Preprint
Article
Qualitative Study to Explore the Occupational and Reproductive Health Challenges among Women Tobacco Farm Laborers in Mysore District, India
Altmetrics
Downloads
92
Views
39
Comments
0
A peer-reviewed article of this preprint also exists.
supplementary.docx (25.10KB )
Submitted:
11 April 2024
Posted:
11 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Alerts
Abstract
Indian tobacco farm laborers are primarily women and children working for very low wages. The aim of this study was to explore occupational and reproductive health challenges faced by women tobacco farm labors in Mysore District, India. We conducted interview and six focus group discussions among 41 women tobacco farm laborers. Codes and themes were generated based on deductive and inductive approaches using the socio-ecological model. Participants reported symptoms of green tobacco sickness including headaches, back pain, gastric problems, weakness, and allergies during menstruation, pre-natal, and post-natal periods. Participants had poor awareness about the health effects of tobacco farming and there were gender inequalities in wages and use of personal protective equipment. Participants received support from family and commu-nity health workers during their pregnancy and post-natal period. Women reported wanting ma-ternity benefits from the tobacco board, monetary support, and nutritional supplements. There is a need for health education about the environmental dangers of tobacco among farm laborers, and more supportive policies for women farmworkers during pregnancy and post-natal periods.
Keywords:
Subject: Public Health and Healthcare - Public, Environmental and Occupational Health
1. Introduction
India is the second largest tobacco growing nation globally producing over 772,152 tons of leaf in 2022 [1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) Framework Convention of Tobacco Control (FCTC) article 17 recommends promoting economically viable alternatives for tobacco workers and growers, and article 18 recommends protection of worker health and the environment with respect to tobacco cultivation [2].
Green tobacco sickness (GTS), an occupational illness associated with tobacco, is commonly seen among workers engaged in tobacco cultivation [3]. Symptoms of GTS include chills, headaches, nausea, vomiting, pallor, dizziness, increased perspiration, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and increased salivation, among other shorter term symptoms based on exposure [3]. Morbidity and mortality rates of GTS around the world have not been widely documented; a morbidity estimate conducted in 1994 based on reports to a poison control center in Kentucky found that approximately one in four people with suspected GTS were admitted to the hospital [4]. Another cross-sectional study in Brazil found 122 (34.5%) cases of GTS among tobacco workers included in their, 39% of whom were smokers and 61% male [5]. A review found that the prevalence of GTS varies globally from 8.2 to 47% [3]. The illness was first reported in 1970 among tobacco workers in Florida, as “cropper sickness.” [6]. Later, the symptoms were found to be caused by the absorption of nicotine from wet tobacco plants and reported as GTS [6]. The use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as water-resistant clothing, chemical-resistant gloves, plastic aprons, and rain-suits with boots are recommended preventive measures that should be used by tobacco farmers to prevent GTS [3].
Prevalence of GTS by gender has varied in the literature, some finding it higher among men and others higher among women [4,5]. However, the prevalence of GTS was found to be higher among women tobacco farmers compared to men in India and Korea [7,8]. It is also possible that the burden among women is underrepresented at times due to the historical lack of female workers in tobacco [9]. During tobacco production women are affected differently from men biologically due to the critical phases of vulnerabilities during pregnancy [10]. In Brazil, among women tobacco farm workers with a family history of asthma, wheezing was associated with tying bundles of tobacco, strenuous work, contact with chemical disinfectants, and GTS [11]. Women additionally have a higher burden of stressors from the nature of the tobacco work [12]. Among women tobacco farmers in Ambulu village in Indonesia, a significant relationship was observed between work stress and menstrual disorders [13]. However, despite these vulnerabilities specific to women working with tobacco, the literature on the health of women tobacco farmers in India is sparse.
In addition to health effects for farm workers, tobacco production results in many other impacts on local communities and the environment. Tobacco cultivation results in detrimental effects on surrounding ecosystems, including deforestation resulting from the demand for wood to cure tobacco leaves, degradation of soil fertility, pollution of ground and surface water, and adverse impacts on biodiversity due to the intensive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides [14,15]. From a socioeconomic perspective, farmers often have contractual arrangements with the tobacco industry and are trapped in debt [16]. Additionally, in some countries, children from poor households miss school to work in tobacco farming [17]. Furthermore, tobacco dependence among tobacco farmers is often high compared to non-tobacco farmers [18].
The aim of this study is to qualitatively explore the challenges in occupational and reproductive health of women tobacco farm laborers across their lifespan. The objectives are, among non-pregnant women working in tobacco farms, to: 1) determine reproductive health support and challenges using the socioecological model (SEM) across the life course; 2) determine occupational health support and challenges; and 3) understand the knowledge, attitudes, and practices towards safe work environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Socioecological Model
This is an exploratory study using interviewer-administered questionnaires and focus group discussions (FGDs) guided by the Socio-ecological model (SEM) to explore the beliefs, attitudes, and practices of women tobacco farm laborers with regards to the social, environmental, and health risks of tobacco farming. The SEM is a framework for explaining the sphere of influence that affects human behaviors. The model dictates that health-seeking behavior is a product of interactions among individual attributes and environmental factors. According to SEM, five spheres of influence affect human behavior: intrapersonal, interpersonal, community, organization, and public policies [19].
Intrapersonal factors include characteristics of the individual such as knowledge, attitudes, behavior, self-concept, skills, etc. This includes the developmental history of the individual. Interpersonal processes include formal and informal social networks and social support systems, including the family, work group, and friendship networks. Institutional factors are social institutions with organizational characteristics, and formal (and informal) rules and regulations for operation. Community factors are relationships among organizations, institutions, and informal networks within defined boundaries. Public policy includes local, state, and national laws and policies [19].
2.2. Study Setting
The study was conducted from May to July 2022 in six randomly selected villages in Hunsur Taluk, Mysore District, India, which is a major tobacco growing area in the southern state of Karnataka. The study was conducted at the Anganwadi centers (rural childcare centers) and the community centers where residents usually gather. The FGDs were conducted outside of regular working hours at a time convenient for the participants.
2.3. Participants and Recruitment
The choice of women farm laborers as study subjects was due to their role in tobacco production, combined with their essential role in providing care for the family, especially related to health of children and the elderly. A representative from the Public Health Research Institute of India (PHRII) first consulted with community members and reached out to community health workers known as accredited social health activists (ASHA) in the communities where the planned recruitment of participants would happen. The ASHA workers living in these villages are well connected to the residents and facilitated recruitment of potential study participants. A flyer about the study was distributed by the ASHA workers during their regular house visits. PHRII has previously conducted several studies in these communities and developed good communication channels with these communities. ASHA workers in each village were provided monetary incentives of Rs. 300 ($3.75 USD) for their time in community engagement.
Inclusion criteria for participation in the study were women tobacco farm laborers in Mysore District, who were 18 years and older, and had experienced pregnancy in the past irrespective of the birth outcome. We included participants who understood and spoke Kannada, consented to audio recording, belonging to different households, and had the ability to undergo informed consent process. Exclusion criteria were currently pregnant women as they are a vulnerable group, women who have never been pregnant, and those not willing to providing written consent and consent for audio recording.
This study was approved and monitored by Institutional Ethics Review Board at PHRII (IERB Protocol number # 2022-05-07-68, 07 May 2022). The University of Arizona IRB confirmed reliance for this study on the external IRB at PHRII as the IRB of Record (STUDY00001243, 08 June 2022).
2.4. Study Sampling
The participants were recruited through convenience sampling with the help of the ASHA workers and the staff from PHRII. Participants were in different age groups were included to capture the different reproductive health concerns across age groups. Six FGDs were conducted with a total of 41 participants (6-7 individuals per group). The consent form was read aloud to the participants in the local language of Kannada and a written informed consent was obtained before the start of the study.
This study consisted of an interviewer-administered questionnaire and six FGDs among 41 participants. Those who agreed to participate were asked questions about their occupation, reproductive health, and tobacco farming experience and challenges.
2.5. Approach and Recruitment
The interview was conducted on the first day of the study to develop rapport and trust among the participants. The interview took 15 minutes per participant. All participants were asked questions regarding demographic characteristics, marital status, religion, caste, socioeconomic status, self-reported smoking and use of smokeless tobacco and arecanut, exposure to second-hand smoke, tobacco farming during pregnancy including exposure to chemicals and pesticides, allergies, allergies of children, and use of personal protection equipment (PPE) at work (Supplemental Material – Appendix 1).
2.6. FGD Data Collection
FGDs were conducted to explore occupational and reproductive health issues. The FGDs ranged from 60 to 70 minutes each. The FGD guide (Supplemental Material – Appendix 2) was based on the domains of the SEM [19]. The FGD guide was pilot tested twice among PHRII staff before use in the field. On the day after the recruitment interviewer-administered questionnaire was answered by a group of participants, the FGD was administered among said participants. The participants were asked about occupational and reproductive health issues and experiences at the individual, inter-personal, community, organizational, and societal levels. The FGD questions assessed access to health care services during pregnancy; how working in tobacco farming would have affected reproductive health with focus on pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause; exposure to pesticides and chemicals during pregnancy; and access to PPE. The questions also explored support from family, friends, doctors, other health care workers, the farming community, and local, state, and national governments. The facilitator and notetaker were women to help participants feel more comfortable answering questions. The facilitator was fluent in Kannada and used the FGD to initiate the discussions, and probing questions were asked to explore more on a particular topic. A note taker took notes and observed the participants' non-verbal communications. The FGDs were audio recorded and transcribed verbatim to Kannada. Data collection continued until data saturation was reached [20]. A trained translator later translated the transcripts in Kannada to English for analysis. We did not do back translation due to limited resources. All participant identifications were removed, and only de-identified data were used for coding and analysis. Participants were paid a compensation of Rs. 250 ($ 3.12 USD) in cash for their participation, and refreshments were served at the end of the FGDs.
2.7. Research Team and Reflexivity Statement
A researchers based at PHRII have intricate knowledge of the local community, language and culture, author SN from PHRII facilitated all of the FGDs. PR was the study Principal investigator and note taker in all the FGDs. Authors PR, MBN and KM who conducted the qualitative analysis are researchers at the University of Arizona and PHRII and all hold graduate degrees in an area of health. MBN was a fellow PhD student with previous experience in qualitative research, and KM was a research physician at PRHII. All researchers conducting data collection and data analysis were female. Authors AAL, KK, AMW, LBG, ZC, and PM have PhD in public health fields of epidemiology, health promotion, and environmental health sciences. A relationship was established prior to study commencement with study participants through PHRII staff who have an extensive history of research among these populations. Participants were familiar with the facilitator. The facilitator and note taker did not provide their opinions during the FGDs verbally or non-verbally.
2.8. Data Analysis
We used MAXQDA 22 software for qualitative data analyses [21]. We used a thematic content analysis approach. Two investigators (PR and MBN) independently developed coding trees based on the SEM using the first interview which were then consolidated into a codebook through discussion and entered into MAXQDA. The codebook was iteratively reviewed throughout the rest of the coding process. They then coded the data and compared for discrepancies through discussion to improve interrater reliability. A third investigator (KM) helped to resolve any discrepancies which could not be resolved through discussion. Codes and themes were generated based on an inductive approach using content analysis and a deductive approach using the SEM model. We used consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ), including a 32-item checklist for focus groups as a standard qualitative study reporting guideline [22].
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
The total sample consisted of 41 participants. The mean age was 38.22 ± 7.95 years, more than half of the participants were 31 to 40 years of age (22/41, 53.7%). The greatest proportions of participants were married (33/41, 80%), belonged to the Hindu religion (41/41, 100%), and self-identified as "scheduled caste" (30/41, 73%). The caste system in India is a complex social structure, in which the schedule caste are officially regarded as socially disadvantaged and occupied the lowest step of the social ladder [23]. Almost half of the participants were illiterate and lacked a formal education (19/41, 46%), and 61% of participants had an annual income of ($240 to $600 USD) Rs. 20,000 to 50,000 (25/41). None of the participants reported using any smoking form of tobacco but 15% reported using smokeless tobacco (6/41) (Table 1).
3.2. Occupational and Reproductive Health
The second part of the interview focused on the reproductive and occupational health of the participants. Most participants were involved in tobacco farming activities like cultivation (36/41, 87.8%), harvesting (40/41, 97.6%), sorting (36/41, 87.8%), stacking (33/41, 80.5%), and packing (22/41, 53.6%). Mean hours of working in the tobacco farming activities ranged from six to eight hours. The duration of the participants working in these activities was 18 to 24 years. Only thirteen participants were involved in curing tobacco leaves (13/41, 31.7%). Most participants had ≤ 2 pregnancies (30/41, 73.2%). One participant reported having had multiple abortions (1/41, 2.4%), and five participants reported having had a miscarriage (5/41, 12.2%). Four participants reported death of infant before reaching one year of age (4/41, 9.8%). Two participants reported using tobacco during pregnancy (2/41, 4.9%). Four-fifths of participants were involved in tobacco farming during pregnancy (33/41, 80.5%). Eighteen participants reported being exposed to tobacco dust during pregnancy (18/41, 43.9%). Only six participants reported wearing PPE during work with tobacco (6/41, 14.6%). Six participants had a history of allergy during pregnancy (6/41, 14.6%) and five had allergies during the post-natal period (5/41, 12.2%). History of allergy in the child six months after birth was reported in eight of the 41 participants (19.5%) and allergy in the child one year after birth was reported in nine of the 41 participants (22.0%) (Figure 1; Table 2).
3.3. Qualitative Analysis
Throughout the results, data extracts are presented with participant number (e.g., P1) and FGD number (e.g., G1). Most participants were involved in all the tobacco farming activities including sowing, harvesting, sorting, and packing. For example, one participant said,
“We tie the tobacco leaves, cut the leaves, manure the leaves, dig holes for the saplings and do the bridging.” (G4, P1)
Another said,
“I do the same work as others, planting the saplings, putting in the fertilizers, removing the weeds, pushing the mud, tying the leaves and the rest of the work.” (G5, P4)
Figure 2 represents the major themes that reflect occupational and reproductive health experiences for women tobacco farmers across the five levels of the SEM.
3.3.1. Intrapersonal
- Health belief
The tobacco plant was believed to be the Hindu deity of wealth ‘Lord Lakshmi’, which impacted the behavior of workers. One participant noted,
“Tobacco is considered as goddess Lakshmi so during the menstrual periods we do not touch the tobacco plants until we take a shower.” (G4, P4)
Participants believed that working in the tobacco fields and touching tobacco leaves while grading their quality produces heat, sucks the blood and makes them look pale and anemic. One participant mentioned,
“It is heat and it also sucks blood.” (G4, P4)
Some participants believed tobacco use can cause cancer, however, not all participants believe working in tobacco will cause any harm. Some participants reported using tobacco with betel quid to get relief from toothaches and when they get bored. For example, several participants stated,
“They eat it when they get toothaches, it reduces the pain.” (G3, P4)
“Chewing tobacco is a habit; people eat it because they get bored.” (G3, P6)
“Now so many people are facing many problems by having tobacco, by smoking the beedis so many people have got kidney problems, doctors tell them to stop smoking but they say yes there, and will not follow it in the house, but then they continue to smoke.” (G1, P3)
Health behavior
Hand washing after work and using PPE were some of the health behavior practices discussed in the FGDs. Most participants reported washing hands after work with soap, detergents, and tamarind water. However, one participant reported not washing hands because washing hands took time:
“I used to feed my child after work, without washing my hands because washing it would take a lot of time.” (G2, P3)
Overall, participants were not interested in using PPE because their use reduced working efficiency. For example, one participant said,
“We cannot pluck the leaves if we wear all that. It will be difficult to work for us when we wear gloves. It keeps on sliding down from our hands and we cannot pluck the leaves quickly and we will feel like falling if we wear the boots.” (G2, P3)
However, in one focus group, participants reported wearing long-sleeve shirts and tying a cloth to cover their head to avoid direct exposure to sunlight. One participant noted,
“We wear a long shirt that covers our hands and also tie a cloth to cover our heads, we work after doing this.” (G2, P2)
One focus group participants reported that after the COVID-19 pandemic, the tobacco board provided them with gloves, masks, and boots, and took their picture wearing these, but that they never subsequently used this PPE.
Most focus groups reported that PPE was provided to the tobacco farm owners and that sometimes the men spraying pesticides in the field. Participants reported male tobacco farm laborers had greater access to PPE. Women tobacco farm laborers generally did not understand the purpose of PPE and thought that its use was restricted to pesticide sprayers and used for COVID-19 pandemic.
- General and occupational health experiences
Participants reported recurring and chronic GTS symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, headache, stomach pain, musculoskeletal pain, back pain, gastric problems, weakness, and allergy during work. They reported that these problems temporarily resolved while taking medicines. Participants experienced GTS symptoms during menstruation, and during pre-natal and post-natal time periods. To seek relief from the pain, in most cases participants self-medicated by using over-the-counter drugs and home remedies such as tea. If symptoms were not relieved, then they consulted doctors.
One participant noted,
“I usually get headaches three to four days a week for the past three years. I used to apply headache balm, took medicines from the medical stores or took injections from the hospital. I cannot do any work if I get headache. I will usually get it during evening hours, and during the morning. The last few days if I get it in the morning it stays till evening. The pain reduces only after getting an injection from the hospital.” (G5, P4)
Another participant said,
“Sometimes I go to the hospital because of body ache. My blood pressure will be low. Doctors tell me not to expose to the sun for long, not to work more and take rest. They tell me that my health is good, and I should take tablets for low blood pressure. In the last 2-3 years after my child was born, they told me that I have less blood (anemia). If they give blood and a tonic, I will be fine. They give tonic and powder (supplements) in the government hospital. I take it. I have a body ache and then the regular common cold. Other than that, I do not have any disease. This is common, I get itching, that is all.” (G4, P3)
Another participant said,
“We have to do the tobacco work. It is compulsory and we cannot sit simply without doing it. We must go together with our husbands. I will be questioned if I am late. Sometimes when I get a head ache I will be having no time to rest even for five minutes. I will take the tablet but cannot rest, and they will be screaming and will not understand our pain. They will ask us to pack the boxes and will scold us if we will be late, even though we do not take the medicine properly. Also we must be on time with them.” (G1, P5)
- Reproductive health
The reporductive health experiences of woman tobacco farm laborers during their menturation, pregnancy and child birth, post-natal period, menopause, and other reproductive concerns were discussed.
- Menstruation
Most participants reported having regular menstrual periods ranging from three to five days a month. One participant shared,
“I have a regular menses. Sometimes it will be for three days and sometimes for five days. I have no problems except lower back pain.” (G3, P4)
A few participants reported irregular periods, either unusually infrequent or unusually frequent. For example, one participant said,
“I get my menses once in six or seven months. Even during that time, there will not be heavy bleeding.” (G2, P3)
Another participant said,
“For the past one month I am having more bleeding, in the same month I got my periods three times. I am almost changing ten pads a day and it happens for six days. This month I had it four times. I had very severe bleeding this month and due to that my eyes became blurry and I also feel giddiness. I feel very tired all the time and I feel uneasy to lift my head.” (G2, P5)
Participants used cloth and sanitary pads as menstrual hygiene products. One participant responded,
“We tie a cloth to cover our head while working. We wear that cloth as a pad if we get periods at work. We cannot speak loudly because there will be five other people. We do not disclose it to all. We adjust among ourselves. When someone get their periods, we make them sit separately and make them work. We will not make them move around much.” (G4, P1)
Participants reported working in the tobacco fields and doing domestic work during menstrual periods. Symptoms of dysmenorrhea and GTS were reported during menstruation. As one participant noted,
“We used to do the same tobacco work even during that time. I used to get stomach pain and lower back pain after I came from work. Despite that, I do the household work and cooking at home.” (G2, P5)
Some farm owners do not allow the women with menstural periods to work. For example, one participant said,
“Some will tell us, nothing will happen, you can come. Some tell us not to come. They will not allow us to touch. Some will not say anything.” (G4, P4)
- Pregnancy and Childbirth
Almost all the participants were involved in tobacco farming activities during their pregnancy. Most participants worked until six to eight months of pregnancy, and a few worked until the day of delivery. For example, one participant stated,
“I did the tobacco work until three days to my delivery. I got my cramps but still I was working.” (G4, P3)
They reported experiencing GTS symptoms such as weakness, nausea, vomiting, and headache during pregnancy. However, it is unclear if the vomiting and nausea were pregnancy related or GTS symptoms. Participants also mentioned being exposed to fertilizers during pregnancy. Some participants reported adverse birth outcomes including miscarriages, still births, and low birthweight (LBW) infants. One participant noted,
“During pregnancy, I used to feel like vomiting while doing the tobacco work. I have vomited while putting the fertilizers.” (G2, P4)
Another participant said,
“We used to bend and do the activities like planting the saplings until we came to our 5th month. After the 5th month, the stomach starts to increase, so we sit and do works like tying the leaves and separating them.” (G2, P3)
- Post-natal period
Most participants returned to work three months to one year post-delivery. Participants spoke about their experiences during the post-natal period with breast feeding the infant and not having a family member for childcare service. Few participants used Anganwadi centers for childcare service. One participant said,
“If there was someone to take care of the baby, we would leave the child and go for work; otherwise, we would carry the baby. Aged people will take care. Either father-mother or father-in-law and mother-in-law. Now, we must take care of our children. If there is work, we have made the baby sleep there and do our work.” (G4, P4)
Another participant noted,
“After my first delivery I started my work in three months. I worked keeping the baby next to me. Sometimes, I would leave the child in the anganwadi from morning to evening. I have suffered a lot.” (G4, P1)
- Other reproductive health experiences
Participants experienced other reproductive health problems such as excess vaginal discharge, itching, and redness. For example, one participant said,
“White discharge started during my last childbirth. Now my son is 16 years old, and I am having it since then. Initially I had little white discharge and along with that I had itching as well. I showed it to the doctor, and they said it is very common in women and they said there is no problem in it. There was smell there in the beginning. Now the itching has reduced a little bit after being consulted with the doctor 2-3 times. But it reoccurs after some time, and it reduces again after washing in hot water.” (G2, P6)
- Menopause
Four participants had gone through menopause. Three of them had natural menopause and one participant had undergone hysterectomy. Participants reported having longer menstrual periods (up to one month) during the beginning of menopause; however, now they do not have any problems while working. For example, one participant said,
“I had lower back and stomach pain. I could not sit down, and I used to find it very difficult. I had been bleeding for five days. I had lot of stomach pain and bleeding for a month on my last period. They gave me an injection saying that it would be like this at the beginning of menopause. Since 1 ½ years, I have not got my period. I am working the same as earlier. I do all the household work at home without a single day leave. I even work at the fields and even go to daily wage work.” (G5, P7)
- Substance use
A few participants reported using chewing tobacco. Two of the participants used tobacco during pregnancy and believed using chewing tobacco during pregnancy does not cause any harm. For example, one participant said,
“I eat chewing tobacco (kaddipuddi) along with betel nut and leaves two to three times a day. I keep it in one corner of the mouth and will spit it after some time.” (G2, P1)
Another participant said,
“I have been chewing tobacco for the past 25 years and nothing has happened to me. I eat 15 times per day. I don’t know why I started, but I used to get teeth pain and swelling. At that time the old people in the village asked me to use this for reducing pain, and then I started having it.” (G5, P4)
3.3.2. Interpersonal
- Family support
Some participants received support from husbands, parents, siblings, and in-laws during their pregnancy and the post-natal period. For example, a participant said,
“My husband helped me during pregnancy and delivery. He did not send me to my father’s house. My husband took care of me.” (G4, P2). Another participant said, “During that time, I used to be in my mother’s place; my sisters-in-law and my mother used to be there for my support.” (G5, P3)
A few participants did not receive support from their families during pregnancy. For example, one participant said,
“No one helped us during that time. We were doing all the work. People would feel jealous. I would bring water even nine months pregnant, do the cooking, cleaning, washing vessels. Everybody would go out to work.” (G4, P1)
- Friends and neighbors
Support from friends and neighbors was sparse. When the family was unavailable, one participant reported receiving support from the neighbors for hospital visits; she stated,
“When I was pregnant, I had fallen down and my neighbor helped me and took me to the hospital.” (G1, P1).
None of the participants mentioned receiving support from their peers or friends.
- Family health
Most of the family members were also involved in tobacco farming activities. Some of the most common health problems reported among the participant’s family members include hypertension, thyroid problems, gastric problems, and respiratory problems such as asthma. For example, one participant said,
“My husband has pain in one of his thighs and blood pressure, for the last four to five years it is increasing. He also works in tobacco fields” (G2, P7). Another participant said, “My mother-in-law is not well. She has breathing problems like asthma. She was doing tobacco work. Now she cannot stand the smell of tobacco.” (G4, P3).
One participant reported acute symptoms while spraying pesticides.
- Substance use in family
Alcohol, smoking beedi, and chewing tobacco products like khaini and ghutka are some of the common substances used by the participants' spouses. For example, one participant mentioned,
“My husband will drink alcohol and smoke beedi.” (G2, P6).
Participants would benefit from addiction counseling services in the community.
3.3.3. Organizational
- Wages
The wages of tobacco farm laborers ranged from Rs. 200 to 300 for women and Rs. 300 to 500 for men, depending on the type of work. This gender inequity in wages exists despite the equal number of hours worked by both women and men. Some landowners provide men with alcohol in addition to their salary, which caused alcohol abuse and addiction problem in some households. As mentioned by a participant,
“Men are paid Rs. 300 and women are paid Rs. 200. Along with Rs. 300, men will be given alcohol. If we ask them for more wages, they will start fighting with us. The prices of daily needs have been raised. One litre of oil costs Rs. 200 and they tell us that they do not have money growing in plants to give us wages whenever we ask. The women will be satisfied even if they are paid Rs. 100. They will just take the money and will not question about it.” (G3, P4)
- Tobacco board
At the organizational level, participants did not receive any maternity benefits from the farming organizations and tobacco board. A participant stated,
“Support must be given from the tobacco sector, as we are working for them for many years. If they provide such support it will be even more helpful and we will also be happy. If they conduct health camp from the tobacco sector, it will help us.” (G1, P7). Another participant said, “We have not got any facilities madam. Those who built the tobacco barn have got some facilities. They give it to the farm owners with license and not to the daily wage workers.” (G6, P3)
- Alternate employment
Some participants were willing to shift to alternate employment. However, there are limited employment opportunities in the village, so they are forced to work in tobacco farming. Some participants' husbands do not allow them to work outside their village, so they are unable to take other work. For example, a participant noted,
“Even we feel like coming out of the village and working in garments, but the problem is our husbands will not allow us to do any other work outside the village.” (G5, P5). However, participants were interested in rearing cows as mentioned by a participant, who said, “We can have a living if they get us a cow. We will give the milk to the dairy and get money.” (G3, P3)
Some participants also mentioned other limitations to shifting to alternate employment, such as not having a formal education and having limited employment opportunities in the village. For example, one participant said,
“If there is any company which can hire people like us who cannot read and write, they usually hire only literate people. If they provide an opportunity even, we can work in such companies.” (G5, P4)
- Needs
Participants need monetary support during pregnancy, health care services from the tobacco board, and holidays. One participant mentioned,
“We are anemic after doing the tobacco work, so if they give us money, we will buy the medicines.” (G3, P6)
3.3.4. Community
- Health care services
Most participants used the government hospital for health care services, although a few participants used private health care services for C-section deliveries, other surgeries, and diagnostic procedures like ultrasound or x-rays. A participant said,
“Most of them go to big hospitals for Cesarean section. At that time they will need more money to pay the hospital bills, so if they give some money for the workers from the board it will be very useful for them.” (G1, P1).
Few participants reported home delivery for childbirth.
- Health care providers
At the community level, participants received support from ASHAs, government hospital nurses, and doctors during their pregnancy and post-natal time period. Most of the occupational health information, such as the importance of wearing PPE, and reproductive health information such as family planning were provided by the health care providers. For example, one participant said,
“My husband would take me to the hospital. Sister (nurse) would give us all the information. She would tell us about the gap between children and operation (family planning). After delivery they came after seven months and they advised for an operation. Since I have anemia, I got the operation late. She helped me in everything.” (G4, P2).
Another participant said,
“My mother-in-law and ASHA worker had helped me during pregnancy.” (G3, P4)
- Needs
Participants needed transportation and ambulance services during medical emergencies. A participant mentioned,
“The transportation in our village is very poor. The ambulance people used to give us reasons when we called them. By the time they came to us, the delivery would have already happened.” (G3, P4)
3.3.5. Public Policy
At the societal level, tobacco farm laborer participants did not receive any support from the local, state, and national government and were in need of monetary and nutritional supplements.
- Policies / schemes
Participants stated that laws or policies were lacking as they did not receive any support for their health needs during pregnancy and post-natal period working as women tobacco farm laborers.
- Needs
From the local, state, and national governments, participants need monetary support during prenatal and post-natal periods and for sudden hospitalizations. Participants also need nutritional supplements for themselves and their families. They believe working in tobacco is making them anemic so they are in need of nutritional supplements to manage it. One participant said,
“If we face any problem related to our health and we need to go the hospital and take the treatment there, but we do not have sufficient money, at that time the government should support for the women like us who depend on daily wages. I am suffering from stomach ache but I have never got it checked from the doctor as I am scared what if they ask me to undergo an operation. The government should help such people.” (G2, P7)
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
This study explored the occupational and reproductive health experiences of women tobacco farm laborers during four distinct phases of their lifespan: menstruation, pregnancy, the post-natal period, and post-menopause. Our study participants worked in tobacco farming activities across their life course including during the reproductive phases of life. This study highlights participants’ needs for maternity and early childhood services, substance use counseling services, and monetary support.
Tobacco farming involves intensive manual labor, and our participants reported musculoskeletal disorders in the lower back, wrists, shoulders, knees, and hips, which is similar to other studies conducted among tobacco farmers from Thailand [24]. Chronic low back pain was a health problem among Brazilian tobacco farmers [25]. Tobacco farmers in Brazil were familiar with GTS, pesticide poisoning, and musculoskeletal disorders as health problems associated with working in tobacco farming [12]. In contrast, most participants in our study were not aware of GTS or these other issues. A relationship between work stress and menstrual disorders has been reported among tobacco farmers in Indonesia [13]. Our participants reported pain and discomfort during menstruation, however we must further investigate the effects of nicotine and pesticide exposure on mensuration in this population.
A study conducted in rural China reported that maternal exposure to chemical fertilizers during pregnancy was associated with birth defects in infants [26]. In this study, participants mentioned being exposed to fertilizers during pregnancy, which, along with pesticide exposures, may explain the high incidence of adverse pregnancy and birth outcomes (Table 2). Pesticide related symptoms such as loss of appetite, headache, eye irritation, dyspepsia/difficult digestion, skin allergy, and dizziness were reported by our participants while grading tobacco leaves, which could be due to exposure to pesticide residues on the tobacco leaves [27]. An exposure assessment could test this hypothesis and provide information needed to develop interventions.
Some participants believed tobacco use can cause harm, and most participants mentioned cancer as a health effect. They reported getting this information from doctors in hospitals, seeing the anti-tobacco advertisements on tobacco packet covers, television, and radio. However, not all participants believed working in tobacco can cause harm. This could be due to limited health communication on the effects of occupational tobacco exposure.
Factors that influence the tobacco farming are organizational factors such as improved access to credit, well-developed supply chains, and governmental assistance [28,29]. The participants in these FGDs, identified education, lack of employment opportunities in the villages, spouses not allowing them to work in other villages as some of the barriers for shifting to an alternate employment. Providing adult education opportunities in the villages, financial and technical support, such as accounting training, could have the potential to increase the likelihood and viability of switching to alternative livelihood [29].
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
The study findings were anchored to the widely adopted SEM to guide future research. However, the study has limitations. First, the FGDs were conducted in Kannada and translated to English and some of the cultural context could have been lost in translation. Second, we lack the perspectives of stakeholders across other organizations and job roles, therefore our study participants do not reflect a representative sample of tobacco farming in general.
4.3. Relevance of the Study and Policy Implications
Findings from this study will enable researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the impacts of tobacco farming on the livelihoods and reproductive and occupational health of the women farm laborers and their families. Our findings support the need for a holistic approach to improving the health of women tobacco farm laborers in India across individual, interpersonal, community, organizational, and broader societal levels. Our findings indicate the need for improved support for women tobacco farm laborers during menstruation, pregnancy, the post-natal period, and menopause, which are all critical reproductive phases of a woman's life. Social policies and community interventions in these areas should be mindful of the needs of women tobacco farm laborers. Economically sustainable alternatives are needed to prevent possible adverse social and economic impacts on the women tobacco farm laborers, whose livelihoods depend on tobacco farming.
5. Conclusions
Women tobacco farm laborers reported GTS symptoms and musculoskeletal disorders during pregnancy and post-natal periods. Policy makers should prioritize the needs of this under-served population while making tobacco policies and improving occupational health practices.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Appendix 1: Interview questionnaire; Appendix 2: FGD guide.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.R., P.M., and L.B.G.; Methodology, A.W., F.v.H., P.M., Z.C., and L.B.G; Software, P.R., and M.N.B.; Formal analysis, P.R., M.N.B.; Investigation, S.N., and P.R.; Resources, P.M., and P.J.; Data curation, S.N.; Writing-original draft preparation, P.R., F.v.H., and M.N.B.; Writing-review and editing, P.M., L.B.G., F.v.H., A.W., A.A.L., K.K., and Z.C.; Visualization, K.M., P.R.; Supervision, A.A.L., K.K., Z.C., P.M., L.B.G., F.v.H.; Project administration, P.J.; Funding acquisition, P.R., P.M., and L.B.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the University of Arizona’s 2022 Global Health Institute Scholars Program. This was awarded to PR for her summer research program in India.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethics approval for this study was obtained from the Institutional Ethics Review Board at PHRII (IERB Protocol number # 2022-05-07-68, 07 May 2022). The University of Arizona IRB office has confirmed reliance for this study that is relying on external IRB PHRII as the IRB of Record (STUDY00001243, 08 June 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data not available due to the conditions of ethical approval. Participants were assured that raw data would not be shared.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Public Health Research Institute of India’s community health workers and Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA) for their help recruiting study participants. We thank the study participants for sharing their experiences.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Tobacco Production, Our World in Data 2022.
- WHO FCTC Viable Alternatives to Tobacco Growing: An Economic Model for Implementing Aticles 17 and 18.
- Fotedar, S.; Fotedar, V. Green Tobacco Sickness: A Brief Review. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 21, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKnight, R.H.; Levine, E.J.; Rodgers, G.C. Detection of Green Tobacco Sickness by a Regional Poison Center. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1994, 36, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Campos, É.; Costa, V.I.-B.D.; Alves, S.R.; Rosa, A.C.S.; Geraldino, B.R.; Meira, B.D.C.; Cunha, V.; Cavalcante, T.M.; Turci, S.R.; Sarpa, M.; et al. Occurrence of Green Tobacco Sickness and Associated Factors in Farmers Residing in Dom Feliciano Municipality, Rio Grande Do Sul State, Southern Region of Brazil. Cad. Saúde Pública 2020, 36, e00122719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizenecker, R.; Deal, W.B. Tobacco Cropper’s Sickness. J. Fla. Med. Assoc. 1970, 57, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Parikh, J.R.; Gokani, V.N.; P. B.Doctor; Kulkarni, P.K.; Shah, A.R.; Saiyed, H.N. Acute and Chronic Health Effects Due to Green Tobacco Exposure in Agricultural Workers. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2005, 47, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Lim, H.-S.; Lee, K.; Yoo, S.-J. Green Tobacco Sickness Among Tobacco Harvesters in a Korean Village. Saf. Health Work 2018, 9, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, J.S.; Altman, D.G.; Klein, M.; White, W. Green Tobacco Sickness. Tob. Control 1998, 7, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Factsheet: Women Have a Right to a Tobacco-Free World.
- Fiori, N.S.; Fassa, A.G.; Faria, N.M.X.; Meucci, R.D.; Miranda, V.I.; Christiani, D.C. Wheezing in Tobacco Farm Workers in Southern Brazil. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2015, 58, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.M.D.; Oliveira, A.P.N. de; Turci, S.R.B.; Dantas, R.M.; Silva, V.D.S.P. da; Gross, C.; Jensen, T.; Silva, V.L. da C.E. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices of women farmers concerning tobacco agriculture in a municipality in Southern Brazil. Cad. Saude Publica 2017, 33Suppl 3, e00080516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indriyanti, I.; Martiana, T.; Rahman, F.S. Correlation Individual Characteristics and Work Stress with Menstrual Disorders in Tobacco Farmers. Indones. J. Occup. Saf. Health 2019, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Tobacco and Its Environmental Impact: An Overview. Geneva, Switzerland. 2017.
- Hussain, A.G.; Rouf, A.S.S.; Shimul, S.N.; Nargis, N.; Kessaram, T.M.; Huq, S.M.; Kaur, J.; Shiekh, M.K.A.; Drope, J. The Economic Cost of Tobacco Farming in Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, E9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chingosho, R.; Dare, C.; van Walbeek, C. Tobacco Farming and Current Debt Status among Smallholder Farmers in Manicaland Province in Zimbabwe. Tob. Control 2021, 30, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Tobacco Production and Trade. Global Infographic.
- Muniswamy, S.; Maliakel, S.F. A Comparative Study on the Health Problems and Substance Abuse among the Tobacco Farmers and Non-Tobacco Farmers in Hassan District, Karnataka. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2021, 25, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeroy, K.R.; Bibeau, D.; Steckler, A.; Glanz, K. An Ecological Perspective on Health Promotion Programs. Health Educ. Q. 1988, 15, 351–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, B.; Sim, J.; Kingstone, T.; Baker, S.; Waterfield, J.; Bartlam, B.; Burroughs, H.; Jinks, C. Saturation in Qualitative Research: Exploring Its Conceptualization and Operationalization. Qual. Quant. 2018, 52, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VERBI Software. (2021) MAXQDA 2022 [Computer Software].
- Tong, A.; Sainsbury, P.; Craig, J. Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ): A 32-Item Checklist for Interviews and Focus Groups. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2007, 19, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, S.; Sekerdej, M.; von Hecker, U. The Role of Indian Caste Identity and Caste Inconsistent Norms on Status Representation. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongtawelert, A.; Buchholz, B.; Sujitrarath, D.; Laohaudomchok, W.; Kongtip, P.; Woskie, S. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Musculoskeletal Disorders among Thai Burley Tobacco Farmers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meucci, R.D.; Fassa, A.G.; Faria, N.M.X.; Fiori, N.S. Chronic Low Back Pain among Tobacco Farmers in Southern Brazil. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2015, 21, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, S.; Wu, J.; Pei, L.; Shang, X. Association between Maternal Exposure to Chemical Fertilizer and the Risk of Birth Defects in a Rural Population in Northern China: A Population-Based Study. Int. Health 2023, 15, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, N.M.X.; Meucci, R.D.; Fiori, N.S.; Carret, M.L.V.; Mello-da-Silva, C.A.; Fassa, A.G. Acute Pesticide Poisoning in Tobacco Farming, According to Different Criteria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahadewo, G.A.; Drope, J.; Li, Q.; Witoelar, F.; Lencucha, R. In-and-Out of Tobacco Farming: Shifting Behavior of Tobacco Farmers in Indonesia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 9416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appau, A.; Drope, J.; Witoelar, F.; Chavez, J.J.; Lencucha, R. Why Do Farmers Grow Tobacco? A Qualitative Exploration of Farmers Perspectives in Indonesia and Philippines. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 16, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallis JF, Owen, N., Fisher, E.B. Ecological Models of Health Behavior. Health Behavior and Health Education. 2008, 465–486.
Figure 1.
Duration of tobacco farming and processing activities.
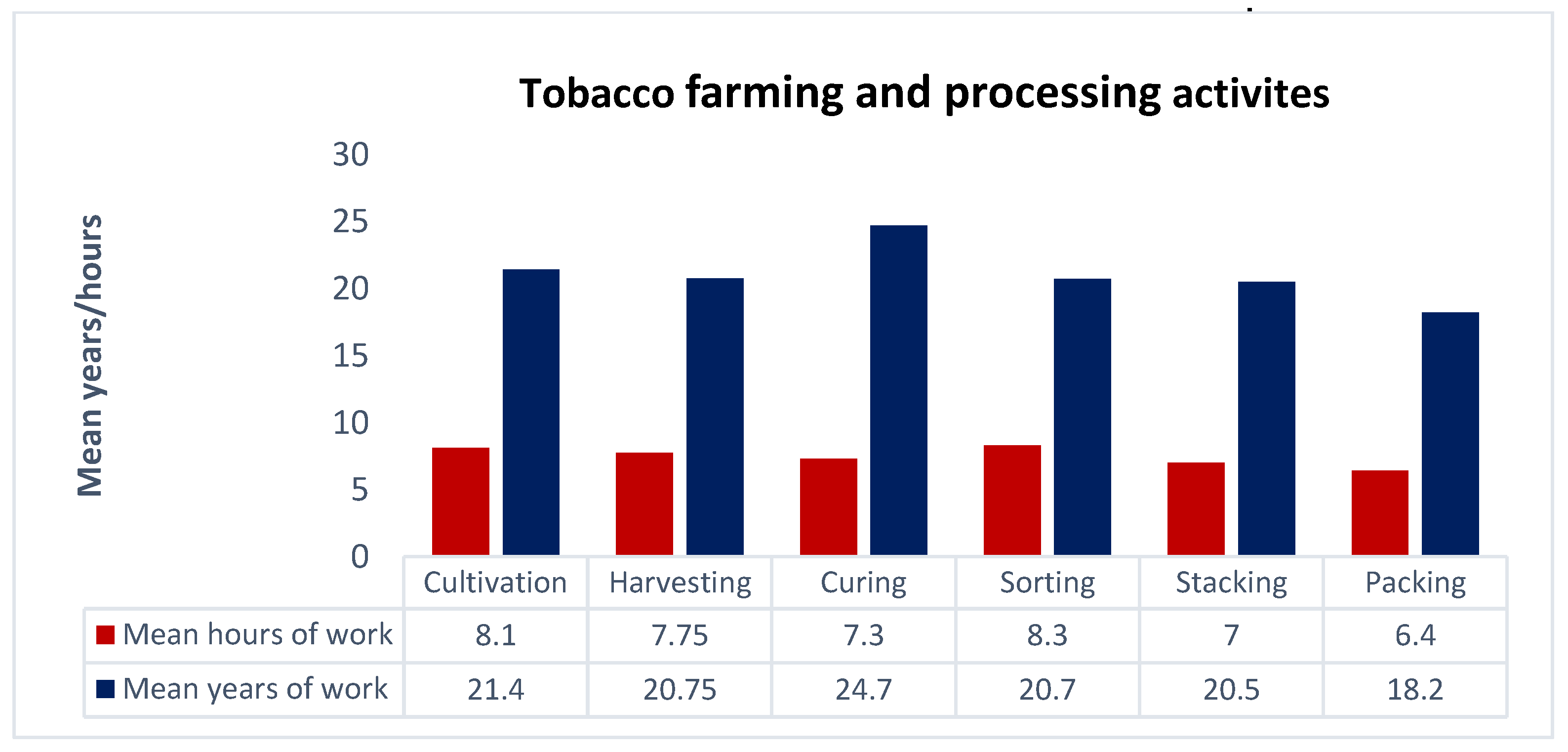
Figure 2.
An overview of the themes that represent occupational and reproductive health challenges for women tobacco farmers across the five levels of the socioecological model.
Figure 2.
An overview of the themes that represent occupational and reproductive health challenges for women tobacco farmers across the five levels of the socioecological model.
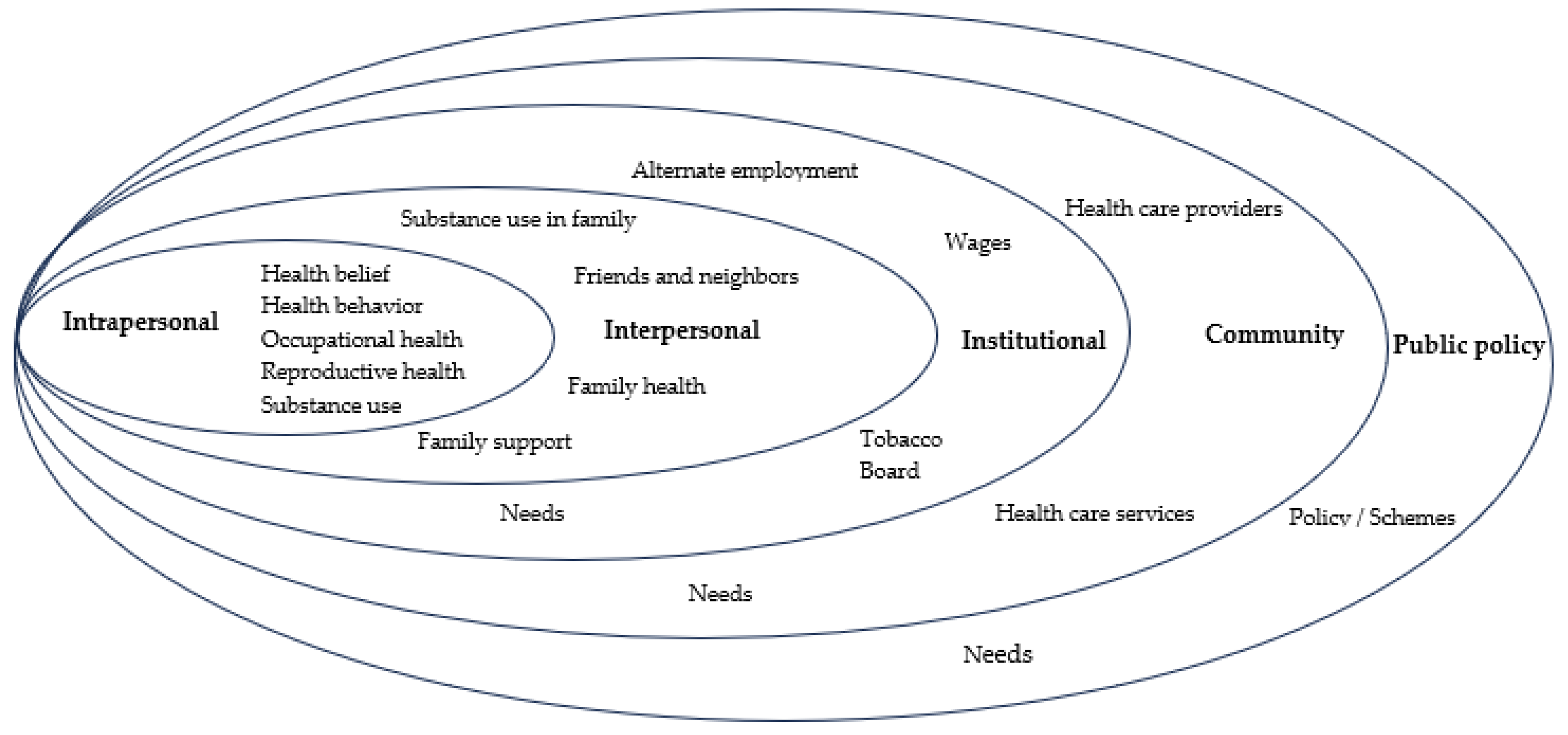
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of participants (n = 41).
| Variable | n (%) |
| Mean age (in years) | 38.22±7.95 |
| Age groups (in years) | |
| 20 to 30 years | 7 (17.1) |
| 31 to 40 years | 22 (53.7) |
| 41 to 50 years | 8 (19.51) |
| 51 to 60 years | 4 (9.76) |
| Marital status | |
| Married | 33 (80.5) |
| Widow | 8 (19.5) |
| Religion | |
| Hindu | 41 (100) |
| Caste | |
| Scheduled caste | 30 (73.2) |
| Scheduled tribes | 1 (2.4) |
| Other backward caste | 3 (7.3) |
| General caste | 7 (17.1) |
| Education | |
| Any college degree | 1 (2.4) |
| Secondary school (class 11 and 12) | 6 (14.6) |
| High school (class 6 to 10) | 12 (29.3) |
| Primary school (class 1 to 5) | 2 (4.9) |
| Literate but no formal education | 1 (2.4) |
| Illiterate | 19 (46.3) |
| Annual Income (In Rupees) | |
| Less than 20000 (< $240 USD*) | 10 (24.4) |
| 20000 to 50000 ($240 to $600 USD*) | 25 (61.0) |
| More than 50000 (> $600 USD*) | 6 (14.6) |
| Tobacco use | |
| Smoking tobacco | 0 |
| Smokeless tobacco | 6 (14.6) |
* United States Dollar (USD)
Table 2.
Occupational and reproductive health of participants (n = 41).
| Variable | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Participants involved in tobacco farming activities | |
| Cultivation | 36 (87.8) |
| Harvesting | 40 (97.6) |
| Curing | 13 (31.7) |
| Sorting | 36 (87.8) |
| Stacking | 33 (80.5) |
| Packing | 22 (53.6) |
| Total number of pregnancies | |
| ≤ 2 pregnancies | 30 (73.2) |
| >2 pregnancies | 11 (26.8) |
| History of abortion/miscarriage/death of child | |
| At least one abortion | 1 (2.4) |
| Miscarriage | 5 (12.2) |
| History of death of child after birth to one year of age | 4 (9.8) |
| Tobacco exposure during pregnancy | |
| Consumed tobacco during pregnancy | 2 (4.9) |
| Tobacco farming during pregnancy | 33 (80.5) |
| Exposed to tobacco dust during pregnancy | 18 (43.9) |
| Wearing personal protection equipment (PPE) during work | 6 (14.6) |
| History of any allergy | |
| During pregnancy | 6 (14.6) |
| During post-natal period | 5 (12.2) |
| In child 6 months after birth | 8 (19.5) |
| In child 1 year after birth | 9 (22.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Copyright: This open access article is published under a Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, which permit the free download, distribution, and reuse, provided that the author and preprint are cited in any reuse.
MDPI Initiatives
Important Links
© 2024 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated







