Submitted:
12 April 2024
Posted:
15 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Sampling the Respiratory Tract Fluid Lining
3. PExA Basics
4. PExA Techniques
4.1. Breathing Manoeuvre
4.2. Analytical Techniques
5. PExA in Pathology
5.1. Smoking
5.2. Asthma
5.3. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
5.4. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
5.5. COVID-19
6. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NHS England. Respiratory disease https://www.england.nhs.uk/ourwork/clinical-policy/respiratory-disease/ (accessed Nov 11, 2023).
- Soriano, J. B.; Kendrick, P. J.; Paulson, K. R.; Gupta, V.; Abrams, E. M.; Adedoyin, R. A.; Adhikari, T. B.; Advani, S. M.; Agrawal, A.; Ahmadian, E.; et al. Prevalence and Attributable Health Burden of Chronic Respiratory Diseases, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Respir Med, 2020, 8, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intensive Care National Audit and Research Centre. INCARC Reports.
- Chang, R.; Elhusseiny, K. M.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Sun, W.-Z. COVID-19 ICU and Mechanical Ventilation Patient Characteristics and Outcomes—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One, 2021, 16, e0246318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campling, J.; Jones, D.; Chalmers, J.; Jiang, Q.; Vyse, A.; Madhava, H.; Ellsbury, G.; Rabe, A.; Slack, M. Clinical and Financial Burden of Hospitalised Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Patients with Selected Underlying Comorbidities in England. BMJ Open Respir Res, 2020, 7, e000703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telenga, E. D.; van den Berge, M.; ten Hacken, N. H. T.; Riemersma, R. A.; van der Molen, T.; Postma, D. S. Small Airways in Asthma: Their Independent Contribution to the Severity of Hyperresponsiveness: Table 1–. European Respiratory Journal, 2013, 41, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, W.; Guo, S.; Yang, F.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, B.; Huang, T.; Li, L.; Wang, K. Association between ARDS Etiology and Risk of Noninvasive Ventilation Failure. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2022, 19, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dushianthan, A. , Goss, V. , Cusack, R., Grocott, M. P., & Postle, A. D. Phospholipid composition and kinetics in different endobronchial fractions from healthy volunteers. BMC pulmonary medicine, 2014, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A. , Dodagatta-Marri, E. , Tsolaki, A. G., & Kishore, U. An Insight into the Diverse Roles of Surfactant Proteins, SP-A and SP-D in Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Frontiers in immunology, 2012, 3, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürch, D. , Ospina, O. L., Cruz, A., & Pérez-Gil, J. Combined and independent action of proteins SP-B and SP-C in the surface behavior and mechanical stability of pulmonary surfactant films. Biophysical journal, 2010, 99(10), 3290–3299. [CrossRef]
- Dushianthan, A., Goss, V., Cusack, R., Grocott, M. P., & Postle, A. D. (2014). Altered molecular specificity of surfactant phosphatidycholine synthesis in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Respiratory research, 15(1), 128. [CrossRef]
- Bake, B.; Ljungström, E.; Claesson, A.; Carlsen, H. K.; Holm, M.; Olin, A. C. Exhaled Particles after a Standardized Breathing Maneuver. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv, 2017, 30 (4), 267–273. [CrossRef]
- Larsson, P.; Lärstad, M.; Bake, B.; Hammar, O.; Bredberg, A.; Almstrand, A.; Mirgorodskaya, E.; Olin, A. Exhaled Particles as Markers of Small Airway Inflammation in Subjects with Asthma. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging, 2017, 37 (5), 489–497. [CrossRef]
- Lärstad, M.; Almstrand, A.-C.; Larsson, P.; Bake, B.; Larsson, S.; Ljungström, E.; Mirgorodskaya, E.; Olin, A.-C. Surfactant Protein A in Exhaled Endogenous Particles Is Decreased in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patients: A Pilot Study. PLoS One, 2015, 10, e0144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiszhar, Z.; Horvath, I. Induced Sputum Analysis: Step by Step. Breathe, 2013, 9, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatakanon, A.; Lim, S.; Barnes, P. J. Changes in Sputum Eosinophils Predict Loss of Asthma Control. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2000, 161, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavord, I. D.; Brightling, C. E.; Woltmann, G.; Wardlaw, A. J. Non-Eosinophilic Cor Ticosteroid Unresponsive Asthma. The Lancet, 1999, 353, 2213–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, K. R.; Ha, D. M.; Schwarz, M. I.; Chan, E. D. Bronchoalveolar Lavage as a Diagnostic Procedure: A Review of Known Cellular and Molecular Findings in Various Lung Diseases. J Thorac Dis, 2020, 12, 4991–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain-Alkhateeb, L.; Bake, B.; Holm, M.; Emilsson, Ö.; Mirgorodskaya, E.; Olin, A. C. Novel Non-Invasive Particles in Exhaled Air Method to Explore the Lining Fluid of Small Airways - A European Population-Based Cohort Study. BMJ Open Respir Res, 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, I.; Hunt, J.; Barnes, P. J. Exhaled Breath Condensate: Methodological Recommendations and Unresolved Questions. European Respiratory Journal, 2005, 26, 523–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, I.; Barnes, P. J.; Loukides, S.; Sterk, P. J.; Högman, M.; Olin, A.-C.; Amann, A.; Antus, B.; Baraldi, E.; Bikov, A. A European Respiratory Society Technical Standard: Exhaled Biomarkers in Lung Disease. European Respiratory Journal, 2017, 49, 1600965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Połomska, J.; Bar, K.; Sozańska, B. Exhaled Breath Condensate—A Non-Invasive Approach for Diagnostic Methods in Asthma. J Clin Med, 2021, 10, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, J. Exhaled Breath Condensate: An Evolving Tool for Noninvasive Evaluation of Lung Disease. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 2002, 110, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, S. R.; Davis, C. S.; Kovacs, E. J. Exhaled Breath Condensate Collection in the Mechanically Ventilated Patient. Respir Med, 2012, 106, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holz, O.; Müller, M.; Carstensen, S.; Olin, A. C.; Hohlfeld, J. M. Inflammatory Cytokines Can Be Monitored in Exhaled Breath Particles Following Segmental and Inhalation Endotoxin Challenge in Healthy Volunteers. Sci Rep, 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effros, R. M.; Dunning, M. B.; Biller, J.; Shaker, R. The Promise and Perils of Exhaled Breath Condensates. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 2004, 287, L1073–L1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, P. C.; Raposo, M.; Vassilenko, V. Breath Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) as Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Pathological Conditions: A Review. Biomed J, 2023, 46, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzatenta, A.; Pokorski, M.; Sartucci, F.; Domenici, L.; Di Giulio, C. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) Fingerprint of Alzheimer’s Disease. Respir Physiol Neurobiol, 2015, 209, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabel, R.; Fijten, R.; Smolinska, A.; Dallinga, J.; Boumans, M.-L.; Stobberingh, E.; Boots, A.; Roekaerts, P.; Bergmans, D.; van Schooten, F. J. Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds in Exhaled Breath to Diagnose Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Sci Rep, 2015, 5, 17179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, P.; Loeseken, C.; Schubert, J. K.; Miekisch, W. Breath Gas Aldehydes as Biomarkers of Lung Cancer. Int J Cancer, 2010, 126, 2663–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P. D.; Latzin, P.; Verbanck, S.; Hall, G. L.; Horsley, A.; Gappa, M.; Thamrin, C.; Arets, H. G. M.; Aurora, P.; Fuchs, S. I.; et al. Consensus Statement for Inert Gas Washout Measurement Using Multiple- and Single- Breath Tests. European Respiratory Journal, 2013, 41, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almstrand, A.-C.; Ljungström, E.; Lausmaa, J.; Bake, B.; Sjövall, P.; Olin, A.-C. Airway Monitoring by Collection and Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Exhaled Particles. Anal Chem, 2009, 81, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viklund, E.; Kokelj, S.; Larsson, P.; Nordén, R.; Andersson, M.; Beck, O.; Westin, J.; Olin, A. C. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Can Be Detected in Exhaled Aerosol Sampled during a Few Minutes of Breathing or Coughing. Influenza Other Respir Viruses, 2022, 16, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, G. R.; Morawska, L. The Mechanism of Breath Aerosol Formation. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv, 2009, 22, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, H.; Gerth, E.; Ljungström, E.; Larsson, P.; Almstrand, A.-C.; Bake, B.; Olin, A.-C. Effects of Breath Holding at Low and High Lung Volumes on Amount of Exhaled Particles. Respir Physiol Neurobiol, 2013, 185, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behndig, A. F.; Mirgorodskaya, E.; Blomberg, A.; Olin, A.-C. Surfactant Protein A in Particles in Exhaled Air (PExA), Bronchial Lavage and Bronchial Wash - a Methodological Comparison. Respir Res, 2019, 20, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östling, J.; Van Geest, M.; Olsson, H. K.; Dahlen, S. E.; Viklund, E.; Gustafsson, P. M.; Mirgorodskaya, E.; Olin, A. C. A Novel Non-Invasive Method Allowing for Discovery of Pathologically Relevant Proteins from Small Airways. Clin Proteomics, 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, E.; Andreasson, J.; Fakhro, M.; Olin, A. C.; Wagner, D.; Hyllén, S.; Lindstedt, S. Mechanically Ventilated Patients Exhibit Decreased Particle Flow in Exhaled Breath as Compared to Normal Breathing Patients. ERJ Open Res, 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koca, H.; Farbrot, A.; Olin, A.-C.; Emilsson, Ö. I. Surfactant Protein A in Particles in Exhaled Air and Plasma. Respir Physiol Neurobiol, 2022, 301, 103899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessler, M. B.; Summer, R. S. Surfactant Lipids at the Host–Environment Interface. Metabolic Sensors, Suppressors, and Effectors of Inflammatory Lung Disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2016, 54, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokelj, S.; Kim, J. L.; Andersson, M.; Eden, G. R.; Bake, B.; Olin, A. C. Intra-Individual Variation of Particles in Exhaled Air and of the Contents of Surfactant Protein A and Albumin. PLoS One, 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helleday, R.; Segerstedt, B.; Forsberg, B.; Mudway, I.; Nordberg, G.; Bernard, A.; Blomberg, A. Exploring the Time Dependence of Serum Clara Cell Protein as a Biomarker of Pulmonary Injury in Humans. Chest, 2006, 130, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh, S. V.; Sorensen, G. L.; Tornoe, I.; Lottenburger, T.; Ytting, H.; Nielsen, H. J.; Junker, P.; Holmskov, U. Long-Term Stability and Circadian Variation in Circulating Levels of Surfactant Protein D. Immunobiology, 2010, 215, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.; Mirgorodskaya, E.; Koca, H.; Viklund, E.; Richardson, M.; Gustafsson, P.; Olin, A. C.; Siddiqui, S. Particles in Exhaled Air (PExA): Non-Invasive Phenotyping of Small Airways Disease in Adult Asthma. J Breath Res, 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmadi, F. H.; Wilkinson, M.; Keevil, B.; Niven, R.; Fowler, S. J. Short- and Medium-Term Effect of Inhaled Corticosteroids on Exhaled Breath Biomarkers in Severe Asthma. J Breath Res, 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokelj, S.; Östling, J.; Fromell, K.; Vanfleteren, L. E. G. W.; Olsson, H. K.; Nilsson Ekdahl, K.; Nilsson, B.; Olin, A.-C. Activation of the Complement and Coagulation Systems in the Small Airways in Asthma. Respiration, 2023, 102, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokelj, S.; Östling, J.; Georgi, B.; Fromell, K.; Ekdahl, K. N.; Olsson, H. K.; Olin, A.-C. Smoking Induces Sex-Specific Changes in the Small Airway Proteome. Respir Res, 2021, 22, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, P.; Holz, O.; Koster, G.; Postle, A.; Olin, A.-C.; Hohlfeld, J. M. Exhaled Breath Particles as a Novel Tool to Study Lipid Composition of Epithelial Lining Fluid from the Distal Lung. BMC Pulm Med, 2023, 23, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almstrand, A.-C.; Josefson, M.; Bredberg, A.; Lausmaa, J.; Sjovall, P.; Larsson, P.; Olin, A.-C. TOF-SIMS Analysis of Exhaled Particles from Patients with Asthma and Healthy Controls. European Respiratory Journal, 2012, 39, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasson, J.; Bodén, E.; Fakhro, M.; von Wachter, C.; Olm, F.; Malmsjö, M.; Hallgren, O.; Lindstedt, S. Exhaled Phospholipid Transfer Protein and Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Respir Res, 2022, 23, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredberg, A.; Josefson, M.; Almstrand, A.-C.; Lausmaa, J.; Sjövall, P.; Levinsson, A.; Larsson, P.; Olin, A.-C. Comparison of Exhaled Endogenous Particles from Smokers and Non-Smokers Using Multivariate Analysis. Respiration, 2013, 86, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, E.; Hyllén, S.; Algotsson, L.; Wagner, D. E.; Lindstedt, S. Particle Flow Profiles from the Airways Measured by Pexa Differ in Lung Transplant Recipients Who Develop Primary Graft Dysfunction. Experimental and Clinical Transplantation, 2019, 17, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, E.; Wlosinska, M.; Algotsson, L.; Olin, A. C.; Wagner, D.; Pierre, L.; Lindstedt, S. A New Way of Monitoring Mechanical Ventilation by Measurement of Particle Flow from the Airways Using Pexa Method in Vivo and during Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion in DCD Lung Transplantation. Intensive Care Medicine Experimental , 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, E.; Pierre, L.; Fakhro, M.; Algotsson, L.; Malmsjö, M.; Hyllén, S.; Lindstedt, S. Different Particle Flow Patterns from the Airways after Recruitment Manoeuvres Using Volume-Controlled or Pressure-Controlled Ventilation. Intensive Care Med Exp, 2019, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, E.; Pierre, L.; Fakhro, M.; Malmsjö, M.; Lindstedt, S.; Hyllén, S. Releasing High Positive End-Expiratory Pressure to a Low Level Generates a Pronounced Increase in Particle Flow from the Airways. Intensive Care Med Exp, 2023, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpaij, O. A.; Muiser, S.; Bell, A. J.; Kerstjens, H. A. M.; Galban, C. J.; Fortuna, A. B.; Siddiqui, S.; Olin, A. C.; Nawijn, M. C.; van Den Berge, M. Assessing Small Airways Dysfunction in Asthma, Asthma Remission and Healthy Controls Using Particles in Exhaled Air. ERJ Open Research. European Respiratory Society October 1, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Emilsson, Ö. I.; Kokelj, S.; Östling, J.; Olin, A.-C. Exhaled Biomarkers in Adults with Non-Productive Cough. Respir Res, 2023, 24, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emilsson, Ö. I.; Benediktsdóttir, B.; Ólafsson, Í.; Cook, E.; Júlíusson, S.; Björnsson, E. S.; Guðlaugsdóttir, S.; Guðmundsdóttir, A. S.; Mirgorodskaya, E.; Ljungström, E. Respiratory Symptoms, Sleep-Disordered Breathing and Biomarkers in Nocturnal Gastroesophageal Reflux. Respir Res, 2016, 17, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericson, P. A.; Mirgorodskaya, E.; Hammar, O. S.; Viklund, E. A.; Almstrand, A.-C. R.; Larsson, P. J.-W.; Riise, G. C.; Olin, A.-C. Low Levels of Exhaled Surfactant Protein A Associated With BOS After Lung Transplantation. Transplant Direct, 2016, 2, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallgren, F.; Stenlo, M.; Niroomand, A.; Broberg, E.; Hyllén, S.; Malmsjö, M.; Lindstedt, S. Particle Flow Rate from the Airways as Fingerprint Diagnostics in Mechanical Ventilation in the Intensive Care Unit: A Randomised Controlled Study. ERJ Open Res, 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirdman, G.; Bodén, E.; Kjellström, S.; Fraenkel, C.-J.; Olm, F.; Hallgren, O.; Lindstedt, S. Proteomic Characteristics and Diagnostic Potential of Exhaled Breath Particles in Patients with COVID-19. Clin Proteomics, 2023, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstedt, S.; Hyllen, S. New Insight: Particle Flow Rate from the Airways as an Indicator of Cardiac Failure in the Intensive Care Unit. ESC Heart Fail, 2023, 10, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungkvist, G.; Tinnerberg, H.; Löndahl, J.; Klang, T.; Viklund, E.; Kim, J.-L.; Schiöler, L.; Forsgard, N.; Olin, A.-C. Exploring a New Method for the Assessment of Metal Exposure by Analysis of Exhaled Breath of Welders. Int Arch Occup Environ Health, 2022, 95, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenlo, M.; Hyllén, S.; Silva, I. A. N.; Bölükbas, D. A.; Pierre, L.; Hallgren, O.; Wagner, D. E.; Lindstedt, S. Increased Particle Flow Rate from Airways Precedes Clinical Signs of ARDS in a Porcine Model of LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 2020, 318, L510–L517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viklund, E.; Bake, B.; Hussain-Alkhateeb, L.; Akdeva, H. K.; Larsson, P.; Olin, A. C. Current Smoking Alters Phospholipid- And Surfactant Protein A Levels in Small Airway Lining Fluid: An Explorative Study on Exhaled Breath. PLoS One, 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwitserloot, A. M.; Verhoog, F. A.; van den Berge, M.; Gappa, M.; Oosterom, H. W.; Willemse, B. W. M.; Koppelman, G. H. Comparison of Particles in Exhaled Air and Multiple Breath Washout for Assessment of Small Airway Function in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. E. The Pulmonary Surfactant: Impact of Tobacco Smoke and Related Compounds on Surfactant and Lung Development. Tob Induc Dis, 2004, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, E. A.; Lynch, D. A.; Curran-Everett, D.; Curtis, J. L.; Austin, J. H. M.; Grenier, P. A.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Bailey, W. C.; DeMeo, D. L.; Casaburi, R. H.; et al. Clinical and Radiologic Disease in Smokers With Normal Spirometry. JAMA Intern Med, 2015, 175, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouwels, S. D.; Klont, F.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Wiersma, V. R.; Faiz, A.; van den Berge, M.; Horvatovich, P.; Bischoff, R.; ten Hacken, N. H. T. Cigarette Smoking Acutely Decreases Serum Levels of the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Biomarker SRAGE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2018, 198, 1456–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D. J.; Yerkovich, S. T.; Towers, M. A.; Carroll, M. L.; Thomas, R.; Upham, J. W. Reduced Soluble Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products in COPD. European Respiratory Journal, 2011, 37, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigham, E. P.; West, N. E. Diagnosis of Asthma: Diagnostic Testing. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorkness, R. L.; Bleecker, E. R.; Busse, W. W.; Calhoun, W. J.; Castro, M.; Chung, K. F.; Curran-Everett, D.; Erzurum, S. C.; Gaston, B. M.; Israel, E.; et al. Lung Function in Adults with Stable but Severe Asthma: Air Trapping and Incomplete Reversal of Obstruction with Bronchodilation. J Appl Physiol, 2008, 104, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochs-Balcom, H. M.; Grant, B. J. B.; Muti, P.; Sempos, C. T.; Freudenheim, J. L.; Browne, R. W.; McCann, S. E.; Trevisan, M.; Cassano, P. A.; Iacoviello, L.; et al. Antioxidants, Oxidative Stress, and Pulmonary Function in Individuals Diagnosed with Asthma or COPD. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2006, 60, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, S. T.; Milovanova, T.; Kierstein, S.; Cao, Y.; Atochina, E. N.; Tomer, Y.; Russo, S. J.; Beers, M. F.; Haczku, A. Surfactant Protein-A Inhibits Aspergillus Fumigatus-Induced Allergic T-Cell Responses. Respir Res, 2005, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledford, J. G.; Addison, K. J.; Foster, M. W.; Que, L. G. Eosinophil-Associated Lung Diseases. A Cry for Surfactant Proteins A and D Help? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2014, 51, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higham, A.; Quinn, A. M.; Cançado, J. E. D.; Singh, D. The Pathology of Small Airways Disease in COPD: Historical Aspects and Future Directions. Respir Res, 2019, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, N.; Hattori, N.; Tanaka, S.; Horimasu, Y.; Haruta, Y.; Yokoyama, A.; Kohno, N.; Kinnula, V. L. Levels of Surfactant Proteins A and D and KL-6 Are Elevated in the Induced Sputum of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients: A Sequential Sputum Analysis. Respiration, 2011, 82, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, W.; Toljamo, T.; Ohlmeier, S.; Vuopala, K.; Nieminen, P.; Kobayashi, H.; Kinnula, V. L. Elevation of Surfactant Protein A in Plasma and Sputum in Cigarette Smokers. European Respiratory Journal, 2011, 38, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, C. W.; Kumley, B. K.; Area-Gomez, E.; Xu, Y.; Dabo, A. J.; Geraghty, P.; Campos, M.; Foronjy, R.; Garcia-Arcos, I. Decreased Surfactant Lipids Correlate with Lung Function in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). PLoS One, 2020, 15 (2), e0228279. [CrossRef]
- Matthay, M.A. , Zemans, R. L., Zimmerman, G.A. et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbaugh, DavidG.; Boyd Bigelow, D.; Petty, ThomasL.; Levine, BernardE. ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS IN ADULTS. The Lancet, 1967, 290 (7511), 319–323. [CrossRef]
- ARDS Definition Task Force, Ranieri, V. M., Rubenfeld, G. D., Thompson, B. T., Ferguson, N. D., Caldwell, E., Fan, E., Camporota, L., & Slutsky, A. S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition. JAMA, 2012,307(23), 2526–2533. [CrossRef]
- Matthay, M. A. , Arabi, Y., Arroliga, A. C., Bernard, G., Bersten, A. D., Brochard, L. J., Calfee, C. S., Combes, A., Daniel, B. M., Ferguson, N. D., Gong, M. N., Gotts, J. E., Herridge, M. S., Laffey, J. G., Liu, K. D., Machado, F. R., Martin, T. R., McAuley, D. F., Mercat, A., Moss, M., … Wick, K. D. A New Global Definition of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 2024, 209(1), 37–47. [CrossRef]
- Hite, R. D. , Grier, B. L., Waite, B. M., Veldhuizen, R. A., Possmayer, F., Yao, L. J., & Seeds, M. C. (2012). Surfactant protein B inhibits secretory phospholipase A2 hydrolysis of surfactant phospholipids. American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology, 2012, 302(2), L257–L265. [CrossRef]
- Dushianthan, A. , Grocott, M. P. W., Murugan, G. S., Wilkinson, T. M. A., & Postle, A. D. (2023). Pulmonary Surfactant in Adult ARDS: Current Perspectives and Future Directions. Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland), 13(18), 2964. [CrossRef]
- Holm, B. A. , Keicher, L., Liu, M. Y., Sokolowski, J., & Enhorning, G. Inhibition of pulmonary surfactant function by phospholipases. Journal of applied physiology, 1991, 71(1), 317–321. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Capote, K. , Manzanares, D., Haines, T., & Possmayer, F. Reactive oxygen species inactivation of surfactant involves structural and functional alterations to surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C. Biophysical journal, 2006, 90(8), 2808–2821. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D. A.; Ausiello, D.; Salzman, J.; Devlin, T.; Langer, R.; Beddingfield, B. J.; Fears, A. C.; Doyle-Meyers, L. A.; Redmann, R. K.; Killeen, S. Z.; et al. Exhaled Aerosol Increases with COVID-19 Infection, Age, and Obesity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2021, 118 (8). [CrossRef]
- Hamid, E. A.; Ali, W.; Ahmed, H.; Megawer, A.; Osman, W. Significance of Acute Phase Reactants as Prognostic Biomarkers for Pneumonia in Children. Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal, 2021, 14 (3), 1309–1321. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, H. K.; Mehra, M. R. COVID-19 Illness in Native and Immunosuppressed States: A Clinical–Therapeutic Staging Proposal. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, 2020, 39 (5), 405–407. [CrossRef]
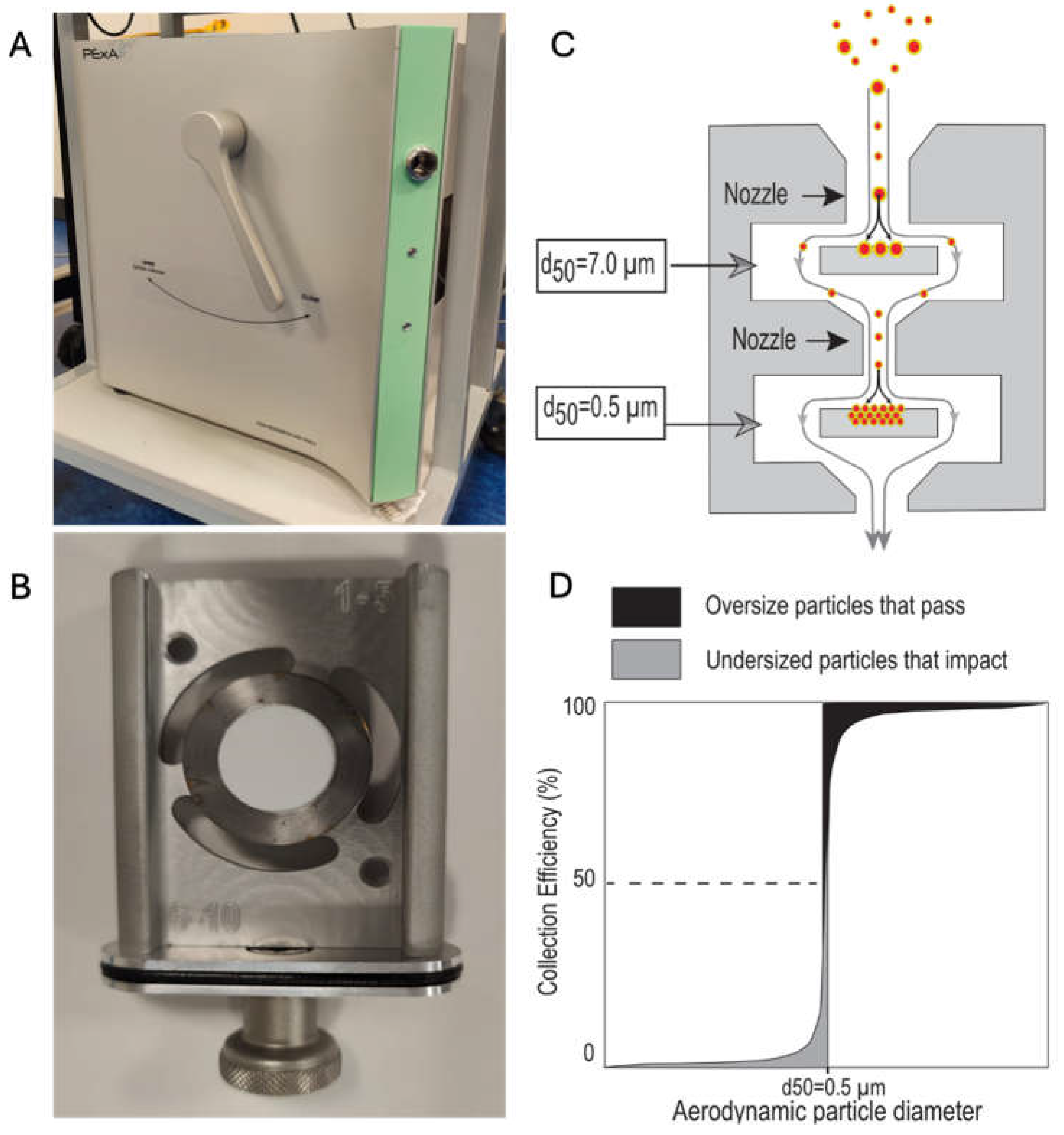
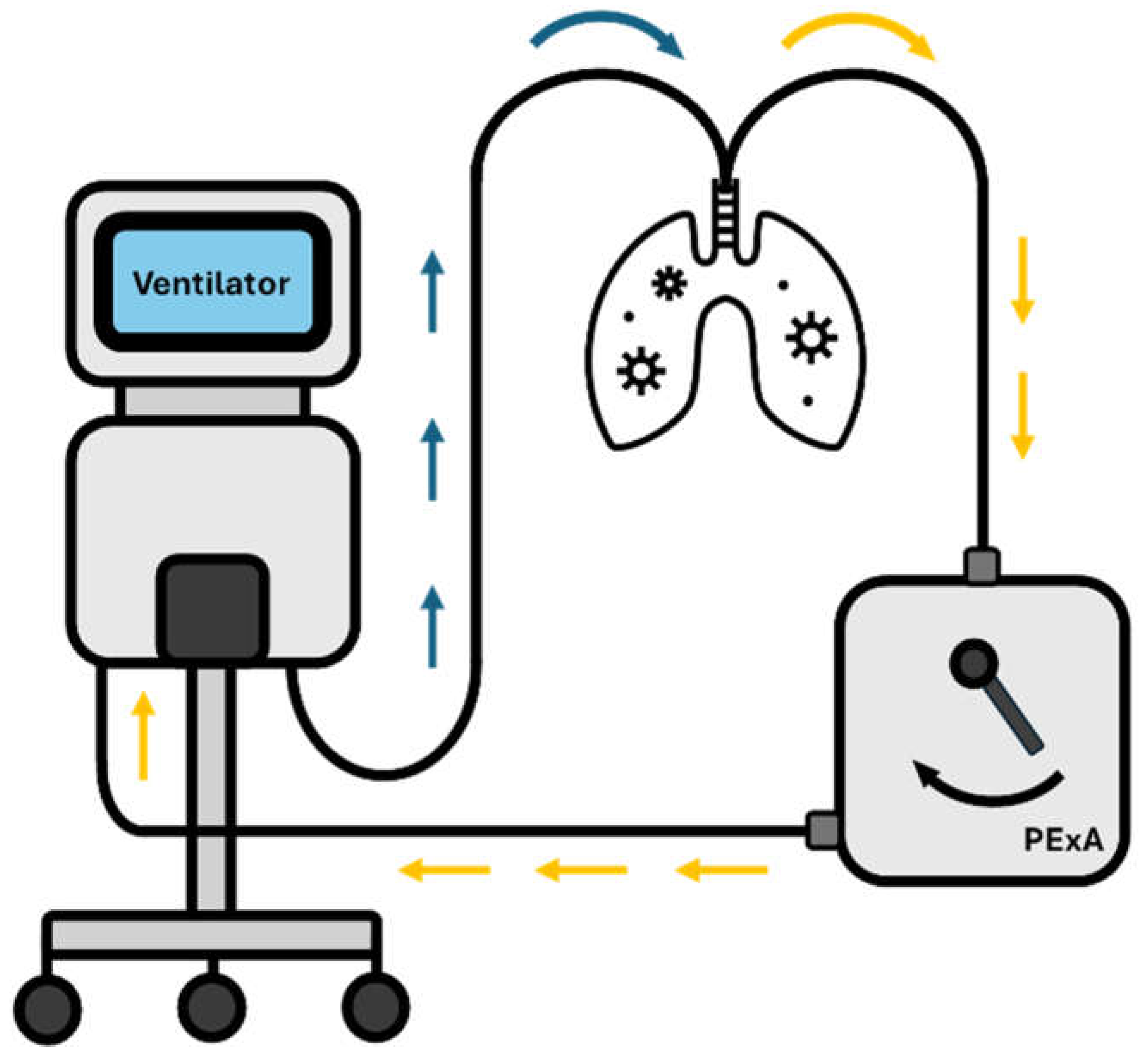
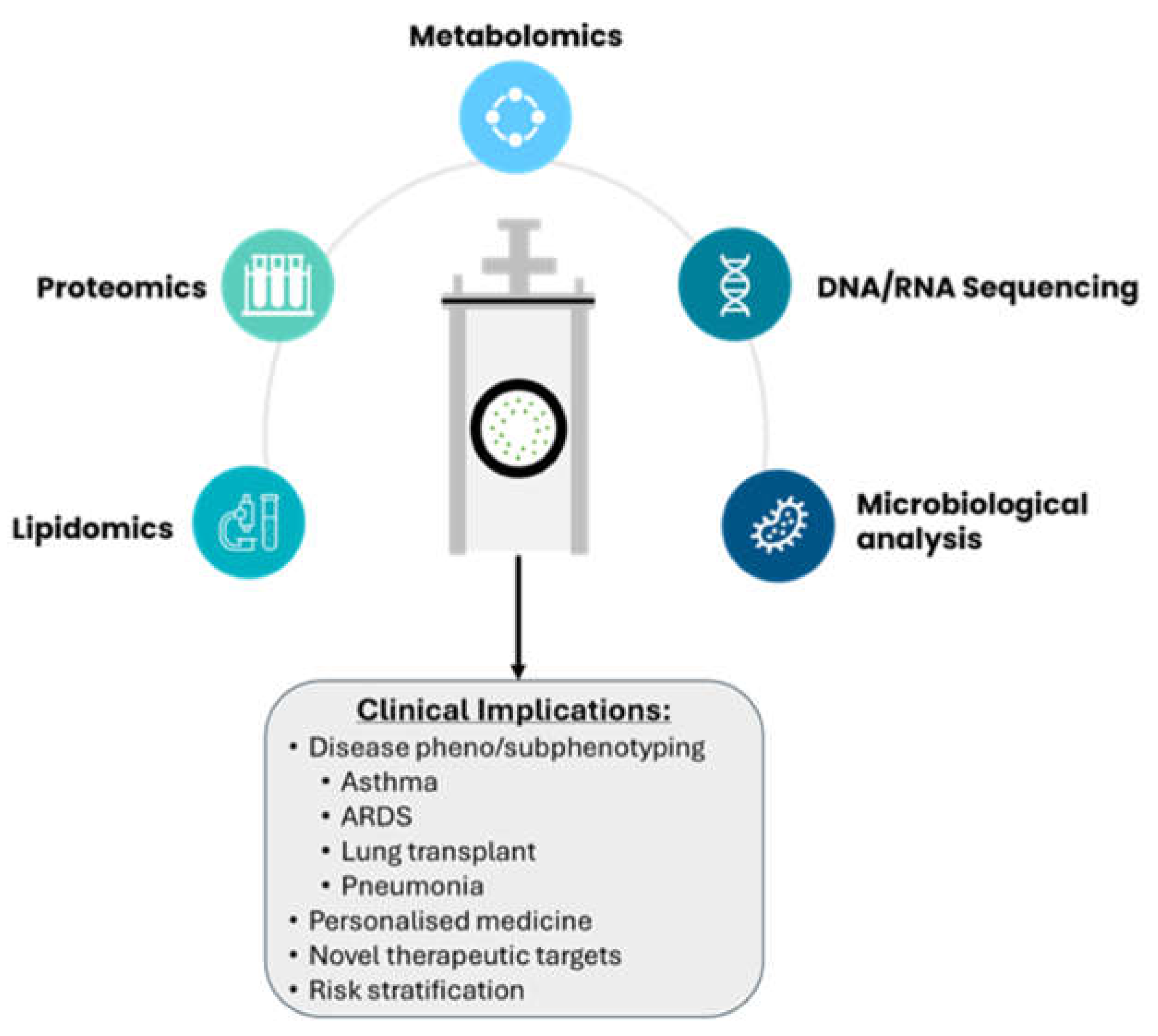
| Authors | Clinical Condition | Biomarker | Outcome/Key Results |
| Alahmadi et al [45] | Asthma (n=17) | Exhaled Breath Tests, FeNO, EBT, PExA and VOCs | 1) After a week of using high dose inhaled corticosteroids, there were falls in FeNO, EBT and two VOCs (p<0.05), but no changes in PExA. 2) There were no significant differences in the calculated weight percentage of SP-A (p=0.989) or albumin (p=0.674) between day 1 and day 7 in PExA samples. |
| Almstrand et al [49] | Asthma (n=15) | Total particle count, Phospholipid composition | 1) Subjects with asthma exhaled significantly lower numbers of particles than controls (23,000 vs 44,000, p=0.03). 2) The ratio of unsaturated to saturated phospholipids was significantly lower in samples from subjects with asthma (0.25 vs 0.35; p=0.036). |
| Andreasson et al [50] | Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) (n=17), non-cancer surgical controls (n=18) |
Particle Flow rate, Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | 1) A significantly higher Particle Flow Rate was seen among LUAD patients before surgery compared to the control patients (p<0.0001). 2) A significantly higher MET concentration was found before surgery in the LUAD group compared to the control group (p<0.0001). |
| Bredberg et al [51] | Smoking (n=12) | Phospholipid composition | 1) Clear discrimination between smokers and non-smokers, where phospholipids from smokers were protonated and sedated to a larger extent. 2) Poor lung function showed a strong association with higher response from all molecular PC species. |
| Broberg et al [38] | Non-small cell lung cancer with mechanical ventilation (n=17), versus controls | Albumin and SP-A, particle flow rate | 1) Mechanically ventilated patients with non-small cell lung cancer showed significantly lower levels of DPPC in PEx samples compared to non-intubated patients (p=0.001). 2) Established the feasibility of PExA device to collect and analyse exhaled particles from lung airways. |
| Broberg et al [52] | Lung Transplant- Primary Graft Dysfunction (n=6) and no primary graft dysfunction (n=6) | C-reactive Protein (CRP), particle flow profile | 1) Patients with PGD had significantly higher CRP levels after transplant on day 0 compared with patients with no PGD (p=0.0420). 2) Lung transplant patients with PGD show a significant difference in total particle count between day 0 and day 1 compared with day 3 (p=0.0065 and p=0.0082, respectively). |
| Broberg et al [53] | Porcine model-Pigs (n=6) | Particle Flow | 1) Particle mass was significantly higher in pressure-controlled ventilation (PCV) than in volume-controlled ventilation (VCV) (p=0.0322). |
| Broberg et al [54] | Porcine models of mechanical ventilation (n=6) | Total particle count | 1) Comparing VCV to PCV from day 1 to day 3, a significant increase in total particle count was observed on day 2 (40,260±10,097 vs 21,238±5625, p=0.0184), with the highest particle count occurring during VCV. |
| Broberg et al [55] | Porcine model of volume controlled mechanical ventilation (n=5) | Total particle count | 1) Total particle count at a PEEP level of 15 cmH2O was lower than that of 5 cmH2O (282 vs 3,754, p<0.009). |
| Carpaij et al [56] | Asthma (n=46) | Particle mass | 1) PExA mass was significantly lower in persistent asthma compared to complete asthma remission and control subjects (p=0.028 and p=0.003, respectively). 2) PExA mass was significantly lower in clinical asthma remission compared to control subjects (p=0.018). |
| Elimsson et al [57] | Chronic non-productive Cough (n=14) | Proteins | 1) Proteomic analysis showed 75 proteins significantly altered in patients with chronic cough compared to control (p<0.05) involved in immune and inflammatory responses, complement and coagulation system, epithelial junction integrity proteins and in neuroinflammatory responses. |
| Emilsson et al [58] | Gastroesophageal reflux, asthma and bronchitis (n=48) | SP-A and albumin | 1) SP-A (25 vs 38 mg/g PEx, p<0.001) and albumin (48 vs 73 mg/g PEx, p<0.001) in PEx were lower among gastroesophageal reflux subjects than controls. |
| Ericson et al [59] | Lung transplant recipients: control (n=26) vs bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (n=7). | Total particle count, SP-A, albumin | 1) Lung transplant recipients exhaled higher numbers of particles (8 vs 1.8 ng/L, p<0.0001) than controls. 2) SP-A in exhaled particles and the SP-A/albumin ratio were lower (18 vs 30 mg/mL, p=0.002; 0.35 vs 0.74, p=0.0001) in the bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) group compared to the BOS-free group. |
| Hallgren et al [66] | Elective open-heart surgery receiving mechanical ventilation (n=30) | Particle flow rate | 1) Ventilation with pressure-regulated volume control (PRVC) resulted in the lowest PFR compared to VCV (p=0.0285) and PCV (p=0.0149). 2) Ventilation with pressure support ventilation (PSV) resulted in significantly higher PFR (2249±426 particles/min) compared to all other ventilation modes used. |
| Hirdman et al [61] | COVID-19 (n=29) | Exhaled breath particles | 1) There was a significant increase in particles per exhaled volume in COVID-positive patients compared to healthy controls (p<0.001). 2) Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein B (SFTPB, E) was significantly downregulated in COV-POS and COV-NEG (symptomatic) patients versus the healthy control group. |
| Holz et al [25] | Segmental and inhalation endotoxin challenge in healthy volunteers (n=10) | Concentrations of IL-6 and IL-8 per ng PExA | 1) Clear increase in the concentrations of IL-6 5 h post-segmental (p<0.001) and post-inhalation LPS challenge (p<0.001) was detected. 2) Clear increase in the concentrations of IL-8 5 h post-segmental (p<0.01) and post-inhalation LPS challenge (p<0.001) was detected. |
| Hussain-Alkhateeb et al [19] | Asthma (n=16) and Smokers (n=17) | Phospholipids, SP-A, Albumin | 1) The phospholipids (PC14:0/16:0 and PC16:0/18:2) and SP-A were higher, and albumin was lower among the subjects with asthma. 2) Higher levels of DPPC observed in smokers compared to non-smokers. |
| Koca et al [39] | Healthy Volunteers (n=97) and smokers (n=15) | SP-A | 1) No correlation between PEx and plasma SP-A levels (p=0.15) in healthy participants. 2) The ratio of plasma to PEx SP-A significantly higher in current smokers compared to healthy participants (p=0.003). |
| Kokelj et al [47] | Current smokers (n=38), Former smokers (n=47), healthy controls (n=22) | Proteins in PExA samples | 1) 81 proteins altered in current smokers compared to never smokers (p<0.05). 2) Relative abundance of 58 proteins significantly altered in female current smokers as compared to non-smokers (p<0.05), while 27 proteins significantly altered in male current smokers (p<0.05). 3) Protein alterations consistent with complement pathway activation in female smokers. |
| Kokelj et al [46] | Asthma (n=20) | Complement and coagulation proteins | 1) 9 proteins were differentially abundant in subjects with asthma as compared to controls. 2) C3 was significantly higher in inadequately controlled asthma as compared to well-controlled asthma. |
| Larsson et al [13] | Asthma (n=13) | Mass of exhaled particles, SP-A, Albumin | 1) Total mass of exhaled particles was lower in the asthma patients (900 pg/L of exhaled air) compared to control (1710 pg/ litre of exhaled air) during pollen season. 2) No significant effect on the concentration of SP-A and albumin in exhaled particles. |
| Larsson et al [48] | Healthy participants with segmental/inhalation LPS challenge (n=10) | Phospholipid composition of PEx | 1) The overall phospholipid composition of BAL, ISP and PEx was similar, with PC(32:0) and PC(34:1) representing the largest fractions in all three sample types. 2) An increase of SM (d34:1) following segmental LPS challenge was detectable in PEx. |
| Larstad et al [14] | COPD (n=13) | Total particle count, SP-A | 1) COPD patients had lower particle number concentration than healthy subjects (p<0.0001). 2) COPD patients exhibited significantly lower SP-A mass content of the exhaled particles (2.7 vs 3.9 wt%, p=0.036). |
| Lindstedt and Hyllen [62] | Cardiac failure with mechanical ventilation (n=10) vs control (n=10) | Particle flow rate | 1) Median PFR in patients with cardiac failure higher than PFR in patients with normal cardiac function (p<0.001). 2) Median particle mass greater in the cardiac failure group compared to the control group (p=0.002). 3) Patients with post-operative cardiac failure following cardiac surgery exhibit an increase in exhaled particles mass and PFR compared with the control group. |
| Ljungkvist et al [63] | Stainless steel welders (n=19) | Metals | 1) All samples, including blanks, had quantifiable amounts of metals; however, no statistically significant increase in the analysed metals in PExA over the working shift (p=0.6 for chromium, manganese, and nickel). |
| Östling et al [37] | Asthma (n=20) and healthy controls (n=10) | Proteins in PExA samples | 1) 207 proteins were detected in up to 80% of the PExA samples. |
| Soares et al [44] | Asthma (n=83) and healthy volunteers (n=32 | SP-A, Albumin | 1) PExA method has the potential to non-invasively sample small airways derived proteins (SP-A and albumin) associated with airway dysfunction phenotypes in asthma. 2) Modest but significant correlations were found for %SP-A with oscillometry parameters of small airways dysfunction. 3) Albumin demonstrated a significant correlation with FVC and GINA treatment (p<0.05). |
| Stenlo et al [64] | Porcine model with LPS-induced ARDS (n=7) | Particle Flow Rate | 1) The Particle flow rate increased significantly over time after LPS administration, from baseline (p=0.0012) to after 60 minutes in all 7 animals. |
| Viklund et al [65] | Smoking (n=37) | Total particle count, phospholipids, SP-A | 1) Smoking increased the exhaled number of particles (20.8 vs 13.2 kn/L, p=0.011). 2) Smoking increased contents of DPPC (11.3 vs 10.3 wt%, p=0.025) and POPC (3.7 vs 2.9 wt%, p=0.008). 3) Smoking increased contents of SP-A (3.9 vs 3.1 wt%, p=0.037). |
| Zwitserloot et al [66] | Cystic Fibrosis (n=23) | Particles in exhaled air mass and number | 1) Correlation between lung clearance index and PEx ng/l was low (p=0.07). 2) PExA device is feasible to use in children, however, it is a less sensitive tool to detect small airway diseases as it does not differentiate healthy children from children with cystic fibrosis. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





