Submitted:
01 May 2024
Posted:
01 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Understanding the Wellness Wheel: A Framework for Holistic Student Development
1.2. Rationale for Team Sports
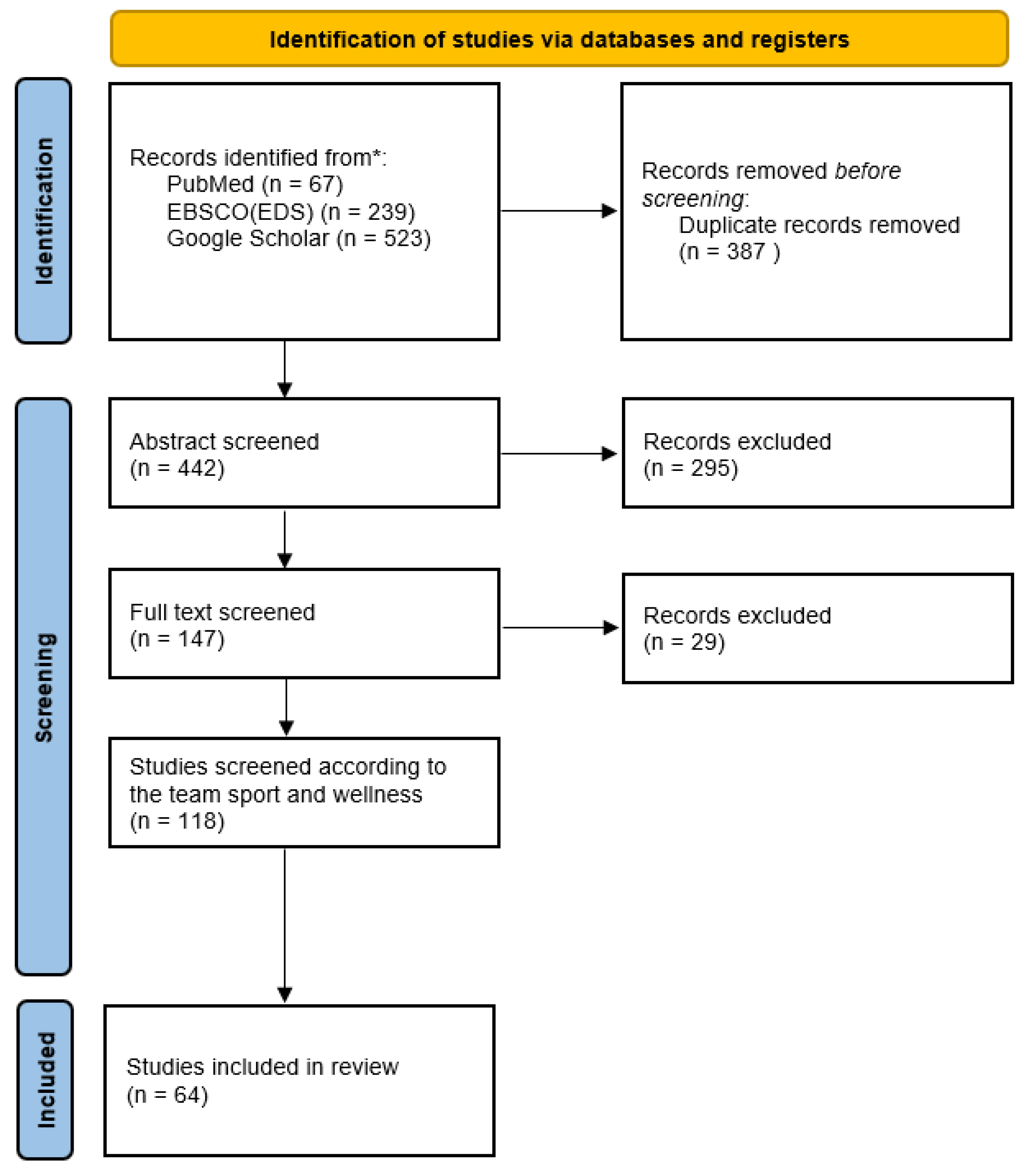
2. Methodology
2.1. Criteria for Literature Selection
2.2. Search Strategy Description
2.3. Selection and Inclusion Criteria
3. The Multidimensional Impact of Team Sports: Exploring the Benefits of Team Sports Across Wellness Domains
3.1. Physical Wellness: Strengthening the Body Through Team Sports
3.2. Emotional Wellness: Cultivating Resilience Through Team Participation
3.3. Intellectual Wellness: Sharpening the Mind Through Team Sports
3.4. Social Wellness: Building Community Through Team Sports
3.5. Spiritual Wellness: Finding Purpose in Team Sports
3.6. Occupational Wellness: Preparing for the Future with Team Sports
3.7. Environmental Wellness: Fostering Environmental Awareness Through Sports
3.8. Interconnected Wellness: Exploring the Multidimensional Impact of Team Sports on Student Development
4. Overcoming Barriers: Enhancing Access and Inclusivity in Team Sports
4.1. Navigating Socioeconomic and Cultural Hurdles
4.1.1. Socioeconomic Challenges
4.1.2. Cultural Barriers
4.2. Educational and Policy Support
4.3. Community and Family Engagement
5. Expanding Impact: Strategic Approaches to Maximize Wellness Through Team Sports
5.1. Research Recommendations
5.2. Policy Recommendations
5.3. Practice Recommendations
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zechner, M.; Fullen, M.; Barrett, N.; Swarbrick, M.; Pratt, C.; Santos, S. Wellness for Older Adults Living With Serious Mental Illness: A Proposed Practical Framework. Innovation in Aging 2020, 4, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strout, K.; Howard, E. The Six Dimensions of Wellness and Cognition in Aging Adults. J. Holist. Nurs. 2012, 30, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.; Stedge, H.; Tischler, D. Students’ Experience of a College Wellness Course. Health Educ. J. 2022, 81, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, M.; Waters, L.; Adler, A.; White, M. A Multidimensional Approach to Measuring Well-Being in Students: Application of the PERMA Framework. J. Posit. Psychol. 2014, 10, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snedden, T.; Scerpella, J.; Kliethermes, S.; Norman, R.; Blyholder, L.; Sanfilippo, J.; McGuine, T.; Heiderscheit, B. Sport and Physical Activity Level Impacts Health-Related Quality of Life Among Collegiate Students. Am. J. Health Promot. 2018, 33, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.; Roskowski, C.; He, Z.; Kong, L.; Chen, W. Effects of Team Sports on Anxiety, Depression, Perceived Stress, and Sleep Quality in College Students. J. Am. Coll. Health 2020, 69, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telford, R.; Telford, R.; Cochrane, T.; Cunningham, R.; Olive, L.; Davey, R. The Influence of Sport Club Participation on Physical Activity, Fitness and Body Fat During Childhood and Adolescence: The LOOK Longitudinal Study. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19(5), 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornstrup, T.; Póvoas, S.; Helge, J.; Melcher, P.; Fristrup, B.; Andersen, J.; Møgelvang, R.; Hansen, P.; Nybo, L.; Krustrup, P. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Health Effects of Team Handball Training in Overweight Women: Impact of Prior Experience. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 30, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarello, N.; Varini, L.; Liparoti, M.; Lopez, E.; Sorrentino, P.; Alivernini, F.; Gigliotta, O.; Lucidi, F.; Mandolesi, L. Boosting Effect of Regular Sport Practice in Young Adults: Preliminary Results on Cognitive and Emotional Abilities. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J.; Hillman, C.; Castelli, D.; Etnier, J.; Lee, S.; Tomporowski, P.; Lambourne, K.; Szabo-Reed, A. Physical Activity, Fitness, Cognitive Function, and Academic Achievement in Children: A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48(6), 1197–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malete, L.; McCole, D.; Tshube, T.; Mphela, T.; Maro, C.; Adamba, C.; Machuve, J.; Ocansey, R. Effects of a Sport-Based Positive Youth Development Program on Youth Life Skills and Entrepreneurial Mindsets. PLoS One 2022, 17(2), e0261809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barghi Moghaddam, J.; Rasouli, S.; Nekufar, M. The Relationship Between Spiritual Intelligence and Team Culture with the Sports Ethics of the Athletes of Sports Teams. J. Bioeth. 2018, 7(26), 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- McEwan, D.; Beauchamp, M. Teamwork in Sport: A Theoretical and Integrative Review. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2014, 7, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berns, G.; Simpson, S. Outdoor Recreation Participation and Environmental Concern: A Research Summary. J. Experiential Educ. 2009, 32, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahira, S. The Association Between Sports Participation and Physical Fitness. Int. J. Sport Stud. Health 2022, 4(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Karim, Z. A. The Effects of Football Specific Anaerobic Training Design on Athletes’ Specific Anaerobic Ability. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2023, 13(2), 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robineau, J. General Aspects of Concurrent Aerobic and Strength Training for Performance in Team Sports. Concurrent Aerobic and Strength Training 2018, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbin, N.; Bloyce, D.; Hughes, S. F. et al. Effects of a 4 Week Touch Rugby and Self-Paced Interval Running Intervention on Health Markers in Active Young Men. Sport Sci. Health 2020, 16, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.; Brito, J.; Figueiredo, P.; Seabra, A.; Mendes, R. Football Can Tackle Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review of the Health Effects of Recreational Football Practice in Individuals with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes. Res. Sports Med. 2021, 29(3), 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudlacek, M. Kudlacek, M. Individual vs. Team Sports-What's the Better Strategy for Meeting PA Guidelines in Children? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18(22), 12074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebryna, A. A.; Rebryna, A. A.; Lyakhova, N. A.; Shaposhnikova, I. I.; Korsun, S. M.; Shuba, L. V.; Shuba, V. V. Analysis of Students' Health Indicators in the Course of Physical Education Classes with a Sports Focus. Wiad. Lek. 2022, 75(6), 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrovatko, Z. V.; Yefremenko, V. M.; Anikeienko, L. V.; Bilokon, V. P.; Korol, S. M.; Riabchenko, V. G.; Кoshel, V. M. Strengthening Students' Health in the Process of Sports and Health Tourism Engagement. Wiad. Lek. 2021, 74(6), 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukh, T.; Bodnar, I.; Pavlova, I.; Svyshch, Y.; Pavlos, O. Perspectives of Using Athletics Means for Improving the Level of Physical Health of Students. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference Society Integration Education; 2019, 4, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, C.; Jakobsson, J.; Isaksson, A. Physical Activity and Sports-Real Health Benefits: A Review with Insight into the Public Health of Sweden. Sports 2019, 7(5), 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, L.; Santos, C.; Medeiros, I.; Freitas, I.; Rosário, D.; Seruffo, M.; Cerqueira, E. A Gamification and Biofeedback-Based Serious Game for Adherence to Physical Activity. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC); Marrakesh, Morocco; 2023; pp. 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Eather, N.; Wade, L.; Pankowiak, A. et al. The Impact of Sports Participation on Mental Health and Social Outcomes in Adults: A Systematic Review and the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ Conceptual Model. Syst. Rev. 2023, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Chopra, A.; Karve, S. Mental Wellbeing and Recreational Sports – Two Together for a Healthy Win - Implications for Higher Education Institutions. Asia Pac. J. Health Manag. 2023, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, C. D.; Shanmugaratnam, A.; Bruner, M. W. Peer-Initiated Motivational Climate, Mental Health, and Adherence in Competitive Youth Sport. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coaching, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, P.; Morrison, T. E. The Impact of COVID-19 Restrictions on Youth Athlete Mental Health: A Narrative Review. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2023, 25(5), 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunitoki, K.; Hughes, D.; Elyounssi, S.; Hopkinson, C. E.; Bazer, O. M.; Eryilmaz, H.; Dunn, E. C.; Lee, P. H.; Doyle, A. E.; Roffman, J. L. Youth Team Sports Participation Associates With Reduced Dimensional Psychopathology Through Interaction With Biological Risk Factors. Biol. Psychiatry Global Open Sci. 2023, 3(4), 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahira, S. The Association Between Sports Participation and Mental Health Across the Lifespan. Int. J. Sport Stud. Health 2023, 5(2), e134601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Rose, S.; Dyson, B. Social and Emotional Learning for Underserved Children Through a Sports-Based Youth Development Program Grounded in Teaching Personal and Social Responsibility. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagogy 2024, 29(1), 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ahmed, K. R.; Hidajat, T.; Edwards, E. J. Examining the Association between Sports Participation and Mental Health of Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19(24), 17078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarello, N.; Varini, L.; Liparoti, M.; Troisi Lopez, E.; Sorrentino, P.; Alivernini, F.; Gigliotta, O.; Lucidi, F.; Mandolesi, L. Boosting Effect of Regular Sport Practice in Young Adults: Preliminary Results on Cognitive and Emotional Abilities. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 957281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Säfvenbom, R.; Strittmatter, A.-M.; Bernhardsen, G.P. Developmental Outcomes for Young People Participating in Informal and Lifestyle Sports: A Scoping Review of the Literature, 2000–2020. Soc. Sci. 2023, 12, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A. L.; Coffee, P.; Barker, J. B. The Effects of Social Identity and Social Identity Content on Cohesion, Efficacy, and Performance Across a Competitive Rugby League Season. Int. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Machado-Oliveira, L.; Oliveira da Silva, A.; Farah, B. Q.; Leão, I. C. S.; Souza, F. T. C.; Santiago, F. L.; Machado, L.; Diniz, P. R. B. Team Sports as a Protective Factor Against Mental Health Problems and Suicidal Ideation in Adolescents. Salud Mental 2023, 46(4), 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latino, F.; Tafuri, F. Physical Activity and Academic Performance in School-Age Children: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidzan-Bluma, I.; Lipowska, M. Physical Activity and Cognitive Functioning of Children: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15(4), 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilopoulos, F.; Jeffrey, H.; Wu, Y. et al. Multi-Level Meta-Analysis of Physical Activity Interventions During Childhood: Effects of Physical Activity on Cognition and Academic Achievement. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2023, 35, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.; Pringle, A.; Mourton, S.; Roscoe, C.M.P. The Effects of Physical Activity on Academic Performance in School-Aged Children: A Systematic Review. Children 2023, 10, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Harmsel-Nieuwenhuis, L.; Alarslan, G.; van Hilvoorde, I.; Koelen, M.; Super, S.; Verkooijen, K. Life Skills Development and Transfer Amongst Socially Vulnerable Adults Through Sports: A Systematic Review. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiel, N.; Abalașei, B. Developing Social Skills in Schools via Physical Education Programs: The Case of Israeli Male High School Students. Sociologie Românească 2023, 20(2), 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R. M.; Sabiston, C. M. Understanding Relationships Between Social Identity, Sport Enjoyment, and Dropout in Adolescent Girl Athletes. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2022, 44(1), 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, D.; Yang, H.; Chi, X.; Yan, J. Associations of Sport Participation With Subjective Well-Being: A Study Consisting of a Sample of Chinese School-Attending Students. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1199782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M. A Study of Role of Games and Sports in National Integration and International Understanding. Int. J. Sports Health Phys. Educ. 2023, 5(1), 60–64. Available online: https://www.physicaleducationjournal.in/archives/2023.v5.i1.A.59/a-study-of-role-of-games-and-sportsin-national-integration-and-international-understanding.
- Höglund, F.; Bruhn, A. Sport-Based Interventions’ – A Tool for Suburban Social Integration? Nordic Soc. Work Res. 2022. [CrossRef]
- LaRocca, D.; James, K. A.; Rosenberg, S.; Ma, M.; Brooks-Russell, A. Team Sports Participation, Depression, and Suicidal Ideation in Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Questioning Adolescents. Psychol. in the Schools 2023, 60(4), 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J. L. Examining Spiritual Development in Collegiate Athletes Participating in Individual and Team Sports. LSU Doctoral Dissertations 2010, No. 1336. https://repository.lsu.edu/gradschool_dissertations/1336.
- Roychowdhury, D. Spiritual Well-Being in Sport and Exercise Psychology. SAGE Open 2019, 9(1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görgüt, İ.; Tutkun, E. The Concept of Morality in National Athletes: A Phenomenological Approach. Akdeniz Spor Bilimleri Dergisi 2022, 5(Özel Sayı 2), 798–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustakas, L.; Reynard, S. Sport as a Vehicle for Entrepreneurship Education: Approaches and Future Directions. In Progress in Entrepreneurship Education and Training; Block, J. H., Halberstadt, J., Högsdal, N., Kuckertz, A., Neergaard, H., Eds.; FGF Studies in Small Business and Entrepreneurship; Springer: Cham, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, A. How Team Sports Can Prepare You for Business Success. TeamSnap Blog. 2 December 2014. Available online: https://www.teamsnap.com/blog/general-sports/how-team-sports-can-prepare-you-for-business-success (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- Acak, M.; Buyukcelebi, H.; Arslanargun, C.; Bayer, R. Life Skills Development Through Sports Among Student-Athletes: A Survey of Secondary Schools. Int. J. Phys. Educ. Fitness Sports 2023, 12(2), 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurle, C. M.; Cadotte, M. W.; Seo, M.; Dooner, P.; Jones, H. P. Considering Humans as Integral Components of “Nature”. Ecol. Solut. Evid. 2023, 4(1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hron, C. L. Nature as Partner: How School Communities Benefit from Ecological Connections. In Schools as Community Hubs; Cleveland, B., Backhouse, S., Chandler, P., McShane, I., Clinton, J. M., Newton, C., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, D. G.; Singh, A.; Chambers, T. Exploring Nature- and Social-Connectedness as Mediators of the Relationship Between Nature-Based Exercise and Subjective Wellbeing. Ecopsychology 2022, Dec, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, M.; Dadgar, H.; Taghavy, A. et al. Providing a Sustainable Green Model for Large Sports Venues. 2023, Mar 21, PREPRINT Version 1 available at Research Square. [CrossRef]
- Dastbarhagh, H.; Afroozeh, M. S.; Mohammadzadeh, Y.; Fadam, A. Investigating the Role of Sport in Sustainable Environmental Development: A Case Study. J. Arch. Mil. Med. 2023, 11(1), e132655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gionfriddo, G.; Rizzi, F.; Daddi, T.; Iraldo, F. The Impact of Green Marketing on Collective Behaviour: Experimental Evidence From the Sports Industry. (2015). Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, L.; Hasanen, E.; Simula, M.; Virmasalo, I.; Muukkonen, P. Perceived Barriers to Physical Activity in the Social Spaces of Low Socioeconomic Status Suburbs. Wellbeing Space Soc. 2023, 5, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprecht, M.; Nagel, S. Inequality and Diversity in Sport - Developments and Perspectives. Curr. Issues Sport Sci. (CISS) 2023, 8(2), 045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulz, L. D.; Gleddie, D. L.; Kinsella, C.; Humbert, M. L. The Health and Educational Impact of Removing Financial Constraints for School Sport. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2023, 29(1), 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponciano Núñez, P. D.; Portela-Pino, I.; Martínez-Patiño, M. J. Understanding the Characteristics of Community Youth Sports Programs Interventions: A Systematic Review and Recommendations. SAGE Open 2023, 13(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, L.; Ruiter, A.; Visser, K.; Lesscher, H. M. B.; Jonker, M. Acquiring Financial Support for Children's Sports Participation: Co-Creating a Socially Safe Environment for Parents from Low-Income Families. Children 2023, 10(5), 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, M.; Talbot, A.; Harrington, D. Adolescent Perspectives on Gendered Ideologies in Physical Activity Within Schools: Reflections on a Female-Focused Intervention. Feminism Psychol. 2023, 33(2), 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungmann, C. K.; Christensen, J. H.; Klinker, C. D.; Pawlowski, C. S.; Johnsen, H. R. Barriers to Sports Participation Among Adolescent Girls from Deprived Neighbourhoods. Eur. J. Public Health 2022, 32(Supplement_2), ckac095.050. [CrossRef]
- Gurleyik, D.; Sen, C.K.N.; Etnier, J.L.; Acar, I.H. Culture in Physical Activity: The Contribution of Basic Psychological Needs and Goal Orientation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, R.; Sharma, V.; Liang, R.; Simon-Kumar, R.; Ameratunga, S.; Lee, A.; Kang, K.; Peiris-John, R. An Intersectional Approach to Exploring Lived Realities and Harnessing the Creativity of Ethnic Minority Youth for Health Gains: Protocol for a Multiphase Mixed Method Study. BMC Public Health 2023, 23(1), 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerde, J. A., Merrin, G. J., Le, V. T., Toumbourou, J. W., Bailey, J. A. Health of Young Adults Experiencing Social Marginalization and Vulnerability: A Cross-National Longitudinal Study. International journal of environmental research and public health 2023, 20, 1711. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter-Thuillier, B.; López-Pastor, V.; Gallardo-Fuentes, F.; Carter-Beltran, J.; Fernández-Balboa, J. M.; Delgado-Floody, P.; Grimminger-Seidensticker, E.; Sortwell, A. After-School Sports Programmes and Social Inclusion Processes in Culturally Diverse Contexts: Results of an International Multicase Study. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1122362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponciano Núñez, P. D.; Portela-Pino, I.; Martínez-Patiño, M. J. Understanding the Characteristics of Community Youth Sports Programs Interventions: A Systematic Review and Recommendations. SAGE Open 2023, 13(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortune, M.; Oncescu, J. Community Sport and Recreation Organizations’ Inclusion of Low-Income Families in Sport and Recreation in New Brunswick. Leisure/Loisir 2022, 48(2), 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volf, K.; Kelly, L.; Bengoechea, E. G.; Casey, B.; Gelius, P.; Messing, S.; Forberger, S.; Lakerveld, J.; Den Braver, N. R.; Zukowska, J.; Woods, C.; on behalf of the PEN Consortium. Evidence of the Impact of Sport Policies on Physical Activity and Sport Participation: A Systematic Mixed Studies Review. Eur. J. Public Health 2022, 32 (Suppl 2), ckac093.047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portas, E., Cowen, C., Birdsall-Strong, L., Scott, C. S01 Providing policymakers with the evidence and practices to act and improve lives through physical activity. The European Journal of Public Health 2022, 32 (Suppl 2), ckac093.001. [CrossRef]
- Scott, C. S01-2 Providing policymakers with the evidence of the true value of physical activity to individuals and communities. The European Journal of Public Health 2022, 32 (Suppl 2), ckac093.003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVinnie, Z.; Plateau, C. R.; Lane, A.; Murphy, N.; Stevinson, C. Effects of Engaging in Mass Participation Sporting Events on Physical Activity Behaviour: A Systematic Review. Health Promot. Int. 2023, 38(2), daad018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Zhou, S.; Crowley-McHattan, Z. J.; Liu, Z. Factors That Influence Participation in Physical Activity in School-Aged Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review from the Social Ecological Model Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18(6), 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Aspect | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Health Outcomes | Significant improvements in cardiovascular fitness, muscular strength, and body composition. | [15,16] |
| Cardiovascular and Metabolic Health | Lowered blood pressure, better lipid profiles, and improved glucose control; reductions in systolic blood pressure and interleukin-6 levels. | [15,18] |
| Obesity and Body Composition | Decrease in fat mass and body fat percentage, increase in lean muscle mass. | [18] |
| Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risks | Recreational football offers significant potential in preventing and managing type 2 diabetes and associated cardiovascular risks. | [19] |
| Motivation and Adherence | Team sports motivate individuals to start and maintain regular exercise routines more effectively than solitary sports. | [20] |
| Student Health and Wellness | Integration of sports and health tourism into physical education results in superior physical development, functional status, and overall health. | [21,22,23,24] |
| Sustainability of Engagement | Team sports enhance the likelihood of continued involvement in physical activities due to the diversity and pleasure associated with them. | [25] |
| Aspect | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|
| Mental Health Benefits | Reduced depression, anxiety, and stress; improved psychological well-being, including self-esteem, life satisfaction, and quality of life. | [26,27] |
| Social Support and Belonging | A sense of community and belonging within team sports environments enhances emotional well-being. | [26,28,29] |
| Emotional Competencies | Cultivation of emotional competencies such as empathy, emotional regulation, and resilience through team dynamics. | [31,32] |
| Depression and Life Satisfaction | Sports participation correlated with reduced symptoms of depression and enhanced life satisfaction among adolescents. | [33] |
| Psychological Support in Sports | Team sports provide vital social and psychological support that is beneficial for mental health. | [34,35] |
| Social Identity and Team Cohesion | Strong social identity within sports teams predicts better team cohesion, self-efficacy, and perceived team performance. | [36,37] |
| Aspect | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Functions and Academic Achievement | Physical activity produces essential changes in the brain, mediating enhancements in attention, memory, and executive functions. | [38,39] |
| Types and Contexts of Physical Activity | Aerobic exercise, coordinative exercise, classroom-based physical activity, active breaks, and extracurricular physical activity can affect cognition and academic achievement. | [38] |
| Impact of Physical Activity on Cognition | Interventions based on physical activity notably enhanced on-task behavior, creativity, fluid intelligence, and working memory. | [40] |
| Physical Activity and Academic Performance | Engaging in physical activity for at least 90 minutes weekly at a moderate to vigorous intensity is linked with enhanced academic performance. | [41] |
| Aspect | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|
| Social Skills and Relationships | Enhancement of social skills, meaningful relationships, and fostering of a strong sense of community belonging through teamwork. | [42,43,44,45] |
| Community Belonging and Team Identity | Sports serve as a crucial arena for young individuals to discover and affirm their social identities, learning valuable lessons in community engagement. | [44] |
| Social Development Through Sports | Sports participation offers a platform to acquire and refine cognitive, emotional, and social skills, contributing to social development. | [42] |
| Impact on Youth Mental Health | Active involvement in sports is linked with greater school involvement, peer acceptance, and reduced engagement in risky behaviors. | [30,42,44,45] |
| Promoting Social Cohesion and Integration | Team sports are pivotal in promoting social cohesion and aiding community integration, offering a valuable means to bridge cultural gaps. | [46,47] |
| Aspect | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|
| Mental Health Improvements | Team sports participation is associated with reduced symptoms of mental disorders, fewer mental health issues, and lower instances of suicidal thoughts. | [37] |
| Personal and Spiritual Growth | Sports participation is associated with pathways to self-transcendence and excellence, contributing to personal and spiritual growth. | [49] |
| Ethical Engagement and Introspection | Sports provide a fruitful ground for nurturing moral values and positive experiences, encouraging ethical engagement and introspection. | [51] |
| Inclusivity and Support in Sports | Involvement in team sports decreases the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts, emphasizing the importance of inclusive and supportive environments within sports. | [48] |
| Spiritual Experiences Among Athletes | Higher levels of spirituality were observed in student-athletes compared to the general student population, varying by gender and ethnicity. | [49] |
| Aspect | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|
| Skills Development | Team sports equip individuals with transferable skills beneficial in academics and future careers, enhancing collaborative abilities and work ethic. | [52,53,54] |
| Sport as a Developmental Tool | Sport provides a practical, interactive setting for experiential learning and developing skills and attitudes, making it a valuable tool for development. | [52] |
| Skills for Life and Business Success | Participating in team sports teaches essential skills like collaboration, strategizing, and leadership, providing a foundation for success in both personal and professional life. | [53] |
| Life Skills Enhancement | Sports contribute to the development of life skills among student-athletes, showing significant growth in areas such as initiative, identity, and social skills. | [54] |
| Aspect | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|
| Connection to Nature | Participation in outdoor team sports reinforces the connection to nature, fostering a sense of responsibility towards environmental conservation. | [55,56] |
| Sustainable Sports Practices | Introducing sustainable green models for sports venues emphasizes energy efficiency, recycling, and green management practices. | [58,59] |
| Environmental Stewardship | Sports events raise environmental awareness and influence societal perceptions and behaviors towards the environment. | [60] |
| Promotion of Eco-Friendly Habits | Nature-based exercise benefits subjective well-being, enhanced by a solid connection to nature and the social community. | [57] |
| Barrier Type | Strategies for Overcoming | References |
|---|---|---|
| Socioeconomic Challenges | They are dismantling social and personal obstacles to ensure equal opportunity for physical activity through community sponsorships, equipment donations, and subsidized access. | [61,62,63,64,65] |
| Cultural Barriers | They addressed stereotypes and societal pressures through tailored community sports initiatives and inclusive programming. | [66,67,68,69,70] |
| Educational and Policy Support | It is mandating sports participation in school curricula and supporting policies that enhance access and engagement in physical activities. | [74,75] |
| Community and Family Engagement | Promoting mass participation in sports events and ensuring access to sports facilities and safety to support youth physical activity. | [77,78] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





