Submitted:
26 April 2024
Posted:
28 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Combination of Immunotherapy with Other Therapies
2.1. Immunotherapy
2.2. Preclinical Stage Combination Immunotherapy
2.3. Clinical Stage Combination Immunotherapy
2.3.1. Pembrolizumab (Anti PD-1 Antibody) Combination
2.3.2. Atezolizumab (Anti PD-L1 Antibody) Combination
2.3.3. Camrelizumab (Anti-PD-1 Antibody) Combination
2.3.4. Durvalumab (PD-L1 Antibody) Combination
2.3.5. Other Immunotherapeutic Combinations
3. Nanotechnology-Based Therapies for TNBC
3.1. Polymer-Based Nanoparticles
3.2. Lipid-Based Nanoparticles
3.3. Inorganic Material-Based Nanoparticle
3.4. Peptide and Protein-Based Nanoparticle
4. Conclusion
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021, 71, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schick, J.; Ritchie, R.P.; Restini, C. Breast Cancer Therapeutics and Biomarkers: Past, Present, and Future Approaches. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2021, 15, 1178223421995854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Aggarwal, R. An overview of triple-negative breast cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016, 293, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, M.A.; Oza, G.; Sharma, A.; Arriaga, L.G.; Hernandez Hernandez, J.M.; Rotello, V.M.; Ramirez, J.T. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Review of Conventional and Advanced Therapeutic Strategies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020, 17, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.J.; Bian, X.W.; Yu, S.C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.R.; Park, T.; Saridakis, A.; Golshan, M.; Greenup, R.A.; Ahuja, N. Immunotherapy Treatment for Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021, 14, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, V.; Kutty, R.V. Recent advances in nanotheranostics for triple negative breast cancer treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahmood, S.; Sapiezynski, J.; Garbuzenko, O.B.; Minko, T. Metastatic and triple-negative breast cancer: challenges and treatment options. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018, 8, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obidiro, O.; Battogtokh, G.; Akala, E.O. Triple Negative Breast Cancer Treatment Options and Limitations: Future Outlook. Pharmaceutics. 2023, 15, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, K.; Bhumika, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Das, A. Combinatorial drug therapy in cancer - New insights. Life Sci. 2020, 258, 118134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emens, L.A. Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer J. 2021, 27, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Kim, K. Theranostics for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023, 13, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Gao, F.; Ahmed, A.; Rafiq, M.; Yu, B.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y. Immunotherapy: cancer immunotherapy and its combination with nanomaterials and other therapies. J Mater Chem B. 2023, 11, 8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S. Nanotechnology in medicine. Indian Heart J. 2016, 68, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, M.A.; Fallica, A.N.; Virzi, N.; Kesharwani, P.; Pittala, V.; Greish, K. The Promise of Nanotechnology in Personalized Medicine. J Pers Med. 2022, 12, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosleh-Shirazi, S.; Abbasi, M.; Moaddeli, M.R.; Vaez, A.; Shafiee, M.; Kasaee, S.R.; Amani, A.M.; Hatam, S. Nanotechnology Advances in the Detection and Treatment of Cancer: An Overview. Nanotheranostics. 2022, 6, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, M.F.; Anton, N.; Wallyn, J.; Omran, Z.; Vandamme, T.F. An overview of active and passive targeting strategies to improve the nanocarriers efficiency to tumour sites. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, T.E.; Tolaney, S.M. Role of Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020, 18, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emens, L.A. Breast Cancer Immunotherapy: Facts and Hopes. Clin Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Li, Y.; El-Gamil, M.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Wang, R.F.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Robbins, P.F. Generation of NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells by a single peptide with dual MHC class I and class II specificities: a new strategy for vaccine design. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 3630. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, G.; Touloukian, C.E.; Wang, X.; Restifo, N.P.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Wang, R.F. Identification of CD4+ T cell epitopes from NY-ESO-1 presented by HLA-DR molecules. J Immunol. 2000, 165, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, W.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.; Chu, J.; Xing, C.; Qian, C.; Du, Y.; Duan, T.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, N.; Yu, J.S.; An, Z.; Wang, R. Development of a TCR-like antibody and chimeric antigen receptor against NY-ESO-1/HLA-A2 for cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. 2022, 10, e004035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuber, T.; Monjezi, R.; Wallstabe, L.; Kuhnemundt, J.; Nietzer, S.L.; Dandekar, G.; Wockel, A.; Einsele, H.; Wischhusen, J.; Hudecek, M. Inhibition of TGF-beta-receptor signaling augments the antitumor function of ROR1-specific CAR T-cells against triple-negative breast cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 2020, 8, e000676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKnight, B.N.; Kim, S.; Boerner, J.L.; Viola, N.T. Cetuximab PET delineated changes in cellular distribution of EGFR upon dasatinib treatment in triple negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manukian, G.; Kivolowitz, C.; DeAngelis, T.; Shastri, A.A.; Savage, J.E.; Camphausen, K.; Rodeck, U.; Zarif, J.C.; Simone, N.L. Caloric Restriction Impairs Regulatory T cells Within the Tumor Microenvironment After Radiation and Primes Effector T cells. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021, 110, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Lee, N.; Pedroza, D.A.; Bado, I.L.; Hamor, C.; Zhang, L.; Aguirre, S.; Hu, J.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, N.; Chen, S.H.; Wan, Y.W.; Liu, Z.; Chang, J.T.; Hollern, D.; Perou, C.M.; Zhang, X.H.F.; Rosen, J.M. Chemotherapy Coupled to Macrophage Inhibition Induces T-cell and B-cell Infiltration and Durable Regression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Bae, J.H.; Choe, E.J.; Park, J.M.; Park, S.S.; Cho, H.J.; Song, B.J.; Baek, M.C. Macitentan improves antitumor immune responses by inhibiting the secretion of tumor-derived extracellular vesicle PD-L1. Theranostics. 2022, 12, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanker, D.J.; Spurling, A.J.; Brockwell, N.K.; Owen, K.L.; Zakhour, J.M.; Robinson, T.; Duivenvoorden, H.M.; Hertzog, P.J.; Mullins, S.R.; Wilkinson, R.W.; Parker, B.S. Intratumoral administration of the Toll-like receptor 7/8 agonist 3M-052 enhances interferon-driven tumor immunogenicity and suppresses metastatic spread in preclinical triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Transl Immunology. 2020, 9, e1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tentler, J.J.; Lang, J.; Capasso, A.; Kim, D.J.; Benaim, E.; Lee, Y.B.; Eisen, A.; Bagby, S.M.; Hartman, S.J.; Yacob, B.W.; Gittleman, B.; Pitts, T.M.; Pelanda, R.; Eckhardt, S.G.; Diamond, J.R. RX-5902, a novel beta-catenin modulator, potentiates the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in preclinical models of triple-negative breast Cancer. BMC Cancer. 2020, 20, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napier, T.S.; Lynch, S.E.; Lu, Y.; Song, P.N.; Burns, A.C.; Sorace, A.G. Molecular Imaging of Oxygenation Changes during Immunotherapy in Combination with Paclitaxel in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Biomedicines. 2023, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; McLaughlin, R.P.; van der Noord, V.; Foekens, J.A.; Martens, J.W.M.; van Westen, G.; Zhang, Y.; van de Water, B. Multi-targeted kinase inhibition alleviates mTOR inhibitor resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019, 178, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.Y.; Barker, C.A.; Arnold, B.B.; Powell, S.N.; Hu, Z.I.; Gucalp, A.; Lebron-Zapata, L.; Wen, H.Y.; Kallman, C.; D'Agnolo, A.; Zhang, Z.; Flynn, J.; Dunn, S.A.; McArthur, H.L. A phase 2 clinical trial assessing the efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab and radiotherapy in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer. 2020, 126, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneeweiss, A.; Michel, L.L.; Mobus, V.; Tesch, H.; Klare, P.; Hahnen, E.; Denkert, C.; Kast, K.; Pohl-Rescigno, E.; Hanusch, C.; Link, T.; Untch, M.; Jackisch, C.; Blohmer, J.U.; Fasching, P.A.; Solbach, C.; Schmutzler, R.K.; Huober, J.; Rhiem, K.; Nekljudova, V.; Lubbe, K.; Loibl, S.; Gbg, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Ago, B. Survival analysis of the randomised phase III GeparOcto trial comparing neoadjuvant chemotherapy of intense dose-dense epirubicin, paclitaxel, cyclophosphamide versus weekly paclitaxel, liposomal doxorubicin (plus carboplatin in triple-negative breast cancer) for patients with high-risk early breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2022, 160, 100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anders, C.K.; Woodcock, M.G.; Van Swearingen, A.E.D.; Moore, D.T.; Sambade, M.J.; Laurie, S.; Robeson, A.; Kolupaev, O.; Cuaboy, L.A.; Garrett, A.L.; McKinnon, K.; Cowens, K.; Bortone, D.; Calhoun, B.C.; Wilkinson, A.D.; Carey, L.; Jolly, T.; Muss, H.; Reeder-Hayes, K.; Kaltman, R.; Jankowitz, R.; Gudena, V.; Olajide, O.; Perou, C.; Dees, E.C.; Vincent, B.G.; Serody, J.S. Evaluating the efficacy of a priming dose of cyclophosphamide prior to pembrolizumab to treat metastatic triple negative breast cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 2022, 10, e003427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscitiello, C.; Marra, A.; Morganti, S.; Zagami, P.; Gandini, S.; Esposito, A.; Curigliano, G. Clinical outcomes of patients with metastatic breast cancer enrolled in phase I clinical trials. Eur J Cancer. 2021, 157, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, H.; Inoue, K.; Kaneko, K.; Ito, Y.; Tsugawa, K.; Hasegawa, A.; Nakagawa, S.; Kuratomi, H.; Tamura, K. Subgroup analysis of Japanese patients in a Phase 3 study of atezolizumab in advanced triple-negative breast cancer (IMpassion130). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2019, 49, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J.R.; Raman, S.S.; Chan, A.; Kalinsky, K.; Baurain, J.F.; Jimenez, M.M.; Garcia, M.M.; Berger, M.D.; Lauer, U.M.; Khattak, A.; Carrato, A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Cha, E.; Keegan, A.; Bhatta, S.; Strassburg, C.P.; Roohullah, A. Phase Ib study of talimogene laherparepvec in combination with atezolizumab in patients with triple negative breast cancer and colorectal cancer with liver metastases. ESMO Open. 2023, 8, 100884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Su, F.; Yao, H.; Su, S.; Wang, Q.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.; Lau, W.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Song, E. Efficacy and safety of camrelizumab combined with apatinib in advanced triple-negative breast cancer: an open-label phase II trial. J Immunother Cancer. 2020, 8, e000696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Su, S.; Zeng, Y.; Jia, W.; Yang, Y.; Xu, S.; Yao, H.; Jiang, W.; Song, E. Multicenter phase II trial of Camrelizumab combined with Apatinib and Eribulin in heavily pretreated patients with advanced triple-negative breast cancer. Nat Commun. 2022, 13, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shao, B.; Tong, Z.; Ouyang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, S.; Li, H. A phase Ib study of camrelizumab in combination with apatinib and fuzuloparib in patients with recurrent or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Fan, L.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhao, S.; Song, X.Q.; Hu, X.; Yang, W.T.; Chai, W.J.; Guo, X.M.; Chen, X.Z.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zou, J.J.; Wang, Z.H.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Shao, Z.M. Combined angiogenesis and PD-1 inhibition for immunomodulatory TNBC: concept exploration and biomarker analysis in the FUTURE-C-Plus trial. Mol Cancer. 2022, 21, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foldi, J.; Kahn, A.; Silber, A.; Qing, T.; Reisenbichler, E.; Fischbach, N.; Persico, J.; Adelson, K.; Katoch, A.; Chagpar, A.; Park, T.; Blanchard, A.; Blenman, K.; Rimm, D.L.; Pusztai, L. Clinical Outcomes and Immune Markers by Race in a Phase I/II Clinical Trial of Durvalumab Concomitant with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Early-Stage TNBC. Clin Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusztai, L.; Yau, C.; Wolf, D.M.; Han, H.S.; Du, L.; Wallace, A.M.; String-Reasor, E.; Boughey, J.C.; Chien, A.J.; Elias, A.D.; Beckwith, H.; Nanda, R.; Albain, K.S.; Clark, A.S.; Kemmer, K.; Kalinsky, K.; Isaacs, C.; Thomas, A.; Shatsky, R.; Helsten, T.L.; Forero-Torres, A.; Liu, M.C.; Brown-Swigart, L.; Petricoin, E.F.; Wulfkuhle, J.D.; Asare, S.M.; Wilson, A.; Singhrao, R.; Sit, L.; Hirst, G.L.; Berry, S.; Sanil, A.; Asare, A.L.; Matthews, J.B.; Perlmutter, J.; Melisko, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Schwab, R.B.; Symmans, W.F.; Yee, D.; Van't Veer, L.J.; Hylton, N.M.; DeMichele, A.M.; Berry, D.A.; Esserman, L.J. Durvalumab with olaparib and paclitaxel for high-risk HER2-negative stage II/III breast cancer: Results from the adaptively randomized I-SPY2 trial. Cancer Cell. 2021, 39, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; Untch, M.; Burchardi, N.; Huober, J.; Sinn, B.V.; Blohmer, J.U.; Grischke, E.M.; Furlanetto, J.; Tesch, H.; Hanusch, C.; Engels, K.; Rezai, M.; Jackisch, C.; Schmitt, W.D.; von Minckwitz, G.; Thomalla, J.; Kummel, S.; Rautenberg, B.; Fasching, P.A.; Weber, K.; Rhiem, K.; Denkert, C.; Schneeweiss, A. A randomised phase II study investigating durvalumab in addition to an anthracycline taxane-based neoadjuvant therapy in early triple-negative breast cancer: clinical results and biomarker analysis of GeparNuevo study. Ann Oncol. 2019, 30, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jia, W.; Deng, H.; Li, G.; Deng, W.; Chen, J.; Kim, B.Y.S.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J. Low-Dose Anti-Angiogenic Therapy Sensitizes Breast Cancer to PD-1 Blockade. Clin Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chick, R.C.; Clifton, G.T.; Hale, D.F.; Vreeland, T.J.; Hickerson, A.T.; Kemp Bohan, P.M.; McCarthy, P.M.; Litton, J.K.; Alatrash, G.; Murthy, R.K.; Qiao, N.; Philips, A.; Lukas, J.; Holmes, J.P.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Peoples, G.E. Subgroup analysis of nelipepimut-S plus GM-CSF combined with trastuzumab versus trastuzumab alone to prevent recurrences in patients with high-risk, HER2 low-expressing breast cancer. Clin Immunol. 2021, 225, 108679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, R.F.; Bakri, H.M.; Abdelfattah, O.N.; Eid, S. Does bevacizumab carry a hope for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer in the era of immunotherapy? Anti-Cancer Drug. 2022, 33, E604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, S.; Tan, A.R.; Rugo, H.S.; Aftimos, P.; Andric, Z.; Beelen, A.; Zhang, J.; Yi, J.S.; Malik, R.; O'Shaughnessy, J. Trilaciclib prior to gemcitabine plus carboplatin for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: phase III PRESERVE 2. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ren, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, N.; Yu, J.; Di, L.; Song, G.; Che, L.; Jia, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, H.; Lyerly, H.K. Prospective study of cyclophosphamide, thiotepa, carboplatin combined with adoptive DC-CIK followed by metronomic cyclophosphamide therapy as salvage treatment for triple negative metastatic breast cancers patients (aged <45). Clin Transl Oncol. 2016, 18, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, X.; Jiang, L.; Zuo, W.J.; Ma, D.; Ding, J.; Zhu, X.; Zou, J.; Verschraegen, C.; Stover, D.G.; Kaklamani, V.; Wang, Z.H.; Shao, Z.M. Molecular subtyping and genomic profiling expand precision medicine in refractory metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: the FUTURE trial. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, A. Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy and Its Role in Overcoming Drug Resistance. Front Mol Biosci. 2020, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, A.; Carreiro, F.; Oliveira, A.M.; Neves, A.; Pires, B.; Venkatesh, D.N.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Eder, P.; Silva, A.M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B. Polymeric Nanoparticles: Production, Characterization, Toxicology and Ecotoxicology. Molecules. 2020, 25, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, J.; Gu, L.; Wu, K.; Xing, H. Nanoparticles for Chemoimmunotherapy Against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022, 17, 5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krausz, A.E.; Adler, B.L.; Makdisi, J.; Schairer, D.; Rosen, J.; Landriscina, A.; Navati, M.; Alfieri, A.; Friedman, J.M.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Rodriguez-Gabin, A.; Ye, K.Q.; McDaid, H.M.; Friedman, A.J. Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Doxorubicin Demonstrates Superior Tumor Cell Kill in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Subtypes Intrinsically Resistant to Doxorubicin. Precis Nanomed. 2018, 1, 173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, F.; Zhou, F. Immunoadjuvant Nanoparticles as Trojan Horses for Enhanced Photo-Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 883428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Shang, H.; Feng, X.; Fan, N.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chu, X.; Zhong, M.; Sun, Y.; Fu, H.; Huang, W.; Li, Y. Self-Assembling Anchorage of Hyaluronic Acid on the Nanoparticle Surface Confers Superiority of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics. 2022, 14, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, A.; McGarry, S.; El-Sahli, S.; Li, L.; Chambers, J.; Phan, A.; Cote, M.; Cron, G.O.; Alain, T.; Le, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Liu, S.; Figeys, D.; Gadde, S.; Wang, L. Co-targeting Bulk Tumor and CSCs in Clinically Translatable TNBC Patient-Derived Xenografts via Combination Nanotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Guo, Q.; Fu, H.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y. Asynchronous blockade of PD-L1 and CD155 by polymeric nanoparticles inhibits triple-negative breast cancer progression and metastasis. Biomaterials. 2021, 275, 120988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcourt, D.M.; Day, E.S. Dual Regulation of miR-34a and Notch Signaling in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Antibody/miRNA Nanocarriers. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020, 21, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcourt, D.M.; Dang, M.N.; Day, E.S. IR820-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for photothermal therapy of triple-negative breast cancer. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019, 107, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcourt, D.M.; Dang, M.N.; Scully, M.A.; Day, E.S. Nanoparticle-Mediated Co-Delivery of Notch-1 Antibodies and ABT-737 as a Potent Treatment Strategy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. ACS Nano. 2020, 14, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnello, L.; Tortorella, S.; d'Argenio, A.; Carbone, C.; Camorani, S.; Locatelli, E.; Auletta, L.; Sorrentino, D.; Fedele, M.; Zannetti, A.; Franchini, M.C.; Cerchia, L. Optimizing cisplatin delivery to triple-negative breast cancer through novel EGFR aptamer-conjugated polymeric nanovectors. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahman, F.; Pittala, V.; Haider, M.; Greish, K. Enhanced Anticancer Activity of Nanoformulation of Dasatinib against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J Pers Med. 2021, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabil, G.; Alzhrani, R.; Alsaab, H.O.; Atef, M.; Sau, S.; Iyer, A.K.; Banna, H.E. CD44 Targeted Nanomaterials for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Deeb, I.M.; Pittala, V.; Eltayeb, D.; Greish, K. Selective Targeting of Breast Cancer by Tafuramycin A Using SMA-Nanoassemblies. Molecules. 2021, 26, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greish, K.; Mathur, A.; Al Zahrani, R.; Elkaissi, S.; Al Jishi, M.; Nazzal, O.; Taha, S.; Pittala, V.; Taurin, S. Synthetic cannabinoids nano-micelles for the management of triple negative breast cancer. J Control Release. 2018, 291, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, J.; Lu, H.; Wang, S. Photo-responsive prodrug nanoparticles for efficient cytoplasmic delivery and synergistic photodynamic-chemotherapy of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Acta Biomater. 2021, 126, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Stewart, S.; Van der Jeught, K.; Agarwal, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, G.; Wan, J.; Lu, X.; He, X. Precise targeting of POLR2A as a therapeutic strategy for human triple negative breast cancer. Nat Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Li, K.K.; Zang, X.L.; Xie, Y.; Song, J.X.; Chen, X.H. ROS-responsive Galactosylated-nanoparticles with Doxorubicin Entrapment for Triple Negative Breast Cancer Therapy. Int J Nanomed. 2023, 18, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Gouw, A.M.; LaGory, E.L.; Guo, S.; Attarwala, N.; Tang, Y.; Qi, J.; Chen, Y.S.; Gao, Z.; Casey, K.M.; Bazhin, A.A.; Chen, M.; Hu, L.; Xie, J.; Fang, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Giaccia, A.J.; Gambhir, S.S.; Zhu, W.; Felsher, D.W.; Pegram, M.D.; Goun, E.A.; Le, A.; Rao, J. Mitochondrial copper depletion suppresses triple-negative breast cancer in mice. Nat Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu Varukattu, N.; Lin, W.; Vivek, R.; Rejeeth, C.; Sabarathinam, S.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, H. Targeted and Intrinsic Activity of HA-Functionalized PEI-Nanoceria as a Nano Reactor in Potential Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Treatment. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wei, T.; Cheng, Q. Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) Enables mRNA Delivery for Cancer Therapy. Adv Mater. 2023, 35, e2303261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskiler, G.G.; Cecener, G.; Egeli, U.; Tunca, B. Talazoparib nanoparticles for overcoming multidrug resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhlis, H.A.; Bayraktar, R.; Kabil, N.N.; Caner, A.; Kahraman, N.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Zambalde, E.P.; Sheng, J.; Karagoz, K.; Kanlikilicer, P.; Abdel Aziz, A.A.H.; Abdelghany, T.M.; Ashour, A.A.; Wong, S.; Gatza, M.L.; Calin, G.A.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Ozpolat, B. The Modulatory Role of MicroRNA-873 in the Progression of KRAS-Driven Cancers. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Gu, C.; Gan, Y.; Shao, L.; Chen, H.; Zhu, H. Exosome-mediated siRNA delivery to suppress postoperative breast cancer metastasis. J Control Release. 2020, 318, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Auguste, D.T.; Moses, M.A. Therapeutic genome editing of triple-negative breast tumors using a noncationic and deformable nanolipogel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019, 116, 18295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayda, S.; Hadla, M.; Palazzolo, S.; Riello, P.; Corona, G.; Toffoli, G.; Rizzolio, F. Inorganic Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: A Transition from Lab to Clinic. Curr Med Chem. 2018, 25, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wen, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Cao, J.; Qi, X.; Shen, S. Ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles cause significant toxicity by specifically inducing acute oxidative stress to multiple organs. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramchandani, D.; Lee, S.K.; Yomtoubian, S.; Han, M.S.; Tung, C.H.; Mittal, V. Nanoparticle Delivery of miR-708 Mimetic Impairs Breast Cancer Metastasis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oei, A.L.; Korangath, P.; Mulka, K.; Helenius, M.; Coulter, J.B.; Stewart, J.; Velarde, E.; Crezee, J.; Simons, B.; Stalpers, L.J.A.; Kok, H.P.; Gabrielson, K.; Franken, N.A.P.; Ivkov, R. Enhancing the abscopal effect of radiation and immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies with magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia in a model of metastatic breast cancer. Int J Hyperthermia. 2019, 36, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Bao, S.; Qiu, G.; Liang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Qin, G.; Liu, J.; Zhao, C. An Magnetic-Targeting Nano-Diagnosis and Treatment Platform for TNBC. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2023, 15, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Liu, B.; Long, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tong, C.; Wang, W.; You, P.; Liu, X. Sequentially-targeted biomimetic nano drug system for triple-negative breast cancer ablation and lung metastasis inhibition. Acta Biomater. 2020, 113, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Guo, Z.; Song, J.; Yang, X.; Wan, G.; Li, R.; Wang, Y. Leukocyte/platelet hybrid membrane-camouflaged dendritic large pore mesoporous silica nanoparticles co-loaded with photo/chemotherapeutic agents for triple negative breast cancer combination treatment. Bioact Mater. 2021, 6, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Piao, S.; Gao, Y.; Tam, A.; Hu, H.; Cheng, W. A Comprehensive Evaluation of ZrC Nanoparticle in Combined Photothermal and Radiation Therapy for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021, 11, 801352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardley, D.A. nab-Paclitaxel mechanisms of action and delivery. J Control Release. 2013, 170, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.; Pyankov, I.; Maretina, M.; Baranov, V.; Kiselev, A. Peptide Nanoparticle-Mediated Combinatorial Delivery of Cancer-Related siRNAs for Synergistic Anti-Proliferative Activity in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021, 14, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Guo, H.; Luan, X.; He, M.; Li, F.; Burnett, J.; Truchan, N.; Sun, D. Albumin Nanoparticle of Paclitaxel (Abraxane) Decreases while Taxol Increases Breast Cancer Stem Cells in Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Mol Pharm. 2020, 17, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, C.; Lu, L.; Jiang, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X. Transcytosable Peptide-Paclitaxel Prodrug Nanoparticle for Targeted Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, H.; Deng, S.; Yue, L.; Weng, Z.; Yang, J.; Zuo, B.; He, Y.; Zhang, B. (cRGD)2 peptides modified nanoparticles increase tumor-targeting therapeutic effects by co-delivery of albendazole and iodine-131. Anticancer Drugs. 2022, 33, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tokheim, C.; Gu, S.S.; Wang, B.; Tang, Q.; Li, Y.; Traugh, N.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Fu, J.; Xiao, T.; Li, W.; Meyer, C.A.; Chu, J.; Jiang, P.; Cejas, P.; Lim, K.; Long, H.; Brown, M.; Liu, X.S. In vivo CRISPR screens identify the E3 ligase Cop1 as a modulator of macrophage infiltration and cancer immunotherapy target. Cell. 2021, 184, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.T.H.; Xu, P.; Chow, A.; Man, S.; Kruger, J.; Khan, K.A.; Paez-Ribes, M.; Pham, E.; Kerbel, R.S. Pre- and post-operative anti-PD-L1 plus anti-angiogenic therapies in mouse breast or renal cancer models of micro- or macro-metastatic disease. Br J Cancer. 2019, 120, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
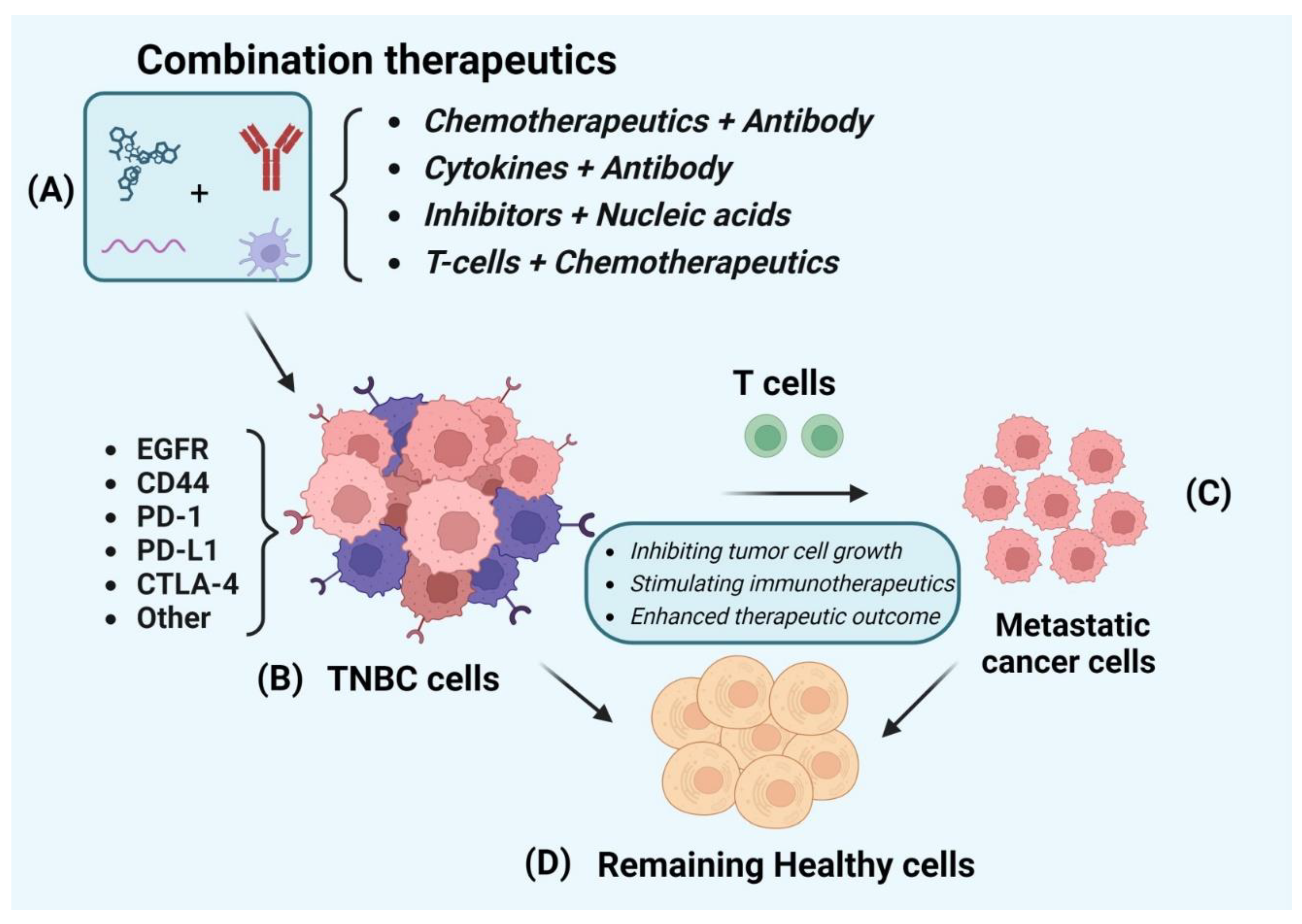
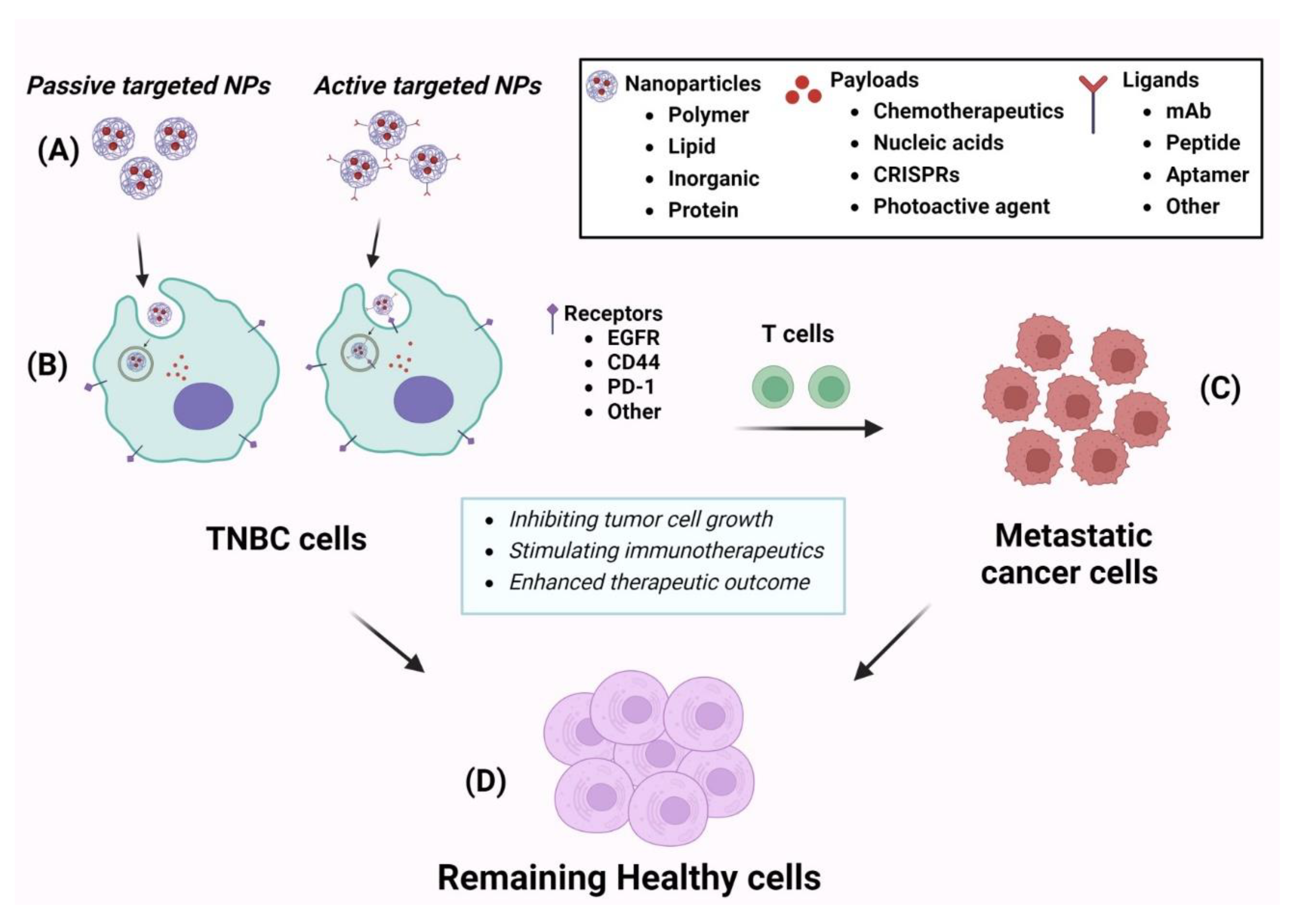
| Comb Therapeutics | Cell line and model | Stage | Results | Molecular target | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monoclonal antibody 2D2 and TCR-like CAR-T cell | HEK293T, MDA-MB231-ESO1, PC3-A2-ESO1T2, Mel586, Mel624, Mel1558 cells; MDA-MD231-N4-ESO-1 | In vitro and in vivo | TCR-like antibody derived CAR-T cells were able to inhibit tumor cell growth and overall survival of mouse. | HLA-A2, NY-ESO-1 | [22] |
| Anti-PD1 antibody and CRISPR knockout |
4T1-tumor bearing mice model |
In vitro and in vivo | In vivo CRISPR knockout enhanced antitumor immunity and strengthened immune checkpoint blockade | E3 ubiquitin ligase Cop1 | [91] |
| ICIs and PTX | 4T1, EO771; 4T1 and E0771 tumor-bearing mice model | In vitro and in vivo | The combination treatment reduced tumor growth . | PD-1 and CTLA-4 | [30] |
| Dasatinib/ radiotracer-attached cetuximab | MDA-MB231 cell and MDA-MB468 PDX tumor model | In vitro and in vivo | The results showed that combination of radiolabeled antibody and dasatinib was able to monitor drug distribution and treatment response in KRAS TNBC. | EGFR | [24] |
| Macitentan/ anti-PD-1 antibody | MDA-MB231, 4T1, CT26 and LL/2, EMT6; MDA-MB231, 4T1, and EMT6 tumor- bearing mice | In vitro and in vivo | The combination of MAC and anti-PD-1 antibody showed strong antitumor effect against TNBC, colon and lung cancer. | PD-1, CD8+T endothelin receptor | [27] |
| Radiotherapy/ caloric restriction ad libitum diet |
4T1-tumor bearing mice model |
In vitro and in vivo | The results revealed that the combination RT and CR enhanced immuno therapy effect against TNBC. | CD+8T cell, TME | [25] |
| 3M-O52 and anti PD1 antibody | E0771, CAL-120 and MDA-MB-231cells; 4T1.2 or E0771 bearing mice | In vitro and in vivo | The results showed the combination treatment reduced tumor growth and metastatic spread to lung | IFN, TME, PD1, Toll like receptor 7/8 | [28] |
| Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) and CSF1R inhibitor or an anti-CSF1R antibody | T11, T12 cell lines; T11, T12 and 215/R tumor -bearing mice model | In vitro and in vivo | The results illustrated the complexity of the tumor immune microenvironment and highlight different immune responses that result from rational immunotherapy combinations. | CSF1R | [26] |
| CAR-T cell and TGF-B inhibitor SA-208 | MDA-MB-231 | In vitro and in vivo | The results showed the combinatorial treatment of CAR-T cell and TGF-B receptor blockade was able to suppress tumor growth. | ROR1, TGF-B receptor | [23] |
| RX-5902 and PD-1 or CTLA-4 combination | 4T1 and MDA-MB231 TNBC tumor bearing mice model | In vitro and in vivo | The combination treatment decreased tumor growth and increased activated T cells | CTLA-4/ PD-1 | [29] |
| Anti-PD-L1 antibody and sunitinib/ Paclitaxel | EMT-6/P, EMT-6/CDDP, REN CA, | In vitro and in vivo | In the EMT-6/CDDP model, combination of anti-PD-L1 with paclitaxel chemotherapy (with or without anti-VEGF) was most effective as a neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer. | PD-L1/ VEGF/VEGFR2 | [92] |
| Pembrolizumab and radiotherapy | 17 patients with TNBC | Phase II trial | Neutral efficacy but encocering? clinical activity | PD-L1 | [32] |
| Pembrolizumab and cyclophosphamide (antineoplastic agent) | 40 patients with TNBC | Phase II | Low outcome for TNBC patients | [34] | |
| Aterolizumab and nabpaclitaxel | 902 patients with TNBC | Phase III | Consistent with the overall IM passion 130 population | PD-L1 | [36] |
| Camrelizumab and Apatinib | 40 patients | Phase II | Objective response rate was much higher than monotherapy | PD-L1 | [38] |
| Durvalumab and nab-paclitaxel, DOX, and Cyclophosphamide | 67 patients with early stage TNBC | Phase I/II | The combination treatment improved survival rate of the patients. | PD-L1 | [42] |
| Nanoparticle | Drug | Cell line and model | Stage | Results | Targeting moiety and receptor | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sol-gel polymer nanoparticle | DOX | SUM149PT, HS578T, MDA-MB157 | In vitro and in vivo | DOX-NPs showed higher cell killing activity in comparison to free DOX. | EPR | [55] |
| HA-coated chitosan NPs | Curcumin | 4T1 cell line, 4T1 tumor-bearing mice |
In vitro and in vivo | It exhibited higher antitumor efficacy in TNBC- tumor model. | CD44 receptor | [57] |
| Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticle | PTX and verterporfin | MDA-MB231 cell line, HCl-002 PDX TNBC mice model |
In vitro and in vivo | As compared free drugs, the NPs showed significant suppression for tumor growth. | NFkB, Wnt and VAP pathways, cancer stem cells | [58] |
| mPEG-PLGA-PLL NPs | siRNA CD155 | 4T1 cell line, 4T1 –orthotopic tumor model |
In vitro and in vivo | The NPs improved early stage CD8+T cell immunosurveillance. | PD-L1 and CD155 receptor | [59] |
| PLGA Nps | miRNA | MDA-MB231 TNBC cell, MCF-10A normal cells | In vitro and in vivo | The NPs was able to impair TNBC cells | Notch-1 signal, miR-34a downstream | [60] |
| PLGA NPs | IR820 dye | MDA-MB231 cell, Tumor-bearing mice |
In vitro and in vivo | The NPs significantly reduced TNBC tumor growth. | EPR | [61] |
| PLGA NPs | ABT-737 (BcL2 inhibitor) | MDA-MB231 cell line, MCF-10A normal cell | In vitro and in vivo | The NPs exhibited high tumor accumulation and strong inhibition of tumor growth in TNBC tumor model. | Notch – 1 signal targeting | [62] |
| SMA polymer NPs | Dasatinib (TKI) | MDA-MB231, MCF7, and 4T1 cells; 4T1-bearing tumor model | In vitro and in vivo | The NPs showed 7-fold higher tumor suppression effect than free drug in tumor-bearing mice model. | EPR, ABL kinase Src (Kin2) receptor TKI | [64] |
| TPGS-SMA polymer NPs | CFM-4.16/ momelotinib | MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB468; MDA-MB231-bearing mice model | In vitro and in vivo | The NP revealed strong targeting ability to CD44 expressing cell | CD44 receptor | [65] |
| SMA polymer micelle | Taluzamycin-A | MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB468, MCF-7 cells; 4T1-tumor bearing mice | In vitro and in vivo | The NPs was uptaken by tumor tissue 4-times greater than free drug. | EPR | [66] |
| Polymer NPs | AL/ camptothecin | 4T1- cell line 4T1-tumor bearing mice model |
In vitro and in vivo | The combinatorial drug-loaded NPs showed tumor suppression effect against metastatic TNBC. | EPR, light sensitive delivery | [68] |
| PLGA polymer and lipid hybrid NPs | siRNA | MDA-MB453, MDA-MB231 cells; MDA-MB453 and MDA-MB231 –bearing mice model | In vitro and in vivo | The results showed that the NPs inhibited POLR2A and significantly reduced POLR2A positive tumor growth | POLR2A | [69] |
| P-glactose – polymethacrylate NPs | DOX | Human MDA-MB231, 4T1, HUVEC cells; 4T1 tumor-bearing mice | In vitro and in vivo | DOX-loaded NPs revealed higher cellular uptake and tumor accumulation as well as tumor suppression effect | Glactose, EPR | [70] |
| SMA-WIN polymer NPs | DOX and canabinoid | MDA-MB231, 4T1, MCF7; 4T1 –bearing mice | In vitro and in vivo | The dual drug-loaded NPs significantly reduced tumor growth as comparison in free drugs. | EPR | [67] |
| PLGA NPs | Cisplatin | MDA-MB231, BT-549, and MDA-231-EGFR-KO cells; MDA-M231 and MDA-MB231-KO- bearing mice | In vitro and in vivo | The cisplatin-PLGA Nps revealed strong tumor suppression efficacy in TNBC mice model | EGFR | [63] |
| HA-CePEI NPs | Cerium oxide (Ceria) | MDA-MB231, and HBL-100 cells | In vitro and in vivo | The NPs showed a strong apoptotic effect in TNBC cells due to its ROS generation and targeting ability | CD44 | [72] |
| SLNPs | PARP inhibitor talaroparib | HCC1937, MCF10A, and HCC1937-RC cells | In vitro and in vivo | The NPs were able to reduce MDR1, BCRP, and MRP1 gene expression, leading efficient therapeutic activity. | EPR | [74] |
| LNPs | microRNA (miR-878) | MCF10A, MDA-MB436, MDA-MB231, MDA-MB453, BT-20, HCC1937, SKBR3, T47D, HEK293 noraml HPDA, PANC1, BxPC3, MiaPaCa-2, Capan -2 | In vitro and in vivo | The NPs inhibited tumor growth in PDAC and TNBC tumor by suppressing cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis | EPR | [75] |
| Lipogel tNLGs | 3CRISPR plasmid | MDA-MB231, MDA-MB436, MCF10A; MDA-MB231-tumor-beairng mice | In vitro and in vivo | The NPs suppressed the expression of LCN2 oncogene and inhibited minimal host toxicity | ICAM1 | [77] |
| LbL- coated Gold NPs | miRNA (miR-708) | MDA-MB231, 293T, MDA-MB231-LM2 cells; 4T1-tumor-bearing mice | In vitro and in vivo | miRNA-gold NPs exhibited minimal host toxicity | EPR | [80] |
| Magnetic iron oxide NPs | Immune check point inhibitor | 4T1 cell line and 4T1 –tumor bearing mice | In vitro and in vivo | The MIO NPs reduced tumor growth in TNBC tumor model | EPR, PD-1, CTLA-4 | [81] |
| Graphene oxide Qdot NPs | Gamma bufotacin and DOX | MDA-MB231, BGC-823, Hela, NIH-3T3 RAW264.7 | In vitro and in vivo | The dual drug-loaded NPs were uptaken 2-fold higher by tumor cells in comparison with naked one and reduced lung metastasis. | TAT, RGD | [83] |
| Peptide-drug conjugate NPs | PTX | 4T1-mcherry-luc cell; 4T1-tumor bearing mice | In vitro and in vivo | The NPs strongly inhibited tumor growth | NRP1 (Neuropilin 1) | [89] |
| RGD-HAS NPs | Aldendarole/ iodine-131 | MDA-MB231; 4T1-cells | In vitro and in vivo | RGA-coupled NPs were able to penetrate into tumor and inhibit tumor growth | cRGD and integrin | [90] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





