Submitted:
25 April 2024
Posted:
01 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LG partial Ablation (G1)
2.1.1. In Vivo Exams
2.1.2. Ex Vivo Assays
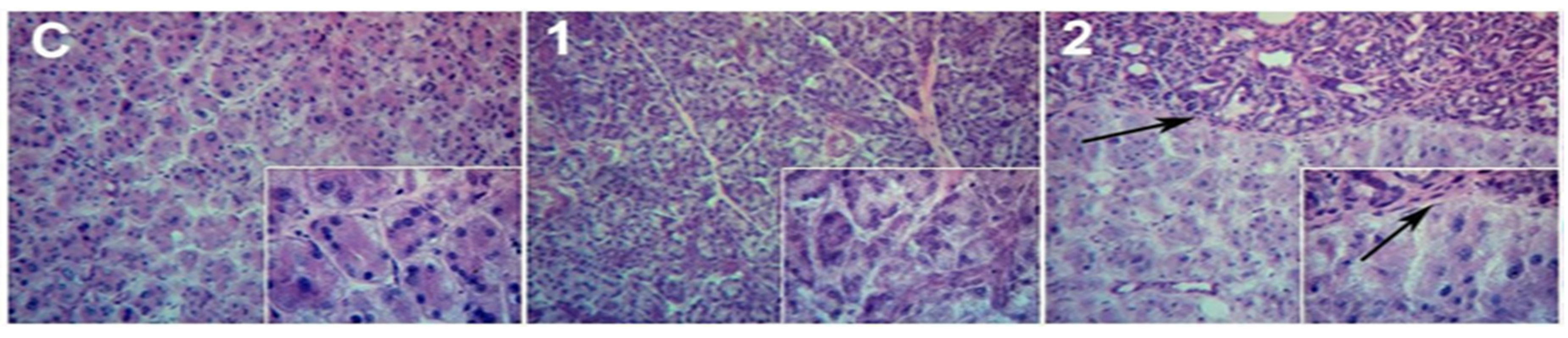
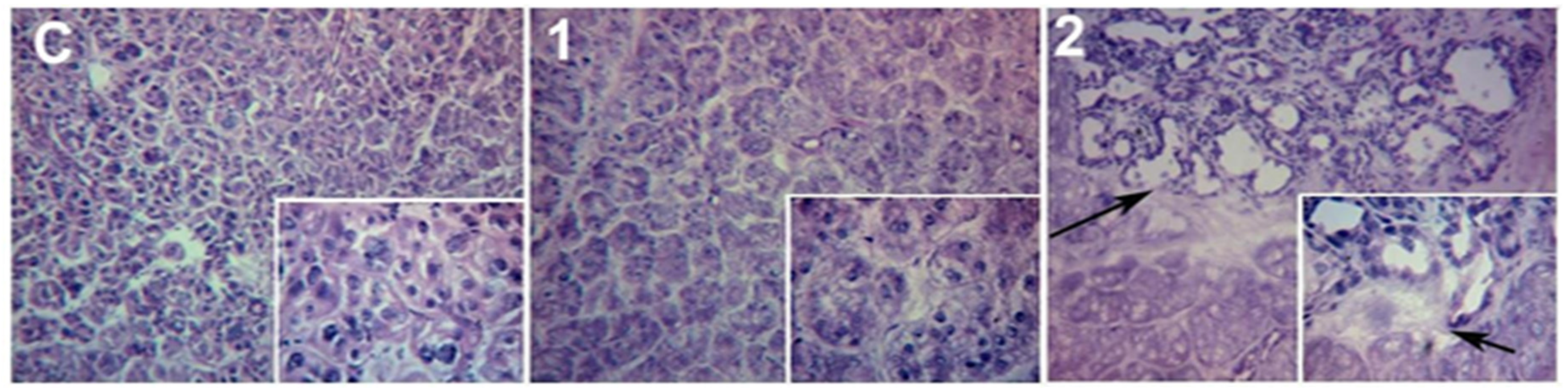
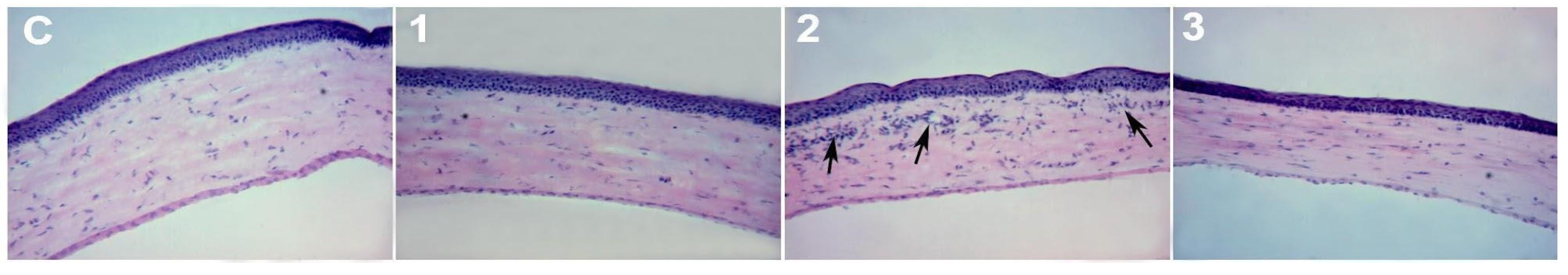
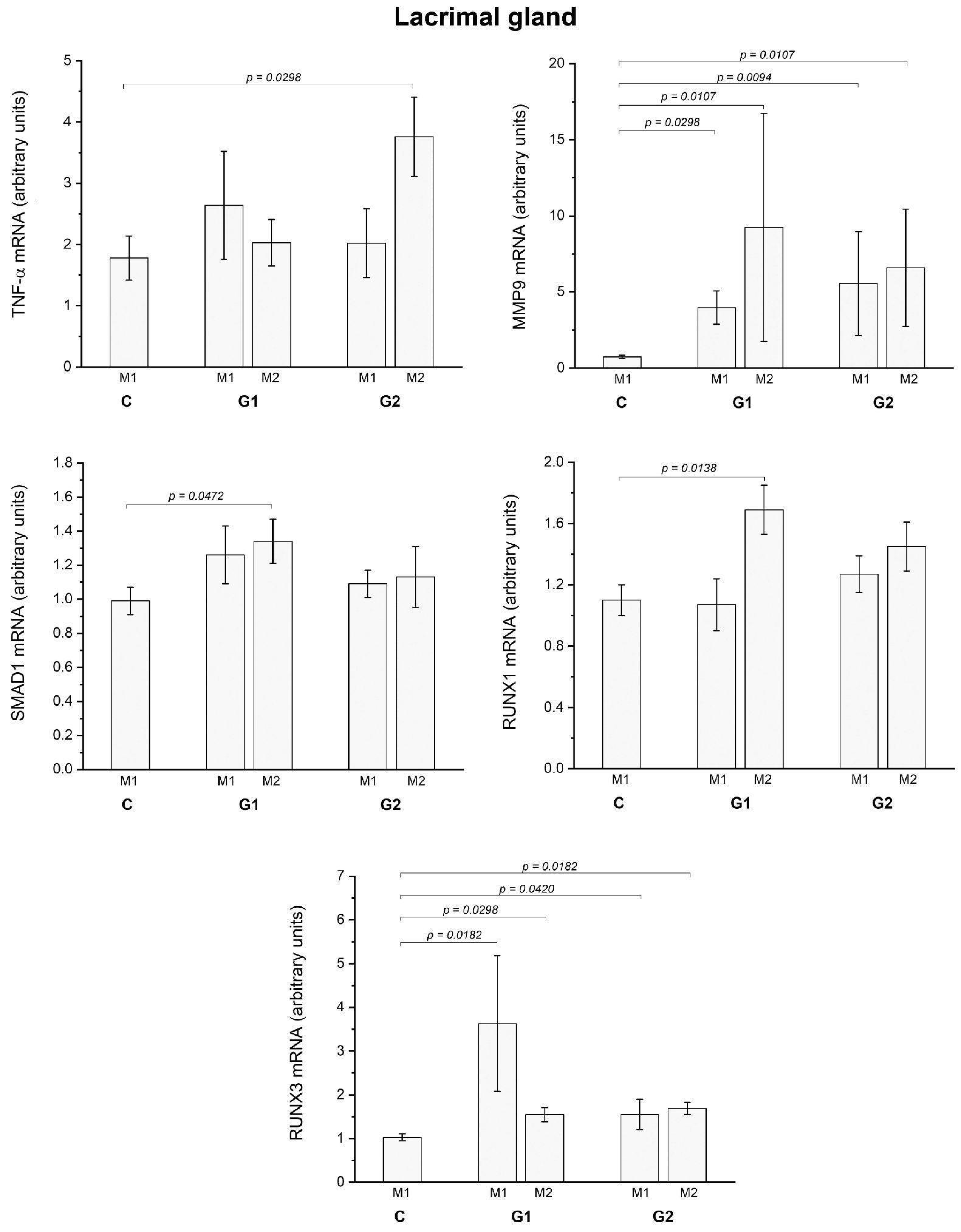
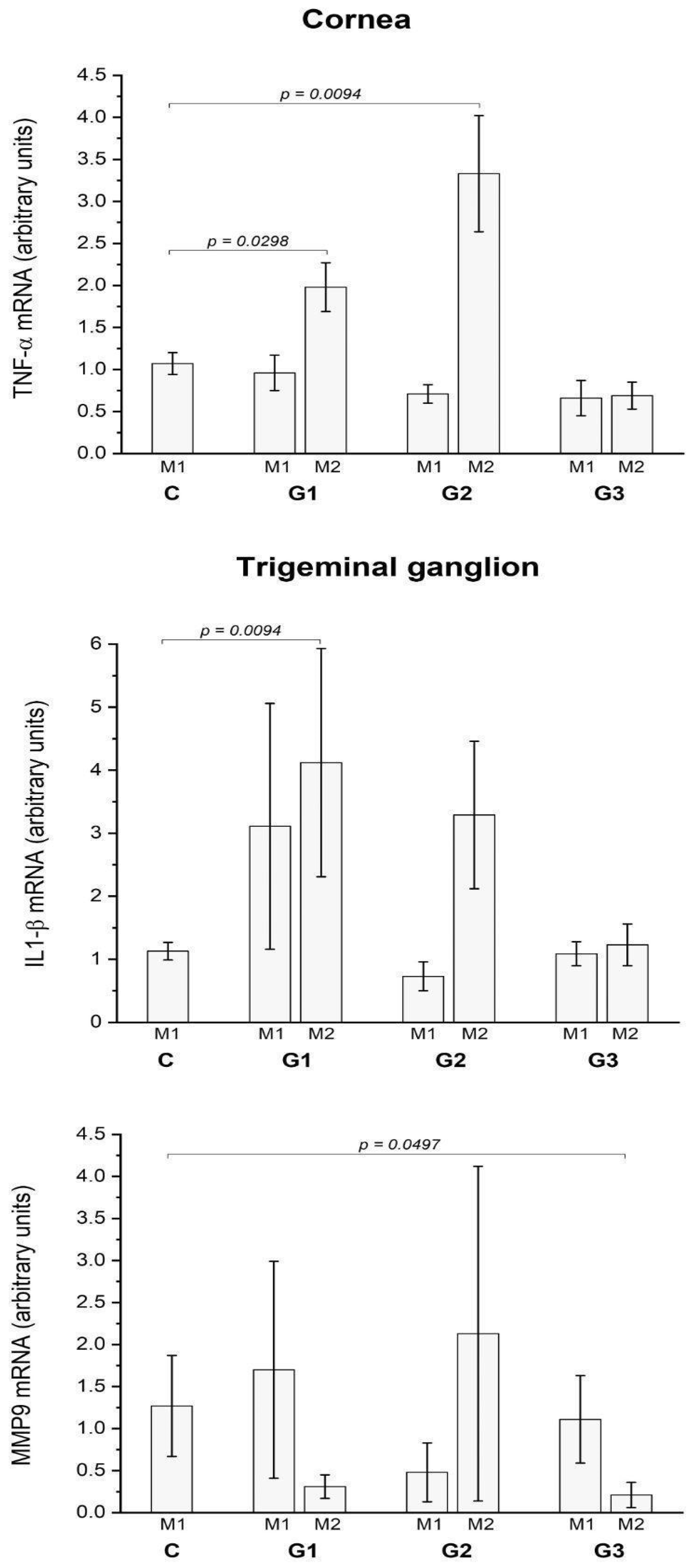
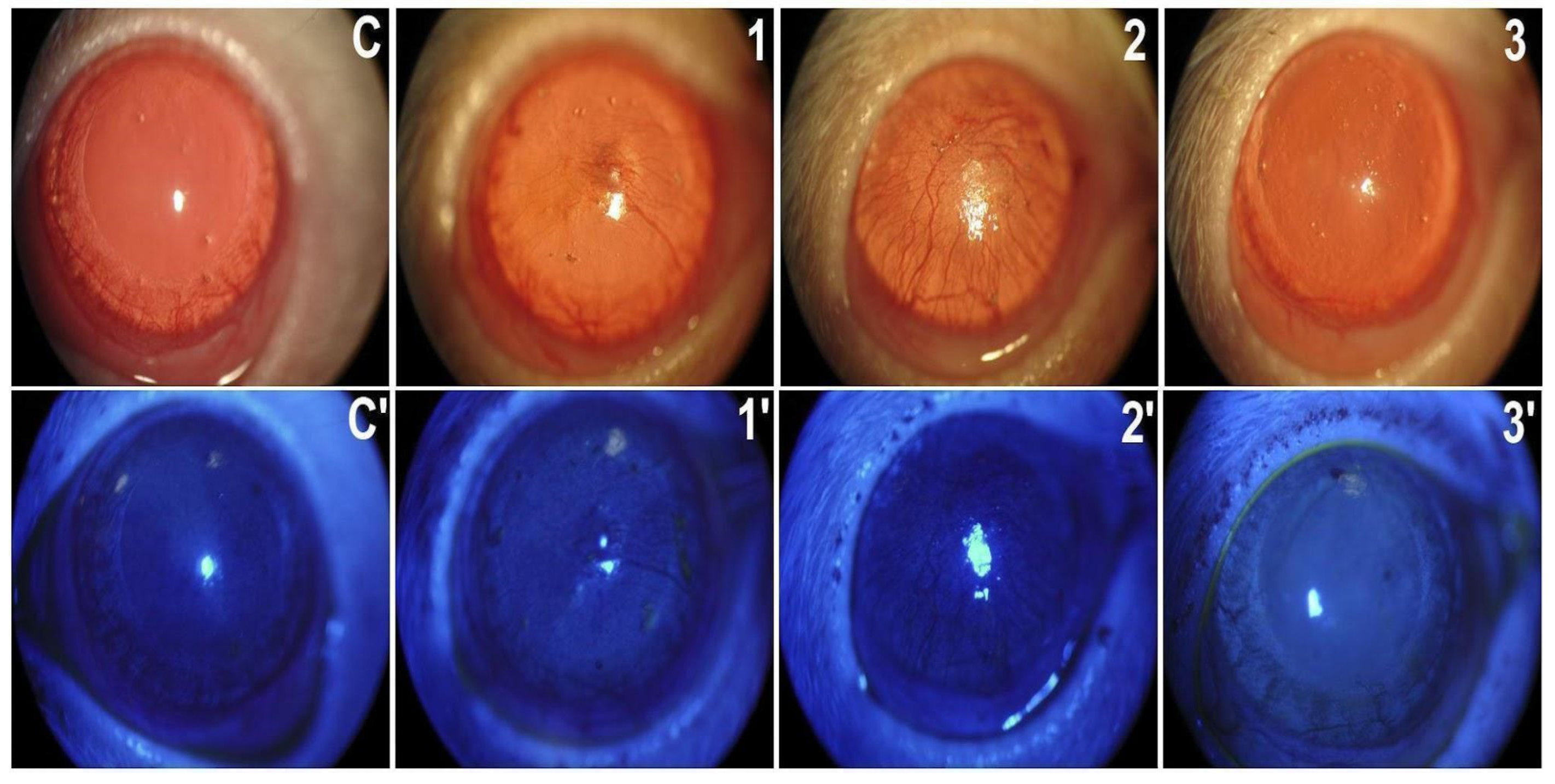
2.2. LG partial Ablation and Allogeneic Transplant (G2)
2.2.1. In Vivo Exams
2.2.2. Ex Vivo Assays
2.3. LG Total Ablation (G3)
2.3.1. In Vivo Exams
2.3.2. Ex Vivo Assays
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design and Animal Procedures
4.1.1. In Vivo Exam
4.1.2. Eye Wipe Test
4.1.3. Tissue Harvesting and Storage for Analysis
4.1.4. Impression Cytology
4.1.5. Western Blotting
4.1.6. Histology
4.1.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.2. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scherz, W.; Dohlman, C.H. Is the Lacrimal Gland Dispensable? Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca after Lacrimal Gland Removal. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1975, 93, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugfelder, S.C. Tear Dysfunction and the Cornea: LXVIII Edward Jackson Memorial Lecture. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 152, 900–909e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, W.; Pugazhendhi, S.; Wang, M. Is the Main Lacrimal Gland Indispensable? Contributions of the Corneal and Conjunctival Epithelia. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2016, 61, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.F.F.; Sant’Ana, A.M.S.; Dias, L.C.; Murashima, A.d.A.B.; da Silva, L.E.C.M.; Fantucci, M.Z.; Rocha, E.M. Comparison of the Effects of Corneal and Lacrimal Gland Denervation on the Lacrimal Functional Unit of Rats. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2022, 85, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.E.; Gao, J.; Siemasko, K.F.; Beuerman, R.W.; Pflugfelder, S.C. The Role of the Lacrimal Functional Unit in the Pathophysiology of Dry Eye. Exp. Eye Res. 2004, 78, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, J.E.; Warren, D.W.; Mircheff, A.K. A Lacrimal Gland Is a Lacrimal Gland, but Rodent’s and Rabbit’s Are Not Human. Ocul. Surf. 2010, 8, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jie, Y.; Labbe, A.; Pan, Z. A New Nonhuman Primate Model of Severe Dry Eye. Cornea 2014, 33, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-C.; Hsu, W.-M.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, F.-L.; Yen, M.-Y.; Chou, C.-K.; Kao, S.-C. Transplantation of the Autologous Submandibular Gland to the Lacrimal Basin in Rats. Ophthalmic Res. 2004, 36, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odaka, A.; Toshida, H.; Ohta, T.; Tabuchi, N.; Koike, D.; Suto, C.; Murakami, A. Efficacy of Retinol Palmitate Eye Drops for Dry Eye in Rabbits with Lacrimal Gland Resection. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2012, 6, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoukhri, D. Mechanisms Involved in Injury and Repair of the Murine Lacrimal Gland: Role of Programmed Cell Death and Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Ocul. Surf. 2010, 8, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Ali, M.J.; Vemuganti, G.K. Human Lacrimal Gland Regeneration: Perspectives and Review of Literature. Saudi J Ophthalmol 2014, 28, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, A.J.; de Paiva, C.S.; Chauhan, S.K.; Bonini, S.; Gabison, E.E.; Jain, S.; Knop, E.; Markoulli, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Perez, V.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Pathophysiology Report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 438–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitchouk, D.Y.; Beuerman, R.W.; Ohta, T.; Stern, M.; Varnell, R.J. Tear Production after Unilateral Removal of the Main Lacrimal Gland in Squirrel Monkeys. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2000, 118, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemet, A.; Belkin, M.; Rosner, M. Transplantation of Newborn Lacrimal Gland Cells in a Rat Model of Reduced Tear Secretion. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2007, 9, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, E.M.; Cotrim, A.P.; Zheng, C.; Riveros, P.P.; Baum, B.J.; Chiorini, J.A. Recovery of Radiation-Induced Dry Eye and Corneal Damage by Pretreatment with Adenoviral Vector-Mediated Transfer of Erythropoietin to the Salivary Glands in Mice. Hum. Gene Ther. 2013, 24, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Macleod, A.M.; O’Brien, B.M.; Hickey, M.J.; Knight, K.R. Microvascular Submandibular Gland Transfer for the Management of Xerophthalmia; an Experimental Study. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1990, 43, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, A.M.; Robbins, S.P. Submandibular Gland Transfer in the Correction of Dry Eye. Aust. N. Z. J. Ophthalmol. 1992, 20, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerling, G.; Borrelli, M. Adnexal Surgery for Severe Ocular Surface Disease. Seminars in Ophthalmology 2005, 20, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, M.; Ogawa, M.; Oshima, M.; Sekine, Y.; Ishida, K.; Yamashita, K.; Ikeda, K.; Shimmura, S.; Kawakita, T.; Tsubota, K.; et al. Functional Lacrimal Gland Regeneration by Transplantation of a Bioengineered Organ Germ. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nover, A. Experimental studies on regeneration and transplantation capacity of the lacrimal gland under local and general hormonal stimulation (thyroxin). II. Albrecht Von Graefes. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1954, 156, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerling, G.; Sieg, P.; Bastian, G.O.; Laqua, H. Transplantation of the Autologous Submandibular Gland for Most Severe Cases of Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca. Ophthalmology 1998, 105, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnoli, S. Morphological, cytochemical and body-weight aspects of regeneration in the submaxillary salivary gland of the rat. Arch. De Vecchi Anat. Patol. 1957, 26, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mac Cord Medina, F.; Silvestre de Castro, R.; Leite, S.C.; Rocha, E.M.; de Melo Rocha, G. Management of Dry Eye Related to Systemic Diseases in Childhood and Longterm Follow-Up. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2007, 85, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, D.B.; Shashi, V.; Kirse, D.J. Case Report: Aplasia of the Lacrimal and Major Salivary Glands (ALSG). Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 73, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, A.F.; Akaishi, P.M.S.; de Molfetta, G.A.; Chodraui-Filho, S.; Cintra, M.; Toscano, A.; Silva, W.A., Jr.; Cruz, A.A.V. Lacrimal Gland Involvement in Blepharophimosis-Ptosis-Epicanthus Inversus Syndrome. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.P.; de Oliveira, F.R.; da Rocha, F.J.; Muglia, V.F.; Rocha, E.M. Lacrimal Gland Atrophy and Dry Eye Related to Isotretinoin, Androgen, and Prolactin: Differential Diagnosis for Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2021, 84, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujihara, T.; Murakami, T.; Fujita, H.; Nakamura, M.; Nakata, K. Improvement of Corneal Barrier Function by the P2Y(2) Agonist INS365 in a Rat Dry Eye Model. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, W.; Chen, Y.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, H.S.; Hua, J.; Dohlman, T.; Shiang, T.; Dana, R. Extraorbital Lacrimal Gland Excision: A Reproducible Model of Severe Aqueous Tear-Deficient Dry Eye Disease. Cornea 2014, 33, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, S.; Basu, S. Rabbit Models of Dry Eye Disease: Current Understanding and Unmet Needs for Translational Research. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 206, 108538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoukhri, D.; Fix, A.; Alroy, J.; Kublin, C.L. Mechanisms of Murine Lacrimal Gland Repair after Experimentally Induced Inflammation. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 4399–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarenkova, H.P.; Ito, M.; Govindarajan, V.; Faber, S.C.; Sun, L.; McMahon, G.; Overbeek, P.A.; Lang, R.A. FGF10 Is an Inducer and Pax6 a Competence Factor for Lacrimal Gland Development. Development 2000, 127, 2563–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, C.; Ito, M.; Makarenkova, H.P.; Faber, S.C.; Lang, R.A. Bmp7 Regulates Branching Morphogenesis of the Lacrimal Gland by Promoting Mesenchymal Proliferation and Condensation. Development 2004, 131, 4155–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, J.; Schrader, S. Towards Lacrimal Gland Regeneration: Current Concepts and Experimental Approaches. Curr. Eye Res. 2020, 45, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolffsohn, J.S.; Arita, R.; Chalmers, R.; Djalilian, A.; Dogru, M.; Dumbleton, K.; Gupta, P.K.; Karpecki, P.; Lazreg, S.; Pult, H.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Diagnostic Methodology Report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 539–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, S.Y.; Jeon, J.W.; Lee, H.K. Impact of Lacrimal Gland Extraction on the Contralateral Eye in an Animal Model for Dry Eye Disease. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Mecum, N.E.; Cyr, D.; Malon, J.; Demers, D.; Cao, L.; Meng, I.D. Evaluation of Corneal Damage After Lacrimal Gland Excision in Male and Female Mice. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 2019, 60, 3264. [Google Scholar]
- Kurose, M.; Meng, I.D. Dry Eye Modifies the Thermal and Menthol Responses in Rat Corneal Primary Afferent Cool Cells. J. Neurophysiol. 2013, 110, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malki, L.T.; Dias, A.C.; Jorge, A.G.; Módulo, C.M.; Rocha, E.M. Lacrimal Gland Primary Acinar Cell Culture: The Role of Insulin. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2016, 79, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, J.; Roth, M.; König, S.; Geerling, G.; Mertsch, S.; Schrader, S. Analysis of Lacrimal Gland Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome and Its Impact on Epithelial Cell Survival. Stem Cell Res. 2019, 38, 101477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, M.; Ko, S.B.H.; Kawakita, T.; Akiyama, T.; Goparaju, S.K.; Soma, A.; Nakatake, Y.; Sakota, M.; Chikazawa-Nohtomi, N.; Shimmura, S.; et al. Identification of Transcription Factors That Promote the Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells into Lacrimal Gland Epithelium-like Cells. NPJ Aging Mech Dis 2017, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, M.; Kawakita, T.; Tsubota, K.; Shimmura, S. Challenges and Strategies for Regenerating the Lacrimal Gland. Ocul. Surf. 2016, 14, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hirayama, M.; Kawakita, T.; Tsubota, K. A Ligation of the Lacrimal Excretory Duct in Mouse Induces Lacrimal Gland Inflammation with Proliferative Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 4923426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, J.; Schlegel, C.; Roth, M.; Witt, J.; Geerling, G.; Mertsch, S.; Schrader, S. Comparative Analysis on the Dynamic of Lacrimal Gland Damage and Regeneration after Interleukin-1α or Duct Ligation Induced Dry Eye Disease in Mice. Experimental Eye Research 2018, 172, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, A.G.; Módulo, C.M.; Dias, A.C.; Braz, A.M.; Filho, R.B.; Jordão, A.A., Jr.; de Paula, J.S.; Rocha, E.M. Aspirin Prevents Diabetic Oxidative Changes in Rat Lacrimal Gland Structure and Function. Endocrine 2009, 35, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.-Q.; Nakamura, H.; Tanaka, T.; Odani, T.; Perez, P.; Ji, Y.; French, B.N.; Pranzatelli, T.J.F.; Michael, D.G.; Yin, H.; et al. Lysosomal Exocytosis of HSP70 Stimulates Monocytic BMP6 Expression in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massie, I.; Dietrich, J.; Roth, M.; Geerling, G.; Mertsch, S.; Schrader, S. Development of Causative Treatment Strategies for Lacrimal Gland Insufficiency by Tissue Engineering and Cell Therapy. Part 2: Reconstruction of Lacrimal Gland Tissue: What Has Been Achieved so Far and What Are the Remaining Challenges? Curr. Eye Res. 2016, 41, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Eye Wipe Test (Mean Wipes in 3min) | Phenol Red Thread Test (mm) | LG Weight (mg) | P versus Control | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1m | 5.6 ± 1.4 | 8.1±2.0 | 132.6±15.4 | |
| 2m | 9.2±2.6 | 125.3±9.2 | |||
| G1 | 1m | 2.6 ± 1.2 | 6.8±1.7 | 50.3±18.3 | |
| 2m | 3.3 ± 1.3 | 10.4± 2.5 | 41.3±14.6# | # 0.0001 | |
| G2 | 1m | 14.4 ± 2.2 | 6.2±1.4 | 59.7±8.6* | * 0.0079 |
| 2m | 7.0 ± 1.1 | 5.8± 1.1 | 45.0±7.8# | # 0.0001 | |
| G3 | 1m | 4.7 ± 2.3 | 8.2±1.9 | N/A | |
| 2m | 15.3± 4.1 § | 5.2± 1.1 | N/A | § 0.0438 |
| Catalog Number | Isotype | |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight (kDa) | Concentration | |
| α-tubulin | Santa Cruz | |
| SC 8035 | Mouse | |
| Monoclonal | 55 | 200µg/mL |
| PCNA | Cell Signaling | |
| # 2586 | Mouse | |
| Monoclonal | 36 | 200 µg/mL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





