Submitted:
11 April 2024
Posted:
11 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
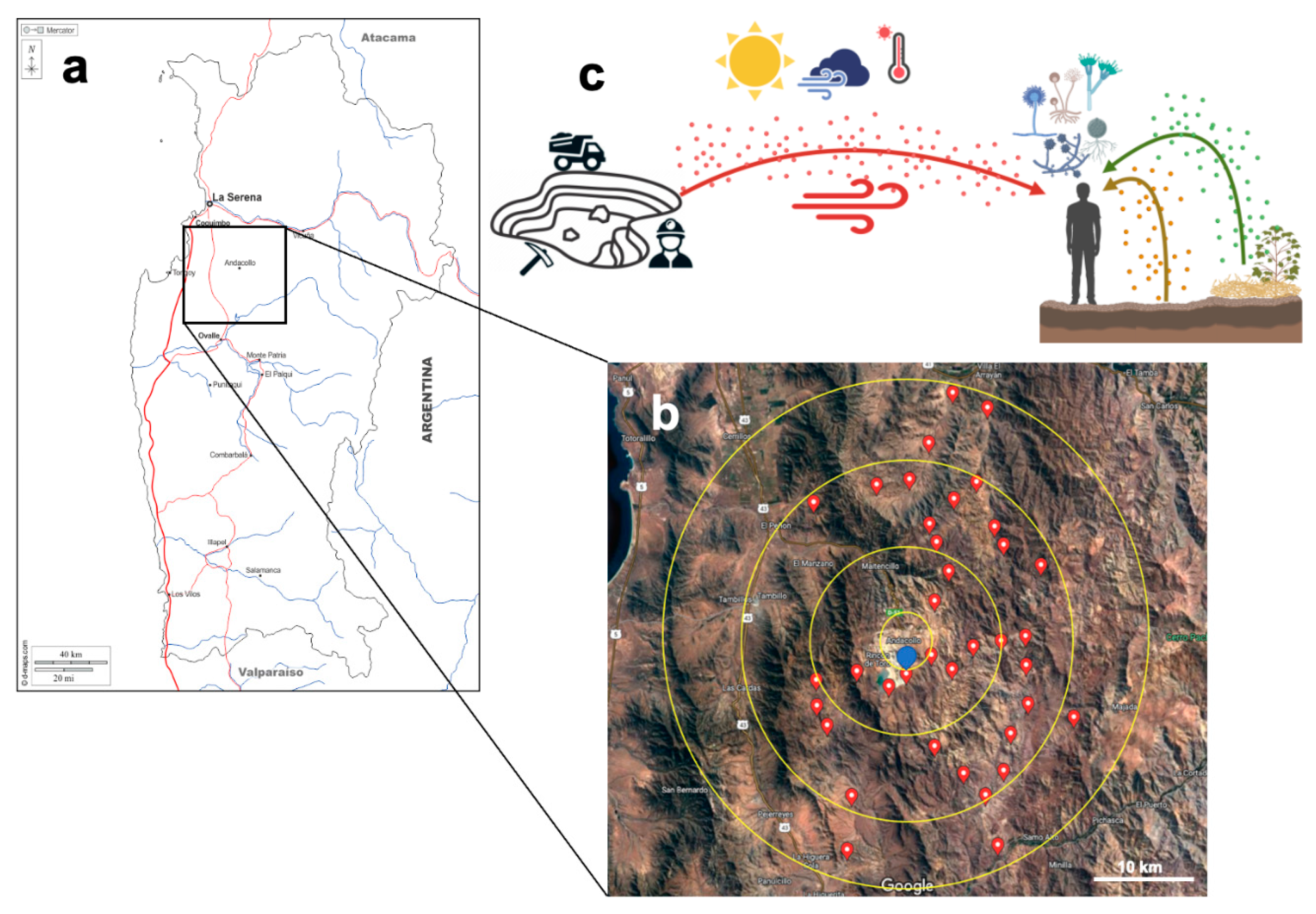
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sampling of Air, Soil, and Vegetal Detritus
2.3. Determination of Metals in Soil
2.4. DNA Extraction, ITS1 Amplification and Sequencing
2.5. Processing of Raw Sequences and Data Analysis
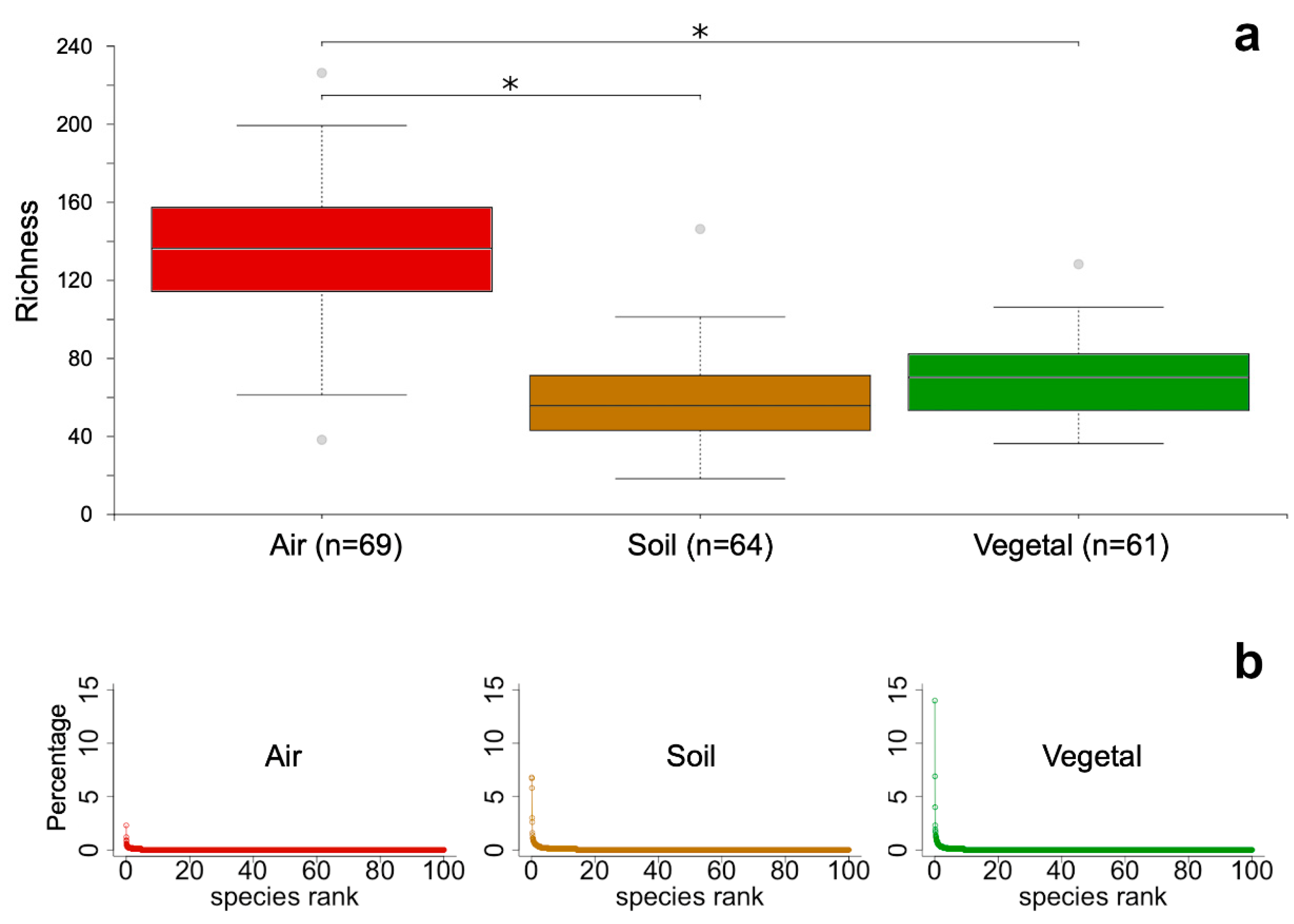
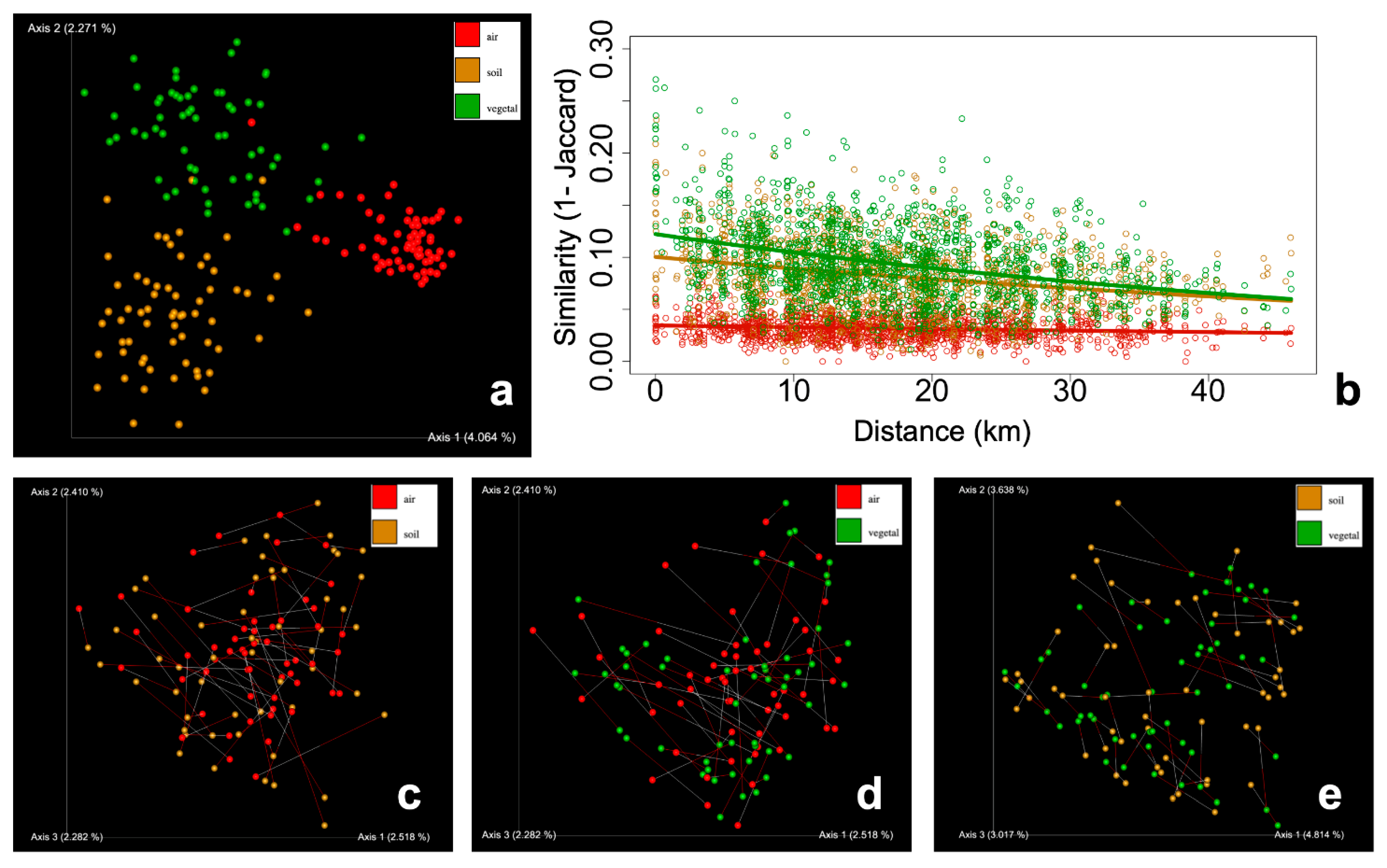
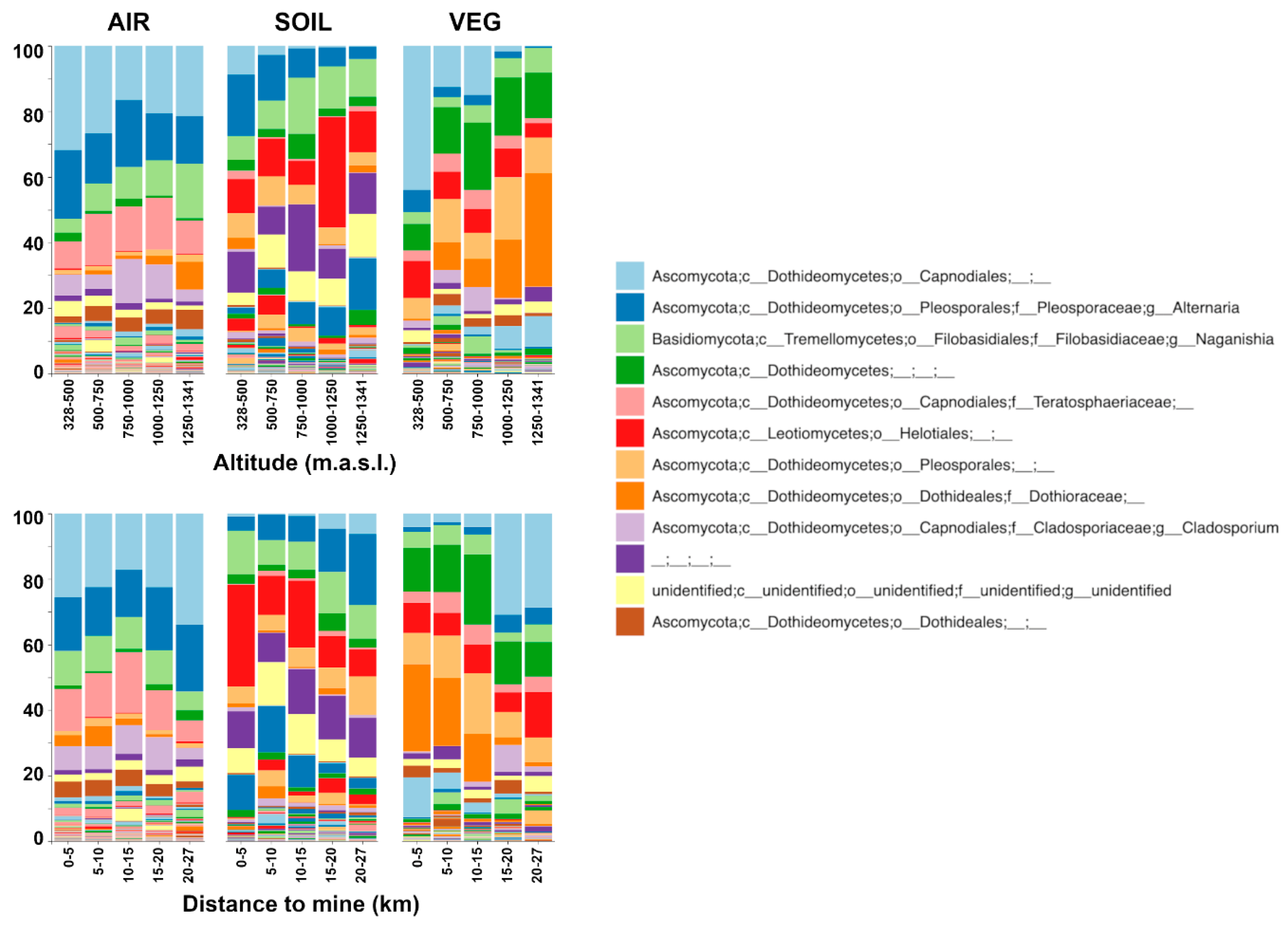
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Airborne Fungal Communities Are Diverse but Homogeneous at the Regional Scale
4.2. Tracking the Drivers and Sources of Airborne Fungal Communities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Després, V.R.; Alex Huffman, J.; Burrows, S.M.; Hoose, C.; Safatov, A.S.; Buryak, G.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Elbert, W.; Andreae, M.O.; Pöschl, U.; et al. Primary Biological Aerosol Particles in the Atmosphere: A Review. Tellus B Chem Phys Meteorol 2012, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Kampf, C.J.; Weber, B.; Huffman, J.A.; Pöhlker, C.; Andreae, M.O.; Lang-Yona, N.; Burrows, S.M.; Gunthe, S.S.; Elbert, W.; et al. Bioaerosols in the Earth System: Climate, Health, and Ecosystem Interactions. Atmos Res 2016, 182, 346–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Fuentes Alburquenque, M.; Torres, R.; D. Cáceres Lillo, D.; Mesías Monsalve, S.; Martín Mateo, M.; Costilla Salazar, R.; Maldonado Alcaíno, A.; Klarián Vergara, J.; Alvarado Orellana, S.; et al. Indoor-Outdoor Concentrations of Fine Particulate Matter in School Building Microenvironments near a Mine Tailing Deposit. AIMS Environ Sci 2016, 3, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jin, L.; Luo, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X. Seasonal Disparities in Airborne Bacteria and Associated Antibiotic Resistance Genes in PM2.5 between Urban and Rural Sites. Environ Sci Technol Lett 2018, 5, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusareva, E.S.; Gaultier, N.E.; Uchida, A.; Premkrishnan, B.N. V; Heinle, C.E.; Phung, W.J.; Wong, A.; Lau, K.J.X.; Yap, Z.H.; Koh, Y.; et al. Short-Range Contributions of Local Sources to Ambient Air. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, A.; García, A.M.; Moreno, D.A.; Guantes, R. Seasonal Changes Dominate Long-Term Variability of the Urban Air Microbiome across Space and Time. Environ Int 2021, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safatov, A.S.; Andreeva, I.S.; Buryak, G.A.; Olkin, S.E.; Reznikova, I.K.; Belan, B.D.; Panchenko, M. V.; Simonenkov, D. V. Long-Term Studies of Biological Components of Atmospheric Aerosol: Trends and Variability. Atmosphere (Basel) 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusareva, E.S.; Gaultier, N.E.; Uchida, A.; Premkrishnan, B.N. V; Heinle, C.E.; Phung, W.J.; Wong, A.; Lau, K.J.X.; Yap, Z.H.; Koh, Y.; et al. Short-Range Contributions of Local Sources to Ambient Air. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drautz-Moses, D.I.; Luhung, I.; Gusareva, E.S.; Kee, C.; Gaultier, N.E.; V Premkrishnan, B.N.; Fook Lee, C.; Ting Leong, S.; Park, C.; Hwee Yap, Z.; et al. Vertical Stratification of the Air Microbiome in the Lower Troposphere. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2022; 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.; Lou, L.; Zheng, P.; Xi, C.; Hu, B. Temporal Discrepancy of Airborne Total Bacteria and Pathogenic Bacteria between Day and Night. Environ Res 2020, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.I.; Miletto, M.; Lindow, S.E.; Taylor, J.W.; Bruns, T.D. Airborne Bacterial Communities in Residences: Similarities and Differences with Fungi. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.I.; Miletto, M.; Taylor, J.W.; Bruns, T.D. Dispersal in Microbes: Fungi in Indoor Air Are Dominated by Outdoor Air and Show Dispersal Limitation at Short Distances. ISME Journal 2013, 7, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivlin, S.N.; Winston, G.C.; Goulden, M.L.; Treseder, K.K. Environmental Filtering Affects Soil Fungal Community Composition More than Dispersal Limitation at Regional Scales. Fungal Ecol 2014, 12, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaisen, M.; West, J.S.; Sapkota, R.; Canning, G.G.M.; Schoen, C.; Justesen, A.F. Fungal Communities Including Plant Pathogens in near Surface Air Are Similar across Northwestern Europe. Front Microbiol 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees-Hill, S.; Douglas, P.; Pashley, C.H.; Hansell, A.; Marczylo, E.L. A Systematic Review of Outdoor Airborne Fungal Spore Seasonality across Europe and the Implications for Health. Science of the Total Environment 2022, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tignat-Perrier, R.; Dommergue, A.; Thollot, A.; Keuschnig, C.; Magand, O.; Vogel, T.M.; Larose, C. Global Airborne Microbial Communities Controlled by Surrounding Landscapes and Wind Conditions. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jin, L.; Wu, D.; Xie, J.W.; Li, J.; Fu, X.W.; Cong, Z.Y.; Fu, P.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.S.; et al. Global Airborne Bacterial Community—Interactions with Earth’s Microbiomes and Anthropogenic Activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022, 119, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhuireach, G.Á.; Betancourt-Román, C.M.; Green, J.L.; Johnson, B.R. Spatiotemporal Controls on the Urban Aerobiome. Front Ecol Evol 2019, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; McEwen, A.; Prospero, J.; Spalink, D.; Chellam, S. Respirable Metals, Bacteria, and Fungi during a Saharan-Sahelian Dust Event in Houston, Texas. Environ Sci Technol 2023, 57, 19942–19955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flies, E.J.; Clarke, L.J.; Brook, B.W.; Jones, P. Urbanisation Reduces the Abundance and Diversity of Airborne Microbes - but What Does That Mean for Our Health? A Systematic Review. Science of the Total Environment 2020, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setti, L.; Passarini, F.; De Gennaro, G.; Barbieri, P.; Pallavicini, A.; Ruscio, M.; Piscitelli, P.; Colao, A.; Miani, A. Searching for SARS-COV-2 on Particulate Matter: A Possible Early Indicator of COVID-19 Epidemic Recurrence. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, N.T.; Cheng, P.C.; Chi, K.H.; Hsiao, T.C.; Jones, T.; BéruBé, K.; Ho, K.F.; Chuang, H.C. Particulate Matter and SARS-CoV-2: A Possible Model of COVID-19 Transmission. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, R.; Sibanda, T.; Ullah, H.; Abia, A.L.K. Beach Sand Mycobiome: The Silent Threat of Pathogenic Fungi and Toxic Metal Contamination for Beachgoers. Mar Pollut Bull 2024, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.N.; Narzary, D. Diversity and Heavy Metal Tolerance of Fungi Associated with Different Coal Overburden Strata of Tikak Colliery, Assam. Curr Microbiol 2023, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, P.; de Melo Texeira, M.; Chander, A.M.; Singh, N.K.; Simpson, A.C.; Yurkov, A.; Karouia, F.; Stajich, J.E.; Mason, C.E.; Venkateswaran, K. Genomic Characterization and Radiation Tolerance of Naganishia Kalamii Sp. Nov. and Cystobasidium Onofrii Sp. Nov. from Mars 2020 Mission Assembly Facilities. IMA Fungus 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.K.; Vimercati, L.; Darcy, J.L.; Arán, P.; Gendron, E.M.S.; Solon, A.J.; Porazinska, D.; Dorador, C. A Naganishia in High Places: Functioning Populations or Dormant Cells from the Atmosphere? Mycology 2017, 8, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, M.L.; Steinnes, E.; Blom, H.A. Vertical and Horizontal Distributions of Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu, and Hg in Uncultivated Soil in the Vicinity of a Zinc Smelter at Odda, Norway. Soil Sediment Contam 2007, 16, 585–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMartin, I.; Henderson, P.J.; Plouffe, A.; Knight, R.D. Comparison of Cu–Hg–Ni–Pb Concentrations in Soils Adjacent to Anthropogenic Point Sources: Examples from Four Canadian Sites. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis 2005, 2, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csavina, J.; Field, J.; Taylor, M.P.; Gao, S.; Landázuri, A.; Betterton, E.A.; Sáez, A.E. A Review on the Importance of Metals and Metalloids in Atmospheric Dust and Aerosol from Mining Operations. Science of the Total Environment 2012, 433, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Fuentes Alburquenque, M.; Torres, R.; D. Cáceres Lillo, D.; Mesías Monsalve, S.; Martín Mateo, M.; Costilla Salazar, R.; Maldonado Alcaíno, A.; Klarián Vergara, J.; Alvarado Orellana, S.; et al. Indoor-Outdoor Concentrations of Fine Particulate Matter in School Building Microenvironments near a Mine Tailing Deposit. AIMS Environ Sci 2016, 3, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higueras, P.; Oyarzun, R.; Lillo, J.; Oyarzún, J.; Maturana, H. Atmospheric Mercury Data for the Coquimbo Region, Chile: Influence of Mineral Deposits and Metal Recovery Practices. Atmos Environ 2005, 39, 7587–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higueras, P.; Oyarzun, R.; Oyarzún, J.; Maturana, H.; Lillo, J.; Morata, D. Environmental Assessment of Copper-Gold-Mercury Mining in the Andacollo and Punitaqui Districts, Northern Chile. Applied Geochemistry 2004, 19, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarzun, R.; Oyarzún, J.; Lillo, J.; Maturana, H.; Higueras, P. Mineral Deposits and Cu-Zn-As Dispersion-Contamination in Stream Sediments from the Semiarid Coquimbo Region, Chile. Environmental Geology 2007, 53, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, J.P.; Nothias, L.F.; Thompson, L.R.; Sanders, J.G.; Salido, R.A.; Couvillion, S.P.; Brejnrod, A.D.; Lejzerowicz, F.; Haiminen, N.; Huang, S.; et al. Standardized Multi-Omics of Earth’s Microbiomes Reveals Microbial and Metabolite Diversity. Nat Microbiol 2022, 7, 2128–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Mills, D.A. Improved Selection of Internal Transcribed Spacer-Specific Primers Enables Quantitative, Ultra-High-Throughput Profiling of Fungal Communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 2013, 79, 2519–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-High-Throughput Microbial Community Analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq Platforms. ISME J 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarenkov, K.; Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.-H.; Taylor, A.F.S.; May, T.W.; Frøslev, T.G.; Pawlowska, J.; Lindahl, B.; Põldmaa, K.; Truong, C.; et al. The UNITE Database for Molecular Identification and Taxonomic Communication of Fungi and Other Eukaryotes: Sequences, Taxa and Classifications Reconsidered. Nucleic Acids Res 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A Versatile Open Source Tool for Metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 2016, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A New Phylogenetic Method for Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation Evaluation and Phylogenetic Diversity. Biol Conserv 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol Biol Evol 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2 - Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS One 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peres-Neto, P.R.; Jackson, D.A. How Well Do Multivariate Data Sets Match? The Advantages of a Procrustean Superimposition Approach over the Mantel Test. Oecologia 2001, 129, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldrian, P.; Větrovský, T.; Lepinay, C.; Kohout, P. High-Throughput Sequencing View on the Magnitude of Global Fungal Diversity. Fungal Divers 2022, 114, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusterholz, H.P.; Baur, B. Changes in Soil Fungal Diversity and Composition along a Rural–Urban Gradient. Forests 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrego, N.; Crosier, B.; Somervuo, P.; Ivanova, N.; Abrahamyan, A.; Abdi, A.; Hämäläinen, K.; Junninen, K.; Maunula, M.; Purhonen, J.; et al. Fungal Communities Decline with Urbanization—More in Air than in Soil. ISME Journal 2020, 14, 2806–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egidi, E.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Plett, J.M.; Wang, J.; Eldridge, D.J.; Bardgett, R.D.; Maestre, F.T.; Singh, B.K. A Few Ascomycota Taxa Dominate Soil Fungal Communities Worldwide. Nat Commun 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, V.E.F.; Patriarca, A. Alternaria Species and Their Associated Mycotoxins. In Mycotoxigenic Fungi; Humana Press Inc., 2017; Vol. 1542, pp. 13–32.
- Grewling, L.; Nowak, M.; Ska, A.S.; Kostecki, L.; Bogawski, P. Temporal Variability in the Allergenicity of Airborne Alternaria Spores. Med Mycol 2019, 57, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Almeida, L.C.S. de S.; Pecoraro, L. Environmental Factors Affecting Diversity, Structure, and Temporal Variation of Airborne Fungal Communities in a Research and Teaching Building of Tianjin University, China. Journal of Fungi 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Bose, T.; Chang, R. Fungal Diversity Associated with Thirty-Eight Lichen Species Revealed a New Genus of Endolichenic Fungi, Intumescentia Gen. Nov. (Teratosphaeriaceae). Journal of Fungi 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banchi, E.; Ametrano, C.G.; Tordoni, E.; Stanković, D.; Ongaro, S.; Tretiach, M.; Pallavicini, A.; Muggia, L.; Verardo, P.; Tassan, F.; et al. Environmental DNA Assessment of Airborne Plant and Fungal Seasonal Diversity. Science of the Total Environment 2020, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberán, A.; Ladau, J.; Leff, J.W.; Pollard, K.S.; Menninger, H.L.; Dunn, R.R.; Fierer, N. Continental-Scale Distributions of Dust-Associated Bacteria and Fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015, 112, 5756–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Berdugo, M.; Guirado, E.; Guerra, C.A.; Egidi, E.; Wang, J.; Singh, B.K.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Temperature Thresholds Drive the Global Distribution of Soil Fungal Decomposers. Glob Chang Biol 2022, 28, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio del Medio Ambiente Sistema de Información Nacional de Calidad Del Aire. Available online: https://sinca.mma.gob.cl/index.php/estacion/index/key/420 (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Oyarzun, R.; Oyarzún, J.; Lillo, J.; Maturana, H.; Higueras, P. Mineral Deposits and Cu-Zn-As Dispersion-Contamination in Stream Sediments from the Semiarid Coquimbo Region, Chile. Environmental Geology 2007, 53, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higueras, P.; Oyarzun, R.; Oyarzún, J.; Maturana, H.; Lillo, J.; Morata, D. Environmental Assessment of Copper-Gold-Mercury Mining in the Andacollo and Punitaqui Districts, Northern Chile. Applied Geochemistry 2004, 19, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higueras, P.; Oyarzun, R.; Lillo, J.; Oyarzún, J.; Maturana, H. Atmospheric Mercury Data for the Coquimbo Region, Chile: Influence of Mineral Deposits and Metal Recovery Practices. Atmos Environ 2005, 39, 7587–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.R.; Underwood, G.J.C.; McGenity, T.J.; Dumbrell, A.J. What Drives Study-Dependent Differences in Distance–Decay Relationships of Microbial Communities? Global Ecology and Biogeography 2021, 30, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Montoya, L.; Gao, C.; Head, J.R.; Remais, J.; Taylor, J.W. The Air Mycobiome Is Decoupled from the Soil Mycobiome in the California San Joaquin Valley. Mol Ecol 2022, 31, 4962–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allali, I.; Arnold, J.W.; Roach, J.; Cadenas, M.B.; Butz, N.; Hassan, H.M.; Koci, M.; Ballou, A.; Mendoza, M.; Ali, R.; et al. A Comparison of Sequencing Platforms and Bioinformatics Pipelines for Compositional Analysis of the Gut Microbiome. BMC Microbiol 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas-Molina, J.A.; Peralta-Sánchez, J.M.; González, A.; McMurdie, P.J.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ursell, L.K.; Lauber, C.; Zhou, H.; Song, S.J.; et al. Advancing Our Understanding of the Human Microbiome Using QIIME. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press Inc., 2013; Vol. 531, pp. 371–444 ISBN 9780124078635.
- King, J.R.; Jackson, D.A. Variable Selection in Large Environmental Data Sets Using Principal Components Analysis. Environmetrics 1999, 10, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrego, N.; Norros, V.; Halme, P.; Somervuo, P.; Ali-Kovero, H.; Ovaskainen, O. Give Me a Sample of Air and I Will Tell Which Species Are Found from Your Region: Molecular Identification of Fungi from Airborne Spore Samples. Mol Ecol Resour 2018, 18, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Beta-distance metric | Air | Soil | Veg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude (m.a.s.l.) |
Jaccard | 0.1468 | 0.2790 | 0.4523 |
| unweighted UniFrac | 0.1367 | 0.1835 | 0.3976 | |
| Distance to mine (km) |
Jaccard | n.s. | n.s. | 0.3240 |
| unweighted UniFrac | n.s. | n.s. | 0.2838 | |
| Pressure (mmHg) |
Jaccard | 0.1527 | n.s. | n.s. |
| unweighted UniFrac | 0.1302 | n.s. | n.s. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





