1. Introduction
In the FinTech sector, risk management is a critical pillar, essential for navigating the complexities of modern financial markets. This research paper delves into the advancements in risk management, particularly focusing on the integration of new technologies and their growing significance in FinTech.
Initially, the paper explores traditional risk management technologies. While these methods laid the foundation for risk analysis, their effectiveness diminishes in the face of increasing market complexity and competition. We detail the limitations of these earlier technologies, notably in terms of scalability, adaptability, and their lag in responding to real-time market changes.
The narrative then shifts to contemporary technologies that fuse AI, machine learning, and big data analytics in risk management software. This section discusses how such a synthesis offers a more effective solution in today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape. We emphasize how these technologies facilitate proactive risk mitigation strategies and significantly enhance decision-making processes.
Figure 1.
Traditional vs New Technologies in Risk Management.
Figure 1.
Traditional vs New Technologies in Risk Management.
Further, the paper presents case studies from various companies that have implemented these latest technologies in real-world scenarios. These studies illustrate the practical applications and benefits of modern risk management approaches.
Challenges in adopting these technologies are also addressed, including issues related to regulatory compliance, data privacy, and the necessity for robust cybersecurity measures. These challenges are critical to ensuring the safe and effective use of advanced risk management software.
Finally, the paper concludes by reaffirming the notion that adopting these technological advancements not only boosts operational efficiency but also substantially reduces financial risks. This paradigm shift is crucial in fostering a more stable and reliable financial market environment, proving indispensable for the future of FinTech.
2. Main Body
The evolution of risk management in FinTech has its roots in historical practices, tracing back to when risk management was predominantly concerned with traditional banking activities. These activities included managing credit, market, and operational risks. Initially, the approach was largely reactive, leaning heavily on statistical models and the analysis of past data. However, this methodology faced several limitations, such as issues with scalability, adaptability, and a delayed response to rapidly changing market dynamics. As the financial landscape evolved, particularly with the advent of digital technology and the internet, these limitations became increasingly apparent. This transition highlighted the need for innovative technical solutions. Modern FinTech risk management now integrates advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and real-time data analytics. These tools offer more agile and predictive risk assessment capabilities, marking a significant shift from the traditional, more static methods. This new era in FinTech risk management is not only more efficient but also better equipped to handle the complexity and speed of today’s financial markets.
2.1. Transition to Advanced Technologies
In today’s complex and dynamic market, traditional methods no longer suffice. New technologies, such as AI, machine learning, Big Data, Predictive analytics, and Sentiment Analysis, are supplanting outdated approaches. These advanced tools excel in processing vast data volumes swiftly, enabling real-time risk evaluation. Their self-learning capabilities empower them to adapt seamlessly to evolving market conditions, including unstructured data sources. The predictive analysis they offer surpasses traditional methods, and their agility ensures compliance with ever-changing regulations in the dynamic regulatory landscape.
2.2. Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Algorithms powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have revolutionized risk management in the FinTech industry. These algorithms excel at processing and analyzing vast datasets, uncovering hidden patterns, correlations, and anomalies that conventional methods might miss. Leveraging techniques such as regression analysis, decision trees, and neural networks, they bolster their predictive capabilities. Real-time risk monitoring is a hallmark of these algorithms, allowing banks to stay informed instantly. They are actively employed across various sectors, including financial institutions, insurance, and portfolio management, offering significant benefits such as data-driven decision-making, proactive risk mitigation, cost savings, and adherence to regulatory requirements.
2.3. Impact of Big Data Analytics
Big Data has ushered in a transformative era in risk management, encompassing vast and diverse datasets, including real-time and historical data from sources like market data, social media feeds, news articles, and customer transactions. This extensive data pool enables organizations to conduct real-time and historical analysis. The fusion of real-time analysis with predictive modeling creates a dynamic early warning system, facilitating the prompt detection of emerging risks. Moreover, Big Data seamlessly integrates with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), leading to comprehensive risk management and data-driven strategic decision-making. In essence, Big Data has revolutionized risk management, offering unparalleled insights and agility in today’s complex business environment.
2.4. Case Studies: Real-World Applications
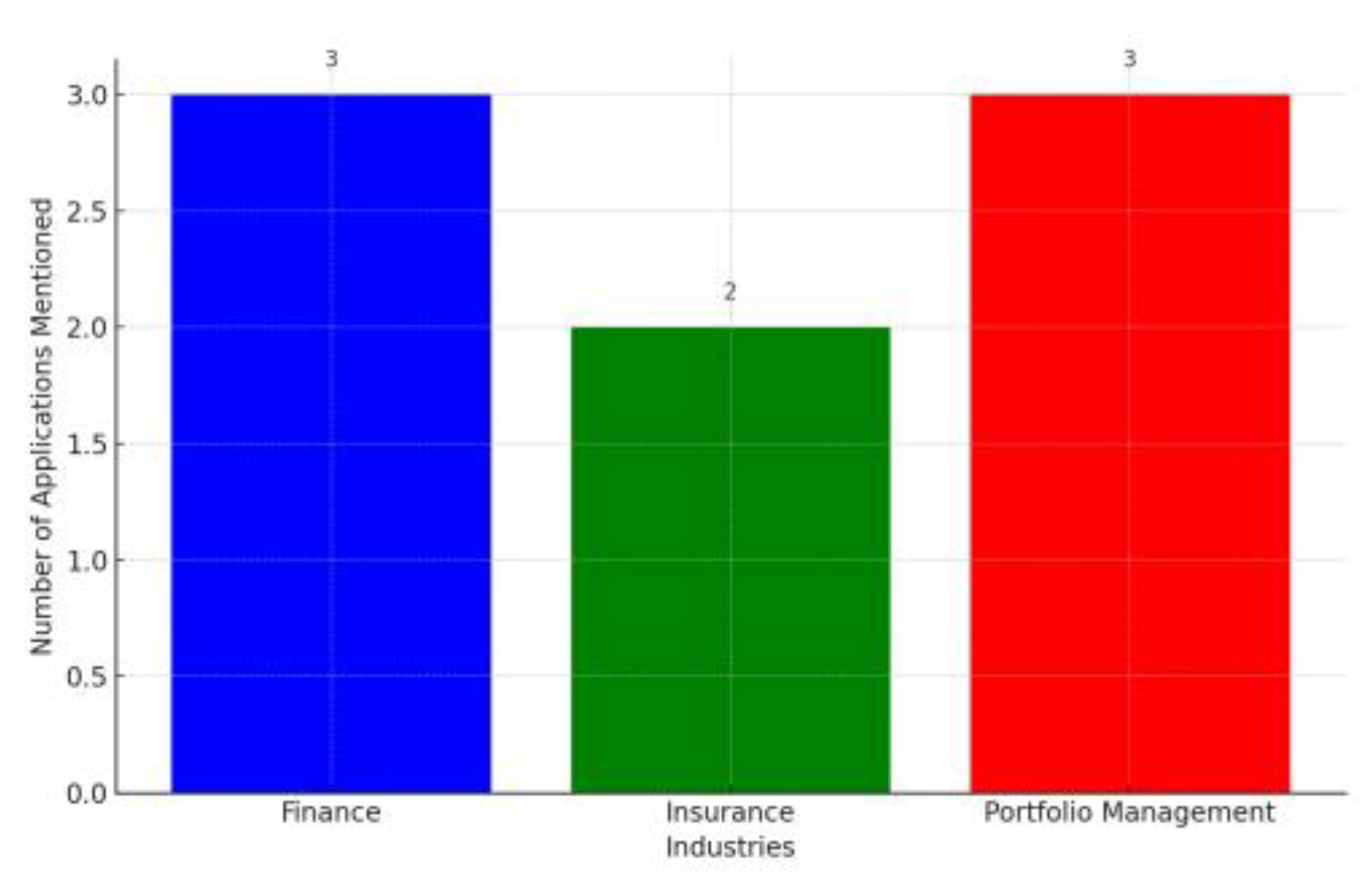
Advanced technologies, including Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Big Data, have revolutionized key industries. In financial institutions, they serve as powerful tools for real-time fraud detection, safeguarding assets, and minimizing financial losses. The insurance sector benefits from AI-driven risk assessment models, enabling more accurate policy pricing and reducing claim fraud. In portfolio management, these technologies analyze market data, news sentiment, and economic indicators, facilitating data-driven investment decisions. Leading companies like JPMorgan Chase, Lemonade Insurance, and Bridgewater Associates have harnessed AI’s potential with remarkable success. For instance, JPMorgan Chase’s AI-powered system streamlines
Figure 2.
Applic¸ations of AI, ML, and Big Data in Various Industries.
Figure 2.
Applic¸ations of AI, ML, and Big Data in Various Industries.
legal document analysis, resulting in cost savings and efficiency. Lemonade Insurance leverages AI algorithms for real-time customer data analysis, fueling rapid growth. Bridgewater Associates utilizes AI for portfolio optimization, consistently outperforming market benchmarks. The graphical representation above highlights the transformative impact of these technologies in different industries.
2.5. Challenges and Future Outlook
While new technologies, including Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data, offer significant advantages, they also present formidable challenges in the realm of risk management. Maintaining regulatory compliance is paramount, but it becomes a complex task as AI and Big Data must navigate through intricate regulatory environments. Regulators often struggle to keep pace with the rapid advancements in technology, leading to slow adaptation. Achieving transparency and explainability in AI systems remains a critical issue, as they can be perceived as ’black boxes.’ Data privacy and ethical considerations are also challenges, with ethical use of these technologies still under scrutiny. The growing reliance on AI and Machine Learning (ML) elevates cybersecurity concerns, increasing the risk of cyber threats and data breaches.
However, looking to the future, these challenges can find solutions through technological advancements. Blockchain promises transparency and security, Regtech streamlines compliance, and quantum computing offers the potential to solve complex problems at unprecedented speeds.
3. Conclusion
In the rapidly evolving FinTech sector, effective risk management is indispensable, particularly for dealers and brokers. This research paper provides a comprehensive overview of the latest technologies and solutions in risk management software development, emphasizing their paramount importance in today’s financial landscape.
We commence by examining traditional risk management techniques and highlighting their inherent limitations, including challenges related to scalability, adaptability, and the ability to respond to real-time market changes. It becomes evident that these conventional methods are ill-suited for the complexities and demands of the modern financial world.
Subsequently, we delve into the transformative role of cutting-edge technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Big Data. Noteworthy industry leaders like JPMorgan Chase, Lemonade Insurance, and Bridgewater Associates have harnessed these technologies to achieve substantial benefits and remarkable success. We explore how AI and ML algorithms process extensive datasets, unveil hidden insights, and drive informed decision-making, revolutionizing risk management practices.
Finally, the research paper addresses the challenges that FinTech companies encounter when embracing these innovative technologies. Compliance and regulatory adherence emerge as pivotal concerns. However, we maintain an optimistic outlook toward the future, where technological advancements, including Regtech solutions and blockchain transparency, promise to mitigate these challenges and pave the way for a more resilient and efficient FinTech landscape.”
References
- A. J. McNeil, R. Frey and P. Embrechts, “Quantitative risk management: Concepts, techniques and tools,”Princeton University Press, 2015.
- R. S. Kenett and G. Shmueli, “Cyber risk management: New analytical approaches,”Risk Management and Insurance Review, 19 2016.
- P. Bromiley, M. McShane, A. Nair and E. Rustambekov, “Enterprise risk management: Review, critique, and research directions,”Long Range Planning, 48 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Hull, “Risk management and financial institutions,”Wiley, 2016.
- K. Buehler, A. Huth and A. Libarikian, “The next frontier in risk management with ai,”McKinsey Quarterly, 2018.
- T. Hagendorff, “The ethics of ai ethics: An evaluation of guidelines,”Minds and Machines, 30 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Gai, M. Qiu and X. Sun, “Big data analytics in financial statement audits,”ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 50 2017. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).