Submitted:
29 April 2024
Posted:
30 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
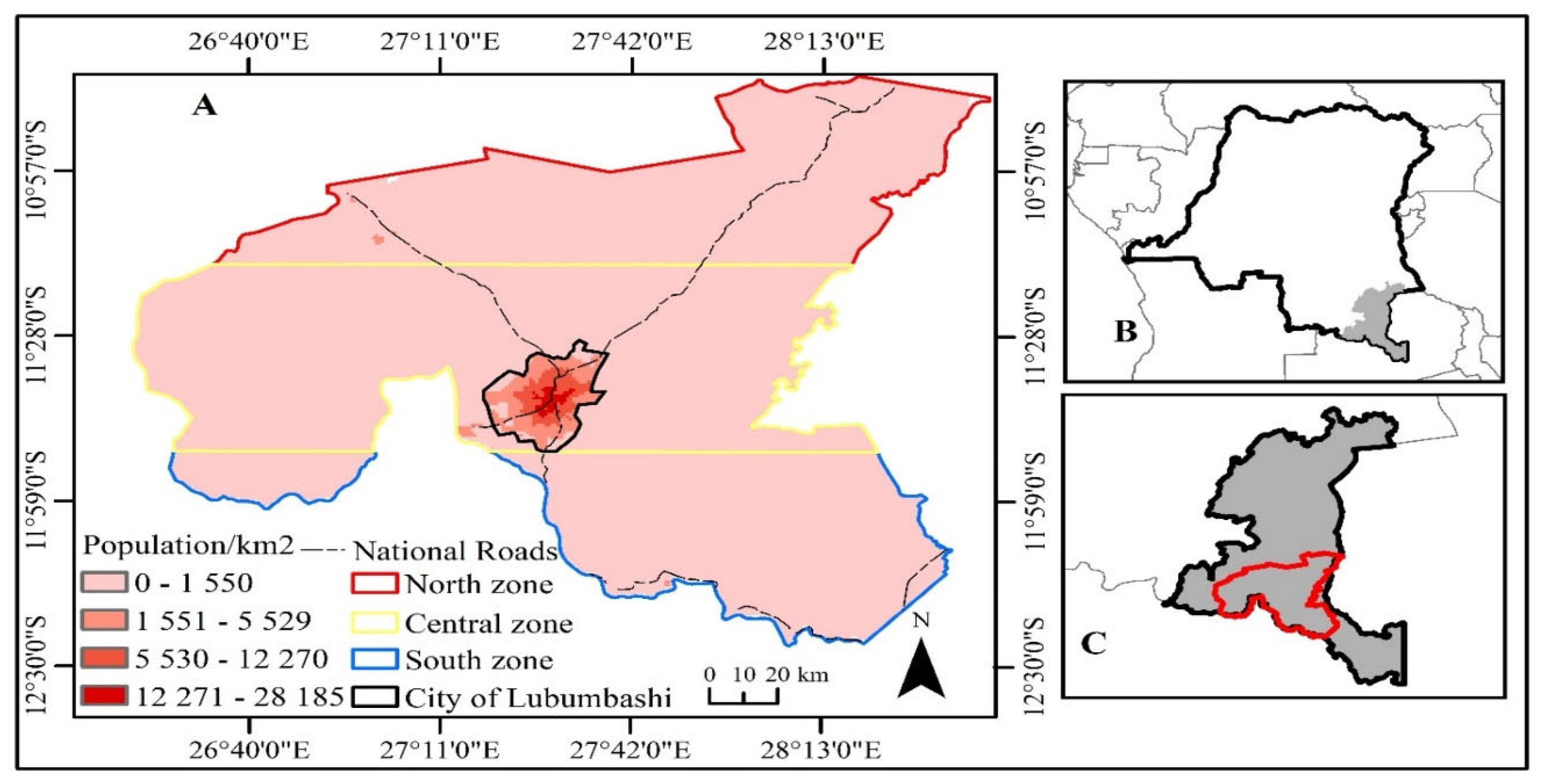
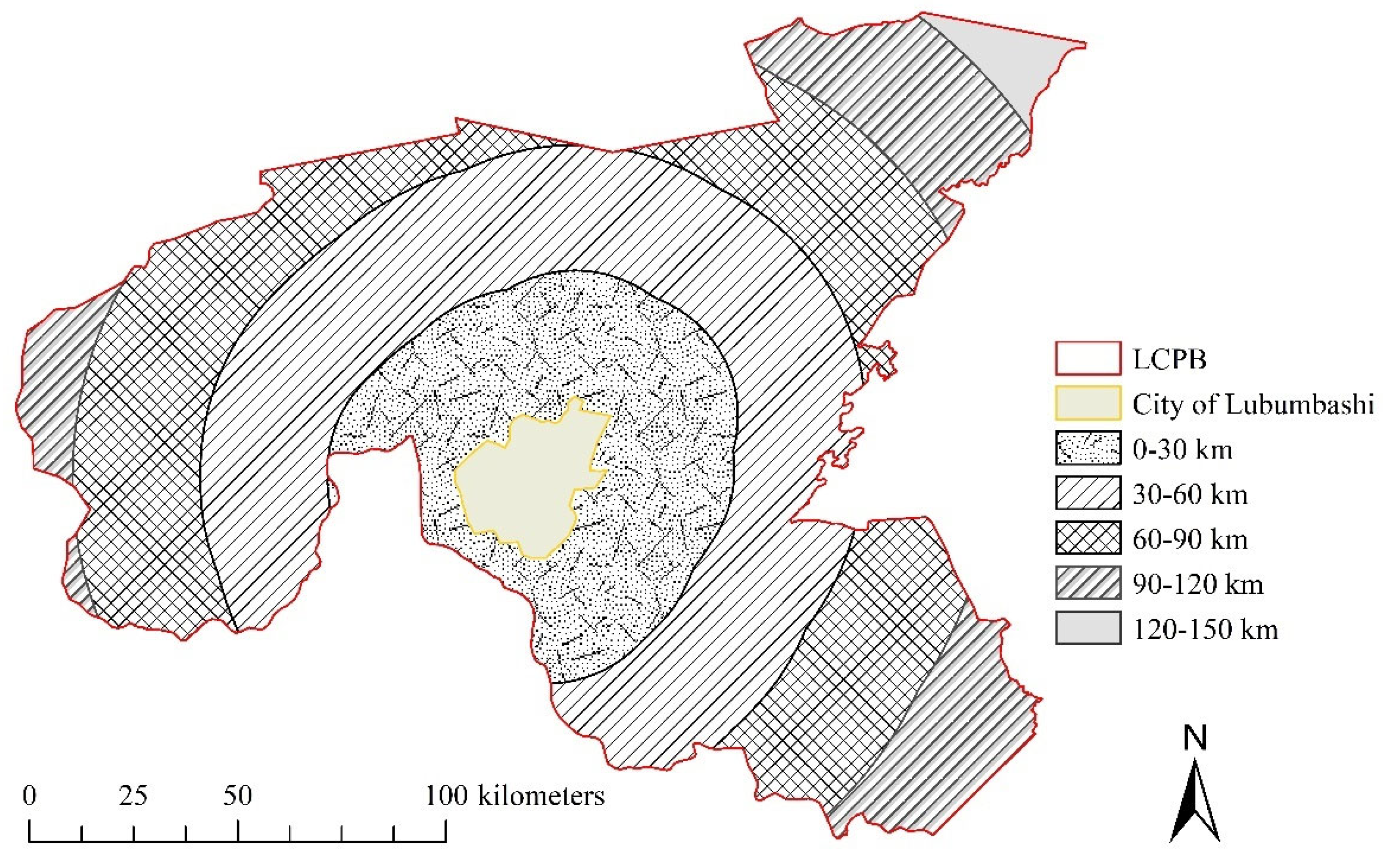
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Sentinel-2 Images Classification
2.4. Land Cover Change Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Classification Accuracy
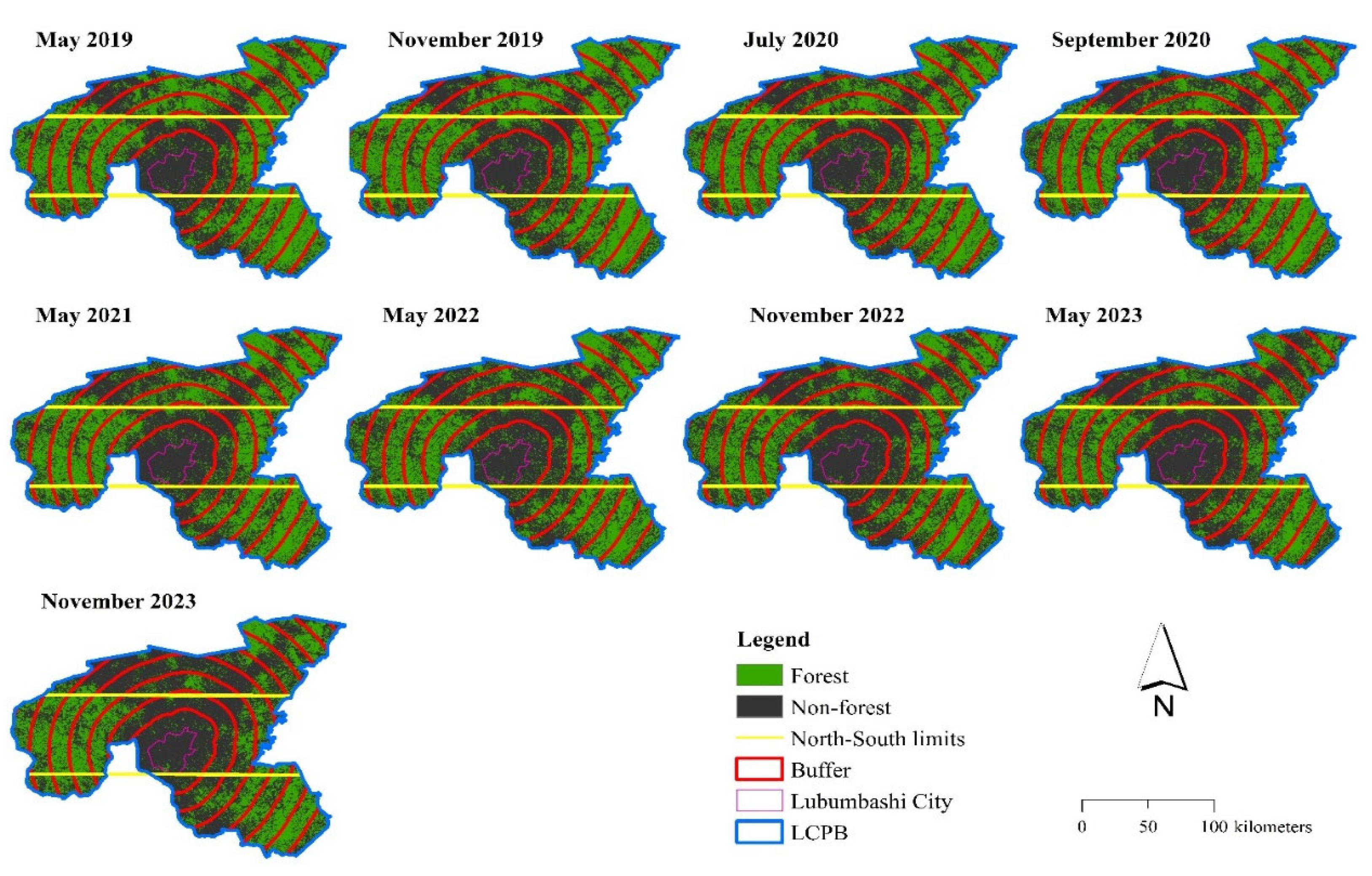
3.2. Land Cover Change Mapping
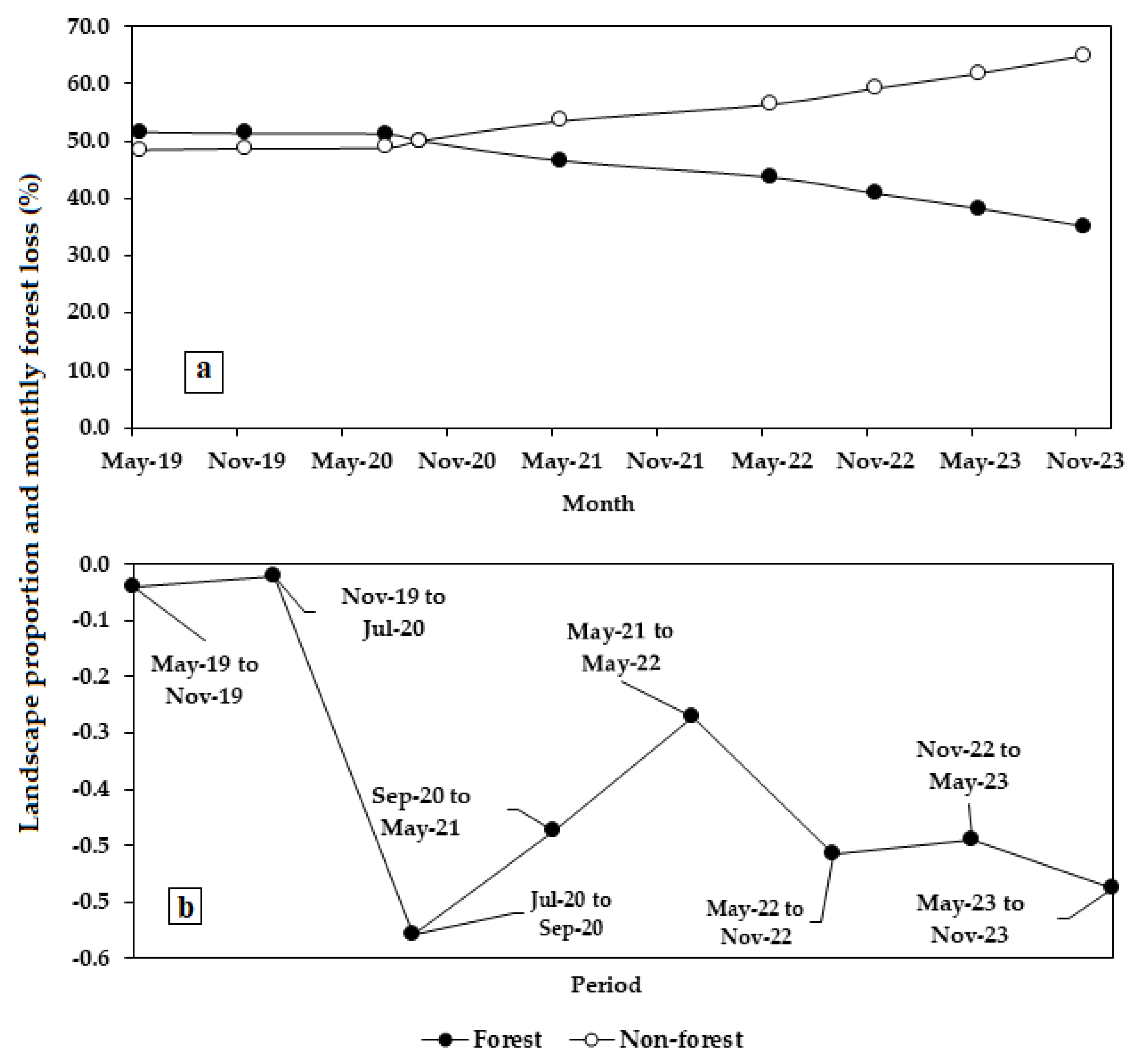
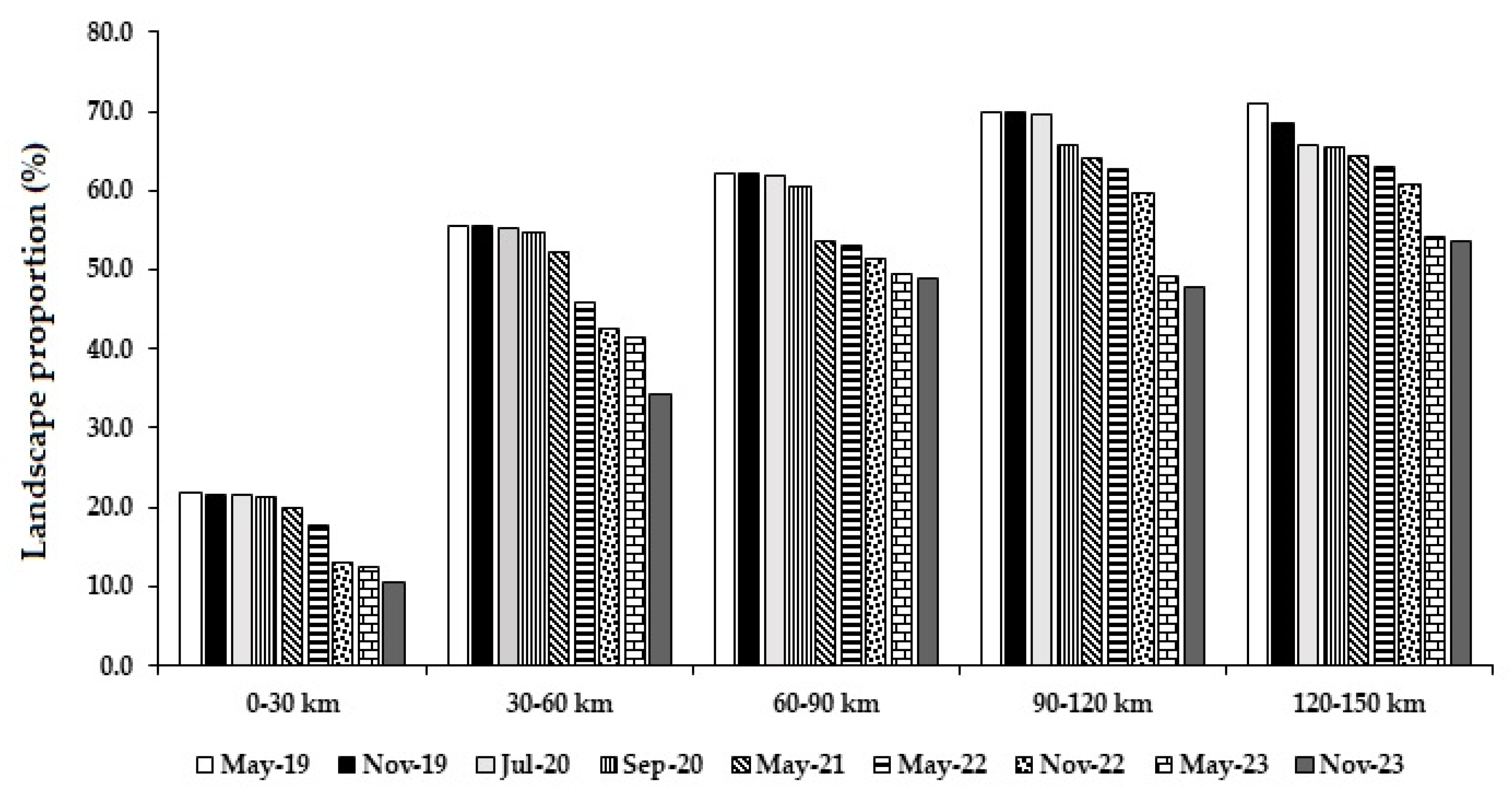
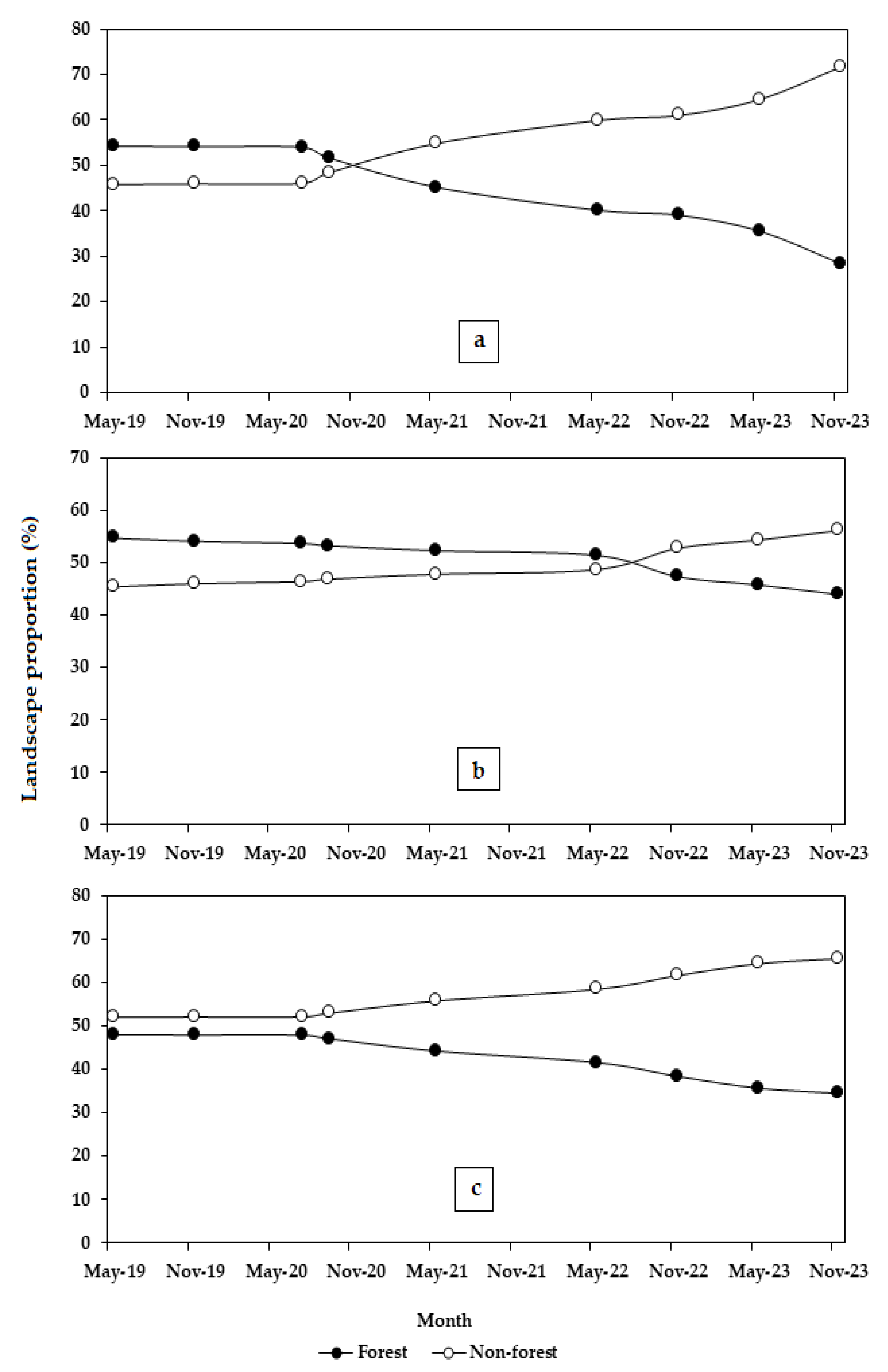
3.3. Landscape Composition Dynamics
3.4. Change in the Configuration of Landscape
4. Discussion
4.1. Methodology
4.2. Forest Cover Loss during Covid-19 Pandemic: Drivers, Extent, and Spatio-Temporal Dynamics
4.2. Implications for Forest Management
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brockerhoff, E.G.; Barbaro, L.; Castagneyrol, B.; Forrester, D.I.; Gardiner, B.; González-Olabarria, J.R.; Lyver, P.O.B.; Meurisse, N.; Oxbrough, A.; Taki, H.; Thompson, I.D. Forest biodiversity, ecosystem functioning and the provision of ecosystem services. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 3005–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, L.; MacFarlane, D. Climate-Smart Forestry: Promise and risks for forests, society, and climate. PLOS Climte 2023, 2, e0000212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukara, E. Tropical Forest Biodiversity to Provide Food, Health and Energy Solution of the Rapid Growth of Modern Society. Procedia Environ Sci 2014, 20, 803–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Useni, S.Y.; Malaisse, F.; Yona, J.M.; Mwamba, T.M.; Bogaert, J. Diversity, use and management of household-located fruit trees in two rapidly developing towns in Southeastern D.R. Congo. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 63, 127220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; O'sullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Gregor, L.; Hauck, J.; Le Quéré, C.; Luijkx, I.T.; Olsen, A.; Peters, G.P.; Peters, W. Global carbon budget 2022. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2022, 1–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN: United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, 2021. The Global Forest Goals Report 2021. Sales No.: E. 21. IV. 3. Available online : https://www.un.org/en/desa/global-forest-goals-report-2021. (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- FAO & UNEP. The State of the World’s Forests 2020. Forests, biodiversity and people. Rome. [CrossRef]
- Vancutsem, C.; Achard, F.; Pekel, J.F.; Vieilledent, G.; Carboni, S.; Simonetti, D.; Gallego, J.; Aragao, L.E.; Nasi, R. Long-term (1990–2019) monitoring of forest cover changes in the humid tropics. Sci. Adv. 2001, 7, p.eabe1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Global Forest Resources Assessment (FRA), 2020. [CrossRef]
- Mulatu, K.A.; Mora, B.; Kooistra, L.; Herold, M. Biodiversity Monitoring in Changing Tropical Forests: A Review of Approaches and New Opportunities. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.G. , Slay, C.M., Harris, N.L., Tyukavina, A.; Hansen, M.C. Classifying drivers of global forest loss. Science 2018, 361(6407), 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahawi, R.A. , Reid, J.L.; Fagan, M.E. Potential impacts of COVID-19 on tropical forest recovery. Biotropica 2020, 52, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Feldman, A.; Chávez, C.; Vélez, M.A.; Bejarano, H.; Chimeli, A.B.; Féres, J.; Robalino, J.; Salcedo, R.; Viteri, C. Environmental impacts and policy responses to Covid-19: a view from Latin America. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2020, p.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Céspedes, J.; Sylvester, J.M.; Pérez-Marulanda, L.; Paz-Garcia, P.; Reymondin, L.; Khodadadi, M. , Tello, J.J.; Castro-Nunez, A. Has global deforestation accelerated due to the COVID-19 pandemic? J. For. Res. 2023, 34, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couch, K.A.; Fairlie, R.W.; Xu, H. . Early evidence of the impacts of COVID-19 on minority unemployment. Journal of public economics, 2020, 192, 104287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, P.C. Ethnophytomedicine in the Amazon: a Future Threatened by Deforestation and COVID-19 Pandemic. Biomed J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2021, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Latin American and Caribbean Forestry 2021. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/cb6027en/cb6027en.pdf (accessed on 01 March 2024).
- Eba’a Atyi, R.; Hiol Hiol, F.; Lescuyer, G.; Mayaux, P.; Defourny, P.; Bayol, N.; Nasi, R. Les forêts du Bassin du Congo: état des Forêts; CIFOR: Bogor, Indonésie, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, P.V.; Turubanova, S.A.; Hansen, M.C.; Adusei, B.; Broich, M.; Altstt, A.; Mane, L.; Justice, C.O. Quantifying forest cover loss in Democratic Republic of the Congo, 2000–2010, with Landsat ETM+data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisse, F. How to live and survive in Zambezian open forest (Miombo Ecoregion). Les presses agronomiques de Gembloux, Gembloux, Belgique, 2010.
- Useni, S.Y.; Malaisse, F.; Kaleba, S.C.; Kankumbi, F.M.; Bogaert, J. Le rayon de déforestation autour de la ville de Lubumbashi (Haut-Katanga, RD Congo): Synthèse. Tropicultura 2017, 35, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Useni, S.Y.; Muteya, H.K.; Bogaert, J. Miombo woodland, an ecosystem at risk of disappearance in the Lufira Biosphere Reserve (Upper Katanga, DR Congo)? A 39-years analysis based on Landsat images. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabala, K.S.; Sikuzani, Y.U.; Yamba, A.M.; Kankumbi, F.M.; Bogaert, J. Activités anthropiques et dynamique des écosystèmes forestiers dans les zones territoriales de l’Arc Cuprifère Katangais (RD Congo). Tropicultura 2022, 40, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoji, M.K.; N’Tambwe, N.D.-D.; Malaisse, F.; Waselin, S.; Sambiéni, K.R.; Cabala, K.S.; Munyemba, K.F.; Bastin, J.-F.; Bogaert, J.; Useni, S.Y. Quantification and Simulation of Landscape Anthropization around the Mining Agglomerations of Southeastern Katanga (DR Congo) between 1979 and 2090. Land 2022, 11, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpanda, M.M.; Muteya, H.K.; Nghonda, D.-D.N.; Sambiéni, K.R.; Malaisse, F.; Kaleba, S.C.; Bogaert, J.; Sikuzani, Y.U. Uncontrolled Exploitation of Pterocarpus tinctorius Welw. and Associated Landscape Dynamics in the Kasenga Territory: Case of the Rural Area of Kasomeno (DR Congo). Land 2022, 11, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’tambwe Nghonda, D.-d.; Muteya, H.K.; Kashiki, B.K.W.N.; Sambiéni, K.R.; Malaisse, F.; Sikuzani, Y.U.; Kalenga, W.M.; Bogaert, J. Towards an Inclusive Approach to Forest Management: Highlight of the Perception and Participation of Local Communities in the Management of miombo Woodlands around Lubumbashi (Haut-Katanga, D.R. Congo). Forests 2023, 14, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happi, C.T.; Nkengasong, J.N. Two years of COVID-19 in Africa: lessons for the world. Nature 2022, 601, 22–5. [Google Scholar]
- Murewanhema, G.; Dzinamarira, T. The COVID-19 Pandemic: Public Health Responses in Sub-Saharan Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukendi, N.K.; Muteya, H.K.; Nghonda, D.-d.N.; Berti, F.; Useni, S.Y.; Ndjibu, L.N.; Mbay, J.-P.K.; Fyama, J.N.M.; Lebailly, P.; Bogaert, J. Quantification and Determinants of Carbonization Yield in the Rural Zone of Lubumbashi, DR Congo: Implications for Sustainable Charcoal Production. Forests 2024, 15, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoji, M.H.; Nghonda, D.-d.N.; Kalenda, F.M.; Strammer, H.; Kankumbi, F.M.; Malaisse, F.; Bastin, J.-F.; Sikuzani, Y.U.; Bogaert, J. Mapping and Quantification of Miombo Deforestation in the Lubumbashi Charcoal Production Basin (DR Congo): Spatial Extent and Changes between 1990 and 2022. Land 2023, 12, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richiardi, C.; Minciardi, M.R.; Siniscalco, C.; Adamo, M. Cumulative Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Anthropogenic Impacts in the Protected Area of the Gran Paradiso National Park in the NW Alps, Italy. Land 2023, 12, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Arai, E.; Duarte, V.; Jorge, A.; Santos, E.G.D.; Gasparini, K.A.C.; Dutra, A.C. Monitoring deforestation and forest degradation using multi-temporal fraction images derived from Landsat sensor data in the Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 5475–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Remote sensing in landscape ecology. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaehringer, J.G.; Hett, C.; Ramamonjisoa, B.; Messerli, P. Beyond deforestation monitoring in conservation hotspots: Analysing landscape mosaic dynamics in north-eastern Madagascar. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 68, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol Zeitschrift 2006, 15, 259–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalombo, K.D. Évolution des éléments du Climat en RDC: Stratégies D’adaptation des Communautés de Base, face aux événements Climatiques de Plus en Plus Fréquents; Éditions Universitaires Européennes: Sarrebruck, Allemagne, 2016; p. 220. [Google Scholar]
- Munyemba, K.F.; Bogaert, J. Anthropisation et dynamique spatiotemporelle de l’occupation du sol dans la région de Lubumbashi entre 1956 et 2009. E-Revue UNILU 2014, 1, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kasongo, L.M.E.; Baert, B.; Ngongo, L.M.; Verdoodt, A.; Van Ranst, E. Esquisse des pédopaysages du Katanga et aperçu sur les potentialités agricoles et activités minières. In Anthropisation des Paysages Katangais; Bogaert, J., Colinet, G., Mahy, G., Eds.; Les Presses Universitaires de Liège—Agronomie: Gembloux, Belgium, 2018; pp. 127–156. [Google Scholar]
- Dibwe, M.D. Lubumbashi, Ville Industrielle Attractive et Repulsive (1910–2008); Los Restos de la Pobreza Urbana: Madrid, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Useni, S.Y.; Kaleba, S.C.; Khonde, C.N.; Mwana, Y.A.; Malaisse, F.; Bogaert, J. & Kankumbi, F.M. Vingt-cinq ans de monitoring de la dynamique spatiale des espaces verts en réponse á ('urbanisation dans les communes de la ville de Lubumbashi (Haut-Katanga, RD Congo). Tropicultura 2017, 35, 300–311. [Google Scholar]
- Main-Knorn, M.; Pflug, B.; Louis, J.; Debaecker, V.; Müller-Wilm, U.; Gascon, F. Sen2Cor for Sentinel-2. Image Sign. Process. Remote Sens. 2017, X23, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, G.; Cawkwell, F.; Wingler, A. Status of phenological research using sentinel-2 data: A review. Remote Sen.s 2020, 12, 10–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segarra, J.; Buchaillot, M.L.; Araus, J.L.; Kefauver, S.C. Remote sensing for precision agriculture: Sentinel-2 improved features and applications. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasniewski, A.; Hoscilo, A.; Zagajewski, B.; Moukétou-Tarazewicz, D. Assessment of sentinel-2 satellite images and random forest classifier for rainforest mapping in Gabon. Forests 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Lewis, P.E.; Gómez-Dans, J.L. Bayesian atmospheric correction over land: Sentinel-2/MSI and Landsat 8/OLI. Geosci Model. Dev. 2022, 15, 7933–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barima, Y.S.S.; Barbier, N.; Bamba, I.; Traoré, D.; Lejoly, J.; Bogaert, J. Dynamique paysagère en milieu de transition forêt-savane ivoirienne. Bois For. Trop. 2009, 299, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Useni, S.Y.; Mpanda, M.M.; Malaisse, F.; Kaseya, P.K.; Bogaert, J. The Spatiotemporal Changing Dynamics of Miombo Deforestation and Illegal Human Activities for Forest Fire in Kundelungu National Park, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Fire 2023, 6, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Useni, S.Y.; Mpanda, M.M.; Khoji, M.H.; Cirezi, C.N.; Malaisse, F.; Bogaert, J. Vegetation Fires in the Lubumbashi Charcoal Production Basin (The Democratic Republic of the Congo): Drivers, Extent and Spatiotemporal Dynamics. Land 2023, 12, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noi Phan, T.; Kuch, V.; Lehnert, L.W. Land cover classification using google earth engine and random forest classifier-the role of image composition. Remote Sens. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Xia, G.-S.; Hu, F.; Zhang, L. A Comparative Study of Sampling Analysis in the Scene Classification of Optical High-Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14988–15013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, R.V.; Krummel, J.R.; Garner, R.H.; Sugihara, G.; Jackson, B.; Deangelis, D.L.; Milne, B.T.; Turner, M.G.; Zygmunt, B.; Christensen, S.W.; et al. Indices of landscape pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 1988, 1, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamine, S.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Singh, S.K.; Szabó, S.; Bachari, N.E.I.; Srivastava, P.K.; Suman, S. . Quantifying land use/land cover spatio-temporal landscape pattern dynamics from Hyperion using SVMs classifier and FRAGSTATS®. Geocarto Int. 2018, 33, 862–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabala, K.S.; Useni, S.Y.; Mwana, Y.A.; Bogaert, J.; Munyemba, K.F. Analyse structurale de la dynamique forestiere dans la région de I’Arc Cuprifére Katangai, I. Pattern Analysis of Forest Dynamics of the Katangese Copper Belt Region in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: II. Complementary Analysis on Forest Fragmentation. Tropicultura 2018, 36, 621–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kabuanga, J.M.; Adipalina Guguya, B.; Ngenda Okito, E.; Maestripieri, N.; Saqalli, M.; Rossi, V.; Iyongo Waya Mongo, L. Suivi de l’anthropisation du paysage dans la région forestière de Babagulu, République Démocratique du Congo. VertigO, 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, J.; Ceulemans, R.; Salvador-Van, E.D. Decision tree algorithm for detection of spatial processes in landscape transformation. Environ. Manag. 2004, 33, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haulleville, T.; Rakotondrasoa, O.L.; Rakoto Ratsimba, H.; Bastin, J.F.; Brostaux, Y.; Verheggen, F.J.; Rajoelison, G.L.; Malaisse, F.; Poncelet, M.; Haubruge, É.; Beeckman, H. Fourteen years of anthropization dynamics in the Uapaca bojeri Baill. Forest of Madagascar. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 14, 135–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, S.R.; Hawbaker, T.J.; Metzger, J.P. Effects of roads, topography, and land use on forest cover dynamics in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.L.; Gergel, S.E.; Coops, N.C. Aerial photography: A rapidly evolving tool for ecological management. Bioscience 2010, 60, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, A.M. Land cover and land use classification performance of machine learning algorithms in a boreal landscape using Sentinel-2 data. GIScience. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.; Riitters, K.H. Influence of high-resolution data on the assessment of forest fragmentation. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 2169–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Sexton, J.O.; Noojipady, P.; Huang, C.; Anand, A.; Channan, S.; Feng, M.; Townshend, J.R. Global, Landsat-based forest-cover change from 1990 to 2000. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serrano, P.M.; Corral-Rivas, J.J.; Díaz-Varela, R.A.; álvarez-González, J.G.; López-Sánchez, C.A. Evaluation of radiometric and atmospheric correction algorithms for aboveground forest biomass estimation using landsat 5 TM data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Neel, M.C.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS: spatial pattern analysis program for categorical maps. Computer software program produced by the authors at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst 2002.
- Zuluaga, S.; Speziale, K.; Lambertucci, S.A. Global Aerial Habitat Conservation Post-COVID-19 Anthropause. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2021, 36, 273–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, A.; Barbieri, E.; Biggeri, M.; Di Tommaso, M.R. Industrial policy for sustainable human development in the post-Covid19 era. World Dev. 2021, 137, 105215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, N.; Soura, A.; Hemler, E.C.; Korte, M.L.; Wang, D.; Abdullahi, Y.Y.; Lankoande, B. , Millogo, O., Chukwu, A., Workneh, F.; Sie, A. Covid-19 knowledge, perception, preventive measures, stigma, and mental health among healthcare workers in three Sub-Saharan African countries: A phone survey. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 105, 342–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroh, B.T.A. Plant species used in traditional medicine against the main symptoms of COVID-19 in sub-saharan Africa: Literature review. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2020, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguma, L.A.; van Noordwijk, M.; Minang, P.A.; Muthee, K. COVID-19 pandemic and agroecosystem resilience: Early insights for building better futures. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulumbati, M.C.; Godoy Jara, M.; Baboy Longanza, L.; Bogaert, J.; Werbrouck, S.; Sikuzani, Y.U.; Mazinga Kwey, M. In Vitro Regeneration Protocol for Securidaca longepedunculata Fresen., a Threatened Medicinal Plant within the Region of Lubumbashi (Democratic Republic of the Congo). Conservation 2023, 3, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, O.K.; Allan, H.L.; Baxter, P.W.J.; Castagnino, R.; Tor, M.C.; Dann, L.E.; Hungerford, J.; Karmacharya, D.; Lloyd, T.J.; López-Jara, M.J.; Massie, G.N. The COVID-19 pandemic is intricately linked to biodiversity loss and ecosystem health. Lancet Planet Heal. 2021, 5, e840–e850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuimika, M.M.; Tshomba, K.J.; Bakari, A.S.; Useni, S.Y.; Werbrouck, S.; Mazinga, MK. Causes de la disparition des plantes médicinales du Miombo Katangais (RD Congo) : Cas du commerce non conventionnel de Securidaca longepedunculata Fresen (Polygalaceae). Rev Afr. Environ. Agr. 2023, 6, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ngamsou Abdel, K.; Mala, W.A.; Chimi, P.M.; Funwi, F.P.; Engoulou, C.; Messi Effa, J.A.; Kamdem, M.E.K.; Djonko, F.N.; Fokoua, U.L.; Adounga, S.B.; Mbolo, M.M. Ethnobotanical study and vulnerability of medicinal plants used against the symptoms of COVID-19 in the Lomié subdivision, East Region of Cameroon. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attah, A.F.; Fagbemi, A.A.; Olubiyi, O.; Dada-Adegbola, H.; Oluwadotun, A.; Elujoba, A.; Babalola, C.P. Therapeutic Potentials of Antiviral Plants Used in Traditional African Medicine With COVID-19 in Focus: A Nigerian Perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, C.; Fatoyinbo, L.; Honzák, M.; Wright, T.M.; Murillo Sandoval, P.J.; Whapoe, Z.E.; Yonmah, J.; Olatunji, E.T.; Garteh, J.; Stovall, A.; Neigh, C.S. Two decades of land cover change and forest fragmentation in Liberia: Consequences for the contribution of nature to people. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2023, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, J.; Barima, Y.S.S.; Iyongo, W.M.L.; Bamba, I.; Mama, A.; Toy, M.; Lafortezza, R. Forest fragmentation: Causes, ecological impacts, and implications for landscape management. In Li, C., Lafortezza, R., Chen, J., Eds.; Springer: Beijing, China; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 273–296. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. 2023. Évaluation finale du projet «Gestion communautaire des forêts miombo dans le sud-est du Katanga». Série évaluation de projet, 24/2023 Rome. [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.A.; Romero Montero, J.A.; Hernández Gómez, I.U. Deforestation processes in the state of quintana roo, mexico: The role of land use and community forestry. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santika, T.; Meijaard, E.; Budiharta, S.; Law, E.A.; Kusworo, A.; Hutabarat, J.A.; Indrawan, T.P.; Struebig, M.; Raharjo, S.; Huda, I. and Ekaputri, A.D. Community forest management in Indonesia: Avoided deforestation in the context of anthropogenic and climate complexities. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 46, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouliot, M.; Treue, T. Rural People’s Reliance on Forests and the Non-Forest Environment in West Africa: Evidence from Ghana and Burkina Faso. World Dev 2013, 43, 180–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juniyanti, L.; Purnomo, H.; Kartodihardjo, H.; Prasetyo, L.B. Understanding the Driving Forces and Actors of Land Change Due to Forestry and Agricultural Practices in Sumatra and Kalimantan: A Systematic Review. Land 2021, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, P.; Schure, J.; Eba’a Atyi, R. ; Gumbo; D.; Okeyo, I.; Awono, A. Woodfuel policies and practices in selected countries in Sub-Saharan Africa—A critical review. Bois For. Trop. 2019, 340, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabulu, D.J.-P.; Vranken, I.; Bastin, J.-F.; Malaisse, F.; Nyembwe, N.S.; Useni, S.Y.; Ngongo, L.M.; Bogaert, J. Approvisionnement En Charbon de Bois Des Ménages Lushois: Quantités, Alternatives et Conséquences. In Anthropisation des Paysages Katangais; Bogaert, J., Colinet, G., Mahy, G., Eds.; Presses Universitaires de Liège: Liège, Belgique, 2018; pp. 297–311. [Google Scholar]
- Trefon, Th.; Kabuyaya, N. "Les espaces périurbains en Afrique centrale." Territoires périurbains: Développement, enjeux et perspectives dans les pays du Sud, Gembloux, les Presses Agronomiques de Gembloux 2015 ; pp 33-42.
- Useni, S.Y.; Sambiéni, K.R.; Maréchal, J.; Ilunga wa Ilunga, E.; Malaisse, F.; Bogaert, J.; Munyemba, K.F. Changes in the Spatial Pattern and Ecological Functionalities of Green Spaces in Lubumbashi (the Democratic Republic of Congo) in Relation With the Degree of Urbanization. Trop Conserv Sci 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, M.; Mörtberg, U.; Balfors, B. Road ecology in environmental impact assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2014, 48, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branch, A.; Agyei, F.K.; Anai, J.G.; Apecu, S.L.; Bartlett, A.; Brownell, E.; Caravani, M.; Cavanagh, C.J.; Fennell, S.; Langole, S. and Mabele, M.B. From crisis to context: Reviewing the future of sustainable charcoal in Africa. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2022, 87, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Useni, S.Y.; Khoji, M.H.; Langunu, S.; Gerardy, A.; Bogaert, J. Amplification of Anthropogenic Pressure Heavily Hampers Natural Ecosystems Regeneration within the Savanization Halo Around Lubumbashi City (Democratic Republic of Congo). Int J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Res. 2019, 17(2), 555958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; De Pinto, A.; Ulimwengu, J.M.; You, L.; Robertson, R.D. Impacts of road expansion on deforestation and biological carbon loss in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Environ. Resou. Econom. 2015, 60, 433–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, J.; Vranken, I.; André, M. Anthropogenic effects in landscapes: Historical context and spatial pattern. In Biocultural landscapes. Diversity, Functions and Values; Hong, S.K., Bogaert, J., Min, Q., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 89–112. [Google Scholar]
- Cabala, K.S.; Useni, S.Y.; Sambieni, K.R.; Bogaert, J.; Munyemba, K.F. Dynamique des écosystèmes forestiers de l’Arc Cuprifère Katangais en République Démocratique du Congo. Causes, Transformations spatiales et ampleur. Tropicultura 2017, 35, 192–202. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, N.M.; Brudvig, L.A.; Clobert, J.; Davies, K.F.; Gonzalez, A.; Holt, R.D.; Lovejoy, T.E.; Sexton, J.O.; Austin, M.P.; Collins, C.D.; Cook, W.M. Habitat fragmentation and its lasting impact on Earth’s ecosystems. Sci. adv. 2015, 1, p–e1500052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurance, W.F.; Camargo, J.L.; Luizão, R.C.; Laurance, S.G.; Pimm, S.L.; Bruna, E.M.; Stouffer, P.C.; Williamson, G.B.; Benítez-Malvido, J.; Vasconcelos, H.L.; Van Houtan, K.S. The fate of Amazonian forest fragments: a 32-year investigation. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodo, T.; Gimah, B.G.; Seomoni, K.J. Deforestation and habitat loss: Human causes, consequences and possible solutions. J. Geogr. Res. 2021, 4, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.; Taubert, F.; Müller, M.S.; Groeneveld, J.; Lehmann, S.; Wiegand, T. & Huth, A. Accelerated forest fragmentation leads to critical increase in tropical forest edge area. Sci. adv. 2021, 7, eabg7012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNicol, I.M.; Keane, A.; Burgess, N.D.; Bowers, S.J.; Mitchard, E.T.; Ryan, C.M. Protected areas reduce deforestation and degradation and enhance woody growth across African woodlands. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieng, M.; Mbow, C.; Skole, D.L.; Ba, B. Sustainable land management policy to address land degradation: linking old forest management practices in Senegal with new REDD+ requirements. Front. environ. sci. 2023, 11, 1088726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuvi, M.T.E.; Kungu, J.B. A transforming traditional community based forest management: the case of Loita community forest, Kenya. Heliyon 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, B.J.; Adeyewa, Z.D.; Oguntunde, P.G.; Salami, A.T.; Ajayi, V.O. Modeling the impacts of reforestation on future climate in West Africa. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 110, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, S.; Pham, T.T.; Karky, B.; Garcia, C. Role of community and user attributes in collective action: case study of community-based forest management in Nepal. Forests 2018, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, P. Deforestation, Carbon dioxide increase in the atmosphere and global warming: A modelling study. Int. J. Model. Simul. 2021, 41, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tole, L. Reforms from the ground up: a review of community-based forest management in tropical developing countries. Environ. Manag. 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, M.; Sun, B. Long-term hydrological response to reforestation in a large watershed in southeastern China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5573–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Tague, C.; Jia, Y. Evaluating the eco-hydrologic impacts of reforestation in the Loess Plateau, China, using an eco-hydrologic model. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 498–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Næss, J.S.; Iordan, C.M.; Huang, B.; Zhao, W.; Cherubini, F. Recent global land cover dynamics and implications for soil erosion and carbon losses from deforestation. Anthropocene 2021, 34, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, M. Poverty reduction saves forests sustainably: Lessons for deforestation policies. World Dev. 2020, 127, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, E.Y.; Barreto, P.; Araújo, E.; Soares-Filho, B. Public policies can reduce tropical deforestation: Lessons and challenges from Brazil. Land use policy 2014, 41, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musyoki, J.K.; Mugwe, J.; Mutundu, K.; Muchiri, M. Factors influencing level of participation of community forest associations in management forests in Kenya. J. Sustain. For. 2016, 35, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, D.; Morante-Filho, J.C.; Baumgarten, J.; Bovendorp, R.S.; Cazetta, E.; Gaiotto, F.A.; Mariano-Neto, E.; Mielke, M.S.; Pessoa, M.S.; Rocha-Santos, L.; Santos, A.S. The breakdown of ecosystem functionality driven by deforestation in a global biodiversity hotspot. Biol. Conserv. 2023, 283, 110126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpanda, M.M.; Kipili, M.I.; Tshomba, K.J.; Kitabala, M.A.; Cabala, K.S.; Useni, S.Y. Perception de la dégradation de la fertilité des sols et de sa gestion par les agriculteurs de la cité de Kasenga en République Démocratique du Congo. Geo-Eco-Trop, 2021; 45, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Loro, M.; Ortega, E.; Arce, R.M.; Geneletti, D. Ecological connectivity analysis to reduce the barrier effect of roads. An innovative graph-theory approach to define wildlife corridors with multiple paths and without bottlenecks. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 139, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuglerová, L.; Ågren, A.; Jansson, R. & Laudon, H. towards optimizing riparian buffer zones: Ecological and biogeochemical implications for forest management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 334, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.E.; Evangelista, P.H.; Mengitsu, T. & Leisz, S. Twenty-three years of forest cover change in protected areas under different governance strategies: A case study from Ethiopia’s southern highlands. Land Use pol. 2020, 91, 104426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefson, J. Why deforestation and extinctions make pandemics more likely. Nature, 2020; 584, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebara, M.F.; May, P.H.; Platais, G. Pandemics, conservation, and human-nature relations. Climate Change Ecol. 2021; 2, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.; Oliveira, A.M. Poverty and food insecurity may increase as the threat of COVID-19 spreads. Public Health Nutr. 2020; 3, 3236–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajudeen, Y.A.; Oladunjoye, I.O.; Bajinka, O.; Oladipo, H.J. Zoonotic Spillover in an Era of Rapid Deforestation of Tropical Areas and Unprecedented Wildlife Trafficking: Into the Wild. Challenges 2022, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, W.; Useni, S.Y.; Kouakou, A.T.M.; Barima, Y.S.S.; Theodat, J.M.; Bogaert, J. Cartographie et quantification de la perte du couvert forestier dans les parcs nationaux du Sud de la République d'Haïti de 1985 à 2018: rôle des activités agricoles locales. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2021; 15, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrouet, L.M.; Machado, J.; Villegas-Palacio, C. . Vulnerability of socio—ecological systems: A conceptual Framework. Ecol. Indic. 2018; 84, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| May 2019_November 2019 | Forest | Forest gain | Forest loss | Non-forest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy measure | ||||
| Prod. acc. | 100.0% | 87.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| User acc. | 98.7% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| Overall acc. | 99.3% | |||
| November 2019-July 2020 | Forest | Forest gain | Forest loss | Non-forest |
| Prod. acc. | 100.0% | 100.0% | 97.0% | 100.0% |
| User acc. | 99.6% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| Overall acc. | 99.8% | |||
| July 2020-September 2020 | Forest | Forest gain | Forest loss | Non-forest |
| Prod. acc. | 100.0% | 98.8% | 94.1% | 100.0% |
| User acc. | 98.8% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 99.8% |
| Overall acc. | 99.4% | |||
| September 2020_May 2021 | Forest | Forest gain | Forest loss | Non-forest |
| Prod. acc. | 100.0% | 100.0% | 99.2% | 100.0% |
| User acc. | 99.8% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| Overall acc. | 99.9% | |||
| May 2021-May 2022 | Forest | Forest gain | Forest loss | Non-forest |
| Prod. acc. | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| User acc. | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| Overall acc. | 100.0% | |||
| May 2022-November 2022 | Forest | Forest gain | Forest loss | Non-forest |
| Prod. acc. | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| User acc. | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| Overall acc. | 100.0% | |||
| November 2022-May 2023 | Forest | Forest gain | Forest loss | Non-forest |
| Prod. acc. | 100.0% | 98.1% | 92.5% | 100.0% |
| User acc. | 99.8% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 99.0% |
| Overall acc. | 99.4% | |||
| May 2023-November 2023 | Forest | Forest gain | Forest loss | Non-forest |
| Prod. acc. | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| User acc. | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| Overall acc. | 100.0% |
| Date | NP | CA | MA | LPI | ED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May-2019 | 400858.0 | 13711.4 | 6.8 | 14.6 | 87.3 |
| November-2019 | 733771.0 | 13654.4 | 6.3 | 13.6 | 88.7 |
| July-2020 | 662269.0 | 13613.0 | 6.9 | 15.6 | 84.8 |
| September-2020 | 1526810.0 | 13297.6 | 4.5 | 13.2 | 116.6 |
| May-2021 | 869037.0 | 12388.0 | 6.2 | 11.4 | 89.2 |
| May-2022 | 1057747.0 | 11607.7 | 4.9 | 10.1 | 89.5 |
| November-2022 | 1171325.0 | 10865.8 | 4.1 | 10.4 | 98.7 |
| May-2023 | 1220557.0 | 10160.1 | 3.4 | 9.8 | 108.3 |
| November-2023 | 1168247.0 | 9849.8 | 3.7 | 8.2 | 85.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





