kitchen, V.; Boucher, C.A.; Tubiana, R.; McBride, M.; Ingrand, D.; Weber, J.; Hill, A.; McDade, H. Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of 3TC (Lamivudine) in Patients with Asymptomatic or Mildly Symptomatic Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection: A Phase I/II Study. J Infect Dis 1995, 171, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, C.M.; Faulds, D. Lamivudine. A Review of Its Antiviral Activity, Pharmacokinetic Properties and Therapeutic Efficacy in the Management of HIV Infection. Drugs 1997, 53, 657–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaniyan, L.W.B.; Maduagwu, E.N.; Akintunde, O.W.; Oluwayelu, O.O.; Brai, B.I.C. Lamivudine-Induced Liver Injury. Open Access Maced J Med Sci 2015, 3, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerschenson, M.; Nguyen, V.T.; St Claire, M.C.; Harbaugh, S.W.; Harbaugh, J.W.; Proia, L.A.; Poirier, M.C. Chronic Stavudine Exposure Induces Hepatic Mitochondrial Toxicity in Adult Erythrocebus Patas Monkeys. J Hum Virol 2001, 4, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lea, A.P.; Faulds, D. Stavudine: A Review of Its Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Properties and Clinical Potential in HIV Infection. Drugs 1996, 51, 846–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johri, S.; Alkhuja, S.; Siviglia, G.; Soni, A. Steatosis-Lactic Acidosis Syndrome Associated with Stavudine and Lamivudine Therapy. AIDS 2000, 14, 1286–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraj, E.; Mohan, S.; Ramanathan, R. HAART and Hepatotoxicity. J App Pharma Sci 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European AIDS Clinical Society (EACS) Guidelines for the Treatment of Adult HIV-Positive Persons. Version 10.1. October 2020.
- Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults and Adolescents with HIVS.
- Reliquet, V.; Allavena, C.; Morineau-Le Houssine, P.; Mounoury, O.; Raffi, F. Twelve-Year Experience of Nevirapine Use: Benefits and Convenience for Long-Term Management in a French Cohort of HIV-1-Infected Patients. HIV Clin Trials 2010, 11, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boissieu, P.; Dramé, M.; Raffi, F.; Cabie, A.; Poizot-Martin, I.; Cotte, L.; Garraffo, R.; Delobel, P.; Huleux, T.; Rey, D.; et al. Long-Term Efficacy and Toxicity of Abacavir/Lamivudine/Nevirapine Compared to the Most Prescribed ARV Regimens before 2013 in a French Nationwide Cohort Study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitti, J.; Frenkel, L.M.; Stek, A.M.; Nachman, S.A.; Baker, D.; Gonzalez-Garcia, A.; Provisor, A.; Thorpe, E.M.; Paul, M.E.; Foca, M.; et al. Maternal Toxicity With Continuous Nevirapine in Pregnancy: Results From PACTG 1022. JAIDS Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 2004, 36, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Gui, X.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, K.; Yang, R.; Yan, Y.; Rong, Y. Antiretroviral Therapy Hepatotoxicity: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Clinical Characteristics in a Cohort of Han Chinese. Hepatology Research 2010, 40, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.M.; Johnson, S.; Belknap, S.M.; Chan, J.; Sha, B.E.; Bennett, C. Serious Adverse Cutaneous and Hepatic Toxicities Associated with Nevirapine Use by Non-HIV-Infected Individuals. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2004, 35, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajulo, M.O.; Omole, M.K.; Moody, J.O.; Dixon-Umo, O.T.; Salami, O.L. Liver Aminotransferases in Under-Five HIV-Positive Children on HAART. Afr J Med Med Sci 2015, 44, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shenton, J.M.; Teranishi, M.; Abu-Asab, M.S.; Yager, J.A.; Uetrecht, J.P. Characterization of a Potential Animal Model of an Idiosyncratic Drug Reaction: Nevirapine-Induced Skin Rash in the Rat. Chem Res Toxicol 2003, 16, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, Z.; Walubo, A.; du Plessis, J.B. The Role of the Immune System in Nevirapine-Induced Subclinical Liver Injury of a Rat Model. ISRN Pharm 2012, 2012, 932542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.; Roberts, L.R.; Jones, B.A.; Gores, G.J. Dysregulation of Apoptosis as a Mechanism of Liver Disease: An Overview. Semin Liver Dis 1998, 18, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M.P.; Lowe, C.M.; Tian, X.; Bourdet, D.L.; Ho, R.H.; Leake, B.F.; Kim, R.B.; Brouwer, K.L.R.; Kashuba, A.D.M. Ritonavir, Saquinavir, and Efavirenz, but Not Nevirapine, Inhibit Bile Acid Transport in Human and Rat Hepatocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2006, 318, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.; Ona, M.A.; Papafragkakis, H.; Carey, J.; Moshenyat, Y.; Alhaddad, A.; Anand, S. Acute Liver Toxicity Due to Efavirenz/Emtricitabine/Tenofovir. Case Reports Hepatol 2015, 2015, 280353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolova, N.; Gomez-Sucerquia, L.J.; Alegre, F.; Funes, H.A.; Victor, V.M.; Barrachina, M.D.; Blas-Garcia, A.; Esplugues, J.V. ER Stress in Human Hepatic Cells Treated with Efavirenz: Mitochondria Again. J Hepatol 2013, 59, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwag, T.; Meng, Z.; Sui, Y.; Helsley, R.N.; Park, S.-H.; Wang, S.; Greenberg, R.N.; Zhou, C. Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor Efavirenz Activates PXR to Induce Hypercholesterolemia and Hepatic Steatosis. Journal of Hepatology 2019, 70, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo, M.; Alegre, F.; Funes, H.A.; Blas-Garcia, A.; Victor, V.M.; Esplugues, J.V.; Apostolova, N. Mitochondrial (Dys)Function - a Factor Underlying the Variability of Efavirenz-Induced Hepatotoxicity? Br J Pharmacol 2015, 172, 1713–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonderup, M.W.; Maughan, D.; Gogela, N.; Setshedi, M.; Wainwright, H.; Meintjes, G.; Spearman, W. Identification of a Novel and Severe Pattern of Efavirenz Drug-Induced Liver Injury in South Africa. AIDS 2016, 30, 1483–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulkowski, M.S.; Thomas, D.L.; Chaisson, R.E.; Moore, R.D. Hepatotoxicity Associated with Antiretroviral Therapy in Adults Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus and the Role of Hepatitis C or B Virus Infection. JAMA 2000, 283, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiodras, S.; Mantzoros, C.; Hammer, S.; Samore, M. Effects of Protease Inhibitors on Hyperglycemia, Hyperlipidemia, and Lipodystrophy: A 5-Year Cohort Study. Arch Intern Med 2000, 160, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, C.-C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, P.-C.; Gao, F.-F.; Bu, L.; Wen, X.-M.; Xiang, Q.-M.; Song, H.; Li, Q.; Wei, L.; et al. Ritonavir-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Ultrastructural Changes of Hepatocytes. Ultrastruct Pathol 2014, 38, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mchunu, G.; van Griensven, J.; Hinderaker, S.G.; Kizito, W.; Sikhondze, W.; Manzi, M.; Dlamini, T.; Harries, A.D. High Mortality in Tuberculosis Patients despite HIV Interventions in Swaziland. Public Health Action 2016, 6, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.; Riek, M.; Winters, K.; Schutz, M.; Grange, S. Unexpected Hepatotoxicity of Rifampin and Saquinavir/Ritonavir in Healthy Male Volunteers. Arch Drug Inf 2009, 2, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, G.W.; Jayaweera, D.; Sherman, K.E. Drug-Induced Liver Injury in HIV Patients. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2006, 2, 430–437. [Google Scholar]
- Benedicto, A.M.; Fuster-Martínez, I.; Tosca, J.; Esplugues, J.V.; Blas-García, A.; Apostolova, N. NNRTI and Liver Damage: Evidence of Their Association and the Mechanisms Involved. Cells 2021, 10, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortgang, I.S.; Belitsos, P.C.; Chaisson, R.E.; Moore, R.D. Hepatomegaly and Steatosis in HIV-Infected Patients Receiving Nucleoside Analog Antiretroviral Therapy. Am J Gastroenterol 1995, 90, 1433–1436. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, E.; Blanco, J.L.; Arnaiz, J.A.; Pérez-Cuevas, J.B.; Mocroft, A.; Cruceta, A.; Marcos, M.A.; Milinkovic, A.; García-Viejo, M.A.; Mallolas, J.; et al. Hepatotoxicity in HIV-1-Infected Patients Receiving Nevirapine-Containing Antiretroviral Therapy. AIDS 2001, 15, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wit, F.W.N.M.; Weverling, G.J.; Weel, J.; Jurriaans, S.; Lange, J.M.A. Incidence of and Risk Factors for Severe Hepatotoxicity Associated with Antiretroviral Combination Therapy. J Infect Dis 2002, 186, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chariot, P.; Drogou, I.; de Lacroix-Szmania, I.; Eliezer-Vanerot, M.C.; Chazaud, B.; Lombès, A.; Schaeffer, A.; Zafrani, E.S. Zidovudine-Induced Mitochondrial Disorder with Massive Liver Steatosis, Myopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Mitochondrial DNA Depletion. J Hepatol 1999, 30, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradon, J.D.; Chapnick, E.K.; Sepkowitz, D.V. Zidovudine-Induced Hepatitis. J Intern Med 1992, 231, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcuera, T.; Alonso, M.J.; Picazo, A.; Gómez, F.; Roldán, M.; Abad, M.; Muñoz, E.; López-Bravo, A. Hepatic Morphological Alterations Induced by Zidovudine (ZDV) in an Experimental Model. Pathol Res Pract 1996, 192, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 63. Global Tuberculosis Report 2021.[Accessed on 2024 Mar 24]. Available from: Https://Www.Who.Int/Publications/i/Item/9789240037021.
- 64. Global Tuberculosis Control : Surveillance, Planning, Financing : WHO Report 2007. [Accessed on 2024 Mar 24]. Available from:Https://Www.Who.Int/Publications/i/Item/9789241563141.
- Anand, A.C.; Seth, A.K.; Paul, M.; Puri, P. Risk Factors of Hepatotoxicity During Anti-Tuberculosis Treatment. Med J Armed Forces India 2006, 62, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhvaryu, M.R.; Reddy, N.; Vakharia, B.C. Prevention of Hepatotoxicity Due to Anti Tuberculosis Treatment: A Novel Integrative Approach. World J Gastroenterol 2008, 14, 4753–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasin, F.P.; Perrier, A.; Rochat, T. Isoniazid Preventive Therapy for Pulmonary Tuberculosis Sequelae: Which Patients up to Which Age? Tuber Lung Dis 1995, 76, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israel, H.L.; Gottlieb, J.E.; Maddrey, W.C. Perspective: Preventive Isoniazid Therapy and the Liver. Chest 1992, 101, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunberg, E.; Schnitzer, R.J. Studies on the Activity of Hydrazine Derivatives of Isonicotinic Acid in the Experimental Tuberculosis of Mice. Q Bull Sea View Hosp 1952, 13, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steenken, W.; Wolinsky, E. Antituberculous Properties of Hydrazines of Isonicotinic Acid (Rimifon, Marsilid). Am Rev Tuberc 1952, 65, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robitzek, E.H.; Selikoff, I.J. Hydrazine Derivatives of Isonicotinic Acid (Rimifon Marsilid) in the Treatment of Active Progressive Caseous-Pneumonic Tuberculosis; a Preliminary Report. Am Rev Tuberc 1952, 65, 402–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilchèze, C.; Morbidoni, H.R.; Weisbrod, T.R.; Iwamoto, H.; Kuo, M.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Jacobs, W.R. Inactivation of the inhA-Encoded Fatty Acid Synthase II (FASII) Enoyl-Acyl Carrier Protein Reductase Induces Accumulation of the FASI End Products and Cell Lysis of Mycobacterium Smegmatis. J Bacteriol 2000, 182, 4059–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, H.; Dhamothrasamy, K.; Duraisamy, K.; Dhanasekaran, M. Isoniazid-Induced Hepatic Injury: A Case Report and Its Mechanism of Liver Injury. J Adv Pharm Educ Res 2022, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, C.M.; Goldberg, S.V.; Buskin, S.E. Hepatotoxicity Associated with Isoniazid Preventive Therapy: A 7-Year Survey from a Public Health Tuberculosis Clinic. JAMA 1999, 281, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fueresz, S.; Timbal, M.T. ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF RIFAMYCINS. Chemotherapia (Basel) 1963, 257, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosset, J.; Leventis, S. Adverse Effects of Rifampin. Rev Infect Dis 1983, 5 Suppl 3, S440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Update: Fatal and Severe Liver Injuries Associated with Rifampin and Pyrazinamide for Latent Tuberculosis Infection, and Revisions in American Thoracic Society/CDC Recommendations--United States, 2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2001, 50, 733–735.
- McNeill, L.; Allen, M.; Estrada, C.; Cook, P. Pyrazinamide and Rifampin vs Isoniazid for the Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis: Improved Completion Rates but More Hepatotoxicity. Chest 2003, 123, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, J.E.; Engemann, J.J.; Cheng, A.C.; Fortenberry, E.R.; Hamilton, C.D. Safety of 2 Months of Rifampin and Pyrazinamide for Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003, 167, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Zhu, J.; Ma, X. Metabolism and Hepatotoxicity of Pyrazinamide, an Antituberculosis Drug. Drug Metab Dispos 2021, 49, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, S.; Gu, R.; Ma, X. Clinical Perspectives of Isoniazid-Induced Liver Injury. Liver Research 2021, 5, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramappa, V.; Aithal, G.P. Hepatotoxicity Related to Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs: Mechanisms and Management. J Clin Exp Hepatol 2013, 3, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipose, J.; Suchman, K.I.; Aronsky, D.; Lee, T.-P. A Case of Acute Liver Failure in a Patient on Isoniazid Prophylaxis for Latent Tuberculosis. Cureus 2022, 14, e22452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakouti, M.; Kataria, A.; Ali, S.K.; Schenker, S. Elevated Liver Enzymes in Asymptomatic Patients - What Should I Do? J Clin Transl Hepatol 2017, 5, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, A.W.; Allan, G.W.; Smith, J.; Tyrrell, W.F.; Fallon, R.J. Toxicity Form Rifampicin plus Isoniazid and Rifampicin plus Ethambutol Therapy. Tubercle 1971, 52, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilheu, J.A.; de Salvo, M.C.; Koch, O.; Barcat, J.A. [Light and electron microscopy studies of the liver in tuberculosis patients receiving rifampin and isoniazid]. Medicina (B Aires) 1981, 41, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.M. Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity. N Engl J Med 1995, 333, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, G.R.; Immanuel, C.; Kailasam, S.; Narayana, A.S.; Venkatesan, P. Rifampin-Induced Release of Hydrazine from Isoniazid. A Possible Cause of Hepatitis during Treatment of Tuberculosis with Regimens Containing Isoniazid and Rifampin. Am Rev Respir Dis 1986, 133, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tostmann, A.; Boeree, M.J.; Peters, W.H.M.; Roelofs, H.M.J.; Aarnoutse, R.E.; van der Ven, A.J.A.M.; Dekhuijzen, P.N.R. Isoniazid and Its Toxic Metabolite Hydrazine Induce in Vitro Pyrazinamide Toxicity. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2008, 31, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarchoan, R.; Klecker, R.W.; Weinhold, K.J.; Markham, P.D.; Lyerly, H.K.; Durack, D.T.; Gelmann, E.; Lehrman, S.N.; Blum, R.M.; Barry, D.W. Administration of 3’-Azido-3’-Deoxythymidine, an Inhibitor of HTLV-III/LAV Replication, to Patients with AIDS or AIDS-Related Complex. Lancet 1986, 1, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuber, P.L.; McKenna, M.T.; Binkin, N.J.; Onorato, I.M.; Castro, K.G. Long-Term Risk of Tuberculosis among Foreign-Born Persons in the United States. JAMA 1997, 278, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, E.L.; Watt, C.J.; Walker, N.; Maher, D.; Williams, B.G.; Raviglione, M.C.; Dye, C. The Growing Burden of Tuberculosis: Global Trends and Interactions with the HIV Epidemic. Arch Intern Med 2003, 163, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubin, G.; Braffman, M.N. Zidovudine-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Ann Intern Med 1989, 110, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, B.S.; Grimsley, E.W. Zidovudine-Associated Type B Lactic Acidosis and Hepatic Steatosis in an HIV-Infected Patient. South Med J 1999, 92, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R.; Sivanesan, K. Investigations on the Influence of Zidovudine in the Pharmacokinetics of Isoniazid and Its Hepatotoxic Metabolites in Rats. J Pharm Pract 2019, 32, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, J.W.; Michael, B.; Sarah, L.; George, M. Medicinal Plants: Can Utilization and Conservation Coexist?”. In Advances in Economic Botany; 1997; Vol. 12.
- Deng, J.F.; Lin, T.J.; Kao, W.F.; Chen, S.S. The Difficulty in Handling Poisonings Associated with Chinese Traditional Medicine: A Poison Control Center Experience for 1991-1993. Vet Hum Toxicol 1997, 39, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrakumar, A.; Xavier, A.; Xavier, A.; Manakkadiyil, A.; Reghu, A.; Thomas, L. Implications of Traditional Medicine in the Treatment of Hepatitis A in Kerala. J Tradit Complement Med 2016, 6, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangwani, N.; Singh, P.K.; Kumar, V. Medicinal Plants: Adjunct Treatment to Tuberculosis Chemotherapy to Prevent Hepatic Damage. J Ayurveda Integr Med 2020, 11, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, C.L.; Teixeira, M.M.; Adelson, D.L.; Braga, F.C.; Buenz, E.J.; Campana, P.R.V.; David, B.; Glaser, K.B.; Harata-Lee, Y.; Howes, M.-J.R.; et al. Future Directions for the Discovery of Natural Product-Derived Immunomodulating Drugs: An IUPHAR Positional Review. Pharmacological Research 2022, 177, 106076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlade, B.; Jeje, S.O.; Adelakun, S.A.; Akingbade, G.T. Moringa Oleifera Restored Semen Quality, Hormonal Profile, and Testicular Morphology against Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy-Induced Toxicity in Adult Male Wistar Rats. JBRA Assist Reprod 2022, 26, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyang, D.; Sonibare, M.A.; Tchamgoue, A.D.; Tchokouaha, L.R.Y.; Yadang, F.S.; Nfor, G.N.; Kom, C.W.; Betote, P.D.H.; Tchinda, C.F.; Tiogo, S.S.K.; et al. Protective and Ameliorative Effects of Hydroethanolic Extract of Piper Nigrum (L.) Stem against Antiretroviral Therapy-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Dyslipidemia in Wistar Rats. J Toxicol 2024, 2024, 5811080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amujal, M.; Ikwap, K.; Tamale, A.; Tumwine, G.; Kateregga, J.; Wamala, S.P.; Kato, C.D. Hepatoprotective Effect of Cymbopogon Citratus Essential Oils against Nevirapine-Induced Hepatic Damage in Wistar Albino Rats. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 2018, 15, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudie, K.; Daniel, S.; Feyissa, C.; Abiy, A.; Asfaw, D.; Atsbeha, G. Hepatoprotective Activity of Aqueous Seed Extract of Nigella Sativa against Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats. Pharmacology OnLine 2014, 3, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah Jan Panezai; Moosa Khan; Syed Muhammad Ishaque; Raheem Ullah; Ahmad Ali Khan; Noshaba Rahat Variable Doses of Nigella Sativa in Isoniazid Induced Liver Toxicity in Rabbits. Pak Euro. J. Med & LS 2022, 5, 187–194. [CrossRef]
- Sankar, M.; Rajkumar, J.; Sridhar, D. Hepatoprotective Activity of Heptoplus on Isoniazid and Rifampicin Induced Liver Damage in Rats. Indian J Pharm Sci 2015, 77, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswari, S.A.; Chetty, C.M.; Chandrasekhar, K.B. Hepatoprotective Activity of Ficus Religiosa Leaves against Isoniazid+rifampicin and Paracetamol Induced Hepatotoxicity. Pharmacognosy Res 2013, 5, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Suo, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Deng, G.; Feng, T. Hepatoprotective Effects of Malus Hupehensis Tea against Isoniazid- and Rifampicin-Induced Liver Injury by Regulating Cytochrome P450 in Mice. Journal of Functional Foods 2021, 84, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P E, S.K.; Mishra, A.; Mandal, S.; Chawla, S.; Kalra, B.S. Hepatoprotective Potential of Phyllanthus Niruri and Andrographis Paniculata in Isoniazid-Rifampicin Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats. Indian Journal of Tuberculosis 2023, S0019570723002263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubiwak, A.D.; Damtew, T.W.; Senbetu, M.W.; Yewhalaw, D.; Asere, T.G.; Nemo, G.; Baye, M.F. Hepatoprotective Effect of Corm of Ensete Ventricosum (Welw.) Cheesman Extract against Isoniazid and Rifampicin Induced Hepatotoxicity in Swiss Albino Mice. Journal of Toxicology 2021, 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanisamy, N.; Manian, S. Protective Effects of Asparagus Racemosus on Oxidative Damage in Isoniazid-Induced Hepatotoxic Rats: An in Vivo Study. Toxicol Ind Health 2012, 28, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvin, S.S.; Esakkimuthu, S.; Toppo, E.; Balakrishna, K.; Paulraj, M.G.; Pandikumar, P.; Ignacimuthu, S.; Al-Dhabi, N.A. Hepatoprotective Effect of Lawsone on Rifampicin-Isoniazid Induced Hepatotoxicity in in Vitro and in Vivo Models. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 2018, 61, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelapelapon, A.A.; Rohmawaty, E.; Herman, H. Evaluation of The Hepatoprotective Effect of Plantago Major Extract in A Rifampicin-Isoniazid Induced Hepatitis Rat Model. Trends Sci 2023, 20, 6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldkar, C.; Jaiswal, A.; Ganeshpurkar, A.; Dubey, N. Evaluation of Protective Effect of Glycyrrhiza Glabra L. Extract on Isoniazid-Rifampicin Induced Hepatocellular Damage in Rats. PC 2019, 10, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eminzade, S.; Uraz, F.; Izzettin, F.V. Silymarin Protects Liver against Toxic Effects of Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs in Experimental Animals. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2008, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasduq, S.A.; Peerzada, K.; Koul, S.; Bhat, R.; Johri, R.K. Biochemical Manifestations of Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs Induced Hepatotoxicity and the Effect of Silymarin. Hepatol Res 2005, 31, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victorrajmohan, C.; Pradeep, K.; Karthikeyan, S. Influence of Silymarin Administration on Hepatic Glutathione-Conjugating Enzyme System in Rats Treated with Antitubercular Drugs. Drugs R D 2005, 6, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.J.S.J.; Mohan, S.; Chellappan, D.K.; Kalusalingam, A.; Ariamuthu, S. Hibiscus Vitifolius (Linn.) Root Extracts Shows Potent Protective Action against Anti-Tubercular Drug Induced Hepatotoxicity. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2012, 141, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pari, L.; Kumar, N.A. Hepatoprotective Activity of Moringa Oleifera on Antitubercular Drug-Induced Liver Damage in Rats. J Med Food 2002, 5, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Medicinal Plant/active compound | Model and Extract dose | Study findings | Impact on liver | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARV Drugs | ||||
| Silibinin | Wistar albino rats; 100mg/kg b. w; orally | Reduction of liver enzymes, oxidative stress markers, hyperlipidemia and liver histology | Protects liver against AZT induced hepatotoxicity | [15] |
| Moringa Oleifera (MO) | Male wistar rats; 100 and 300 mg/kg MO leaf extract; orally |
Increased antioxidant markers and liver function | Protects against HAART induced hepatotoxicity | [101] |
| Piper Nigrum Stem (PNS) | Male wistar rats; 200, 400 and 600 mg/kg PNS extract; orally |
Reduction in triglycerides and alkaline phosphatase, increase in antioxidant enzymes and histological improvement | Hepatoprotective activity against tenofovir/ lamivudine/efavirenz (TLE)-induced hepatotoxicity and dyslipidemia | [102] |
| Cymbopogon citratus | Wistar albino rats; 200, 400 and 800 mg/kg Cymbopogon citratus oil extract; oral intubation |
Improvement in liver architecture and liver serum biochemistry. | Hepatoprotection activity against Nevirapine induced hepatotoxicity | [103] |
| Nigella Sativa Seed | Wistar albino rats; 100, 200, 400 and 800 mg/kg Nigella sativa aqueous extract; oral intubation |
Improvement in liver histology and liver biochemistry. | Hepatoprotection activity against AZT, 3TC and EFV induced hepatotoxicity | [104] |
| ATD Drugs | ||||
| Nigella Sativa | Oryctolagus cuniculus Rabbits; 500 and 1000 mg/kg orally |
Improvement in liver biochemistry. | Hepatoprotection activity against INH induced hepatotoxicity | [105] |
| Heptoplus (Polyherbal formulation) | Sprague Dawely rats; 50 and 100 mg/kg b. w; orally |
Improvement in liver biochemistry, antioxidant and histology. | Hepatoprotection activity against INH and RIF induced hepatotoxicity | [106] |
| Ficus religiosa (Moraceae) | Male Wistar albino rats; 100, 200 and 300 mg/kg b. w; p.o extract | Improvement in liver marker enzymes, antioxidant and histology. | Hepatoprotection activity against INH and RIF induced hepatotoxicity | [107] |
| Malus hupehensis (MHE) | Kunming male mice; 30, 60 and 120 mg/kg b. w; p.o of methanolic extract | Improvement in liver serum markers, antioxidant and histology. | Hepatoprotection activity against INH and RIF induced hepatotoxicity | [108] |
| Phyllanthus niruri and Andrographis paniculata | Sprague Dawley rats; 125 mg/kg b. w; p.o | Improvement in liver serum markers, antioxidant and histology. | Hepatoprotection activity against INH and RIF induced hepatotoxicity | [109] |
| Corn of Ensete Ventricosum (Welw) cheesman extract | Swiss albino mice; 200 and 400 mg/kg b. w; p.o | Improvement in liver serum markers, antioxidant and histology. | Hepatoprotection activity against INH and RIF induced hepatotoxicity | [110] |
| Asparagus racemosus extract | Male albino rats; 50 mg/kg b. w; p.o | Improvement in liver serum markers, antioxidant and histology. | Hepatoprotection activity against INH induced hepatotoxicity | [111] |
| Lawsonia inermis | Male wistar rats; 50 and 100 mg/kg b. w; intraperitoneal | Improvement in liver serum markers, antioxidant and histology. | Hepatoprotection activity against INH and RIF induced hepatotoxicity | [112] |
| Plantago major extract | Male wistar rats; 20.3, 40.5 and 81 mg/kg b. w; p.o | Improvement in liver serum markers, antioxidant and histology. | Hepatoprotection activity against INH and RIF induced hepatotoxicity | [113] |
| Glycyrrhiza glabra L. Extract | Wistar rats; 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg b. w; p.o | Improvement in liver serum markers, antioxidant and histology. | Hepatoprotection activity against INH and RIF induced hepatotoxicity | [114] |
| Silibinin | Wistar albino rats; 100mg/kg b. w; orally | Reduction of liver enzymes, oxidative stress markers, hyperlipidemia and liver histology | Protects liver against INH + AZT induced hepatotoxicity | [11,13] |
| Silymarin | Male Wistar albino rats; 200mg/kg b. w; intra-gastric administration | Reduction of liver enzymes, oxidative stress markers and liver histology | Protects liver against INH + RIF + PYR induced hepatotoxicity | [115,116,117] |
| Hibiscus Vitifolius (Linn.) root extract | Wistar albino rats; 400mg/kg b. w; orally | Reduction of liver enzymes, oxidative stress markers, hyperlipidemia and liver histology | Protects liver against INH + AZT induced hepatotoxicity | [118] |
| Moringa Oleifera (MO) extract |
Male Wistar albino rats; 150, 200 and 250mg/kg b. w; intra-gastric administration | Reduction of liver enzymes, oxidative stress markers and liver histology | Protects liver against INH + RIF + PYR induced hepatotoxicity | [119] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





