Submitted:
16 April 2024
Posted:
17 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Validation of Oncomine™ Focus Assay Results
3.2. Validation of the Pan Lung Cancer PCR Panel Results
3.3. Validation of RT-PCR Results
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Three Platforms Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gherardi E: Birchmeier W, Birchmeier C, Vande Woude G. Targeting MET in cancer: rationale and progress. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12:89-103. [CrossRef]
- Socinski MA, Pennell NA, Davies KD. MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Overview of Biology, Clinical Outcomes, and Testing Considerations. JCO Precis Oncol 2021; 5.
- Tong JH, Yeung SF, Chan AW, Chung LY, Chau SL, Lung RW, et al. MET Amplification and Exon 14 Splice Site Mutation Define Unique Molecular Subgroups of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma with Poor Prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 2016; 22:3048-56.
- Ding C, Qiu Y, Zhang J, Wei W, Gao H, Yuan Y, Wang X. Clinicopathological characteristics of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) patients with c-MET exon 14 skipping mutation, MET overexpression and amplification. BMC Pulm Med 2023; 23:240. [CrossRef]
- Hellmann MD, Ciuleanu TE, Pluzanski A, Lee JS, Otterson GA, Audigier-Valette C, et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Lung Cancer with a High Tumor Mutational Burden. N Engl J Med 2018; 378:2093-104. [CrossRef]
- Yatabe Y, Sunami K, Goto K, Nishio K, Aragane N, Ikeda S, et al. Multiplex gene-panel testing for lung cancer patients. Pathol Int 2020; 70:921-31. [CrossRef]
- Teishikata T, Shiraishi K, Shinno Y, Kobayashi Y, Kashima J, Ishiyama T, et al. An Alert to Possible False Positives With a Commercial Assay for MET Exon 14 Skipping. J Thorac Oncol 2021; 16:2133-8. [CrossRef]
- Onodera Y, Sekine A, Hagiwara E, Yamada S, Ikeda S, Tabata E, et al. Successful tepotinib treatment of adenocarcinoma with MET exon 14 skipping and discordant results between Oncomine Dx target test and ArcherMET: A case report. Mol Clin Oncol 2023; 18:49. [CrossRef]
- Lee A, Lee SH, Jung CK, Park G, Lee KY, Choi HJ, et al. Use of the Ion AmpliSeq Cancer Hotspot Panel in clinical molecular pathology laboratories for analysis of solid tumours: With emphasis on validation with relevant single molecular pathology tests and the Oncomine Focus Assay. Pathol Res Pract 2018; 214:713-9. [CrossRef]
- Williams HL, Walsh K, Diamond A, Oniscu A, Deans ZC. Validation of the Oncomine() focus panel for next-generation sequencing of clinical tumour samples. Virchows Arch 2018; 473:489-503. [CrossRef]
- Arora S, Balasubramaniam S, Zhang H, Berman T, Narayan P, Suzman D, et al. FDA Approval Summary: Olaparib Monotherapy or in Combination with Bevacizumab for the Maintenance Treatment of Patients with Advanced Ovarian Cancer. Oncologist 2021; 26:e164-e72. [CrossRef]
- Kunimasa K, Matsumoto S, Kawamura T, Inoue T, Tamiya M, Kanzaki R, et al. Clinical application of the AMOY 9-in-1 panel to lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2023; 179:107190. [CrossRef]
- Lee JK, Madison R, Classon A, Gjoerup O, Rosenzweig M, Frampton GM, et al. Characterization of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancers With MET Exon 14 Skipping Alterations Detected in Tissue or Liquid: Clinicogenomics and Real-World Treatment Patterns. JCO Precis Oncol 2021; 5. [CrossRef]
- Mazieres J, Vioix H, Pfeiffer BM, Campden RI, Chen Z, Heeg B, Cortot AB. MET Exon 14 Skipping in NSCLC: A Systematic Literature Review of Epidemiology, Clinical Characteristics, and Outcomes. Clin Lung Cancer 2023. [CrossRef]
- Chen L, Chen M, Lin J, Chen X, Yu X, Chen Z, Jin L. Identifying a wide range of actionable variants using capture-based ultra-deep targeted sequencing in treatment-naive patients with primary lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2020; 13:525-35.
- Kato K, Okami J, Nakamura H, Honma K, Sato Y, Nakamura S, et al. Analytical Performance of a Highly Sensitive System to Detect Gene Variants Using Next-Generation Sequencing for Lung Cancer Companion Diagnostics. Diagnostics (Basel) 2023; 13. [CrossRef]
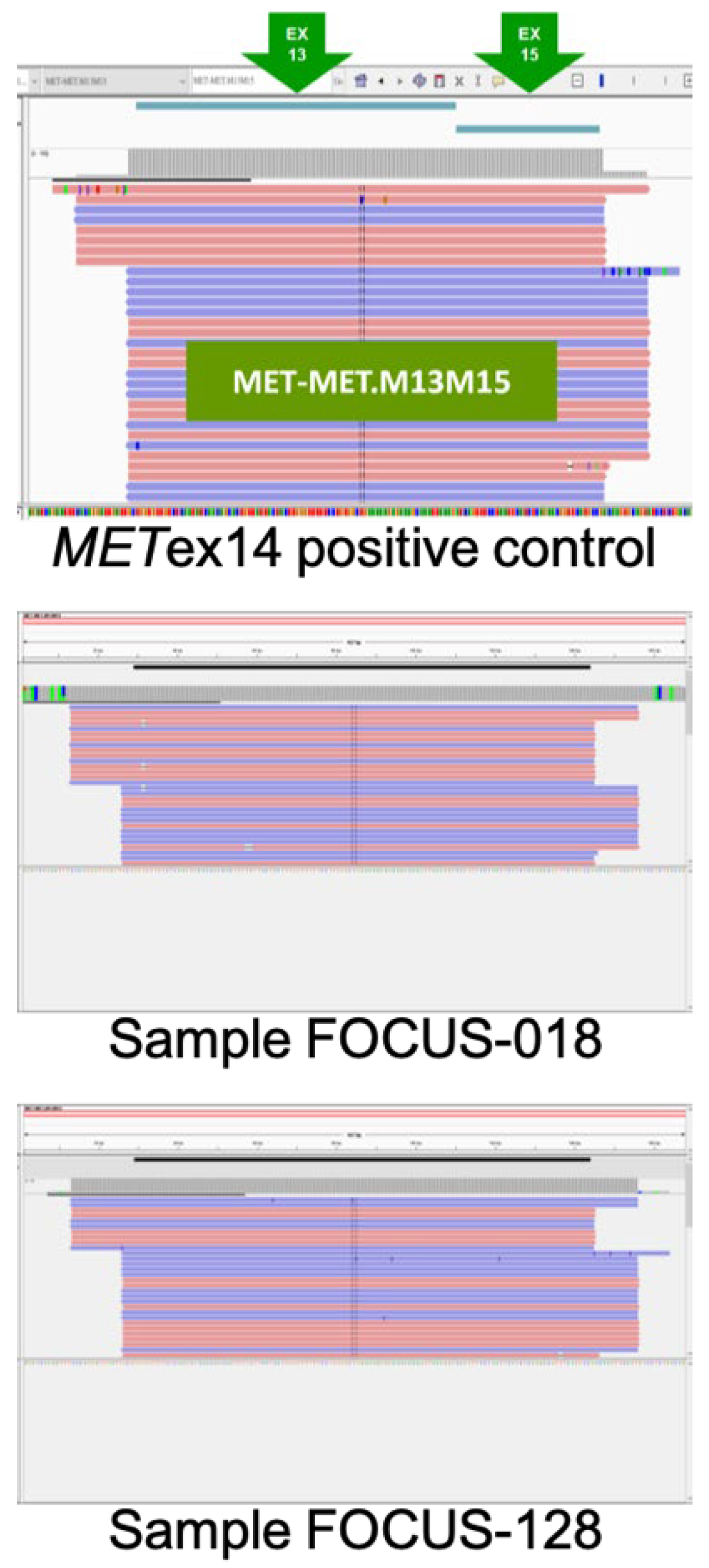
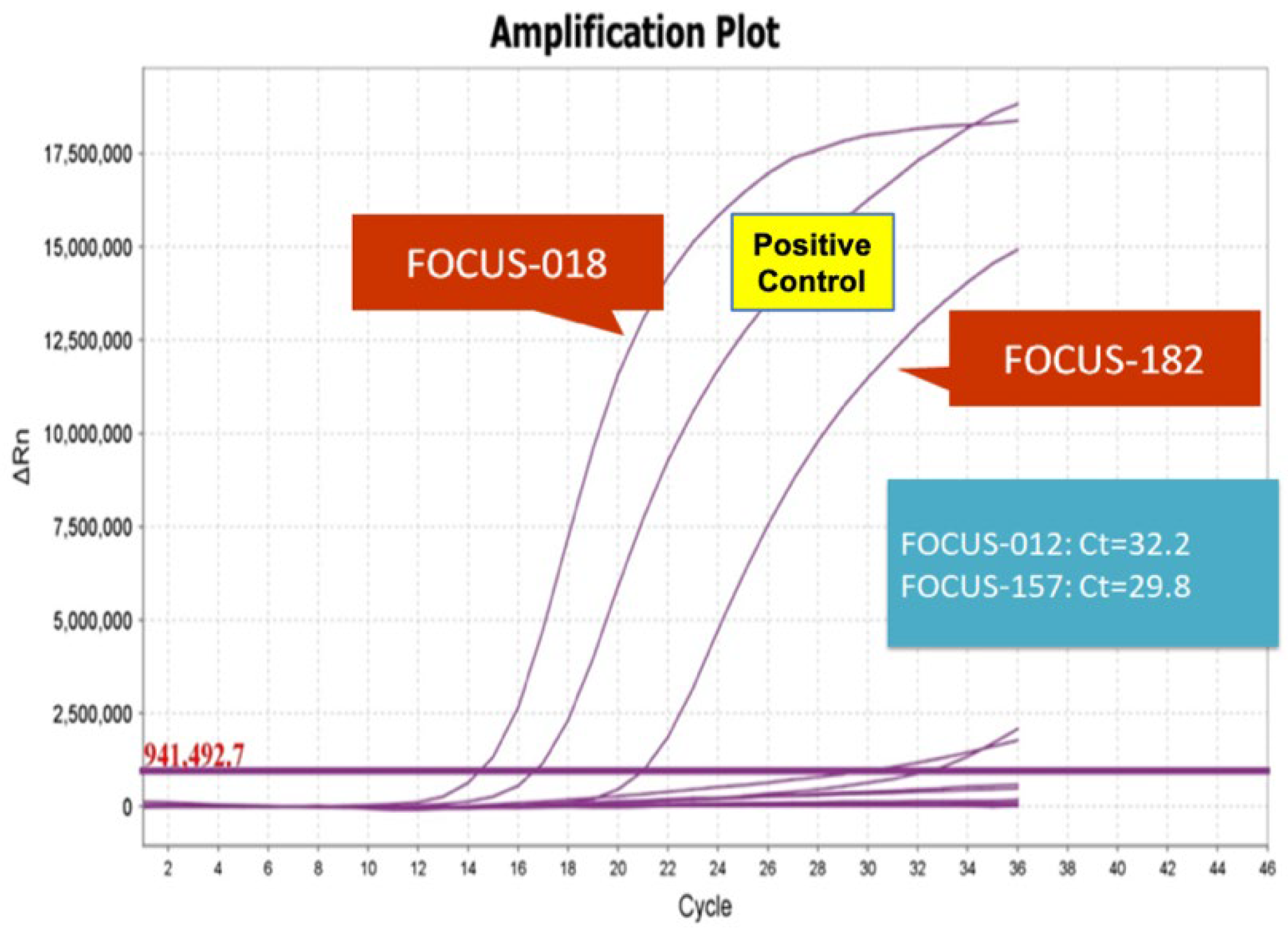
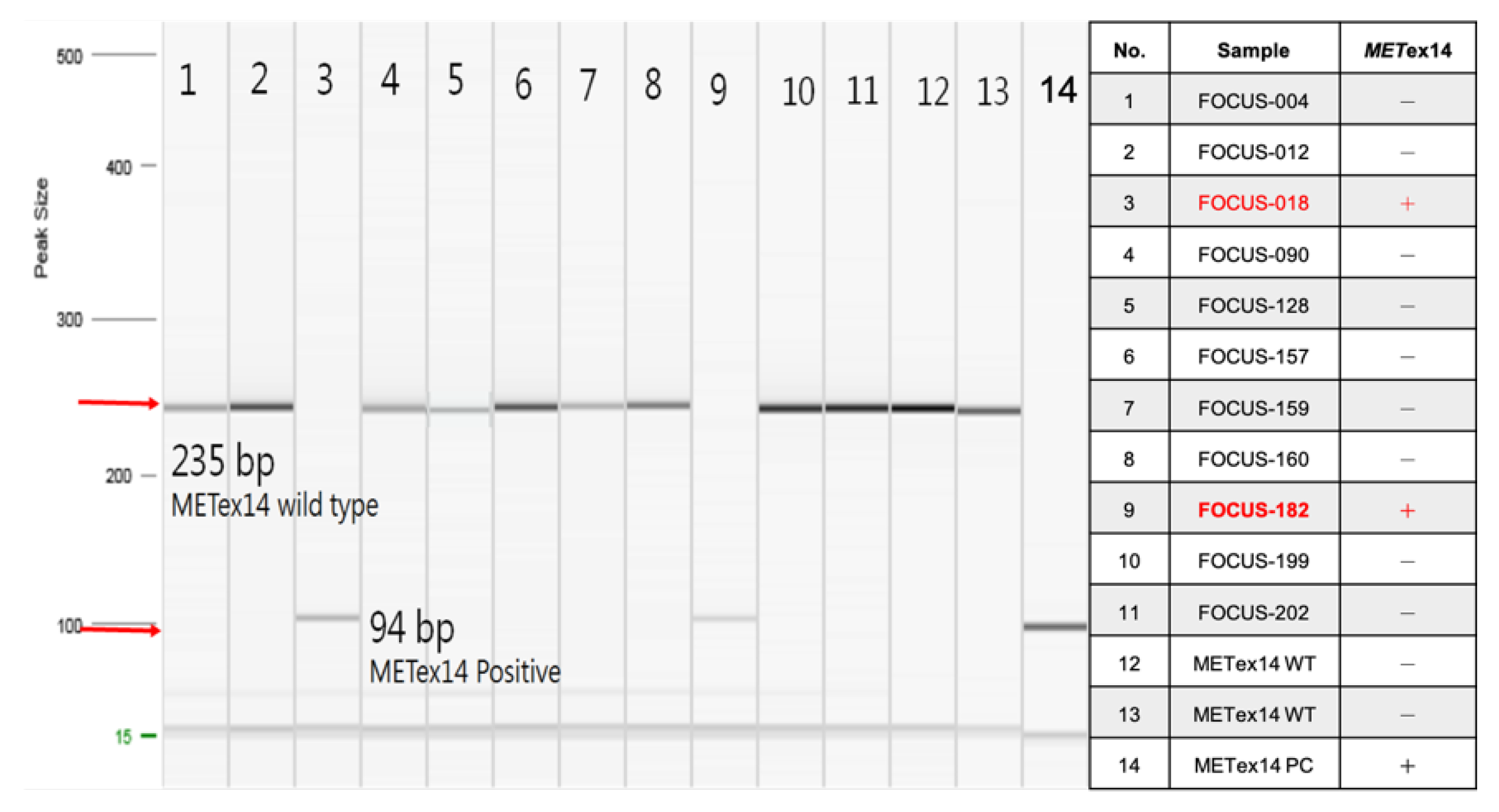
| Sample | Oncomine Focus Assay | AmoyDx (Ct<28) | RT-PCR | ||
| Read count (Cut Off >120) |
Total Mapped Fusion Reads | Fusion Reads Count/ Total Mapped Fusion Reads | |||
| FOCUS-004 | 302 | 221438 | 0.13% | - | - |
| FOCUS-012 | 612 | 280337 | 0.22% | - | - |
| FOCUS-018 | 10177 | 218892 | 4.65% | +* | +* |
| FOCUS-090 | 261 | 318617 | 0.08% | - | - |
| FOCUS-128 | 154 | 282856 | 0.05% | - | - |
| FOCUS-157 | 201 | 153230 | 0.13% | - | - |
| FOCUS-159 | 179 | 476881 | 0.04% | - | - |
| FOCUS-160 | 319 | 581357 | 0.05% | - | - |
| FOCUS-182 | 2540 | 197851 | 1.28% | +* | +* |
| FOCUS-199 | 333 | 133050 | 0.25% | - | - |
| FOCUS-202 | 212 | 122505 | 0.17% | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





