1. Introduction
Extrinsic stains on teeth develop when the normal salivary pellicle layer (unstained pellicle) takes up stains from the diet, including from chlorhexidine mouthwashes, tea, coffee, red wine, and other colored foods and drinks, to become stained pellicle [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Extrinsic staining of teeth is unsightly, and this cosmetic problem has driven the development of dentifrices.
The primary purposes of dentifrices are to remove dental plaque biofilm and stained pellicle from teeth, oral appliances, and prostheses [
5,
6]. To achieve this, current commercial dentifrices include various insoluble abrasive particles, including silica, calcium pyrophosphate, and calcium carbonate [
7,
8,
9]. The intention is that, during brushing, some of the force applied to the toothbrush will be directed onto abrasive particles located between the bristle ends and the tooth surface. The movement of the abrasive particles horizontally along the tooth surface as they are pushed along by the toothbrush filaments (i.e., without vertical pressure) should then dislodge some stained pellicle and some biofilm. If abrasive particles were “pushed” into the surface by the bristles, that would likely remove more stained pellicle [
10,
11].
How well this theory applies in practice depends on the interaction of multiple variables, including the function of saliva as both a diluent and a lubricant; the rheological properties of the dentifrice as it is diluted by saliva; the presence of more complex topography (enamel pitting, supragingival calculus, restoration contours); the applied geometry of the brush and its bristles, the toothbrushing technique used (angulation, direction, force); and subjective reactions of users to components of the dentifrice, such as flavors and detergents. These factors also influence how much the abrasive particles in dentifrices will abrade dentin [
12].
Marketed toothpastes vary in the extent to which they can remove stained pellicles, and in how much abrasive wear they cause to dentin [
13]. There is a long-standing belief that increasing the loading of abrasive particles in a dentifrice should increase stain removal, but at the risk of abrasion to dentin and root surfaces [
14,
15]. Marketed dentifrices vary from, at one extreme, those designed for aggressive extrinsic stain removal, for “whitening,” with high RDA values, to those intended for use by patients with cervical dentin hypersensitivity, with low RDA values [
16,
17]. This inherent trade-off between stain removal and dentin abrasion has characterized dentifrices for many years [
18,
19].
Changing the fundamental cleaning technology of a dentifrice to achieve more effective cleaning provides a situation where the prevailing paradigms may be challenged. A notable example is the inclusion of micro-fibrillated cellulose (MFC) into a dentifrice. This dramatically increases its ability to remove dental plaque, as shown in a recent clinical trial [
20]. Including MFC can mitigate the problems caused by saliva acting as a lubricant and a rheology-transforming agent [
21]. Entrapped silica abrasive particles within the MFC matrix can reach the tooth surface and provide the necessary shear force to dislodge biofilm [
22]. Based on the same considerations, the action of MFC with entrapped abrasive should enhance stain removal [
23].
Hence, the primary aim of this study was to compare the performance of a novel dentifrice containing MFC with entrapped silica with conventional dentifrices, in terms of extrinsic stain removal and dentin abrasion, using established in vitro assessments, with the pellicle cleaning ratio (PCR) and the radioactive dentin abrasivity (RDA) being the primary outcome measures. The results of a stained pellicle removal test using dentifrice slurries may be considered to predict clinical findings for extrinsic stain removal with a reasonable degree of confidence [
24,
25]. As controls in assays, versions of the MFC product were included that were free of silica or fluoride, since the abrasiveness of a dentifrice increases with the weight percentage of included silica [
11]. Under standardized laboratory conditions, the removal of stained pellicle was assessed to calculate the PCR. This approach was used as it is one of the best-known and most accepted laboratory methods worldwide for assessing the stain removal ability of dentifrice. The PCR method was developed at Indiana University by Stookey and colleagues [
24]. Dentin abrasion was determined using a toothbrushing machine, and the relative dentin abrasivity (RDA) score was calculated by comparing dentifrice samples with a reference material that had known abrasive qualities [
12,
26,
27,
28]. Past work has shown that the PCR and RDA measures are helpful ways of comparing the performance of novel dentifrices with recognized standard preparations and marketed products [
8,
29,
30].
The secondary purpose of the present study was to assess the efficacy of fluoride in the novel dentifrice containing MFC, using laboratory assays for in vitro enamel remineralization and fluoride bioavailability, including using a pH cycling model (White model) [
31,
32,
33] and assays for enamel fluoride uptake [
34]. These methods are used widely for assessing novel dentifrice formulations [
8,
29,
35].
2. Methods
2.1. Pellicle Cleaning Ratio
In this part of the study, the PCR was determined for the novel MFC dentifrice, five other commercial dentifrices, and an ISO/ADA reference material. This work was undertaken in compliance with the US Food and Drug Administration Guidelines for Good Laboratory Practice for Nonclinical Laboratory Studies. The following six products were included: Protegera® (Protegera Inc, Madison, WI, USA) containing MFC, 7% silica and sodium fluoride (NaF)); Crest Cavity Protection™ (Procter and Gamble, Cincinnati, OH, USA) containing NaF and silica; Crest ProHealth™ (Procter and Gamble, Cincinnati, OH, USA) containing stannous fluoride, sodium hexametaphosphate and silica; Arm & Hammer™ Advance White™ (Church & Dwight, Trenton, NJ, USA) containing NaF and sodium bicarbonate and hydrogen peroxide); Sensodyne™ Pronamel™ (Haleon Inc, Warren, NJ, USA) containing NaF and silica); and Colgate™ Optic White™ (Colgate Palmolive, Piscataway, NJ, USA) containing sodium monofluorophosphate plus pyrophosphates and hydrogen peroxide.
An ISO/ADA reference material was also included for comparison. This was prepared by mixing 10 g of calcium pyrophosphate powder (RDA standard grade, Odontex Inc, Lawrence, KS, USA) into 50 mL of glycerin containing 0.5% (w/v) carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC-7MF, Hercules Inc, Wilmington, DE, USA).
Specimens were prepared from bovine permanent central incisors to a size of 8 x 8 mm, then embedded into 15 mm square blocks of auto-polymerizing methacrylate resin so that only the enamel surface was exposed. The enamel surfaces were then smoothed on a lapidary wheel, polished with flour of pumice and water to allow uniform instrumental color readings, and placed in an ultrasonic cleaner to remove debris. The finished specimens were examined under a dissecting microscope, and any samples with surface imperfections were discarded. To enhance extrinsic stain adherence and accumulation, the enamel was etched lightly using the following protocol: 0.12 M hydrochloric acid for 60 secs, followed by saturated sodium carbonate solution for 30 secs, and then 1.0% phytic acid for 60 secs.
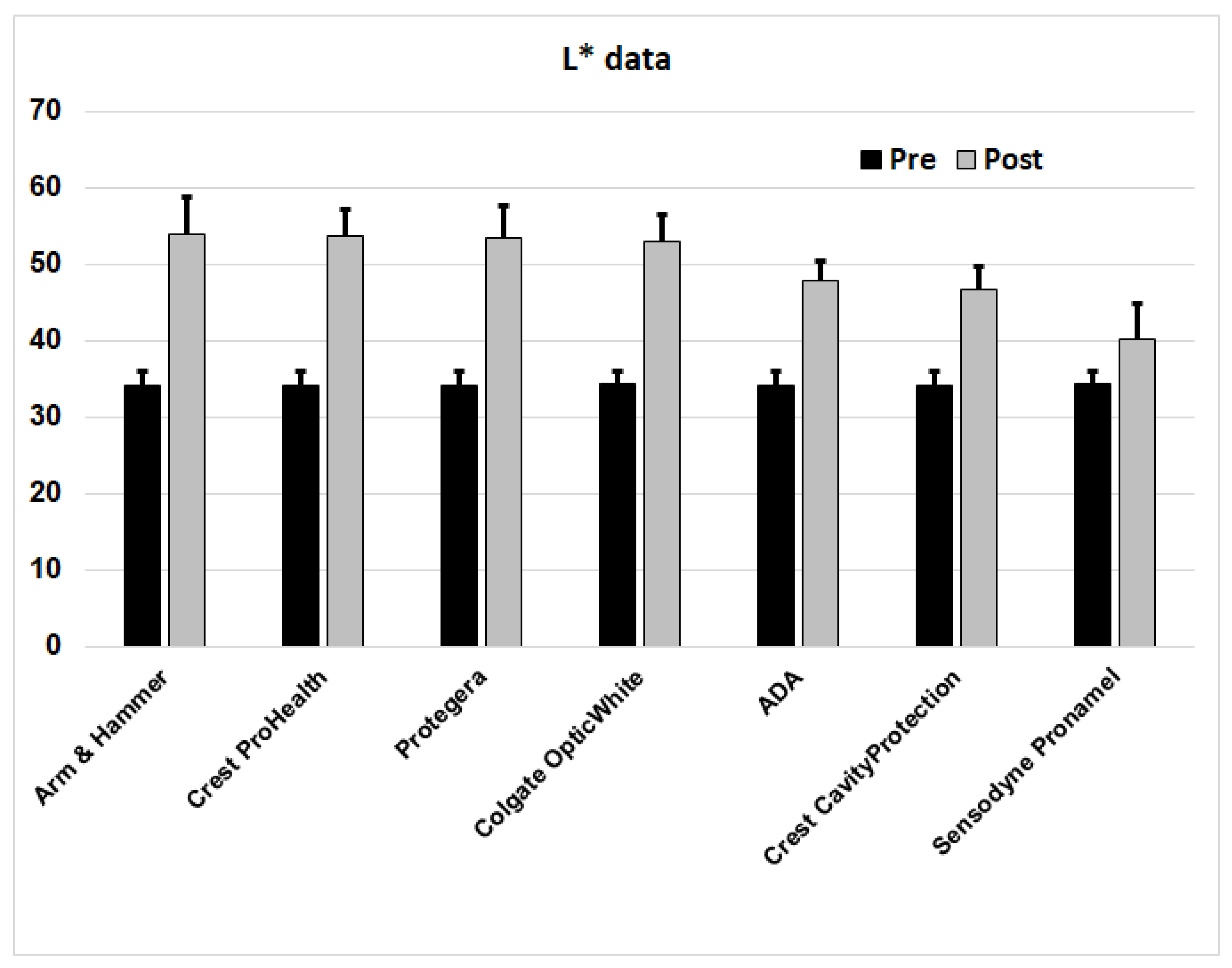
To generate extrinsic stains, the samples were connected to a rod rotating at 1.5 rpm to alternately immerse them into a trough containing a staining broth, and to air drying, for a total period of 10 days at 37°C, with the specimens rotating continuously through the staining broth and air. The staining broth contained porcine gastric mucin as a protein source, instant coffee, instant tea, and ferric chloride. The broth was replaced once daily for ten consecutive days. By the end of this time, the enamel surface had developed a visibly dark pellicle stain. The extent of external staining was assessed from a 3 mm diameter circular region in the center of the enamel surface using a portable sphere spectrophotometer with a 3 mm aperture and an internal xenon light source (model CM-26dG, Konica Minolta, Osaka, Japan), to determine the L* (lightness) value of the CIELAB color space scale. The lower this value, the darker the stain. The stained enamel specimens were air-dried at room temperature for 30 mins before color measurements were made by aligning the center of the stained enamel square directly over the targeting aperture of the spectrophotometer. Three color readings were made and averaged for each specimen. All specimens after staining had L* values between 30-38. Based on their individual L* values, the specimens were then stratified and distributed into groups of N = 16, so that each group had the same average L* score at baseline.
To assess stained pellicle removal, samples were exposed to the 6 test products and an ISO/ADA reference material using toothbrushes (Oral-B™ Indicator 40 brushes with soft nylon filaments, Procter and Gamble, Cincinnati, OH, USA) in a mechanical V-8 cross-brushing machine (Sabri Dental Enterprises, Downers Grove, IL, USA) at a constant load of 150 g. The load used for pellicle removal test was based on past studies of RDA [
12,
26].
Before use, the toothbrushes were conditioned by running the brushing machine for 1,000 strokes with deionized water. For testing, slurries were prepared by mixing 25 g of the test dentifrices or reference standard with 40 mL of deionized water. A different portion of the appropriate slurry was used to brush each specimen. The specimens were brushed for 800 double strokes, after which they were rinsed, blotted dry, and scored again for stain using the spectrophotometer.
Differences between the pre- and post-brushing L* values were calculated. Group data was assessed for normality before calculating means, standard deviations and standard errors (SEM). The cleaning ratio for the reference material (an increase in L* score of 13.55, from 34.25 to 47.80) was assigned a reference PCR value of 100.0, and the reduction achieved by the reference material group was divided into 100, to provide a scale on which to place the 6 test materials. The higher the calculated PCR, the greater the amount of stained pellicle removed.
2.2. Dentin Abrasion
Relative dentin abrasion (RDA) testing was undertaken following the American Dental Association recommended procedure for determination of dentifrice abrasivity as detailed in Section 5.2 and Annex A of ISO 11609:2017 (Dentifrices - Requirements, test methods, and marking) and the corresponding ANSI/ADA Standard No. 130, as described previously [
17,
26]. This radiotracer method was used since it is more reliable and robust than the alternative surface profilometry method, and is better for differentiating between products [
36].
RDA was determined for five dentifrices: Crest Pro-Health, Crest 3D-White, and two versions of Protegera (one with no silica, and the other with 7% high cleaning silica (Zeodent® 103, Evonik, Theodore, AL, USA)). The version with zero silica was included to assess the impact of the base vehicle with MFC on dentin abrasion.
Human root dentin specimens from permanent teeth (N = 8) were placed in a neutron flux under the controlled conditions outlined in ISO 11609. During irradiation, a part of the phosphorus (P31) in hydroxyapatite is converted into radioactive P32, while some of the calcium, by neutron capture, also changes to radioactive isotopes [
12]. The dentin specimens were then mounted in polymethylmethacrylate resin to fit into the same V-8 cross-brushing machine used for the PCR assessment. The same toothbrush type (Oral B Indicator 40) and load (150 g) were used throughout the RDA component of the study.
The specimens were first brushed for a 1500-stroke precondition run using a slurry of 10 g of the same ISO/ADA reference material as used previously (10 g calcium pyrophosphate in 50 mL glycerin with 0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose) for 1500 strokes. Following this, a sandwich design was used so that a slurry of each test dentifrice (25 g in 40 mL of deionized water) was flanked by the ISO/ADA reference material.
To assess the radioactivity of the dentin removed from the surface, 1.0 mL samples of the post-brushing slurry were taken, weighed to the nearest 10 mg, and added to 4.5 mL of a liquid scintillation cocktail. After thorough mixing, radioactivity was determined using a scintillation counter. After correcting for background radiation, the net counts per minute (CPM) were then divided by the measured weight of the sample to determine the CPM per gram of slurry. For comparison, the CPM/g of the two flanking samples using the ISO/ADA reference material was calculated, and the average was used to assign a relative value based on a ratio, setting the ISO/ADA reference at 100. After checking for normality, the means, standard deviations and standard errors were calculated from the collated data sets, with N = 8 replicates for each test dentifrice.
2.3. Cleaning Efficiency Index
The Cleaning Efficiency Index (CEI) was calculated according to the equation: CEI = (RDA + PCR – 50) ÷ RDA. This index emphasizes the importance of effective stain removal properties and low dentin abrasion, and is based on clinical data that indicates a PCR value of at least 50 is needed to provide acceptable extrinsic stain removal [
25].
2.4. In Vitro Enamel Remineralization and Fluoride Bioavailability
These evaluations explored the efficacy of fluoride dentifrices in promoting enamel fluoride uptake, and in promoting the remineralization of incipient enamel lesions, under dynamic conditions simulating in vivo caries formation, using a pH cycling model (White model) [
31,
32,
33]. Briefly, the caries-like lesions produced by this approach have a lesion depth of 70 µm and a dense surface mineral zone of 15 microns thick.
Specimens of bovine enamel (3 mm in diameter) were prepared from extracted sound bovine maxillary central incisors by cutting perpendicular to the labial surface with a hollow-core diamond drill bit. This was performed underwater to prevent overheating of the specimens. The enamel specimens were then embedded in the end of a Plexiglass® rod using poly-methyl methacrylate resin. The excess acrylic resin was cut away, exposing the enamel surface. The samples were ground (using 600 grit wet/dry paper) and then polished to a high luster using gamma alumina.
The baseline microhardness of the sound enamel of the specimens was determined using a Vickers micro-indentation hardness tester (model AM247AT, Leco, St. Joseph, MI, USA) at a load of 200 g for 15 seconds. Four indentations were made on the surface of each specimen, and the average microhardness (Vicker’s hardness number, VHN) was determined. These baseline values ranged from 300-390 VHN.
Artificial incipient carious lesions were formed in the enamel specimens by immersing them for 33 hr in a demineralization solution (0.1 M lactic acid, 0.2% Carbopol C907, 50% saturated with hydroxyapatite, pH 5.0). This created lesions of approximately 70 µm in depth. A second (post- demineralization) measurement of surface microhardness was then undertaken. The target VHN for lesions required for acceptance into this part of the study was 25-45 VHN. Based on these values, specimens were allocated into seven groups (N=18 in each) and, from there, into two subgroups of N=9 for each of the seven products to be tested. The included products were as follows: Tom’s of Maine Fluoride-Free (negative control), two fluoride-free versions of Protegera (as vehicle controls), Protegera (1100 ppm fluoride from NaF), Crest Cavity Protection Regular Paste (1100 ppm fluoride from NaF), Crest Pro Health (1100 ppm fluoride from SnF2), and Sensodyne Pronamel (1100 ppm fluoride from NaF).
During treatment, the specimens were immersed in dentifrice slurries to simulate daily brushing. The slurries were prepared by adding 5.0 g of dentifrice to 10.0 g of deionized (DI) water (1:3 w/w dilution) in a beaker with a magnetic stirrer. Two fresh slurries of each test sample were prepared just before each treatment period and each slurry was used to treat N=9 specimens per subgroup.
The cyclic treatment regimen consisted of the following daily routine for ten days: 8.00 AM: a soak in the test dentifrice (120 sec), followed by a running deionized water rinse, then into artificial saliva, 10.00AM: a 4 hr soak in the lactic acid lesion-forming solution, followed by a running deionized water rinse, then into artificial saliva, 4.00 PM: a second soak in the test dentifrice (120 sec followed by a running deionized water rinse), and then overnight into artificial saliva. The artificial saliva comprised 20 mM HEPES buffer with 1.45 mM calcium chloride dihydrate, 5.4 mM potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate, and 130 mM potassium chloride (pH 7.0) [
37]. The lactic acid solution exposure was conducted under static conditions, while the other directions were under agitation conditions (350 rpm).
Following ten days of treatment, the average specimen surface microhardness was determined from four indentations. The difference between the surface microhardness following the treatment regimen and initial lesion surface microhardness was calculated (Δ VHN), and the percent surface microhardness recovery (%SMHR) was determined.
In addition, at the end of the 10-day treatment regimen, the fluoride concentration of each enamel specimen was determined using a microdrill biopsy technique to a depth of 100 µm [
38]. The diameter of the drill hole was determined by microscopic examination. The enamel powder from the drill hole was collected, and dissolved into a mixture comprising 20 µL of HClO4, 40 µL citrate/EDTA buffer, and 40 µL deionized water. The fluoride concentration was then measured using a fluoride ion-selective electrode (ISE)m by interpolation from a standard curve. The enamel fluoride concentration of each specimen was expressed in µg F/cm3, factoring in the dilution factor and drilling volume. Data were expressed as the mean Δ VHN and %SMHR for each dentifrice for N = 18 replicates.
2.4. Soluble Available Fluoride
Soluble available fluoride concentrations were determined using method 29 in the FDA Monograph for three independent lots of freshly made Protegera with NaF, with samples tested in triplicate. A 1:100 dilution of each sample into deionized water was prepared (0.25 g into 25 mL), and the solution mixed thoroughly for 5 min, before being centrifuged for 10 min at 10,000 rpm. To assess the fluoride level, a 1.0 mL aliquot of the supernatant was added to 1.0 mL of total ionic strength adjustment buffer (TISAB II), and the fluoride concentration measured using a fluoride ion selective electrode. The measurement approach employed a standard curve (using fluoride standards at 1, 10, 100 and 475 ppm F).
The same set of samples from three different lots were used to determine 1-minute fluoride release. The same approach was used, but this time the baseline samples were 4.00 + 0.10 g, and were added to 12.0 mL deionized water (1:4 dilution), with immediate homogenizing using a non-aerating stirrer for exactly 60 sec, followed immediately by centrifugation for 10 min, before assessment of fluoride concentration. The test was designed on the ADA requirement that at least 80% of the labeled fluoride concentration is released within 1 min of homogenization at a 1:4 dilution.
2.5. Fluoride Uptake into Incipient Enamel Lesions
In a variation of the above methods, a further experiment was conducted using Procedure 40 in the FDA Monograph 21 for dentifrices (Part 355 Anticaries Drug Products for Over-the-Counter Human Use). Lesions were formed in enamel using a solution of 0.1 M lactic acid in 0.2% Carbopol 907 that was 50% saturated with hydroxyapatite, at a pH of 5.0. Supernatants of selected dentifrices were used to treat incipient enamel lesions, rather than a slurry, and then the fluoride level in the treated lesion was determined.
Slurries were made by combining 9 g of dentifrice with 27 g of deionized water. The products tested were Protegera with NaF, Tom’s of Maine Fluoride-Free (as a negative control), and the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) reference dentifrice with NaF (1100 ppm fluoride). After thorough mixing for 5 min, the slurries were centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min. The specimens with incipient enamel lesions (N = 12 per group) were then immersed into 25 mL of their assigned supernatant with constant stirring (350 rpm) for 30 min. Samples were then washed thoroughly to remove traces of the treatment supernatants. Fluoride levels were determined following immersion of samples into 0.5 mL of 1M HClO4 for 15 sec, before and after treatment with the supernatants.
2.6. Enamel Solubility Reduction (ESR)
The final part of the study explored the effect of test dentifrices on the promotion of enamel resistance to demineralization from 0.1 M lactate buffer, using method 33 in the FDA Monograph. The 7 test products were Protegera with NaF, Crest ProHealth, Crest Cavity Protection, and Sensodyne Pronamel. Two formulations of Protegera with no fluoride, and Tom’s of Maine Fluoride- Free served as fluoride-free controls.
Sound human third molar teeth were placed in a disc of red boxing wax so that only the enamel surfaces were exposed. Twelve sets of three teeth each were prepared. All specimens were cleaned and polished with a flour of pumice slurry and a rag wheel to remove any deposits or stains.
For deprotection, before every use cycle, any residual anti-solubility protection afforded by the previous treatment was eliminated by etching the teeth in 0.1 M lactate buffer two periods of 60 mins each, with constant agitation, at room temperature. After deprotection, the samples were rinsed thoroughly with deionized water. A pre-treatment etch was undertaken using 0.1 M lactate buffer at 37°C in an incubator with constant agitation of the deprotected tooth samples for 15 mins. The used buffer samples were retained for phosphate analysis.
The treatment regimen involved exposing samples a slurry of the test dentifrices (9.0 g added to 27.0 g pooled human saliva) for 5 mins. A second acid exposure was then performed using the same method as the pre-treatment etch, and once again the used lactate buffer solutions were retained for phosphorus analysis. The tooth sets were deprotected, and the procedure repeated so that each of the 7 dentifrices was treated and assayed on each tooth set. A Latin square treatment design was utilized for this purpose.
Phosphate levels in pre- and post-treatment solutions were analyzed using a Klett-Summerson photoelectric colorimeter (Bel-Art Products, Wayne, NJ, USA), with inorganic phosphate concentrations being interpolated from an 8-point standard curve. The percent of enamel solubility reduction was computed from the difference between pre- and post-acid exposure solutions, divided by the amount of phosphate in the pre-solution and multiplied by 100. Mean values were calculated for N = 12 experimental runs.
2.7. Statistical Analyses
Data sets for PCR, RDA, Δ VHN, %SMHR, fluoride uptake and ESR were assessed for normality, and then analyzed using one-way analysis of variance, with Student-Newman-Keuls or Tukey-Kramer post-hoc tests, using SigmaPlot version 13 and version 14.5 software (Graffiti, Palo Alto, CA, USA).
4. Discussion
The results of this study show that a novel dentifrice containing MFC (Protegera
®) is highly effective at removing stained pellicle, whilst having relatively low dentin abrasiveness when compared to marketed dentifrices. At the same time, the MFC dentifrice is effective for delivering fluoride for enamel remineralization. Taking these qualities together, the MFC dentifrice challenges the generally accepted view that effective removal of external stains necessitates having a high content of abrasives, which pose an inherent risk of dentin abrasion. The reason for the surprisingly good performance of the low RDA MFC dentifrice is that its mode of action involves more than simple abrasion of stained pellicles by abrasive particles that are trapped momentarily between the toothbrush bristles and the stained pellicle. The MFC particles themselves have cleaning actions, and they also entrap silica particles to move these across the surface. They also collect extrinsic stains that have been dislodged from the surface [
22].
The current laboratory data add to results from randomized clinical trials that show superior plaque removal for the MFC dentifrice [
20]. Logically, better removal of the dental plaque biofilm should contribute to preventing dental caries and improving gingival health, while better removal of stained pellicle should give cosmetic benefits. While the 3-dimensional cellulose network in the MFC dentifrice is responsible for both actions, it is not inherently abrasive.
The fundamental concept is that the network structure of the MFC particles enhances the rheological properties of the dentifrice. The particles intimately contact the tooth surface, with the force applied by the bristles of the brush. The motion of the toothbrush back and forth (or other motions) propels the MFC dentifrice and creates optimal shear forces, which remove both stained pellicle and biofilm together. The MFC dentifrice structure does this without using high loadings of silica or other abrasives. Moreover, this new cleaning mechanism is associated with enhanced fluoride uptake, because the surface is now free of deposits that could act as barriers to diffusion. The absence of these layers facilitates the diffusion of fluoride ions into incipient enamel lesions, thus enhancing their remineralization.
As mentioned earlier, an ideal dentifrice should provide the removal of both dental plaque biofilms and stained pellicle, whilst at the same time causing minimum abrasion to dental hard tissues. For traditional dentifrices, those that are most effective at removing extrinsic stains in standardized laboratory tests (giving high PCR values) are also among the most abrasive (with high RDA values) [
23]. This has led to the belief that maximum removal ability for dental plaque biofilms and extrinsic stains, and low abrasivity of dentin, are diametrically opposed concepts [
23]. The present results challenge this long-held view, since the MFC dentifrice achieved a high PCR value, but showed an RDA of 87.9, which was below the ISO/ADA reference material, and well below the threshold RDA limit of 250.
Due to the array of colored foods and beverages in a modern diet, and the influence of tobacco and other lifestyle factors on extrinsic stains, many individuals in the community will likely require some degree of abrasive action to prevent the accumulation of extrinsic stains on their teeth. Thus, the challenge lies in finding the least abrasive approach in a dentifrice to achieve this goal. In keeping with the guiding healthcare principle of “first do no harm”, in the context of tooth cleaning, this could be stated as “use only as much abrasion as necessary to clean the teeth.”
As far back as the 1940s, due to concerns with hard tissue abrasion by dentifrices, it was hoped that one day, a nonabrasive, stained pellicle-removing agent suitable for use in a dentifrice would be found [
39,
40,
41]. One 1948 publication commented that “Dentifrice abrasion will be a necessary evil until a non-abrasive, stain-removing or preventing agent is found” [
39].
Some modern dentifrices marketed as “whitening” products have taken this concept in the opposite direction, by including higher loading of abrasives, making some of these more abrasive than other products [
17]. However, there is no simple direct relationship between the stain-removal ability of a dentifrice and its abrasivity, as supported by the present study’s data.
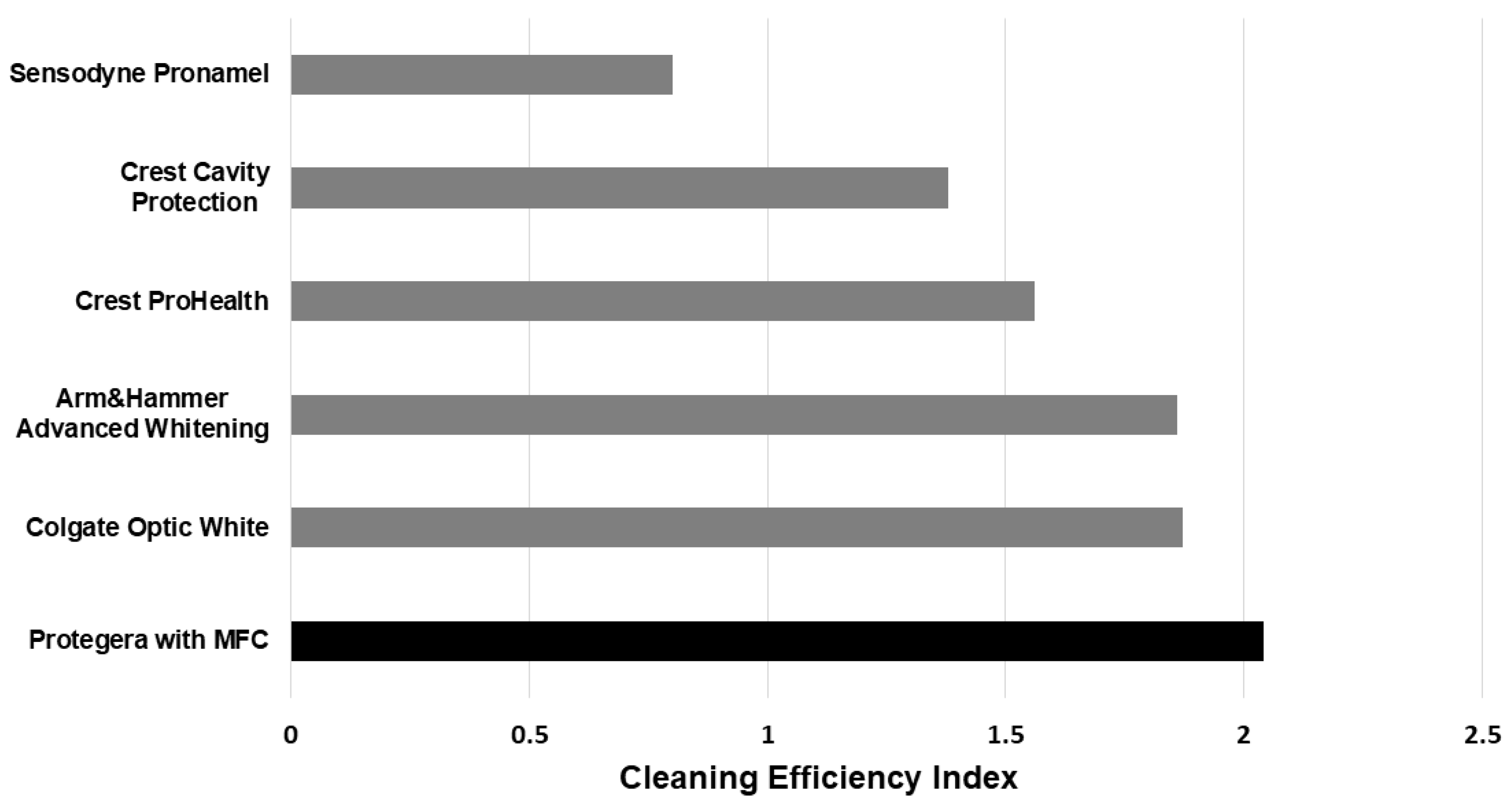
The present results indicate that including MFC in a dentifrice is a viable strategy. In that regard, MFC may be the non-abrasive staining removing agent that has been hoped for since the 1940s. The RDA assessment revealed that the dentifrice vehicle with MFC had extremely low dentin abrasivity, and that even when silica was added, the RDA was still below 100. The combination of MFC and low-dose high-cleaning silica gave a strong performance for stained pellicle removal, being comparable to several marketed whitening products, but with much less dentin abrasivity. As a result, the CEI index for the MFC product Protegera (2.04) was superior to that for Crest ProHealth (1.56).
There are published values for RDA for the four other dentifrices used in the PCR component of the present study, and these RDA data were obtained by previous tests performed in the same facility using the same methods [
17]: Sensodyne Pronamel RDA 34; Crest Cavity Protection RDA 108; Colgate Optic White RDA 100; Arm & Hammer Advanced Whitening RDA 110. A key point from comparing the CEI scores across all six dentifrices is that the score for the MFC dentifrice is higher than the five comparison products (
Figure 2).
While PCR and RDA assessments are well-known laboratory assessment parameters with clinical correlates, the ultimate performance measure of a dentifrice is seen when it is used in the clinical setting. Past work has shown that the MFC dentifrice has superior dental plaque removal performance compared to Crest Cavity Protection, being at least three times and up to four times more effective in whole-mouth plaque reductions when used for a single brushing episode or daily over one week [
20]. Longer-term studies are needed to assess the relative performance of the MFC and other dentifrices for reducing the formation of extrinsic stains, especially in individuals whose diet and lifestyle habits encourage the deposition of stained material onto tooth surfaces. A limitation of the current study was that enamel was the only substrate used for assessments of stain removal. Hence, further work is needed to explore how well the MFC dentifrice removes stains from denture teeth and various types of restorations, appliances and prostheses.
In terms of protecting enamel, in vitro assessments of fluoride bioavailability at 1 and 5 minutes, fluoride uptake into lesions, increased surface microhardness of treated incipient enamel lesions, and enamel solubility reductions all show that the Protegera dentifrice with NaF (1100 ppm fluoride) performs well. Across these measures, it was similar to other products containing NaF, and superior to fluoride-free products, and to those with stannous fluoride. In the 10-day pH cycling study, Protegera with NaF toothpaste have a high enamel fluoride uptake, and this did not differ significantly from the other two NaF dentifrices (Sensodyne and Crest). In the ESR assay, its performance was superior to other dentifrices that had NaF and similar levels of fluoride, and was no different from the stannous fluoride dentifrice (Crest ProHealth). This is an unexpected result, and indicates that delivery and efficacy of fluoride is greater than expected in terms of the protection afforded to the enamel.
When combined with the high CEI and low RDA, these positive results for fluoride efficacy indicate that using MFC in a dentifrice can enhance multiple aspects of its performance. Future work should explore the ability of MFC dentifrices to prevent enamel demineralization and impede caries progression in the clinical setting. This would provide a more comprehensive view of the dynamic process of dental caries (both preventing demineralization and promoting remineralization) that could benefit from enhanced plaque removal and high fluoride effectiveness.